regions of body in anatomical position
...
head
cephalic / cranial
skull
cranial
face
facial
chin
mental
neck
cervical
chest
pectoral
armpit
axillary
arm
brachial
front of elbow
antecubital / cubital
forearm
antebrachial
wrist
carpal
palm
palmar
fingers
digital / phalangeal
thigh
femoral
anterior surface of knee
patellar
forehead
frontal
eye
orbital
cheek
buccal
ear
otic
nose
nasal
mouth
oral
breastbone
sternal
breast
mammary
naval
umbilical
hip
coxal
groin
inguinal
hand
manual
pubis
pubic
chest
thoracic
abdomen
abdominal
breastbone to pelvis
trunk
base of skull
occipital
shoulder
acromial
shoulder blade
scapular
spinal column
vertebral
back of elbow
olecranal
between hips
sacral
buttock
gluteal
hollow behind knee
popliteal
calf
sural
sole
plantar
heel
calcaneal
hips to heel
lower limb
back of hand
dorsal
upper limb
hand to shoulder
loin
lumbar
Standard anatomical position
SAP
- palms up
- forearm underside is ANTERIOR
anterior
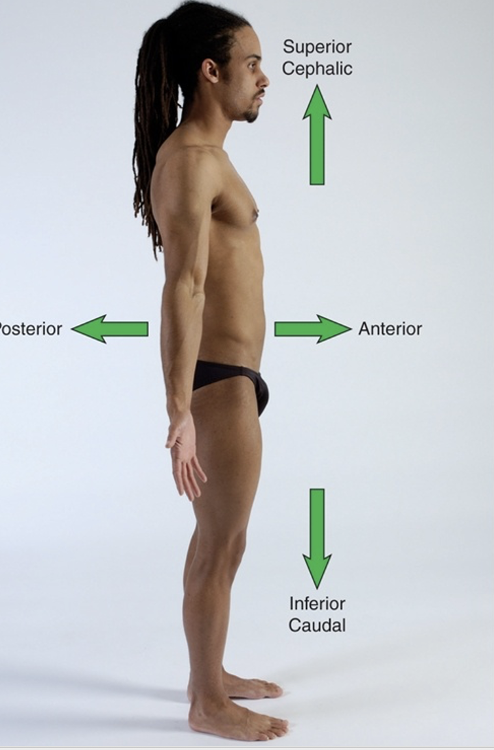
towards the front
superior

cephalic (upper body direction)
posterior

towards the back
inferior

caudal (lower body direction)
proximal
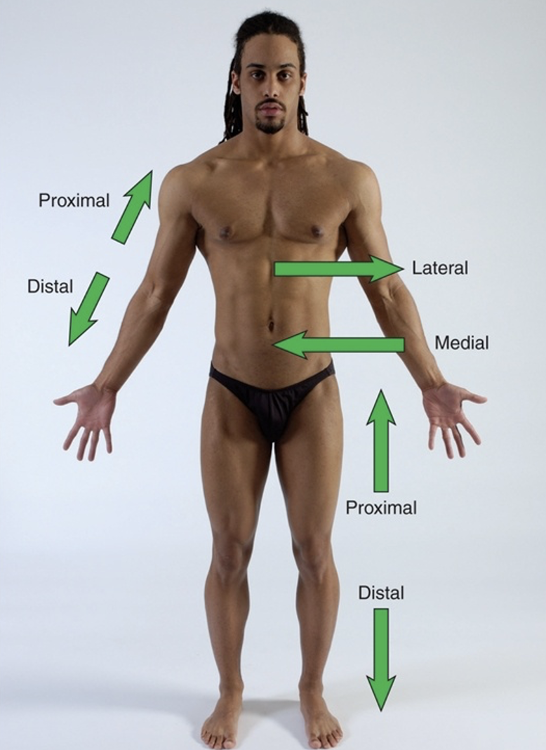
proximal means closer to the origin of the body part of the point of attachement of a limb to the body trunk
distal

further away from origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
lateral

Lateral - to be farther away from midline of body, in direction of either side from midline of body OR a structure
away from the midline of the body
medial

Medial - to be closer to the midline of the body or a structure (internal opposed to external)
toward the midline of the body
sagittal plane of movement and motions
cuts body into right vs. left
motions: flexion and extension
frontal plane of movement and motions
cuts body into anterior vs. posterior
motions: abduction and adduction
transverse plane and motions
cuts body into superior and inferior
motions: rotation
axes
imaginary line at right angles to the plane at which it rotates or spins
each plane perpendicular to its axis
frontal axis
line thru side of body
plane spinning: sagittal plane
sagittal axis
line anterior - posterior of body
plane: frontal axis
longitudinal axis
line head/heels
plane: transverse
tissue types in body
- epithelial
- connective
- muscle
- nervous
epithelial tissue location
- outer layer of skin
- line body cavities
- in glands
epithelial tissue function and functional categories
protect, absorb, filter, secretes substances in body
functional categories:
- Glandular: sweat, tear, pituitary, thyroid, adrenal
- Sensory: specialized cells related to hearing, sight, smell, taste
- Surface: skin
regenerate fast, constantly repair/replace
connective tissue locations
bones, tendons, ligaments, fascia, cartilage, adipose (fat), blood
connective tissue types differ by
density
connective tissue components
Extracellular matrix (EXM): various fibers suspended in fluid
Ground substance: fluid portion of extracellular matrix
Three fiber types: collagen, reticular, elastic
exm vs ground substance
...
