Light can be thought of a particles called photons. The energy, E( measured in joules), of a photon is proportional to its frequency, according to the formula, E=hv. In this formula, what is "h"?
Planck's constant
What are the components of a typical single-beam spectrophotometer include which of the following?
- light source
- entrance slit
- monochromator
- exit slit
- cuvette
- detector
Absorbance is proportional to the concentration of light absorbing molecules in a sample and the pathlength of substance through which the light travels. The dependence on concentration and pathlength is expressed by the formula A=εbc which is also known as:
Beer-Lambert's law
List three difference between atomic absorption spectrometry and atomic emission spectrometry:
atomic absorption:
- Detects light absorption
- Requires light source
- Temperature in the atomizer is adjusted to atomize atoms when electrons are in the ground state
emission:
- Detects light emission
- Doesn’t require a light source
- Temperature in the atomizer is adjusted to atomize atoms and excite electrons to higher energy levels
What is the definition of spectral interference?
When analyte signal overlaps signal from other species
What is the definition of chemical interference?
Caused by any substance that decreases the extent to which an analyte breaks apart into gaseous atoms
What is the definition of ionization interference?
A problem often associated with the presence of alkali metals with low ionization potentials
What is the definition of atomization?
The process of breaking an analyte into gaseous atoms
The pH of a buffer depends on which of the following?
- temperature
- molarity
The central equation for buffers is the ______ equation, which is simply a rearranged for of the Ka equilibrium expression.
Henderson-Hasselbalch
What is the definition of autoprotolysis?
A substance that acts as both an acid and a base
What is the definition of Kb?
- Base dissociation constant
- base hydrolysis constant
What is the definition of a weak base?
substance that reacts with water by abstraction of a proton to H2O
What is the definition of a weak acid?
Substances that reacts with water by donating a proton to H2O
What is the definition of mean?
- the sum of the measured values divided by the number of values.
What is the definition of median?
the middle number in a series of measurements
What is the definition of standard deviation?
- the measure of the scatter of a data set
- the measure of how fat a set of numbers in spread out form their average value.
What is the definition of range?
The difference between the highest and the lowest values in a data.
What is the definition of selectivity?
The ability of a method to distinguish the analyte of interest form other species in the sample
What is the definition of sensitivity?
The ability of a method to respond reliably and measurable to changes in analyte concertation
What is the definition of detection limit
The smallest quantity of analyte that is significantly different from the blank.
What is the definition of linear range?
The analyte concentration range over which response in proportional to concentration.
What is the definition of retention time?
The maximum time of elution of an analyte measured from the time of injection or from the hold-up time
What is the definition of retention factor?
Measurement of how long analytes spend on the column compared to the mobile phase.
What is the definition of resolution?
The ability to separate co-eluting analytes to yield distinct peaks with no overlap.
What is the definition of chromatogram?
The two-dimensional visualization of how analytes elute based on the time (volume) and detector response.
The______ equation describes the various factors influencing plate height (H) in terms of eddy diffusion(multiple paths), longitudinal diffusion, mass transfer and the flow rate.
Van Deemter
In 1-2 sentences, explain why preparatory LC methods, such as solid phase extraction, size exclusion, partition, or affinity chromatography are sometimes performed prior to introducing the sample into an automated HPLC system:
to clean up the sample matrix, enrich target analytes and, if necessary, convert the analytes into species amenable to instrumental analysis through chemical reaction.
The components of a typical HPLC system include which of the following?
- pump
- column
- injector
- detector(s)
- data system
- column compartment
- mobile phase reservoirs
In electrophoresis, cations flow towards the cathode while anions flow towards the anode. In capillary electrophoresis, ____________ cause the bulk flow of all solute polarities towards the cathode.
electroosmosis
What is the definition of redox reactions?
The transfer of electrons from one species to another.
What is the definition of potentiometry?
The use of voltage measurements to extract chemical information.
What is the definition of voltammetry?
