Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Lecture Exam Chapters - (1,3,4,9,10,11,18)
front 1 Bacteria
| back 1 Prokaryotic |
front 2 Protozoa
| back 2 Eukaryotic |
front 3 Viruses
| back 3 Acellular |
front 4 _________________ is a Symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits, the other is unaffected. | back 4 Commensalism |
front 5 ______________ is a Symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit. | back 5 Mutualism |
front 6 ______________ is a Symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits, the other is harmed. | back 6 Parasitism |
front 7 ______________ protect us from overgrowth of harmful bacteria.
| back 7 Normal microbiota (used to be called flora) |
front 8 Bacteria that are photosynthetic are _______________. | back 8 Producers |
front 9 Bacteria/fungus that recycle essential nutrients are _______________ | back 9 Decomposers |
front 10 Bioremediation is | back 10 Ex. Conveting pollutants to harmless molecules
|
front 11 ROBERT HOOKE | back 11 1665 - See first Cells
|
front 12 Anton van Leeuwewnhoek | back 12 "Father of Microscopy"
|
front 13 Francesco Redi | back 13 1699
|
front 14 CELL THEORY | back 14 1.) All living things are composed of cells
|
front 15 John Needham | back 15 1745
|
front 16 Lazzaro Spallanzani | back 16 1765
|
front 17 Rudolf Virchow | back 17 1858
|
front 18 Louis Pasteur | back 18 1861-disproved spontaneous generation *Biogenesis – life comes from life
|
front 19 Ignaz Semmelweiss | back 19 1840’s
|
front 20 John Lister | back 20 1860s (Listerine named after him)
|
front 21 Robert Koch | back 21 1846
|
front 22 Koch's Postulates | back 22 1. The specific organism should be shown to be present in all cases of animals suffering from a specific disease, but should not be found in healthy animals
|
front 23 John Snow | back 23 Founder of Epidemiology
|
front 24 Edward Jenner | back 24 1796 - (Vaccination) Discovered exposure to cowpox prevented smallpox |
front 25 Alexander Fleming | back 25 1928 - Penicillium fungus killed S. aureus
|
front 26 _________________is the ability of the lenses to distinguish two points. | back 26 Resolution |
front 27 ______________________wavelengths of light provide greater resolution | back 27 Shorter |
front 28 ___________________ is a measure of the light-bending ability of a medium | back 28 refractive index |
front 29 Microscope Requiring - Ultrathin sections of specimens, therefore specimen is killed and fixed to side, however allows you to see what is inside specimen.
| back 29 Transmission Electron Microscopy |
front 30 Microscope Allowing whole specimen, allows visualizing surface of specimen
| back 30 Scanning Electron Microscopy |
front 31 Coloring a specimen with a dye that emphasizes certain structures | back 31 Staining |
front 32 Specimen stained with only one dye is a _____________ stain | back 32 Simple |
front 33 ___________________ Colored ion in stain | back 33 Chromophore |
front 34 In ______________ Dyes the chromophore is positively charged | back 34 Basic dyes (pH) |
front 35 In _____________ Dyes the chromophore is negatively charged. | back 35 Acidic dyes (pH) |
front 36 ________________ Intensifies the stain | back 36 Mordant |
front 37 Bacteria have a slightly ___________________ charge | back 37 Negative |
front 38 _________________ Stains used to distinguish between bacteria | back 38 Differential
|
front 39 In Gram Staining ____________ is the Primary Stain | back 39 Crystal Violet |
front 40 In Gram Staining ____________ is the Mordant | back 40 Iodine |
front 41 In Gram Staining ______________ is the Decolorizing Agent. | back 41 Alcohol/Acetone |
front 42 In Gram Staining the counterstain is __________________. | back 42 Safranin |
front 43 The color of Crystal Violet is _____________. | back 43 Purple |
front 44 The color of Safranin is ________________. | back 44 Red/Pink |
front 45 Bacterium with a waxy cell wall are best stained with __________. | back 45 Acid-fast stain |
front 46 Mycobacterium and Nocardia are best stained with ________________ because of their waxy cell wall. | back 46 Acid-Fast
|
front 47 Primary Stain of Acid-Fast is __________________. | back 47 Carbolfuchsin |