fibroblasts
in connective tissue
cells that secrete proteins that make up fibers in matrix
include osteoblasts (bone) and chondroblasts (cartilage)
macrophages
part of connective tissue
respond to injury / infection
fat cells
part of connective tissue
adipose
types of connective tissues
-
lose
- high lvls ground substance, fewer fibers
- ex: adipose tissue + superficial fascia
-
dense
- thicker + stronger, more fibers, less ground substance
- ex: tendons, ligaments, joint capsules, periosteum
-
fluid
- contain plasma (90% water)
- ex: blood + lymph
-
supporting
- strong + solid
- ex: bone + cartilage
muscle tissue
network of muscle cells containing myofibrils
myofibrils
contractile protein structures
stimulated by nervous system to contract / shorten = movement
force generated by shortening myofibrils -> transmitted into surrounding myofascia -> force drives internal + external human movement
myofibril unit
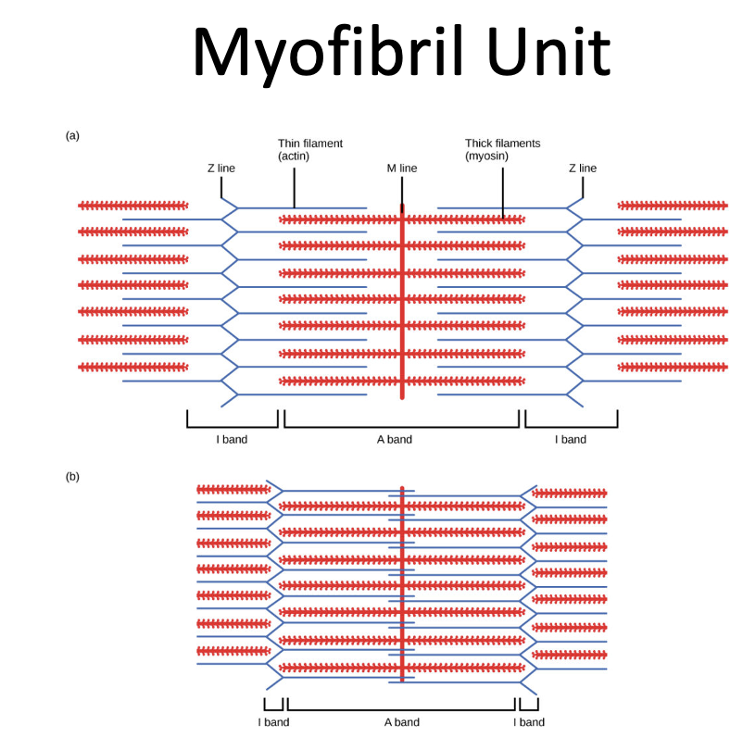
sarcomere, actin, myosin, I band, A band, Z line, H zone, M line
sarcomere
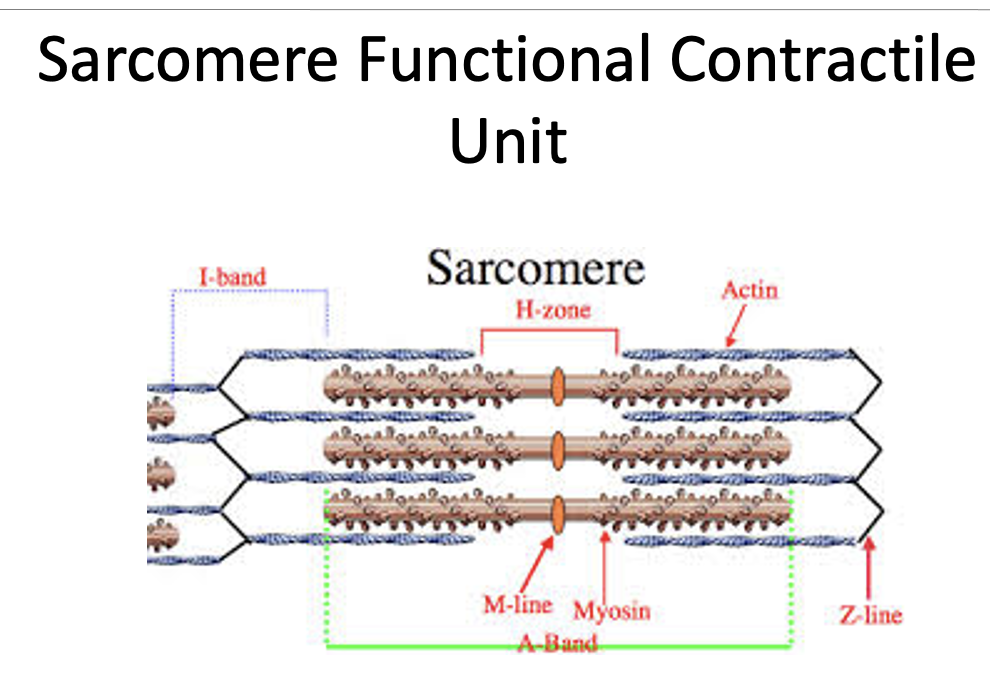
basic contractile unit of a myofibril
actin
thin filament
myosin
thick filament
I band
primarily contains actin (thin) filaments
A band
primarily contains myosin (thick) filaments
Z line
defines boundary of sarcomere and anchors the actin filament
H zone
zone of myosin filaments with no actin filaments
M line
runs down the middle of the H zone
