How do you prepare a 1:24 dilution?
- 1 part sample
- 23 part H2O
- add the component to an
actual amount ex sample has 5 uL and the H2O has 115uL
- total
volume = 120uL
-120/5 = 24
therefore 1:24
What if you have too much of something?
DILUTION!
You have 5 mL of sample and 5 mL of H2O
- how many parts do you have?
- What's the ratio?
- What is the dilution factor?
- What is the concentration of the sample after its diluted?
- 10 parts
- 1:2
- 2
- 0.5
You have 5 mL of sample and 10 mL of H2O
- How many parts do you have?
- Whats the ratio
- What is the dilution factor?
- What is the concentration of the sample after its been diluted?
- 15 parts
- 1:3
- 3
- 0.3333
When would we use serial dilution in the lab?
when we want to access antibody concentration/strength
aka titers.
7 mL of a 23 mg/dL sample is dilutes up to a final volume of 83 ml. what is the final concentration?
1.94 mg/dl
1 mL of a 20 mg/dL sample is diluted and the final concentration is 17 mg/dl. what is the final VOLUME.
1.18 mL
(notice how final volume is in different units compared
to final concentration)
12 mL of a 0.5 mg/dl sample is diluted and the final concentration is 0.012 mg/dl. what is the final VOLUME?
500 mL
You need 115 mL of a 4% solution. How many mL of a 10% stock solution do you need?
46 mL
How would you perform serial dilutions to get 1:125? Which tubes would you pre fill and how much?
125 cubed is 5.
- 1 part sample
- 4 parts H2O
-
prefill 3 tubes up with H2O
1 part sample + 4 parts H2O = 1:5 + 4
parts water = 1:25 + 4 parts water = 1:125
Convert to metric: 1 Quart
0.95 liter
Convert to metric: 1 Fl Oz
30 mL
Convert to metric: 1 ounce
28.350 grams
Convert to metric:1 pound
454 grams
Convert to metric: 1 meter
3.28 feet
Convert: Fahrenheit to Celsius
C=(F-32)/1.8
Convert: Celsius to Fahrenheit
(C x 1.8) + 32
convert: 35g/dL as mg/l
350,000
convert Normality to Molarity
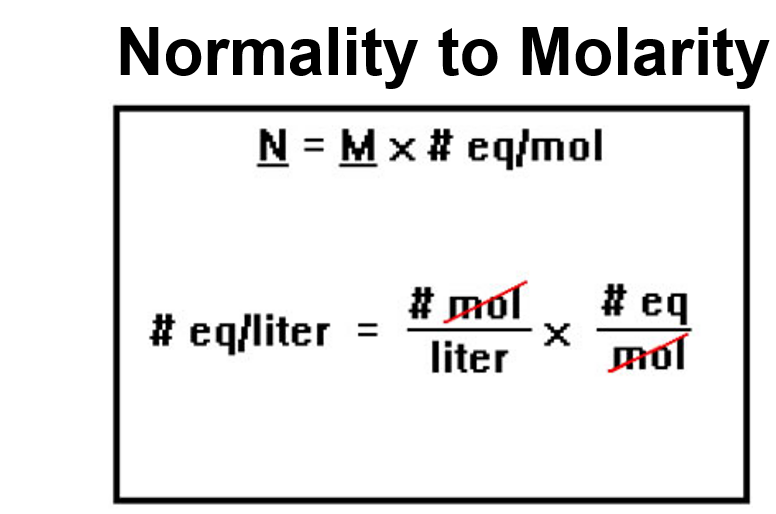
Normality = Molarity * eq/mol
You have 370 mL of urine in your bladder. How many liters of fluid are in your bladder?
0.370 L
You have 5.0 mg/dL of calcium in your blood. what is the molar concentration of Ca in your blood?
(1 mol Ca= 40 g)
0.00125 mol/L{M) Ca
What is Avogadro's number ?
6.02 x 1023
What are equivalents?
charged particles given off from a substance
What is the formula for Normality ?
molarity * Valence
What is the normality of HCl
HCL = 36.5 g/mol
36.5 g/L HCL = 1 M
36.5 g/L HCL = 1 N
What is the normality of H2SO4
H2SO4 = 98 g/mol
98g/L H2SO4 = 1M
98g/L H2SO4 = 2N
Give the instructions for preparing one liter of a 2N solution of Mg (OH)2
Molar mass = 58
valence = 2
Normality = molarity * valence,
1*2 = 2 N
therefore take 58 grams of Mg (OH) 2 and fill up
wither water 1L, then you get 1M solution or 2N
What are the different types of percent Solutions?
(w/v)% = g of solute/100mL of solution
(w/w) = g of solute / 100
g of solution
(v/v) = mL of solute / 100mL of solution
Calculated osmolality from slides?
2 x [Na] + [glucose/18] + [urea BUN/2.8] + [EtOH/4.6] aka optional only used in suspected alcohol overdose.
What is the Specific gravity of pure water?
