Integumentary System
The integument
-the largest system of the body
-16% of body weight
-1.5 to 2 m^2 in area
Two Parts of the Integument
1.Cutaneous Membrane (skin)
2.Accessory Structures
Two Components of the Cutaneous Membrane
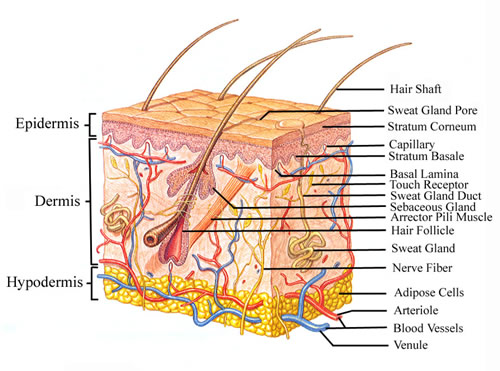
1. Outer Epidermis
-superficial epithelium (epithelial tissues)
2.Inner Dermis
-connective tissues
Accessory Structures

-originate in the dermis
-extend through the epidermis to skin surface
*hair
*nails
*multicellular exocrine glands
Cardiovascular System
-blood vessels in the dermis
Nervous System
-sensory receptors for pain, touch, and temperature
Hypodermis

-loose connective tissue
-below the dermis
-location of hypodermic injections
Functions of Skin
-protection of underlying tissues and organs
-excretion of salts, water, and organic wastes (glands)
-maintenance of body temperature
-production of melanin
-production of keratin
-synthesis of vitamin D
-storage of lipids
-detection of touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
Epidermis
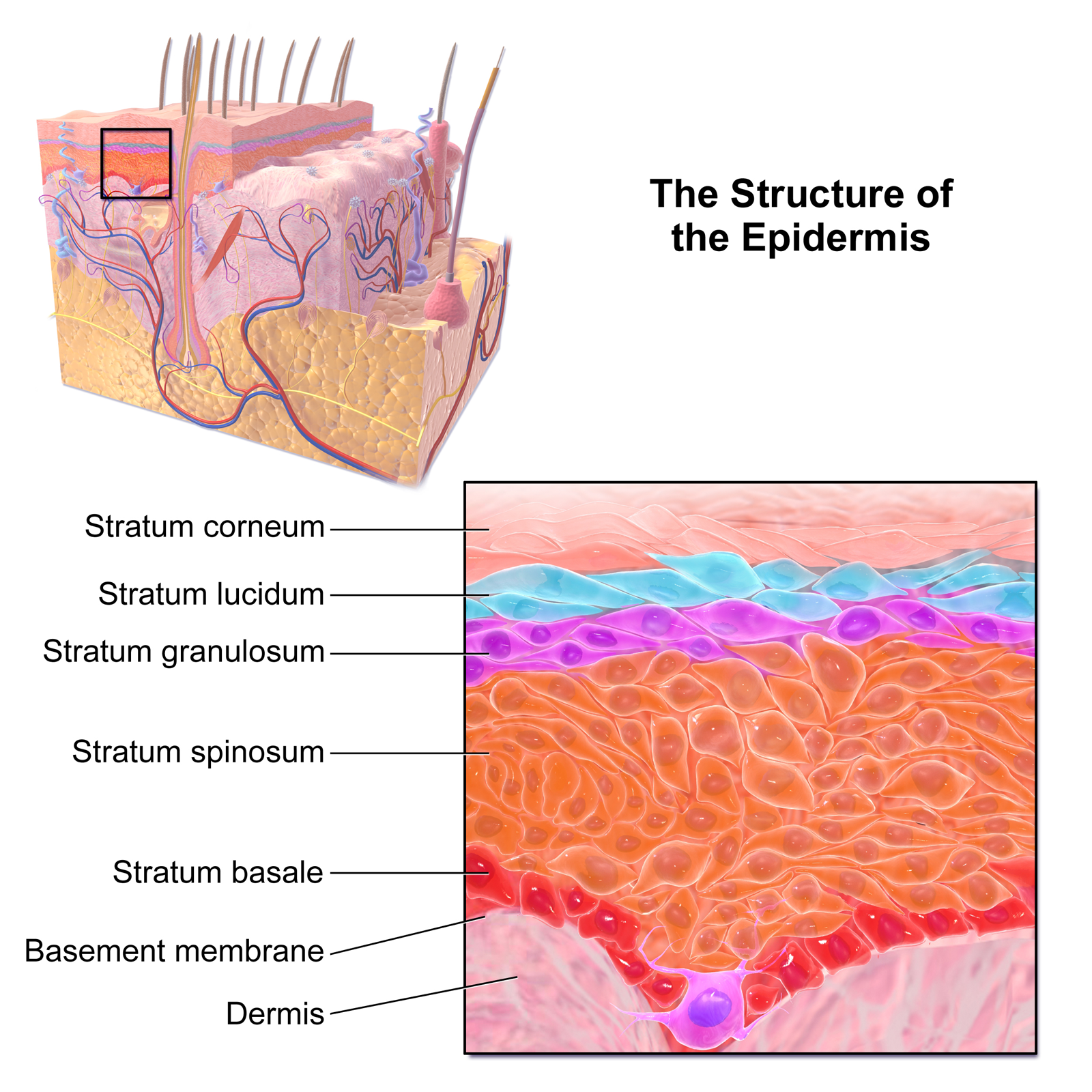
-avascular stratified squamous
*nutrients and oxygen diffuse from capillaries in the dermis
Keratinocytes

