What is Electrolysis?
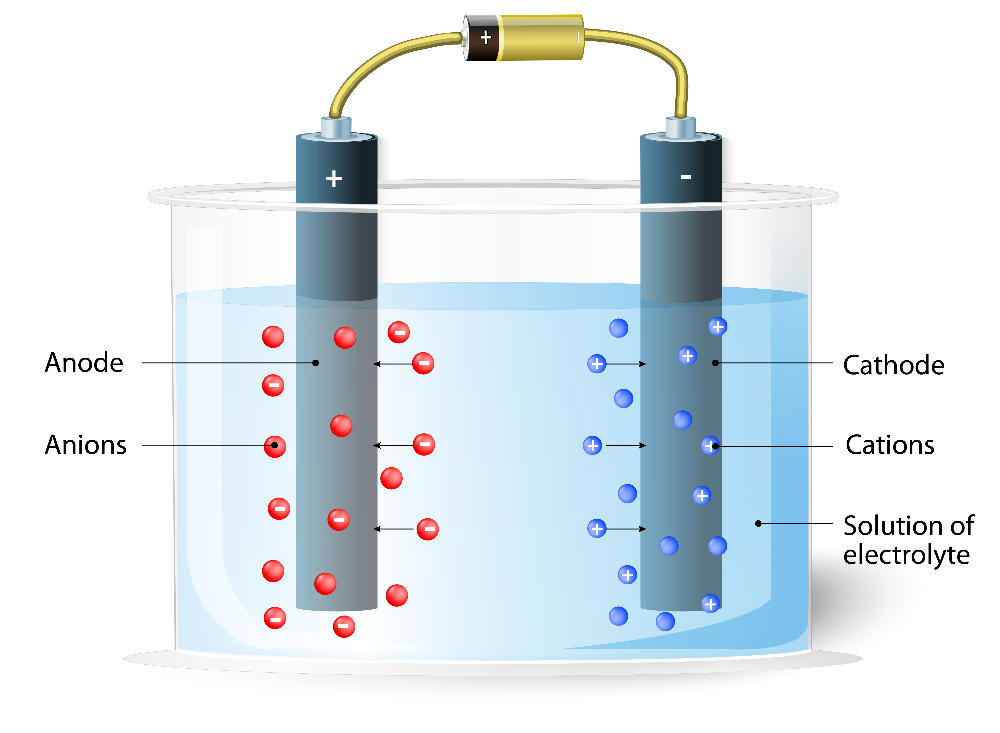
a chemical reaction in which we apply a voltage to drive a redox reaction that would not otherwise occur
What is an electroactive species?
it is a one that can be oxidized or reduced at an electrode.
What is electrogravimetric analysis?
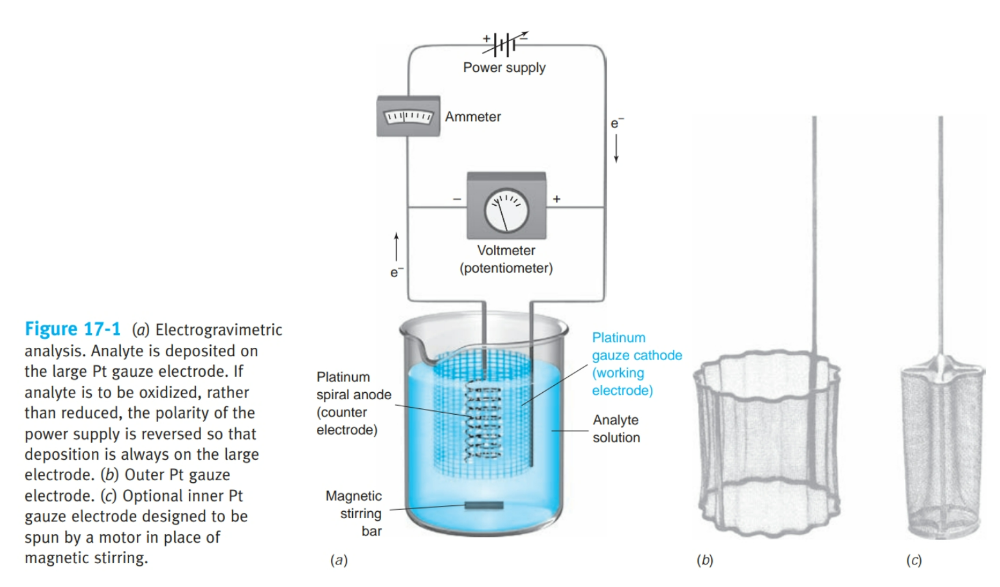
analyte is plated out on an electrode and weighed.
