Endocrine system
Classify the types of glands
Exocrine: produce sweat and saliva, etc. and have ducts
Endocrine: produce hormones and are ductless. They release their hormones directly into capillaries to be carried all over the body
What is the secretion of endocrine glands called
hormones
List some of the endocrine glands
Thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary, adrenal, pineal, thymus
Chemicals that exerts their effect on the same cells that secrete them are?
autocrines
write the chemical classification of hormones
amino acid based and steroids
List the changes produced by the hormones in the target cells
-alters plasma membrane permeability or membrane potential by opening or closing ion channels
-stimulates synthesis of proteins or enzymes within the cell
- activates or deactivates enzymes
- induces secretory activity
-stimulates mitosis
List the mechanism of hormone action
-cAMP signaling mechanism
-PIP- calcium signal mechanism
- Steroid hormones-direct gene activation
The target cells respond to a hormone only due to the presence of specific
protein receptors
List the factors involved in the activation of hormone receptor complex
- Blood levels of the hormone
- Relative number of receptors for that hormone on or in the target cells
- Affinity of the bond between the hormone and the receptor
Rising level of specific hormone acting on specific type of cell increases the production of the specific receptors in that cell is the phenomenon as
up-regulation
The concentration of hormone at any time in the blood reflects
- its rate of release
- the speed at which it is inactivated and removed from the body
List the ways hormones interact with each other
- Permissiveness
-synergism
- antagonism
Hormones producing amplified effects when working together on a target cell is what type of hormonal interaction
synergism
What are the three major types of endocrine gland stimuli
hormonal
humoral
neural
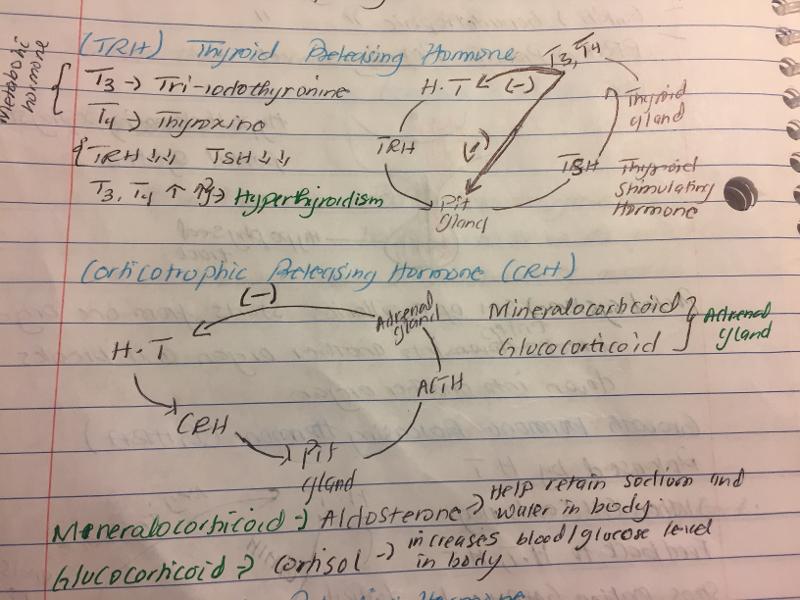
List the hormones released by the anterior pituitary gland
Growth Hormone
thyroid stimulating hormone
adrenocorticotropic hormone
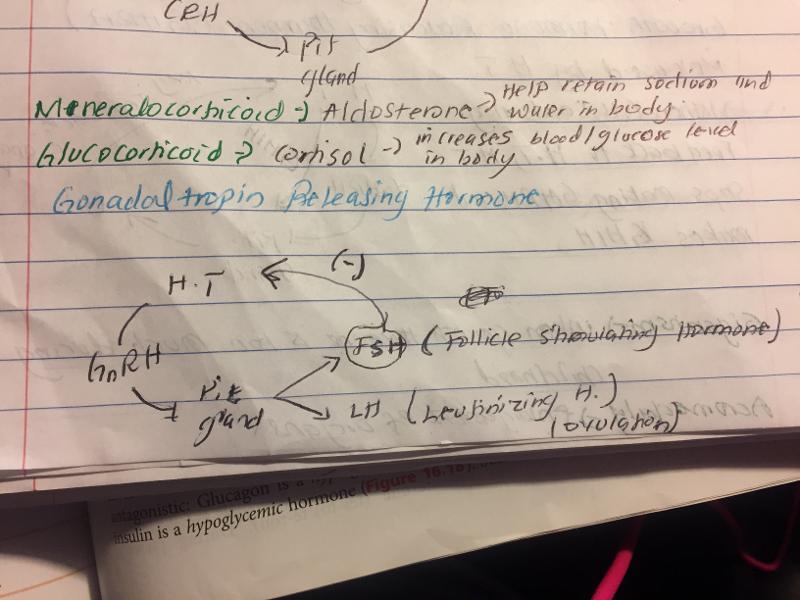
follicle stimulating hormone
Luteinizing hormone
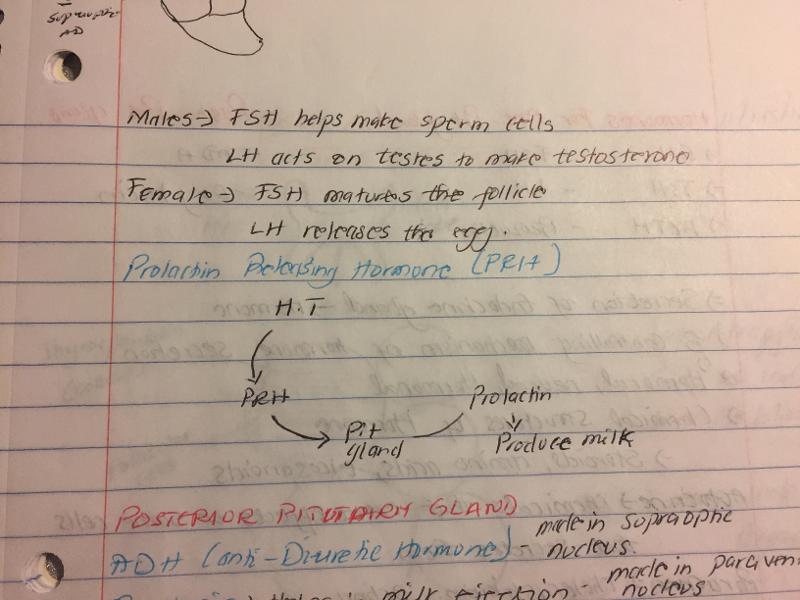
Prolactin
List the hormones of posterior pituitary gland
Antidiuretic hormone
oxytocin
Function of ADH
made in supraoptic nucleus.
prevents urine formation.
prevents wide swings in water balance, helping the body avoid dehydration and water balance
Function of oxytocin
released in higher amounts during childbirth and in nursing women
acts as a hormonal trigger for milk ejection
Function of Growth Hormone (somatrotopin cells)
increases blood levels of fatty acids
decreases rate of glucose uptake and metabolism
encourages glycogen breakdown in liver
stimulates most body cells to enlarge and divide.