A quantitative procedure in which the current is measured while voltage between two electrodes is varied
What is the definition of coulometry?
A quantitative procedure in which electrons participation in a chemical reaction are counted to determine how much analyte reacted.
What is the definition of stripping analysis?
A quantitative procedure in which analyte from a dilute solution is first concentrated into a single drop, or thin film,
What is the definition of amperometry?
A quantitative procedure in which the electric current between a pair of electrodes that are driving an electrolysis reaction is measured.
What is the definition of junction potential?
the voltage difference that develops when two dissimilar electrolyte solution are placed in contact.
What is the definition of electrogravimetric analysis ?
A quantitative procedure in which an an analyte is plated out on an electrode and weighed.
What is the definition of Ion selective electrode?
A conductor that responds preferentially to one ionic species in a solution.
What is the definition of polarography?
A quantitative procedure in which voltammetry is conducted with a dropping-mercury electrode.
Select the correct word from the bracketed section.
In a redox reaction, a molecule is said to be oxidized when it [loses, gains] electrons and reduced when it [loses, gain] electrons. An oxidizing agent [takes, gives] electrons from another substance; whereas a reducing agent [takes, gives] electrons to another substance.
- loses
- gains
- takes
- gives
[True or false] Electric current is proportional to the rate of a redox reaction
True
[True or false] A reference electrode maintains a (fixed) potential against which the potential of another half-cell may be measured.
True
The net driving force for a redox reaction is expressed by the ______ equation, whose two term include the driving force under standard condition and a term that shows the dependence on concentrations.
Nerst
What is the definition of heterogenous?
immunoassay technique that requires separation of the analyte-antibodies complex from the remaining sample prior to analysis.
What is the definition of homogeneous?
Immunoassay technique that does not require separation of the analyte-antibody complex prior to analysis
What is the definition of Radial immunodiffusion(RID)?
Single diffusion technique in which reagent antibodies are incorporated into the agar and patient sample is added to a well in the agar. Patient antigens diffuse into the agar and complex with the antibodies to form a measurable precipitate ring.
What is the definition of ouchterlony immunodiffusion?
Double diffusion technique in which reagent antibodies are added to a well in the agar and patient sample is added to another well. Both the antibodies and antigens diffuse into the agar where they can complex and form a precipitate line.
What is the definition of rocket immunoelectrophoresis?
single diffusion technique in which reagent antibodies are incorporated into the agar and patient samples are added to individual wells in the agar. Patient antigens migrate into the agar n an electric field and complex with the antibodies to form measurable precipitate peaks.
What is the definition of counter immunoelectrophoresis?
Double diffusion technique in which reagent antibodies are added to a well in the agar and patient sample is added to another well. An electrical current is applied to speed up the migration of the antibodies and antigens into the agar where they can complex and form a precipitate line.
What is the definition of nephelometry?
Immune complexes form between the patient analyte and the reagent antigen/antibody competes with analyte in the sample for binding sites.
What is the definition of turbidimetry?
immune complexes form between the patient analyte and the reagent antigen/antibody in solution causing precipitation. The amount of light transmitted through the solution is measured by a light detector placed at a 180° angle.
What could cause falsely altered patient results using immunoassay techniques?
- biotin
- autoantibodies
- heterophile antibodies
In 1-2 sentences, describe how the "hook effect" may alter patient results when using immunoassay techniques?
It gives falsely low results with certain immunoassays in the presence of excess amount of analyte of interest
If a discrepant/discordant result occurs when testing a patient sample by immunoassay, what is the first step in investigating the possibility of the hook effect?
perform a serial dilution.
What is the definition of chromatography?
a process in which compounds are separated from on another by passing a mixture through a column that retain some compounds longer than others.
What is the definition of effluent?
The fluid entering the chromatographic column
What is the definition of eluate?
The fluid exiting the chromatographic column
What is the definition of theoretical plates?
a concept wherein a column in thought of as having discrete sections in which a solute molecule equilibrates between the mobile and stationary phases.
What is the definition of adsorption chromatography?
