Crystalline solids ________.
A) have their particles arranged
randomly
B) have ordered structures
C) are usually very
soft
D) exist only at high temperatures
E) exist only at
very low temperatures
B
In liquids, the attractive intermolecular forces are
________.
A) very weak compared with kinetic energies of the
molecules
B) strong enough to hold molecules relatively close
together
C) strong enough to keep the molecules confined to
vibrating about their fixed lattice points
D) not strong enough
to keep molecules from moving past each other
E) strong enough to
hold molecules relatively close together but not strong enough to keep
molecules from moving past each other
E
As a gaseous element condenses, the atoms become ________ and they
have ________ attraction for one another.
A) more separated,
more
B) more separated, less
C) closer together,
more
D) closer together, less
E) larger, greater
C
A gas is ________ and assumes ________ of its container, whereas a
liquid is ________ and assumes ________ of its container.
A)
compressible, the volume and shape, not compressible, the shape of a
portion
B) compressible, the shape, not compressible, the volume
and shape
C) compressible, the volume and shape, compressible,
the volume
D) condensed, the volume and shape, condensed, the
volume and shape
E) condensed, the shape, compressible, the
volume and shape
A
Together, liquids and solids constitute ________ phases of
matter.
A) the compressible
B) the fluid
C) the
condensed
D) all of the
E) the disordered
C
Which statement is true about liquids but not true about
solids?
A) They flow and are highly ordered.
B) They are
highly ordered and not compressible.
C) They flow and are
compressible.
D) They assume both the volume and the shape of
their containers.
E) They flow and are not compressible.
E
The strongest interparticle attractions exist between particles of a
________, and the weakest interparticle attractions exist between
particles of a ________.
A) solid, liquid
B) solid,
gas
C) liquid, gas
D) liquid, solid
E) gas, solid
B
Which species has London dispersion forces as the only intermolecular
force?
A) CH3CH2OH
B) Ar
C) NH3
D) HBr
E) H2O
B
Which molecule has hydrogen bonding as the predominant intermolecular
force?
A) CH4
B) C6H6
C) CH3OH
D) CO2
E) C4H10
C
Which species has London dispersion forces as the only intermolecular
force?
A) KBr
B) HI
C) CH3OH
D) CH3CH3
E) CH3F
D
When KBr dissolves in water, aqueous K+ and Br- ions result. The
force of attraction that exists between K+ and H2O is called a(n)
________ interaction.
A) dipole-dipole
B) ion-dipole
C)
ion-ion
D) London dispersion force
E) hydrogen bonding
B
________ are particularly polarizable.
A) Small nonpolar
molecules
B) Small polar molecules
C) Large nonpolar
molecules
D) Large polar molecules
E) Large molecules,
regardless of their polarity,
E
The ease with which the charge distribution in a molecule can be
distorted by an external electrical field is called the
________.
A) electronegativity
B) hydrogen bonding
C)
polarizability
D) volatility
E) viscosity
C
The intermolecular force(s) responsible for the fact that CH4 has the
lowest boiling point in the set CH4, CH3CH3, CH3CH2CH3, CH3CH2CH2CH3
is/are ________.
A) hydrogen bonding
B) London dispersion
forces
C) mainly hydrogen bonding but also dipole-dipole
interactions
D) dipole-dipole interactions
E) mainly
London-dispersion forces but also dipole-dipole interactions
B
Elemental iodine (I2) is a solid at room temperature. What is the
major attractive force that exists among different I2 molecules in the
solid?
A) London dispersion forces
B) dipole-dipole
interactions
C) ionic-dipole interactions
D) covalent-ionic
interactions
E) dipole-dipole attractions
A
Hydrogen bonding is a special case of ________.
A)
London-dispersion forces
B) ion-dipole attraction
C)
dipole-dipole attractions
D) ion-ion interactions
E) none of
the above
C
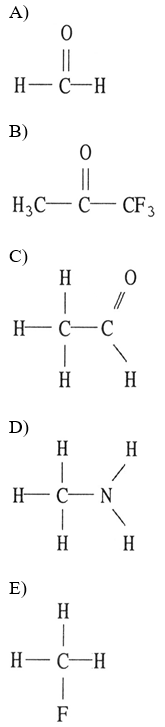
Which one of the following substances will have hydrogen bonding as one of its intermolecular forces?
D
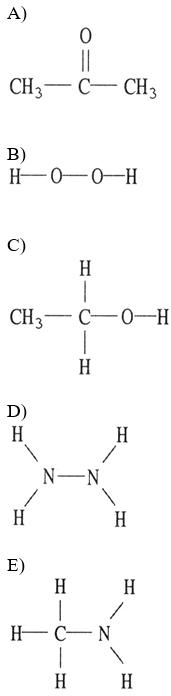
Which one of the following substances will not have hydrogen bonding as one of its intermolecular forces?
A
What intermolecular force is responsible for the fact that ice is
less dense than liquid water?
A) London dispersion forces
B)
dipole-dipole forces
C) ion-dipole forces
D) hydrogen
bonding
E) ionic bonding
D
The predominant intermolecular force in water is ________.
A)
London dispersion forces
B) hydrogen bonding
C) ion-dipole
forces
D) dipole-dipole forces
E) ionic bonding
B
Octane C8H18 molecules are held together by ________.