How do you find out when electrolysis is complete?
1. Disappearance of color
2. Deposition on freshly exposed electrode surface
3. Qualitative test for analyte in solution
What is coulometry?
- electrons participating in a chemical reaction are counted to learn how much analyte reacted.
- the quantitative determination of any substance that can be made to undergo an electrochemical reaction with 100% current efficiency, i.e. the number of Coulombs required to carry out a chemical reaction is measured (integration is needed).
What is amperometry?
- the measured electric current between a pair of electrodes that are driving an electrolysis reaction.
- we measure an electric current that is proportional to the concentration of a species in solution
What is a Clark electrode?
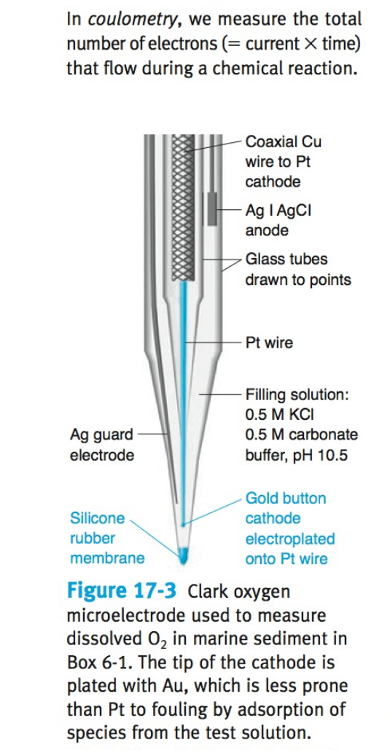
an electrode that measures ambient oxygen partial pressure in a liquid using a catalytic platinum surface according to the net reaction
What is a biosensor?
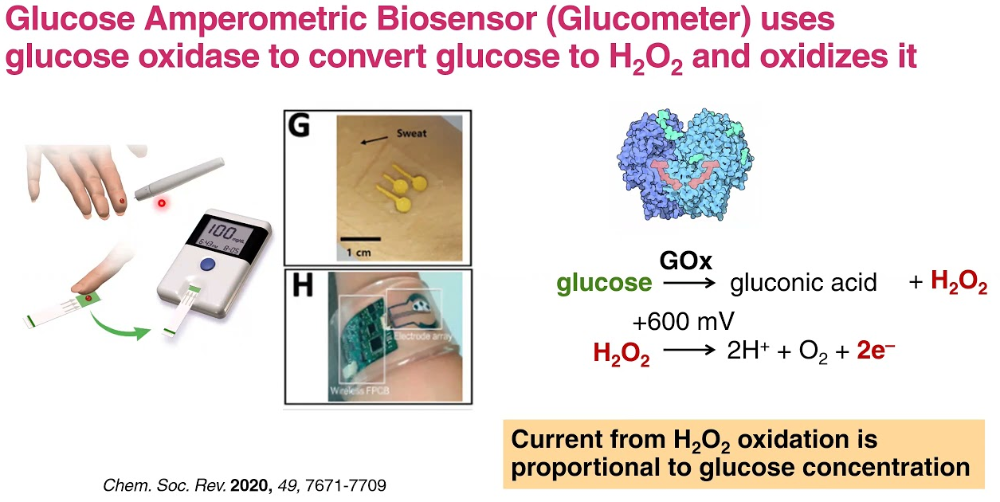
a device that uses a biological component such as an enzyme or anti- body for highly selective response to one analyte.
What is a mediator?
transports electrons between analyte and the working electrode. The mediator undergoes no net reaction itself.
What is a Reference electrode?
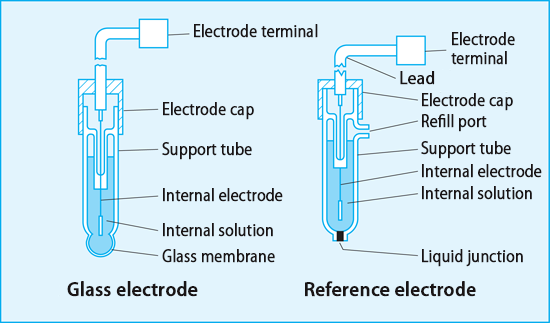
- Provides fixed reference potential with negligible current flow
- an electrode which has a stable and well-known electrode potential.
