Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Microbiology: Lab Exercises (1-7)
front 1 Which container would you put a used coverslip in? | back 1 Broken glass container |
front 2 Which container would you put used gloves in? | back 2 Biohazardous waste |
front 3 Which container would you place a razor in? | back 3 Sharps container |
front 4 Which piece of glassware has an equal circumference were the opening has a much smaller circumference? | back 4 Media bottle |
front 5 Which piece of glassware has a progressively smaller circumference from the bottom to the top? | back 5 Erlenmeyer flask |
front 6 Which machine is used to heat a mixture and stir a mixture using electromagnetic forces? | back 6 Hot plate and magnetic stirrer |
front 7 Which piece of equipment is used to sterilize equipment and media? | back 7 Autoclave |
front 8 Which piece of equipment is used to avoid contamination when working with microbes? | back 8 Laminar flow hood |
front 9 Which piece of equipment is used to measure the amount of material based on absorbance? | back 9 Spectrophotometer |
front 10 Which machine is used to perform polymerase chain reactions? | back 10 Thermocycler |
front 11 Which machine is used to keep liquids at a constant temperature? | back 11 Waterbath |
front 12 Which machine is used to grow and maintain microorganisms at optimal physical conditions? | back 12 Incubator |
front 13 Which tool is used to move microorganisms between cultures and can be repeatedly sterilized? | back 13 Inoculating loop |
front 14 Which machine agitates a mixture in a test tube to make a homogenized mixture? | back 14 Vortex micture |
front 15 Which machine rotates a mixture to separate out the different parts? | back 15 Centrifuge |
front 16 Which machine is used to measure masses? | back 16 Analytical balance |
front 17 Which piece of glassware is used to move liquid culture around an agar plate evenly? | back 17 Spreader |
front 18 Which piece of glassware is the most precise way to measure large amounts of liquid? | back 18 Graduated cylinder |
front 19 Which piece of glassware has an equal circumference from the top to the bottom and cannot be used for precise measuremnts? | back 19 Beaker |
front 20 Which piece of glassware is used to grow microbes in liquid culture? | back 20 Test tube |
front 21 Which piece of glassware is used to grow microbes in solid or semisolid agar? | back 21 Petri dish |
front 22 Which piece of glassware/plastic is used to hold small amounts of liquid in molecular biology? | back 22 Microcentrifuge tube |
front 23 Which pipet is used to transfer the smallest amounts of liquids? | back 23 Micropipet |
front 24 Which pipet moves a fixed volume | back 24 Pasteur pipet |
front 25 Which pipet is used to transfer the largest amounts of liquid? | back 25 Serological pipet |