front 48 Decolorizing Agent of Acid-Fast staining is _______________. | back 48 Acid/Alcohol |
front 49 Couterstain in Acid-Fast is _________________. | back 49 Methylene Blue |
front 50 What color is Carbolfuchsin? | back 50 Red |
front 51 Name some examples of why you need to use "Special Stains" | back 51 1.)Capsule Stain (negative staining)
|
front 52 Small, unicellular cells with DNA NOT enclosed in a nucleus are _____________ cells. | back 52 Prokaryotic |
front 53 Typically larger cells, with membrane bound organelles, sometimes multicellular are ___________________ cells. | back 53 Eukaryotic |
front 54 Name the shape of prokaryotic cells that appear round or spherical. | back 54 Cocci |
front 55 Name the shape of prokaryotic cells that appear rod-shaped. | back 55 Bacilli |
front 56 Name the shape of prokaryotic cells that appear spiral shaped. | back 56 Spiral |
front 57 Name some rare-shapes for prokaryotic cells | back 57 Star
|
front 58 Name and Describe the (5) possible arrangements of cocci bacteria | back 58 1.) a single cocci
|
front 59 What is the shape of Bacillus? | back 59 Rod Shapped |
front 60 Name and describe the (4) possible arrangements of bacilli | back 60 1.) Single Bacillus (rod)
|
front 61 Describe a palisade Arrangement. | back 61 Joined at the ends, but at angles to each other, usually only a few hooked together. Example Corynebacteria (Causes diphtheria) |
front 62 The bacteria shape with a slight curve is _________________ | back 62 Vibrio
|
front 63 The bacteria with a wave shape is __________________ | back 63 Spirillum |
front 64 The bacteria with a corkscrew shape is ______________ | back 64 Spirochete
|
front 65  What Colony Morphology - Shape is this | back 65 Circular |
front 66  What Colony Morphology - Shape is this | back 66 Rhizoid |
front 67  What Colony Morphology - Shape is this | back 67 Irregular |
front 68  What Colony Morphology - Shape is this | back 68 Filamentous |
front 69  What Colony Morphology - Shape is this | back 69 Spindle |
front 70  What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN? | back 70 Entire |
front 71  What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN? | back 71 Undulate |
front 72  What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN? | back 72 Lobate |
front 73  What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN? | back 73 Curled |
front 74  What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN? | back 74 Rhizoid |
front 75  What is the Colony Morphology of this MARGIN? | back 75 Filamentous |
front 76  Describe the elevation Morphology of these colonies. | back 76 1. Flat
|
front 77 A sticky gelatinous polymer, made up of polysaccharides and/or, usually made inside the cell and secreted to outside the cell wall is called | back 77 Glycocalyx (Sugar coat) |
front 78 Name 2 types of Glycocalyx | back 78 1.) Slime Layer
|
front 79 A Glycocalyx that is unorganized, loosely attached to cell wall is a ________________ layer. | back 79 Slime |
front 80 A Glycocalyx organized, firmly attached to cell wall, contributes to pathogenicity and prevents phagocytosis is a __________________. | back 80 Capsule |
front 81 What is a biofilm? | back 81 Glycolcalyx and other material make up biofilm.
|
front 82 Prokaryotic flagellum are made up of chains of _________. | back 82 flagellin |
front 83 Prokaryotic flagellum are attached at their base by a structure called the _____________. | back 83 Protein hook |
front 84 Prokaryotic flagellum are anchored to the wall and membrane by their _______________. | back 84 Basal body
|
front 85 Describe a prokaryotic cell with Peritrichous flagellum. | back 85  Flagellum all-over |
front 86 Describe a prokaryotic cell with Monotrichous/polar flagellum. | back 86  single flagella (at one end if polar) |
front 87 Describe a prokaryotic cell with Lophotrichous/Polar flagellum. | back 87 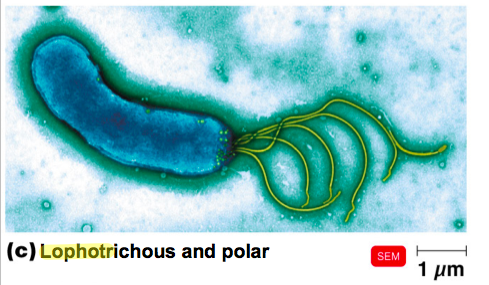 A tuft of flagella (at one end if polar) |
front 88 Describe a prokaryotic cell with Amphitrichous/polar flagellum. | back 88 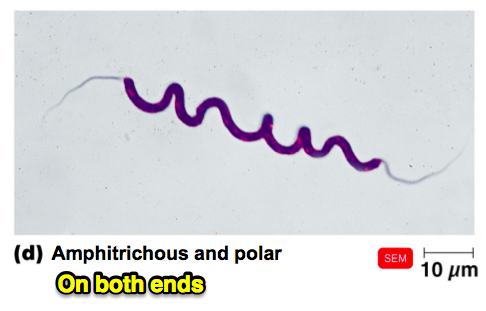 flagella on both ends |
front 89 The flagella in a gram positive cell attaches in a cell wall with _______ Rings.