1.0 g/mL OR 1.0 kg/L and has a SG of 1.0
If a solution has a SG greater than 1it will ?
If a solution has a SG less than 1 it will?
sink in water
float in water
How would you prepare 100 mL of a 2% w/v solution of MgSO4 * 7H2O
NOTICE THOSE WATER IONS WILL SCREW UP THE CALCULATION.
- we need
to ratio 1 mol of MgSO4 = 120.366g and 7 mol H2O = 126 g
(120.366+126=246g) 246/120.366 = 2.05 ratio.
YOU NEED 2.05 TIMES
THE AMOUNT OF MGSO4 to get enough.
(2.05 * 2 MgSO4) + then fill
it up to 100 mL of H2O
How do i know when to multiply or divide by the hydration ratio?
Multiply the ratio of the Hydrated Compound divided by the Anhydrous Compound
Hydrated Compound / Anhydrous Compound = Hydration Correction Ratio
note: The hydration correction ratio is always greater than 1.
calculate how much you would need to weigh out to get 3.4 g of CuSo4
from a bottle containing 1000 g of CuSO4*5H2O
molar mass of CuSO4
= 160 g
molar mass of H2O = 250 G
5.3 g
serum glucose is ran 5 times and you got the results of 127, 124, 112, 116, 127. whats the mean median and mode. Does this patient have diabetes?
mean- 121.2
median - 124
mode- 127
Diabetes is defined
as a fasting blood sugar of 126. the mean and median tell me no but
the mode tells me yes. they should be diagnosed with insulin
insensitivity leading to a lifestyle change before getting full on diabetes.
Find the SD of 3,4,2,3,5
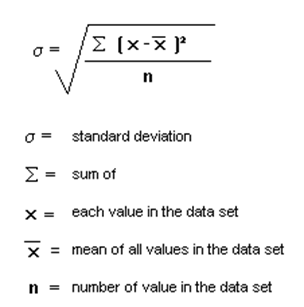
1.019
Compare the coefficients of variation when you have two tests. The first test had an SD of 2 and the second one a sd of 1. The mean in both cases is 10. what test has the greater coefficient of variation?
SD of 2 = (2 / 10) x 100 = 20
SD of 1 = (1 / 10) x 100 =
10
SD of 2 has a greater coefficient of variation because, as a
general rule, the values will vary more from sample to sample than
they do with an SD of 1.
True of False we call normal or undiseased patient values "normal range"
FALSE. we call them reference intervals this is because what is normal for one hospital will be different than what's "normal" at another
What is critical range, and what should you do with it?
is a result over a specific value, over which deleterious effects are
nearly uncertainty
- they are require immediate attention by the
attending physician.
- a documented phone call is required
because the result could mean immediate intervention.
phone call for a critical value should include what 5 things?
1- ask if they are taking care of the pt
2- give 2nd pt
identifier
3- report out the result
4- have them repeat the
result
5- document the Dr.'s or nurse's name to whom you reported to
What is the Westgard rule for 12s ?
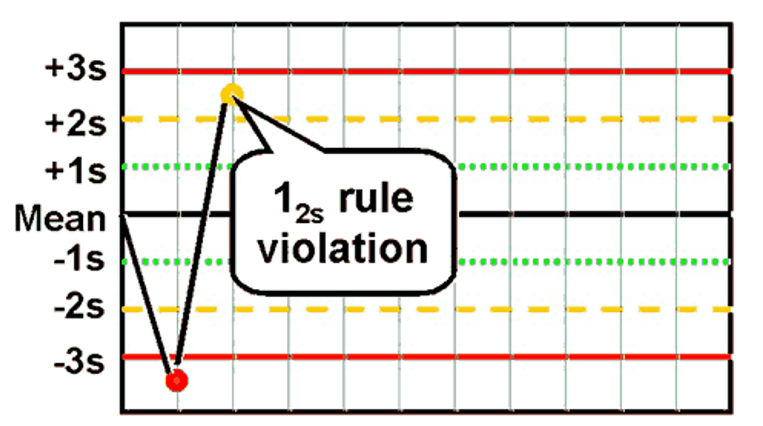
One value >2SD away from the mean (if the limits of the test are 2SD)
What is the Westgard rule for 13s ?
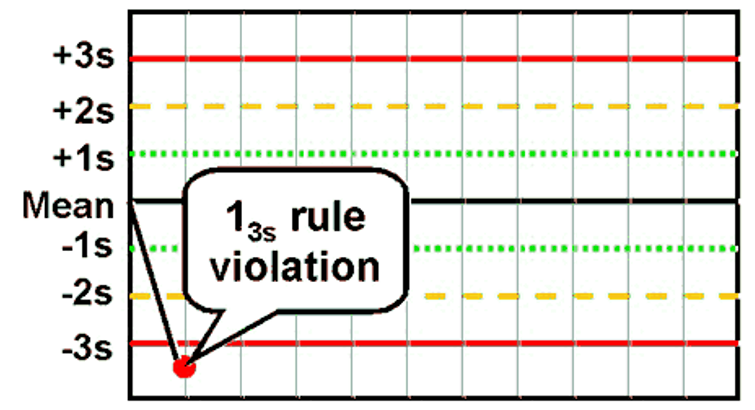
One value >3SD away from the mean
What is the Westgard rule for 22s?
