Which container would you put a used coverslip in?
Broken glass container
Which container would you put used gloves in?
Biohazardous waste
Which container would you place a razor in?
Sharps container
Which piece of glassware has an equal circumference were the opening has a much smaller circumference?
Media bottle
Which piece of glassware has a progressively smaller circumference from the bottom to the top?
Erlenmeyer flask
Which machine is used to heat a mixture and stir a mixture using electromagnetic forces?
Hot plate and magnetic stirrer
Which piece of equipment is used to sterilize equipment and media?
Autoclave
Which piece of equipment is used to avoid contamination when working with microbes?
Laminar flow hood
Which piece of equipment is used to measure the amount of material based on absorbance?
Spectrophotometer
Which machine is used to perform polymerase chain reactions?
Thermocycler
Which machine is used to keep liquids at a constant temperature?
Waterbath
Which machine is used to grow and maintain microorganisms at optimal physical conditions?
Incubator
Which tool is used to move microorganisms between cultures and can be repeatedly sterilized?
Inoculating loop
Which machine agitates a mixture in a test tube to make a homogenized mixture?
Vortex micture
Which machine rotates a mixture to separate out the different parts?
Centrifuge
Which machine is used to measure masses?
Analytical balance
Which piece of glassware is used to move liquid culture around an agar plate evenly?
Spreader
Which piece of glassware is the most precise way to measure large amounts of liquid?
Graduated cylinder
Which piece of glassware has an equal circumference from the top to the bottom and cannot be used for precise measuremnts?
Beaker
Which piece of glassware is used to grow microbes in liquid culture?
Test tube
Which piece of glassware is used to grow microbes in solid or semisolid agar?
Petri dish
Which piece of glassware/plastic is used to hold small amounts of liquid in molecular biology?
Microcentrifuge tube
Which pipet is used to transfer the smallest amounts of liquids?
Micropipet
Which pipet moves a fixed volume
Pasteur pipet
Which pipet is used to transfer the largest amounts of liquid?
Serological pipet
Which piece of equipment is used to sterilize tools and glassware on the benchtop?
Microincinerator
Which piece of equipment is used for visualizing microbes?
Microscope
This is the most common type of microscope used
Bright field
This type of microscope causes the light source to hit the specimen at a severely oblique angle
Dark field
A benefit of this microscope is the ability to view live organisms without stains
Phase contrast
When using the scanning objective, the objective magnification would be
4x
When using the low-power objective, the objective magnification would be
10x
When using the high-dry objective, the objective magnification would be
40x
When using the oil immersion objective, the objective magnification would be
100x
Using the provided values for multiple microscopes, what is the mean field of view in micrometers for the 4x objective?
4216.667
Using the provided values for multiple microscopes, what is the mean field of view in micrometers for the 10x objective?
1760.417
Using the provided values for multiple microscopes, what is the mean field of view in micrometers for the 40x objective?
421.667
Using the provided values for multiple microscopes, what is the mean field of view in micrometers for the 100x objective?
176.042
Using the scale bar, what is the size of a single E. coli cell in micrometers using the given picture?
3
Using the scale bar, what is the size of a P. aeruginosa cell in micrometers using the given image?
3.5
Using the scale bar, what is the size of S. epidermidis in micrometers using the provided image?
1.5
Using the scale bar, what is the size of Bacillus in micrometers using the provided image?
2.5
Using the scale bar, what is the size of a single fungi cell in micrometers?
4.5
Which type of cell wall was E. coli?
Gram negative
Which type of cell wall was Pseudomonas?
Gram negative
Which type of cell wall was Bacillus?
Gram positive
Which type of cell wall was Staphylococcus?
Gram positive
Which supergroup do Kinetoplastida, Dipomonads, Euglenazoonans, and Euglenoids belong to?
Excavata
Which supergroup do Cercozoa, Radiolarians, and Foraminiferans belong to?
Rhizaria
Which supergroup to Apicomplexans, Ciliates, and Dinoflagellates belong to?
Alveolata
The phylum Nematodes belongs to which kingdom?
Animals
The phylum Platyhelminthes belongs to which kingdom?
Animals
Which fungus phylum contains bread molds?
Zygomycota
Which phylum contains the fungus that produces penicillin and brewer's yeast?
Ascomycota
Which phylum contains the plant pathogens fungi known as smuts and rusts?
Basidiomycota
Which virus classification includes double stranded DNA?
Class I
Which virus classification includes single stranded DNA?
Class II
Which virus classification includes double stranded RNA?
Class III
Which virus classification includes positive sense single stranded RNA?
Class IV
Which virus classification includes negative sense single stranded RNA?
Class V
Which virus classification includes single stranded RNA with a DNA intermediate?
Class VI
Which virus classification includes double stranded DNA with an RNA intermediate?
Class VII
Which type of stain sticks to the cell and gives them color?
Positive staining
Which type of stain does not stick to the cell, but dries around the cell boundary creating a silhouette?
Negative staining
Which type of stain uses both basic and acidic dyes?
Positive stain
Which type of stain uses acidic dyes?
Negative stain
Which type of stain uses a single dye?
Simple stain
Which type of stain uses two dyes- a primary dye and a counterstain?
Differential stain
Which cell structure does Gram staining react to?