Function of thyroid hormone (thyrotropin cells)
increases basal metabolic rate and body heat production
regulates tissue growth and development
maintains blood pressure by increasing the number of adrenergic receptors in blood vessels
disorders associated with growth hormone
dwarfism, gigantism, and acromegaly
disorders associated with thyroid hormone
myxedema, goiter, grave's disease
Growth hormone releasing hormone

hypercortisolism
A syndrome caused by an increased production of ACTH
excessive intake of glucocorticoids
corticotrophic releasing hormone
Gonadaltropin releasing hormone (FSH and LH)
Prolactin releasing hormone
supraoptic nucleus of hypothalamus release____ hormone, and paraventricular nucleus in hypothalamus secretes____ hormone
ADH; oxytocin
A set of capillaries arising in the hypothalamus forming a vein which enters into the pituitary gland and breaks down into another set of capillaries, this system is called ___
hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system
catabolic hormone
Adrenaline, cortisol, and glucagon
anabolic hormone
stimulate protein synthesis, muscle growth, and insulin.
ex. growth hormone, testosterone and estrogen
diabetogenic hormone
ADH deficiency ( diabetes insipidus)
insulin dificiency (diabetes mellitus)
Marked retention of fluid, edema, weight gain, and hypo-osmolarity of the blood due to excessive secretion of ADH is a syndrome called
syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion
deficiency of iodine will cause which hormone deficiency condition
goiter
deficiency of thyroxine since birth will cause mental retardation and the condition is called
cretinism
which of the following is not a category of endocrine gland stimulus
enzyme
oxytocin
is an example of positive feedback control mechanism during labor
stimulated by suckling of infant at breast and labor
inhibited by lack of appropriate neural stimuli
ADH
is inhibited by alcohol and hydrationn
stimulated by pain, some drugs, low blood pressure
The ability of a specific tissue or organ to respond to the presence of a hormone is dependent on
the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ
a patient with normal kidney function test came with polyuria and polydipsia complains and you identified the low urine osmolality and no blood or pus in the urine. The most probable diagnosis is
pituitary diabetes insipidus
Insulin, a small protein, is released in response to
when the body's glucose level rises
insulin, a small protein, is synthesized by
beta cells of pancreas
Hormone that regulates the blood calcium level by enhancing the reabsorption of calcium from the gut, kidney, and bones by increasing the osteoclast activity is
parathyroid hormone
Growth hormones act via
somatomeidin
Which of the following is sometimes used as a second messenger of amino acid-base hormones?
