What is the definition of potentiometry?
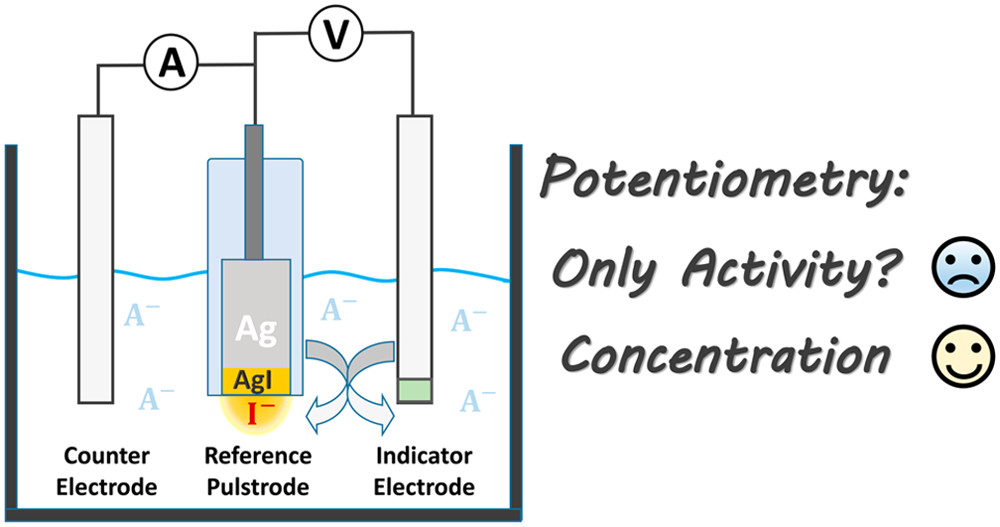
measurement of the electrical potential difference between two
electrodes in an
electrochemical cell, when no current is
allowed to flow.
What is the definition of oscillating reactions?
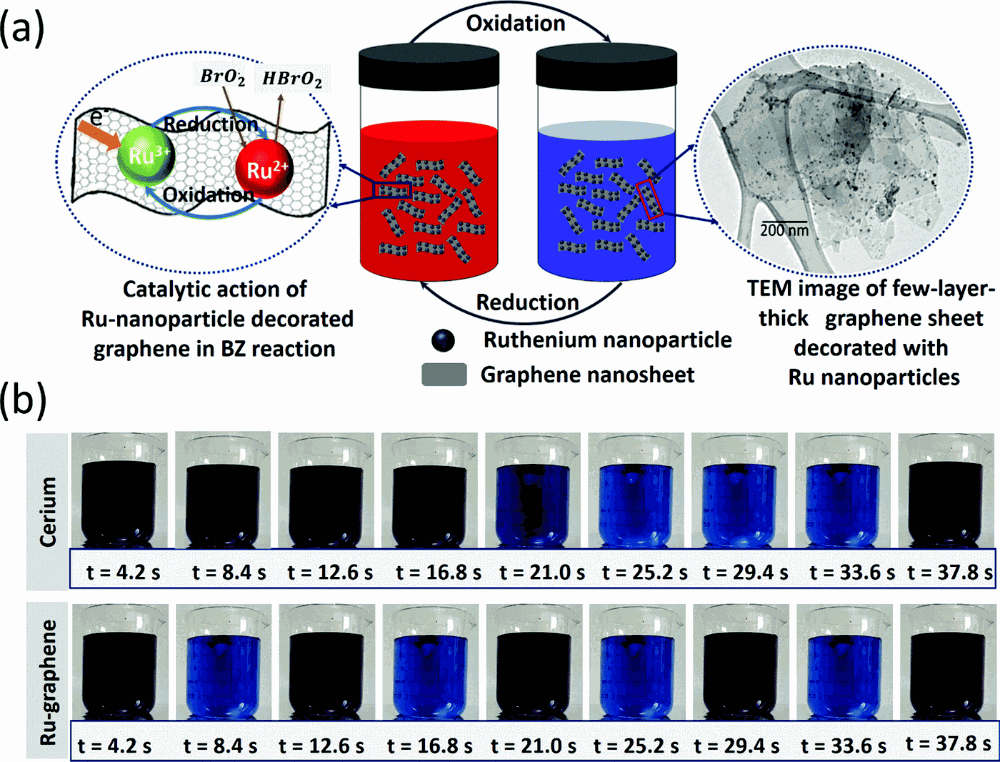
in which chemical concentrations oscillate between high and low values.