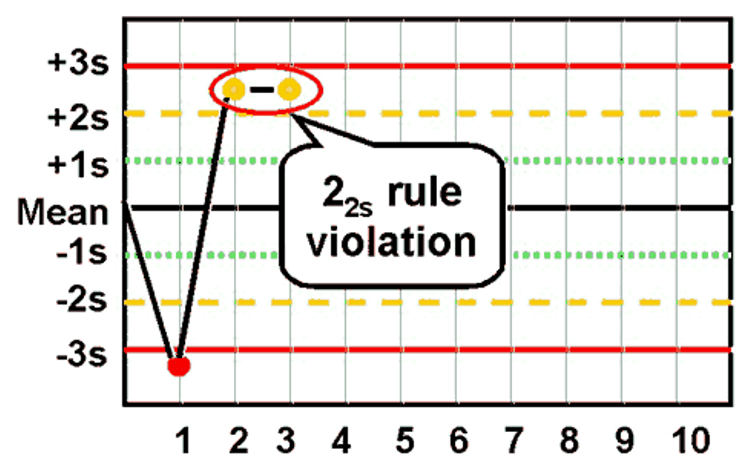
Two consecutive values exceed the same 2SD away from the mean
What is the Westgard rule for R4s ?
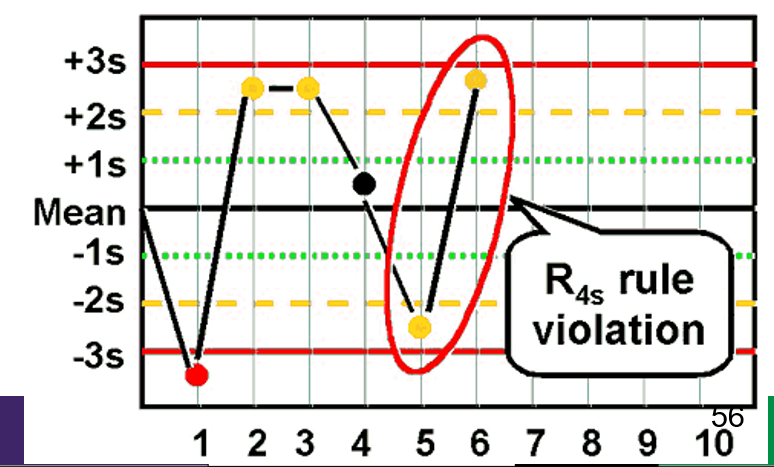
- Two consecutive values that exceed 4SD from one another
What is the Westgard rule for 41s ?
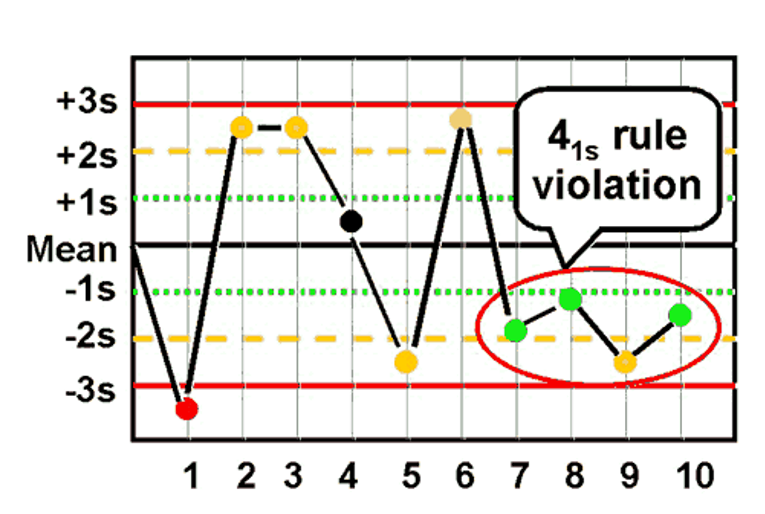
- Four consecutive values exceeding the same 1SD from the mean
What is the Westgard rule for 10x?
