Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Central Science: Chapter 11
front 1 Crystalline solids ________. | back 1 B |
front 2 In liquids, the attractive intermolecular forces are
________. | back 2 E |
front 3 As a gaseous element condenses, the atoms become ________ and they
have ________ attraction for one another. | back 3 C |
front 4 A gas is ________ and assumes ________ of its container, whereas a
liquid is ________ and assumes ________ of its container. | back 4 A |
front 5 Together, liquids and solids constitute ________ phases of
matter. | back 5 C |
front 6 Which statement is true about liquids but not true about
solids? | back 6 E |
front 7 The strongest interparticle attractions exist between particles of a
________, and the weakest interparticle attractions exist between
particles of a ________. | back 7 B |
front 8 Which species has London dispersion forces as the only intermolecular
force? | back 8 B |
front 9 Which molecule has hydrogen bonding as the predominant intermolecular
force? | back 9 C |
front 10 Which species has London dispersion forces as the only intermolecular
force? | back 10 D |
front 11 When KBr dissolves in water, aqueous K+ and Br- ions result. The
force of attraction that exists between K+ and H2O is called a(n)
________ interaction. | back 11 B |
front 12 ________ are particularly polarizable. | back 12 E |
front 13 The ease with which the charge distribution in a molecule can be
distorted by an external electrical field is called the
________. | back 13 C |
front 14 The intermolecular force(s) responsible for the fact that CH4 has the
lowest boiling point in the set CH4, CH3CH3, CH3CH2CH3, CH3CH2CH2CH3
is/are ________. | back 14 B |
front 15 Elemental iodine (I2) is a solid at room temperature. What is the
major attractive force that exists among different I2 molecules in the
solid? | back 15 A |
front 16 Hydrogen bonding is a special case of ________. | back 16 C |
front 17 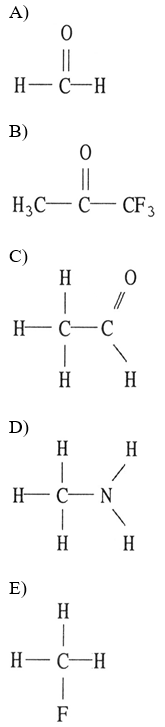 Which one of the following substances will have hydrogen bonding as one of its intermolecular forces? | back 17 D |