A) ion-ion
interactions
B) hydrogen bonding
C) ion-dipole
interactions
D) London dispersion forces
E) dipole-dipole interactions
D
Which of the following molecules has hydrogen bonding as its only
intermolecular force?
A) HCl
B) NH3
C) H2O
D)
CH3OH
E) None, all of the above exhibit dispersion forces.
E
Which of the following molecules has London Forces as its only
intermolecular force?
A) H2O
B) CH3CH2NH2
C)
HOCH2CH2OH
D) CH3CH3
E) None, all of the above exhibit
dispersion forces.
D
What types of intermolecular forces exist between CH3OH and
H2O?
A) dipole-dipole and ion-dipole
B) dispersion forces,
dipole-dipole, and hydrogen bonding
C) dispersion forces,
dipole-dipole, and ion-dipole
D) dispersion forces, hydrogen
bonding, dipole-dipole, and ion-dipole
E) dispersion forces and ion-dipole
B
What type(s) of intermolecular forces exist between Cl2 and
CCl4?
A) dispersion forces and ion-dipole
B) dispersion
forces and dipole-dipole
C) dispersion forces
D) dispersion
forces, ion-dipole, and dipole-dipole
E) None. Since both are
gases at room temperature, they do not interact with each other.
C
What type(s) of intermolecular forces exist between NH3 and
PO43-?
A) dispersion forces
B) dispersion forces,
ion-dipole, and dipole-dipole
C) dispersion forces and
dipole-dipole
D) dispersion forces and ion-dipole
E)
dispersion forces, ion-dipole, dipole-dipole, and hydrogen bonds
D
What types of intermolecular forces exist between NH3 and
H2O?
A) dispersion forces
B) dispersion forces and hydrogen
bonds
C) dispersion forces and ion-dipole forces
D)
dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds
E)
dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, and ion-dipole forces
D
What types of intermolecular forces exist between water and
HF?
A) dispersion forces and dipole-dipole forces
B)
dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds
C)
dispersion forces and hydrogen bonds
D) dispersion forces
E)
dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, and ion-dipole forces
B
________ is the energy required to expand the surface area of a
liquid by a unit amount of area.
A) Viscosity
B) Surface
tension
C) Volatility
D) Meniscus
E) Capillary action
B
Which statements about viscosity are true?
(i) Viscosity increases as temperature decreases.
(ii)
Viscosity increases as molecular weight increases.
(iii)
Viscosity increases as intermolecular forces increase.
A) (i) only
B) (ii) and (iii)
C) (i) and (iii)
D)
none
E) all
E
The shape of a liquid's meniscus is determined by ________.
A)
the viscosity of the liquid
B) the type of material the container
is made of
C) the relative magnitudes of cohesive forces in the
liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and its
container
D) the amount of hydrogen bonding in the liquid
E)
the volume of the liquid
C
Viscosity is ________.
A) the "skin" on a liquid
surface caused by intermolecular attraction
B) the resistance to
flow
C) the same as density
D) inversely proportional to
molar mass
E) unaffected by temperature
B
How high a liquid will rise up a narrow tube as a result of capillary
action depends on ________.
A) the magnitudes of cohesive forces
in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and the tube, and
gravity
B) gravity alone
C) only the magnitude of adhesive
forces between the liquid and the tube
D) the viscosity of the
liquid
E) only the magnitude of cohesive forces in the liquid
A
The property responsible for the "beading up" of water is
________.
A) density
B) viscosity
C) vapor
pressure
D) surface tension
E) hydrogen bonding
D
Heat of sublimation can be approximated by adding together ________
and ________.
A) heat of fusion, heat of condensation
B)
heat of fusion, heat of vaporization
C) heat of freezing
(solidification), heat of condensation
D) heat of freezing
(solidification), heat of vaporization
E) heat of deposition,
heat of vaporization
B
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The absolute
value of the heat of sublimation is equal to the absolute value of the
heat of deposition.
B) The heat of sublimation is equal to the
sum of the heat of vaporization and the heat of deposition.
C)
The heat of sublimation is equal to the sum of the heat of
vaporization and the heat of freezing.
D) The absolute value of
the heat of sublimation is equal to the absolute value of the sum of
the heat of condensation and the heat of freezing.
E) The
absolute value of the heat of deposition is equal to sum of the
absolute value of the heat of vaporization and the absolute value of
the heat of freezing.
