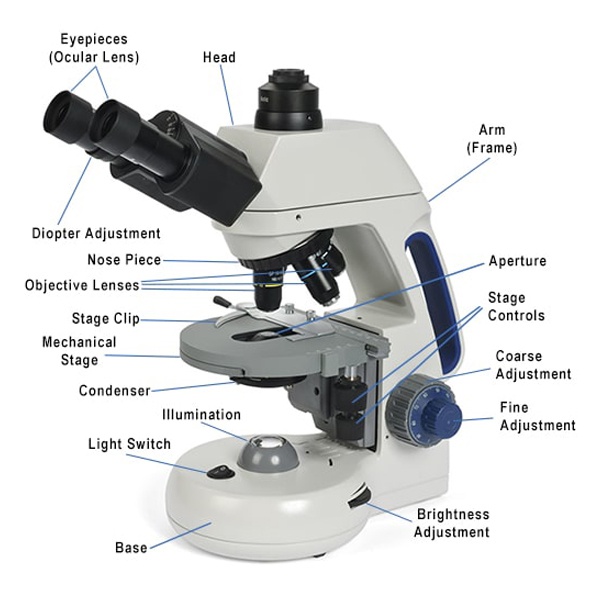
Name of the objectives in the microscope
1. Scanning objective (4x)
2. Medium power objective (10x)
3. High (power) dry objective (40x)
4. Oil immersion objective (100x)
it is best to start with which objective?
Scanning objective (4x)
When using the high power objective, you should not adjust ?????
Coarse focus adjustment knob
total magnification for the objectives
1. 4x (scanning)
2. 10x (medium)
3. 40x or 45x (high dry)
4. 100x (oil immersion)
If the magnification increases, the actual size of the field of view…what ?
decreases
What the Fine adjustment knob do?
This knob raises and lowers the stage in very small increments; it is possible to bring the image into sharp focus
Part of microscope that control the pass of light
Field diaphragm
Aseptic Techniques…..what is that
The method of handling microbes and materials in a way that minimizes contamination
Streak Plate Inoculation …for what is used
Method to separate individual bacteria from mixtures
Eosine…..what is ? for what is used?
widely used as a dye for laboratory microscopy; to stain the cytoplasm of cells and bacteria
place the plates in the incubator, you should make it…how?
Petri dishes need to be incubated upside-down to lessen contamination risks from airborne particles landing on them
objective lenses can be found to have a magnification of all of the following, EXCEPT?
1000x
Why immersion oil can be used to minimize light scattering?
Since light scattering is decreased, the image is clearer and sharper and has better contrast
compound microscope
1. Typical binocular compound microscope
2. two oculars
3. two lenses or mirrors to produce an image
inoculation…what it means?
The process of transferring a microbe from one medium to the next
pure culture or a colony contains:`
A single bacterium
negative stains
1. Is an example of an indirect simple stain
2. The dyes used in negative staining have an acidic chromogen (negatively charged) that is repelled by the bacterial cell
Acidic dyes…..what it means?
Is negatively charged & stains the inside of a cell
Ex. Eosin, Nigrosin, and Congo red
fixed smear of bacterial cells and stains them with Loeffler's methylene blue. All the cells appear blue under the oil lens. This is an example of:…what kind of staining
Simple staining
The process of transferring a microbe ….true or false
Inoculation; true
you need to heat fix your sample first by waving the slide through the blue flame on a Bunsen burner a few times. Why do you do this?
Heat-fixing smears can distort cell size and cell shape
“streptobacilli” indicate?
1. genus of fastidious microaerophilic Gram-negative bacteria
2. Grow in culture as rods in chains.
A microbiologist inoculates Staphylococcus aureus into a culture medium. Following incubation, both Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis are determined to be growing in this culture. What is the most likely explanation?
The culture is contaminated
The dinoflagellates …….true or false about them
1. single-celled eukaryotes
2. usually considered algae
3. mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats
The slide is held in place by the?????
Mechanical stage
The diaphragm in the micrsoscope….what it does?
Opens and closes to increase and decrease light from the light source
Total magnification using an objective lens……2 numbers calculate total magnification
multiply the power of the ocular lens by the power of the objective lens
the magnification is decreased from 400× to 100×, the field of view…what ?
Increases
using the microscope, when you move the slide to the left, it appears to move
Right
Contrast
a measure of the differences in appearance between two objects
Resolution
The ability of a lens system to distinguish as separate entities objects that are small and very close together
preferable to use to inoculate a nutrient broth….What kind of inoculating INSTRUMENT?
Inoculating loop
using aseptic technique in the lab…WHAT NEED TO DO WITH INSTRUMENT before inoculate
Sterilized using Bunsen burner flame
purpose of flaming the loop before use
to prevent contamination of the bench surface and as a consideration to others in the lab who may later use the inoculating loops
When nutrient broth is cloudy, it indicates that
bacterial growth
Simple stain
1. Uses only one stain
2. When simple stain are done using basic dyes, safranin or methylene blue, the cells are the same color
3. Useful for observing the morphology or shape and the arrangement of cells
Which of the following are magnifying lenses?
Objective and ocular
Which staining technique does not need heat-fix step?
Capsule staining
Which of the following microscope is proper to use? Something that measure 0.2 micrometers?
Compound Light Microscope
Safranin is a type of…what ?
Basic dye commonly used as a counter-stain
All about Euglena…
1. Mostly green in color due to the presence of chlorophyll pigment
2. Euglena is unicellular having one nucleus
3. it is both heterotrophic (must consume food) and autotrophic (can make its own food)
The Ziehl-Neelson technique involves steaming/heat-fixing
True
Procedures that stain cells are called indirect stains
False
Gram positive gram negative ….what are their colors
Gram positive- purple
Gram negative- pink
following organisms will NOT test positive for endospores:
Bacillus and Clostridium
The primary stain used in Gram stain
Crystal violet
Acid-fast cells have ______ ___ in the cell walls, making them resistant to?????
waxy cell walls; Makes them resistant to desiccation (drying) and disinfectants
Why is agar preferable to gelatin
Agar sets more firmly at room temperature than gelatin
Starch is a polymer of;
two polymers: amylose and amylopectin
Gram stain decolorizing agent?
Ethanol
What color phenol red changes to when bacteria produce acid
Yellow
What does PPE in health care places stands
Personal Protective Equipment
basic principles of microscopy include(s)
magnification, resolution, numerical aperture, illumination, and focusing
techniques are used for observation of motility?
Wet and hanging drop mount
A dichotomous key …what it is?
a method of identification whereby groups of organisms are divided into two categories repeatedly
purpose of isolation streak plate technique
to obtain isolated colonies from an inoculum by creating areas of increasing dilution on a single plate
Aseptic techniques in microbiology are carried out to;
Prevent contamination of the specific microorganism we are working with
Bacteria with spherical morphology are referred to as;
Coccus
If you are using Nigrosin,
1. quick and easy method to gain information about the presence or absence of capsules or any other layer
2. Acidic stain
3. Heat-fixing
4. indirect stain used for determining bacterial morphology