front 18 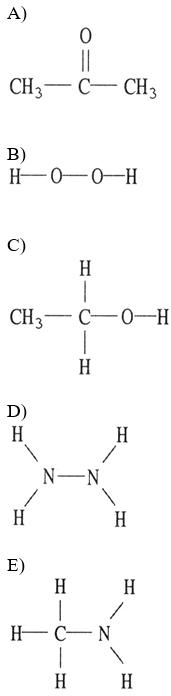 Which one of the following substances will not have hydrogen bonding as one of its intermolecular forces? | back 18 A |
front 19 What intermolecular force is responsible for the fact that ice is
less dense than liquid water? | back 19 D |
front 20 The predominant intermolecular force in water is ________. | back 20 B |
front 21 Octane C8H18 molecules are held together by ________. | back 21 D |
front 22 Which of the following molecules has hydrogen bonding as its only
intermolecular force? | back 22 E |
front 23 Which of the following molecules has London Forces as its only
intermolecular force? | back 23 D |
front 24 What types of intermolecular forces exist between CH3OH and
H2O? | back 24 B |
front 25 What type(s) of intermolecular forces exist between Cl2 and
CCl4? | back 25 C |
front 26 What type(s) of intermolecular forces exist between NH3 and
PO43-? | back 26 D |
front 27 What types of intermolecular forces exist between NH3 and
H2O? | back 27 D |
front 28 What types of intermolecular forces exist between water and
HF? | back 28 B |
front 29 ________ is the energy required to expand the surface area of a
liquid by a unit amount of area. | back 29 B |
front 30 Which statements about viscosity are true? (i) Viscosity increases as temperature decreases. A) (i) only | back 30 E |
front 31 The shape of a liquid's meniscus is determined by ________. | back 31 C |
front 32 Viscosity is ________. | back 32 B |
front 33 How high a liquid will rise up a narrow tube as a result of capillary
action depends on ________. | back 33 A |
front 34 The property responsible for the "beading up" of water is
________. | back 34 D |
front 35 Heat of sublimation can be approximated by adding together ________
and ________. | back 35 B |
front 36 Which of the following statements is false? | back 36 C |
front 37 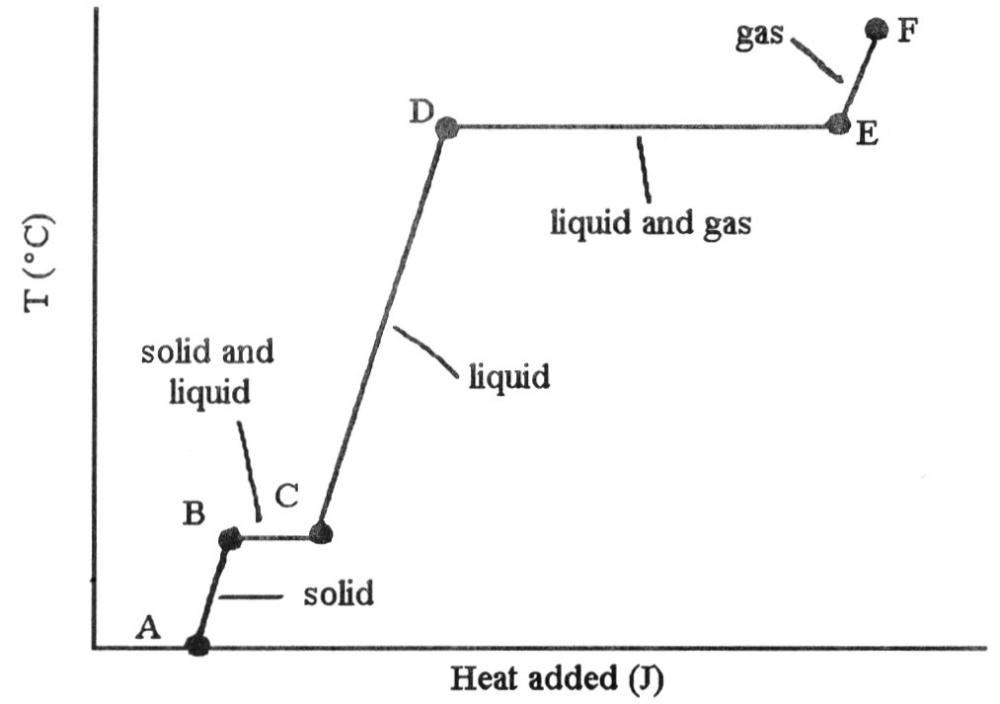 The ________ (is)are associated with the heat energy being used up to
increase distances between molecules. | back 37 B |
front 38 Based on the following information, which compound has the strongest intermolecular forces?