What is a Potentiostat?
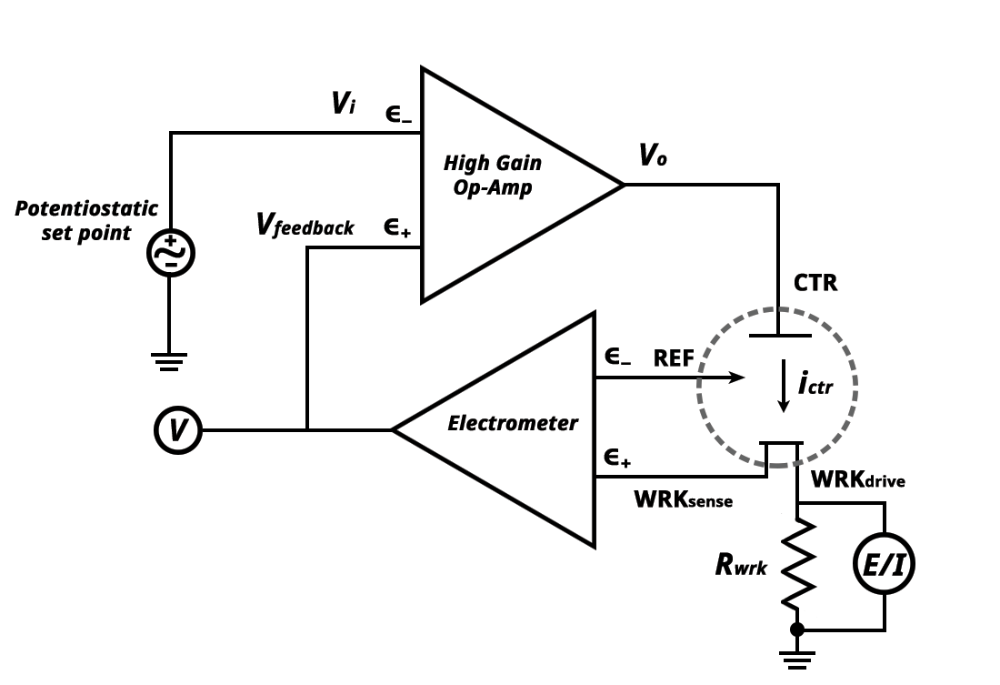
- Controls potential difference between working and reference electrodes
- an analytical instrument designed to control the working electrode's potential in a multiple electrode electrochemical cell.
What is a Working electrode?
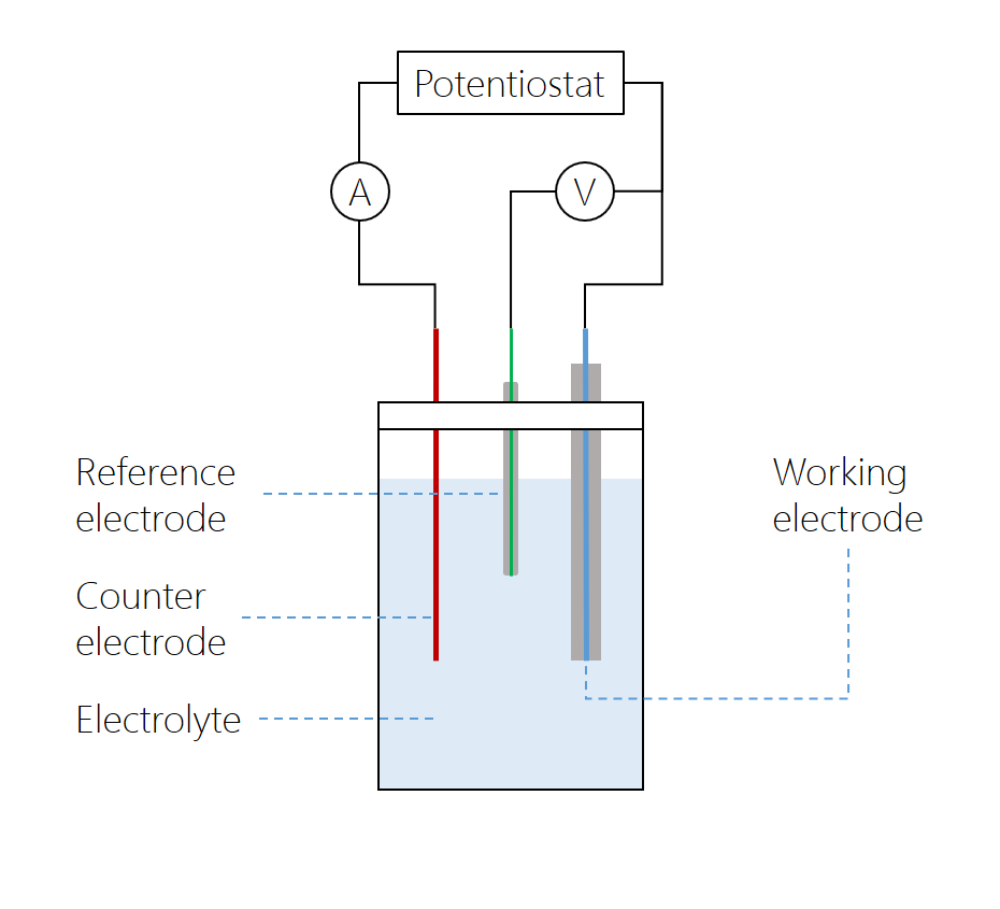
- Analyte reacts here, voltage is measured between working and reference electrodes
- the electrode in an electrochemical system on which the reaction of interest is occurring.