front 26 Which piece of equipment is used to sterilize tools and glassware on the benchtop? | back 26 Microincinerator |
front 27 Which piece of equipment is used for visualizing microbes? | back 27 Microscope |
front 28 This is the most common type of microscope used | back 28 Bright field |
front 29 This type of microscope causes the light source to hit the specimen at a severely oblique angle | back 29 Dark field |
front 30 A benefit of this microscope is the ability to view live organisms without stains | back 30 Phase contrast |
front 31 When using the scanning objective, the objective magnification would be | back 31 4x |
front 32 When using the low-power objective, the objective magnification would be | back 32 10x |
front 33 When using the high-dry objective, the objective magnification would be | back 33 40x |
front 34 When using the oil immersion objective, the objective magnification would be | back 34 100x |
front 35 Using the provided values for multiple microscopes, what is the mean field of view in micrometers for the 4x objective? | back 35 4216.667 |
front 36 Using the provided values for multiple microscopes, what is the mean field of view in micrometers for the 10x objective? | back 36 1760.417 |
front 37 Using the provided values for multiple microscopes, what is the mean field of view in micrometers for the 40x objective? | back 37 421.667 |
front 38 Using the provided values for multiple microscopes, what is the mean field of view in micrometers for the 100x objective? | back 38 176.042 |
front 39 Using the scale bar, what is the size of a single E. coli cell in micrometers using the given picture? | back 39 3 |
front 40 Using the scale bar, what is the size of a P. aeruginosa cell in micrometers using the given image? | back 40 3.5 |
front 41 Using the scale bar, what is the size of S. epidermidis in micrometers using the provided image? | back 41 1.5 |
front 42 Using the scale bar, what is the size of Bacillus in micrometers using the provided image? | back 42 2.5 |
front 43 Using the scale bar, what is the size of a single fungi cell in micrometers? | back 43 4.5 |
front 44 Which type of cell wall was E. coli? | back 44 Gram negative |
front 45 Which type of cell wall was Pseudomonas? | back 45 Gram negative |
front 46 Which type of cell wall was Bacillus? | back 46 Gram positive |
front 47 Which type of cell wall was Staphylococcus? | back 47 Gram positive |
front 48 Which supergroup do Kinetoplastida, Dipomonads, Euglenazoonans, and Euglenoids belong to? | back 48 Excavata |
front 49 Which supergroup do Cercozoa, Radiolarians, and Foraminiferans belong to? | back 49 Rhizaria |
front 50 Which supergroup to Apicomplexans, Ciliates, and Dinoflagellates belong to? | back 50 Alveolata |
front 51 The phylum Nematodes belongs to which kingdom? | back 51 Animals |