Cell wall
What waxy material in the cell wall does acid-fast staining react to?
Mycolic acid
What cell structure gets stained when the cell is under environmental stress?
Endospore
Name the two stains used in Gram staining
- Crystal violet
- Safranin
Name the two stains used in acid-fast staining
- Methylene blue
- Fuchsin
Name the two stains used in spore staining
- Malachite green
- Safranin
Name the one stain that can be used in negative staining
Nigrosin
Which type of cell wall is indicated by purple/blue in Gram staining?
Gram positive
Which type of cell wall is indicated by pink in Gram staining?
Gram negative
With spore staining, green indicates which structure?
Endospore
With spore staining, red indicates what type of cell?
Vegatative cell
With acid-fast staining, Mycobacterium (acid-fast bacteria) will stain which color because of the presence of mycolic acid?
Red
With acid-fast staining, non-acid-fast bacteria will stain which color?
Blue
Looking at the micrograph, is Staphylococcus aureus Gram positive or Gram negative (blue)?
Gram positive
Looking at the micrograph, is Pseudomonas aeruginosa Gram positive or Gram negative (pink)?
Gram negative
Looking at the micrograph, is Bacillus megaterium Gram positive or Gram negative (blue)?
Gram positive
Looking at the micrograph, is Moraxella cararrhalis Gram positive or Gram negative (pink)?
Gram negative
Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Clostridium difficile produce spores (green spores)?
Yes
Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Bacillus cereus produce spores (green spores)?
Yes
Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Staphylococcus sp. produce spores (pink, no green spores)?
No
Looking at the micrograph does the bacteria Bacillus megaterium produce spores (green spores)?
Yes
Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Mycobacterium smegmatis produce the waxy material in its cell wall (pink)?
Yes
Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Bacillus cereus produce the waxy material in its cell wall (blue)?
No
Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Mycobacteroum tuberculosis produce the waxy material in its cell wall (pink)?
Yes
These media are designed to grow a broad spectrum of microbes that do not have special growth requirements
General Purpose
These media contain complex organism substances such as growth factors that are required for the microbes to grow
Enriched
These media contain substances that absorb oxygen or slow the penetration of oxygen
Anaerobic growth
This type of media is used to maintain and preserve the microbe for a period of time before testing
Specimen transport
This type of media contains one or more agents that inhibit the growth of certain microbes but not another
Selective
This type of media can grow several types of microbes but are designed to bring out visible differences among these microbes
Differential
This type of media is used to count the number of microbes in agricultural, industrial, or environmental samples
Enumeration
This type of media is used to test the effectiveness of microbial drugs, disinfectants and antiseptics
Assay
This type of media contain pure chemical nutrients that vary little from one source to another and have a molecular content with an exact formula
Synthetic media
This type of media is not chemically definable by an exact formula
Nonsynthetic media
This type of media has large molecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids that can vary greatly in exact composition
Complex media
Nutrient agar or nutrient broth is a general purpose media used for which groups?
Bacteria and Fungi
Potato dextrose agar (PDA) is a general purpose media use for which group?
Fungi
Trypticase soy agar (TSA) or broth is a general purpose media for which group?
Bacteria
Which of the following is commonly used to culture algae?
Salt agar
Which of the following is commonly used to culture paramecium?
Hay infusion
Which of the following is commonly used to culture viruses?
Live host cell
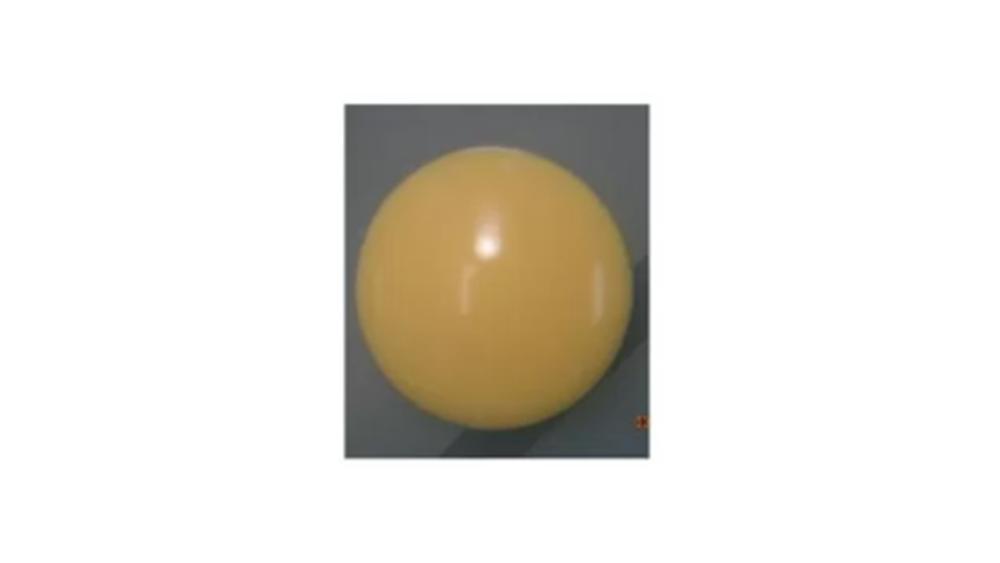

The image of the colony has which type of form?