nervous tissue
network of neurons (nerve cells)
can be stimulated, conduct stimulus, respond to stimulus
electrical impulses travel in btw neurons + btw them and other cells
impulses allow communication btw nervous system + other tissues
nervous system monitor + regulate body functions
sensory vs. motor
sensory
- afferent nerves input info to CNS + brain
- ARRIVE
motor
- efferent nerves provide motor output info to skeletal muscle
- EXIT
structures involved in movement
- bones
- ligaments
- muscles
- tendons
- fascia
bone characteristics
- easy to palpate + provides bony landmarks for finding muscles, tendons, ligaments
- made up of collagen fibers and minerals
- covered with layer of dense connective tissue (periosteum)
- epiphysis are bone ends with only ossify once skeleton matures as an adult
- diaphysis is shaft of bone
epiphysis
epiphysis are bone ends with only ossify once skeleton matures as an adult
diaphysis
shaft of bone
bone anatomy
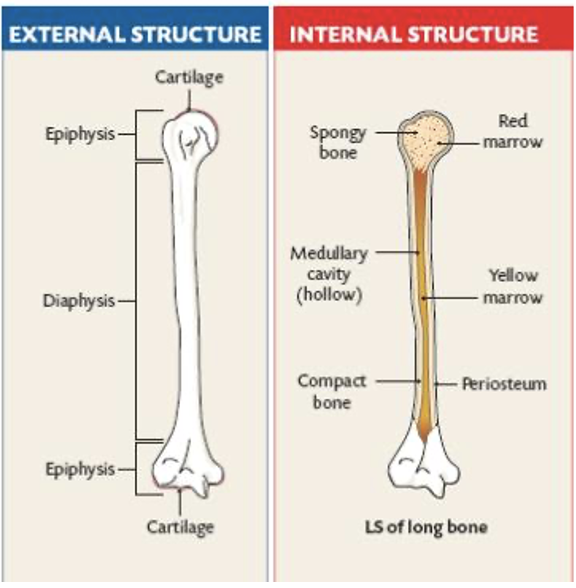
long bone shape
shaft in middle w/ bumpy ends
small bone shape
cube-shaped; allows fine, gliding movements in hand + foot
flat bone shape
sternum, lilium
irregular bone shape
unique; vertebrae + fascial bones
sesamoid
encased in tendon; helps improve leverage + strength of muscle that cross it (patella)
bone functions
- framework support movement
- protect vulnerable structure (brain, spinal cord, organs, etc.)
