A&P 1
integumentary system
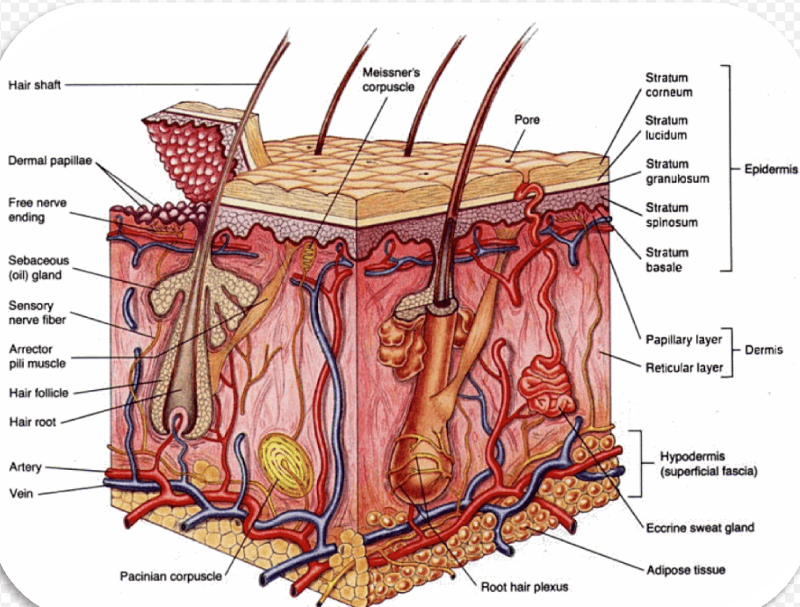
The integumentary system is the organsystem that protects the body from various kinds of damage, such as loss of water or abrasion from outside. The system comprises the skin and its appendages (including hair, scales, feathers, hooves, and nails).
skeletal system
protects and support body organs and provides a framework the muscle use to cause movement.Blood cells are formed within the the bones.Bones store minerals.
Muscular system
Allows manipulation of the environment , locomotion and facial expression , Mantains posture and produces heat
Nervous system
As the fast acting control system of the body , it responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscle and glands
Endocrine system
Gland secrete hormones that regulate process such as growth ,reproduction and nutrient use (metabolism by body cells
Cardiovascular system
Blood vessels transport blood , which carries oxygen ,carbon dioxide, nutrients waste, etc.The heart pumps blood
Lymphatic system/immunity
picks up fluid from blood vessels and return it to blood .Disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream .Houses white blood cells (lymphocytes )involved in immunity
Respiratory system
keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
Digestive system
breaks down food into more absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells to indigesable food stuff are eliminated as feces.
Urinary system
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body. Regulates water electrolyte and electrolyte and acid base balance of the the blood.
anabolism
breaking down substances into simpler building blocks
Anabolism
synthesizing more complex cellular from simpler substances
Homeostasis
is the ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions even though the the outside world changes continuously
Process of homeostatic control
#1. receptor
#2. control system
#3 afferent pathway
Regional terms
Axial:the head trunk
Appendicular: limbs