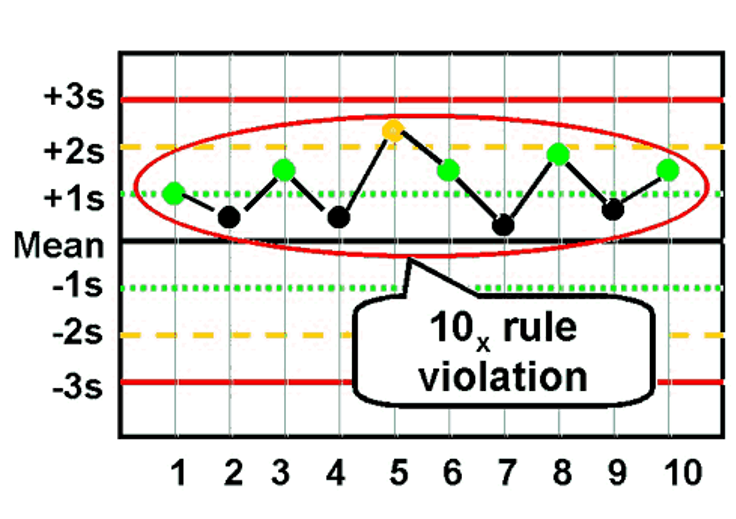
10 consecutive values on one side of the mean
Which Westgard rule is the warning rule? ie probation.
12S
What is a Chemical Hygiene Plan?
list of all chemicals in the lab and instructions of proper disposal. directions on maintaining safety devices. keeps record of employee training with PPE
What is a chemical exposure plan?
list of steps that should be preformed upon exposure to a chemical
What is a laboratory infection control plan?
designed to ensure the protection of lab employees against potential expose of blood born pathogens
What is a laboratory exposure control plan?
designed to ensure the protection of the lab employees against potential exposure to blood borne pathogens. every lab is required to have sops for this plan.
Name the 5 most common reasons for specimen error values?
1- Glucose drawn from an IV line infusing dextrose (Dextrose has a
higher concentration than normal glucose)
2- cations measured
from plasma collected in a short EDTA tube
3- Short sampling may
leave elevated anticoagulant to blood ration. It dilutes the
sample
4- inappropriate test performed
5- specimen mislabeling
How long are controls good for?
only good for one day or a few hours on the day of testing, but they are performed to improve reliability.
When performing QUANTITATIVE ASSAYS how many controls are required to be ran with the patient specimens?
Two controls (high and low)
When performing QUALITATIVE ASSAYS, how many controls do we run?
One (positive or negative) without a range of values
What are some reasons the controls could be out? List 7 examples.
1) Bad/incorrect reagents
2) Bad/incorrect standards
3)
contaminated glassware
4) incorrect pipette
5) incorrect
calculations
6) incorrect temp
7) improper technique
What does the blue represent on the diamond-shaped hazardous materials placard.
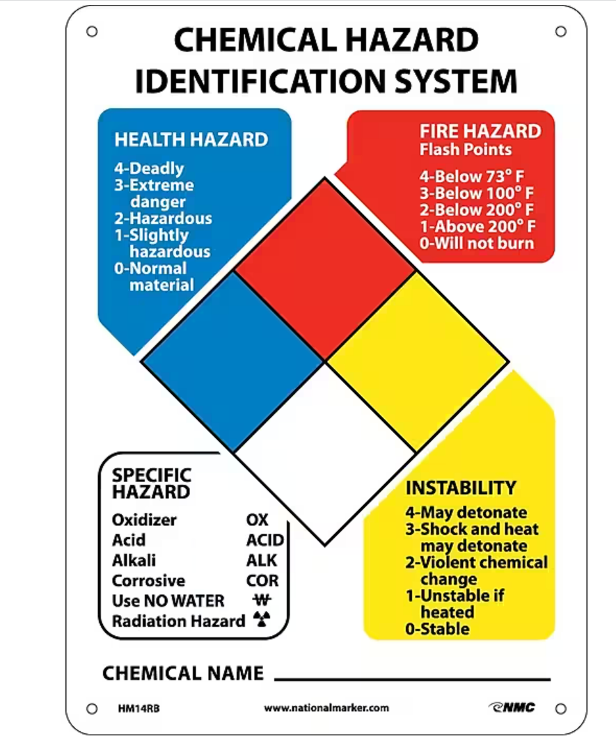
- Health hazard blue diamond
- 0-4 the higher the # the more deadly.
0 = normal material
4 = deadly
Note: water= health
What does the red represent on the diamond shaped hazardous materials placard?

- Fire hazard red diamond
- 0-4 highest temps stuff will burn to lowest. the lower the temp the more dangerous.
0 = will not burn at all
4 = will burn at room temp (73 F)
note:fire= red
What does the yellow represent on the diamond shaped hazardous materials placard?

- Reactive isotopes yellow diamond.
0-4
0 = stable
4 = may detonate @ rest
Note: yellow= yellow hazmat for radiation
What does the white represent on the diamond shaped hazardous materials placard?

"grab bag for whatever doesn't fit in the other
categories"
ACID, ALK, COR, OXY, RADIOACTIVE, USE NO WATER
How is purification done to get clinical laboratory reagent water (CLRW) ?
reverse osmosis or distillation.
Define reverse osmosis.