Substance | ΔHvap (kJ/mol) A) Argon | back 38 D |
front 39 Which compound has the strongest intermolecular forces? | back 39 B |
front 40 Large intermolecular forces in a substance are manifested by
________. | back 40 E |
front 41 A supercritical fluid can expand like a ________ to fill a container
and has a density similar to that of a ________ so can behave as a
solvent. | back 41 E |
front 42 The critical temperature and pressure of CS2 are 279 °C and 78 atm,
respectively. A supercritical fluid can only exist at a temperature
________ 279 °C and pressure ________ 78 atm. | back 42 C |
front 43 The substance with the largest heat of vaporization is
________. | back 43 C |
front 44 Of the following, ________ is an exothermic process. | back 44 C |
front 45 Of the following, ________ should have the highest critical
temperature. | back 45 A |
front 46 A volatile liquid is one that ________. | back 46 E |
front 47 In general, the vapor pressure of a substance increases as ________
increases. | back 47 E |
front 48 The vapor pressure of any substance at its normal boiling point is
________. | back 48 C |
front 49 Volatility and vapor pressure are ________. | back 49 B |
front 50 Some things take longer to cook at high altitudes than at low
altitudes because ________. | back 50 A |
front 51 The vapor pressure of a liquid ________. | back 51 B |
front 52 -ΔHvap/R is the slope of a plot of the natural log of the vapor
pressure of a substance versus ________. | back 52 C |
front 53 On a phase diagram, the critical pressure is ________. | back 53 E |
front 54 On a phase diagram, the critical temperature is ________. | back 54 B |
front 55 On a phase diagram, the melting point is the same as
________. | back 55 C |
front 56 When the phase diagram for a substance has a solid-liquid phase
boundary line that has a ________ slope, the substance can go from
solid to liquid, within a small temperature range, via the application
of pressure. | back 56 D |
front 57 The predominant intramolecular force in CaBr2 is ________. | back 57 C |