- store minerals (potassium, calcium)
- serves as site for hematopoiesis (formation of blood cells) in red bone marrow + epiphysis of long bones
ligaments
fibrous structures made of dense connective tissue that connects bones to each other
prevent movements at joints + help stabilize joints (static stabilizers)
poorly vascularized
structure of ligaments
complex networks of collagen fibers that resist stress in multiple directions (grisltly feel)
present at both ends of bones, help form joints, joint capsules
interosseous membrane - broad sheet of dense connective tissue, thinner than ligaments; connects bones along length of shaft
types of muscle
smooth
- walls hollow organs, vessels, resp. pathways
- involuntary
cardiac
- involuntary
- walls of heart
- creates pulsing action to circulate blood thru body
skeletal muscle
- voluntary + involuntary
- produces movement by pulling on tendons + bones
- reflexes
- provide thermogenesis via muscle contraction
smooth muscle
- walls hollow organs, vessels, resp. pathways
- involuntary
cardiac muscle
- involuntary
- walls of heart
- creates pulsing action to circulate blood thru body
skeletal muscle
- voluntary + involuntary
- produces movement by pulling on tendons + bones
- reflexes
- provide thermogenesis via muscle contraction
muscle features
- made of bundles of parallel fibers
- fibers have distinct alignment/fiber direction
- muscle memory
- changes shape as body moves
- stretch - long + taught
- contract - thicker + firmer
tendon
connect muscle to bone
abundant in collagen fibers = strength + elasticity
change shape as moves
smother than muscle
fascia
- thin membrane of loose/dense connective tissue covering structures of body (bones, muscles, joints, etc.)
- protects structures + binds them into structural unit
- separate skin, muscle layers, body compartments, cavities, etc.
- make sheaths of nerve, vessels
- create cont. matrix that interconnects all structures of body
fascia layers
- superficial
- deep
- subserous
superficial fascia
under dermis of skin
stores fat + water, passage for nerves + vessels
deep fascia
form network around muscles + internal structures
help muscle movement, make passageways for nerves + vessels, make muscle attachment sites, cushion muscle
subserous fascia
separates deep fascia from membranes, allow movement of internal organs
skin functions