What is a Auxiliary electrode?
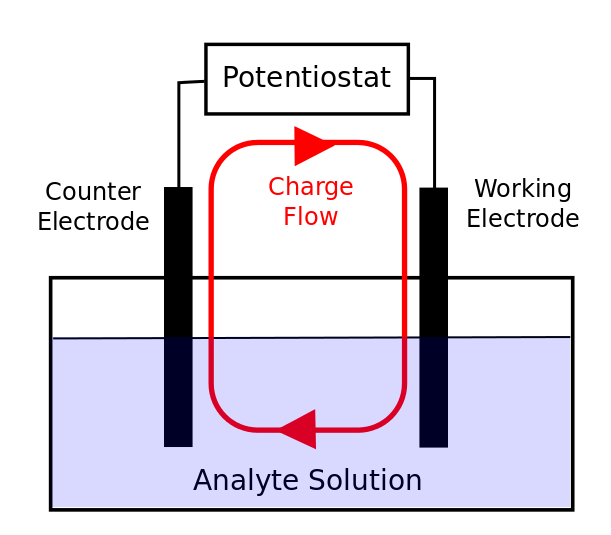
- Other half of the electrochemistry occurs here, current flows between working and auxiliary electrodes
- An electrode that serves merely to carry the current flowing through an electrochemical cell
- also called a counter electrode
What is voltammetry?
- current is measured while voltage between two electrodes is varied.
- the study of the current response of a chemical under an applied potential difference.
What is Polarography?
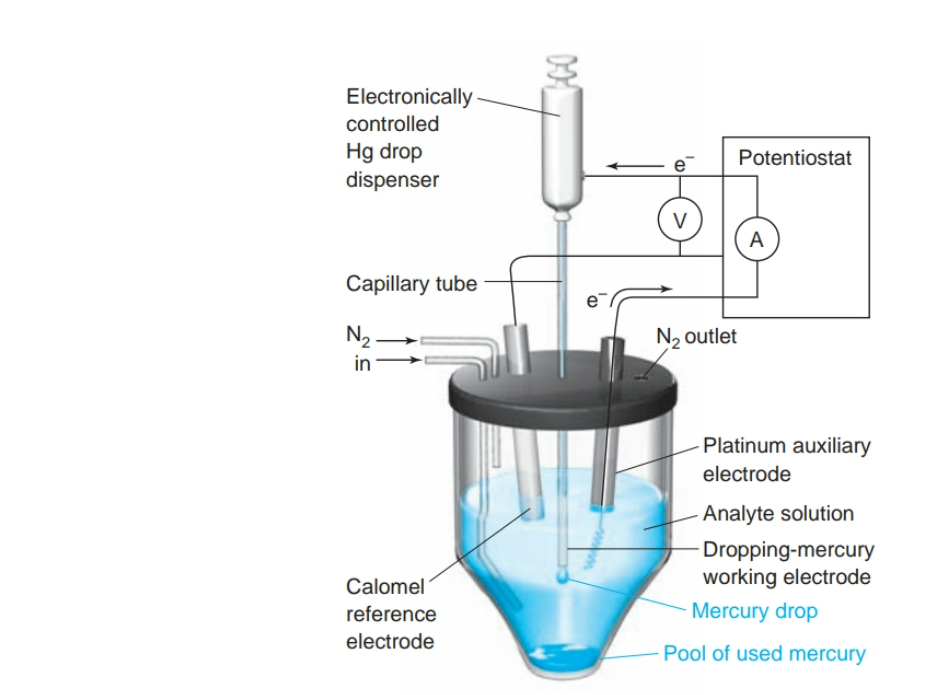
- a voltammetry conducted with a dropping-mercury electrode.