front 52 The phylum Platyhelminthes belongs to which kingdom? | back 52 Animals |
front 53 Which fungus phylum contains bread molds? | back 53 Zygomycota |
front 54 Which phylum contains the fungus that produces penicillin and brewer's yeast? | back 54 Ascomycota |
front 55 Which phylum contains the plant pathogens fungi known as smuts and rusts? | back 55 Basidiomycota |
front 56 Which virus classification includes double stranded DNA? | back 56 Class I |
front 57 Which virus classification includes single stranded DNA? | back 57 Class II |
front 58 Which virus classification includes double stranded RNA? | back 58 Class III |
front 59 Which virus classification includes positive sense single stranded RNA? | back 59 Class IV |
front 60 Which virus classification includes negative sense single stranded RNA? | back 60 Class V |
front 61 Which virus classification includes single stranded RNA with a DNA intermediate? | back 61 Class VI |
front 62 Which virus classification includes double stranded DNA with an RNA intermediate? | back 62 Class VII |
front 63 Which type of stain sticks to the cell and gives them color? | back 63 Positive staining |
front 64 Which type of stain does not stick to the cell, but dries around the cell boundary creating a silhouette? | back 64 Negative staining |
front 65 Which type of stain uses both basic and acidic dyes? | back 65 Positive stain |
front 66 Which type of stain uses acidic dyes? | back 66 Negative stain |
front 67 Which type of stain uses a single dye? | back 67 Simple stain |
front 68 Which type of stain uses two dyes- a primary dye and a counterstain? | back 68 Differential stain |
front 69 Which cell structure does Gram staining react to? | back 69 Cell wall |
front 70 What waxy material in the cell wall does acid-fast staining react to? | back 70 Mycolic acid |
front 71 What cell structure gets stained when the cell is under environmental stress? | back 71 Endospore |
front 72 Name the two stains used in Gram staining | back 72
|
front 73 Name the two stains used in acid-fast staining | back 73
|
front 74 Name the two stains used in spore staining | back 74
|
front 75 Name the one stain that can be used in negative staining | back 75 Nigrosin |
front 76 Which type of cell wall is indicated by purple/blue in Gram staining? | back 76 Gram positive |
front 77 Which type of cell wall is indicated by pink in Gram staining? | back 77 Gram negative |
front 78 With spore staining, green indicates which structure? | back 78 Endospore |
front 79 With spore staining, red indicates what type of cell? | back 79 Vegatative cell |
front 80 With acid-fast staining, Mycobacterium (acid-fast bacteria) will stain which color because of the presence of mycolic acid? | back 80 Red |
front 81 With acid-fast staining, non-acid-fast bacteria will stain which color? | back 81 Blue |
