Bitter taste is elicited by ________.
alkaloids
Which of the following is true about gustatory receptors?
Complete adaptation occurs in about one to five minutes.
The blind spot of the eye is where ________.
the optic nerve leaves the eye
Which of the follow types of neurons are replaced throughout adult life?
olfactory receptor cells
The first "way station" in the visual pathway from the eye, after there has been partialcrossover of the fibers in the optic chiasma, is the ________.
lateral geniculate body of the thalamus
Seventy percent of all sensory receptors are located in the ________.
eye
Dark adaptation ________.
involves accumulation of rhodopsin
What prevents the eyelids from sticking together when the eyes close?
tarsal gland secretions
Select the correct statement about olfaction.
Some of the sensation of olfaction is actually one of pain.
Taste buds are not found ________.
in filiform papillae
Damage to the medial rectus muscles would probably affect ________.
convergence
An essential part of the maculae involved in static equilibrium is (are) the ________.
otoliths
Which pairing of terms is incorrectly related?
frequency of sound waves: loudness of the sound
The first vestiges of eyes in the embryo are called ________.
optic vesicles
The tarsal plate of the eyelid ________.
is connected to the levator palpebrae
The receptor membranes of gustatory cells are ________.
gustatory hairs
The eye muscle that elevates and turns the eye laterally is the ________.
inferior oblique
Which of the following taste sensations is incorrectly matched to the chemicals that produce it?
umamitriglycerides and fatty acids
Which of the following is not a characteristic of olfactory receptor cells?
They are unipolar neurons.
Which of the following is true about photoreceptors?
Rods absorb light throughout the visual spectrum but confer only gray tone vision.
As sound levels increase in the spiral organ (of Corti), ________.
outer hair cells stiffen the basilar membrane
Information from balance receptors goes directly to the ________.
brain stem reflex centers
Most newborns ________.
often use only one eye at a time
Which statement about malnutrition-induced night blindness is most accurate?
Vitamin supplements can reverse degenerative changes.
What is the main function of the rods in the eye?
vision in dim light
Tinnitus, vertigo, and gradual hearing loss typify the disorder called ________.
Ménière's syndrome
There are three layers of neurons in the retina. The axons of which of these neuron layers form the optic nerves?
ganglion cells
Select the correct statement about equilibrium.
Cristae respond to angular acceleration and deceleration.
Visual processing in the thalamus does not contribute significantly to ________.
night vision
What is a modiolus?
a bone pillar in the center of the cochlea
Visual inputs to the ________ serve to synchronize biorhythms with natural light and dark.
suprachiasmatic nucleus
The only special sense not fully functional at birth is the sense of ________.
vision
Light passes through the following structures in which order?
cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor
The oval window is connected directly to which passageway?
scala vestibuli
Which statement about sound localization is not true?
It requires processing at the cortical level.
Farsightedness is more properly called __________.
hyperopia
Conscious perception of vision probably reflects activity in the ____________.
occipital lobe of the cortex
Visible light fits between ____________.
UV and infrared
Which of the following is not a possible cause of conduction deafness?
cochlear nerve degeneration
Olfactory cells and taste buds are normally stimulated by ______________.
substances in solution
Nerve fibers from the medial aspect of each eye ____________.
cross over to the opposite side at the chiasma
The receptor for static equilibrium is the ___________.
macula
The cells of the retina in which action potentials are generated are the ____________.
ganglion cells
Which of the following structures is not part of the eternal ear?
pharyngotympanic tube
Ceruminous glands are _________.
modified apocrine sweat glands
Ordinarily, it is not possible to transplant tissues from one person to another, yet corneas can be transplanted without tissue rejection. This is because the cornea:
Has no blood supply
Receptors for hearing are located in the __________.
Cochlea
Another name for the primary visual cortex is ___________.
Striate cortex
In the visual pathways to the brain, the optic radiations project to the _____________.
Primary visual cortex
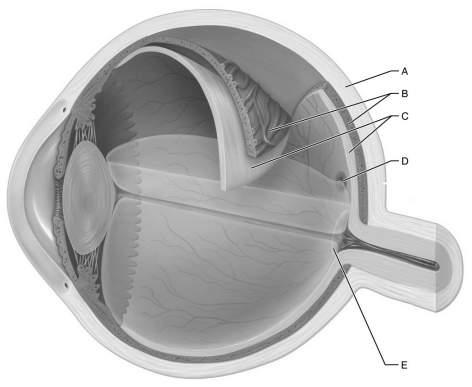
Consists of a pigmented layer and a neural layer.
C

Fluid blockages cause glaucoma.
D

The only tissue in the body that can be transplanted from one person to another with little or no rejection.
B

Blood vessels supply nutrition to all eye layers.
B

Lacks photoreceptors; where optic nerve exits the eye.
E

Acts as a reflexively activated diaphragm to vary pupil size.
C

Holds the retina firmly against the pigmented layer.
E

Contains only cones; provides detailed colored vision.
D

Controls lens shape.
A
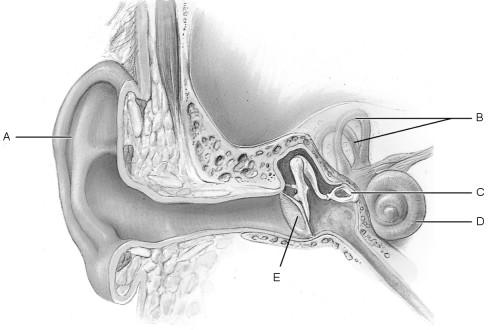
Tympanic membrane.
E

Houses organ of Corti.
D

Cochlea.
D

Semicircular canals.
B

Pinna.
A

Balance organ.
B
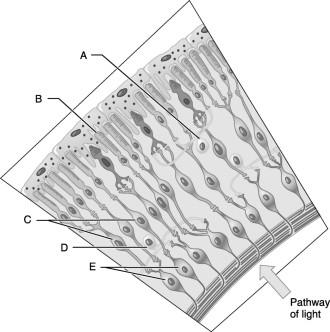
Horizontal cell.
A

Ganglion cells.
E

Amacrine cell.
D

Bipolar cells.
C