Light behaves as a
particle and wave
Define: Period
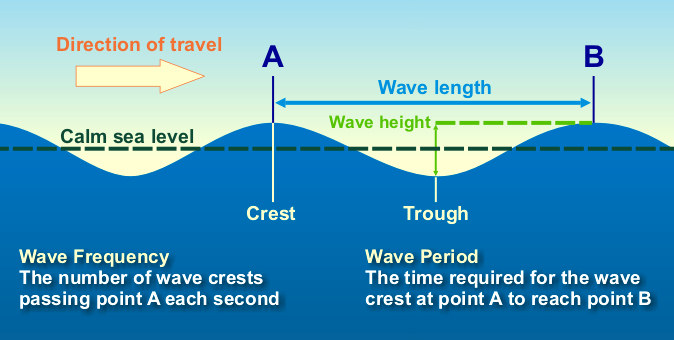
Time between passage of successive crests
Define: Amplitude
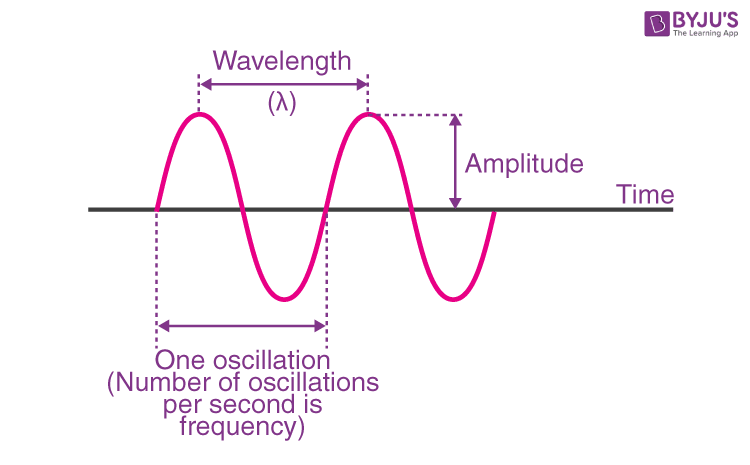
Height of peak or trough from the midline
Define: wavelength

distance from crest to crest (or trough to trough)
what formula should you know for Beers law equation/
C1/A1=C2/A2
Beers law equation is used when you are dealing with
Absorbances
The instrument that has a photomultiplier tube is the
Spectrophotometer
In a fluorometer the light waves from the light source hits what first?
The diffracting gradient
A nephelometer measures what?
Light scatter by particles in a solution
A collimator is a device that creates what?
Parallel beams of light
A collimator is found in what instrument?
A nephelometer
In the mass spec, ionization refers to what process?
ions getting separated by a quadrupole
List in order the stages within the mass spec
ionization, acceleration, deflection, detection
During which stage in the mass spec are the ions sorted by their mass:charge ratio?
Deflection
Gas chromatography separates compounds based on their
differential affinities for the carrier gas and the column
What are the components of flurometer
1.Light Source
2.Diffraction Grating
3.Light Slit
4.Sample Cuvette
5.Detector (or filter) at an angle
6.Readout
Densitometers are generally used to separate and detect
proteins in a sample/specimen
List in order from left to right the different peaks seen on a serum protein electrophoresis
Albumin, Alpha1, Alpha2, Beta, Gamma
Color with longest wavelength and lowest energy
Red
Color with the shortest wavelength and the highest energy
Violet
X rays have ___ wavelengths than IR waves
Shorter
Define: Reflected light
light that bounces off a surface
Define: Transmitted light
light that passes through the object
Define: Absorbed light
light that enters but does not leave an object
Define: Diffuse reflection
Reflection of light in all directions
Before traveling through the sample which is being assayed, what must happen to the incident light for accurate measurements?
The incident light travelling from the light source is white light and must be split into different wavelengths for more accurate measurements. This is done with a monochromator by diffraction through a prism or diffraction grating of some sort. The adjustable aperture can move up and down to allow for the use to determine which wavelength of light will hit the sample. It is very precise and you may need to change this for each assay, so make sure that you’re using the proper wavelength for assessment.
What is the mechanism which deflects the ions after they are accelerated in mass spectrometry?
A magnet is used to deflect the already-accelerated ions in the tube. If the ions are too big and heavy, then they will keep moving forward and hit the side of the tube with all of their momentum. If ions are too light, then the magnetic field will pull them significantly and they will hit the other side of the tube. Now, that’s how we look at ionic size. Let’s take a look at ionic charge. If the ion is highly charged, then the pull in the electric field will overcome the force of momentum, and it will hit the side of the tube. Likewise, if the ion is not highly ionized, then it will also hit the side of the tube. Only the ions with the proper mass/charge ratio will hit the detector!