front 82 Looking at the micrograph, is Staphylococcus aureus Gram positive or Gram negative (blue)? | back 82 Gram positive |
front 83 Looking at the micrograph, is Pseudomonas aeruginosa Gram positive or Gram negative (pink)? | back 83 Gram negative |
front 84 Looking at the micrograph, is Bacillus megaterium Gram positive or Gram negative (blue)? | back 84 Gram positive |
front 85 Looking at the micrograph, is Moraxella cararrhalis Gram positive or Gram negative (pink)? | back 85 Gram negative |
front 86 Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Clostridium difficile produce spores (green spores)? | back 86 Yes |
front 87 Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Bacillus cereus produce spores (green spores)? | back 87 Yes |
front 88 Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Staphylococcus sp. produce spores (pink, no green spores)? | back 88 No |
front 89 Looking at the micrograph does the bacteria Bacillus megaterium produce spores (green spores)? | back 89 Yes |
front 90 Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Mycobacterium smegmatis produce the waxy material in its cell wall (pink)? | back 90 Yes |
front 91 Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Bacillus cereus produce the waxy material in its cell wall (blue)? | back 91 No |
front 92 Looking at the micrograph, does the bacteria Mycobacteroum tuberculosis produce the waxy material in its cell wall (pink)? | back 92 Yes |
front 93 These media are designed to grow a broad spectrum of microbes that do not have special growth requirements | back 93 General Purpose |
front 94 These media contain complex organism substances such as growth factors that are required for the microbes to grow | back 94 Enriched |
front 95 These media contain substances that absorb oxygen or slow the penetration of oxygen | back 95 Anaerobic growth |
front 96 This type of media is used to maintain and preserve the microbe for a period of time before testing | back 96 Specimen transport |
front 97 This type of media contains one or more agents that inhibit the growth of certain microbes but not another | back 97 Selective |
front 98 This type of media can grow several types of microbes but are designed to bring out visible differences among these microbes | back 98 Differential |
front 99 This type of media is used to count the number of microbes in agricultural, industrial, or environmental samples | back 99 Enumeration |
front 100 This type of media is used to test the effectiveness of microbial drugs, disinfectants and antiseptics | back 100 Assay |
front 101 This type of media contain pure chemical nutrients that vary little from one source to another and have a molecular content with an exact formula | back 101 Synthetic media |