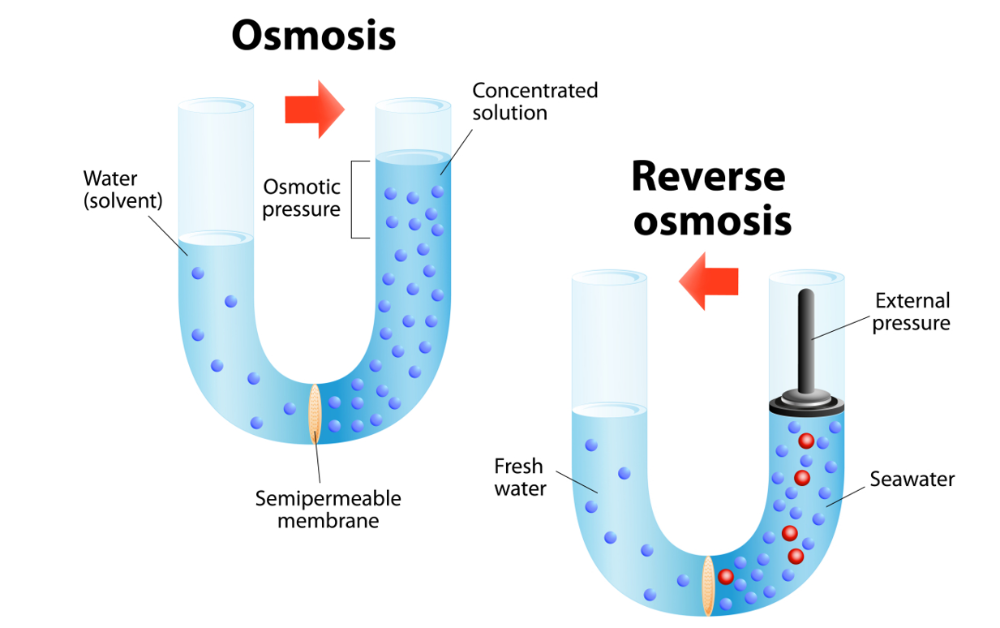
water is forced through a semipermeable membrane that acts as a filter.
How does deionization work in osmosis?
1) reverse osmosis
2) Deionization filter water passes through ion-exchanged filters and reduces mineral content in water.
3) charcoal filters may be added to further reduce organic compounds present.
4) particulate filter" gatekeeper filter then blocks anything bigger than 0.22 Micrometers from passing through.
(relatively inefficient at removing glucose or other biomolecules
What are the 3 grades of water in clinic?
type 1 - Most pure critical laboratory applications
ex: HPLC, Gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, cell culture, and
in-vitro fertilization
type 2 -don’t need ultra
pure non-critical laboratory applications (buffers, ph
solutions, micro culture medias, incubators,
type 3 -sink
water in house not used for testing (rinsing glassware,
autoclaves, heating baths, humidifiers.
Identify the 5 clinical laboratory reagent water minimum standards.
1) resistivity - @ 25 C > 10 mega alms (too much means a lot of
ions to conduct electricity
2) not a lot of bugs so maximum of 10
CFU mL
3) can not have carbons - <500 ng/g (parts per
billion)
4) can't have silicates (0.05 mg SIO2/L
5) Cant
have particulates. water needs to pass through 0.22 micro meters filter
What are the types of plastic and what are there uses?
PolyProPylene - Plastic Pipette tips, flexible or rigid, chemically resistant.
PolyeThylene - Test tubes, bottles, stoppers, racks. May (e)bsorb proteins, dyes, stains, and picric acid.
PolyCarbonate - Centrifuge tubes, graduated Cylinders, and flasks. Usable temperature range is -100˚C to 160˚C. Not for strong acids, strong bases, or oxidizing agents.
PolyStyrene - Rigid, should NOT be autoclaved. Will crack and Splinter when crushed. Not resistant to most hydrocarbons, ketones, and alcohols.
What are the different types of glass ware?
Low actinic glass, used in control material, calibrators, and reagents
high thermal resistance, with red color added to provide protection from light and still permit visibility
Regular glass, used in old, decrepit houses, and possibly some outdated beakers and flasks
Low thermal resistance, no/minimal protection from light, break easily
What are the two categories of pipettes?
1) Transfer - volumetric
2) Measuring - graduated or serologic
What are the 3 subclassifications of pipettes?
To contain (TC) - how much the pipette holds, Class A is the most accurate
To deliver (TD) - how much the pipette actually delivers
To deliver/blowout (TD/blowout) - requires an extra step which may introduce some inaccuracy
What is a serological pipette used for ?
to transfer amount of sample between 2 lines.
What is a volumetric pipetmost used for?
most accurate in measuring volume. bubble in the center. T/C.
What is air displacement micropipettes used for?
uses a piston to displace air and facilitate aspiration and ejection
of the sample. ex- disposable pipette tips.
nothing comes in
contact with plunger.
What is a positive displacement and micropipettes used for ?
uses a capillary tip made of glass or plastic with a teflon coated plunger. requires washing to flushing between samples.