front 58 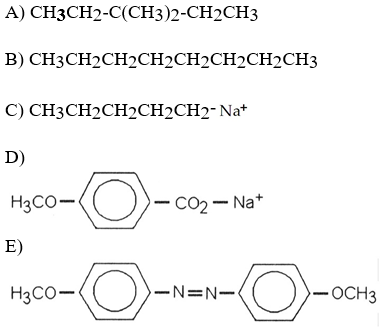 Which of the following is most likely to exhibit liquid-crystalline behavior? | back 58 E |
front 59 All of the following are characteristics of liquid crystal behavior
except ________. | back 59 D |
front 60 In the ________ liquid-crystalline phase,the molecules are arranged
in sheets, with their long axes parallel and their ends aligned as
well. | back 60 C |
front 61 In the ________ liquid crystalline phase, the component molecules
exhibit ________ dimensional ordering. | back 61 A |
front 62 What are the common types of smectic liquid-crystalline
phases? | back 62 C |
front 63 ________ liquid crystals are colored because the molecular layers are
arranged in slightly twisted planes with respect to one
another. | back 63 B |
front 64 Molecules with ________ do not generally exhibit liquid-crystalline
properties because they lack the rigidity necessary for
alignment. | back 64 D |
front 65 For a given substance that exhibits liquid-crystalline properties,
the transition from solid to liquid-crystal state occurs
________. | back 65 B |
front 66 There are ________ types of smectic liquid-crystalline
phases. | back 66 D |
front 67 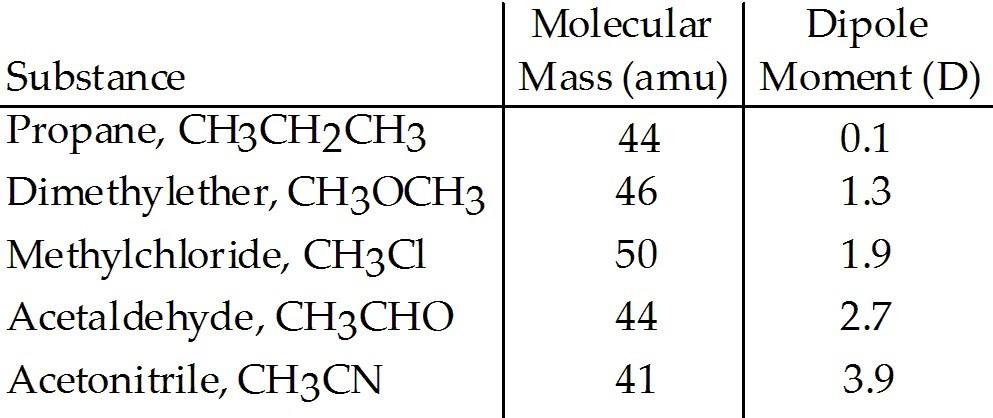 Based on molecular mass and dipole moment of the five compounds in the table below, which should have the highest boiling point? A) CH3CH2CH3 | back 67 E |
front 68 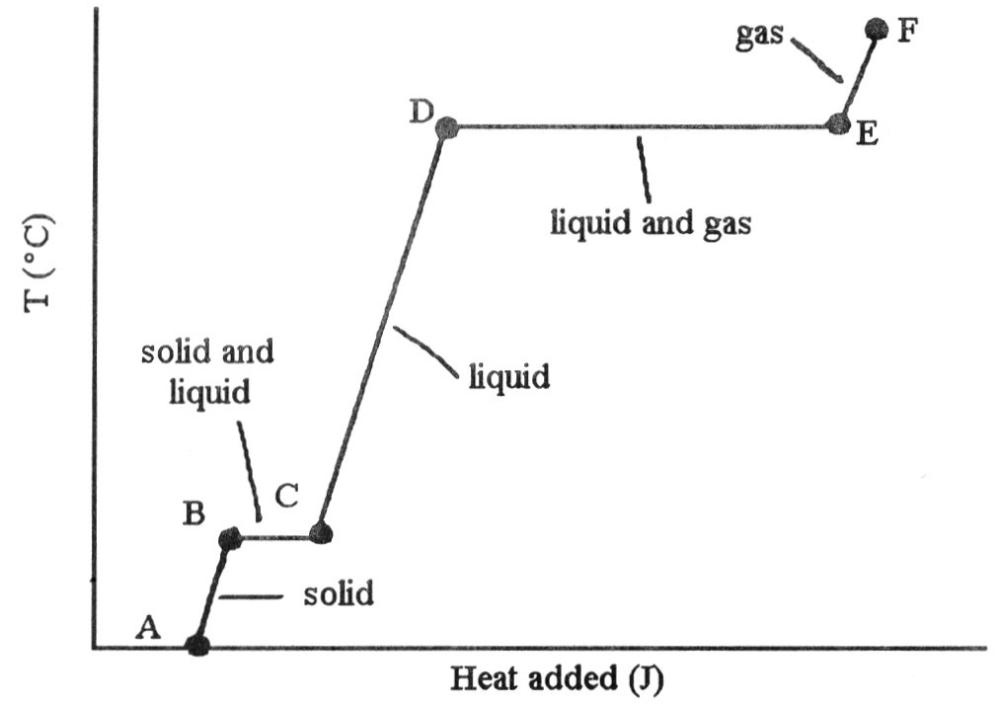 The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature for a solid as it was heated. The slope of the ________
segment corresponds to the heat capacity of the liquid of the
substance. | back 68 C |
front 69  The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature for a solid as it was heated. The slope of the ________
segment corresponds to the heat capacity of the solid. | back 69 A |
front 70  The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature for a solid as it was heated. The slope of the E-F segment
corresponds to the heat capacity of the ________. | back 70 C |