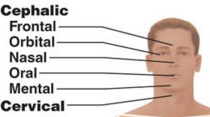
Cephalic
THORACIC
STERNAL(STERNUM), AXILLARY AND MAMMARY
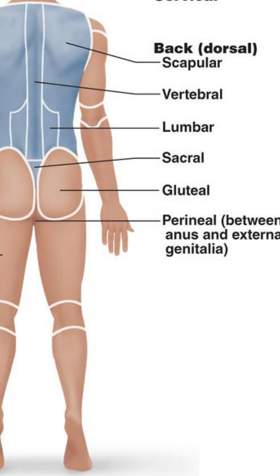
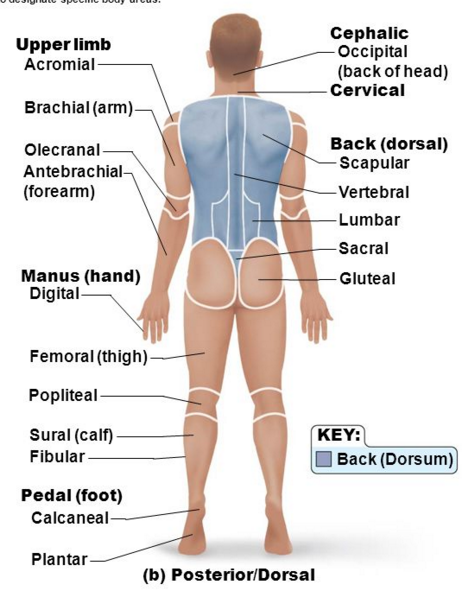
BACK
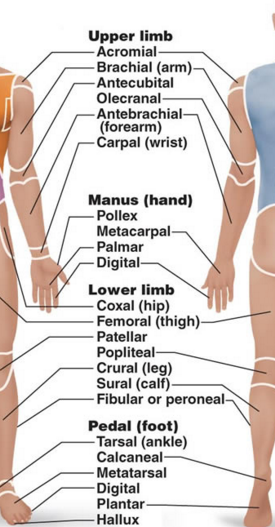
UPPER LIMB,MANUS, LOWER LIMB PEDAL(FOOT)REGIONS
SUPERIOR (CRANIAL)
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body above.(ex)the head is superior to the shoulder
Inferior (caudal)
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure of the body;below ex)the navel is inferior to the the chin
Anterior (ventral)
toward at the front of the body ;in front of.EX) the breastbone is anterior to the spine
Posterior(dorsal)

Toward or at the front of the body;behind
the heart is posterior to the breastbone
Medial
Toward or at the mid line of the body; on the inner side of
the heart is medial to trunk
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body l on the outer side of
the arms are lateral to the chest
Intermediate

Between a more medial and a more lateral structure
The collar bone is intermediate between the breastbone and shoulder
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point or the attachment of the a limb to the trunk
the elbow is proximal to the wrist
Distal
Farther from the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
the knee is is distal to the tigh
Superficial (external )
toward or at the body surface
Deep (INTERNAL)
The lungs are deep to the skin
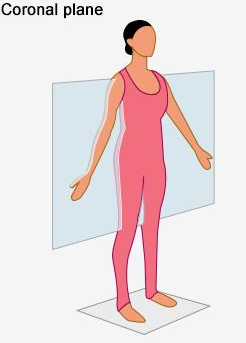
Sagittal plane
Is a vertical plane that divides the body into right and left parts
Median plane or mid sagittal plane
Lies exactly in the middle of the body
Parasagittal plane
divides the body into unequal halves
frontal and coronal planes
CRANIAL CAVITY
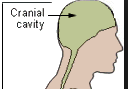
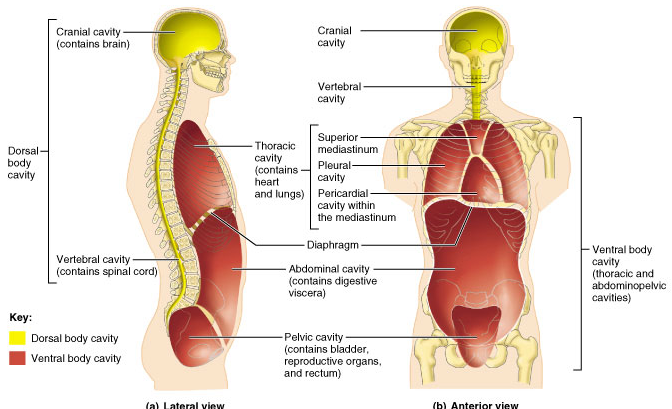
DORSAL AND VENTRAL CAVITIES
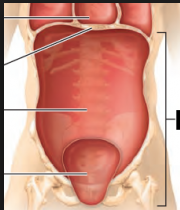
ABDOMINO PELVIC CAVITY, ABDOMIAL
THORACIC CAVITY
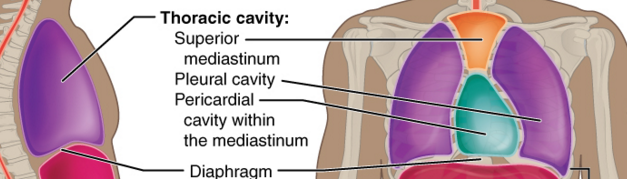
Ventral cavity:houses the pleura cavities which encases the lungs .
