Chapter 7: The Endocrine System - Endocrinology

Chapter 7 Introduction and Overview of the Endocrine System

Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
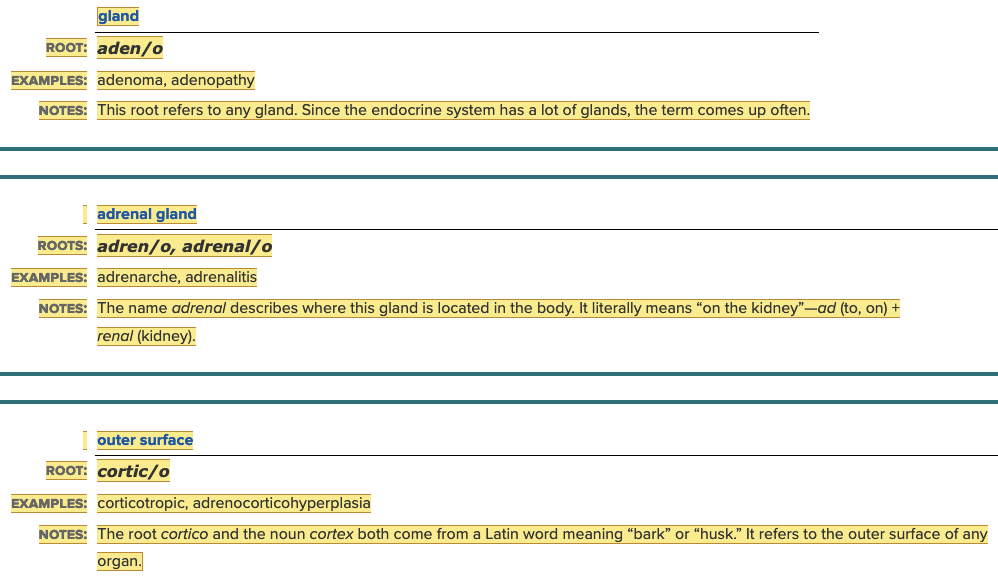
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 1
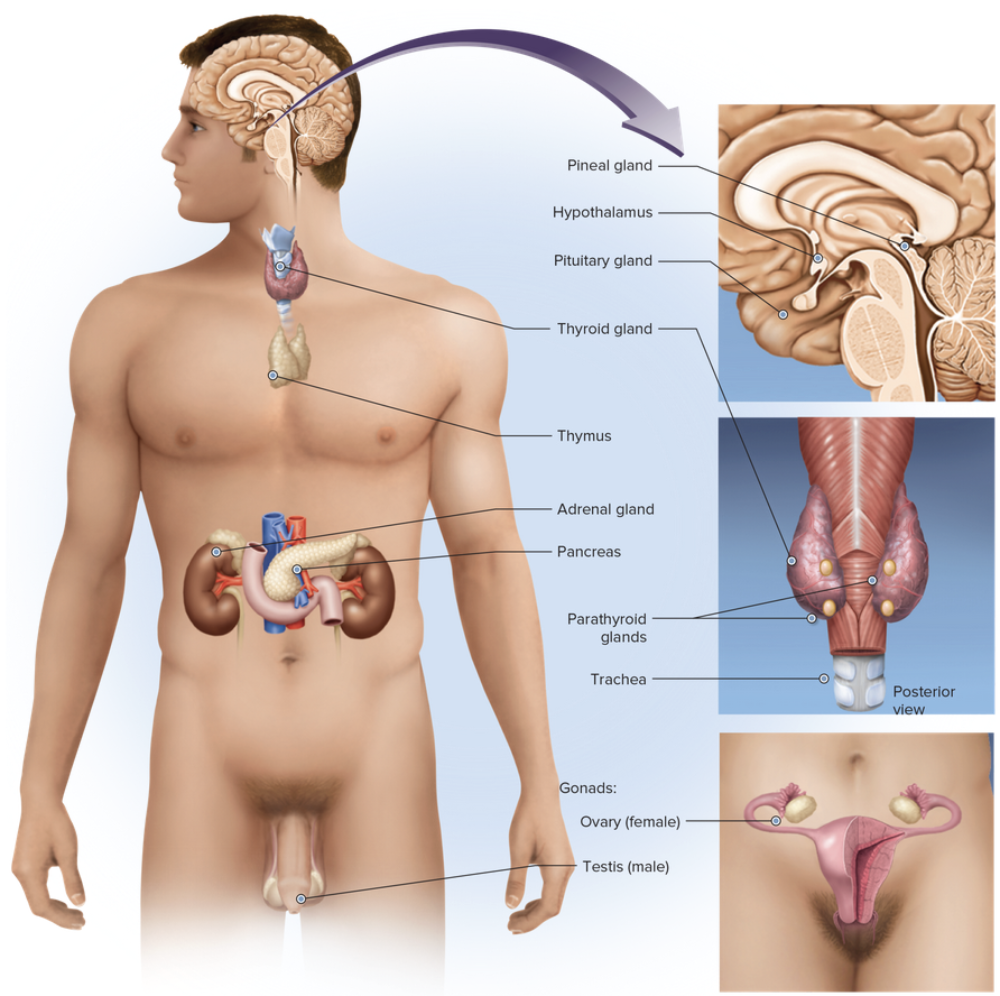
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 2

Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 3
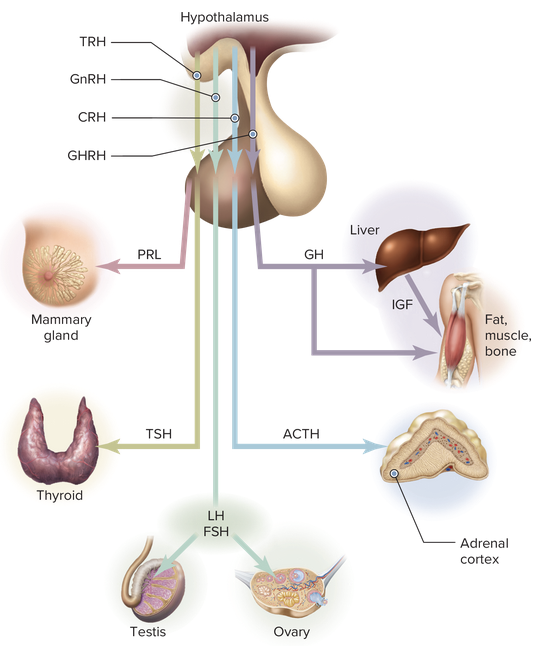
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 4
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 5
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 1
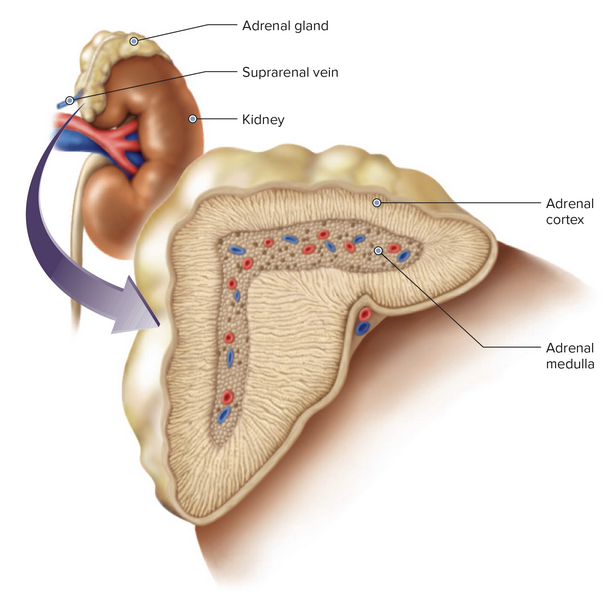
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 2
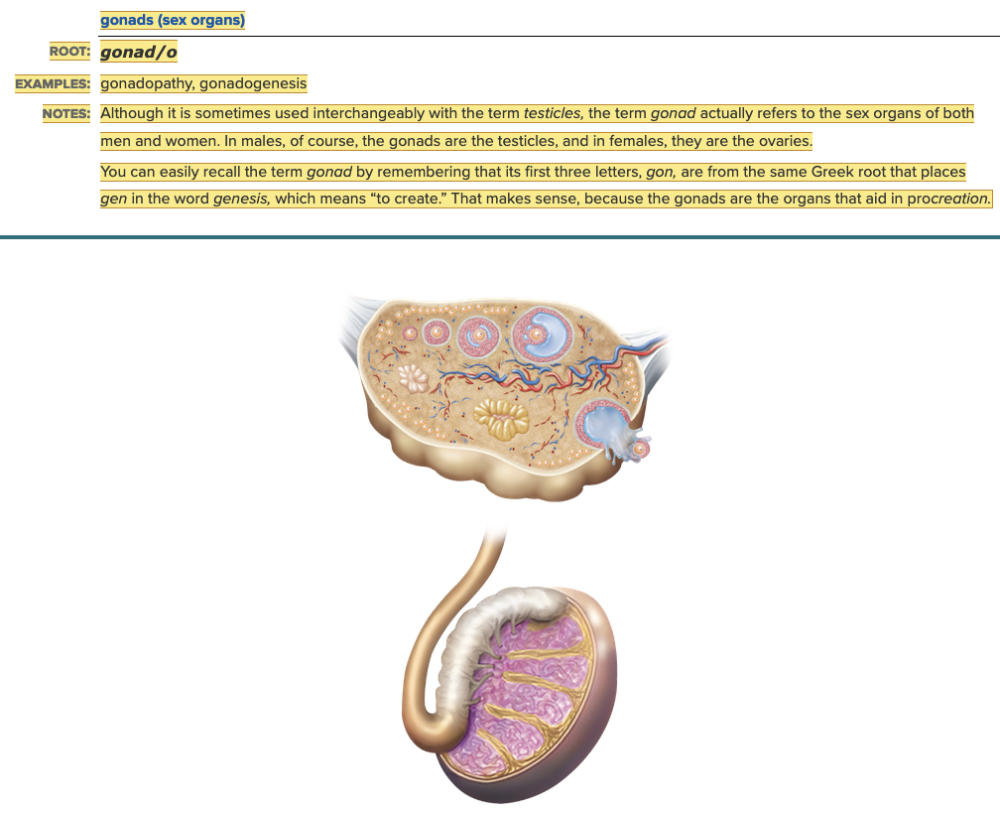
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 3
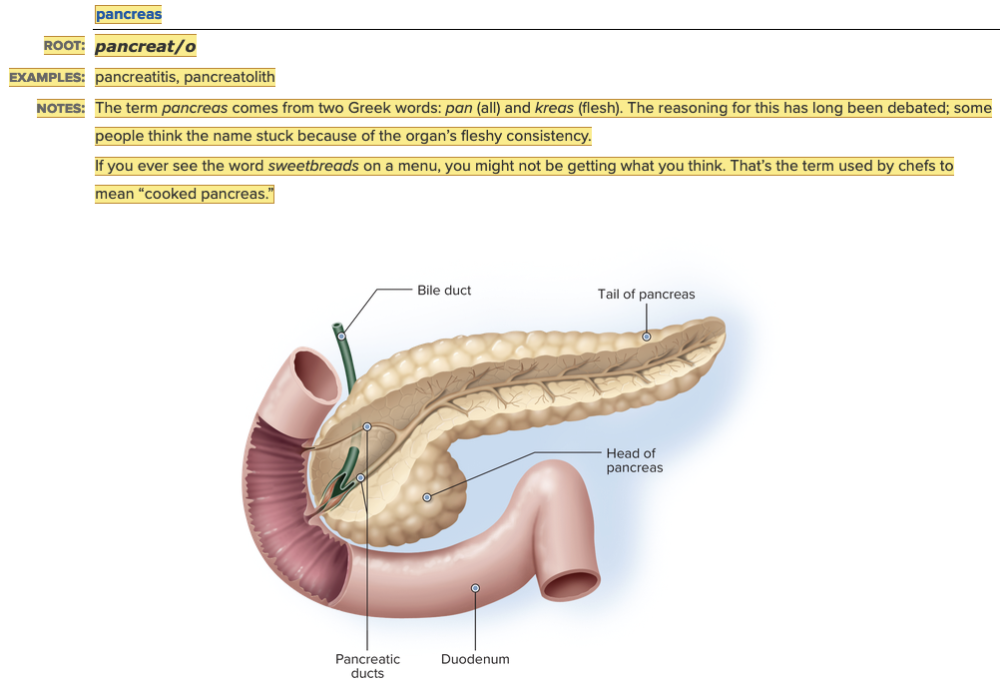
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 4

Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 5

Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 6
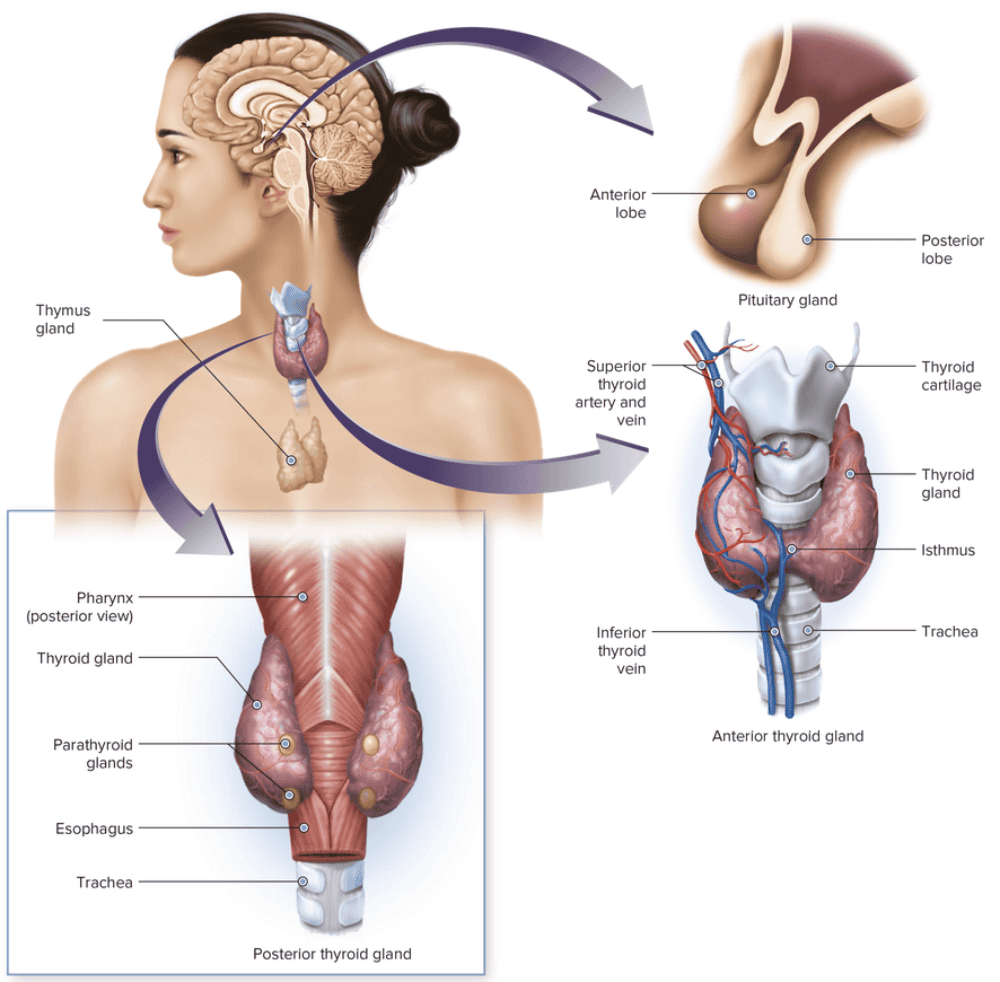
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 7
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 8

Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 9

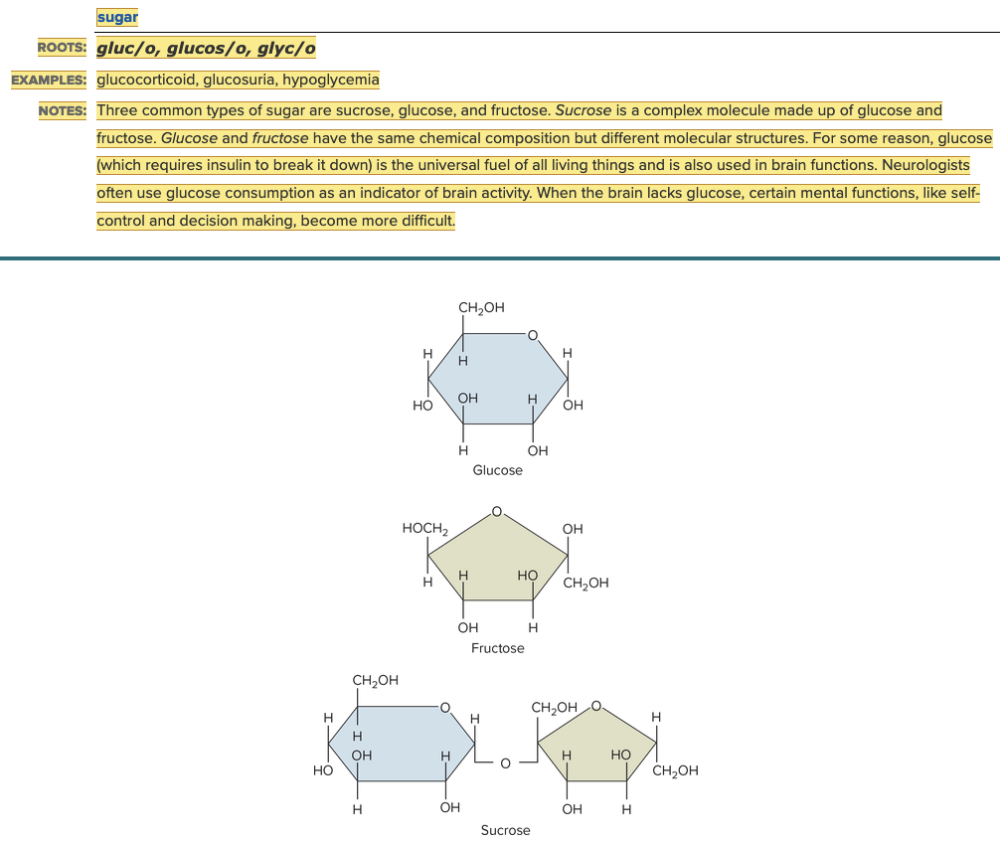
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Part 1
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Part 2

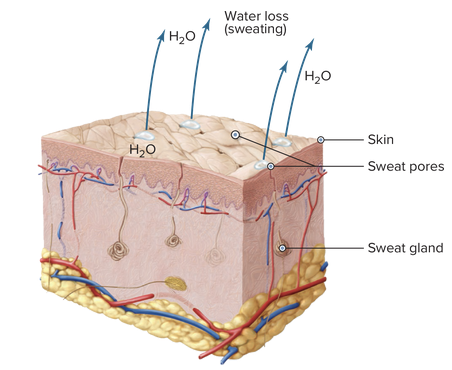
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Part 3
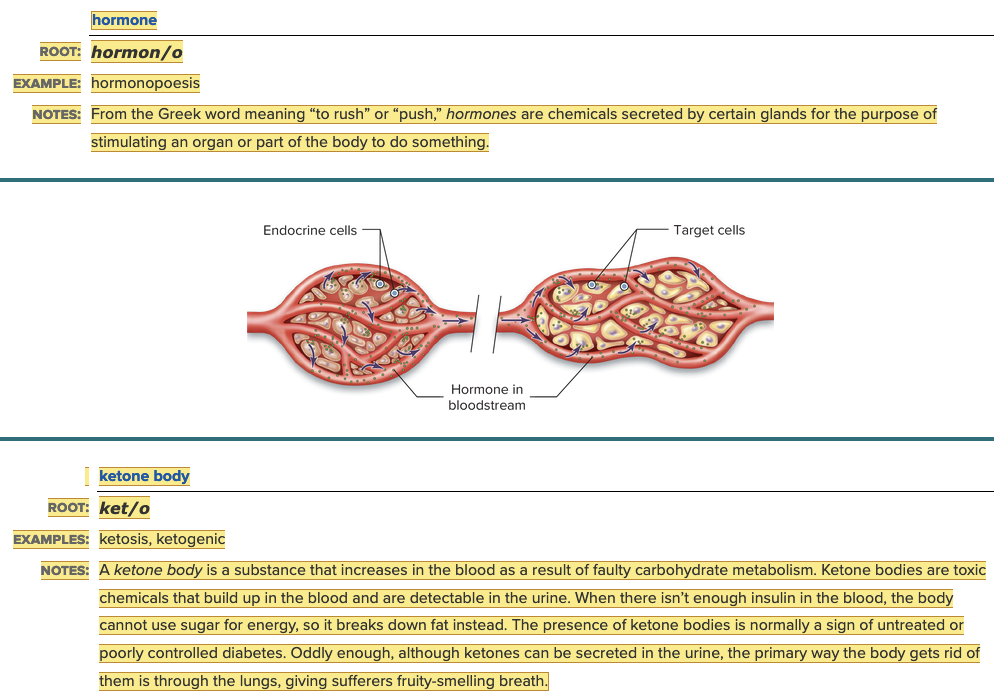
Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Word Roots for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Table

Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Suffixes for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Table Part 1

Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System
Suffixes for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Table Part 2

Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2.
Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4.

Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 5, 6.

Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 7, 8.

Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10.

Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective Part 1
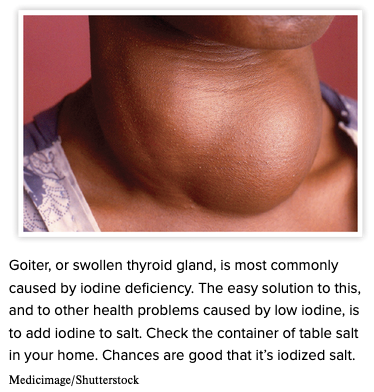
Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective Part 2
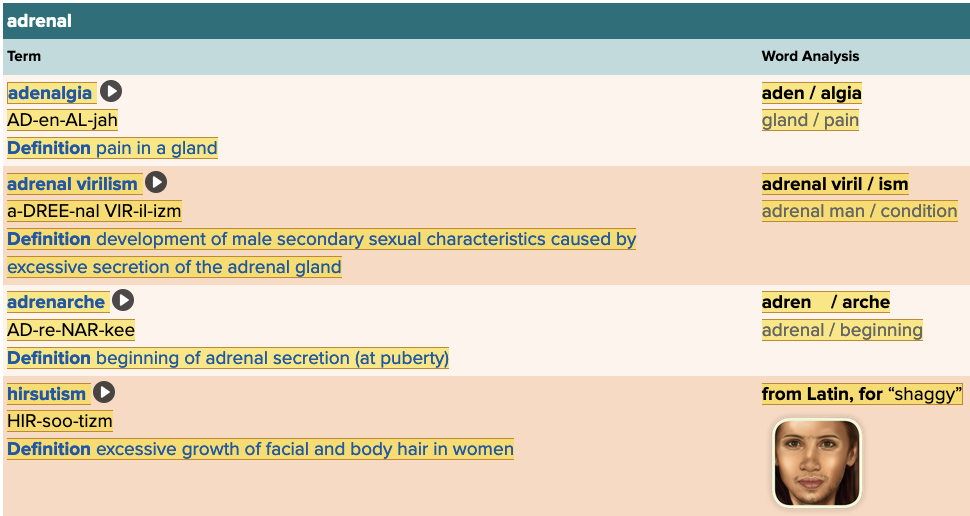
Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective: Adrenal Table
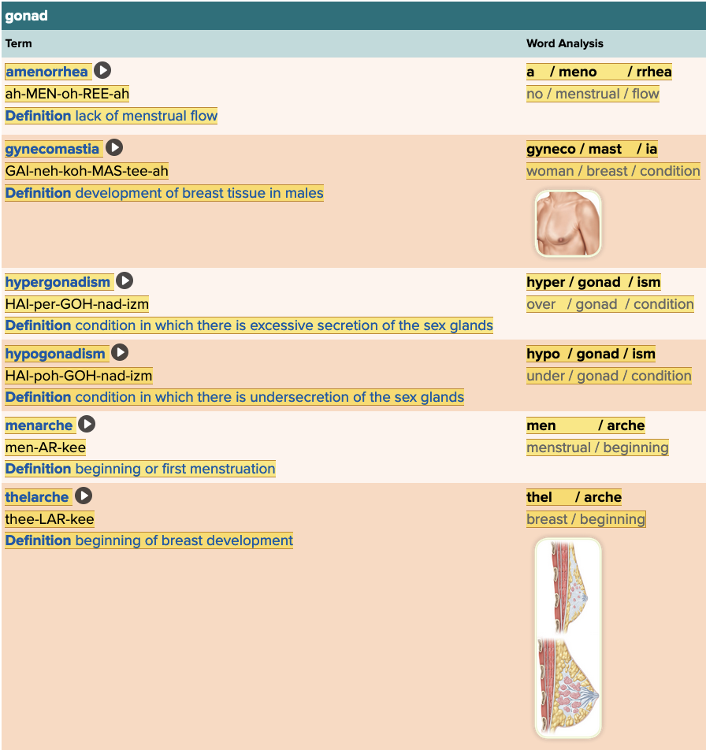
Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective: Gonad Table
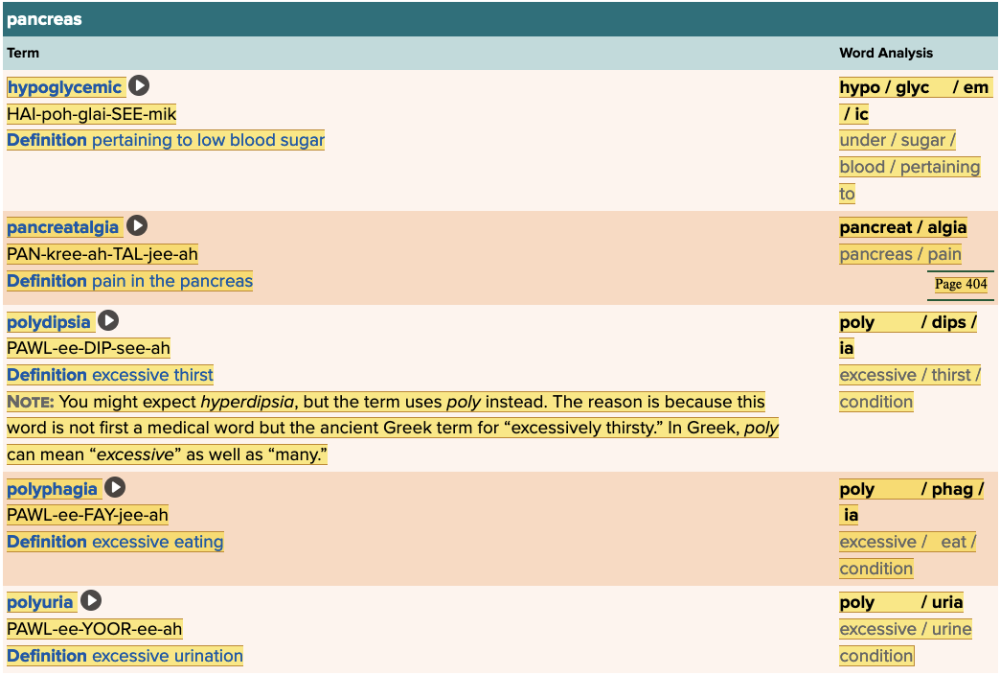
Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective: Pancreas Table
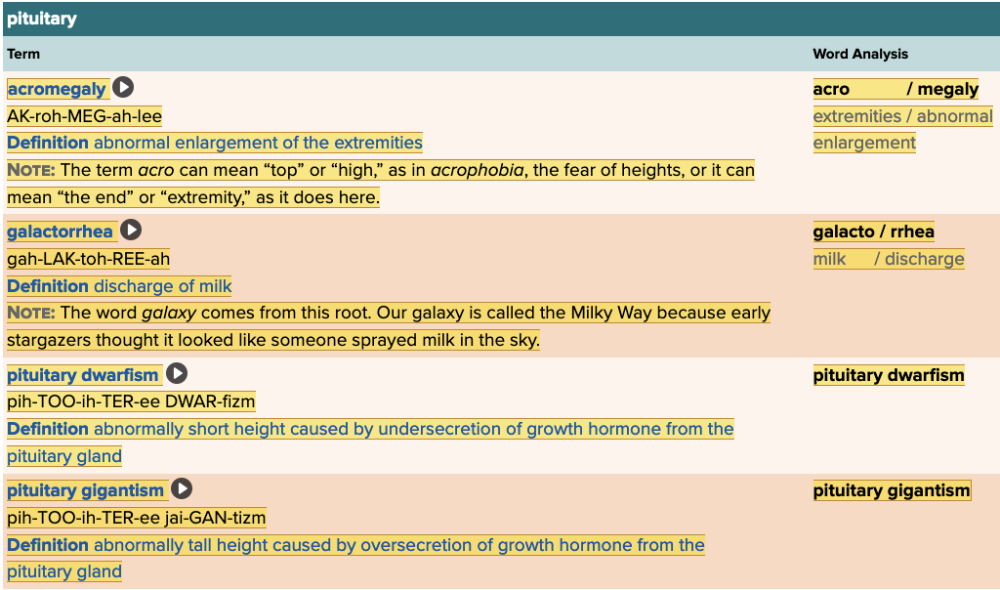
Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective: Pituitary Table
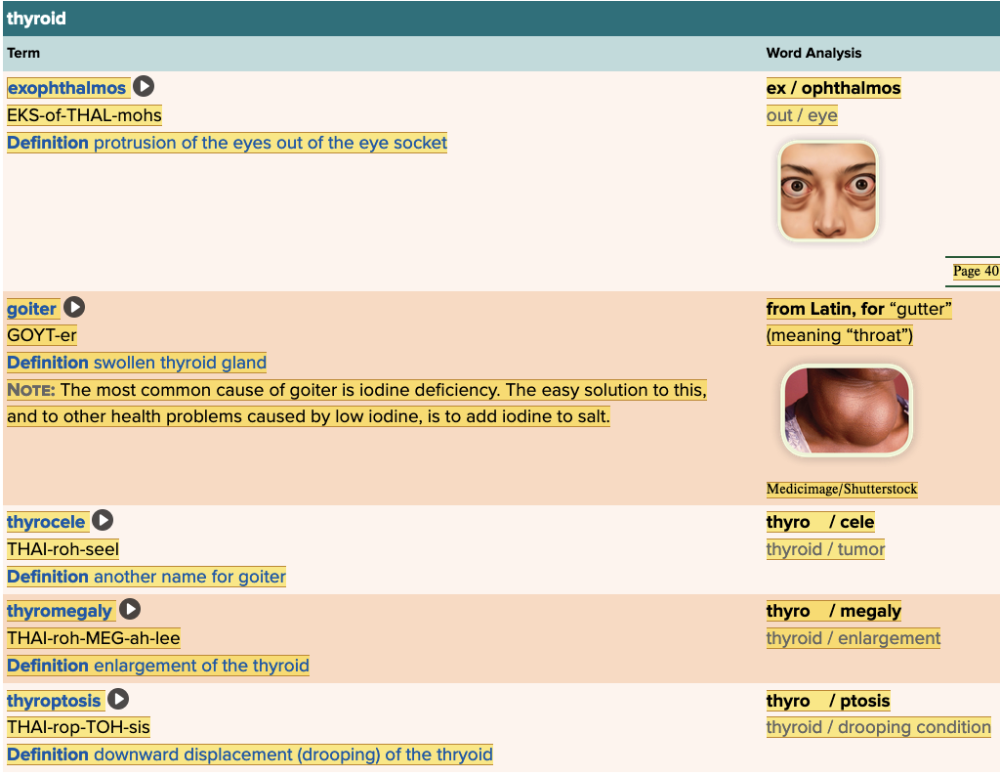
Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective: Thyroid Table

Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 1.

Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 2.

Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4.

Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 5.

Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 6 Part 1.


Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 6 Part 2.

Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 7.

Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective Part 1
Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective Part 2
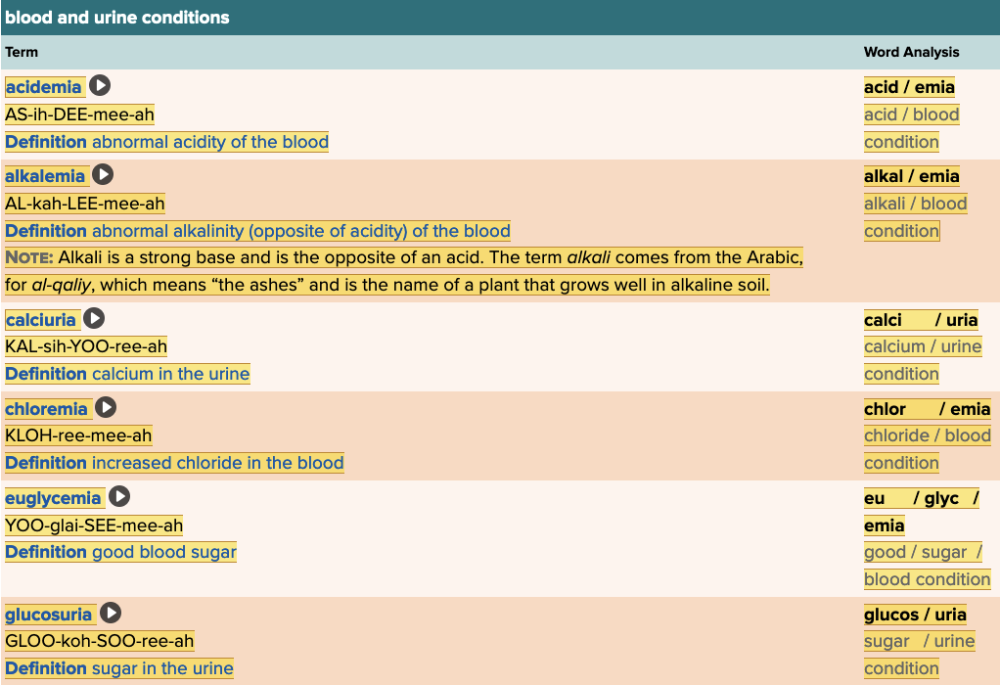
Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Blood And Urine Conditions Table Part 1

Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Blood And Urine Conditions Table Part 2

Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Blood And Urine Conditions Table Part 3

Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Blood And Urine Conditions Table Part 4
Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Hormones Table Part 1

Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Hormones Table Part 2
Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Results Table
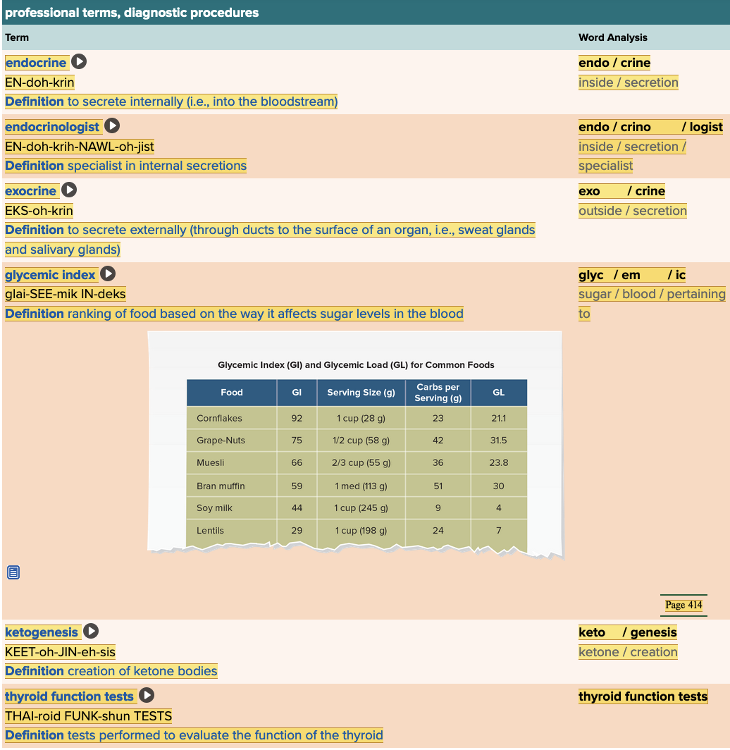
Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Professional Terms, Diagnostic Procedures Table

Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Radiology Table

Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 1.

Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 2.
Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 3.

Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5.
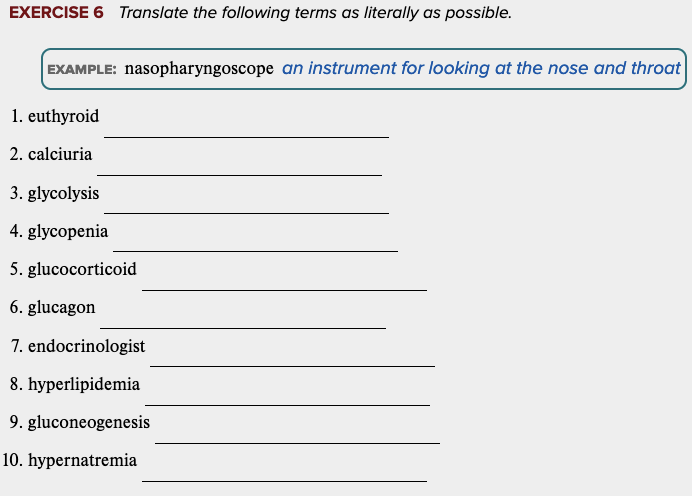
Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 6.

Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 7.

Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 8.

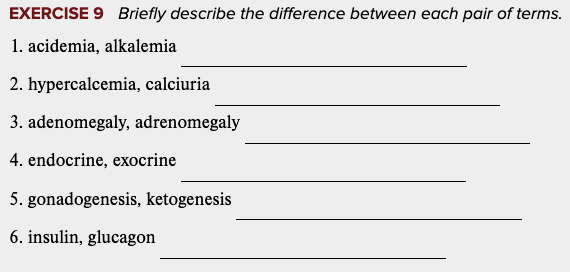
Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 9.

Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment Part 1

Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment Part 2
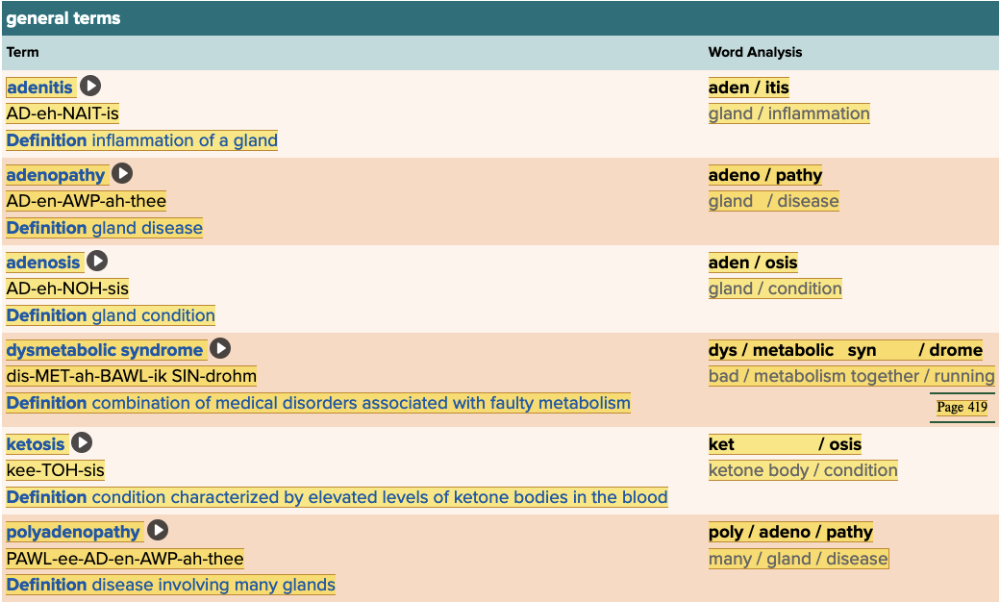
Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: General Terms Table
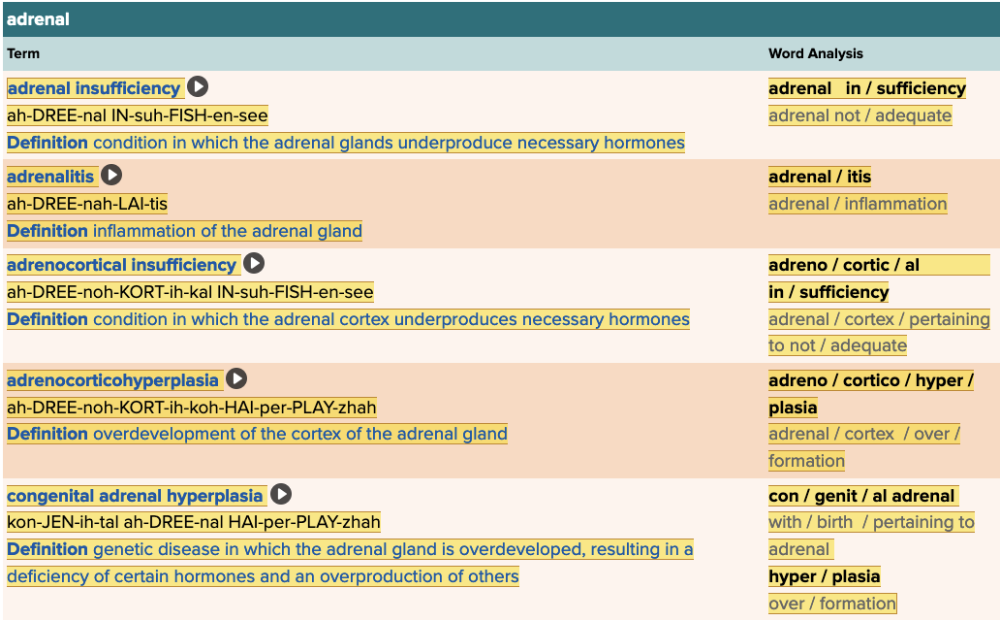
Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Adrenal Table
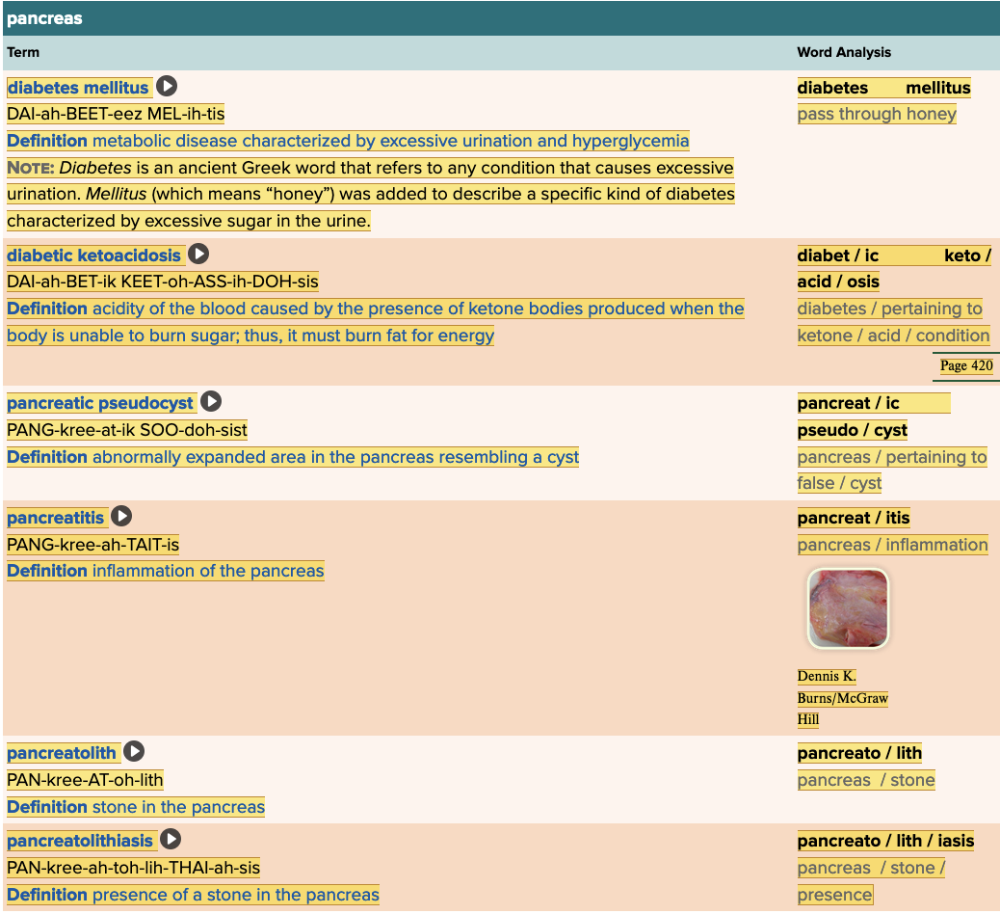
Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Pancreas Table
Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Pituitary Table
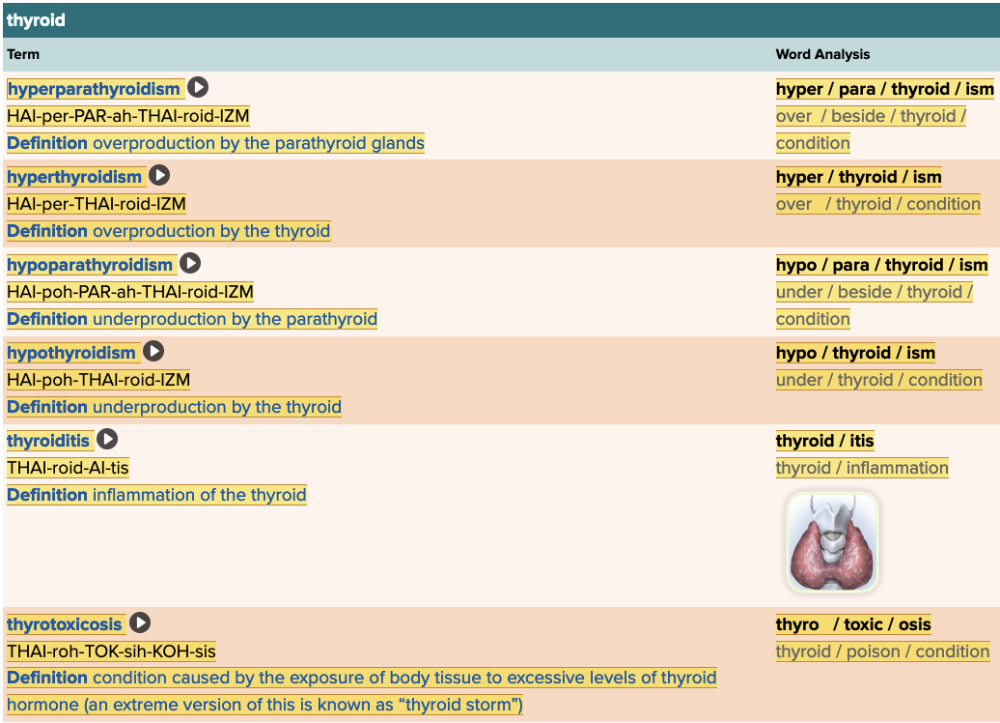
Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Thyroid Table

Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Oncology Table Part 1
Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Oncology Table Part 2

Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 1.
Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 2.

Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 3.

Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 4.
Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 5.

Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 6.

Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 7.

Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan Part 1
Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan Part 2
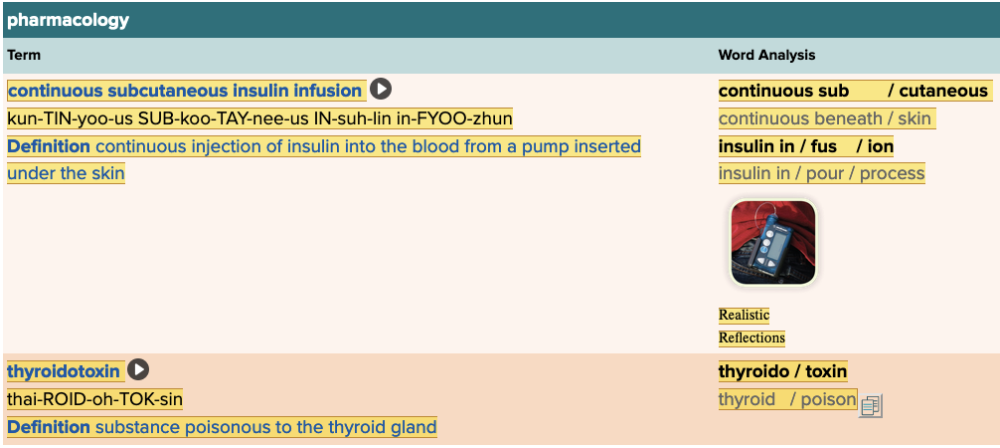
Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Pharmacology Table

Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: General Terms Table
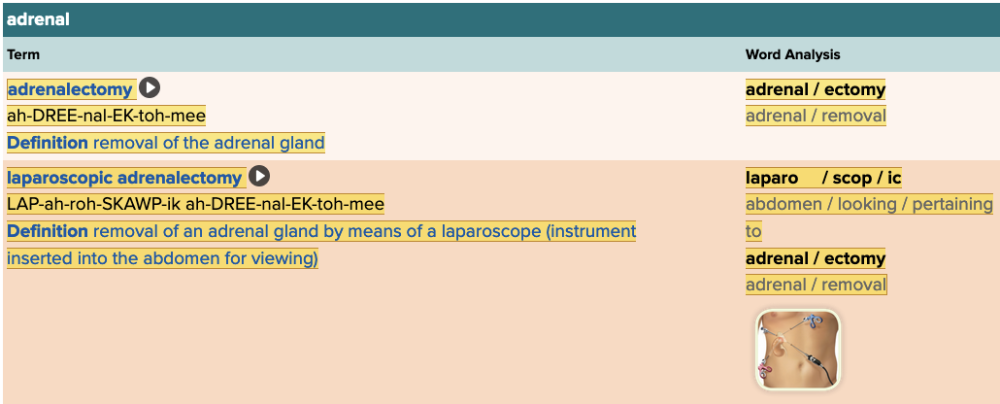
Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Adrenal Table
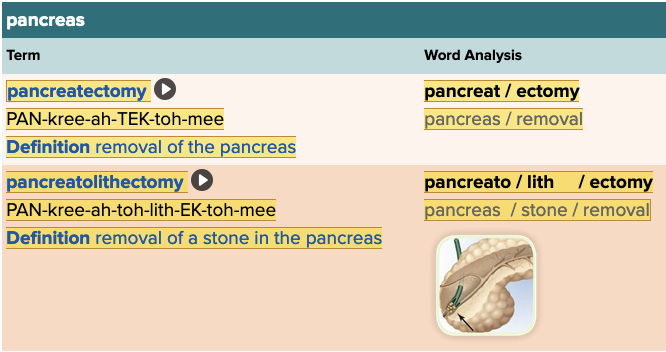
Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Pancreas Table
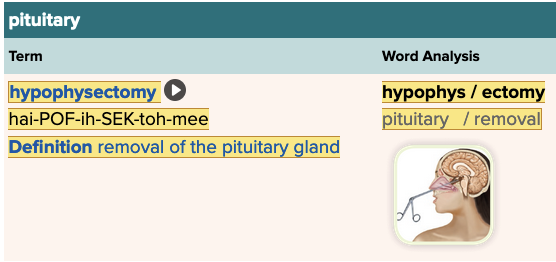
Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Pituitary Table
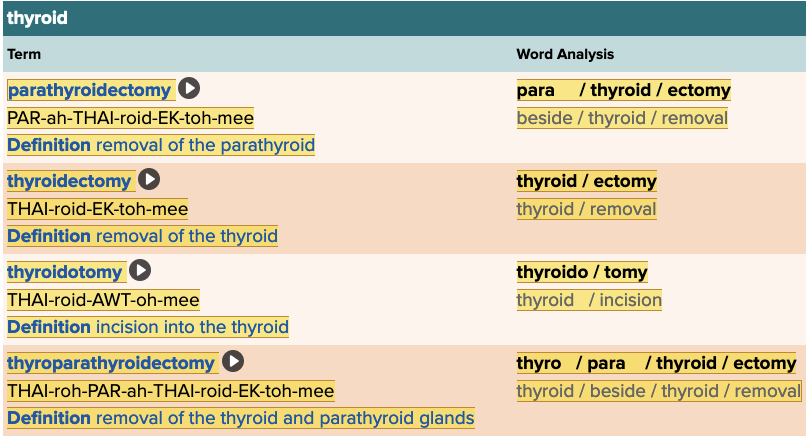
Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Thyroid Table