What is the largest size of a particulate that could be in any grade of CLRW?
0.21 micro meters
if a patient has a positive result does that mean they have the disease.
NO. we have true positives but it can also be a false positive. Be more specific with test types.
What an explosive compound used in the laboratory similar to TNT?
Picric acid - caution when using glass jars with evaporated picrate on lid. associated with Jaffe reagent for creatine testing
what is a swinging-bucket rotor?
allows sample to move in a horizontal position creating a solid pellet at bottom of tube.
What is a fixed - angle rotor centrifuge?
centrifuges at angles between 25-52. during centrifuge particles move down the sides of the tube and form sediment. designed for much faster speeds and forces
What is an ultra centrifuge?
MUCH larger, used to fractionate lipoproteins, drug-binding assays, and prepare tissue.
If you have a single pellet at the bottom of the test tube, what centrifuge was used?-
a swinging bucket rotor
What the 4 types of chemical grades?
1 - analytical grade : the most pure substances available, list all
impurity's
2 - chemically pure grade : good quality, but meeting
no official standard, no listing of impurities
3 - practical
grade : good enough quality for industrial processes not lab
4 -
reagent grade : quality chemicals which can be used for most reagents.
What was the purpose of Resource Conservation and Recovery Act?
If you see an answer that has to do with proper use and conservation of any resource that you use in the labs, that’s going to be the right answer. We don’t need to go into these in depth, because they make up such a miniscule portion of your test and there are so many regulations, that you would put in so much effort for such little benefit.
What is the most important factor in infection control and chemical hygiene?
Washing your hands after you take your gloves off. The use of antibacterial soap is NOT as important as the physical act of washing your hands with water.
Juan is transferring two saliva samples, housed in their containers,
and packaged
in plastic bags. The sample is sitting at the
requisitioning table and he needs to
take it over to the lab for
analysis. What should he do first?
He is walking into the laboratory with a POTENTIALLY hazardous substance. If he is only taking it over to the lab, he should put on gloves. If he is performing the test, then he will need a lab coat, possibly a respirator if they are performing Tuberculosis testing. If this sample is to be assessed for a suspicion of Tuberculosis, then it should be transported with special flags.
Jane, the new lab tech, accidentally spills an old bottle of acid in
the lab and is
astonished that her hand seems to be melting away.
After copious irrigation, she
survives the ordeal with 3rd degree
burns on her hand. Where would she find out
RELIABLE information
on this acid?
SDS in the laboratory. Sure, she could roll the dice and try to find a website, but unless her google-fu is strong, she is likely to find some misleading information.
Friederich is a German exchange student in Medical Laboratory
Sciences. His
laboratory skills are very good as he was a Chemist
back in Bavaria. He says
something that you don’t understand
“tree-nee-tro-toh-loo-ol ge-vahndt” is what it sounds like. He helps
you look up the proper translation which is, “related
to
trinitrotoluene.” What reagent is he likely making and what
substance is he
using?
Jaffe reagent and he is using picric acid
1. A 37-year-old male walks into a bar, he starts a bar fight, ya
know, the kind you only see in movies. Chairs are breaking, liquor is
flowing all over the floor, and women and children are running for the
hills. He decides that he needs a cigarette because he forgot to put
on his nicotine patch before he started this brawl. He ends up being
irresponsible and doesn’t dispose of his cigarette butt properly and
was acting like he hadn’t done anything irresponsible up to that
point. The butt was thrown at an opponent behind the bar, which
immediately went up in flames
along with the rival’s clothing and
the entire building. What class of fire is this and what type of
extinguisher should be used to put out the fire?
A. A, high
pressure water
B. A, B, dry chemical
C. B, C, carbon
dioxide
D. C, D, metal X
The correct answer is B) A, B, dry chemical. This would be considered a class B fire because of all the oozing booze on the floor. Remember, flammable liquids kick the classification up to class B. There are also elements of ordinary burning material, like various linens, wood, the bar, and chairs are probably made of wood. If there is metal in the chairs, then it may or may not combust, but the firefighters are prepared for that if it should happen.
What policy in the alphabet soup below provides guidelines for
general laboratory safety and exposure control for
laboratorians?
A. CAP
B. CLSI
C. OSHA
D. TJC
The correct answer is B) CLSI. The Clinical Laboratory Safety Institute was previously called the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act (CLIA), so you may hear that term as well. If you do, they mean the same thing.