Circular
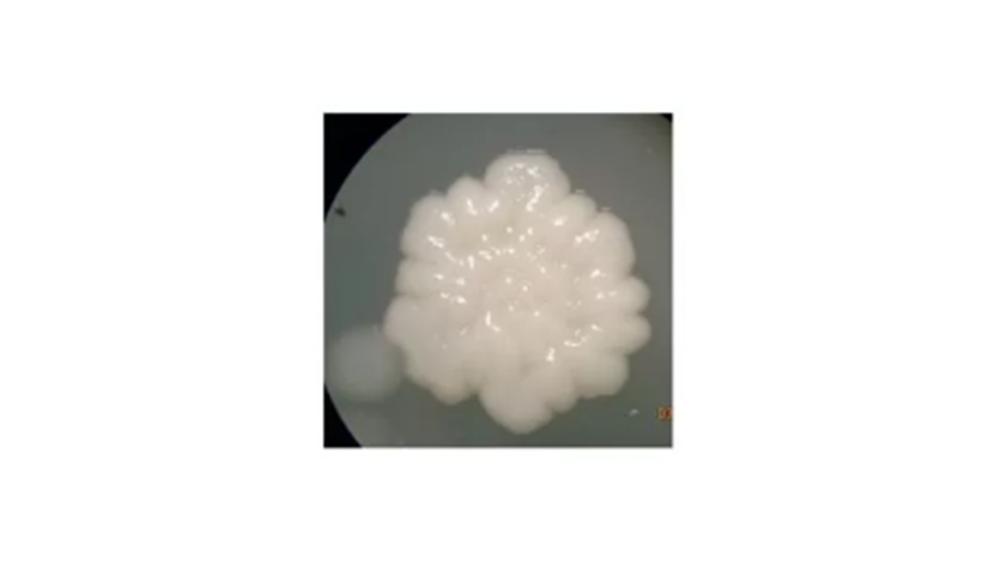

The image of the colony has which type of form?
Iregular
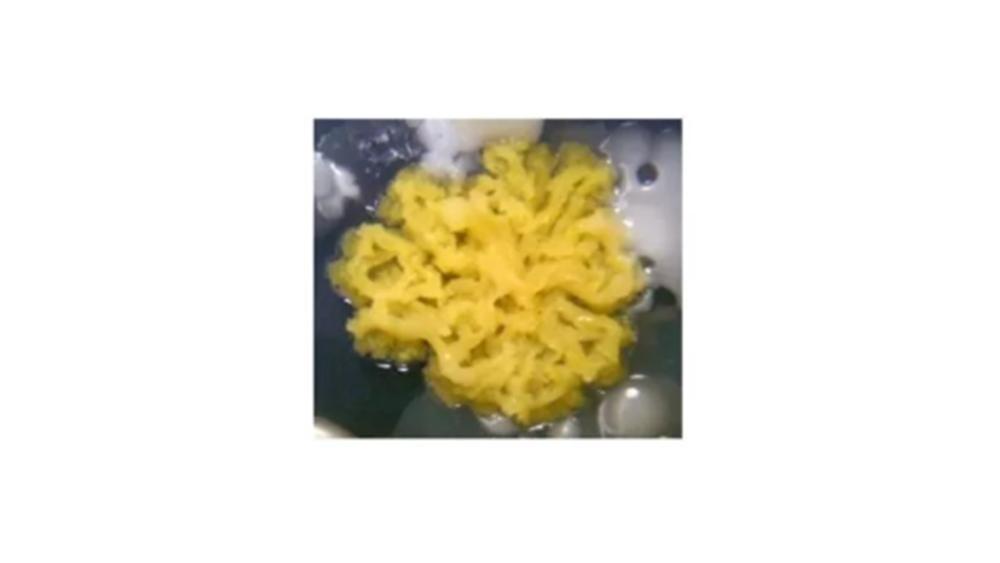

The image of the colony has which type of form?
Rhizoid
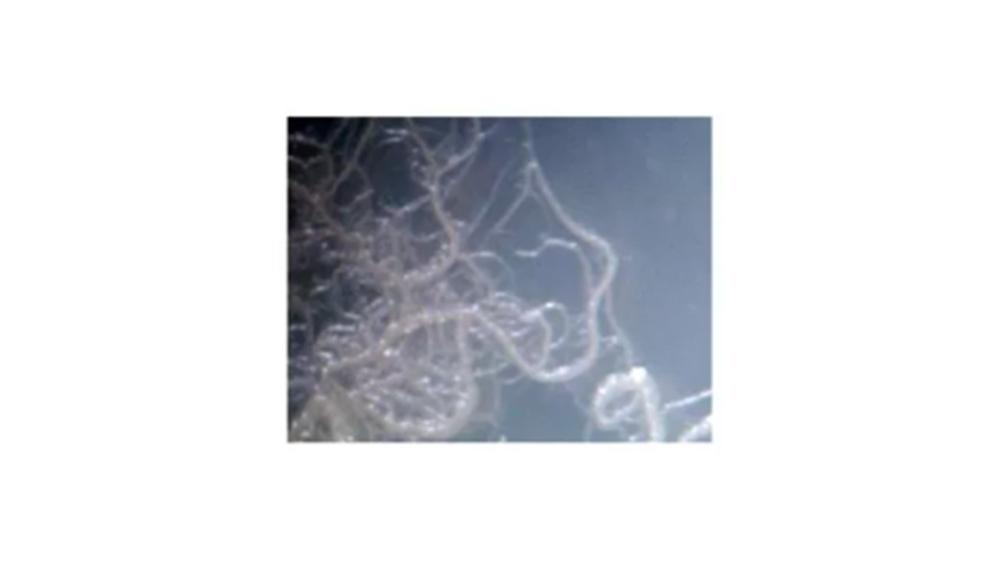

The image of the colony has which type of form?
