Experiment 4 Prelaboratory Assignment: Inorganic Compounds and Metathesis Reactions
1. a. Copper(II) sulfate dissolves in water to form a blue solution. What species are present in solution, i.e., what is actually swimming around in solution? Write the formulas.
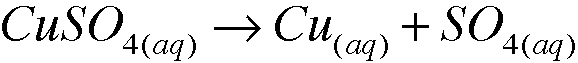
species in the solution are C2+ and SO4^2-
1. b. Sodium carbonate carbonate dissolves in water to form a colorless solution. What species are present in solution? Write the formulas.
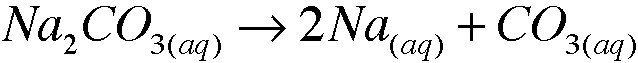
species present are Na+ and CO3^2-
1. c. When solutions of copper(II) sulfate and sodium carbonate are mixed, blue copper(II) carbonate precipitates. What species remain in solution? (These are spectator ions.) What is the color? [Assume that stoichiometric amounts of copper(II) sulfate and sodium carbonate are mixed.] Write the formulas
Na+, CO3^2-, colorless
CuSO$(aq)+Na2CO3(aq) –> CuCO3(aq) + SO4(aq) + 2Na
2. a. An aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide is labeled 0.010M NaOH. What are the molar concentrations of NaOH, Na+ and OH- in the aqueous solution? Explain.
0.010M NaOH, and an OH would remain because there are one mol of each
2. b. An aqueous solution of calcium chloride is labeled 0.010 M CaCl2. What are the molar concentrations CaCl2, Ca2+, and Cl- in the aqueous solution? Explain.
CaCl2 0.010M CaCl2 –> Ca + 2Cl
Ca2 0.010M 1 mol in both CaCl2+Ca2
Cl 0.02M 2 moles of Cl8
3. Sodium phosphate dodecahydrate, Na3PO4(12H2O), is crystalline salt that is water soluble. Describe what is present in an aqueous solution of sodium phosphate dodecahydrate.
Na+ and P ions are in solution
4. When aqueous solutions of ferrous sulfate and barium chloride are mixed, a white precipitate forms. With time the aqueous solution turns a red-orange color.
a. Refer to Apendix G. What is the white precipitate? Write the formula.
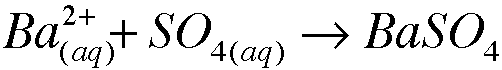
Barium sulfate
5. Write molecular equations for each of the following metathesis reactions:
a.
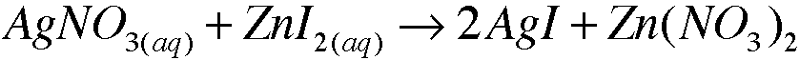
5. Write molecular equations for each of the following metathesis reactions:
b.
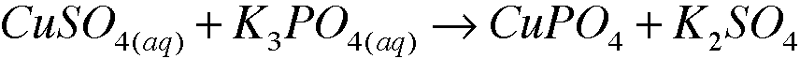
5. Write molecular equations for each of the following metathesis reactions:
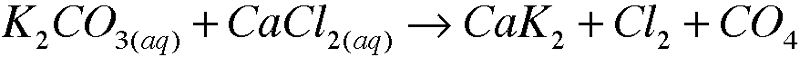
5. Write molecular equations for each of the following metathesis reactions:
c.
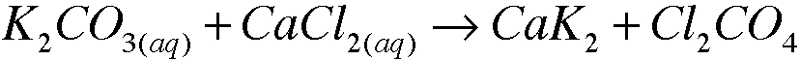
5. Write molecular equations for each of the following metathesis reactions:
d.
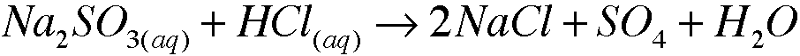
5. Write molecular equations for each of the following metathesis reactions:e.

6. List 5 observations, appealing to your senses, that indicate a chemical reaction has occurred. In each case, identify an example where you have experienced that observation.
Odor: poop
Gas formation: calcium carbonate
Color change: copper experiment
Formation of participate: Milk into lactic acid
energy released: car engine