Superior Mediastenum houses the
DORSAL CAVITY
Protects the fragile nervous system organs,has two subdivisions the cranial and the vertebral cavities
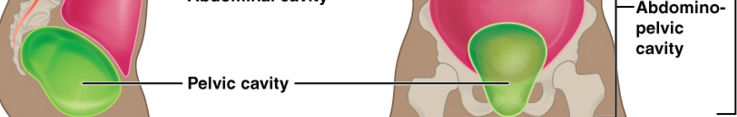
PELVIC CAVITY
VENTRAL BODY CAVITY
HAS TWO MAJOR SUBDIVISIONS THE THORACIC AND THE ABDOMINO PELVIC AREA CAVITY .IT HOUSES THE INTERNAL ORGANS CALLED VISCERA OR VISCERAL ORGANS
PELURAL CAVITIES IN THE THORACIC CAVITY ENCLOSE ?
THE LUNGS
THE MEDIAL MEDIASTENUM IN THE THORACIC CAVITY ENCLOSE ?
IT CONTAINS THE PERICARDIAL CAVITY ,WHICH IT ENCLOSES THE HEART , ESOPHAGUS and THE THRACHEA
SEROUS MEMEBRANE
The walls of the ventral cavity and the outer surfaces of the organs on the ventral cavity are protected by a thin double layer membrane called serosa or serous membrane
Regional name =
regional term
The axial part is:
Head neck and trunk
The appendicular part is:
The limbs
Cephalic
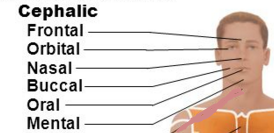
Cephalic (back)
Thoracic
Sternal ,Axillary ,mamary
Abdominal
Umbilical
Pelvic
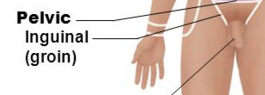
Inguinal(groin)
Regional terms Ventral (anterior)
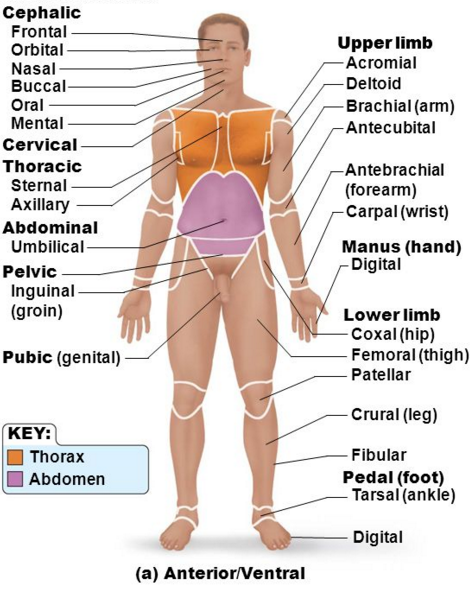
Regional terms dorsal(posterior)
Superior mediastenum

Medial Mediastenum

Poterior Mediastenum

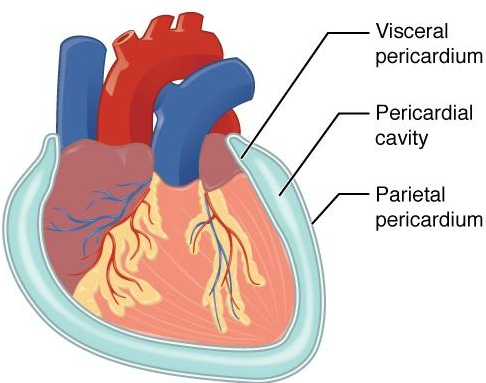
Pericardial cavity encloses?