What is the definition of junction potential?
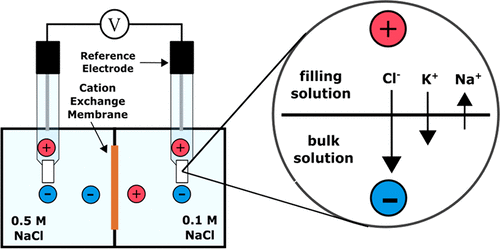
When two dissimilar electrolyte solutions are placed in contact, a voltage difference develops at the interface.
What is the difference between direct and relative potentiometric measurements?
Direct
- Inherent inaccuracy
Liquid-liquid junction at 4% among 14 measurements by direct potentiometry
- different indicator electrodes
- varying liquid junction potential
Relative
- By titration
- relatively precise
- permit an end point to be identified with little uncertainty
What is a junction potential?
- Caused by unequal mobility of different ions at liquid-liquid interfaces.
- Unknown junction potentials can result in a limitation of accuracy of potentiometric measurements.
What are double-junction reference electrodes used for?
typically used for ISE [Ion selective electrode] analysis where the leached electrolyte must not interfere with the ISE being used.
They are also particularly useful for pH analysis of products that must not have KCl or a strong electrolyte contaminating the sample
What is an ISE and what are some advantages?
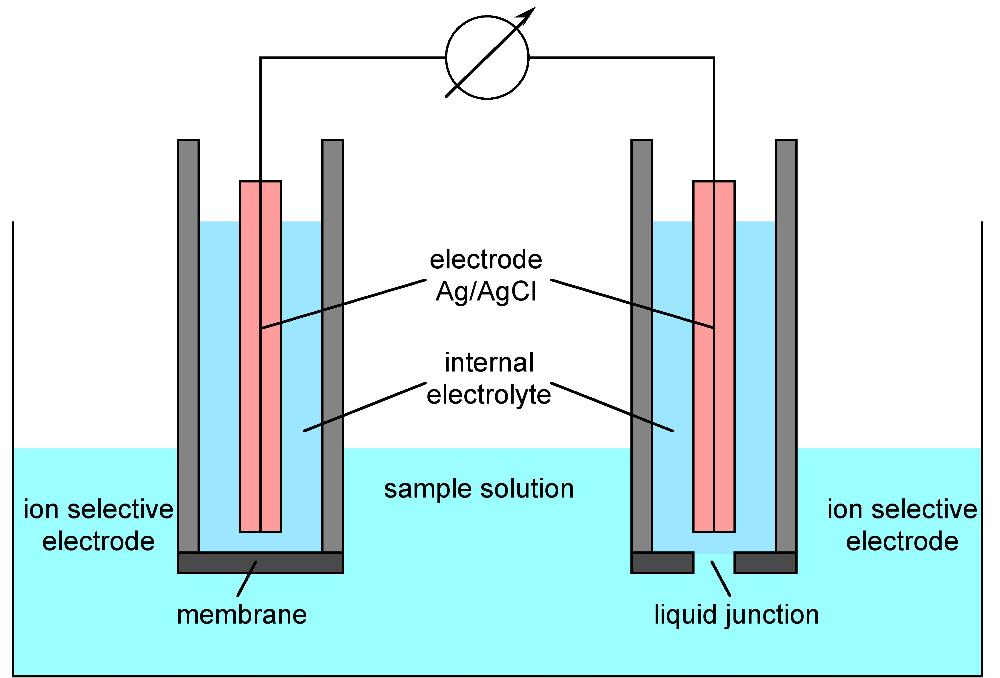
is an analytical technique used to determine the activity of ions in aqueous solution by measuring the electrical potential.