- an instrumental method of chemical analysis used for qualitative and quantitative determinations of reducible or oxidizable substances
What is a polarogram?
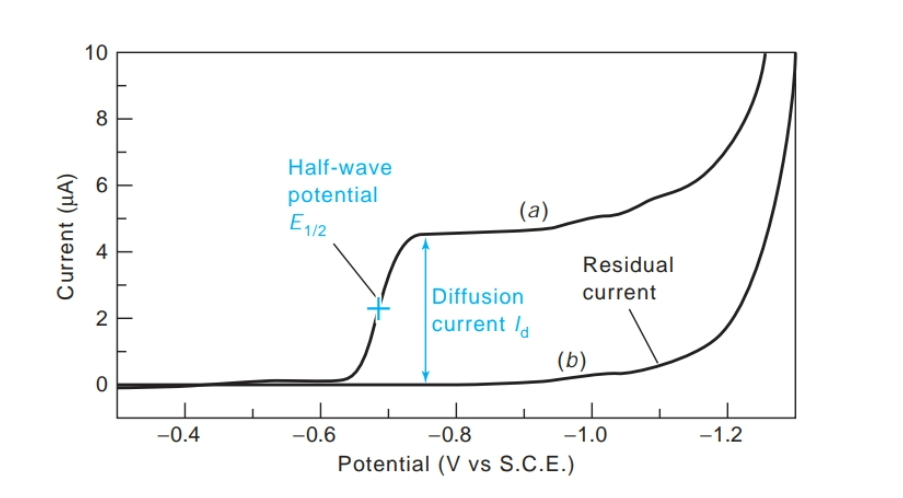
is a graph of current versus voltage
What is the half-wave potential (E1/2)?

The potential at which half the maximum current is reached
What is the diffusion current?

- The constant current in the plateau region
- because it is limited by the rate of diffusion of analyte to the electrode. For quantitative analysis, diffusion current is proportional to the concentration of analyte.
What is the residual current?

the absence of analyte due mainly to reduction of impurities in the solution and on the surface of the electrodes
What is faradaic current?
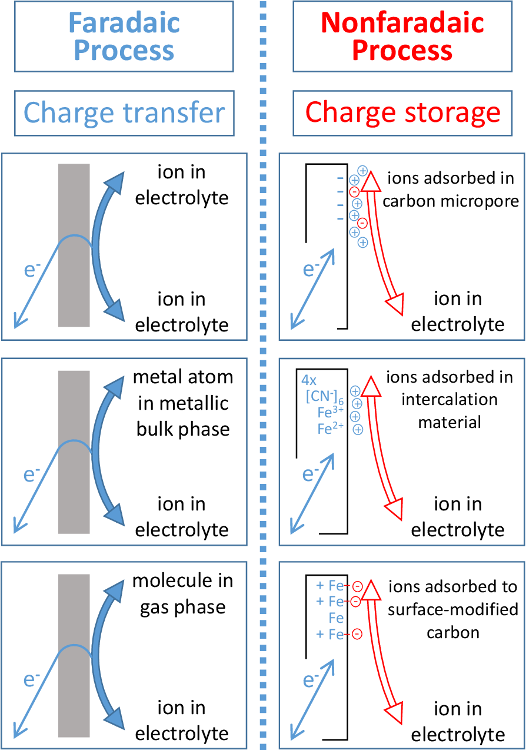
- The current that we seek to measure in voltammetry due to reduction (or oxidation) of analyte at the working electrode.
What is Charging current (capacitor current)?
- Due to migration of ions toward or away from an electrode because of electrostatic attraction or repulsion; redox reactions have no role in charging current
- interferes with every measurement
What are Advantages of square wave voltammetry?