| back 89 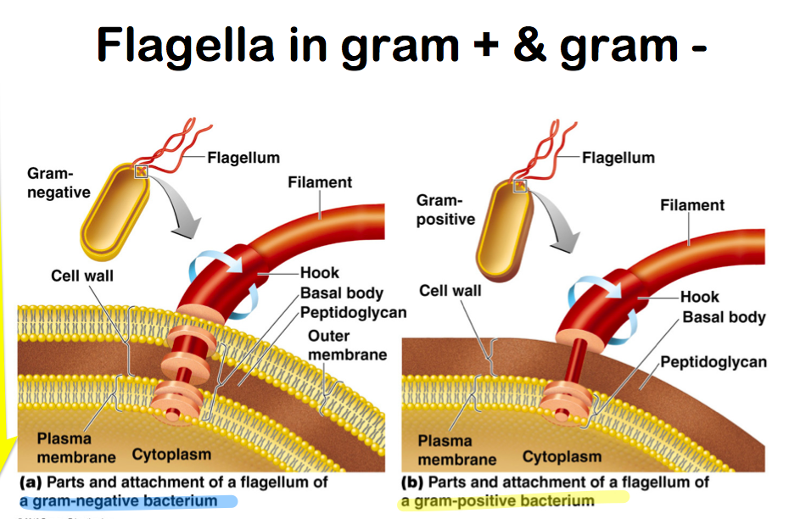 Gram Positive has - 1 Ring
|
front 90 Name and describe the flagella like structure in spirochetes. | back 90 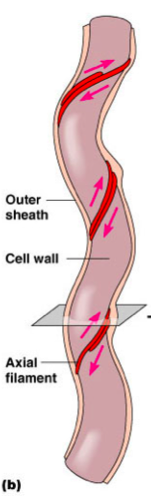 Axial Filament
|
front 91 Flagellum movement in Eukaryotic cells is caused by ______________. | back 91 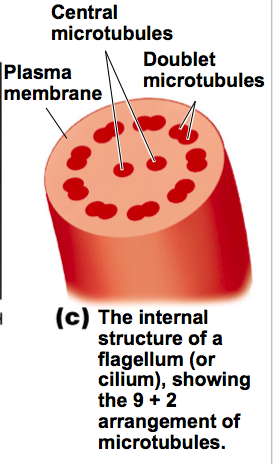 Central microtubules:Doublet Microtubles in a 9+2 arrangement. |
front 92 Are Fimbriae found in some Gram POSITIVE or Gram NEGATIVE bacteria? | back 92 Some Gram Negative |
front 93 What are Fibriae | back 93 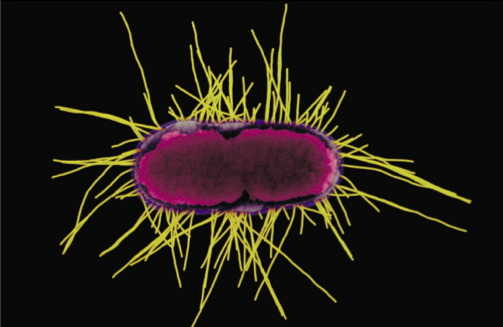 Made of protein Pilin, used for adherence of other cells/surfaces (biofilms/epithelial cells) |
front 94 What are Pili | back 94 - Structure similiar to Fimbriae, but used for motility (grappling hook/gliding).
|
front 95 ____________________ bacteria have no cell wall, plasma membranes have sterols. | back 95 Mycoplasma |
front 96 ___________________ have no cell wall or walls without peptidoglycan appear gram-negative, but not same as gram-negative bacteria | back 96 Archaea |
front 97 ___________________ & __________________ species have mycolic acid in cell wall prevents uptake of Gram stain dyes identified with acid-fast stain | back 97 Mycobacterium & Nocardia |
front 98 What type of Cell Wall do animal cells have? | back 98 No Cell Wall |
front 99 What type of Cell Wall do Plants have? | back 99 Cellulose |
front 100 What type of Cell Wall do Fungi have? | back 100 Chitin |
front 101 What type of Cell Wall do Algae have? | back 101 cellulose |
front 102 What type of Cell Wall do Protozoa have? | back 102 Pellicle (protein) |
front 103 ________________ proteins are on inner and outer surfaces include Enzymes, receptors, support | back 103 Peripheral |
front 104 ___________ proteins Transmembrane include Channels, carriers, pumps | back 104 Integral |
front 105 Active Transport requires | back 105 ATP |
front 106 Simple and Facilitated diffusion are ?