C
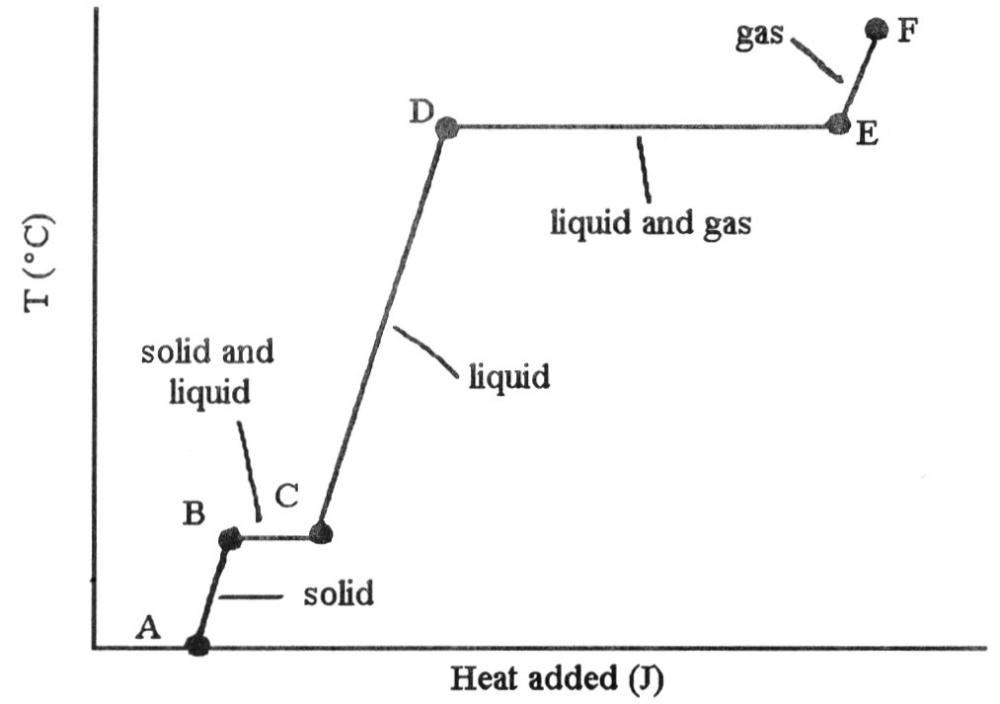
The ________ (is)are associated with the heat energy being used up to
increase distances between molecules.
A) phase change B →
C
B) phase changes B → C and D → E
C) phase change D →
E
D) phase change B → E
E) phase change C → E
B
Based on the following information, which compound has the strongest intermolecular forces?
Substance | ΔHvap (kJ/mol)
Argon (Ar) | 6.3
Benzene (C6H6) | 31.0
Ethanol (C2H5OH) |
39.3
Water (H2O) | 40.8
Methane (CH4) | 9.2
A) Argon
B) Benzene
C) Ethanol
D) Water
E) Methane
D
Which compound has the strongest intermolecular forces?
A)
CCl4
B) CI4
C) CH4
D) H2
E) O2
B
Large intermolecular forces in a substance are manifested by
________.
A) low vapor pressure
B) high boiling
point
C) high heats of fusion and vaporization
D) high
critical temperatures and pressures
E) all of the above
E
A supercritical fluid can expand like a ________ to fill a container
and has a density similar to that of a ________ so can behave as a
solvent.
A) gas, plasma
B) gas, solid
C) solid,
gas
D) liquid, gas
E) gas, liquid
E
The critical temperature and pressure of CS2 are 279 °C and 78 atm,
respectively. A supercritical fluid can only exist at a temperature
________ 279 °C and pressure ________ 78 atm.
A) exactly,
exactly
B) above, below
C) above, above
D) below,
above
E) below, below
C
The substance with the largest heat of vaporization is
________.
A) H2
B) Cl2
C) I2
D) N2
E) O2
C
Of the following, ________ is an exothermic process.
A)
melting
B) subliming
C) freezing
D) boiling
E) All
of the above are exothermic.
C
Of the following, ________ should have the highest critical
temperature.
A) CBr4
B) CCl4
C) CF4
D) CH4
E) H2
A
A volatile liquid is one that ________.
A) is highly
flammable
B) is highly viscous
C) is highly
hydrogen-bonded
D) is highly cohesive
E) readily evaporates
E
In general, the vapor pressure of a substance increases as ________
increases.
A) surface tension
B) molecular weight
C)
hydrogen bonding
D) viscosity
E) temperature
E
The vapor pressure of any substance at its normal boiling point is
________.
A) 1 Pa
B) 1 torr
C) 1 atm
D) equal to
atmospheric pressure
E) equal to the vapor pressure of water
C
Volatility and vapor pressure are ________.
A) inversely
proportional to one another
B) directly proportional to one
another
C) not related
D) the same thing
E) both
independent of temperature
B
Some things take longer to cook at high altitudes than at low
altitudes because ________.
A) water boils at a lower temperature
at high altitude than at low altitude
B) water boils at a higher
temperature at high altitude than at low altitude
C) heat isn't
conducted as well in low density air
D) natural gas flames don't
burn as hot at high altitudes
E) there is a higher moisture
content in the air at high altitude
A
The vapor pressure of a liquid ________.
A) increases linearly
with increasing temperature
B) increases nonlinearly with
increasing temperature
C) decreases linearly with increasing
temperature
D) decreases nonlinearly with increasing
temperature
E) is totally unrelated to its molecular structure
B
-ΔHvap/R is the slope of a plot of the natural log of the vapor
pressure of a substance versus ________.
A) -1/T
B)
-T
C) 1/T
D) T
E) 2T
C
On a phase diagram, the critical pressure is ________.
A) the
pressure required to melt a solid
B) the pressure below which a
substance is a solid at all temperatures
C) the pressure above
which a substance is a liquid at all temperatures
D) the pressure
at which a liquid changes to a gas
E) the pressure required to
liquefy a gas at its critical temperature
E
On a phase diagram, the critical temperature is ________.
A) the
temperature below which a gas cannot be liquefied
B) the
temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied
C) the
temperature at which all three states are in equilibrium
D) the
temperature required to melt a solid
E) the temperature required
to cause sublimation of a solid
B
On a phase diagram, the melting point is the same as
________.
A) the triple point
B) the critical point
C)
the freezing point
D) the boiling point
E) the
vapor-pressure curve
C
When the phase diagram for a substance has a solid-liquid phase
boundary line that has a ________ slope, the substance can go from
solid to liquid, within a small temperature range, via the application
of pressure.