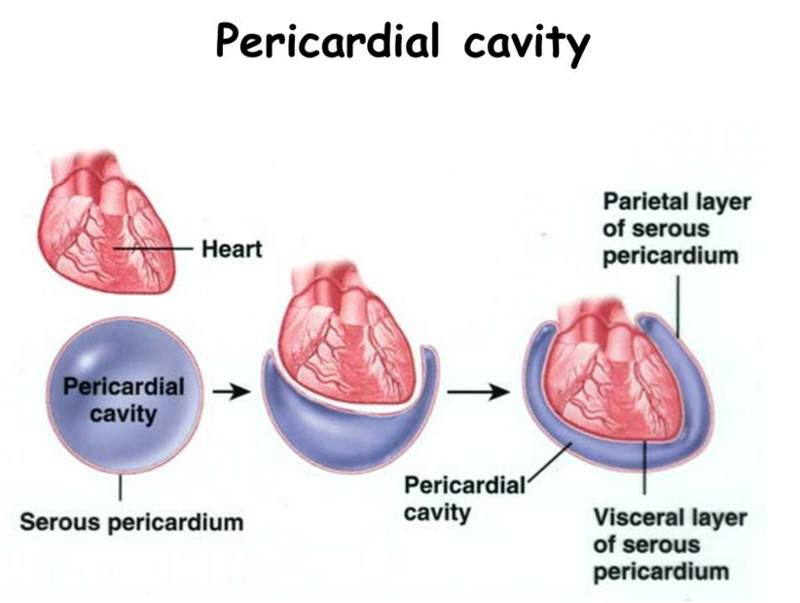
Encloses the heart and it also surrounds the other remaining thoracic organs (esophagus, trachea and others)
The abdominopelvic cavity
The abdominopelvic cavity is divided into the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity.
Abdominal cavity contains the intestines,the stomach,spleen, liver and other organs.
The pelvic cavity contains the urinary bladder, some reproductive organs and rectum
SEROSA