-contain large amounts of keratin
-are the most abundant cells in the epidermis
Thin Skin

-covers most of the body
-has four layers of keratinocytes
Thick Skin

-covers the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
-has five layers of keratinocytes
Stratum Basale

-is attached to basement membrane b hemidesmosomes
-forms a strong bond between the epidermis and dermis
-forms epidermal ridges (e.g. fingerprints)
-has many basal cells or germinative cells
Merkel Cells

-specialized cell of the stratum basale
-found in hairless skin
-respond to touch
Melanocytes
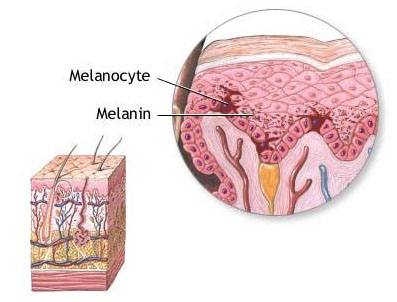
-specialized cell of the stratum basale
-contains the pigment melanin
-scattered throughpout stratum basale
Stratum Spinosum

-the spiny layer
-produced by division of stratum basale
-eight to ten layers of keratinocytes bound by desmosomes
-cells shrink until cytoskeletons stick out
-continue to divide, increasing thickness of epithelium
-contain dendritic (Langerhans) cells, active in immune response
Stratum Granulosum

-the grainy layer
-stops dividing, starts producing
Keratin
-a tough, fibrous protein
-makes up hair and nails
Keratohyalin
-dense granules
-cross link keratin fibers
Stratum Lucidum

-the clear layer
-found only in thick skin
-covers stratum granulosum
Stratum Corneum

-the horn layer
-exposed surface of skin
-15 to 30 layers of keratinized cells
-water resistant
-shed and replaced every 2 weeks
Keratinization
-the formation of a layer of dead, protective cells filled with keratin
-occurs on all exposed skin surfaces except the eyes
-skin life cycle
-it takes 15 to 30 days for a cell to move from the stratum basale to stratum corneum
Insensible Perspiration
-interstitial fluid lost by evaporation through the stratum corneum
Sensible Perspiration
-water excreted by sweat glands
Skin Color Influenced by two Pigments
1.Carotene
2.Melanin
Carotene
-orange-yellow pigment
-found in orange vegetables
-accumulates in epidermal cells and fatty tissues of the dermis
-can be converted to vitamin A
Melanin
-yellow-brown or black pigment
-produced by melanocytes in stratum basale
-stored in transport vesicles (melanosomes)
-transferred to keratinocytes
-protects the skin from sun damage
-skin color depends on melanin production, not number of melanocytes
Capillaries and Skin Color
-oxygenated red blood contributes to skin color
-blood vessel dilate from heat, skin reddens
-blood flow decreases, skin pales
Cyanosis
-bluish skin tint
-caused by severe reduction in blood flow or oxygenation
Jaundice

-buildup of bile produced by liver
-yellow color
Pituitary Tumor
-excess MSH
Addison's Disease

-a disease of the pituitary gland
-skin darkening
Vitiligo
-loss of melanocytes
-loss of color
Vitamin D
-epidermal cells produce cholecalciferol (vitamin D)
-liver and kidneys convert vitamin D into calcitriol
-insufficient Vitamin D can cause rickets
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
-powerful peptide growth factor
-produced by glands (salivary and duodenum)
-used in laboratories to grow skin grafts
-promotes division of germinative cells
-accelerates keratin production
-stimulates epidermal repair
-stimulates glandular secretion
The Dermis

-located between the epidermis and hypodermis
-anchors epidermal accessory structures (hair follicles and sweat glands)
2 Layers
-Papillary Layer
-Reticular Layer
The Papillary Layer

-consists of areolar tissue
-contains small capillaries, lymphatics, and sensory neurons
-has dermal papillae projecting between epidermal ridges
The Reticular Layer