- It is relatively inexpensive and easy to operate.
- It has wide concentration measurement range.
- As it measure the activity, instead of concentration, it is particularly useful in biological/medical application.
- It is a real-time measurement, which means it can monitor the change of activity of ion with time.
- It can determine both positively and negatively charged ions.
What is the function of an ISE (Ion-selective electrode)?
selectively binds one ion—no redox chemistry
What is the function of a Metal electrode?
It is a surface on which redox reaction takes place.
How does a glass pH electrode work?
- pH glass surfaces from a hydrate gel in water where metal diffuses out and H+ in.
- an ion exchange equilibrium occurs
- the porous plug serves as the salt bridge.
What are different errors of pH measurement?
- Standards{Buffer accuracy}
- Junction potential {analyte composition different that electrode}
- Junction potential drift{ precipitate in the plug recalibrate pH meter }
- Sodium error{ H+ is low Na+ is high}
- Acid error{glass is saturated with H+}
- Equilibrium time{ didn't wait for pH to equilibrate}
- Hydration of Glass{ electrode too dry}
- Temperature{pH meter not at same temp as sample}
- Cleaning{probe has hydrophobic liquid}
What is a combination electrode?
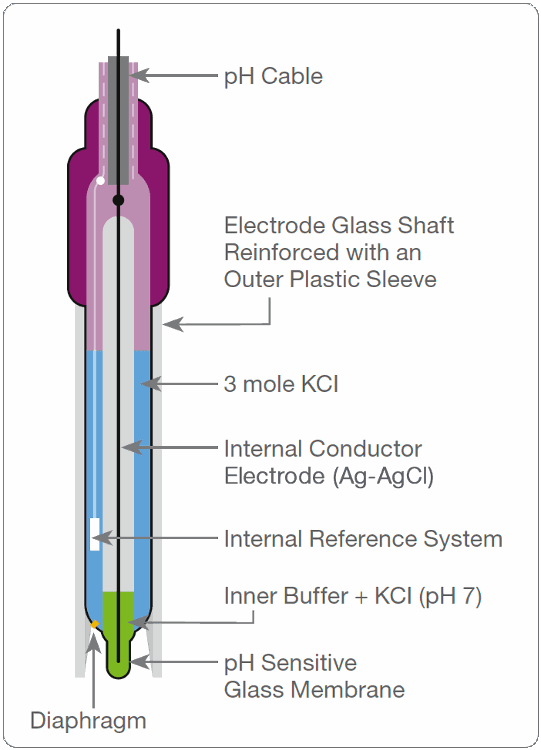
incorporating both the glass and reference electrodes in one body
What should be done to pH electrode before use?
They must be calibrated before use. It should be calibrated every 2 h in sustained use. Ideally, calibration standards should bracket the pH of the unknown.
What should you not do to a glass electrode?
Don’t leave it out of water (or in a nonaqueous solvent) longer than necessary.
What are some advantages and disadvantages of ISE (Ion-selective electrode)?
Advantages:
- unaffected by color turbidity
- short response time
- Non-contaminating
Disadvantages:
- electrodes can be fouled by organic solutes
- precision ≤ 1%
- certain ions can interfere
What is a solid-state ion-selective electrode?