front 102 This type of media is not chemically definable by an exact formula | back 102 Nonsynthetic media |
front 103 This type of media has large molecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids that can vary greatly in exact composition | back 103 Complex media |
front 104 Nutrient agar or nutrient broth is a general purpose media used for which groups? | back 104 Bacteria and Fungi |
front 105 Potato dextrose agar (PDA) is a general purpose media use for which group? | back 105 Fungi |
front 106 Trypticase soy agar (TSA) or broth is a general purpose media for which group? | back 106 Bacteria |
front 107 Which of the following is commonly used to culture algae? | back 107 Salt agar |
front 108 Which of the following is commonly used to culture paramecium? | back 108 Hay infusion |
front 109 Which of the following is commonly used to culture viruses? | back 109 Live host cell |
front 110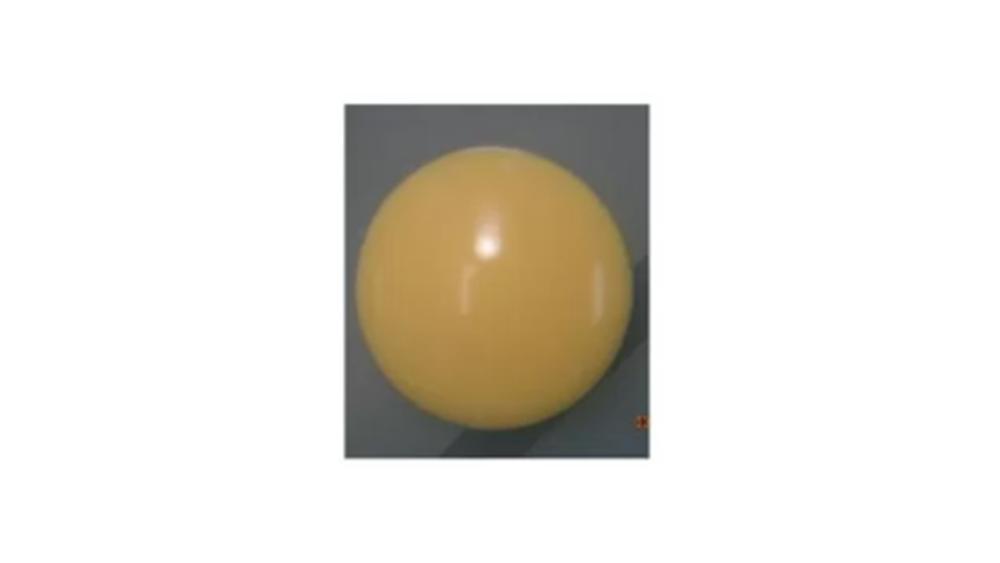  The image of the colony has which type of form? | back 110 Circular |
front 111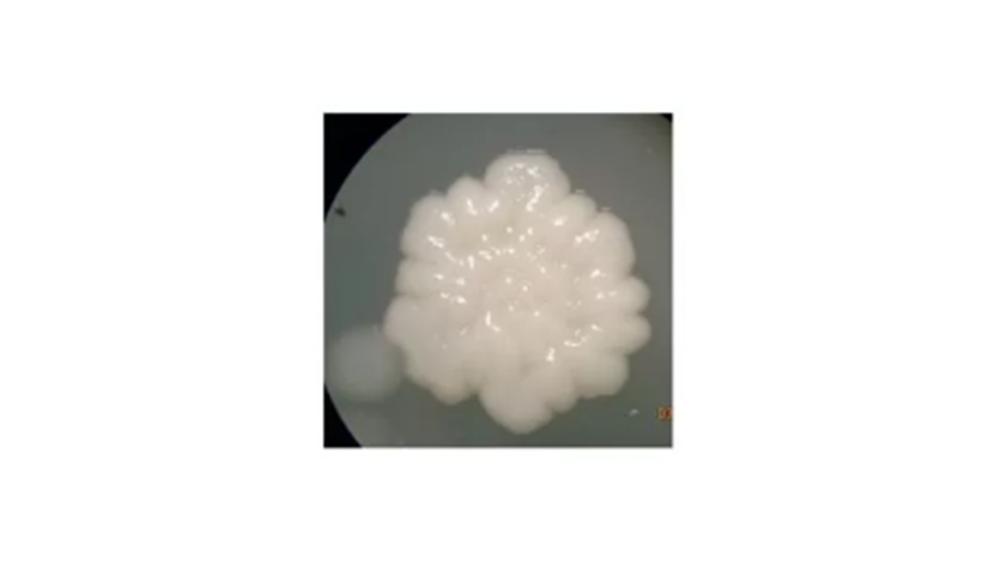  The image of the colony has which type of form? | back 111 Iregular |
front 112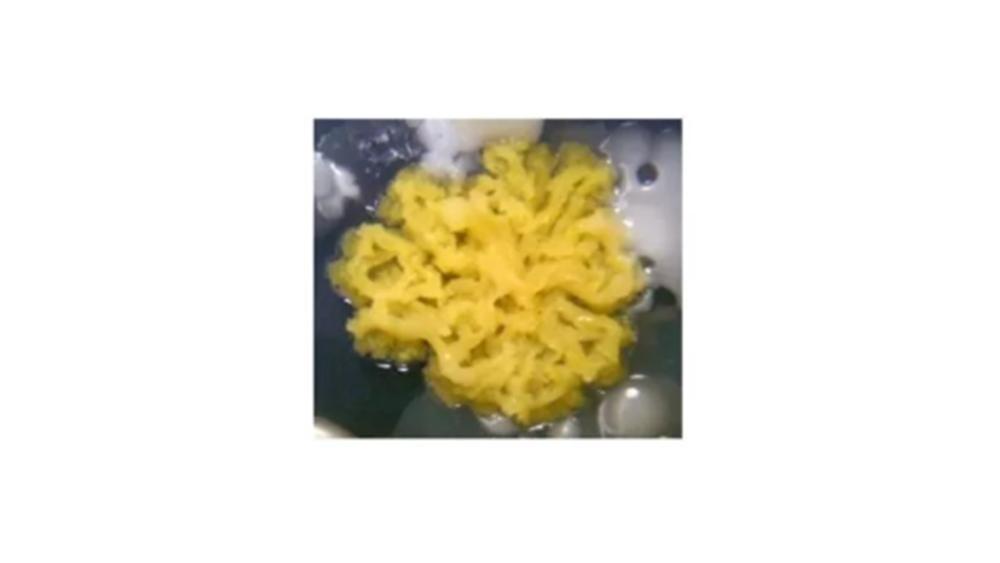  The image of the colony has which type of form? | back 112 Rhizoid |
front 113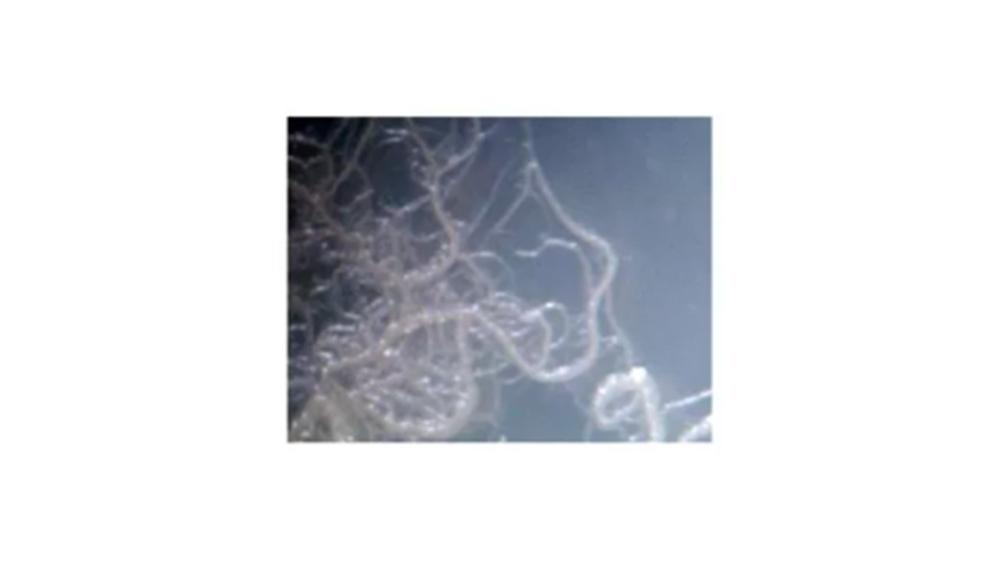  The image of the colony has which type of form? | back 113 Filamentous |
front 114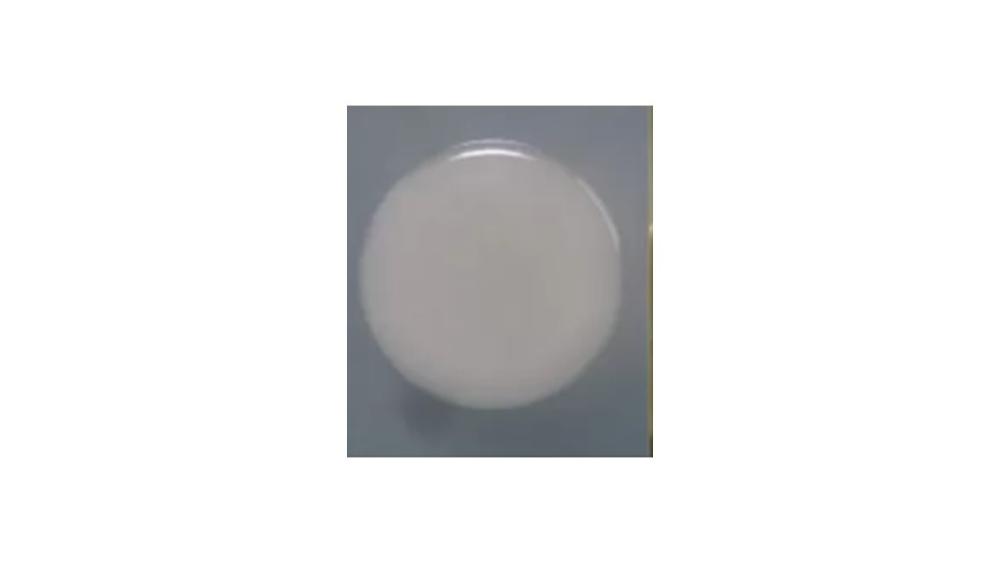  The image of the colony has which type of margin? | back 114 Entire |
front 115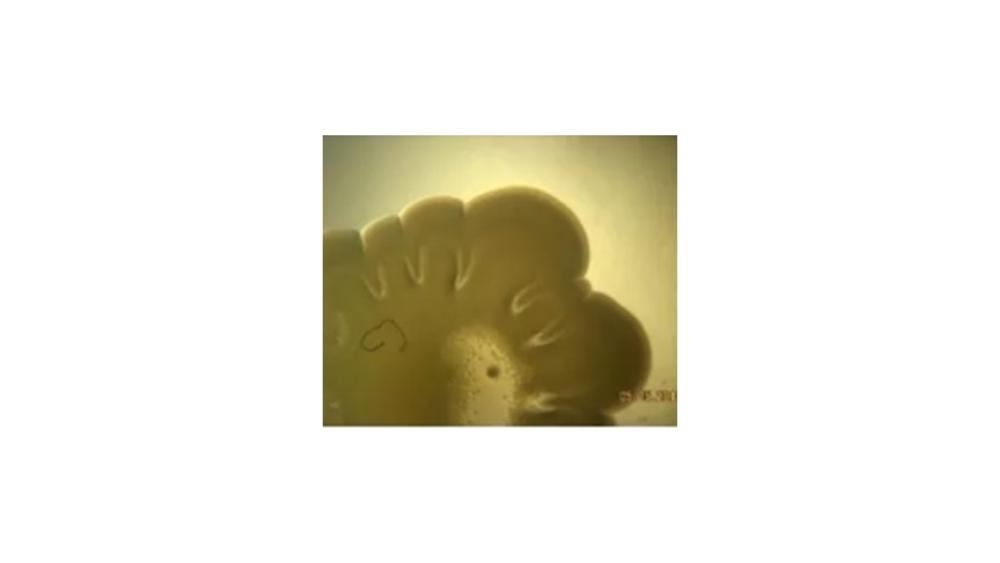  The image of the colony has which type of margin? | back 115 Lobate |
front 116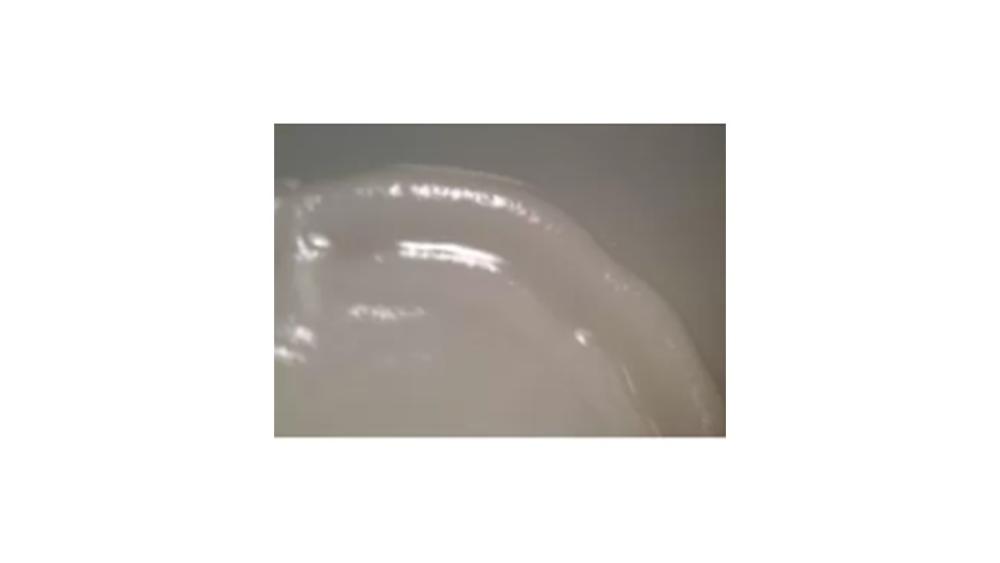  The image of the colony has which type of margin? | back 116 Curled |
front 117 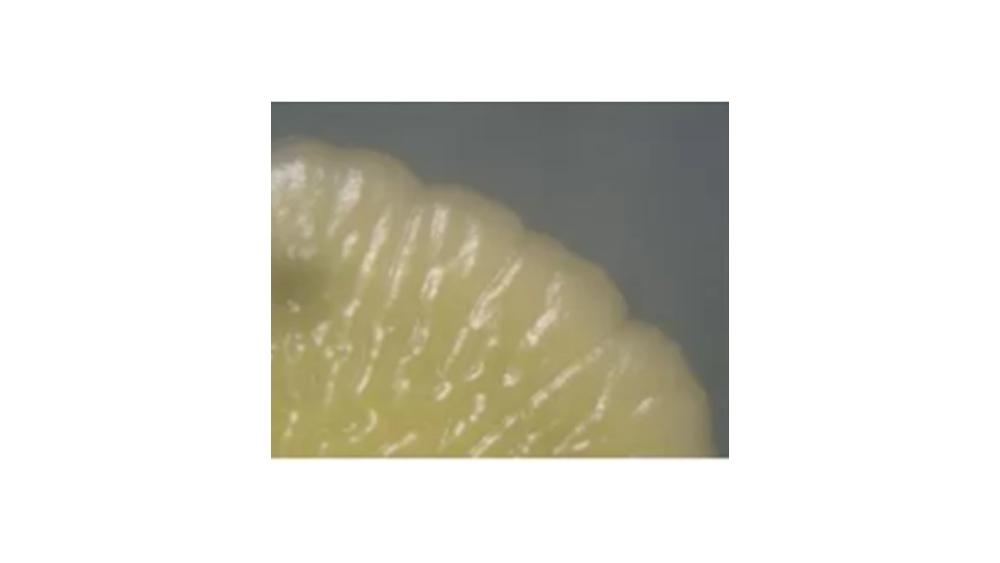 The image of the colony has which type of margin? | back 117 Undulate |
front 118 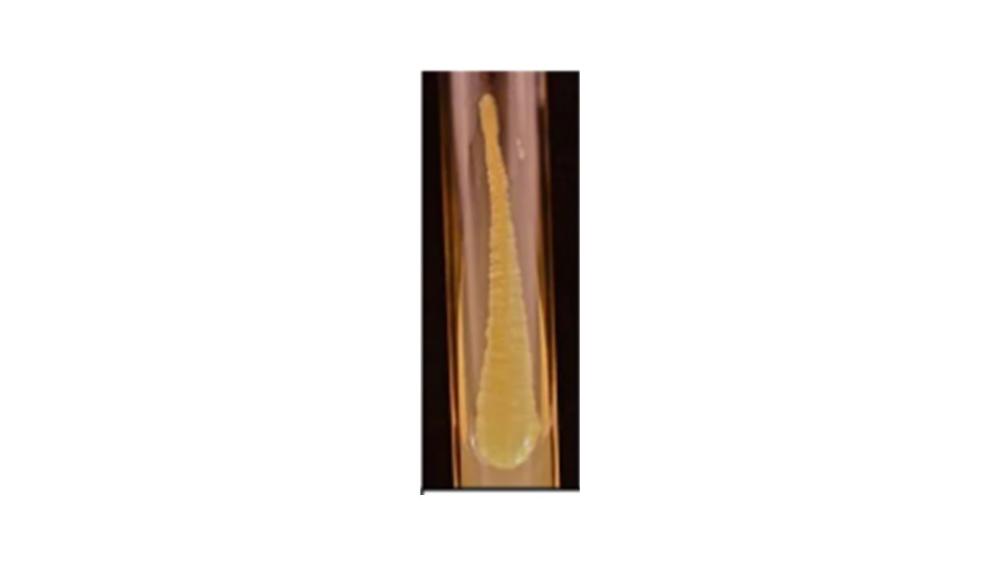 The image of the colony on the agar shows which form? | back 118 Filiform |
front 119 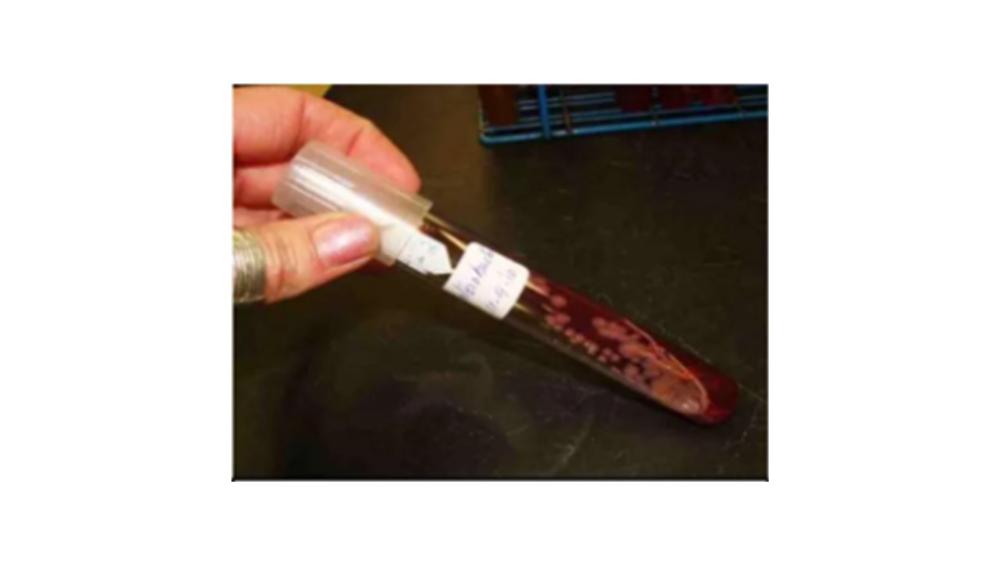 The image of the colony on the agar slant shows which form? | back 119 Beaded |
front 120 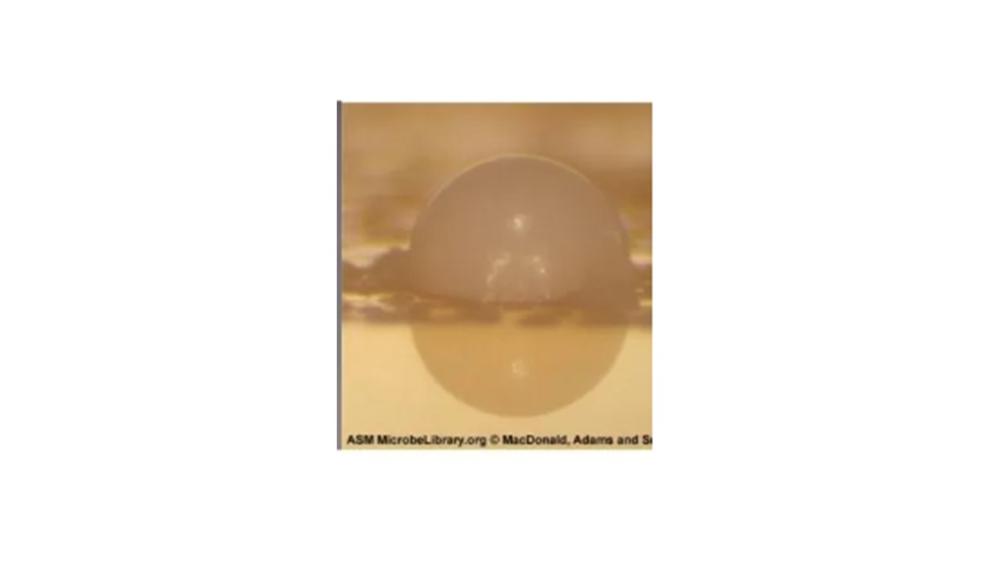 The image of the colony has which elevation? | back 120 Convex |
front 121 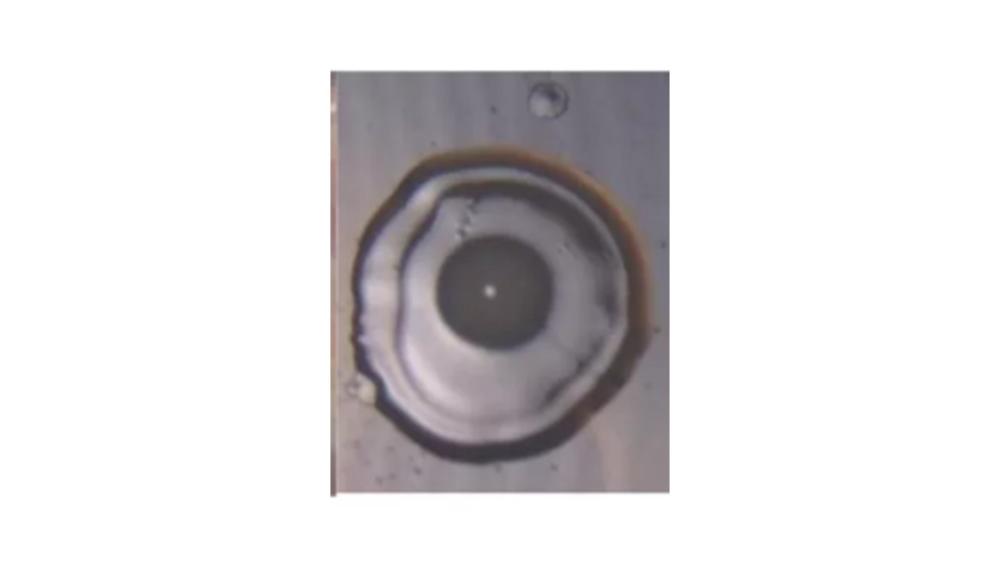 The image of the colony has which elevation? | back 121 Umbonate |
front 122 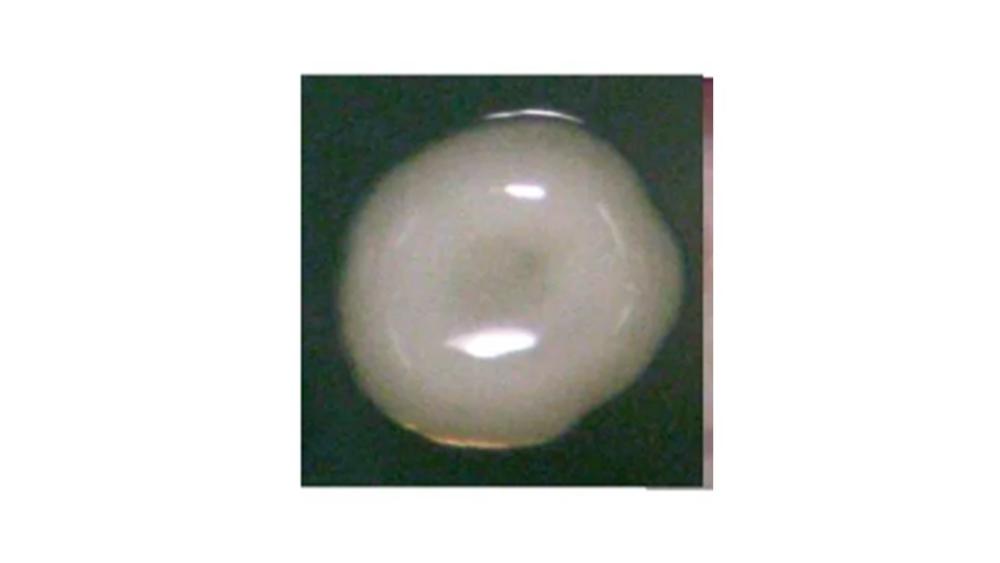 The image of the colony has which elevation? | back 122 Crateriform |
front 123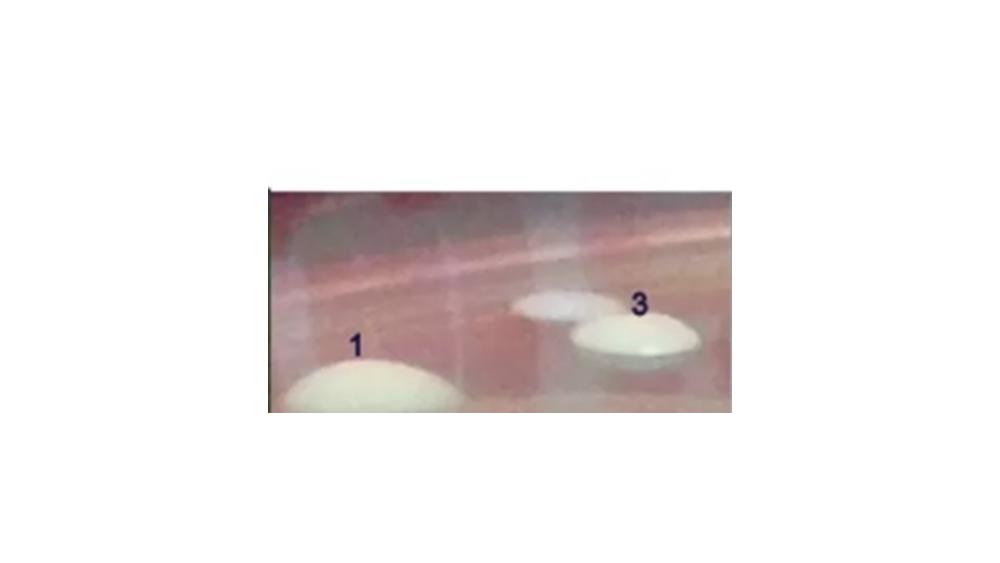  The image of the colony has which elevation? | back 123 Raised |
front 124 This selective and differential media is used to isolate Staphylococcus | back 124 Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) |
front 125 This selective and differential media is used to isolate enteric bacteria that hydrolyze urea | back 125 Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) |