Filamentous
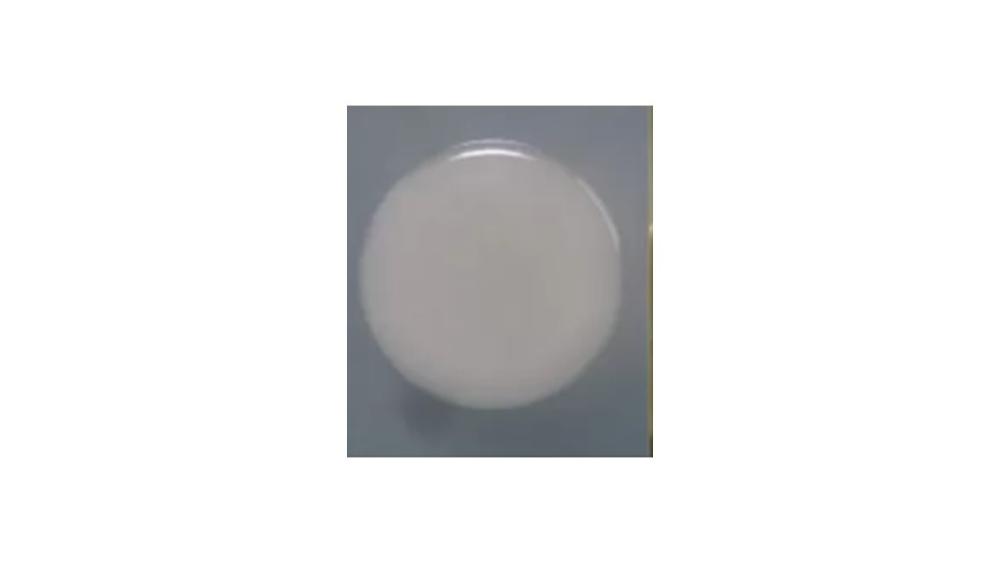

The image of the colony has which type of margin?
Entire
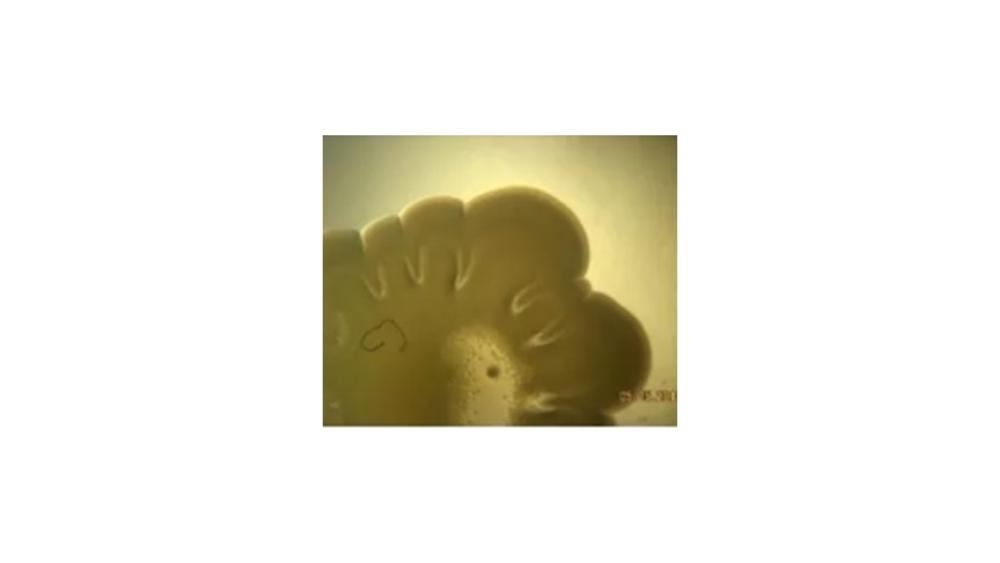

The image of the colony has which type of margin?
