Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
The Urinary System
front 1 Which is not a major function of the kidney?
| back 1 B |
front 2 This is the formation of a new glucose molecule.
| back 2 B |
front 3 Which of the following is a waste product normally excreted by the kidneys?
| back 3 A |
front 4 This is smooth dense irregular connective tissue that is continuous with the outer coat of the ureter.
| back 4 B |
front 5 The portion of the kidney that extends between the renal pyramids is called the
| back 5 A |
front 6 Which is the correct order of blood flow?
| back 6 B |
front 7 Which is the correct order of filtrate flow?
| back 7 A |
front 8 Which structure of the nephron reabsorbs the most substances?
| back 8 E |
front 9 This is the structure of the nephron that filters blood.
| back 9 A |
front 10 This term means the return of substances into the blood stream from the filtrate.
| back 10 A |
front 11 This is a nephron process that results in a substance in blood entering the already formed filtrate.
| back 11 C |
front 12 This layer of filtration membrane is composed of collagen fibers and proteoglycans in a glycoprotein matrix.
| back 12 B |
front 13 This occurs when stretching triggers contraction of smooth muscle walls in afferent arterioles.
| back 13 C |
front 14 This occurs when a substance passes from the fluid in the tubular lumen through the apical membrane, across the cytosol, and then into the interstitial fluid.
| back 14 B |
front 15 Once fluid enters the proximal convoluted tubule
| back 15 C |
front 16 The proximal convoluted tubules reabsorb what percentage of filtered water?
| back 16 C |
front 17 Which of the following is NOT a way angiotensin II affects the kidneys?
| back 17 A |
front 18 Urea recycling can cause a buildup of urea in the
| back 18 D |
front 19 Increased secretion of Hydrogen ions would result in a ______________ of blood ____________?
| back 19 D |
front 20 Increased secretion of Aldosterone would result in a ______________ of blood ____________?
| back 20 E |
front 21 The ascending loop of Henle is impermeable to
| back 21 B |
front 22 An analysis of the physical, chemical and microscopic properties of urine is called
| back 22 A |
front 23 Water accounts for what percentage of the total volume of urine?
| back 23 E |
front 24 This is a test to measure kidney function.
| back 24 A |
front 25 This transports urine from the kidney to the bladder.
| back 25 B |
front 26 This layer of the ureter is composed of connective tissue, elastic and collagen fibers.
| back 26 C |
front 27 This lies in the anterior cornea of the trigone of the bladder.
| back 27 D |
front 28 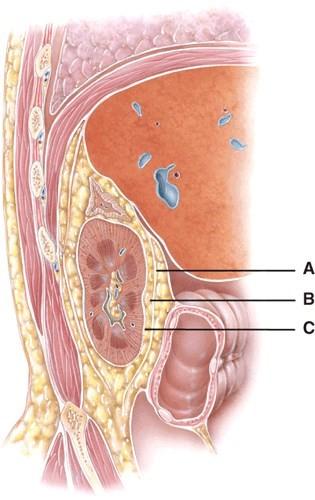 This is composed of dense irregular tissue that runs continuous with the ureter.
| back 28 C |
front 29  This layers main function is to protect the kidney from trauma and hold it in place within the abdominal cavity.
| back 29 B |
front 30  This layer runs deep to the peritoneum on the anterior surface of the kidneys.
| back 30 A |
front 31 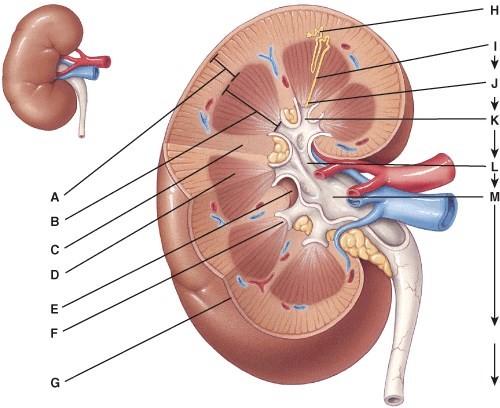 This can be divided into the cortical zone and the juxtamedullary zone.
| back 31 A |
front 32  Where is the parenchyma?
| back 32 C |
front 33  Each kidney can have anywhere from 8 to 18 of these.
| back 33 C |
front 34  This structure is the apex of a renal pyramid.
| back 34 A |
front 35  This is where the hilum extends into the kidney.
| back 35 A |
front 36  Urine formed by the nephrons first drains into these.