Which component of HPLC and gas chromatography allows for separation of the solutes?
The column
Calculate the absorbance when the specimen blank reads 0.997 and the sample has a transmittance of 0.217.
Answer:
Transmitted light / Incident light = %T
0.217 / 0.997 x 100 = 21.8
2 - log %T = A
2 - log 21.8 = 0.662
What principle do both pH and pCO2 electrodes use to detect H+?
Potentiometry
What will impurities do to any liquid solution?
Increase the boiling point and Decrease the freezing point. Freezing point depression is really the only colligative property that we use clinically.
Does the wide band on the right side of lane 1 correlate with the largest DNA fragment?
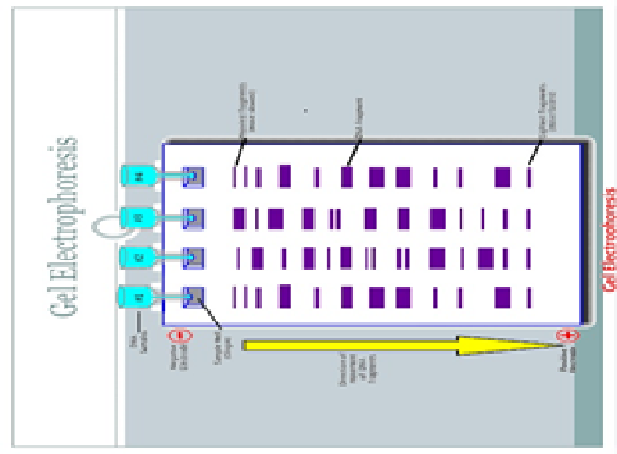
No. Don’t be fooled by the optical density (thickness) of the band. This just signifies the amount of the substance present. Even though the band size is larger to the right, the size of the individual molecules in that band are actually smaller.
Define: Specular reflection
mirror-like reflection of light in a single direction
what is the Absorbance equation?
A=2-log %T
What is the equation for %T?
%T=T X 100
Absorbance is ____ while % transmittance is ____
linear; logarithmic
What does Potentiometry measure?
Measurement of the current produced by an oxidation-reduction reaction
What do Potentiometry electrodes measure
PCO2, pH, ion-selective, reference
Wire used in potentiometry is made of what?
Ag/AgCl
What does Amperometry measure?
current produced by an oxidation-reduction reaction
What does Amperometry electrodes detect?
PO2 and heavy metals
Note: Clark PO 2 electrode and electrodes measuring heavy metals (e.g. Lead)
What equation should you know for Ohms law?
V=IR
The relationship of voltage, current, and resistance
What does Coulometry measure?
Measures the quantity of electricity by quantifying the amount of a substance that can be reduced or oxidized. The entire sample is consumed .
Reported in Coulombs
What does Voltammetry measure?
In voltammetry, there is minimal analyte consumption, as opposed to coulometry, which essentially converts all of the analyte to the new state.
Voltammetry = NO analyte consumption??
What is Conductometry?
Measures the current-carrying potential of the solution
Conductance is the reciprocal of Resistance G = 1/R
Expressed in ohms (
What is Resistivity?
Required for CLRW
To meet Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) requirements, resistivity must be >10M⇼cm
What are the colligative properties of a solution?
Freezing point depression
Boiling point elevation
Vapor pressure depression
Osmotic pressure
note: Freezing point depression and Osmotic pressure are the most commonly used in the medical laboratory
Flow cytometry is used predominantly for
hematology to evaluate Leukemias
Flow cytometry measures what of every single cell?
size, cytoplasmic complexity, DNA, RNA, membrane-bound and intracellular proteins
Define: Retention time
Time from injection to detection
What does retention factor refer to?
the differential affinity of the substance to the cellulose acetate / mobile phase, used in thin layer chromatography
what is the Retention factor equation
Rf = Solute distance / solvent distance
What Factors affect chromatographic resolution?
- The composition of the column (stationary phase) and mobile phase
- Length of the column
- Reduction in size of the stationary phase molecules
- Changing the temperature in GC or temperature and mobile phase in LC
Osmotic pressure is measured across the membrane comparing the
two chambers
note: measure the height to get an accurate reading.
What does the Nernst equation measure
the reduction potential in a cell
In electrophoresis separation is based on?
the size and charge of the molecules (usually proteins)
Lipophilic molecules are typically what charge?
No charge
What do you need to know about the Nernst equation?
Need to know the result is directedly related to concentration of the reduced species over the oxidized species. Cred/Cox more reduced species the higher the electric potential will be.