A) positive
B) zero
C) y = 1
D)
negative
E) y = 0
D
The predominant intramolecular force in CaBr2 is ________.
A)
London-dispersion forces
B) ion-dipole forces
C) ionic
bonding
D) dipole-dipole forces
E) hydrogen bonding
C
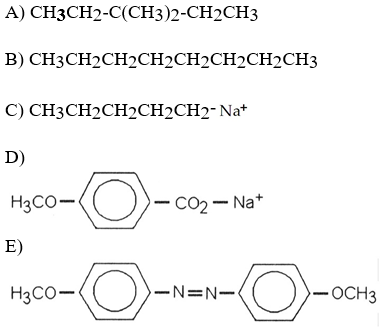
Which of the following is most likely to exhibit liquid-crystalline behavior?
E
All of the following are characteristics of liquid crystal behavior
except ________.
A) long axial structure
B) carbon-carbon
single bonds
C) double bonding
D) ionic
configuration
E) polar groups
D
In the ________ liquid-crystalline phase,the molecules are arranged
in sheets, with their long axes parallel and their ends aligned as
well.
A) smectic B
B) smectic C
C) smectic A
D)
smectic E
E) smectic D
C
In the ________ liquid crystalline phase, the component molecules
exhibit ________ dimensional ordering.
A) nematic, one
B)
smectic A, one
C) nematic, two
D) nematic, three
E)
smectic B, one
A
What are the common types of smectic liquid-crystalline
phases?
A) A, C, and D
B) A only
C) A and C
D) A
and D
E) C and D
C
________ liquid crystals are colored because the molecular layers are
arranged in slightly twisted planes with respect to one
another.
A) smectic B
B) cholesteric
C) smectic
A
D) smectic C
E) smectic D
B
Molecules with ________ do not generally exhibit liquid-crystalline
properties because they lack the rigidity necessary for
alignment.
A) both single and double bonds
B) double or
triple bonds
C) single, double, and triple bonds
D) only
single bonds
E) only single and double bonds
D
For a given substance that exhibits liquid-crystalline properties,
the transition from solid to liquid-crystal state occurs
________.
A) over a range of temperatures between the melting
point of the solid and the boiling point of the liquid
B) at the
melting point of the solid
C) over a range of temperatures that
includes the melting point of the solid
D) at a well-defined
temperature above the melting point of the solid
E) at a
well-defined temperature below the melting point of the solid
B
There are ________ types of smectic liquid-crystalline
phases.
A) 6
B) 5
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
D
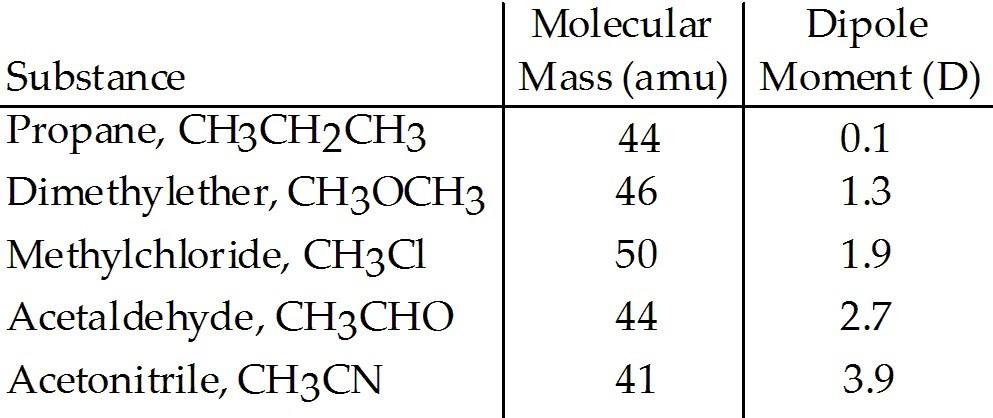
Based on molecular mass and dipole moment of the five compounds in the table below, which should have the highest boiling point?