| back 36 B |
front 37 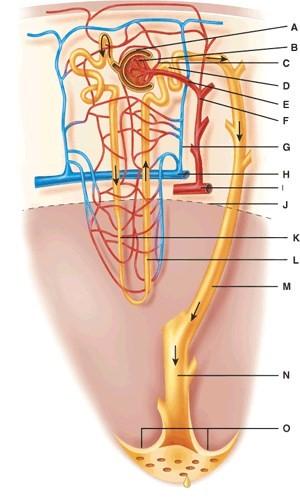 What two structures comprise the renal corpuscle?
| back 37 A |
front 38  Where is the distal convoluted tubule?
| back 38 A |
front 39  Where is the arcuate vein?
| back 39 D |
front 40  Where is the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle?
| back 40 E |
front 41  Where is the corticomedullary junction?
| back 41 B |
front 42  Where is the papillary duct?
| back 42 D |
front 43  What does line “M” point to?
| back 43 C |
front 44  What is line “C” pointing to?
| back 44 C |
front 45 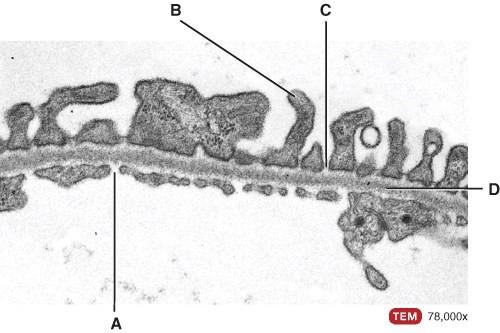 What is line “A” pointing to?
| back 45 A |
front 46  What is line “B” pointing to?
| back 46 B |
front 47  What is line “C” pointing to?
| back 47 C |
front 48  What is line “D” pointing to?
| back 48 D |
front 49 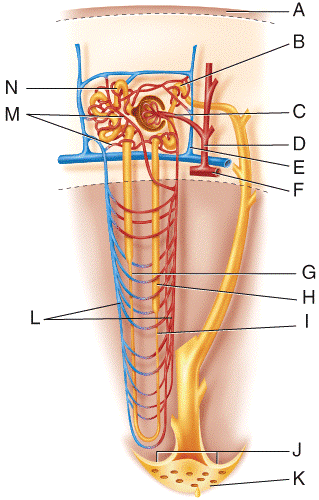 Fluid flowing from point N in the figure will go to which structure next?
| back 49 A |
front 50  Fluid flowing from point G in the figure will go to which structure next?
| back 50 C |
front 51  Fluid flowing from point H in the figure will go to which structure next?
| back 51 B |
front 52  Fluid flowing from point B in the figure will go to which of the following structures?
| back 52 A |
front 53  Which vessel in the diagram is the afferent arteriole?
| back 53 A |
front 54  Which vessel in the diagram is the interlobular vein?
| back 54 C |
front 55  Which vessel(s) in the diagram are the vasa recta?
| back 55 E |
front 56  Which vessel in the diagram is the interlobular artery?
| back 56 A |
front 57  Which vessel in the diagram is the arcuate artery?
| back 57 D |
front 58  Which vessel(s) in the diagram are the peritubular capillaries?
| back 58 D |
front 59 An increase in permeability of the filtration membrane due to disease, injury, or irritation of kidney cells by substances such as bacterial toxins, ether, or heavy metals indicates which condition?
| back 59 A |
front 60 Anorexia, starvation, or a diet too low in carbohydrates indicates which condition?
| back 60 D |
front 61 Stress, causing excessive amounts of epinephrine secretion which stimulates glycogen breakdown, indicates which condition? This condition can also indicate diabetes mellitus.
| back 61 B |
front 62 Excessive urine concentration of a normal breakdown product of hemoglobin, caused by pernicious anemia, infectious hepatitis, jaundice or cirrhosis, indicates which condition?
| back 62 C |
front 63 This substance gives bile its major pigmentation:
| back 63 D |
front 64 These are tiny masses of material, hardened in the lumen of the urinary tubule and are flushed out when filtrate builds up behind them:
| back 64 C |
front 65 Candida albicans and E. coli are which type of abnormal constituent of urine:
| back 65 D |
front 66 Which is the normal pH range of urine in humans?
| back 66 B |
front 67 What is the normal volume of urine produced in humans?
| back 67 B |
front 68 What is the normal specific gravity range of urine in humans?
| back 68 D |
front 69 This hormone is released when the blood volume increases.
| back 69 D |
front 70 Consumption of salty food will cause an increase in this hormone.
| back 70 E |
front 71 Absence of angiotensin converting enzyme will lead to
| back 71 A |