Storage form of iron
A. Ferritin
B. Transferrin
C. Ferrous
D. Ferric
B, D
Black, inorganic compound formed from heme and used to treat some porphyrias
A. Porphyrin
B. Hemoglobin
C. Hemin
D. Sulfide
C
Porphyrias result from
A. Bilirubin misprocessing
B. Enzyme deficiencies in the heme production pathway
C. Abnormal hemoglobin
D. Lactic acid overproduction
B
Class of pigments including heme and chlorophyll
A. Hemin
B. Ferritin
C. Porphyrin
D. Myoglobin
C
Inhibition of most of the enzymes of the synthetic pathway is caused by
A. Liver Disease
B. Iron Deficiency Anemia
C. Acute Intermittent Porphyria
D. Lead Poisoning
D
Erythropoietic Porphyria shows an increase in
A. Urine Porphobilinogen
B. Serum Porphyrin
C. Ferrochelatase
D. Total Erythrocyte Protoporphyrin
D
Urine Porphobilinogen is the best test to order for which porphyria
A. Acute Intermittent Porphyria
B. Erythropoietic Porphyria
C. Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
D. ALA-Dehydratase Deficiency
A
Reagent for the Watson-Schwartz test
A. Hoesch
B. Ehrlich’s Reagent
C. Diazo
D. Cellulose Acetate
B
Porphyrins are primarily evaluated using
A. Electrophoresis
B. Spectrophotometrically
C. HPLC
D. Fluorometry
C
Porphobilinogen Testing is used to evaluate/confirm
A. Acute Intermittent Porphyria
B. Hemoglobin H Disease
C. Erythropoietic Porphyria
D. Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
A
Used as a screening test for lead poisoning
A. Watson-Schwartz
B. Ferrochalatase
C. Electrophoresis
D. Evelyn-Malloy
B
Bilirubin undergoes conjugation to..
A. Be broken down
B. Be made more lipophilic
C. Be made more hydrophilic
D. Decrease size
C
Unconjugated bilirubin is
A. Hydrophilic
B. Lipophilic
C. Indirect
D. Direct
B,C
Conjugated bilirubin covalently bound to albumin
A. Unconjugated bilirubin
B. Conjugated bilirubin
C. Indirect bilirubin
D. Delta Bilirubin
D
Icteric patients appear
A. Yellow
B. Flushed
C. Blue
D. Red
A
Unconjugated bilirubin increases with all EXCEPT
A. Hemolysis
B. Dublin-Johnson Syndrome
C. Crigler-Najjar Syndrome
D. Gilbert Syndrome
B
Weak autosomal recessive conjugated hyperbilirubinemia
A. Rotor Syndrome
B. Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
C. Crigler-Najjar Syndrome
D. Gilbert Syndrome
A
Which of these is NOT a cause of pre-hepatic jaundice?
A. DIC
B. Medication
C. Necator americanus Infection
D. Cholestasis
D
An overabundance of heme in the blood results in
A. Pre-Hepatic Jaundice
B. Post-Hepatic Jaundice
C. Porphyria
D. Necator americanus Infection
A
What is drastically increased in pre-hepatic jaundice?
A. Direct Bilirubin
B. Indirect Bilirubin
B
Physiologic jaundice of the newborn is an example of
A. Post-Hepatic Jaundice
B. Hepatic Jaundice
C. Pre-Hepatic Jaundice
D. Obstructive Jaundice
B
Post-Hepatic Jaundice results from all EXCEPT
A. Cholestasis
B. Blocked Bile Duct
C. Hemolysis
D. Biliary Tract Tumor
C
Uses 50% methanol as an accelerator
A. Evelyn-Malloy Method
B. Jendrassik-Grof Method
C. Electrophoresis
D. Hoesch Method
A
Which is NOT an advantage of the Jendrassik-Grof method
A. Not affected by pH
B. Insensitive to variation in protein concentration
C. Not affected by Hemoglobin up to 10,000 mg/dL
D. Minimal turbidity
C
Which of these is NOT a preanalytical concern for bilirubin analysis?
A. Evelyn-Malloy Method
B. Jendrassik-Grof Method
C. Electrophoresis
D. Watson-Schwartz Method
B
Which of these is NOT a preanalytical concern for bilirubin analysis?
A. Fasting Sample
B. Light Sensitive
C. Lipemia
D. Time Sensitive
D
Hemoglobin A2 is comprised of
A. 2 α chains + 2 β chains
B. 2 α chains + 2 δ chains
C. 2 α chains + 2 γ chains
D. 2 α chains + 2 α chains
B
Slowest to fastest hemoglobin on electrophoresis
A. AFSC
B. CSFA
C. FACS
D. CASF
B
Hemoglobin electrophoresis is first used to detect abnormal hemoglobin using what medium?