Lobate
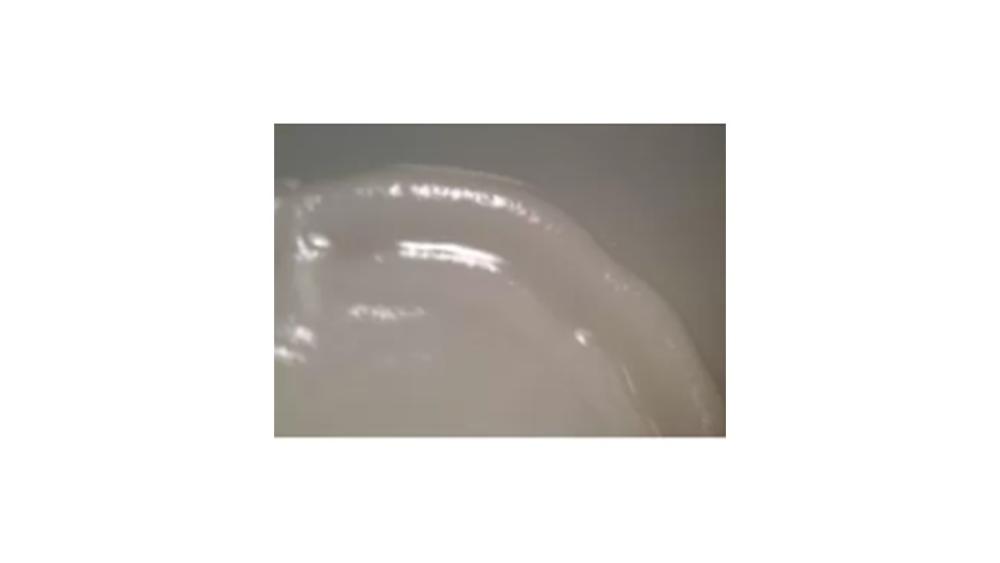

The image of the colony has which type of margin?
Curled
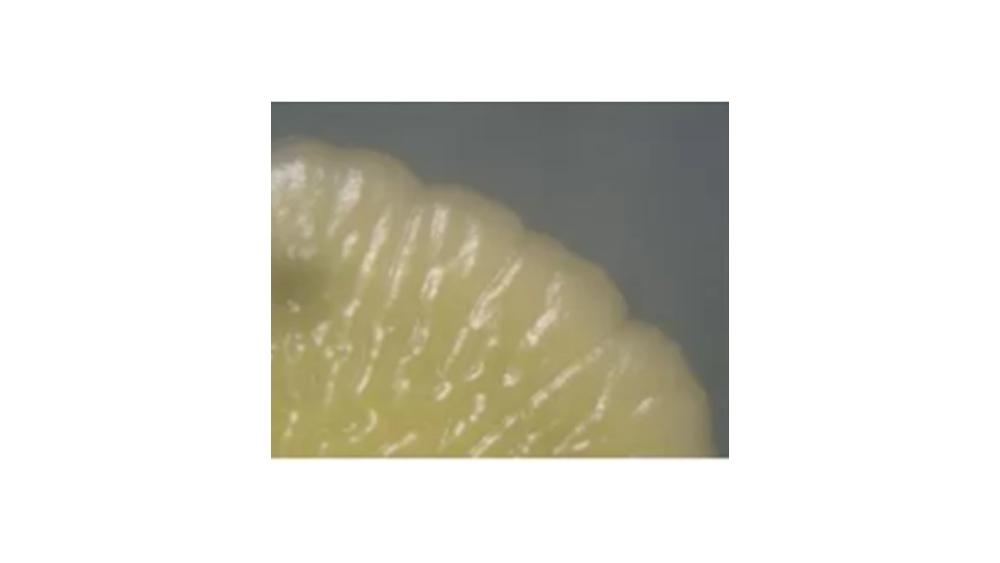
The image of the colony has which type of margin?
Undulate
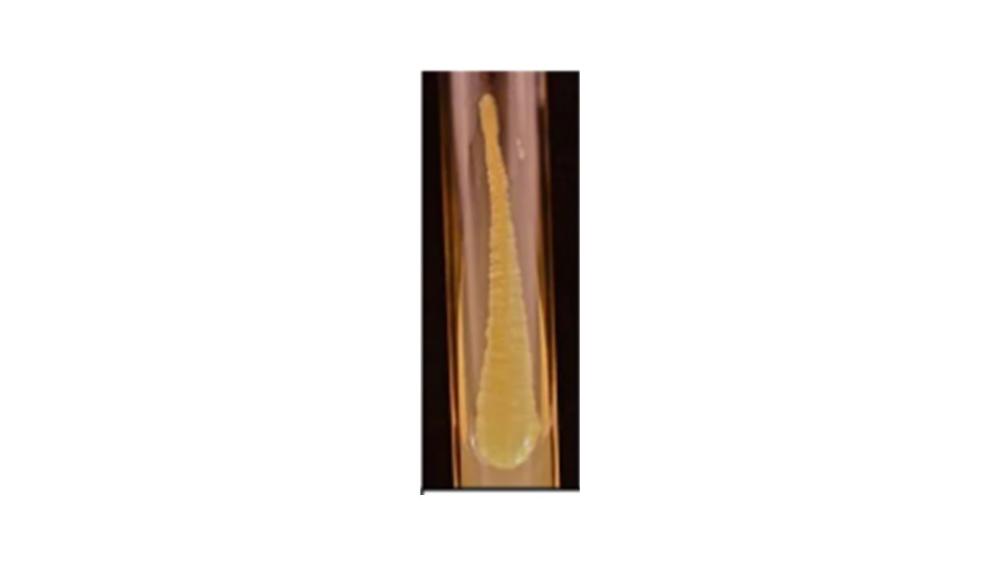
The image of the colony on the agar shows which form?