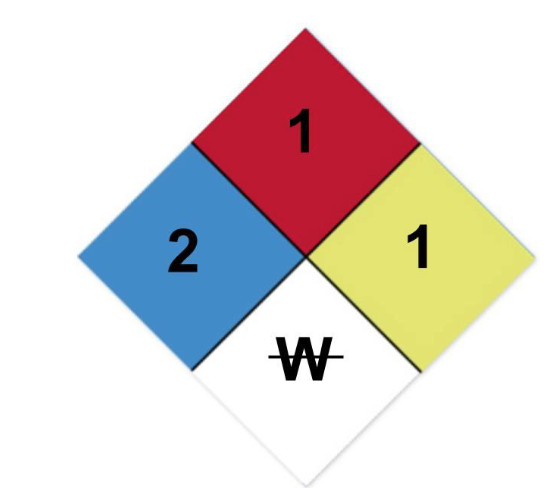
Correctly interpret the hazardous materials placard with the given
labels:
A. Deadly, Flash point <73 ̊F, May detonate,
Acidic
B. Extreme danger, Above 100 ̊F, Violent chemical change,
radioactive
C. Hazardous, Above 200 ̊F, Unstable if heated, Use
no water
D. Slightly hazardous, Will not burn, Shock and heat may
detonate, corrosive
correct answer is C) Hazardous is the 2 in the blue square, Flash
point >200 ̊F is
the 1 in the red square, Unstable if heated
is the 1 in the yellow square, and the W with a line through it means,
don’t use water.
Testing for serum albumin, the first value is 2SD above the mean, and
the next
value is 2SD below the mean. What should be done with
this run?
The run should be rejected because of the R4s rule.
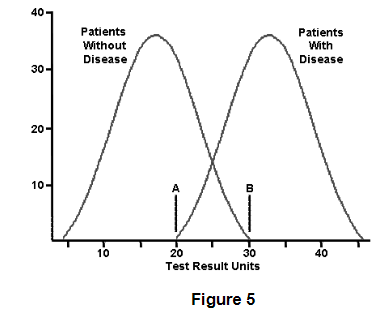
What patients with a plasma HCO3- of 23 mg/dL have acetaminophen toxicity according to Figure 5?
10 patients do have acetaminophen toxicity when the disease is at 23 mg/dL. 20 patients do NOT have acetaminophen toxicity at 23 mg/dL. Roughly 2/3 do NOT have the disease at the same level that 1/3 of patients with acetaminophen toxicity do have the condition. You can never be too careful when interpreting test results because some values can exist in this normal/disease curve overlap.
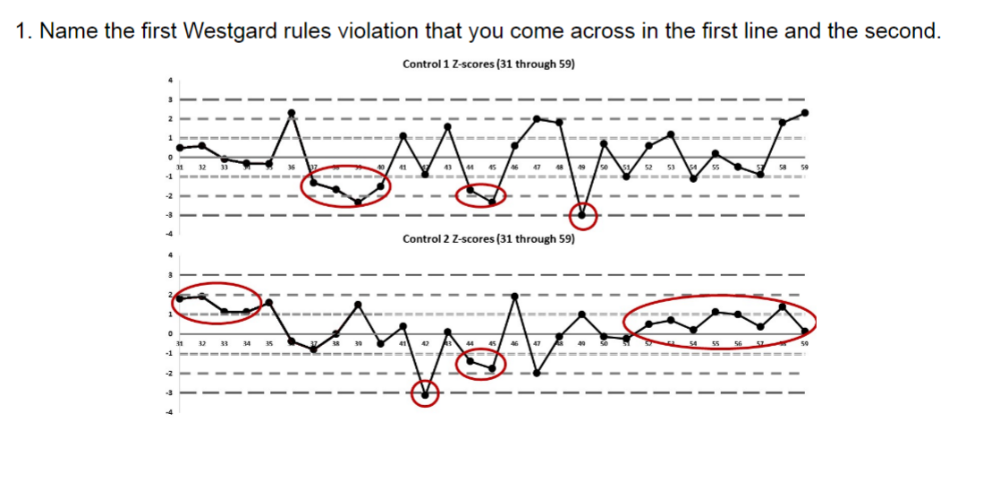
Name the first Westgard rules violation that you come across in the first line and the second.
A. 13s
B. 22s
C.
41s
D. 10x
The correct answer is C) 41S,
because you see there are 4 values in a row above the 1SD line. This might suggest a shift or a drift. The proper procedure would be to reject the QC run and rerun the samples. Then if they are still out, consider grabbing different bottles of standards
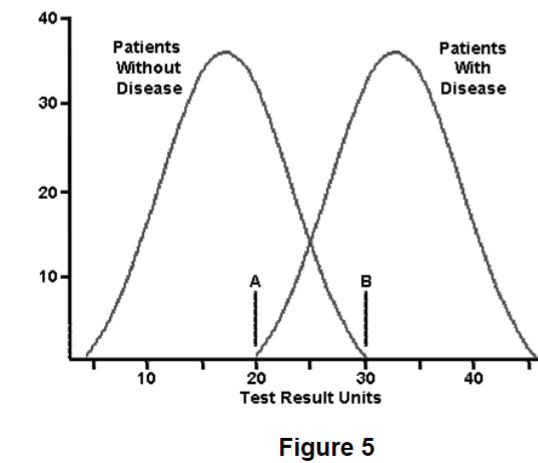
A 52-year-old male patient with diabetes has an glucose level of 125 mg/dL. He has been working on his diet and exercise over the past few weeks and takes aspirin, metoprolol, and lisinopril religiously. His prior blood sugar was 140 mg/dL one month ago. A blood sugar of 126 mg/dL is diagnostic of diabetes, where do you think he falls on the disease reference curve seen in Figure 5 right now?
