Lecture Exam Chapters - (1,3,4,9,10,11,18)
Bacteria
Archaea
Fungi
Prokaryotic
Protozoa
Algae
Multicellular animal parasites
Eukaryotic
Viruses
Prions
Acellular
_________________ is a Symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits, the other is unaffected.
Commensalism
______________ is a Symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit.
Mutualism
______________ is a Symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits, the other is harmed.
Parasitism
______________ protect us from overgrowth of harmful bacteria.
Help produce Vit. K and some B vitamins
Normal microbiota (used to be called flora)
Bacteria that are photosynthetic are _______________.
Producers
Bacteria/fungus that recycle essential nutrients are _______________
Decomposers
Bioremediation is
Ex. Conveting pollutants to harmless molecules
(Microbs eating oil spills, or cleaning sewage)
ROBERT HOOKE
1665 - See first Cells
Beginning of cell theory (all living things are composed of cells)
Anton van Leeuwewnhoek
"Father of Microscopy"
"animalcules" 1673-1723
Francesco Redi
1699
Disproved spontaneous generation with experiment of meat in a jars some covered with Gauze
CELL THEORY
1.) All living things are composed of cells
2.) Cells can only come from preexisting cells
John Needham
1745
Microbes appeared after pouring boiled nutrient broth into flasks that were then covered.
Lazzaro Spallanzani
1765
Microbes did not grow when the second flasks were heated after the broth was poured in.
Rudolf Virchow
1858
Claimed living cells can only come from preexisting cells Second tenet of the cell theory
Louis Pasteur
1861-disproved spontaneous generation *Biogenesis – life comes from life
Using flask w/ S Shaped neck.
Discovered HOW vaccinations worked after Jenner's 1796 cowpox discovery
Ignaz Semmelweiss
1840’s
Realized Germs were transmitted on our hands b/c post-partum mothers did not die with midwives, but did often die at Hospitals.
Saw his co-work get sick/die after cutting himself while working on corpse
John Lister
1860s (Listerine named after him)
Put together Semmelweiss’ handwashing observations and Pasteur’s work
Began disinfecting surgical wounds & surgical instruments Proved microorganisms caused surgical wound infections (use Carboxlic Acid to disinfect tools)
Robert Koch
1846
Discovered:
the bacterium that caused Anthrax in cattle
Bacterium that caused TB
Rules for controlling cholera outbreaks
Koch's Postulates
1. The specific organism should be shown to be present in all cases of animals suffering from a specific disease, but should not be found in healthy animals
2. The specific microorganism should be isolated from the diseased animal and grown in pure culture on artificial laboratory media
3. This freshly isolated microorganism, when inoculated into a healthy non-immune laboratory animal, should cause the same disease seen in the original animal
4. The microorganism should be re-isolated in pure culture from the experimental infection
John Snow
Founder of Epidemiology
1854 Broad Street Pump (Cholera outbreak)
Edward Jenner
1796 - (Vaccination) Discovered exposure to cowpox prevented smallpox
Alexander Fleming
1928 - Penicillium fungus killed S. aureus
1940 - Penicillin mass produced
_________________is the ability of the lenses to distinguish two points.
Resolution
______________________wavelengths of light provide greater resolution
Shorter
___________________ is a measure of the light-bending ability of a medium
refractive index
Microscope Requiring - Ultrathin sections of specimens, therefore specimen is killed and fixed to side, however allows you to see what is inside specimen.
magnifies 10,000-100,000x can see viruses
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Microscope Allowing whole specimen, allows visualizing surface of specimen
Resolution 10nm - 1000-10,000x
Scanning Electron Microscopy
Coloring a specimen with a dye that emphasizes certain structures
Staining
Specimen stained with only one dye is a _____________ stain
Simple
___________________ Colored ion in stain
Chromophore
In ______________ Dyes the chromophore is positively charged
Basic dyes (pH)
In _____________ Dyes the chromophore is negatively charged.
Acidic dyes (pH)
________________ Intensifies the stain
Mordant
Bacteria have a slightly ___________________ charge
Negative
_________________ Stains used to distinguish between bacteria
Differential
(ex. Gram stain/Acid-fast stain)
In Gram Staining ____________ is the Primary Stain
Crystal Violet
In Gram Staining ____________ is the Mordant
Iodine
In Gram Staining ______________ is the Decolorizing Agent.
Alcohol/Acetone
In Gram Staining the counterstain is __________________.
Safranin
The color of Crystal Violet is _____________.
Purple
The color of Safranin is ________________.
Red/Pink
Bacterium with a waxy cell wall are best stained with __________.
Acid-fast stain
Mycobacterium and Nocardia are best stained with ________________ because of their waxy cell wall.
Acid-Fast
Mycobacterium causes TB
Primary Stain of Acid-Fast is __________________.
Carbolfuchsin
Decolorizing Agent of Acid-Fast staining is _______________.
Acid/Alcohol
Couterstain in Acid-Fast is _________________.
Methylene Blue
What color is Carbolfuchsin?
Red
Name some examples of why you need to use "Special Stains"
1.)Capsule Stain (negative staining)
2.)Endospore Stain
3.)Flagella stain
Small, unicellular cells with DNA NOT enclosed in a nucleus are _____________ cells.
Prokaryotic
Typically larger cells, with membrane bound organelles, sometimes multicellular are ___________________ cells.
Eukaryotic
Name the shape of prokaryotic cells that appear round or spherical.
Cocci
Name the shape of prokaryotic cells that appear rod-shaped.
Bacilli
Name the shape of prokaryotic cells that appear spiral shaped.
Spiral
Name some rare-shapes for prokaryotic cells
Star
Rectangular
Name and Describe the (5) possible arrangements of cocci bacteria
1.) a single cocci
2.) a diplococci (2 bound together in a single plane)
3.) Streptococci (chain)
4.) tetrad (bound in 2 planes x,y)
5.) Sarcinae (orderly bound in 3 planes - x,y.z)
6.) Staphylococci - (NONorderly, in 3 planes, CLUMPS)
What is the shape of Bacillus?
Rod Shapped
Name and describe the (4) possible arrangements of bacilli
1.) Single Bacillus (rod)
2.) Diplobacilli (2 hooked together end to end)
3.) Streptobacilli (multiple cells, hooked end to end in a chain)
4.) Coccobacillus (Squished/Pill shaped, stacked next to each other)
Describe a palisade Arrangement.
Joined at the ends, but at angles to each other, usually only a few hooked together. Example Corynebacteria (Causes diphtheria)
The bacteria shape with a slight curve is _________________
Vibrio
Ex. V. cholerae (Causes cholera)
The bacteria with a wave shape is __________________
Spirillum
The bacteria with a corkscrew shape is ______________
Spirochete
Ex. Treponema pallidum (causes syphilis)

