Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Integumentary System
front 1 The integument | back 1 -the largest system of the body
|
front 2 Two Parts of the Integument | back 2 1.Cutaneous Membrane (skin)
|
front 3 Two Components of the Cutaneous Membrane | back 3 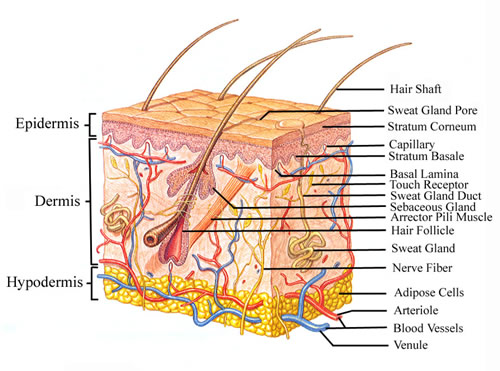 1. Outer Epidermis
|
front 4 Accessory Structures | back 4  -originate in the dermis
|
front 5 Cardiovascular System | back 5 -blood vessels in the dermis |
front 6 Nervous System | back 6 -sensory receptors for pain, touch, and temperature |
front 7 Hypodermis | back 7  -loose connective tissue
|
front 8 Functions of Skin | back 8 -protection of underlying tissues and organs
|
front 9 Epidermis | back 9 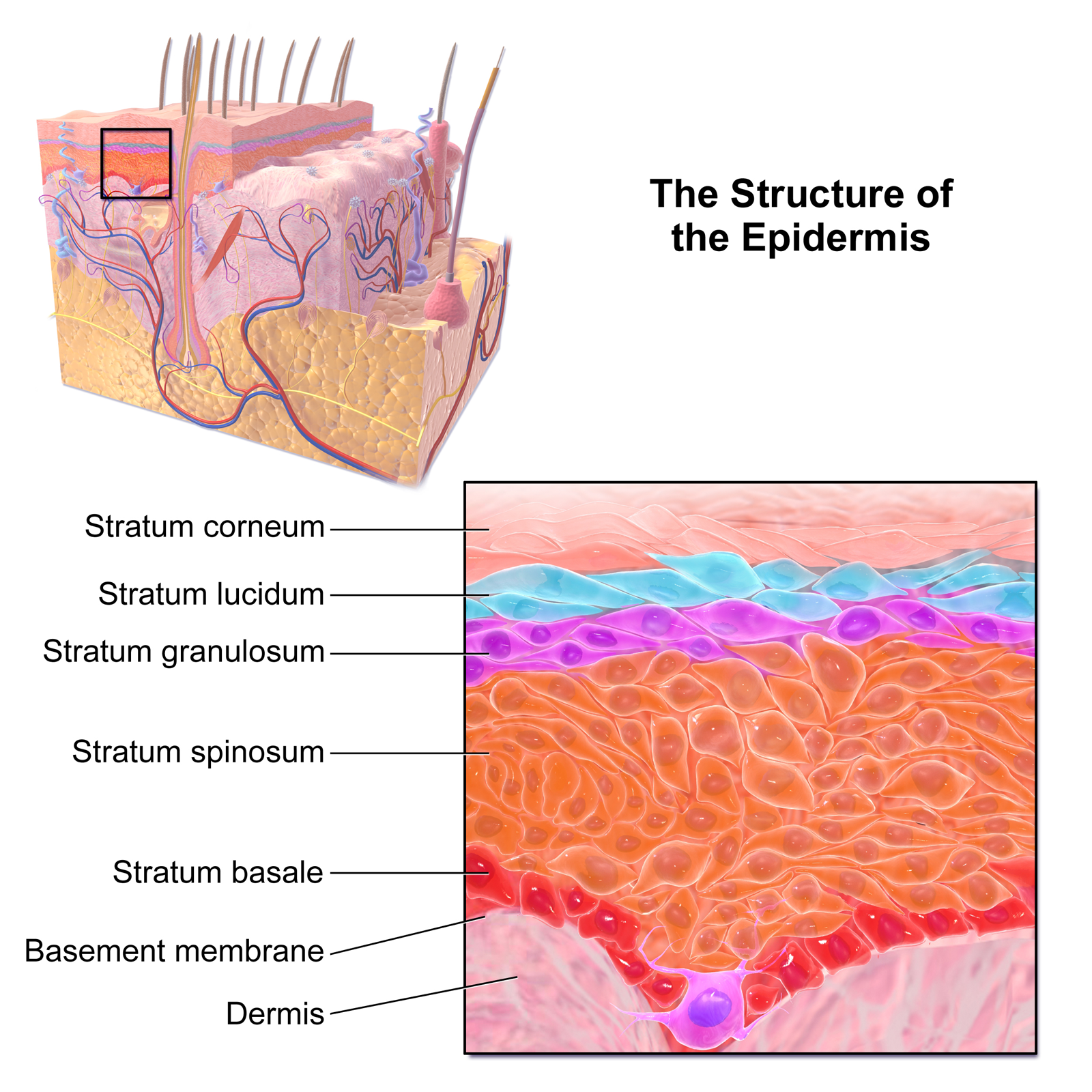 -avascular stratified squamous
|
front 10 Keratinocytes | back 10  -contain large amounts of keratin
|
front 11 Thin Skin | back 11  -covers most of the body
|
front 12 Thick Skin | back 12  -covers the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
|
front 13 Stratum Basale | back 13  -is attached to basement membrane b hemidesmosomes
|
front 14 Merkel Cells | back 14  -specialized cell of the stratum basale
|
front 15 Melanocytes | back 15 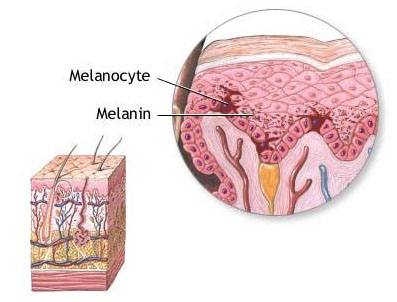 -specialized cell of the stratum basale
|
front 16 Stratum Spinosum | back 16  -the spiny layer
|
front 17 Stratum Granulosum | back 17  -the grainy layer
|
front 18 Keratin | back 18 -a tough, fibrous protein
|
front 19 Keratohyalin | back 19 -dense granules
|
front 20 Stratum Lucidum | back 20  -the clear layer
|
front 21 Stratum Corneum | back 21  -the horn layer
|
front 22 Keratinization | back 22 -the formation of a layer of dead, protective cells filled with keratin
|
front 23 Insensible Perspiration | back 23 -interstitial fluid lost by evaporation through the stratum corneum |
front 24 Sensible Perspiration | back 24 -water excreted by sweat glands |
front 25 Skin Color Influenced by two Pigments | back 25 1.Carotene
|
front 26 Carotene | back 26 -orange-yellow pigment
|
front 27 Melanin | back 27 -yellow-brown or black pigment
|
front 28 Capillaries and Skin Color | back 28 -oxygenated red blood contributes to skin color
|
front 29 Cyanosis | back 29 -bluish skin tint
|
front 30 Jaundice | back 30  -buildup of bile produced by liver
|
front 31 Pituitary Tumor | back 31 -excess MSH |
front 32 Addison's Disease | back 32  -a disease of the pituitary gland
|
front 33 Vitiligo | back 33 -loss of melanocytes
|
front 34 Vitamin D | back 34 -epidermal cells produce cholecalciferol (vitamin D)
|
front 35 Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) | back 35 -powerful peptide growth factor
|
front 36 The Dermis | back 36  -located between the epidermis and hypodermis
