chapter 18: the heart
the first sound of the heart is valuable in diagnosis because it provides information about the function of the heat's pulmonary and aortic valves
true
the aortic valves prevent back flow of blood from the aorta into right ventricle
False
the visceral and parietal layers of pericardium are the layers of serous pericardium
True
Superior and inferior vena cava returns venous blood from the upper and lower half of the body into the right atrium of the heart
True
Increase of systemic blood pressure will increase the preload
False
Preload is the stretching of right atrium, the greater the venous return more will be the preload
true
Foramen ovale connects the two ventricles in fetal heart
False
coarctatioin of aorta may increase the afterload and causing left ventricular hypertrophy
True
pulmonary stenosis will lead to right ventricular hypertrophy
True
cor-pulmonnale is the condition of lung congestion secondary to left ventricular failure
False
the dicrotic notch refers to the brief rise in aortic pressure caused by back flow of blood rebounding off semilunar valves of aorta during ventricular diastole
True
inotropic drugs can increase the force of cardiac muscle contraction
True
abnormal heart sounds are called murmurs
True
cardioacceleratory center is located in the medulla oblongata, which innervates SA and AV nodes, heart muscles, and coronary arteries through sympathetic nerves.
false
the difference between resting and maximum state of cardiac output is called bainbridge reflex in heart
False
anterior interventricular artery is a branch of?
left coronary artery
circumflex coronary artery is a branch of?
left coronary artery
right marginal artery is a branch of:
right coronary artery
posterior interventricular artery is a branch of
right coronary artery
endothelial layer of the inner myocardial surface is called
endocardium
left ventricle pumps blood into the
aorta
the semilunar valve lies between the right atrium and pulmonary trunk is called
pulmonary valve
The first heart sound is due to the closure of AV valves
True
the second peak in left atrial pressure is due to atrial systole
False
hemorrhage with a large loss of blood causes
a lowering of blood pressure due to change in cardiac output
the left ventricular wall of the heart is thicker than the right wall in order to
pump blood with greater pressure
blood within the pulmonary veins returns to the
left atrium
If cardiac muscle is deprived of its normal blood supply, primarily damage result from
a decreased delivery of oxygen
the pericardial cavity
is the region of the thoracic cavity that contains the heart
circulation of the blood through the heart