Solutes tick to the surface of the solid stationary phase.
What is the definition of partition chromatography?
Solutes equilibrate between the mobile phase and a thin liquid station film
What is the definition of molecular exclusion chromatography?
Solutes penetrate into pores in the station phase allowing the largest solutes to elute first.
What is the definition of Ion-exchange chromatography?
Solute ions are attracted to specific groups attached to the stationary phase.
Describe the differences between classical liquid chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography.
the solvent in LC travels by the force of gravity. In the application of HPLC, the solvent travels under high pressure obtained by means of a pump to overcome the pressure drop in the packed column, which reduces the time of separation.
Elution with a single solvent of a constant solvent mixture is called______
elution; whereas, in ______ elution, the solvent in changed continuously from weak to stronger eluent strength.
- isocratic
- gradient
What is the definition of electrophoresis?
The migration of ions in an electric field
What is the definition of capillary electrophoresis?
A high-resolution separation Technique conducted with solution of icons in a narrow bore tube.
What is the definition of electro osmosis?
The propulsion of fluid inside a fused-silica capillary form the anode toward the cathode caused by the applied electric field
What is the definition of capillary gel electrophoresis?
a separation technique in which macromolecules are separated by sieving as they migrate through a gel inside a capillary tube.
What is the definition of electric charge(q)?
A fundamental property of some subatomic particles (electrons, protons) that is measured in coulombs
What is the definition of electric current(I)?
The movement or flow of charged particles measured in amperes
What is the definition of capillary gel electrophoresis electrical work(W)?
The work done as electrons move between two points that is expressed in joules
What is the definition of potential difference (E)?
The difference in electric potential between two points that is measured in points.
What is the correct word in each bracketed section? In electrochemistry, the [anode, cathode] is the electrode where [oxidation, reduction] occurs resulting in a loss of electrons; where as the [ anode, cathode] is the electrode where [oxidation, reduction] occurs resulting in a gain of electrons.
- anode
- oxidation
- cathode
- reduction
Zn(s) +H2SO4(aq) →ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
In this reaction the electron donor is ___ and the electron acceptor is_____
- H2; H2SO4
- H2;Zn
- H2SO4; ZnSO4
- Zn;H+
- Zn; ZnSO4
d
A device used to maintain electrical neutrality in a galvanic cell is termed the;
- anode
- cathode
- battery
- voltmeter
- saltbridge
e
A(n)_____ electrode is designed to respond preferentially to a particular a species in solution.
- calomel
- indicator
- reference
- ion selective
- potentiometric
d
samples introduced into a mass spectrometry system are volatilized and then ionized so the charged molecules and fragments can be separated according to their___?
- pH
- Solubility
- conductivity
- concentration
- mass to charge ratio
e
What are the basic components that are standard in all mass spectrometers.
- ion detector
- sample inlet
- mass analyzer
- ionization source
What is the definition of electron ionization?
ionization technique in which molecules are bombarded with high-energy electrons resulting in the formation of charge molecular ions and fragments
What is the definition of electrospray ionization?
Ionization technique in which the LC effluent passes through a capillary to which a voltage has been applied. Energy is transferred to the solvent droplets, becoming charged, and evaporation of the solvent leads to coulombic repulsion and election of ions.
What is the definition of atmospheric pressure chemical ionization?
Ionization technique in which the LC effluent is rapidly desolvated to from a gas phase that interacts with a cloud of electrons formed by a corona discharge needle to become ionized
What is the definition of Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization?
Ionization technique in which the sample is mixed with a matrix solvent and spotted onto a stainless-steel plate. A laser pulse irradiates the sample causing desorption and ionization of the matrix and the sample.
Which of the following mass spectrometer technologies can effectively concentrate the ions of interest yielding greater analytical sensitivity?
- quadrupole
- ion trap
- time of flight
- magnetic sector
b
In a tandem mass spectrometer, or triple quad, which of the quadrupoles function as a collision cell?