front 126 This selective and differential media is used to isolate enteric bacteria that ferment lactose | back 126 MacConkey Agar (MCA) |
front 127 Which selective media uses high salt concentration to inhibit the growth of non-target bacteria? | back 127 Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) |
front 128 Which selective media uses crystal violet and bile salts to inhibit the growth of non-target bacteria? | back 128 MacConkey Agar (MCA) |
front 129 Which selective media uses methylene blue to inhibit the growth of non-target bacteria? | back 129 Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) |
front 130 Mannitol Salt Agar is selective for which bacteria? | back 130 Staphylococcus |
front 131 Eosin Methylene Blue agar is selective for which bacteria? | back 131
|
front 132 MacConkey's agar is selective for which bacteria? | back 132
|
front 133 Which media turns yellow when fermentation occurs? | back 133 Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) |
front 134 Which media turns colonies of Enterobacter (Klebsiella) aerogenes pink? | back 134 Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) |
front 135 Which media turns colonies of coliform bacteria red? | back 135 MacConkey agar (MCA) |
front 136 Cell division where genome replication is followed directly by the physical separation into two new, identical cells | back 136 Binary fission |
front 137 Cell division where genome replication is separated by a gap phase from the physical separation into two new identical cells | back 137 Mitosis |
front 138 In this phase, limiting factors intensify becoming detrimental to any cell growth | back 138 Death phase |
front 139 In this phase, the cells are adjusting to the environment | back 139 Lag phase |
front 140 In this phase, the cells reach the maximum rate of cell division | back 140 Log phase |
front 141 In this phase, cells will stop growing or grow very slowly | back 141 Stationary phase |
front 142 In this phase, the majority of the cells are alive, but dead cells start to accumulate | back 142 Stationary phase |
front 143 In this phase, there are many living cells and few to none dead cells | back 143 Log phase |
front 144 In this phase, there are few cells present | back 144 Lag phase |
front 145 In this phase, the dead cells take up a larger portion of the culture and little to no growth occurs | back 145 Death phase |
front 146 Of the following absorbance reading samples, which one has more cells present? | back 146 0.85 |
front 147 Of the following absorbance reading samples, which one has fewer cells present? | back 147 0.05 |
front 148 How many cells are present after 9 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth? | back 148 512 |