The walls of the ventral body cavity and the outer surfaces of the organs it contains are covered by a thin double layer called the "serosa" or the serorus membrane
Parietal pericardium
lines into the pericardial cavity and folds back as the visceral pericardium, which it cover the heart
Parietal pleurae
line the walls of the of the thoracic cavity and the visceral pleurae cover the lungs.
Parietal peritoneum
is associated with the walls of the abodominopelvic cavity while the visceral peritoneum covers most of the organs within that cavity
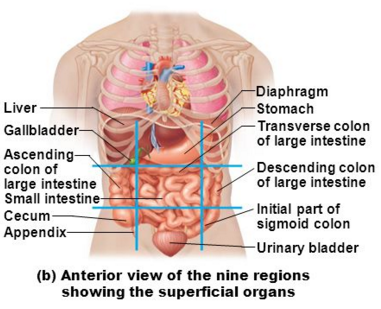
ABDOMINOPELVIC REGIONS AND QUADRANTS
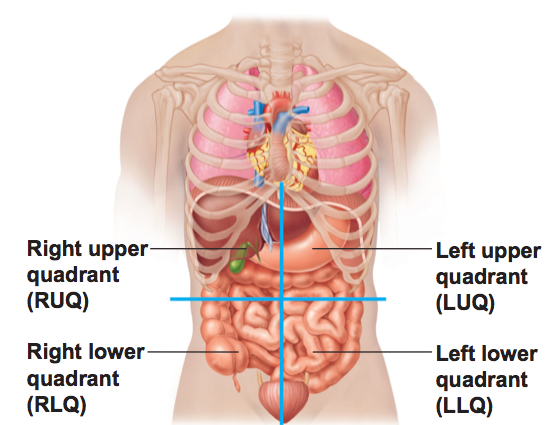
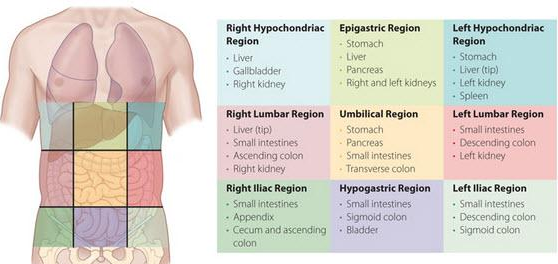
ABDOMINOPELVIC REGIONS
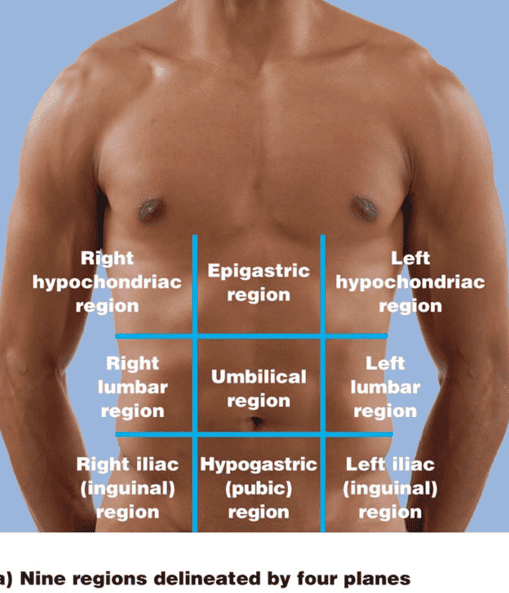
THE 9 REGIONS SHOWING THE SUPERFICIAL ORGANS
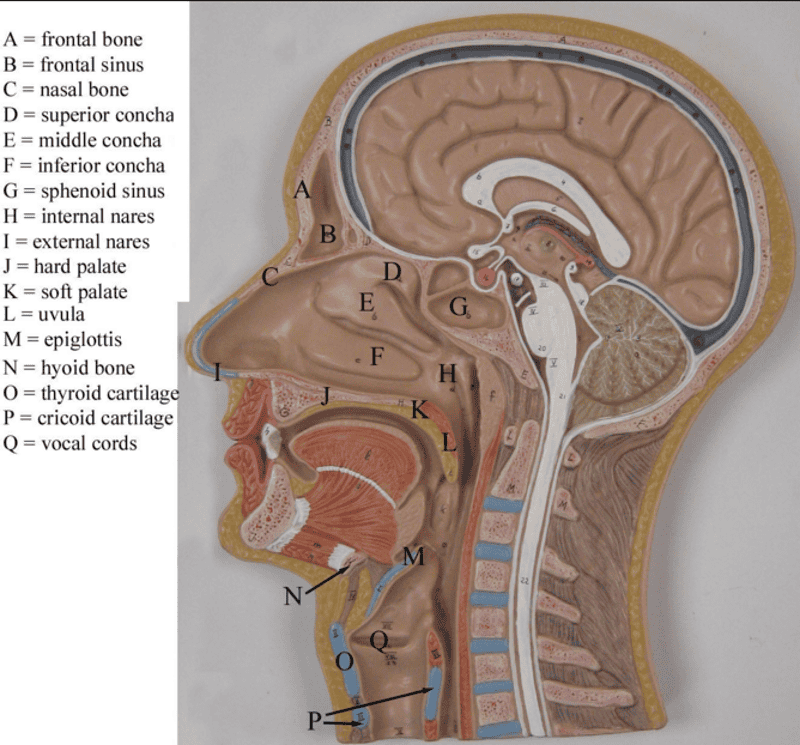
MID SAGITTAL CROSS CUT SECTION
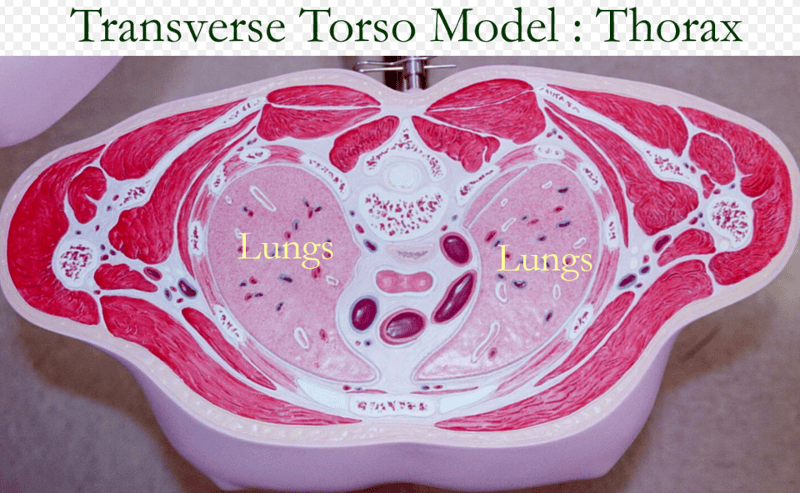