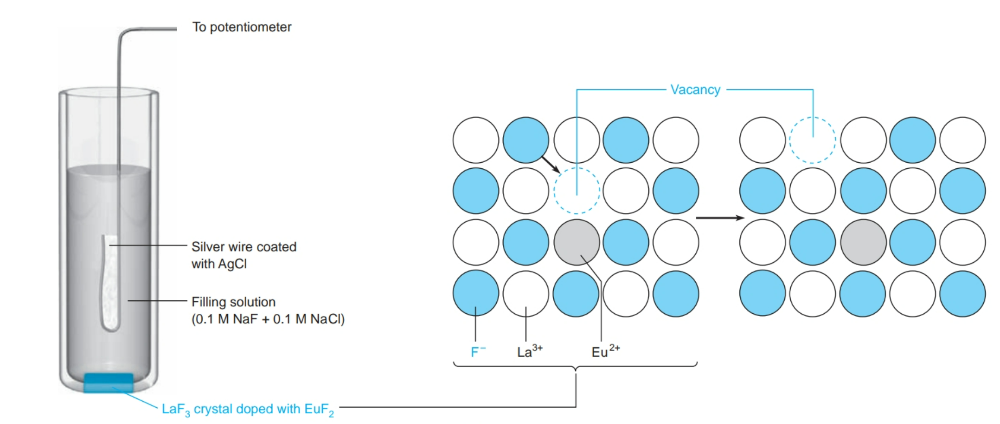
- Inorganic crystal act as the membrane
- ion of interest moves through the crystal lattice by going to each vacant site.
What is a liquid-based ion-selective electrode?
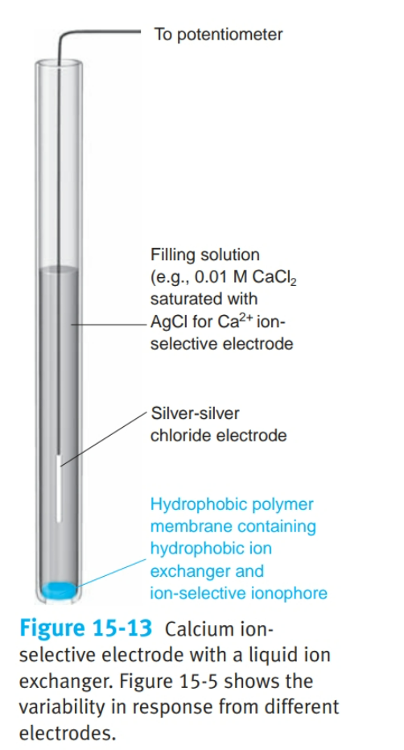
- uses a hydrophobic membrane that contains a liquid organic complexing agent that reacts selectively with the analyte
- Potential difference builds up between inside and outside of the membrane depending on the analyte.
What is a compound electrode?
a conventional electrode surrounded by a membrane that isolates (or generates) the analyte to which the electrode responds.
- Electrode have membrane of multiple type
What are the different types of membrane electrodes?
There are four main types of ion-selective membrane used in ion-selective electrodes (ISEs): glass, solid state, liquid based, and compound electrode.
What is the quantity, method, and analyte for potentiometry?

- Quantity: potential voltage
- Unit: voltage
- Analyte: H+ and PCO2
What is the quantity, method, and analyte for coulometry?
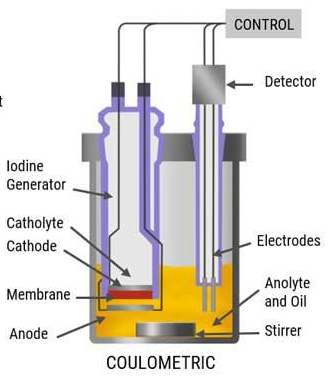
- Quantity: Electric charge
- Unit: Coulombs
- Analyte: Cl-
What is the quantity, method, and analyte for amperometry?

- Quantity: Current
- Unit: Ampere
- Analyte:PO2
What is the quantity, method, and analyte for voltammetry?
- Quantity: Current
- Unit: Volt
- Analyte: Vitamin C