The Urinary System
Which is not a major function of the kidney?
- regulation of blood ionic composition
- regulation of blood cell size
- regulation of blood volume
- regulation of blood pressure
- regulation of blood pH
B
This is the formation of a new glucose molecule.
- glycolysis
- gluconeogenesis
- glucosamine
- glucose
- calcitriol
B
Which of the following is a waste product normally excreted by the kidneys?
- urea
- glucose
- insulin
- cholesterol
- carbon dioxide
A
This is smooth dense irregular connective tissue that is continuous with the outer coat of the ureter.
- adipose capsule
- renal capsule
- renal hilus
- renal cortex
- renal medulla
B
The portion of the kidney that extends between the renal pyramids is called the
- renal columns
- renal medulla
- renal pelvis
- calyces
- renal papilla
A
Which is the correct order of blood flow?
- renal artery-segmental artery-interlobular artery-peritubular capillaries- afferent arterioles
- interlobar arteries-arcuate arteries-glomerular capillaries-arcuate veins
- arcuate veins-arcuate arteries- glomerular capillaries- renal vein
- renal vein-segmental arteries-interlobar arteries- efferent arterioles
- interlobar veins- afferent arterioles- efferent arterioles- glomerular capillaries
B
Which is the correct order of filtrate flow?
- glomerular capsule, Proximal Convoluted tubule (PCT), Loop of Henle, Distal Convoluted tubule (DCT), Collecting duct
- Loop of Henle, glomerular capsule, PCT, DCT, Collecting duct
- Ascending limb of Loop, PCT, DCT, Collecting duct
- Collecting duct, DCT, PCT, Collecting duct, glomerular capsule
- PCT, glomerular capsule, DCT, Collecting duct, Loop of Henle
A
Which structure of the nephron reabsorbs the most substances?
- glomerular capsule
- Loop of Henle
- Ascending limb
- Collecting duct
- Proximal convoluted tubule
E
This is the structure of the nephron that filters blood.
- glomerular capsule
- Loop of Henle
- Ascending limb
- Collecting duct
- Renal corpuscle
A
This term means the return of substances into the blood stream from the filtrate.
- reabsorption
- filtration
- secretion
- excretion
- none of the above
A
This is a nephron process that results in a substance in blood entering the already formed filtrate.
- reabsorption
- filtration
- secretion
- excretion
- none of the above
C
This layer of filtration membrane is composed of collagen fibers and proteoglycans in a glycoprotein matrix.
- glomerular endothelial cells
- basal lamina
- pedicels
- filtration slites
- slit membrane
B
This occurs when stretching triggers contraction of smooth muscle walls in afferent arterioles.
- glomerular filtration rate
- tubulomerular feedback
- myogenic mechanism
- renal autoregulation
- capsular hydrostatic pressure
C
This occurs when a substance passes from the fluid in the tubular lumen through the apical membrane, across the cytosol, and then into the interstitial fluid.
- paracellular reabsoprtion
- transcellular reabsoprtion
- apical reasborption
- basolateral reabsorption
- active transport
B
Once fluid enters the proximal convoluted tubule
- it is less dense
- it has a higher K+ concentration
- it is called tubular fluid
- all the Na+ is removed
- it is headed to the ascending loop
C
The proximal convoluted tubules reabsorb what percentage of filtered water?
- 25%
- 50%
- 65%
- 80%
- 99%
C
Which of the following is NOT a way angiotensin II affects the kidneys?
- It increases GFR
- It can decrease GFR
- It enhances reabsorption of certain ions
- It stimulates the release of aldosterone
- None of the above
A
Urea recycling can cause a buildup of urea in the
- Renal capsule
- Loop of Henle
- Ascending tubule
- Renal medulla
- Renal pelvis
D
Increased secretion of Hydrogen ions would result in a ______________ of blood ____________?
- increase, pressure
- decrease, volume
- increase, sodium levels
- decrease, pH
- increase, urea
D
Increased secretion of Aldosterone would result in a ______________ of blood ____________?
- increase, potassium
- decrease, volume
- increase, calcium levels
- decrease, pH
- increase, sodium
E
The ascending loop of Henle is impermeable to
- urea
- water
- albumin
- sodium
- chloride
B
An analysis of the physical, chemical and microscopic properties of urine is called
- Urinalysis
- Filtration study
- Concentration study
- Diuretic
- Osmolarity
A
Water accounts for what percentage of the total volume of urine?
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 80%
- 95%
E
This is a test to measure kidney function.
- Plasma creatinine
- Renal study
- Kidney assay
- Renal clearance
- Hilus study
A
This transports urine from the kidney to the bladder.
- Urethra
- Ureter
- Descending loop of Henle
- Renal hilus
- None of the above
B
This layer of the ureter is composed of connective tissue, elastic and collagen fibers.
- Mucosa
- Transitional epithelium
- Lamina propria
- Adventitia
- Lamina elastica
C
This lies in the anterior cornea of the trigone of the bladder.
- Urethral sphincter
- Adventitia bundle
- Ureter
- Internal urethral orifice
- Muscularis bundle
D
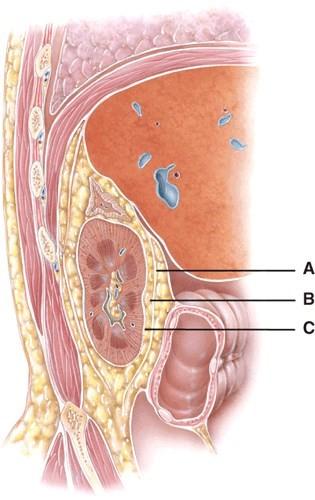
This is composed of dense irregular tissue that runs continuous with the ureter.
- A
- B
- C
C