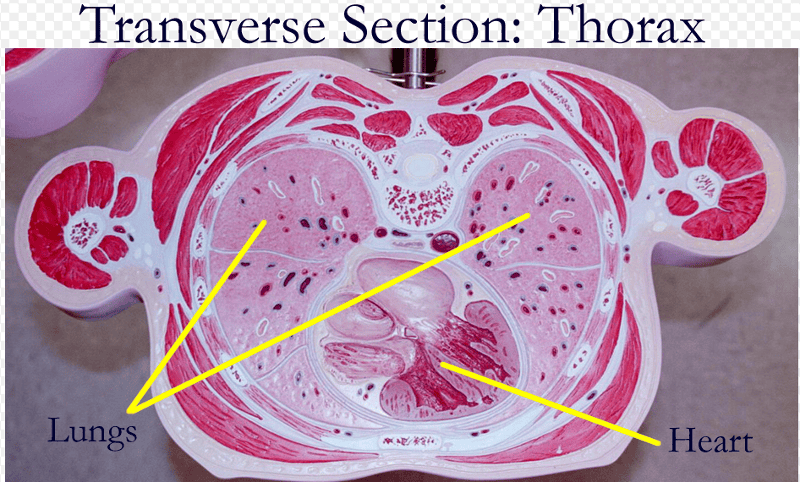
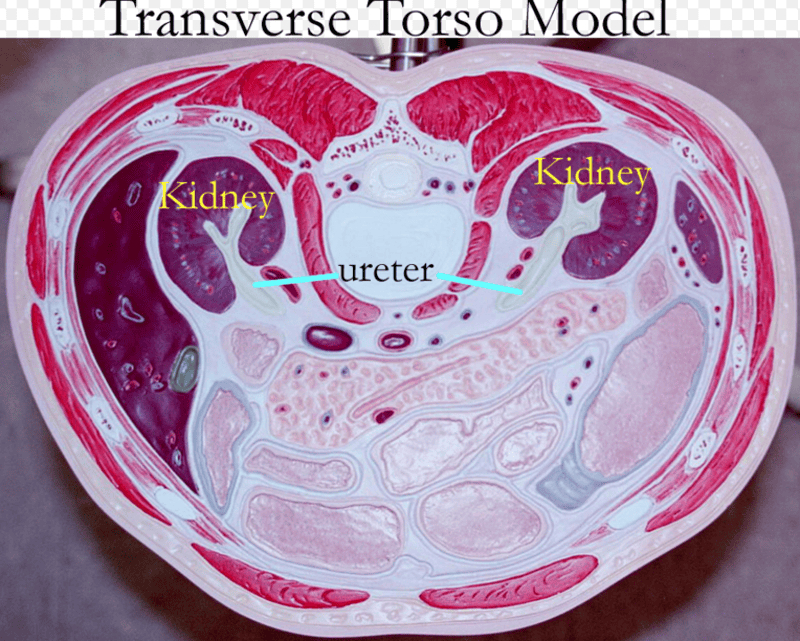
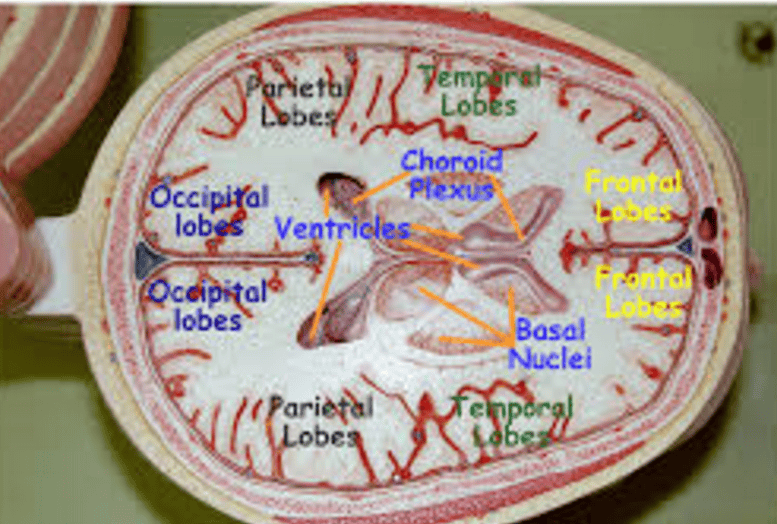
TRANSVERSE PLANE SECTION
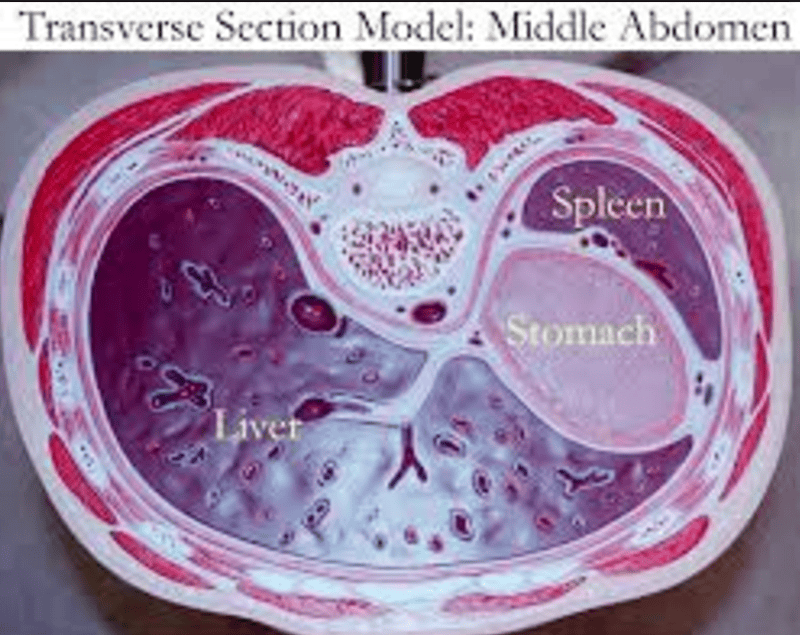
MORE TRANsVERSE PLANE CUT SECTIONS
coronal plane of cephalic area or head
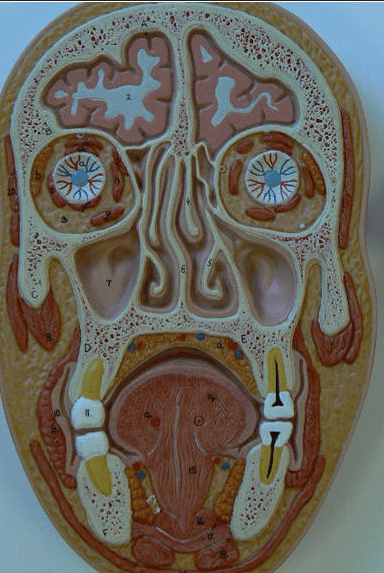
transverse section of cephalic area or head
Forehead is superior to?
the forehead is superior to the nose
The navel is inferior to?