front 149 How many cells are present after 13 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth? | back 149 8,102 |
front 150 How many cells are present after 18 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth? | back 150 262,144 |
front 151 How many cells are present after 11 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth? | back 151 2,048 |
front 152 How many cells are present after 7 generations (starting from 1 cell) of exponential growth? | back 152 128 |
front 153 A dilution of 1mL bacteria from broth into 1mL broth or water | back 153 1:2 |
front 154 A dilution of 1mL bacteria from broth into 3mL broth or water | back 154 1:4 |
front 155 A dilution of 1mL bacteria from broth into 11mL broth or water | back 155 1:12 |
front 156 A dilution of 1mL bacteria from broth into 7mL broth or water | back 156 1:8 |
front 157 A serial dilution of 1:10 followed by 1:100 by 1:100 gives a final dilution of | back 157 1:100,000 |
front 158 A serial dilution of 1:10 followed by 1:10 followed by 1:100 gives a final dilution of | back 158 1:10,000 |
front 159 A serial dilution of 1:10 followed by 1:10 followed by 1:10 gives a final dilution of | back 159 1:1,000 |
front 160 A serial dilution of 1:6 followed by 1:8 gives a final dilution of | back 160 1:48 |
front 161 A serial dilution of 1:6 followed by 1:10 gives a final dilution of | back 161 1:60 |
front 162 A serial dilution of 1:4 followed by 1:6 gives a final dilution of | back 162 1:24 |
front 163 A serial dilution of 1:2 followed by 1:6 gives a final dilution of | back 163 1:12 |
front 164 A serial dilution of 1:6 followed by 1:12 gives a final dilution of | back 164 1:72 |
front 165 A dilution of 0.1mL bacteria from broth into 9.9mL | back 165 1:100 |
front 166 A dilution of 0.1mL bacteria from broth in 999.9mL broth or water | back 166 1:10,000 |
front 167 A dilution of 0.1mL bacteria from broth in 99.9mL broth or water | back 167 1:1,000 |
front 168 A 1:1,000,00 is which dilution factor? | back 168 -6 |
front 169 A 1:100,000 is which dilution factor? | back 169 -5 |
front 170 A 1:100,000,000 is which dilution factor? | back 170 -8 |
front 171 A 1:10,000,000 is which dilution factor? | back 171 -7 |
front 172 Microbes that require oxygen to grow but at much lower levels than 20% are | back 172 Microaerophiles |
front 173 Microbes that can only grow when oxygen is not present are | back 173 Obligate anaerobes |
front 174 Microbes that can only grow when oxygen is present are | back 174 Obligate aerobes |
front 175 Microbes that can grow in oxygen but do not require oxygen for energy metabolism are | back 175 Aerotolerant anaerobes |
front 176 Microbes that are flexible and can grow with or without oxygen are | back 176 Facultative anaerobes |
front 177 Which bacteria have optimal growth between -5°C to 15°C? | back 177 Psychrophiles |