- Q1
- Q2
- Q3
- Q4
b
The conjugate base of HNO3 would be:
- NO2
- NO3 _
- NO3 2_
- H2NO3 +
b
A solution with a [H]=1.0x10-4 M has a pH of _____ and would be considered_____
- 2.5; acidic
- 4.0; acidic
- 8.1; basic
- 10.5;basic
b
Which of these is the strongest acid listed?
- 2.0 M phenol (Ka=1.0x1.10-10)
- 2.0 M acetic acid (Ka=1.8x1.10-5)
- 0.5 M oxalic acid (Ka=5.4x1.10-2)
- 0.5M hypochlorous acid (Ka=2.9x1.10-8)
c
Which parameters are required for evaluation of a FDA approved method?
- Precision
- Accuracy
- Reference values/intervals
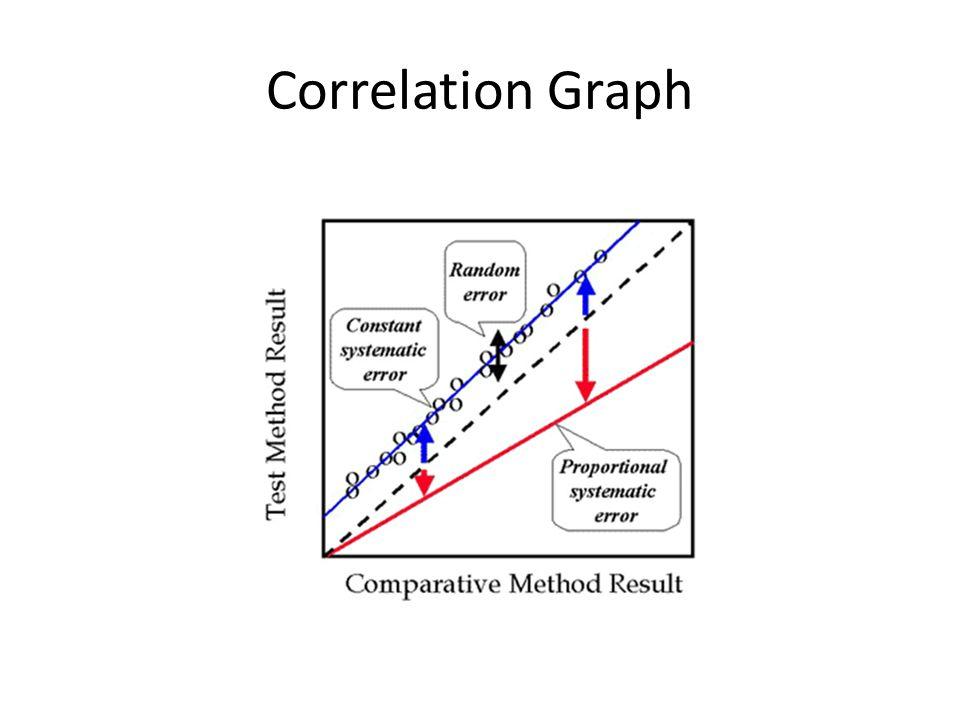
Know the different lines represent the different types of errors.
Know the different lines represent the different types of errors.
Which of the following test parameters could be evaluated by testing 5 samples with known concentration, in duplicate and assessing the linearity between the expected and measured values?
- Precision
- accuracy
- reportable range
- analytical sensitivity
- analytical specificity
- reference values/intervals
c
What are the labels used in immunoassays?
- Enzymes
- radioactive substance
- fluorescent substances
- luminescent substances
Chose the correct word in the bracketed section
In a competitive immunoassay, labeled[antigens, antibodies] in the reagent compete with antigens in the patient sample for a limited number of binding sites. In this type of immunoassay, the generated signal is [ directly, inversely] proportional to the a pro
- antibodies
- directly
What term refers to an immunologic phenomenon that occurs when excess analyte{ such as patient antigen or antibody} overwhelms the test system leading to a false inaccurate result?
Hook effect