A. Far left of the normal reference curve
B. Far right of the
disease curve
C. Overlapping region, but on the disease
curve
D. Overlapping region, but on the normal reference curve
Answer:
The correct answer is D) Overlapping region, but on the
normal reference curve.
Even though 126 is technically diagnostic of diabetes, this patient has been steadfast in performing lifestyle modification to reduce his risks for diabetic complications. This is the likely reason why the fasting plasma glucose came down to 126 mg/dL. That value is technically considered negative for diabetes, but in the clinical context the physician needs to watch this patient closely over the next few weeks. He is still hyperglycemic, just not as much as he was last month. He might be diagnosed with insulin insensitivity.
You begin running QC on a chemistry analyzer, but as you look at the
Levy-Jennings chart, you notice something awful, you will be forced to
start your assay over again. Breaking which of the Westgard Rules
would NOT force you to do this?
A. 12s
B.
22s
C. 13s
D. 10x
The correct answer is A) 12s.
This is the initial test before moving on to any other tests. If there is not a single value >2SD, then you can accept the run. 68.2% of the time, this will be the case. For the other 31.8% of the time, when the value exceeds 1SD, then we go down the laundry list of other Westgard Rules we need to follow. Basically, if you have a standard that is >2SD, then it flags us to a potential problem. That is okay if it happens once, but we need to keep our ears to the ground because if anything was fishy, then if something is wrong or is getting worse, then it will likely break one of the other Westgard Rules on the next run. If you are back within 2SD, that means that the value was just an outlier. 4.2% of the time, the value will be between 2-3SD from the mean value ... and that is completely fine. We just have to make sure that weird values like that don’t continue
A patient comes into the emergency room with a broken arm after
falling off the
stool at a local burger joint while eating a
burger and a shake. His electrolytes
come back and show that he
has hyponatremia! What happened?
The sample is likely lipemic because he just ingested an entire
burger and a
shake. With lipemia, the fats take up physical space
in your blood. So, when
the sample is taken in to the vacutainer
tube, it contains your blood, and also
fats, which take up
physical space. The quantity of electrolytes is affected
because
they are hydrophilic, meaning that they like to hang out in
water.
Because the lipids are occupying one side of the couch the
electrolytes can
only sit in the other two seats of the couch,
but the machine calculates a
volume. It counts the fatty space as
volume which electrolytes should occupy,
but they don’t.
Therefore the result which the computer spits out is
falsely
decreased. The real concentration is much higher than
that! Of note, potassium
and bicarbonate are less likely to be
affected by this problem.
A tube of blood comes from the ED for stat chemistry testing. You see
that it is
only filled with about 1 mL of blood. Why is this
specimen unacceptable?
Granted, crazy things happen in the ED, so it’s not easy to get 5 mL of blood on each patient. The issue is that depending on which vacutainer tube was used, it could have an anticoagulant in it that will interfere with the testing at such high concentrations, because now the proper anticoagulant :blood ratio has been thrown off. In all likelihood, I think this sample could still be ran with a note on the result informing the doctor what happened with the sample. They’re used to this sort of thing and know how to interpret it
1 mL of a 50 mg/dL sample is diluted up to a final volume of 15 mL. What is the final concentration?
3.33
What is the normality of 1 M HCl?
1 N HCL because there is 1 equivalent in 1 mol of HCl
A 37-year-old male feels extremely hot in his Arizona apartment, but
looks at the thermometer and realizes that it’s a chilly 42.4 ̊. He
immediately seeks medical treatment because he is sweating and it’s so
cold. What is most likely to have happened and how hot is it
really?
A. He didn’t look closely at the units, 100 ̊
B. He
missed the preceding 1, 142.4 ̊
C. He is straight crazy 42.4
̊
D. He wasn’t in his house 42.4 ̊
The correct answer is A)
He didn’t look closely at the units. 42.4 ̊C is 100 ̊F, which is pretty hot.
What is the molarity of 3.7 mg of HCL in 0.7 L of water? GMW of HCL = 36.46g/mol
The correct answer is 0.00014 M.
3.7 mg x (1 g / 1000 mg) =
0.0037 g
0.0037 g / 36.46 g/mol = 0.0001 mol
0.0001 mol /
0.7 L = 0.00014 M
What is the final concentration if 1 L of a 3.5 mg/dL NaCl solution is diluted in 2 dL of water?
The correct answer is 2.9 mg/dL
1 L = 10 dL
C1V1 =
C2V2
V2 = initial volume of 10 dL + 2 dL of water = total volume
of water (12 dL)
3.5 x 10 = C2 x 12
C2 = 35 / 12
C2 =
2.9 mg/dL