front 178 Which bacteria have optimal growth between 45°C to 75°C? | back 178 Thermophiles |
front 179 Which bacteria have optimal growth between 25°C to 45°C? | back 179 Mesophiles |
front 180 Which bacteria have optimal growth above 75°C? | back 180 Hyperthermophiles |
front 181 A bacterium that grows at a pH of 10 is a | back 181 Alkaliphiles |
front 182 A bacterium that grows at a pH of 4 is a | back 182 Acidophiles |
front 183 A bacterium that grows at a pH of 7 is a | back 183 Neutrophiles |
front 184 These microbes can grow in excessive sugar concentrations | back 184 Osmophiles |
front 185 These microbes require a high concentration of sodium chloride in order to grow | back 185 Obligate halophiles |
front 186 These microbes can grow in moderate concentration of sodium chloride | back 186 Halotolerant |
front 187 A cell that has more solutes than the surrounding environment is | back 187 Hypertonic |
front 188 A cell that has fewer solutes than the surrounding environment | back 188 Hypotonic |
front 189 Water flows (into/out of) a cell that is hypotonic | back 189 Out of |
front 190 Water flows (into/out of) a cell that is hypertonic | back 190 Into |
front 191 When the temperature increases past the optimal, the hydrogen bonding in the RNA breaks down and the proteins denature in this structure | back 191 Ribosome |
front 192 When the temperature increases past the optimal, lipids can be destroyed affecting which structure? | back 192 Cell membrane |
front 193 Which temperature results in white colonies of Serratia? | back 193 37°C |
front 194 When the temperature decreases past the optimal, lipids can freeze affecting which structure? | back 194 Cell membrane |
front 195 When the temperature decreases past the optimal, the activity of this molecule will slow down | back 195 Enzyme |
front 196 When the temperature increases past the optimal, these denature | back 196 Enzyme |
front 197 Which temperature results in pinkish/red colonies of Serratia? | back 197 25°C |
front 198 Which temperature does Serratia grow best at? | back 198 37°C |
front 199 Which temperature does E. coli grow best at? | back 199 37°C |
front 200 Which temperature does GST grow best at? | back 200 55°C |
front 201 Which temperature does Serratia grow the worst at? | back 201 55°C |
front 202 Which temperature does E. coli grow the worst at | back 202 55°C |
front 203 Which temperature does GST grow the worst at? | back 203 37°C |
front 204 Which pH does E. coli grow best at? | back 204 7 |
front 205 Which pH does S. epidermidis grow best at? | back 205 5 |
front 206 Which pH does A. faecalis grow best at? | back 206 7 |
front 207 Which pH does E. coli grow the worst at? | back 207 3 |
front 208 Which pH does S. epidermidis grow the worst at? | back 208 3 |
front 209 Which pH does A. faecalis grow the worst at? | back 209 3 |