front 71  The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature of a solid as it was heated. The heat flow into the sample
in the segment D-E will yield the value of the ________ of this
substance. | back 71 B |
front 72  The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and
temperature of a solid as it was heated. The heat flow into the sample
in the segment ________ will yield the value of the ΔHfusion of this
substance. | back 72 B |
front 73 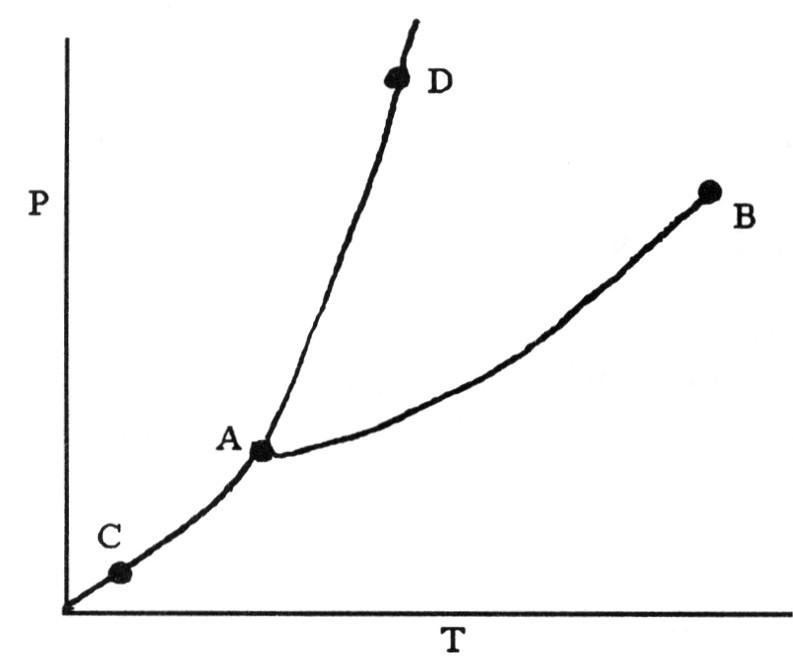 On the phase diagram shown above, segment ________ corresponds to the
conditions of temperature and pressure under which the solid and the
gas of the substance are in equilibrium. | back 73 B |
front 74  On the phase diagram shown above, the coordinates of point B
corresponds to the ________. | back 74 A |
front 75  On the phase diagram shown above, the coordinates of point ________
correspond to the triple point. | back 75 A |
front 76 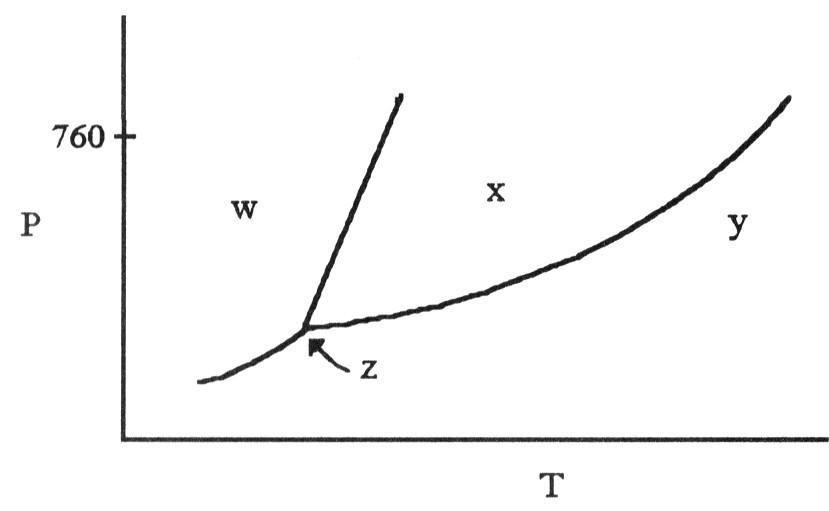 The phase diagram of a substance is given above. The region that
corresponds to the solid phase is ________. | back 76 A |
front 77 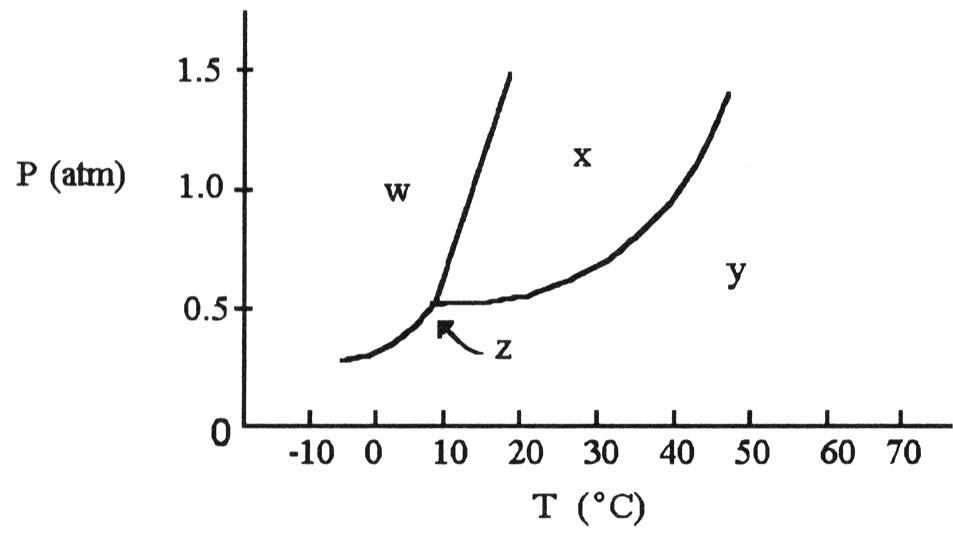 According to the phase diagram shown above, what is the normal
boiling point (°C)? | back 77 D |
front 78  According to the phase diagram shown above, what is the normal
melting point (°C)? | back 78 A |
front 79 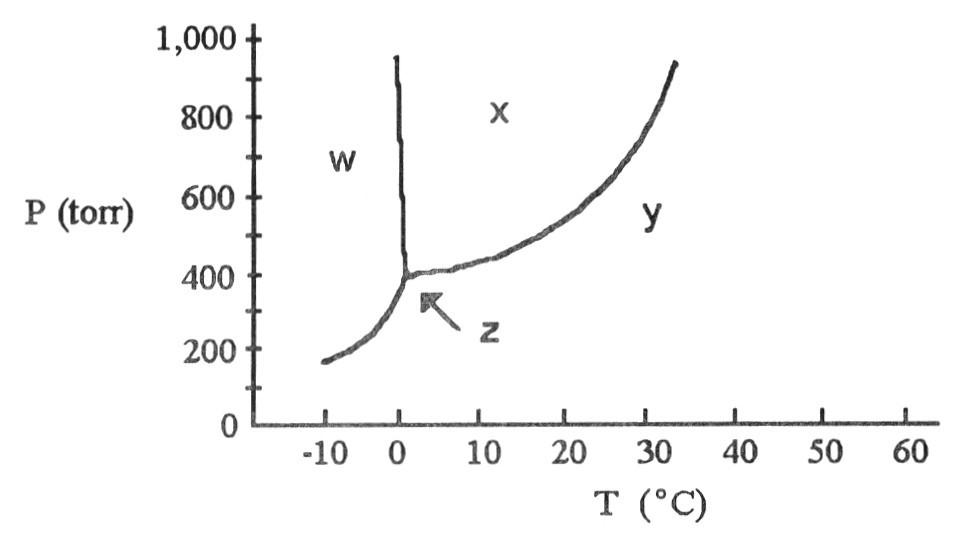 The phase diagram of a substance is shown above. The area labeled
________ indicates the gas phase for the substance. | back 79 C |
front 80  The phase diagram of a substance is shown above. The area labeled
________ indicates the solid phase for the substance. | back 80 A |
front 81  The phase diagram of a substance is shown above. The area labeled
________ indicates the liquid phase for the substance. | back 81 B |
front 82  According to the phase diagram shown above, what is the normal
boiling point (°C)? | back 82 D |
front 83  According to the phase diagram shown above, what is the normal
melting point (°C)? | back 83 B |