What does Valinomycin do ?
it is a selectively permeable membrane that only allows K+ to cross
We are using a machine that has a light bulb, diffraction grating, and a detector at a 90 ̊ angle from the light path. There are no mirrors. What is this method called and how does the light hit the detector?
A. Chromatography, forward scatter
B. Nephelometry,
reflected from the particles in the sample
C. Osmometry,
percolates through the particle density
D. Turbidimetry,
detected after being blocked by the sample
Answer:
The correct answer is B) Nephelometry which is also
called 90 ̊ angle scatter or side
scatter. Every compound on
earth reflects light. Yes, even black things. We use
this
principle in spectrophotometry to assess the presence of
stuff in our sample. D)
Turbidimetry is similar to Nephelometry,
but don’t get them confused! Turbidimetry only measures the direct
incident light to detect how much light is blocked. Nephelometry only
measures the light bounced off at 90 ̊.
What was the Transmittance reading on a sample with a %T of 75 and a
blank of 0.784?
A. 0.588
B. 1.04
C. 44.1
D. 95.7
The correct answer is A) 0.588.
%T = Transmitted incident light
/ Incident light
0.75 = X / .0784 X = 0.588
A pH electrode has what two special features?
A. Cl- selective
membrane and a Mg/MgCl standard solution
B. Pl/PlCl membrane and
uses amperometry for analysis
C. Semipermeable glass membrane and
Ag/AgCl internal reference
D. Valinomycin and a Hg/HgCl internal
reference solution
The correct answer is C) Semipermeable glass membrane and Ag/AgCl internal
reference.
This semipermeable glass membrane is only permeable to H+, not H2 or other funky types of hydrogen. 2H+ are able to combine with 2e- to create H2, but in the presence of a copper bar, copper has a much higher affinity for electrons than H2 does, so H2 quickly becomes 2H+ again. H+ then goes on and creates a potential difference in a hydrogen-gas electrode.
what causes a sample to go into the prozone?
too many antibodies
`what causes a sample to go into the postzone?
too many antigens
What are three ways to cause interference to the immunoassay? (Hint,
there are
more than three, but we only listed a few)
The most commonly-tested ones are when an antibody binds to junk,
interfering
antibodies, or when we are in prozone or postzone. We
have to think of the downstream effects of antibody binding. We can
detect the binding, usually by the free Fc region that is
sticking out. We perform a reaction with the enzyme attached to it, or
we measure the radioactivity of the specimen, or we observe the
formation of the precipitant.
What method functions to separate based on differential affinity of
the solid
phase and the mobile phase?
Adsorption
What is the Rf of an analyte that traveled halfway down the lane?
Rf = 0.5. Just think of the Rf as a proportion of the gel that the
solute
traveled with the solvent.
What has the business world given to the name of the process which
reduces
waste and reduces error in automation?
Lean Six Sigma
A patient with a rip-roaring infectious mononucleosis infection has a negative monospot immunoassay. How is this possible?
A. The sample is in prozone
B. The sample is in
postzone
C, The avidity of the antibody is weak
D. The
avidity of the antibody is strong
he correct answer is B) the sample is in postzone. This means that the sample has too many antigens in the reaction. This is a “rip-roaring infection”, so the antigenic burden will likely be high and may kick an immunoassay into postzone, producing a false result.
You are performing a testosterone assay via HPLC and your substance
of interest is eluting off the column and hitting the detector after
15 minutes. Since the assay only last 15 minutes,
what can you
say about the substance that you’re testing for?
A. It has a high
affinity for the column
B. It has a high affinity for the mobile
phase
C. It has a low affinity for the column
D. It has a
low affinity for the mobile phase
The correct answers are A) It has a high affinity for the column, and
D) It has a low
affinity for the mobile phase. Because it has a
high affinity to the column and low affinity for the mobile phase, it
will stick in the column for a long period of time.
The clinical chemistry laboratory is audited and it is found that it
takes on average 295.3 minutes to perform an electrolyte test and
report the results. The pathologists realize that the samples are
sitting on the bench for batch testing for an extended period of time.
This was an old practice, but they have since bought a new analyzer
that does not require batch testing for electrolytes. This practice is
corrected and the average time has now dropped to 63.1
minutes.
What is this process called?
A. Lean
B. Six
Sigma
C. Kaizen
D. Lean Six Sigma
Answer:
The correct answer is B. Six Sigma is the reduction of
error and streamlining the
processes. Holding the samples for
batch testing would be considered an error because it was no longer
required for the test to be performed accurately. Lean principles is
the reduction of waste. Lean Six Sigma is the combination of Lean
principles with Six Sigma principles. Kaizen is continual improvement
of the processes