Filiform
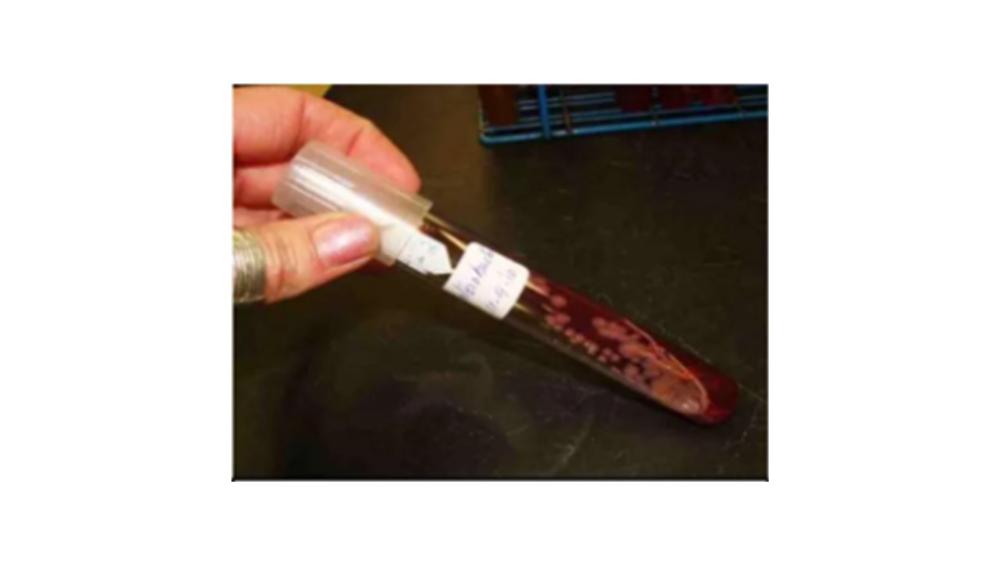
The image of the colony on the agar slant shows which form?
Beaded
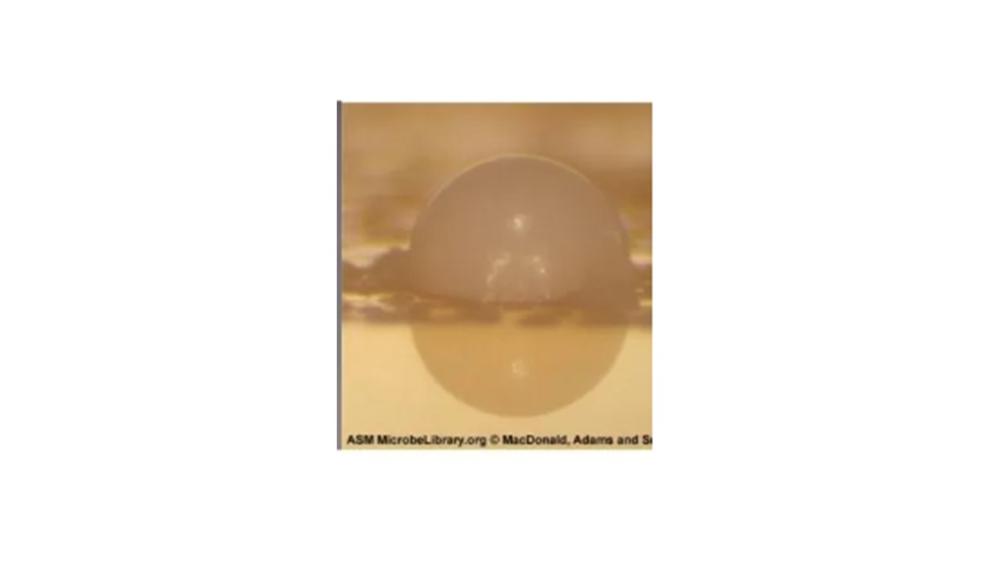
The image of the colony has which elevation?
Convex
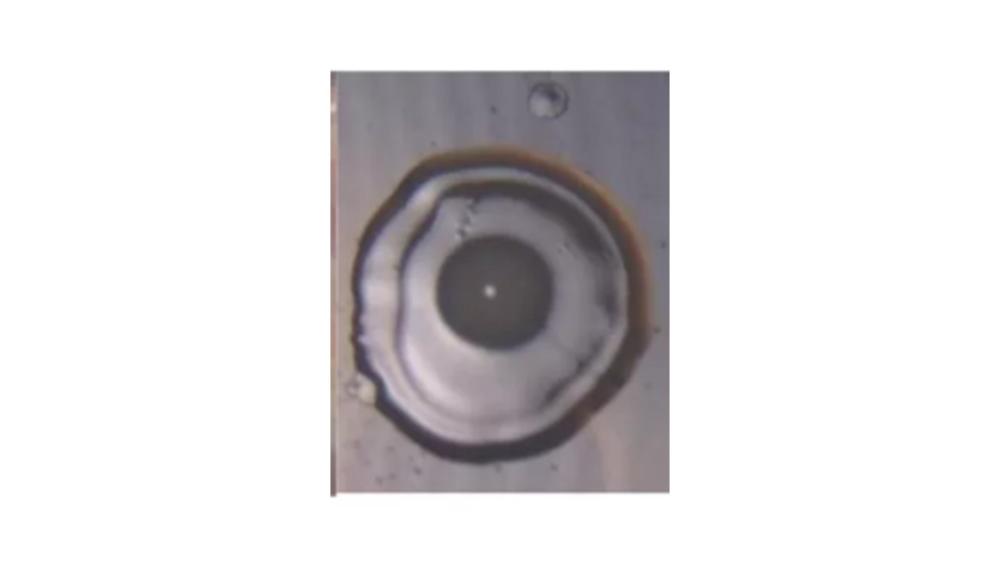
The image of the colony has which elevation?