front 84 A ________ liquid crystal has the least order and is the most
liquid-like. | back 84 A |
front 85 ________ liquid crystals are colored and change color with
temperature changes. | back 85 C |
front 86 As a gaseous element condenses, the atoms become ________ and they
have ________ attraction for one another. | back 86 A |
front 87 What is the predominant intramolecular force in NaNO3? | back 87 A |
front 88 With what compound will NH3 experience only dispersion intermolecular
forces? | back 88 A |
front 89 With what compound will NH3 experience only ion-dipole intermolecular
forces? | back 89 A |
front 90 Which one of the following exhibits dipole-dipole attraction between
molecules? | back 90 A |
front 91 Which one of the following exhibits dipole-dipole attraction between
molecules? | back 91 A |
front 92 Of the following substances, only ________ has London dispersion
forces as its only intermolecular force. | back 92 A |
front 93 Which of the following has London dispersion forces as its only
intermolecular force? | back 93 C |
front 94 Which molecule has the lowest boiling point? | back 94 D |
front 95 Which one of the following should have the lowest boiling
point? | back 95 A |
front 96 Of the following substances, ________ has the highest boiling
point. | back 96 A |
front 97 Of the following substances, ________ has the highest boiling
point. | back 97 A |
front 98 Of the following substances, ________ has the highest boiling
point. | back 98 A |
front 99 Which one of the following derivatives of methane has the highest
boiling point? | back 99 A |
front 100 What is the predominant intermolecular force in CH4? | back 100 A |
front 101 What is the predominant intermolecular force in H2NNH2? | back 101 A |
front 102 What is the predominant intermolecular force in HCN? | back 102 A |
front 103 Ethanol melts at -114 °C and boils at 78 °C at a constant pressure of
1 atm. What state of matter must a sample of ethanol be in at 0°C and
1 atm? | back 103 A |
front 104 At 1 atm, an unknown sample melts at 49.9 °C and boils at 209.5 °C.