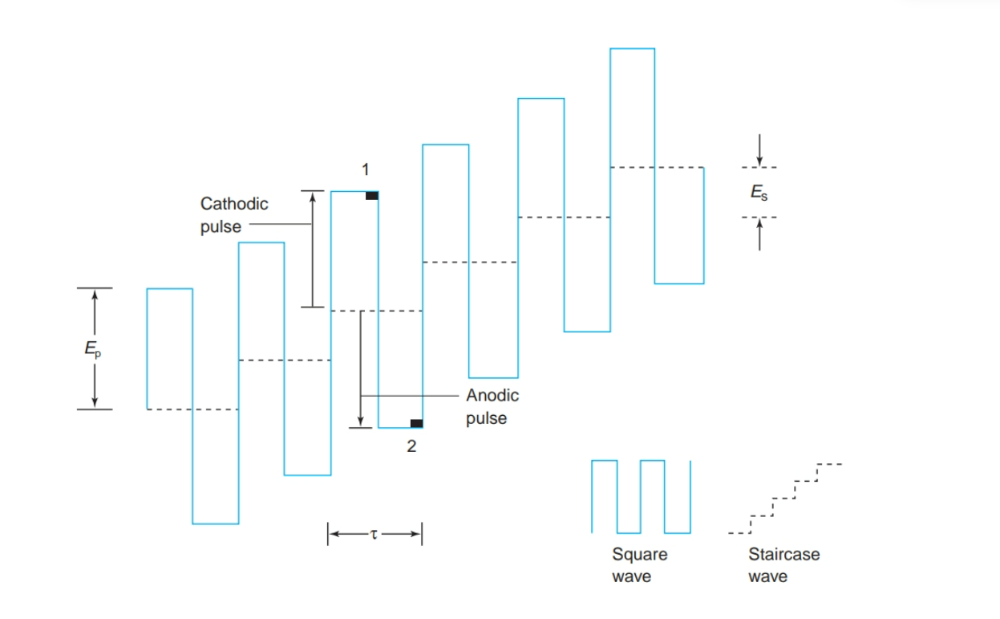
• Increased signal
• Derivative (peak) shape provides better resolution of neighboring signals
•Faster measurements
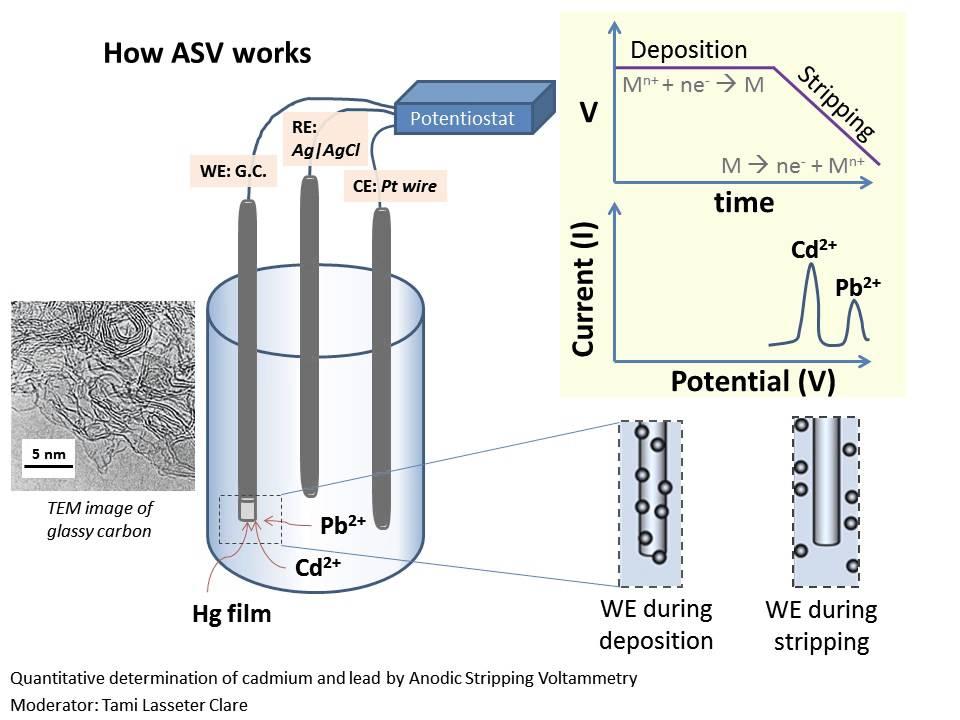
What are the steps of stripping analysis?
1. Concentrate analyte into a drop of Hg by reduction.
2. Reoxidize analyte by making the potential more positive.
3. Measure polarographic signal during oxidation.