protect vs environment
help regulate internal temp
excretes waste
skin layers
epidermis
dermis
hypodermis
epidermis
epithelial tissue; thin layers of cells cont. keratin, melanin, defensive cells
dermis
dense connective tissue; contains hair follicles, glands, nerves, blood vessels, tiny muscles
hypodermis
loose connective tissue, lying under dermis;
contains adipose cells -> cushion + protect structures
burns
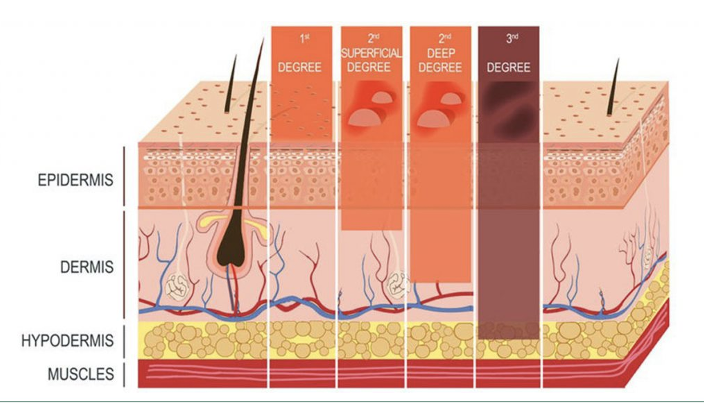
1st degree - superficial thickness
2nd degree - partial thickness burn
3rd degree - full thickness burn
4th degree - burn to bone / muscle, result in loss of limb / part
blood vessel functions
path blood flow
deliver oxygen + nutrients to tissue
removes waste
types blood vessels
- arteries/arterioles
- veins, venules
- capillaries
lymph vessels and node functions
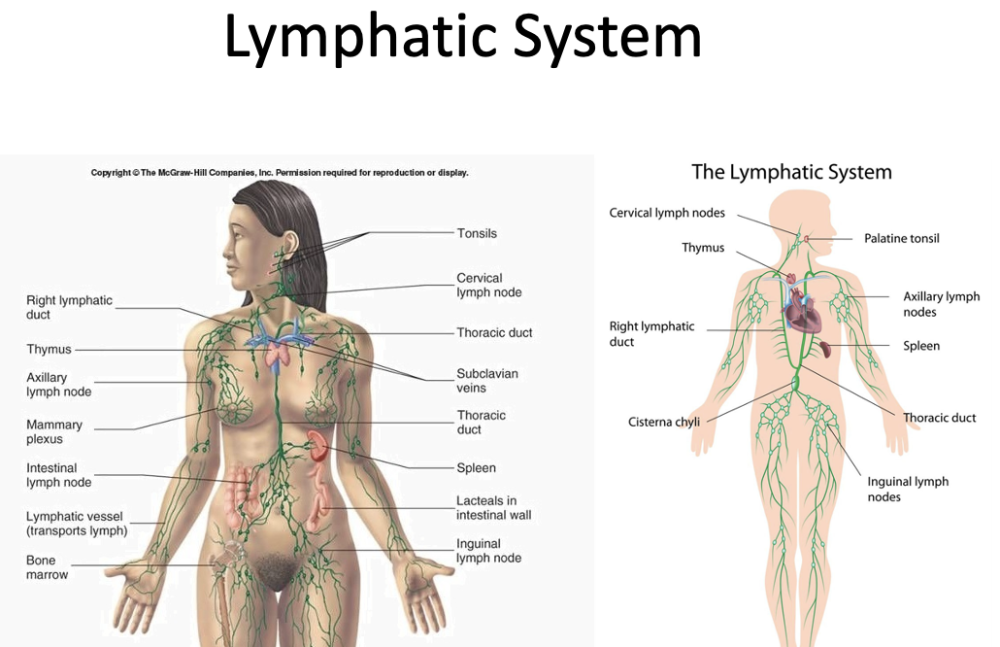
- collect excess fluid (lymph) from body tissues + return to circulatory system
- make lymphocytes
- dependent on muscle contraction for flow
circulation of lymphatic system
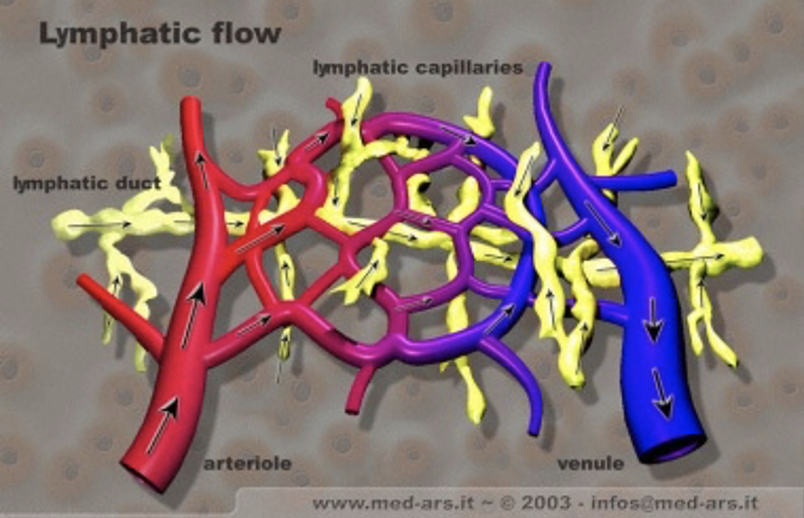
- lymphatic capillaries collect lymph + metabolic waste from capillaries
- lymph transported to lymph nodes
- nodes filter foreign particles, viruses, bacteria, etc.
nerves
- part of nervous system (brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves)
- cable-like bundles of neurons
- carry electrical signals to/from brain/spinal cord + body periphery
= cell body (nucleus), dendrites, axon
nerve types
-
sensory
- monitor internal + external environment + relay sensory data to brain (afferent)
-
motor
- carry out motor response to skeletal muscle (efferent)
cartilage
supporting connective tissue
- limited ability to heal after injury
cartilage types
-
elastic
- in nose + ears
- highest proportion of elastic fibers
-
hyaline
- in voice box, btw ribs + sternum, bone surfaces
- smooth + rubbery
- help reduce friction in movement
-
fibrous
- in disks btw vertebrae + in meniscus btw femur + tibia
- cushion joint surfaces
labrum
fibrocartilaginous ring
deepen concavity of joint
attachment site for many joint ligaments
ex: in shoulder + hip joints
bursae
small/flat sacs w/ synovial fluid
in shoulder, elbow, hip, knee
become big + swollen when exposed to excess friction (bursitis)
synovial fluid
lubricant helps decrease friction + create gliding movement btw structures