sup/inf vena cava -> right atrium -> through tricuspid valve to the right ventricle -> through pulmonary valve to the pulmonary trunk -> right and left pulmonary artery -> lungs -> right and left pulmonary veins -> left atrium -> through bicuspid valve to left ventricle -> aortic valves into aorta -> body
List the layers of the sac around human heart
pericardium, fibrous pericardium, serous pericardium (Parietal and visceral layers)
space between the pericardia layers is called what? and the content is called?
pericardial cavity
serous fluid
collection of excess amount of fluid int he pericardial space is called
cardiac temponade
general term for the arteries that supply blood to the heart is
coronary arteries
the major blood vessels entering the right atrium are
superior/interior vena cava, coronary sinus, anterior cardiac vein
the right side of the hear is filled with
deoxygenated blood
a valve between the right atrium and right ventricle is called
tricuspid valve
a valve between the left atrium and left ventricle is called
mitral valve
the property of self-stimulation of heart by speacialized tissure in the right atrium is called
autorhythmic
what are those autorhythmic tissue in the walls of the right atrium called
SA node
SA node generates electrical stimulation about
60-100 times per minute
list the ECG waves in the order of occurence
P waves
QRS complex
T waves
a wave obtained in the ECG tracing during atrial depolarization is
P wave
a wave obtained in ECG tracing during ventricular depolarization is
QRS complex
a wave obtained in ECG tracing during ventricular repolarization is
T wav
define cardiac output
whats the formula
cardiac output is the amount of blood pumped out of each ventricle in one minute
CO = HR x SV
define heart rate
number of beats per minute
define stroke volume
formula
volume of blood pumped out of each ventricle per beat
SV = EDV - ESV
define end diastolic volume
maximum amount of blood ventricles will contain in the cycle
define end systolic volume
blood remaining in chambers when ventricles relaxes
what is cardiac reserve
difference between resting and maximal CO
the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute can be expressed as
stroke volume X heart rate
atrial cotraction occurs
following P wave
if the vagus nerves to the heart were cut, the result will be that
the heart rate would increase
the AV valves are supported by______ so that they do not blow back up into the atria during ventricular contraction
chordae tendineae
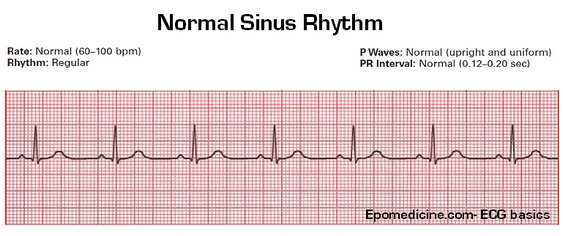
normal sinus rhythm
normal ECG trace
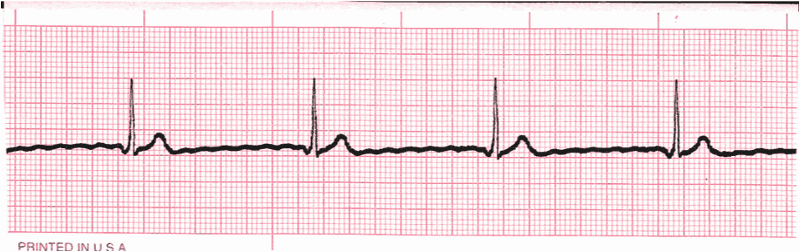
Junctional rhythm
The SA node is nonfunctional. As a result:
P waves are absent
AV node paces heart 40-60 beats/minute
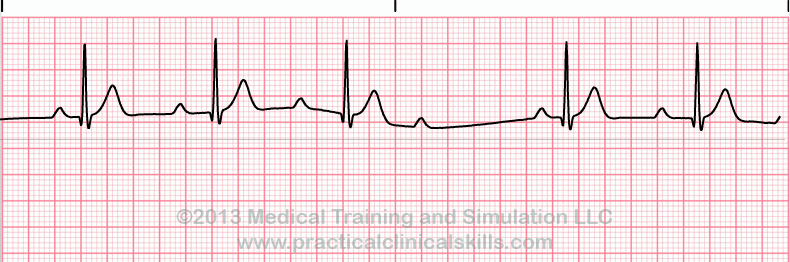
second degree heart block
the AV node fails to conduct some SA node impulses. As a result:
