What are two examples of indirect body composition methods?
- DXA scan
- Bioelectrical impedance analysis
What is an example of a doubly indirect body composition method?
Skinfold measures
Describe the procedure for skinfolds.
- grasp skinfold firmly between thumb+index finger
- lift 1cm up + place clippers
- take from 3 sites w/ 1mm between each take
Bioelectrical impedance is based on what law?
Ohm's Law
How does it measure body composition?
measure tissue resistance to electrical currents (fat tissue=less efficient conductor)
Calculate %body fat when provided skinfolds from 3 sites.
- Density= from 3 sites
- Men= (495/density)-450
- Women= (505/density)-462
Remember the steps
- Sum the average measurements of the 3 sites
- Calculate body density using the given equation
- Calculate body fat using the given equation
What is one factor that causes RMR to be different than BMR?
- can be increased for a short time with exercises
- BMR based on body rest for 24hours
Describe Non-exercise thermogenesis
writing/typing/fidgeting
Describe the fat cell development pattern
- 1 fat cell → more in #
- → @max size ==> cell # increase
- → cells shrink but not lose #
What are two ways one can increase fat metabolism?
- increase from low to mod. intensity
- eat carbs hours before exercise (to lower fat oxidation)
Describe the traditional carbohydrate loading model (how it is done and its benefits).
- Day 6-4 (70% effort) w/ mod. carbs (5),
- Day 3-2 (light training)
- Day 1 (rest) w/ high carb (10)
- Benefits: extends performance time prior to fatigue
Describe what happens to excess carbohydrates that cannot be stored as glycogen.
converted and stored as fat
What are the recommendations for carbohydrate intake:
- During long endurance exercise?
- 30-60 grams of carbohydrate per hour of endurance performance
What are the recommendations for carbohydrate intake
- After endurance exercise?
- 1.5g of carb / kg body weight
What are the recommendations for carbohydrate intake
- After strength or power exercise?
- 1-1.2 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight (per hour)
What is the protein recommendation after resistance exercise to promote muscle growth?
- 20-25gram of protein
- 1.6-1.7g/kg/day
- small dose (20g) every 2-3 hours
Describe the importance of various minerals in the body as related to exercise performance.
- hydration, nerve transmission and muscle contraction
- synthesis and repair of muscle tissue during recovery
- energy production
- maintains bone health
What is the difference between Heme and Non-Heme Iron?
- Heme
animal flesh like meat, poultry, and seafood.
What is the difference between Heme and Non-Heme Iron?
- Non-heme iron:
(plant foods) whole grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, and leafy greens.
How do we assess if an athlete is iron deficient?
blood test to see if low protein ferritin
What is the role of the protein Ferritin in the body?
- makes iron available for cellular processes
- protect lipids, DNA, and proteins iron toxins.
- make healthy RBCs
Benefits of Collagen
- help relieve joint inflammation
- ease the extra pressure put on cartilage and bones
Benefits of Creatine
- stim body’s ability to create ATP
- increase energy/strength/lean BM/muscle recovery
BMI Calculator

Claire weighs 140 lb. and is 5 ft. 6 in. tall. What is her BMI?
- 22.6
- (140*703)/(66^2)
- (63.5029)/(167.64)^2
Based on Claire's BMI, what category does she fall into?
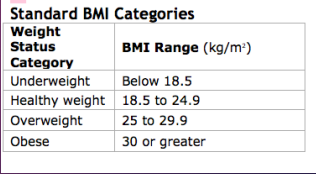
Normal
Claire also performed a BodPod assessment and found out that she has 116 lb. of fat free mass and 24 lb. of fat mass. What is her fat mass index?
- 3.87
- fat free mass [kg]/ (height [m])²
What is Claire's fat-free mass index based on her BodPod assessment showing she has 116 lb. of fat free mass and 24 lb. of fat mass?
- 18.73
- fat-free mass [kg]/ (height [m])²
Tony just went through a skinfold assessment. He is 36 years old. The technician measured his abdomen, thigh, and chest skinfolds.
His abdomen was 15 mm, chest was 20 mm, and thigh was 33 mm. Based on these measures what is his percent body fat?
20.8%
Appendicular lean mass index is used to assess and diagnose sarcopenia.
True
Skinfold measurement (DENSITY)
-
Men
- Db = 1.10938 – (0.0008267*∑SKF3)
+
(0.0000016*[∑SKF3]2) – (0.0002574*age)
- Db = 1.10938 – (0.0008267*∑SKF3)
+
-
Women
- Db = 1.0994921 – (0.0009929*∑SKF3)
+
(0.0000023*[∑SKF3]2)
- Db = 1.0994921 – (0.0009929*∑SKF3)
+
How exercise helps to improve body composition
- Increases daily caloric expenditure
-
Increases lean mass leading to an increase
in
metabolic rate - Increases growth hormone and testosterone, which help to increase lean body mass
Hydrostatic weighing
- Density = Mass/Volume (M/V)
- Determination of body
volume
- Amount of water displaced
Body composition methods
Direct
- Chemical analysis of whole body
- Not suitable in the living body
Body composition methods
Indirect
- Component and property based
Body composition methods
Doubly indirect methods
- Provide estimates of body composition based on results from direct or indirect methods
- Depends on biological interrelationships
- Larger predictive error but easier to perform