A. Cellulose Acetate Strip
B. Citrate Agar Gel
C. Capillary
D. FACS
A
Sulfation of hemoglobin causing inability to bind oxygen
A. Methemoglobin
B. HbA1c
C. Carboxyhemoglobin
D. Sulfhemoglobin
D
The final step of iron spectrophotometry
A. Release iron from transferrin
B. React Fe2+ with a chromogen
C. Reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+
D. Ferrous capture
B
Hemochromatosis results in what TBIC levels and Fe levels
A. TIBC: increased, Fe: decreased
B. TIBC: decreased, Fe: decreased
C. TIBC: decreased, Fe: increased
D. TIBC: increased, Fe: increased
C
What condition primarily results in a quantitative defect in hemoglobin
A. Beta-Thalassemia
B. Alpha-Thalassemia
C. Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
D. Acute Intermittent Porphyria
B
Thoracentesis obtains fluid through a large bore needle inserted into the
A. Peritoneal Cavity
B. Pleural Cavity
C. Pelvic Cavity
D. Joints
B
An effusion that is classified as a chylous would likely contain
A. Pus
B. Cholesterol
C. Inflammatory cells
D. Plasma
A,C
Generally joint aspirates and urine samples will have extra crystals in them if they are
A. Left at RT
B. Heated above RT
C. Refrigerated
D. Frozen
C
In a CSF sample the third tube taken is for
A. Cytology
B. Microbiology
C. Chemistry and Serology
D. Hematology
D
A Pleural Effusion that has a putrid odor suggests
A. Anaerobic empyema
B. Chylothorax
C. Malignant Melanoma
D. Charcoal-containing empyema
A
Transudates have a specific gravity of greater than 1.010
A. True
B. False
B
Pericardial fluid would be ordered for all situations except
A. Therapeutic pericardiocentesis
B. Suspicion of TB
C. Suspicion of neoplastic pericarditis
D. Pericardial effusion of known etiology
D
Normal synovial fluid is not viscous
A. True
B. False
B
Amniocentesis samples
A. Are usually cloudy
B. Are taken at 20-22 weeks
C. Are used to asses for genetic disorders
D. Do not contain hair or cells
C
To distinguish between urine and amniotic fluid one should assess
A. Protein
B. Creatinine
C. Uric Acid
D. BUN
B
Seminal Fluid evaluation would include all of the following except.
A. size of the head
B. movement of the sperm
C. concentration
D. Ejaculate volume
A
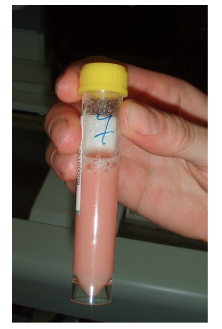
A CSF sample of this clarity and color would be most consistent with
A. clean tap
B. Xanthochromia
C. lipid excess
D. Lysed
C
In a traumatic tap the last tube of CSF contains less blood than the first
A. True
B. False
A
In bacterial meningitis the CSF glucose would be ____ and the WBC count would be ___
A. decreased, decreased
B. decreased, increased
C. increased, increased
D. increased, decreased
B
The presence of oligoclonal bands in the CSF in indicative of
A. Multiple Myeloma
B. PKU
C. Multiple Sclerosis
D. Meningitis
C
A CSF/serum Albumin index of >9 indicates an intact blood brain barrier
A. True
B. False
B
Accumulation of serous fluid can be caused by
A. increased plasma oncotic pressure
B. decreased capillary hydrostatic pressure
C. decreased plasma oncotic pressure
D. decreased capillary permeability
C
SAAG >1.1
A. Portal Hypertension
B. Not portal hypertension
A
If dilution of synovial fluid is necessary, water should be used
A. True
B. False
B
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals are consistent with ____ and will appear ____ in color
A. gout, yellow
B. gout, blue
C. pseudogout, yellow
D. psuedogout, blue
D
A glucose concentration of 20-100 mg/dL in the synovial fluid in consistent with which group?
A. Normal
B. Infectious
C. Inflammatory
D. Hemorrhagic
B
Bilirubin concentration correlates with absorbance at
A. 550 nm
B. 250 nm
C. 450 nm
D. 350 nm
C
The normal cutoff for AFAFP is 2.5 MoMs
A. True
B. False
B
The Foam Stability Index assesses for fetal surfactant production
A. True
B. False
A
Compared to amniotic fluid urine should have lower ___ and higher ___
A. glucose, protein
B. protein, glucose
C. creatinine, glucose
D. glucose, creatinine
D
An elevated sweat chloride is seen in
A. SIADH
B. cystic fibrosis
C. Liddle Disease
D. Hypoaldosteronism
B
Which is a characteristic of an exudate?
A. Straw-colored
B. normal WBC count
C. low glucose
D. clear
C
To officially diagnose an exudate you must have
A. elevated total protein ratio
B. elevated LD ratio
C. elevated TP ratio and decreased LD ratio
D. Elevated TP ratio and elevated LD ratio
D
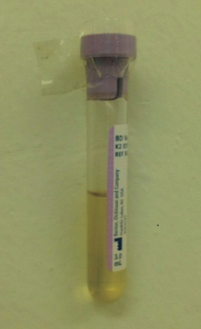
This fluid would be classified as a
A. Transudate
B. Exudate
A