A) CH3CH2CH3
B) CH3OCH3
C) CH3Cl
D) CH3CHO
E) CH3CN
E
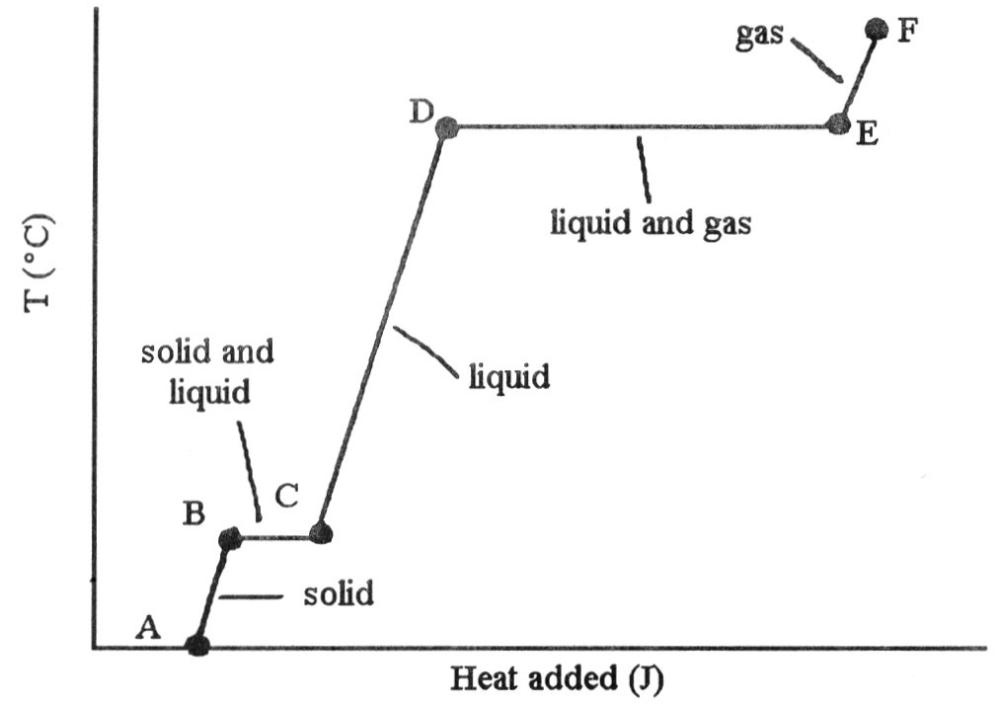
The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature for a solid as it was heated. The slope of the ________
segment corresponds to the heat capacity of the liquid of the
substance.
A) AB
B) BC
C) CD
D) DE
E) EF
C

The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature for a solid as it was heated. The slope of the ________
segment corresponds to the heat capacity of the solid.
A)
AB
B) BC
C) CD
D) DE
E) EF
A

The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature for a solid as it was heated. The slope of the E-F segment
corresponds to the heat capacity of the ________.
A)
liquid-gas
B) solid-gas
C) gas
D) solid
E) liquid
C

The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature of a solid as it was heated. The heat flow into the sample
in the segment D-E will yield the value of the ________ of this
substance.
A) ΔHsub
B) ΔHvap
C) ΔHmelting
D)
ΔHfusion
E) ΔHrxn
B

The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature of a solid as it was heated. The heat flow into the sample
in the segment ________ will yield the value of the ΔHfusion of this
substance.
A) AB
B) BC
C) CD
D) DE
E) EF
B
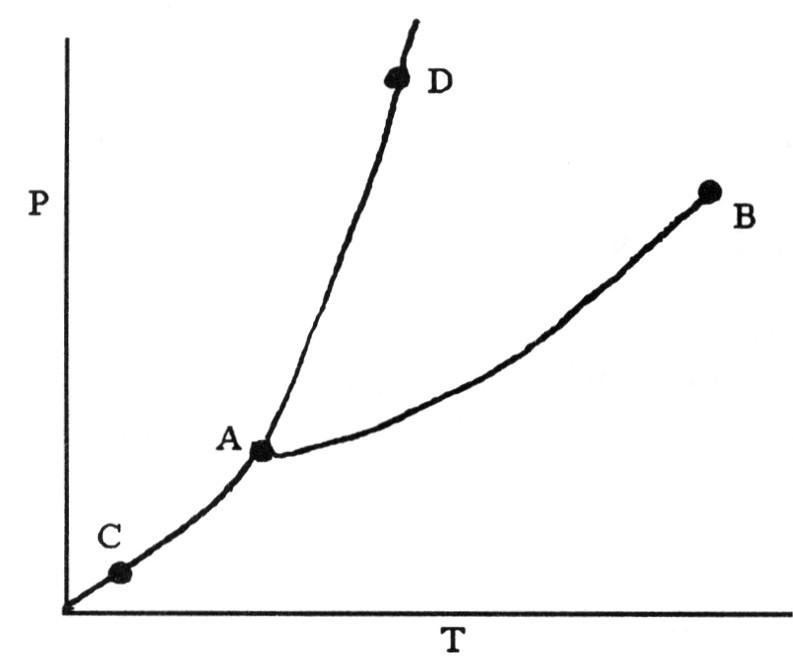
On the phase diagram shown above, segment ________ corresponds to the
conditions of temperature and pressure under which the solid and the
gas of the substance are in equilibrium.
A) AB
B)
AC
C) AD
D) CD
E) BC
B

On the phase diagram shown above, the coordinates of point B
corresponds to the ________.
A) critical temperature and
pressure
B) critical pressure
C) critical
temperature
D) boiling point
E) triple point
A

On the phase diagram shown above, the coordinates of point ________
correspond to the triple point.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D)
D
E) E
A
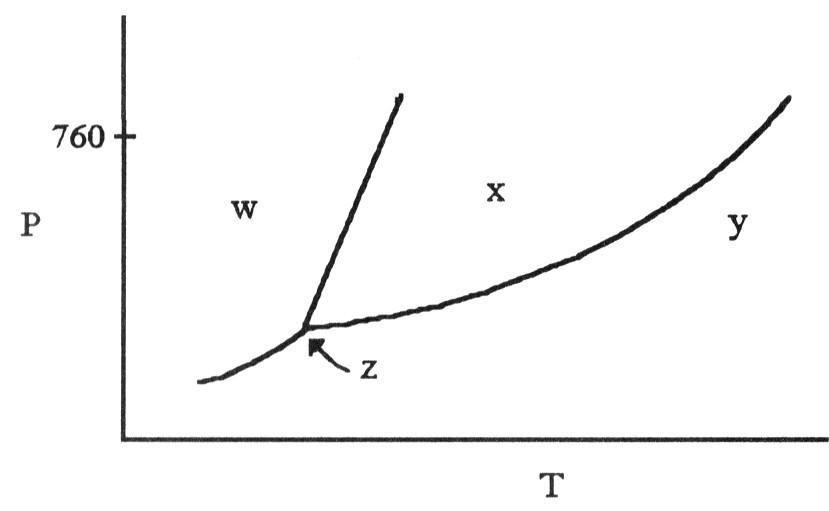
The phase diagram of a substance is given above. The region that
corresponds to the solid phase is ________.