What Colony Morphology - Shape is this
Circular

What Colony Morphology - Shape is this
Rhizoid

What Colony Morphology - Shape is this
Irregular

What Colony Morphology - Shape is this
Filamentous

What Colony Morphology - Shape is this
Spindle

What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN?
Entire

What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN?
Undulate

What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN?
Lobate

What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN?
Curled

What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN?
Rhizoid

What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN?
Filamentous

Describe the elevation Morphology of these colonies.
1. Flat
2. Raised
3. Convex
4. Pulvinate
5. Umbonate
A sticky gelatinous polymer, made up of polysaccharides and/or, usually made inside the cell and secreted to outside the cell wall is called
Glycocalyx (Sugar coat)
Name 2 types of Glycocalyx
1.) Slime Layer
2.) Capsule
A Glycocalyx that is unorganized, loosely attached to cell wall is a ________________ layer.
Slime
A Glycocalyx organized, firmly attached to cell wall, contributes to pathogenicity and prevents phagocytosis is a __________________.
Capsule
What is a biofilm?
Glycolcalyx and other material make up biofilm.
Helps cells attach to surfaces and each other.
Prokaryotic flagellum are made up of chains of _________.
flagellin
Prokaryotic flagellum are attached at their base by a structure called the _____________.
Protein hook
Prokaryotic flagellum are anchored to the wall and membrane by their _______________.
Basal body
(like a drywall anchor)
Describe a prokaryotic cell with Peritrichous flagellum.

Flagellum all-over
Describe a prokaryotic cell with Monotrichous/polar flagellum.