This layers main function is to protect the kidney from trauma and hold it in place within the abdominal cavity.
- A
- B
- C
B

This layer runs deep to the peritoneum on the anterior surface of the kidneys.
- A
- B
- C
A
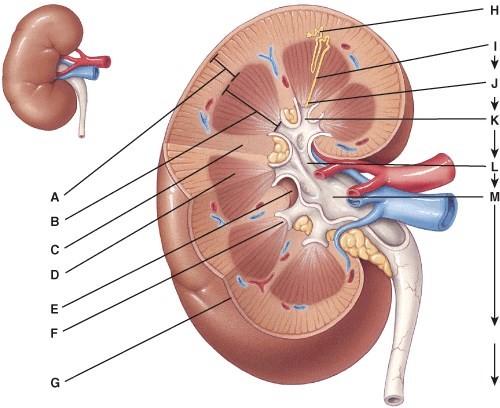
This can be divided into the cortical zone and the juxtamedullary zone.
- A
- D
- E
- F
- G
A

Where is the parenchyma?
- B
- M
- C
- D
- F
C

Each kidney can have anywhere from 8 to 18 of these.
- I
- J
- K
- L
- H
C

This structure is the apex of a renal pyramid.
- F
- D
- G
- K
- L
A

This is where the hilum extends into the kidney.
- E
- D
- G
- K
- L
A

Urine formed by the nephrons first drains into these.
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
B
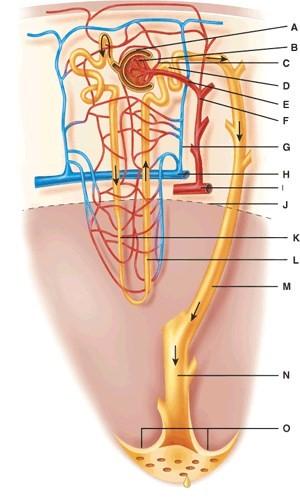
What two structures comprise the renal corpuscle?
- A and B
- C and D
- E and F
- K and L
- N and O
A

Where is the distal convoluted tubule?
- D
- E
- J
- K
- L
A

Where is the arcuate vein?
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
D

Where is the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle?
- C
- D
- J
- K
- L
E

Where is the corticomedullary junction?
- G
- J
- M
- N
- O
B

Where is the papillary duct?
- C
- F
- H
- N
- O
D

What does line “M” point to?
- Arcuate artery
- Arcuate vein
- Collecting duct
- Descending loop
- Efferent arteriole
C

What is line “C” pointing to?
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Interlobular artery
- Efferent arteriole
- Arcuate artery
- Corticomedullary junction
C
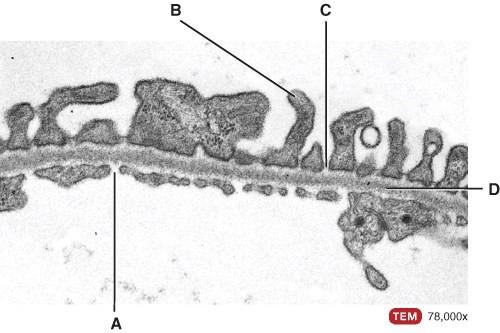
What is line “A” pointing to?
- Fenestrations
- Pedicels
- Filtration slit
- Basal lamina
- Lumen of the glomerulus
A