-consists of dense irregular connective tissue
-contains larger blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibers
-contains collagen and elastic fibers
-contains connective tissue proper
Dermatitis
-an inflammation of the papillary layer
-caused by infection, radiation, mechanical irritation, or chemicals
-characterized by itch or pain
Dermal Strength & Elasticity
Two Fibers
1COllagen
2.Elastic FIbers
Collagen Fibers
-very strong, resist stretching but bend easily
-provide flexibility
Elastic Fibers
-permit stretching and then recoil to original length
-limit the flexibility of collagen fibers to prevent damage to tissue
Sagging and Wrinkles are caused by:
-dehydration
-age
-hormonal changes
-UV exposure
Stretch Marks

-thickened tissue resulting from excessive stretching of skin due to:
*pregnancy
*weight gain
Cleavage Lines

-collagen and elastic fibers in the dermis
-arranged in parallel bundles
-resist force in a specific direction
Cutaneous Plexus
-a network of arteries along the reticular layer
Papillary plexus
-capillary network from small arteries in papillary layer
Venous Plexus
-capillary return deep to the papillary plexus
Contusion
-damage to blood vessels resulting in black and blue bruising
Tactile Corpuscles

-light touch
-located in dermal papillae
Lamellated Corpuscles
-deep pressure and vibration
-located in the reticular layer
The Hypodermis/Subcutaneous Layer
-lies below the integument
-stabilizes the skin
-allows separate movement
-made of elastic areolar and adipose tissues
-connected to the reticular layer of the integument by connective tissue fibers
-few capillaries and no vital organs
-the site of subcutaneous injections using hypodermic needles
Hair
-the human body is covered with except palms, soles, lips, and portions of external genitalia
-protects and insulates
-guards openings against particles and insects
-is sensitive to very light touch
Hair Follicle

-located deep in dermis
-produces nonliving hairs
-wrapped in dense connective tissue sheath
-base is surrounded by sensory nerves
Arrector Pili
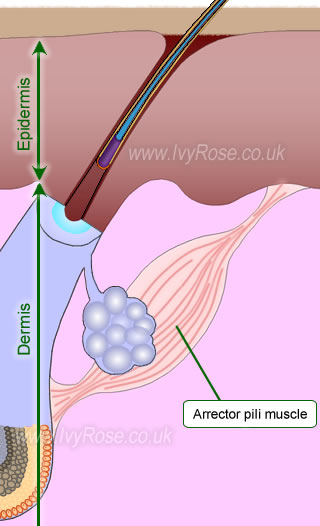
-involuntary smooth muscle
-causes hairs to stand up
-produces goose bumps
Sebaceous Glands

-lubricate the hair
-control bacteria
Hair ROot

-lower part of the hair
-attached to the integument
Hair Shaft

-upper part of the hair
-not attached to the integument
Hair Shaft Structure
-Medulla
*The central core
*Contains flexible soft keratin
-Cortex
*The Middle Layer
*contain stiff hard keratin
-Cuticle
*The Surface Layer
*contain stiff hard keratin
Vellus Hairs
-soft, fine
-covers body surface
Terminal Hairs

-heavy, pigmented
-head, eyebrows, and eyelashes
-other parts of the body after puberty
Hair Color
-produced by melanocytes at the hair papilla
-determined by genes
Sebum
-contains lipids and other ingredients
-lubricates and protects the epidermis
-inhibits bacteria
Apocrine Sweat Glands
-found in armpits, around nipple, and groin
-secrete products into hair follicles
-produce sticky, cloudy secretions
-break down and CAUSE ODORS
-surrounded by myoepithelial cells
Merocrine (Eccrine) Sweat Glands
-widely distributed on body surface
-especially on palms and soles
-coiled, tubular glands
-discharge directly onto skin surface
-sensible perspiration
-water,salts, and organic compounds
-cools skin
--excretes water and electrolytes
-flushes microorganisms and harmful chemicals from skin
Mammary Glands
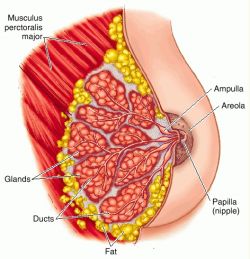
-produce milk
Ceruminous Glands
-produce cerumen (earwax)
-protect the ear
Nails
-protect the fingers and toes
-made of dead cells packed with keratin
-metabolic disorders can change nail structure
Nail Production
-occurs in a deep epidermal fold near the bone called nail root
Nail Body

-the visible portion of the nail
-covers the nail bed
Lunula

-the pale crescent at the base of the nail
Sides of nails

-lie in lateral nail grooves
-surrounded by lateral nail folds