Umbonate
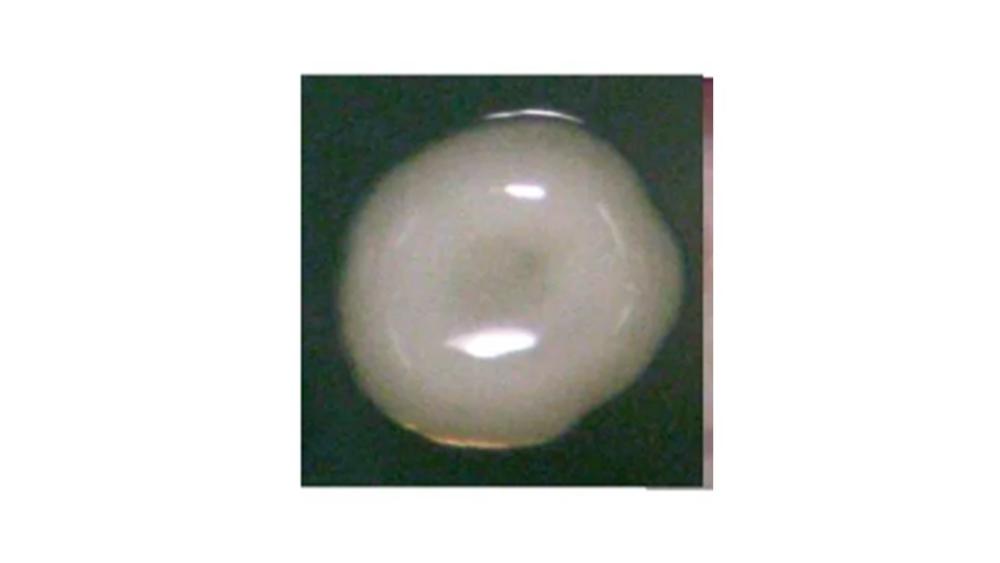
The image of the colony has which elevation?
Crateriform
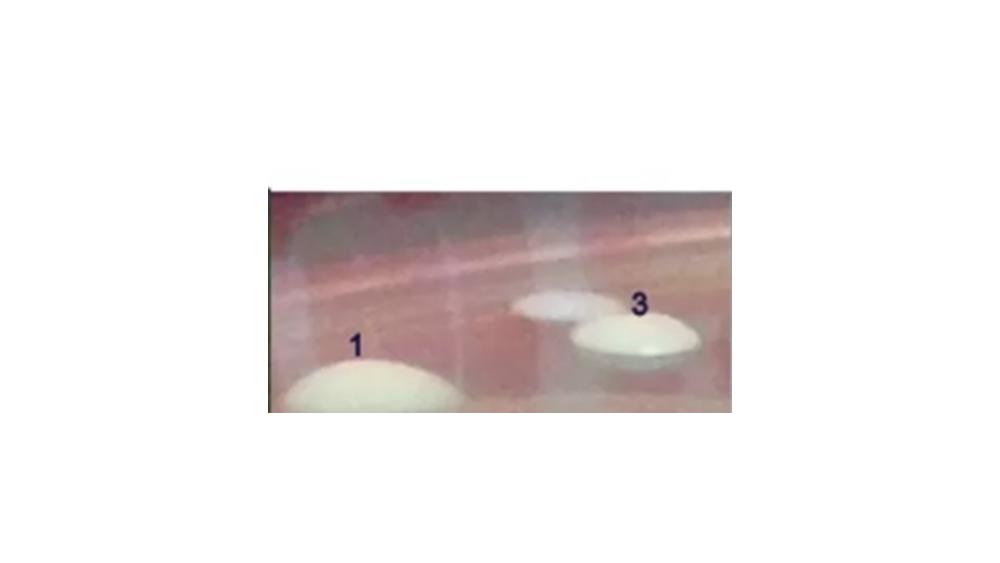

The image of the colony has which elevation?
Raised
This selective and differential media is used to isolate Staphylococcus
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
This selective and differential media is used to isolate enteric bacteria that hydrolyze urea
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB)
This selective and differential media is used to isolate enteric bacteria that ferment lactose
MacConkey Agar (MCA)
Which selective media uses high salt concentration to inhibit the growth of non-target bacteria?
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
Which selective media uses crystal violet and bile salts to inhibit the growth of non-target bacteria?
MacConkey Agar (MCA)
Which selective media uses methylene blue to inhibit the growth of non-target bacteria?
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB)
Mannitol Salt Agar is selective for which bacteria?
Staphylococcus
Eosin Methylene Blue agar is selective for which bacteria?
- Gram-negative
- Enterobacter
- Escherichia
- Salmonella
MacConkey's agar is selective for which bacteria?
- Salmonella
- Shigella
Which media turns yellow when fermentation occurs?
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
Which media turns colonies of Enterobacter (Klebsiella) aerogenes pink?