The navel is inferior to the breast bone
The breast bone is anterior to?
The breast bone is anterior to the the spine
The heart is posterior to ?
The heart is posterior ton the breastbone
The heart is medial to ?
The heart is medial to the arms
The arms are lateral to?
The armas are lateral to the chest
The elbow is proximal to?
The elbow is proximal to the wrist
The knee is distal to?
The knee is distal to the thigh
The skin is superficial to?
The skins superficial to the skeleton
The lungs are deep to?
The lungs are deep to the rib cage
the aorta is __________ to the vertebral column
ventral
the vertebral column is ________ to the aorta
dorsal
the sternum is _______ to the heart
anterior
the esophagus is _________ to the trachea
posterior
the _______ end of the embryonic neural tube develops into the brain
cephalic
the forebrain is _______ to the brainstem
rostral
the spinal cord is ________ to the brain
caudal
the heart is _______ to the diaphragm
superior
the liver is _______ to the diaphragm
inferior
the heart is ________ to the lungs
medial
the eyes are _______ to the nose
lateral
the fingernails are at the _______ ends of the fingers
distal
the bones are _______ to the muscle
deep
The serous membranes
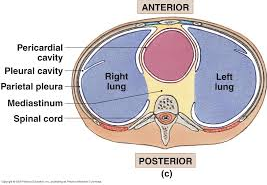
Are double thin layer composed of connective and epithelial tissue.they line the walls of the thoracic and abdominal cavities and then fold back to cover the organs within the cavities.A slippery serous fluid produced by the cells of the membrane is found in between the two layers. This fluid permits the free sliding of the two layers during movement. THE portion of the membrane attached to an organ is called the visceral layer. The external layer or the portion of the membrane that attaches the body wall is called the parietal layer.
PERICARDIAL MEMBRANE(PERICARDIUM)
Surrounds the heart
PLEURAL MEMEBRANES
Surround the lungs
PERITONEAL MEMBRANE(PERITONUM)
Surrounds many organs in the abdominopelvic cavity
respiratory system
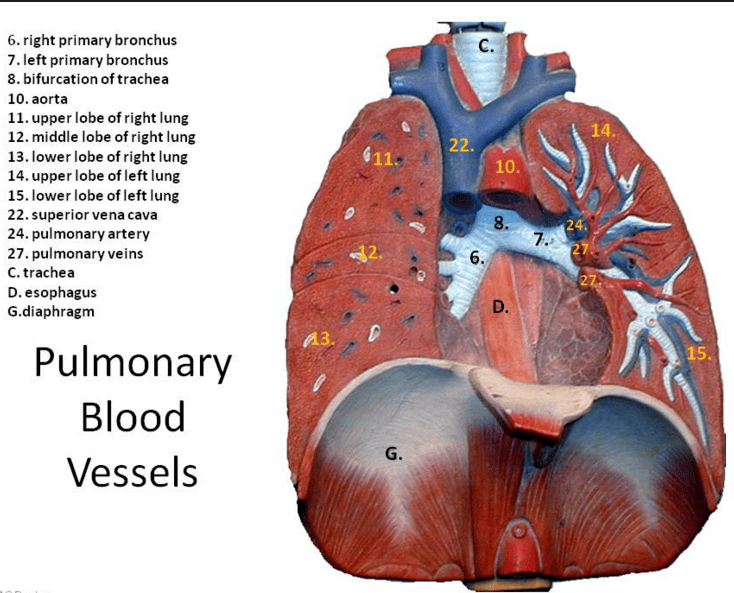
The heart is in the ?
The heart is in the thoracic cavity over the ventral cavity
The trachea is located in ?
The trachea is locate din the superior is in the superior mediastenum cavity of the thoracic cavity over the ventral cavity
The stomach is located where?
in the abdominal cavity on the ventral cavity
the uterus is in the ?
pelvic cavity on the ventral cavity
The spinal cord is in located ?
is located in the vertebral cavity o the dorsal cavity