inflammation
first response to tissue damage, alerts immune system, attempts to limit tissue, repairs the tissues, can be acute or chronic
acute inflammation
immediate and rapid, short time frame, innate immune system, noxious stimuli that trigger these responses such as bacteria/pathogens/chemicals
chronic inflammation
persistent immune reactions/slow, repeated acute inflammation, cell mediated immunity, response to monocytes/macrophages/lymphocytes, may have fibrosis
4 cardinal signs of inflammation
calor (heat), rubor (redness), tumor (swelling), dolor (pain)
cascade of events inflammatory response
vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation, cells become more permeable, exudate leaks out (protein), neutrophils begin phagocytosis and attach to endothelium (diapedisis occurs), chemotaxis occurs (attraction of neutrophils to infected cell), increase in WBC and liver is stimulated to produce c-reactive proteins to get rid of microbes, chemical mediators (prostaglandins) trigger pain response
6 chemicals of inflammation
cytokines, complements, kinins, histamines, leukotrienes/prostaglandins
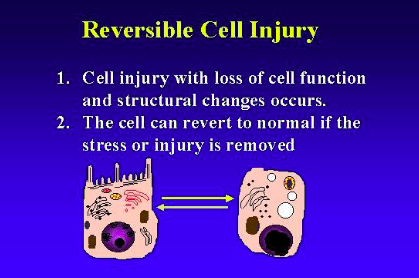
reversible cell injury
1. cell injury with loss of cell function and structural changes occurs.
2. Cell can revert to normal if the stress/injury is removed.
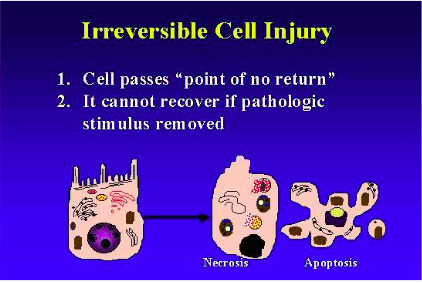
irreversible cell injury
1. cell passes "point of no return"
2. it cannot recover if pathologic stimulus removed
hyperplasia
increase in # of cells
hypertrophy
increase in the volume of the cells
metaplasia
reversible change of one mature cell type to another
often a response to chronic irritation, may result in malignant transformation
dysplasia
excess cell growth, loss of normal cell structure can revert to normal or become malignant
necrosis
pathological, due to external factors, membrane gets damaged, cells swell, nucleus shrinks/leaks out/ and ruptures/absorbed into system
4 types of necrosis
coagulative, liquefactive, gangrenous, caseous
apoptosis
physiological or pathological, targeted pre programmed cell death, DNA damaged, no inflammation
2 pathways of apoptosis
ligand binding & mitochondrial pathways
9 factors that injure cells
hypoxia, infection, chemicals/toxins, mechanical forces, trauma, radiation, immune system, genetics, nutritional deficits
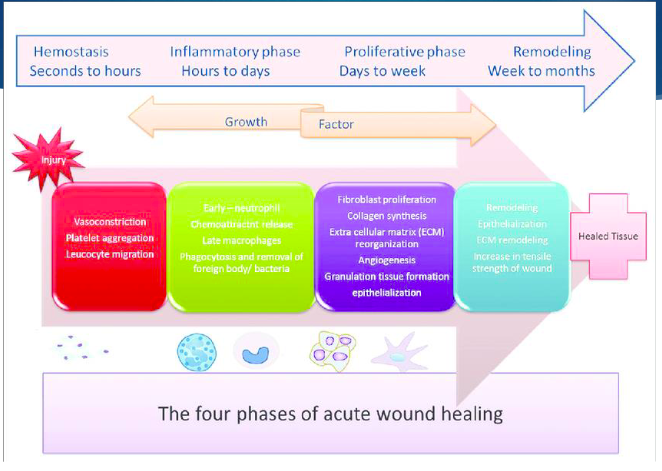
3 Phases of Healing after cell injury
1. inflammation
2. proliferation/migration
3. remodeling and maturation