A) w
B)
x
C) y
D) z
E) x and y
A
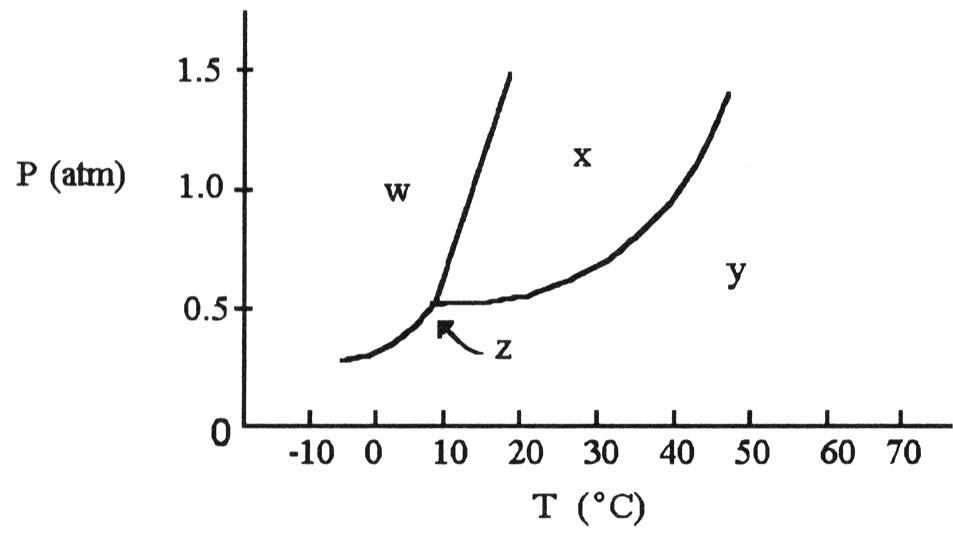
According to the phase diagram shown above, what is the normal
boiling point (°C)?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D)
40
E) 50
D

According to the phase diagram shown above, what is the normal
melting point (°C)?
A) 15
B) 25
C) 35
D)
45
E) 55
A
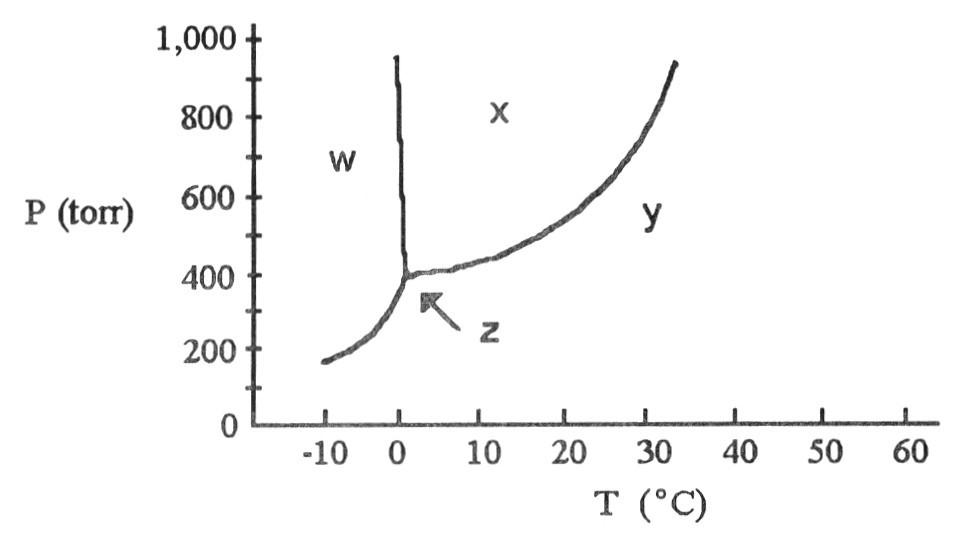
The phase diagram of a substance is shown above. The area labeled
________ indicates the gas phase for the substance.
A) w
B)
x
C) y
D) z
E) y and z
C

The phase diagram of a substance is shown above. The area labeled
________ indicates the solid phase for the substance.
A)
w
B) x
C) y
D) z
E) y and z
A

The phase diagram of a substance is shown above. The area labeled
________ indicates the liquid phase for the substance.
A)
w
B) x
C) y
D) z
E) y and z
B

According to the phase diagram shown above, what is the normal
boiling point (°C)?
A) 10
B) -3
C) 38
D)
29
E) 0
D

According to the phase diagram shown above, what is the normal
melting point (°C)?
A) -13
B) 0
C) 38
D)
10
E) 29
B
A ________ liquid crystal has the least order and is the most
liquid-like.