If the temperature is 0°C, what is the state of matter for the
sample? | back 104 D |
front 105 The enthalpy change for converting 1.00 mol of ice at -25.0 °C to
water at 50.0 °C is ________ kJ. The specific heats of ice, water, and
steam are 2.09 J/g-K, 4.18 J/g-K, and 1.84 J/g-K, respectively. For
H2O, ΔHfus = 6.01 kJ/mol, and ΔHvap = 40.67
kJ/mol. | back 105 C |
front 106 The enthalpy change for converting 10.0 g of ice at -50.0 °C to water
at 50.0 °C is ________ kJ. The specific heats of ice, water, and steam
are 2.09 J/g-K, 4.18 J/g-K, and 1.84 J/g-K, respectively. For H2O,
ΔHfus = 6.01 kJ/mol, and ΔHvap = 40.67
kJ/mol. | back 106 D |
front 107 The heat of fusion of water is 6.01 kJ/mol. The heat capacity of
liquid water is 75.3 J/mol ∙ K. The conversion of 50.0g of ice at 0.00
°C to liquid water at 0.00°C requires ________ kJ of heat. | back 107 B |
front 108 Calculate the enthalpy change (in kJ) associated with the conversion
of 25.0 grams of ice at -4.00 °C to water vapor at 109.0 °C. The
specific heats of ice, water, and steam are 2.09 J/g-K, 4.18 J/g-K,
and 1.84 J/g-K, respectively. For H2O, ΔHfus = 6.01 kJ/mol,
and ΔHvap = 40.67 kJ/mol. | back 108 B |
front 109 Ethanol ( OH) melts at -114 °C. The enthalpy of fusion is 5.02
kJ/mol. The specific heats of solid and liquid ethanol are 0.97 J/g-K
and 2.3 J/g-K, respectively. How much heat (kJ) is needed to convert
25.0 g of solid ethanol at -135 °C to liquid ethanol at -60
°C? | back 109 C |
front 110 Of the following, ________ is the most volatile. | back 110 A |
front 111 Which molecule is the least volatile? | back 111 B |
front 112 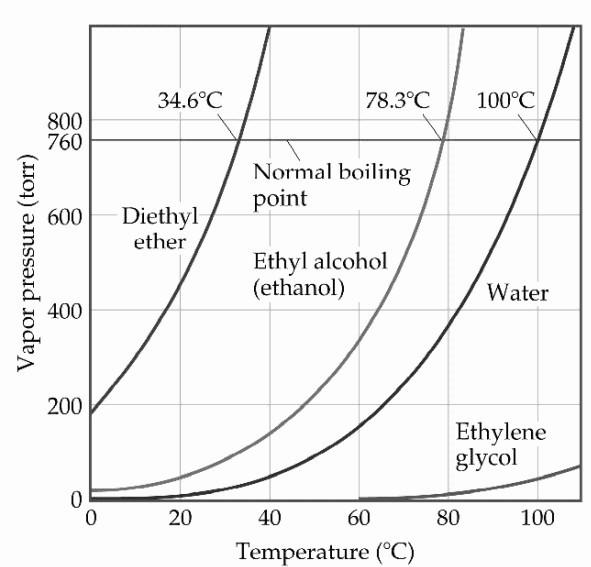 Based on the figure above, the boiling point of diethyl ether under
an external pressure of 0.605atm is ________ °C. | back 112 D |
front 113  Based on the figure above, the boiling point of diethyl ether under