|
front 37 The Papillary Layer | back 37  -consists of areolar tissue
|
front 38 The Reticular Layer | back 38  -consists of dense irregular connective tissue
|
front 39 Dermatitis | back 39 -an inflammation of the papillary layer
|
front 40 Dermal Strength & Elasticity | back 40 Two Fibers
|
front 41 Collagen Fibers | back 41 -very strong, resist stretching but bend easily
|
front 42 Elastic Fibers | back 42 -permit stretching and then recoil to original length
|
front 43 Sagging and Wrinkles are caused by: | back 43  -dehydration
|
front 44 Stretch Marks | back 44  -thickened tissue resulting from excessive stretching of skin due to:
|
front 45 Cleavage Lines | back 45  -collagen and elastic fibers in the dermis
|
front 46 Cutaneous Plexus | back 46 -a network of arteries along the reticular layer |
front 47 Papillary plexus | back 47 -capillary network from small arteries in papillary layer |
front 48 Venous Plexus | back 48 -capillary return deep to the papillary plexus |
front 49 Contusion | back 49 -damage to blood vessels resulting in black and blue bruising |
front 50 Tactile Corpuscles | back 50  -light touch
|
front 51 Lamellated Corpuscles | back 51 -deep pressure and vibration
|
front 52 The Hypodermis/Subcutaneous Layer | back 52 -lies below the integument
|
front 53 Hair | back 53 -the human body is covered with except palms, soles, lips, and portions of external genitalia
|
front 54 Hair Follicle | back 54  -located deep in dermis
|
front 55 Arrector Pili | back 55 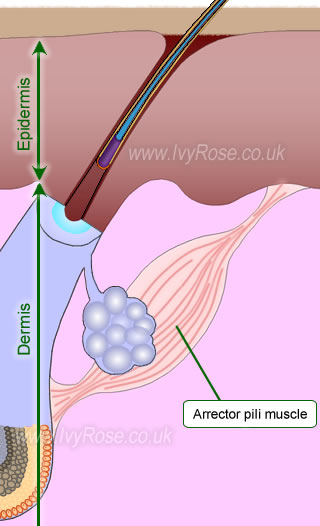 -involuntary smooth muscle
|
front 56 Sebaceous Glands | back 56  -lubricate the hair
|
front 57 Hair ROot | back 57  -lower part of the hair
|
front 58 Hair Shaft | back 58  -upper part of the hair
|
front 59 Hair Shaft Structure | back 59 -Medulla
|
front 60 Vellus Hairs | back 60 -soft, fine
|
front 61 Terminal Hairs | back 61  -heavy, pigmented
|
front 62 Hair Color | back 62 -produced by melanocytes at the hair papilla
|
front 63 Sebum | back 63 -contains lipids and other ingredients
|
front 64 Apocrine Sweat Glands | back 64 -found in armpits, around nipple, and groin
|
front 65 Merocrine (Eccrine) Sweat Glands | back 65 -widely distributed on body surface
|
front 66 Mammary Glands | back 66 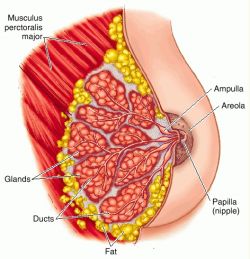 -produce milk |
front 67 Ceruminous Glands | back 67 -produce cerumen (earwax)
|
front 68 Nails | back 68 -protect the fingers and toes
|
front 69 Nail Production | back 69 -occurs in a deep epidermal fold near the bone called nail root |
front 70 Nail Body | back 70  -the visible portion of the nail
|
front 71 Lunula | back 71  -the pale crescent at the base of the nail |
front 72 Sides of nails | back 72  -lie in lateral nail grooves
|