single flagella (at one end if polar)
Describe a prokaryotic cell with Lophotrichous/Polar flagellum.
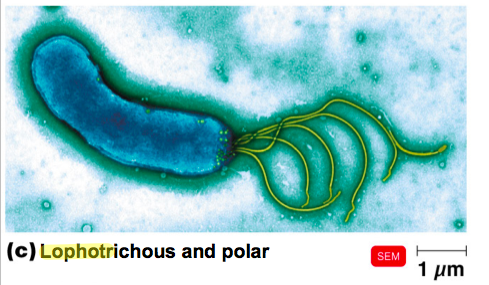
A tuft of flagella (at one end if polar)
Describe a prokaryotic cell with Amphitrichous/polar flagellum.
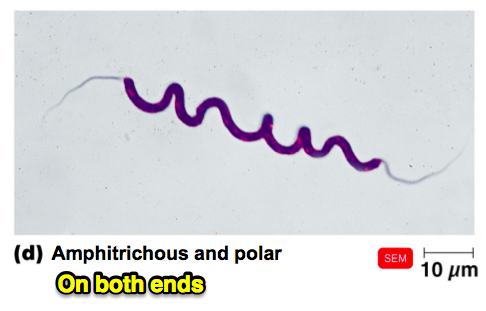
flagella on both ends
The flagella in a gram positive cell attaches in a cell wall with _______ Rings.
The flagella in a gram negative cell attaches in a cell wall with ______ Rings.
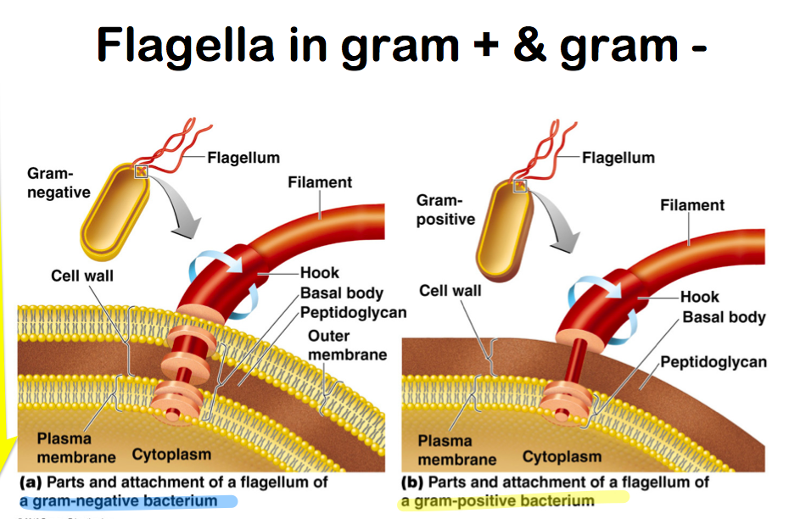
Gram Positive has - 1 Ring
Gram Negative has - 2 Rings
Name and describe the flagella like structure in spirochetes.
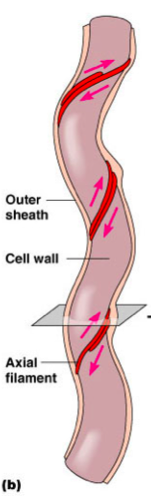
Axial Filament
Corkscrew-like movement provide taxis.
Flagellum movement in Eukaryotic cells is caused by ______________.
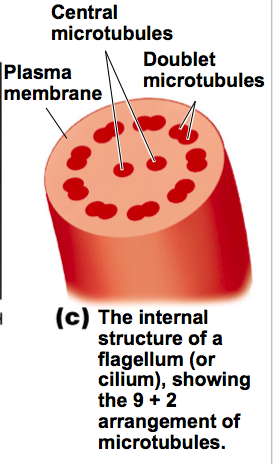
Central microtubules:Doublet Microtubles in a 9+2 arrangement.
Are Fimbriae found in some Gram POSITIVE or Gram NEGATIVE bacteria?
Some Gram Negative
What are Fibriae
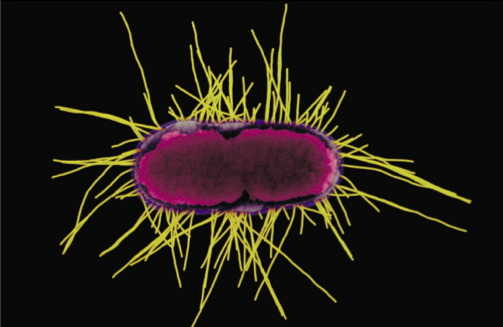
Made of protein Pilin, used for adherence of other cells/surfaces (biofilms/epithelial cells)
What are Pili
- Structure similiar to Fimbriae, but used for motility (grappling hook/gliding).
Also used for DNA transfer b/w bacteria conjugation.
____________________ bacteria have no cell wall, plasma membranes have sterols.
Mycoplasma
___________________ have no cell wall or walls without peptidoglycan appear gram-negative, but not same as gram-negative bacteria
Archaea
___________________ & __________________ species have mycolic acid in cell wall prevents uptake of Gram stain dyes identified with acid-fast stain
Mycobacterium & Nocardia
What type of Cell Wall do animal cells have?
No Cell Wall
What type of Cell Wall do Plants have?
Cellulose
What type of Cell Wall do Fungi have?
Chitin
What type of Cell Wall do Algae have?
cellulose
What type of Cell Wall do Protozoa have?
Pellicle (protein)
________________ proteins are on inner and outer surfaces include Enzymes, receptors, support
Peripheral
___________ proteins Transmembrane include Channels, carriers, pumps
Integral
Active Transport requires
ATP
Simple and Facilitated diffusion are ?
A.) Passive
B.) Active
A.) Passive
True or False:
Eukaryotic cells DO NOT use group translocation.
True
Eukaryotic cell membrane carbohydrates function as___________________?
Identity Markers
Cell membranes containing carbohydrates and sterols are found in Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic cell???
uses endocytosis (active process) - pinocytosis, phagocytosis, receptor-mediated
Eukaryotic
Gram POSITIVE or NEGATIVE? cell walls contain2 types of teichoic acid and many peptidoglycans.
Gram Positive
True or False
Gram Positive Cell Walls have an outer membrane
FALSE
True or False
Gram Negative Cell Walls have an outer membrane
TRUE
True or False
Animal cells contain Peptidoglycan.
FALSE!!!!!
A type of transport unique to prokaryotes in which glucose passes through a channel is phosphorylated and then too large to leave the cell is ____________________.
Group Translocation (of Glucose)
Crenation is ___________________.
Shrinking/wrinkling up of cell (such as in hypertonic solutions)