calcium
in the event of prolonged fasting the blood sugar can be maintained by increased release of which of the following hormones causing glycogenolysis from the liver and gluconeogenesis
glucagon
suckling stimulates the release of which hormone that encourages the continued milk production
prolactin releasing hormone
from where is PRH and PIH released
hypothalamus
Which neurotransmitter is now recognized as prolactin and inhibitor
dopamine
The hormone responsible for setting basal metabolic rate is
thyroid hormones
the terminology for posterior pituitary gland is
neurohypophysis
leukotrienes and prostaglandins are classified as
eicosanoids
define half life
it is the duration from the time of release of a hormone to the time when its concentration is reduce by 50%
superior thyroid artery is a branch of internal carotid artery
false
locally acting chemicals that affect cells other than those that secrete them is classified as paracrines
true
eicosanoids, which inhibits the production of blood clots are called prostaglandin PGE2
false
corticotrophic releasing hormone is released from the hypothalamus
true
one hormone cannot exert its effect without another hormone being present is antagonism
false
superior thyroid artery is a branch of
external carotid artery
Name the structures present in spermatic cord
nerve fibers, blood vessels, and lymphatic
Which of the following statements is applicable to antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
is released by neurohypophysis
Which of the following is true of neurohypophysis
it is only a hormone storage area that receives hormones from the hypothalamus for release
In the event of a high blood sugar level, the increased release of which of the following hormones is anticipated
glucagon
ACTH
is secreted by corticotropic cells
stimulates adrenal cortex to release corticosteroid hormones.
its release is elicited by hypothalamic CRH.
Which of the following is true about calcium homeostasis
high calcium levels cause bone resorption
Which of the following statement is true for aldosterone
production is greatly influenced by rennin angiotensin system activation
an infant born with ambiguous genitalia is most likely to have which of the following condition in the blood
high androgen
which of the following does not stimulate endocrine glands
enzyme
addison's disease
over secretion of cortisol
increase in ACTH
gigantism
over secretion of hormone from pituitary somatotrophs
pheochromocytoma
hypoadrenalism
diabetes insipidus
deficiency of ADH
cushing's disease
malignant hypertension
supraoptic nucleus
antidiuretic hormone
paraventricular nucleus
oxytocin
oral mucosa
adenohypophysis
hypercortisolism
A syndrome caused by an increased production of ACTH from a tumor of the adrenal cortex or of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, or by excessive intake of glucocorticoids
diabetes mellitus
results from either hyposecretion or hypoactivity of insulin
type I diabetes mellitus
absent of insulin
type II diabetes mellitus
insulin is present but effects are deficient
hyperadrenalism
marked by the presence of high cortisol levels in the blood
hyperthyroidism
Grave's disease
overactivity of the thyroid gland, resulting in a rapid heartbeat and an increased rate of metabolism
hypothyroidism
cretinism in infants when it is due to iodine deficiency and congenital hypothyroidism when it's due to congenital abnormality of the thyroid gland.