Learning Outcome 7.5 Exercises: Exercise 1.
Learning Outcome 7.5 Exercises: Exercise 2, 3.

Learning Outcome 7.5 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5.

Learning Outcome 7.5 Exercises: Exercise 6.

Chapter 7.6 Abbreviations
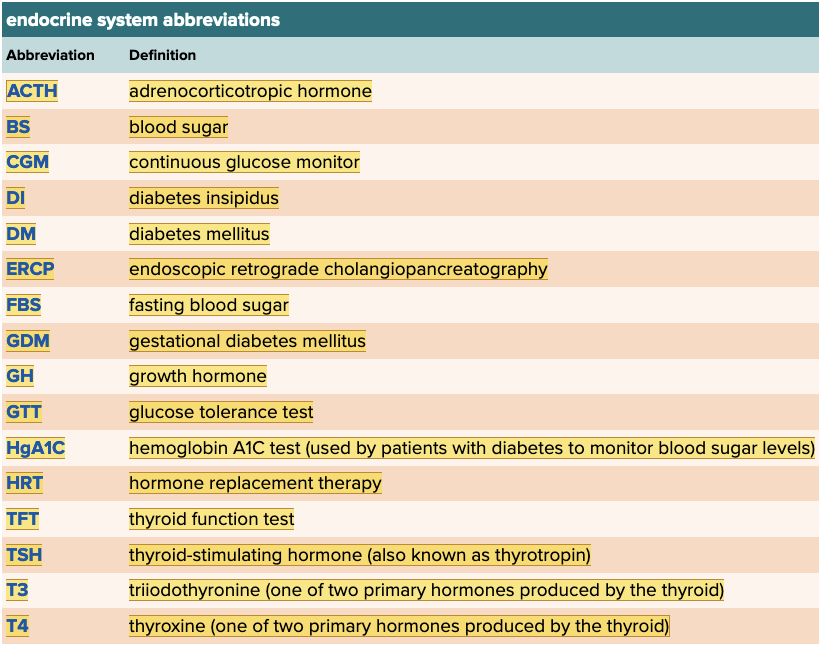
Chapter 7.6 Abbreviations
- Endocrine System Abbreviations Table

Learning Outcome 7.6 Exercises: Exercise 1.

Learning Outcome 7.6 Exercises: Exercise 2.

Learning Outcome 7.6 Exercises: Exercise 3.

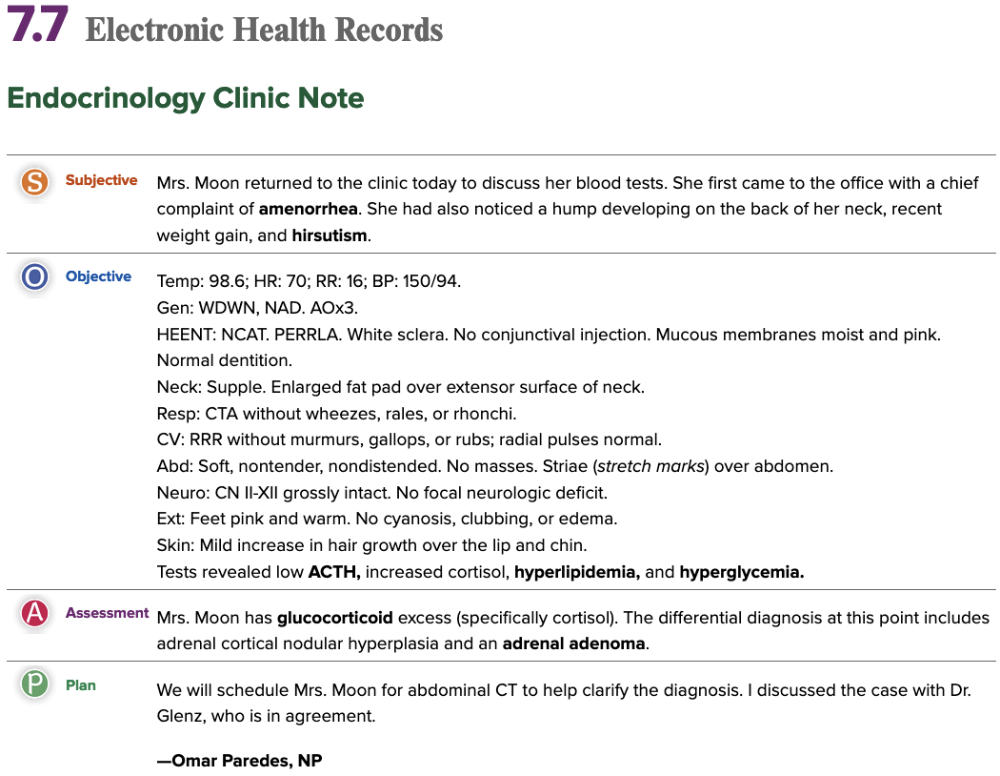
Chapter 7.7 Electronic Health Records
Endocrinology Clinic Note

Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2, 3.

Chapter 7.7 Electronic Health Records
Emergency Department Visit

Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5.

Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 6, 7.

Chapter 7.7 Electronic Health Records
Surgery Follow-Up Note

Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 8, 9.

Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 10, 11.
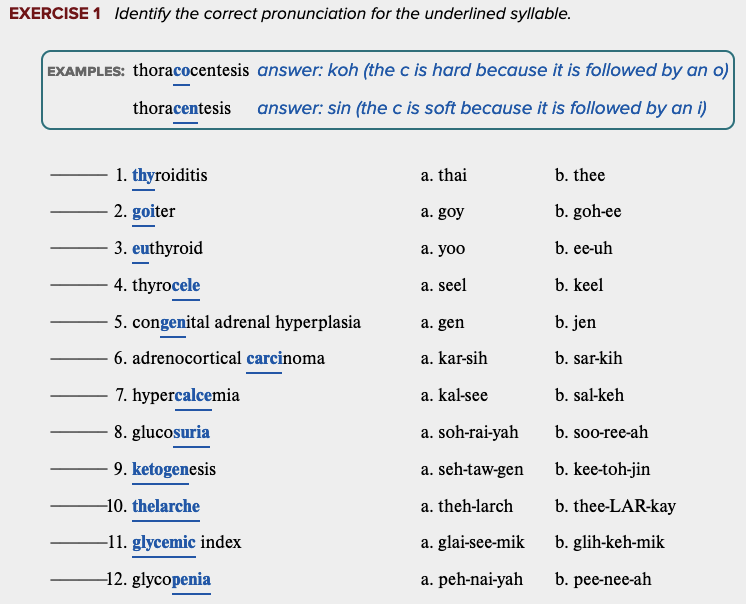
Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 1.

Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 2, 3.

Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 4, 5.

Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 6.

Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 7.