A) nematic
B) smectic
C)
cholesteric
D) smectic C
E) smectic B
A
________ liquid crystals are colored and change color with
temperature changes.
A) Smectic A
B) Nematic
C)
Cholesteric
D) Smectic B
E) Smectic C
C
As a gaseous element condenses, the atoms become ________ and they
have ________ attraction for one another.
A) less separated,
more
B) less separated, less
C) more separated, more
D)
more separated, less
E) smaller, lesser
A
What is the predominant intramolecular force in NaNO3?
A) ionic
bonding
B) ion-dipole attraction
C) dipole-dipole
attraction
D) hydrogen bonding
E) London-dispersion forces
A
With what compound will NH3 experience only dispersion intermolecular
forces?
A) BF3
B) LiF
C) CH3I
D) CH3OH
E) HCN
A
With what compound will NH3 experience only ion-dipole intermolecular
forces?
A) LiCl
B) SiH4
C) CH3I
D)
C3H7OH
E) OCl2
A
Which one of the following exhibits dipole-dipole attraction between
molecules?
A) HCl
B) CF4
C) CS2
D) F2
E) BI3
A
Which one of the following exhibits dipole-dipole attraction between
molecules?
A) NH3
B) CF4
C) C10H22
D) O2
E) SF6
A
Of the following substances, only ________ has London dispersion
forces as its only intermolecular force.
A) CCl4
B) SnF3
C) CH3OH
D) HI
E) H2O
A
Which of the following has London dispersion forces as its only
intermolecular force?
A) NBr3
B) CH3COOH
C) SiCl4
D) HBr
E) Cl2O
C
Which molecule has the lowest boiling point?
A)
CH3CH2CH2CH3
B) CH3CH2CH3
C) CH3CH3
D) CH4
E) H2O
D
Which one of the following should have the lowest boiling
point?
A) CH4
B) PCl3
C) C2H5COOH
D)
LiCl
E) Cl2S
A
Of the following substances, ________ has the highest boiling
point.
A) H2O
B) SiH4
C) Ar
D) Cl2
E) BF3
A
Of the following substances, ________ has the highest boiling
point.
A) HOCH2CH2CH2OH
B) CH3CH2OH
C) C4H10
D)
N2
E) Cl2
A
Of the following substances, ________ has the highest boiling
point.
A) Br2
B) N2
C) Cl2
D) O2
E) H2
A
Which one of the following derivatives of methane has the highest
boiling point?
A) CI4
B) CBr4
C) CCl4
D) CF4
E) CH4
A
What is the predominant intermolecular force in CH4?
A)
London-dispersion forces
B) ion-dipole attraction
C) ionic
bonding
D) dipole-dipole attraction
E) hydrogen bonding
A
What is the predominant intermolecular force in H2NNH2?
A)
hydrogen bonding
B) ion-dipole attraction
C) ionic
bonding
D) dipole-dipole attraction
E) London-dispersion forces
A
What is the predominant intermolecular force in HCN?
A)
dipole-dipole attraction
B) ion-dipole attraction
C) ionic
bonding
D) hydrogen bonding
E) London dispersion forces
A
Ethanol melts at -114 °C and boils at 78 °C at a constant pressure of
1 atm. What state of matter must a sample of ethanol be in at 0°C and
1 atm?
A) liquid
B) gas
C) solid
D) solid and
liquid in equilibrium
E) liquid and gas in equilibrium
A
At 1 atm, an unknown sample melts at 49.9 °C and boils at 209.5 °C.
If the temperature is 0°C, what is the state of matter for the
sample?
A) solid and liquid in equilibrium
B) liquid
C)
gas
D) solid
E) liquid and gas in equilibrium
D
The enthalpy change for converting 1.00 mol of ice at -25.0 °C to
water at 50.0 °C is ________ kJ. The specific heats of ice, water, and
steam are 2.09 J/g-K, 4.18 J/g-K, and 1.84 J/g-K, respectively. For
H2O, ΔHfus = 6.01 kJ/mol, and ΔHvap = 40.67
kJ/mol.
A) 12.28
B) 6.27
C) 10.71
D) 4709
E) 8.83
C
The enthalpy change for converting 10.0 g of ice at -50.0 °C to water
at 50.0 °C is ________ kJ. The specific heats of ice, water, and steam
are 2.09 J/g-K, 4.18 J/g-K, and 1.84 J/g-K, respectively. For H2O,
ΔHfus = 6.01 kJ/mol, and ΔHvap = 40.67
kJ/mol.
A) 12.28
B) 4.38
C) 3138
D) 6.47
E) 9.15
D
The heat of fusion of water is 6.01 kJ/mol. The heat capacity of
liquid water is 75.3 J/mol ∙ K. The conversion of 50.0g of ice at 0.00
°C to liquid water at 0.00°C requires ________ kJ of heat.
A)
6.01
B) 16.7
C) 75.3
D) 17.2
E) Insufficient data
are given.
B
Calculate the enthalpy change (in kJ) associated with the conversion
of 25.0 grams of ice at -4.00 °C to water vapor at 109.0 °C. The
specific heats of ice, water, and steam are 2.09 J/g-K, 4.18 J/g-K,
and 1.84 J/g-K, respectively. For H2O, ΔHfus = 6.01 kJ/mol,
and ΔHvap = 40.67 kJ/mol.