there are more P waves than QRS waves

Ventricular fibrillation
electrical activity is disorganized.results in chaotic, grossly abnormal ECG deflections
all events associated with blood flow through the heart during systole and diastole is called
cardiac cycle
ventricular repolarization wave:
T wave
the first sound of the heart s valuable in diagnosis because it provides information about the function of the heat's pulmonary and aortic valves
true
the mediastinal cavity
is the region of the thoracic cavity that contains the heart
the difference between resting and maximal cardiac output is called
cardiac reserve
the apex of the heart is directed towards
the left
tetralogy of fallot is a common finding in
infants with down syndrome
when the second stimulation is provided to the hear immediately before the ventricular repolarization starts:
second depolarization will not take place
cardiac center in the brain is located in
medulla oblongata
the direction of the blood flow during ventricular contraction in an infant with ventricular septal defect will be
left ventricle to right ventricle
the left coronary arteries arises from the
ascending aorta
the coronary arteries arise from the
aorta
left coronary artery is a branch of ascending aorta
true
all of the structures below are components of conduction system of the heart. Except
fossa ovalis
to ausculate the aortic valve, you would place your stethoscope in the
second intercostal space to the right of the sternum
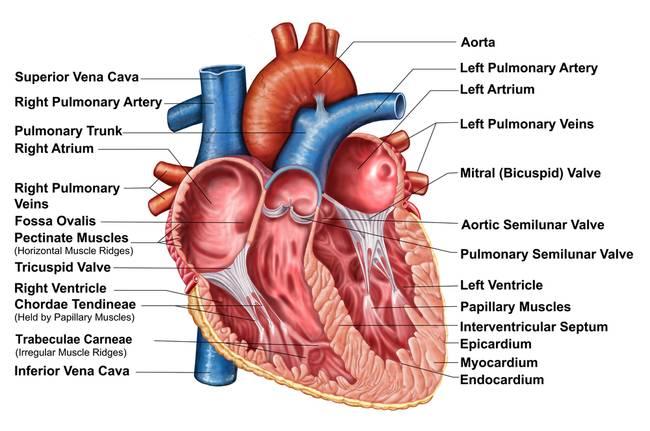
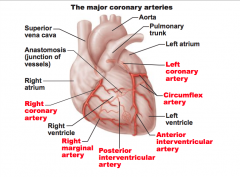
coronary arteries
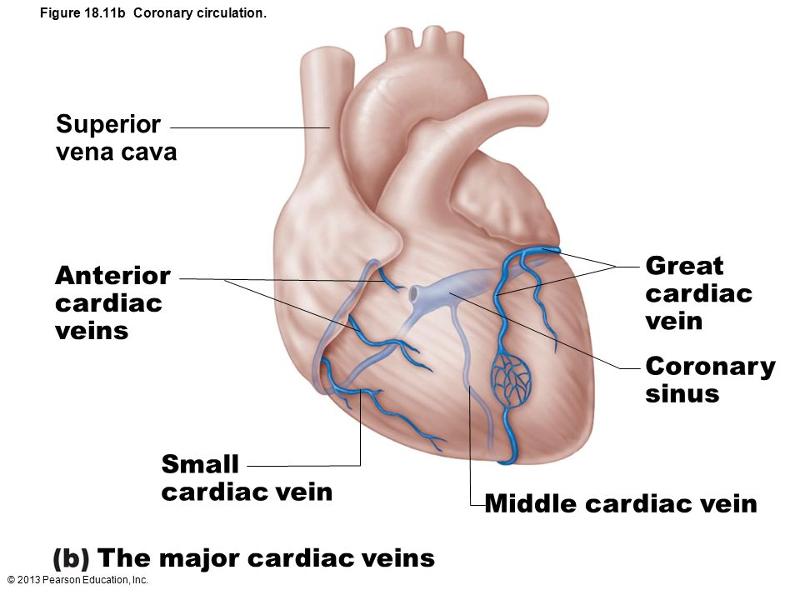
Veins of the heart
volume of blood pumped by each ventricle with each contraction is the
stroke volume
the difference between resting and maximal cardiac output is
cardiac reserve
increase in the heart rate initiated by the increased blood in atria which in turn causes the stimulation of the SA node is the
bainbridge reflex
the degree of stretch of cardiac muscle cells before they contract is
Frank-starling's law
relaxation of the ventricular muscle is called
diastole
amount of blood collected in a ventricle during full relaxation
end diastolic volume
pressure exerted by blood in the large arteries leaving the hear, against which heart must force the blood to eject out the ventricles is the
afterload
which of the following occurs as AV valves close and signifies beginning of ventricular contraction
first heart beat
all events associated with blood flow through the heart during relaxation and contraction
cardiac cycle
which of the following occurs when semilunar valves of great vessels closes at the beginning of the ventricular diastole?
second heart sound
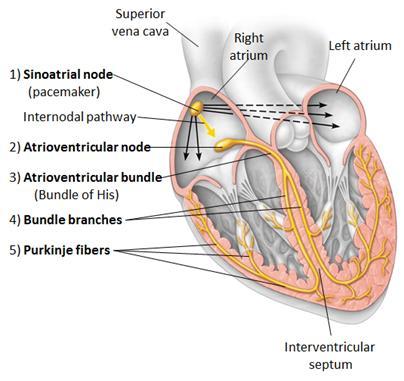
intrinsic conducting system of the heart