Cytolysis is _________________________.
bursting of cell wall (such as in hypotonic solutions)
Plasmolysis is _________________.
Shrinking away/wrinkling of a plasma membrane from a cell membrane (such as when plant cell placed in hypertonic solution)
Region in prokaryotes where DNA is located
Nucleoid
True or False
Bacteria DNA is bound to histone proteins.
FALSE
Most bacterial DNA is located on one single large circular chromosome
What is a plasmid?
In Prokaryotes - Small circular, contain DNA, generally genes coded here not critical for survival (Plasmids may be exchanged b/w organisms - thought to help replicate, segregate chromosome)
Site of protein synthesis (translation) in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
RIBOSOMES
_________________ cells have free Ribosomes and Bound Ribosomes (ER).
Eukaryotic
________________ cells have only free ribosomes (no ER)
Prokaryotic
Contins 80S ribosomes, composed of 60S and 40S sub-units
Eukaryotes
tip (remember E-even #, E-eukaryotes)
Contains 70S ribosomes, composed of 50S and 30S sub-units
Prokaryotes
__________________ inclusions are reserves of inorganic phosphate for making ATP. Made by cells in phosphate-rich environment
VOLUTIN (metachromatic granules)
Diagnostic for C. diphtheria
______________ inclusisons are glycogen and starch storage, common in bacterial but found in eukaryotic cells too
Polysaccharide granules
____________ Inclusions are stored poly-hydroxybutyric acid found in bacteria for an energy reserve
LIPID
___________ Inclusions take CO2 from air to make organic compounds
Carboxysomes
____________ gas surrounded by protein to provide buoyance in aquatic prokaryotes
Gas Vacuoles
_______________ inclusions found in bacteria that use sulfur for energy
Sulfur granules
_______________ inclusion that contain Iron Oxide, allows geo-magnetic orientation, may detoxify H2O2
Magnetosomes
A thick Wall Cell produced under unfavorable Conditions, resistant to antibiotics, temperature, dehydration, starvation.
Endospore
Endospore returning to "life"
vegitation
Process of forming an endospore
Sporulation
Site of metabolism in prokaryotes is _____________________.
Plasma membrane.
Pneumonic:
Do Keep Plates Clean Or Family Gets Sick
King Philip Came Over For Good Soup
Life
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
The science of classifying organisms, provides universal names, and reference for identifying organisms
TAXONOMY
Classified by cell types (differences in rRNA, membrane lipid structure, tRNA, sensitivity to Antibiotics
DOMAINS
(Proposed by Carl Woese in 1978)
ENDOSYMBIOSIS
Carolus Linnaeus
Defined Hierarchical classification (TAXONOMY) 1700's
Eukaryotic species (definition)
a group of closely related organism that breed among themselves.
Prokaryotic Species (definition)
a population of cells with similar characteristics
Culture
Cells grown in laboratory
Clone
Population of cells derived from a single cell
Strain
genetically different cells w/in a clone
Selective Media
Suppresses unwanted microbs; encourages desired microbs
Differential Media
Differentiation of colonies of desired microbs from others
Phage
a virus that infects bacteria
Western Blot is used for Protein or DNA?
PROTEIN ONLY