A) 64.8
B) 75.9
C)
11100
D) 12000
E) 112
B
Ethanol ( OH) melts at -114 °C. The enthalpy of fusion is 5.02
kJ/mol. The specific heats of solid and liquid ethanol are 0.97 J/g-K
and 2.3 J/g-K, respectively. How much heat (kJ) is needed to convert
25.0 g of solid ethanol at -135 °C to liquid ethanol at -60
°C?
A) 207.3
B) -13.3
C) 6.34
D) 3617
E) 8.63
C
Of the following, ________ is the most volatile.
A) C2H6
B)
C2I6
C) C2Br6
D) C2Cl6
E) C2F6
A
Which molecule is the least volatile?
A) CH3Cl
B)
CH3I
C) CH3F
D) CH4
E) CH3Br
B
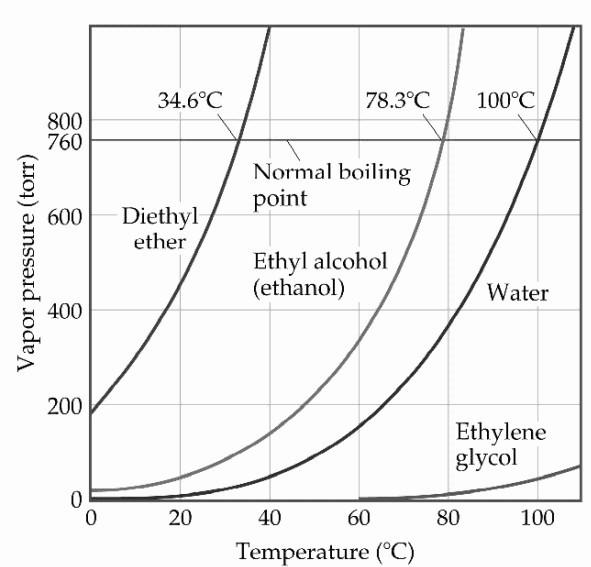
Based on the figure above, the boiling point of diethyl ether under
an external pressure of 0.605atm is ________ °C.
A) 40
B)
10
C) 30
D) 20
E) 0
D

Based on the figure above, the boiling point of diethyl ether under
an external pressure of 0.658atm is ________ °C.
A) 20
B)
40
C) 60
D) 80
E) 70
E
Based on the figure above, what is the boiling point (°C) of water
under an external pressure of 0.724atm.
A) 40
B) 60
C)
70
D) 90
E) 80
D
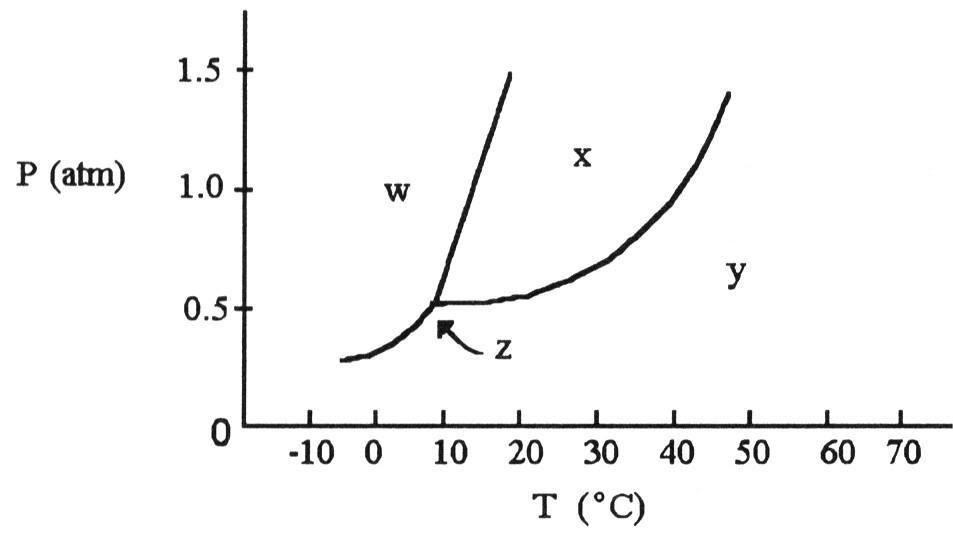
The phase diagram of a substance is given above. This substance is a
________ at 30 °C and 0.5 atm.
A) liquid
B) gas
C)
solid
D) supercritical fluid
E) crystal
B
In general, intramolecular forces determine the ________ properties of a substance and intermolecular forces determine its ________ properties.
chemical, physical
London Dispersion Forces tend to ________ in strength with increasing molecular weight.
increase
The conversion of a solid to a liquid is called ________.
melting
The initial discovery of a liquid crystal resulted from studies of a ________ derivative.
cholesterol
The principal source of the difference in the normal boiling points of ICl (97 °C; molecular mass 162 amu) and Br2 (59 °C; molecular mass 160 amu) is both dipole-dipole interactions and London dispersion forces.
false
The boiling points of normal hydrocarbons are higher than those of branched hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight because the London-dispersion forces between normal hydrocarbons are greater than those between branched hydrocarbons.
true
Heats of vaporization are greater than heats of fusion.
true
Under ordinary conditions, a substance will sublime rather than melt if its triple point occurs at a pressure above atmospheric pressure.
true
Molecules containing many double bonds do not exhibit liquid-crystal behavior because free rotation can occur only around single bonds making these molecules rigid.
false