an external pressure of 0.658atm is ________ °C. | back 113 E |
front 114 Based on the figure above, what is the boiling point (°C) of water
under an external pressure of 0.724atm. | back 114 D |
front 115 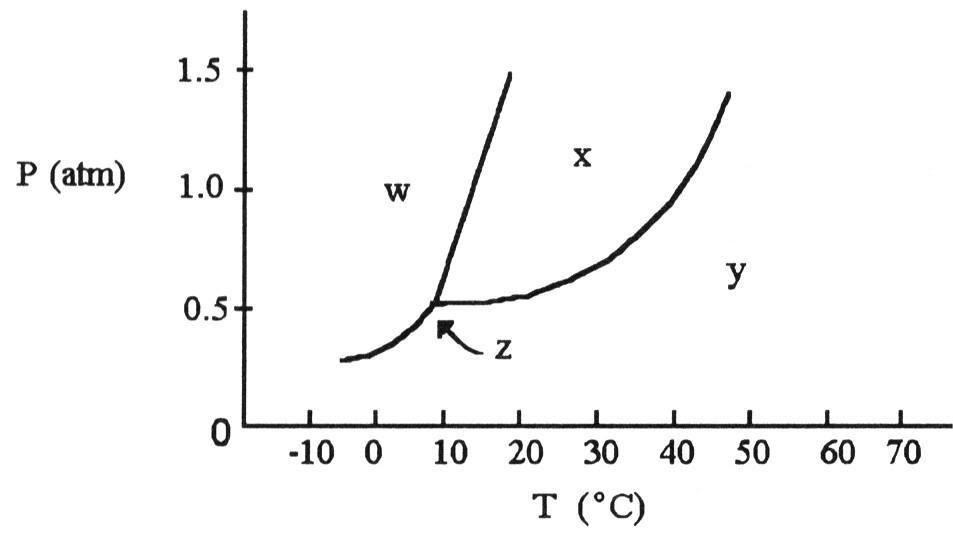 The phase diagram of a substance is given above. This substance is a
________ at 30 °C and 0.5 atm. | back 115 B |
front 116 In general, intramolecular forces determine the ________ properties of a substance and intermolecular forces determine its ________ properties. | back 116 chemical, physical |
front 117 London Dispersion Forces tend to ________ in strength with increasing molecular weight. | back 117 increase |
front 118 The conversion of a solid to a liquid is called ________. | back 118 melting |
front 119 The initial discovery of a liquid crystal resulted from studies of a ________ derivative. | back 119 cholesterol |
front 120 The principal source of the difference in the normal boiling points of ICl (97 °C; molecular mass 162 amu) and Br2 (59 °C; molecular mass 160 amu) is both dipole-dipole interactions and London dispersion forces. | back 120 false |
front 121 The boiling points of normal hydrocarbons are higher than those of branched hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight because the London-dispersion forces between normal hydrocarbons are greater than those between branched hydrocarbons. | back 121 true |
front 122 Heats of vaporization are greater than heats of fusion. | back 122 true |
front 123 Under ordinary conditions, a substance will sublime rather than melt if its triple point occurs at a pressure above atmospheric pressure. | back 123 true |
front 124 Molecules containing many double bonds do not exhibit liquid-crystal behavior because free rotation can occur only around single bonds making these molecules rigid. | back 124 false |