What is line “B” pointing to?
- Fenestrations
- Pedicels
- Filtration slit
- Basal lamina
- Lumen of the glomerulus
B

What is line “C” pointing to?
- Fenestrations
- Pedicels
- Filtration slit
- Basal lamina
- Lumen of the glomerulus
C

What is line “D” pointing to?
- Fenestrations
- Pedicels
- Filtration slit
- Basal lamina
- Lumen of the glomerulus
D
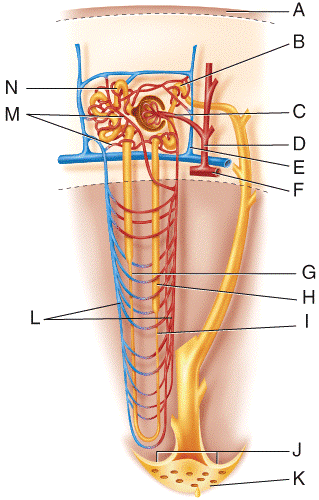
Fluid flowing from point N in the figure will go to which structure next?
- G
- H
- C
- B
- K
A

Fluid flowing from point G in the figure will go to which structure next?
- N
- H
- I
- M
- K
C

Fluid flowing from point H in the figure will go to which structure next?
- L
- B
- I
- G
- N
B

Fluid flowing from point B in the figure will go to which of the following structures?
- J
- M
- I
- G
- H
A

Which vessel in the diagram is the afferent arteriole?
- C
- D
- E
- F
- L
A

Which vessel in the diagram is the interlobular vein?
- C
- D
- E
- F
- L
C

Which vessel(s) in the diagram are the vasa recta?
- C
- D
- E
- M
- L
E

Which vessel in the diagram is the interlobular artery?
- D
- E
- F
- L
A

Which vessel in the diagram is the arcuate artery?
- C
- D
- E
- F
- L
D

Which vessel(s) in the diagram are the peritubular capillaries?
- C
- D
- E
- M
- L
D
An increase in permeability of the filtration membrane due to disease, injury, or irritation of kidney cells by substances such as bacterial toxins, ether, or heavy metals indicates which condition?
- albuminuria
- lucosuria
- robilinogenuria
- ketonuria
- bilirubinuria
A
Anorexia, starvation, or a diet too low in carbohydrates indicates which condition?
- albuminuria
- glucosuria
- urobilinogenuria
- ketonuria
- bilirubinuria
D
Stress, causing excessive amounts of epinephrine secretion which stimulates glycogen breakdown, indicates which condition? This condition can also indicate diabetes mellitus.
- albuminuria
- glucosuria
- urobilinogenuria
- hematuria
- bilirubinuria
B
Excessive urine concentration of a normal breakdown product of hemoglobin, caused by pernicious anemia, infectious hepatitis, jaundice or cirrhosis, indicates which condition?
- albuminuria
- glucosuria
- urobilinogenuria
- hematuria
- bilirubinuria
C
This substance gives bile its major pigmentation:
- ketone bodies
- erythrocytes
- casts
- bilirubin
- glucose
D
These are tiny masses of material, hardened in the lumen of the urinary tubule and are flushed out when filtrate builds up behind them:
- ketone bodies
- erythrocytes
- casts
- microbes
- urobilinogen
C
Candida albicans and E. coli are which type of abnormal constituent of urine:
- ketone bodies
- erythrocytes
- casts
- microbes
- urobilinogen
D
Which is the normal pH range of urine in humans?
- 8.1 – 10.6
- 4.6 – 8.0
- 1.0 – 3.0
- 3.1 – 4.0
- 10.0 – 12.0
B
What is the normal volume of urine produced in humans?
- 1L / hr
- 2L / day
- 2L / hr
- 3L / week
- 10L / 24 hours
B
What is the normal specific gravity range of urine in humans?
- 2.350 – 3.700
- 0.002 – 1.000
- 4.6 – 8.0
- 1.001 – 1.035
- 1.04 – 2.60
D
This hormone is released when the blood volume increases.
- Parathyroid Hormone
- Renin
- ADH
- Atrial Natriuretic Peptide
- Aldosterone
D
Consumption of salty food will cause an increase in this hormone.
- Aldosterone
- Renin
- ANH
- Angiotensin-II
- ADH
E
Absence of angiotensin converting enzyme will lead to
- decreased blood pressure
- increased blood pressure
- will not have any effect on blood pressure
- All of these choices
- None of these choices
A