| back 106 A.) Passive |
front 107 True or False:
| back 107 True |
front 108 Eukaryotic cell membrane carbohydrates function as___________________? | back 108 Identity Markers |
front 109 Cell membranes containing carbohydrates and sterols are found in Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Cells | back 109 Eukaryotic |
front 110 Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic cell???
| back 110 Eukaryotic |
front 111 Gram POSITIVE or NEGATIVE? cell walls contain2 types of teichoic acid and many peptidoglycans. | back 111 Gram Positive |
front 112 True or False
| back 112 FALSE |
front 113 True or False
| back 113 TRUE |
front 114 True or False
| back 114 FALSE!!!!! |
front 115 A type of transport unique to prokaryotes in which glucose passes through a channel is phosphorylated and then too large to leave the cell is ____________________. | back 115 Group Translocation (of Glucose) |
front 116 Crenation is ___________________. | back 116 Shrinking/wrinkling up of cell (such as in hypertonic solutions) |
front 117 Cytolysis is _________________________. | back 117 bursting of cell wall (such as in hypotonic solutions) |
front 118 Plasmolysis is _________________. | back 118 Shrinking away/wrinkling of a plasma membrane from a cell membrane (such as when plant cell placed in hypertonic solution) |
front 119 Region in prokaryotes where DNA is located | back 119 Nucleoid |
front 120 True or False
| back 120 FALSE
|
front 121 What is a plasmid? | back 121 In Prokaryotes - Small circular, contain DNA, generally genes coded here not critical for survival (Plasmids may be exchanged b/w organisms - thought to help replicate, segregate chromosome) |
front 122 Site of protein synthesis (translation) in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes | back 122 RIBOSOMES |
front 123 _________________ cells have free Ribosomes and Bound Ribosomes (ER). | back 123 Eukaryotic |
front 124 ________________ cells have only free ribosomes (no ER) | back 124 Prokaryotic |
front 125 Contins 80S ribosomes, composed of 60S and 40S sub-units | back 125 Eukaryotes
|
front 126 Contains 70S ribosomes, composed of 50S and 30S sub-units | back 126 Prokaryotes |
front 127 __________________ inclusions are reserves of inorganic phosphate for making ATP. Made by cells in phosphate-rich environment | back 127 VOLUTIN (metachromatic granules)
|
front 128 ______________ inclusisons are glycogen and starch storage, common in bacterial but found in eukaryotic cells too | back 128 Polysaccharide granules |
front 129 ____________ Inclusions are stored poly-hydroxybutyric acid found in bacteria for an energy reserve | back 129 LIPID |
front 130 ___________ Inclusions take CO2 from air to make organic compounds | back 130 Carboxysomes |
front 131 ____________ gas surrounded by protein to provide buoyance in aquatic prokaryotes | back 131 Gas Vacuoles |
front 132 _______________ inclusions found in bacteria that use sulfur for energy | back 132 Sulfur granules |
front 133 _______________ inclusion that contain Iron Oxide, allows geo-magnetic orientation, may detoxify H2O2 | back 133 Magnetosomes |
front 134 A thick Wall Cell produced under unfavorable Conditions, resistant to antibiotics, temperature, dehydration, starvation. | back 134 Endospore |
front 135 Endospore returning to "life" | back 135 vegitation |
front 136 Process of forming an endospore | back 136 Sporulation |
front 137 Site of metabolism in prokaryotes is _____________________. | back 137 Plasma membrane. |
front 138 Pneumonic:
| back 138 Life
|
front 139 The science of classifying organisms, provides universal names, and reference for identifying organisms | back 139 TAXONOMY |
front 140 Classified by cell types (differences in rRNA, membrane lipid structure, tRNA, sensitivity to Antibiotics | back 140 DOMAINS
|
front 141 ENDOSYMBIOSIS | back 141 no data |
front 142 Carolus Linnaeus | back 142 Defined Hierarchical classification (TAXONOMY) 1700's |
front 143 Eukaryotic species (definition) | back 143 a group of closely related organism that breed among themselves. |
front 144 Prokaryotic Species (definition) | back 144 a population of cells with similar characteristics |
front 145 Culture | back 145 Cells grown in laboratory |
front 146 Clone | back 146 Population of cells derived from a single cell |
front 147 Strain | back 147 genetically different cells w/in a clone |
front 148 Selective Media | back 148 Suppresses unwanted microbs; encourages desired microbs |
front 149 Differential Media | back 149 Differentiation of colonies of desired microbs from others |
front 150 Phage | back 150 a virus that infects bacteria |
front 151 Western Blot is used for Protein or DNA? | back 151 PROTEIN ONLY |