hyperparathyroidism
excessive calcium
kidney stones and arteriosclerosis
excess PTH
hypoparathyroidism
tripod sign. diminishing concentration of parathyroid hormone in the blood
PTH deficiency
autocrines
chemicals that exerts their effect on the same cells that secrete them
paracrines
acts within the same tissue but affects cell types other than those releasing them
amino acid base
water soluble and can't cross plasma membrane
steroids
synthesized from cholesterol
gonadal and adrenocortical hormones
lipid soluble and can cross plasma membrane
target cells
hormones influences the activity of only those tissue cells that have receptors for it
humoral stimuli
hormone release caused by altered levels of certain critical ions or nutrients
stimulus: low concentration of Ca in blood
response: parathyroid glands secrete PTH which increases Ca
Neural stimuli
hormone released caused by neural input
stimulus: action potentials in preganglionic sympathetic fibers to adrenal medulla
response: adrenal medulla cells secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine
hormonal stimuli
hormone release caused by another hormone
stimulus: hormones from hypothalamus
response: anterior pituitary gland secretes hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands to secrete hormones
upregulation
target cells form more receptors in response to low hormone levels
down regulation
target cells lose receptors in response to high hormone levels
permissiveness
situation in which one hormone can't exert its full effect without another hormone
synergism
more than one hormone produces same effects at the target cell and combined effects are amplified
antagonism
one hormone opposes the action of another
Thyroid gland
largest endocrine gland
2 lobes connected by the isthmus
composed of follicles that produce glycoprotein thyroglobulin
thyroid hormone
the body's major metabolic hormone. consist of T3 and T4
T3
formed by conversion of T4. has two tyrosines with 3 bound iodine atoms
T4 Thyroxine
has two tyrosines with 3 bound iodine atoms
the major hormone secreted by the thyroid follicles
Thyroid hormone is concerned
glucose oxidation
increasing metabolic rate
heat production
Thyroid hormone plays a role in
maintaining blood pressure
regulating tissue growth
developing skeletal and nervous system
maturation and reproductive capabilities
calcitonin
produced by parafollicular cells
lowers blood calcium levels in children
antagonist action to parathyroid hormone
targets skeleton, where it inhibits osteoclast activity
mechanism of release is regulated by humoral.
effects of parathyroid hormone
PTH release increases Ca in blood
enhances the reabsorption of Ca
increases absorption of Ca
raising of Ca in blood inhibits PTH release
adrenal cortex
synthesizes corticosteroids
- zona glomerulosa
- zona fasciculata
- zona reticularis
Zona glomerulosa
produce mineralocorticoids.
aldosterone
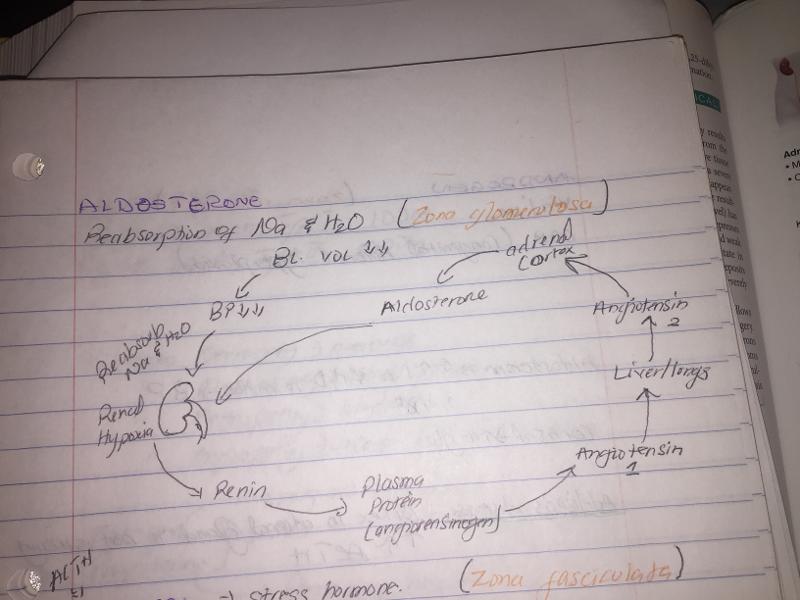
in the zona glomerulosa
stimulates Na absorption (increasing blood volume and blood pressure)
causes K secretion into the tubules for elimination from body
produced by mineralocorticoid
zona fasciculata
produces glucocorticoids
cortisol
in the zona fasciculata
stress hormone
produced by glucocorticoids
pure anti-inflamatory
increases blood glucose levels
glycogenolysis
breakdown glycogen and make sugar
glucogenesis
convert protein/aminos acids to glucose
zona reticularis
produces gonadocorticoids
Androgen (gonadocorticoids)
male sex hormones
secreted by adrenal cortex
contributes to sex drive in women.
adrenal medulla
synthesizes epinephrine and norepinephrine
fight or flight response.
pancreas
beta cells -> insulin -> decrease blood glucose
alpha cells -> glucagon -> increase blood glucose
polyuria
huge urine output that decreases blood volume and causes dehydration
polydipsia
excessive thirst
polyphagia
excessive hunger and food consumption
glucagon
major target is liver
promotes breakdown of glycogen to glucose
synthesis of glucose from lactic acid and from noncarbohydrate molecules
release of glucose to the blood by liver cells causing blood glucose levels to rise
insulin
main effect is to lower blood glucose levels but also promotes protein synthesis and fat storage.
it enhances membrane transport of glucose
inhibits the breakdown of glycogen to glucose
it inhibits the conversion of amino acids or fats to glucose.