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB)
Which media turns colonies of coliform bacteria red?
MacConkey agar (MCA)
Cell division where genome replication is followed directly by the physical separation into two new, identical cells
Binary fission
Cell division where genome replication is separated by a gap phase from the physical separation into two new identical cells
Mitosis
In this phase, limiting factors intensify becoming detrimental to any cell growth
Death phase
In this phase, the cells are adjusting to the environment
Lag phase
In this phase, the cells reach the maximum rate of cell division
Log phase
In this phase, cells will stop growing or grow very slowly
Stationary phase
In this phase, the majority of the cells are alive, but dead cells start to accumulate
Stationary phase
In this phase, there are many living cells and few to none dead cells
Log phase
In this phase, there are few cells present
Lag phase
In this phase, the dead cells take up a larger portion of the culture and little to no growth occurs
Death phase
Of the following absorbance reading samples, which one has more cells present?
0.85
Of the following absorbance reading samples, which one has fewer cells present?
0.05
How many cells are present after 9 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth?
512
How many cells are present after 13 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth?
8,102
How many cells are present after 18 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth?
262,144
How many cells are present after 11 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth?
2,048
How many cells are present after 7 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth?
128
A dilution of 1mL bacteria from broth into 1mL broth or water
1:2
A dilution of 1mL bacteria from broth into 3mL broth or water
1:4
A dilution of 1mL bacteria from broth into 11mL broth or water
1:12
A dilution of 1mL bacteria from broth into 7mL broth or water
1:8
A serial dilution of 1:10 followed by 1:100 by 1:100 gives a final dilution of
1:100,000
A serial dilution of 1:10 followed by 1:10 followed by 1:100 gives a final dilution of
1:10,000
A serial dilution of 1:10 followed by 1:10 followed by 1:10 gives a final dilution of
1:1,000
A serial dilution of 1:6 followed by 1:8 gives a final dilution of
1:48
A serial dilution of 1:6 followed by 1:10 gives a final dilution of
1:60
A serial dilution of 1:4 followed by 1:6 gives a final dilution of
1:24
A serial dilution of 1:2 followed by 1:6 gives a final dilution of
1:12
A serial dilution of 1:6 followed by 1:12 gives a final dilution of
1:72
A dilution of 0.1mL bacteria from broth into 9.9mL
1:100
A dilution of 0.1mL bacteria from broth in 999.9mL broth or water
1:10,000
A dilution of 0.1mL bacteria from broth in 99.9mL broth or water
1:1,000
A 1:1,000,00 is which dilution factor?
-6
A 1:100,000 is which dilution factor?
-5
A 1:100,000,000 is which dilution factor?
-8
A 1:10,000,000 is which dilution factor?
-7
Microbes that require oxygen to grow but at much lower levels than 20% are
Microaerophiles
Microbes that can only grow when oxygen is not present are
Obligate anaerobes
Microbes that can only grow when oxygen is present are
Obligate aerobes
Microbes that can grow in oxygen but do not require oxygen for energy metabolism are
Aerotolerant anaerobes
Microbes that are flexible and can grow with or without oxygen are
Facultative anaerobes
Which bacteria have optimal growth between -5°C to 15°C?
Psychrophiles
Which bacteria have optimal growth between 45°C to 75°C?
Thermophiles
Which bacteria have optimal growth between 25°C to 45°C?
Mesophiles
Which bacteria have optimal growth above 75°C?
Hyperthermophiles
A bacterium that grows at a pH of 10 is a
Alkaliphiles
A bacterium that grows at a pH of 4 is a
Acidophiles
A bacterium that grows at a pH of 7 is a
Neutrophiles
These microbes can grow in excessive sugar concentrations
Osmophiles
These microbes require a high concentration of sodium chloride in order to grow
Obligate halophiles
These microbes can grow in moderate concentration of sodium chloride
Halotolerant
A cell that has more solutes than the surrounding environment is
Hypertonic
A cell that has fewer solutes than the surrounding environment
Hypotonic
Water flows (into/out of) a cell that is hypotonic
Out of
Water flows (into/out of) a cell that is hypertonic
Into
When the temperature increases past the optimal, the hydrogen bonding in the RNA breaks down and the proteins denature in this structure
Ribosome
When the temperature increases past the optimal, lipids can be destroyed affecting which structure?
Cell membrane
Which temperature results in white colonies of Serratia?
37°C
When the temperature decreases past the optimal, lipids can freeze affecting which structure?
Cell membrane
When the temperature decreases past the optimal, the activity of this molecule will slow down
Enzyme
When the temperature increases past the optimal, these denature
Enzyme
Which temperature results in pinkish/red colonies of Serratia?
25°C
Which temperature does Serratia grow best at?
37°C
Which temperature does E. coli grow best at?
37°C
Which temperature does GST grow best at?
55°C
Which temperature does Serratia grow the worst at?
55°C
Which temperature does E. coli grow the worst at
55°C
Which temperature does GST grow the worst at?
37°C
Which pH does E. coli grow best at?
7
Which pH does S. epidermidis grow best at?
5
Which pH does A. faecalis grow best at?
7
Which pH does E. coli grow the worst at?
3
Which pH does S. epidermidis grow the worst at?
3
Which pH does A. faecalis grow the worst at?
3