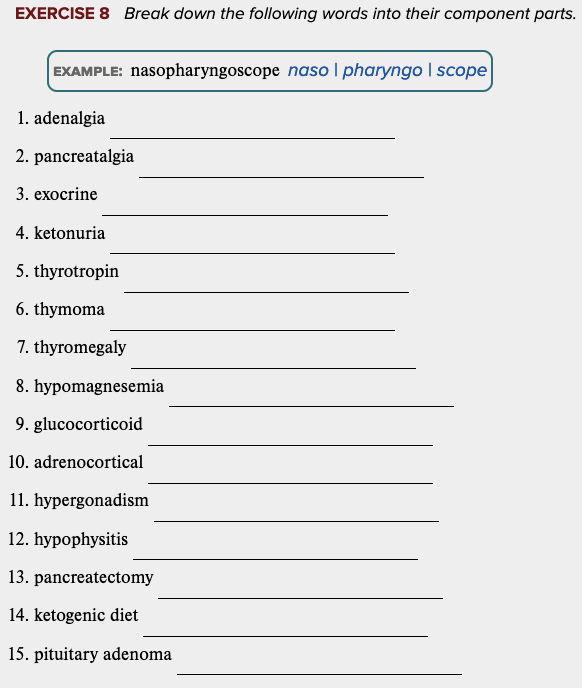
Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 8.

Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 9.
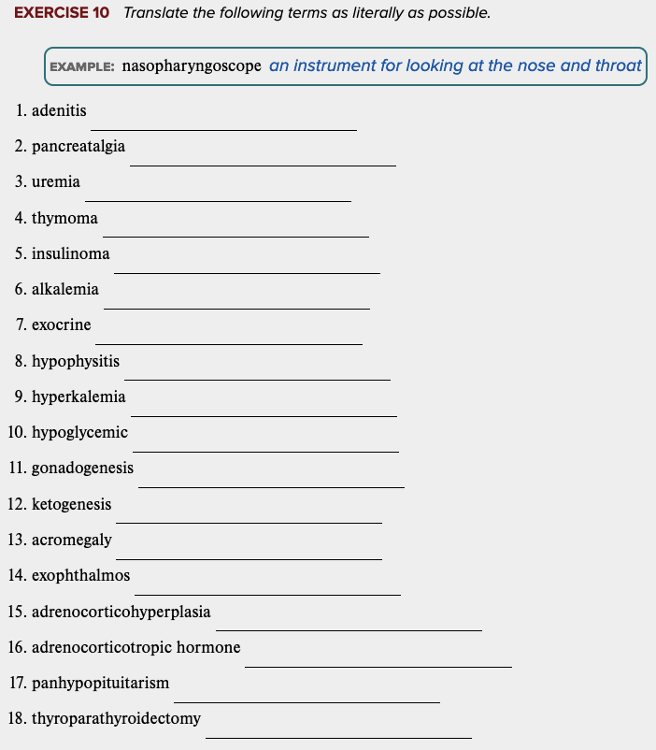
Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 10.

Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 11, 12.

Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 13, 14, 15.
Hormones generally cause ______ changes to their target cells than the nervous system.
Multiple choice question.
- faster
- slower
- the same
- no
slower
The thyroid gland and parathyroid gland release hormones that ______.
Multiple choice question.
- drive sexual development
- stimulate milk production
- stimulate a "fight or flight" response
- keep critical minerals like calcium and sodium in balance
- control the level of sugar in the blood
- help the body grow to adult height
keep critical minerals like calcium and sodium in balance
Select all that apply
Identify all the glands associated with the endocrine system.
Multiple select question.
- Parathyroid
- Pituitary
- Sweat glands
- Thyroid
- Tonsils
- Salivary glands
- Parathyroid
- Pituitary
- Thyroid
The main function of the hypothalamus is to direct the activity of the ______.
Multiple choice question.
- pituitary gland
- pineal gland
- thymus
- adrenal gland
- thyroid gland
pituitary gland
What does thyroid hormone refer to?
Multiple choice question.
- T3 and T4
- Triiodothyronine only
- Thymosin and thyroxine
- Thyroxine only
T3 and T4
Which of the following organ is not an endocrine organ?
Multiple choice question.
- adrenal gland
- liver
- pancreas
- parathyroid gland
- pituitary gland
liver
The gland that is both an endocrine gland and a gastrointestinal organ is the ______.
pancreas
Growth hormone functions to ______.
Multiple choice question.
- stimulate milk production
- stimulate a "fight or flight" response
- keep critical minerals like calcium and sodium in balance
- control the level of sugar in the blood
- help the body grow to adult height
- drive sexual development
help the body grow to adult height
The inner layer of the adrenal gland makes the fight-or-flight hormone called ______.
adrenaline or epinephrine
The signal makers and senders of the endocrine system are called ______.
Multiple choice question.
- vitamins
- hormones
- neurotransmitters
- glands
glands
The male gonads are the ______ and the female gonads are the ______.
Blank 1: testes, teste, testicles, or testicle
Blank 2: ovaries or ovary
The chemical signals used by the hypothalamus to affect the function of the pituitary are called ______.
Multiple choice question.
- amines
- releasing hormones
- bodily humors
- neurotransmitters
releasing hormones
In the words corticotropic and adrenocorticohyperplasia, the root cortic (combining form cortic/o) means ______.
Multiple choice question.
- gland
- hormone
- on the kidney
- outer surface
outer surface
Select all that apply
What two glands help to regulate calcium levels in the blood?
Multiple select question.
- pancreas
- thyroid gland
- adrenal gland
- parathyroid gland
- bone
- thyroid gland
- parathyroid gland
The suffix -pathy means disease. A disease of the sex organs is called ______.
Multiple choice question.
- adenopathy
- pancreatopathy
- thyropathy
- gonadopathy
gonadopathy
Select all that apply
The pancreas functions to ______.
Multiple select question.
- regulate blood pressure
- regulate sugar levels
- aid in digestion
- regulate metabolism
- produce milk
- regulate sugar levels
- aid in digestion
The suffix -lith means stone. A stone in the pancreas is called a(n) ______.
Multiple choice question.
- otolith
- gonadolith
- pancreatolith
- renal lithiasis
pancreatolith
Select all that apply
The outer cortex of the adrenal gland functions to ______.
Multiple select question.
- affect the body's response to inflammation
- regulate digestion in the body
- regulate water levels in the blood
- regulate sugar levels in the blood
- regulate mineral levels in the blood
- affect the body's response to inflammation
- regulate water levels in the blood
- regulate sugar levels in the blood
- regulate mineral levels in the blood
What endocrine organ is named for its resemblance to a shield and lies in the throat region?
Multiple choice question.
- Pancreas
- Thyroid
- Testis
- Ovary
Thyroid
Select all that apply
What hormones are secreted by the gonads?
Multiple select question.
- adrenaline
- estrogen
- testosterone
- insulin
- estrogen
- testosterone
Select all that apply
Which of the following are examples of glands used for excessive exocrine responses?
Multiple select question.
- Sweat
- Salivary
- Paracrine
- Pancreas
- Sweat
- Salivary
- Pancreas
In the words adenoma and adenopathy, the root aden (combining form aden/o) means ______.
Multiple choice question.
- hormone
- outer surface
- on the kidney
- gland
gland
In the term gonadogenesis, the word genesis means ______.
Multiple choice question.
- ovaries
- gonads
- testicles
- to create
to create
Which of the following is a term used for secretion?
Multiple choice question.
- hypo
- hyper
- crino
- pan
crino
Select all that apply
Which of the following are the Greek terms for pancreas?
Multiple select question.
- Kreas
- Bark
- Pan
- Husk
- Kreas
- Pan
Select all that apply
The hormones produced by the pancreas include ______.
Multiple select question.
- adrenaline
- glucagon
- insulin
- glycogen
- calcitonin
glucagon
insulin
What root (combining form) is used to describe the pituitary?
- Multiple choice question.
- Gonad/o
- Thym/o
- Thyr/o
- Hypophys/o
Hypophys/o
Which of the following is a hormones produced in the gonads of the male?
Multiple choice question.
- Epinephrine
- Glucocorticoids
- Estrogen
- Testosterone
Testosterone
What word means to secrete internally?
Multiple choice question.
- Paracrine
- Endocrine
- Exocrine
- Autocrine
Endocrine
In the words corticotropic and adrenocorticohyperplasia, the root cortic (combining form cortic/o) means ______.
Multiple choice question.
- hormone
- gland
- on the kidney
- outer surface
outer surface
When the level of glucose is measured as high the patient would be diagnosed as having ______.
Multiple choice question.
- hypoglycemia
- hyperglycemia
- ketonuria
- glucosuria
hyperglycemia
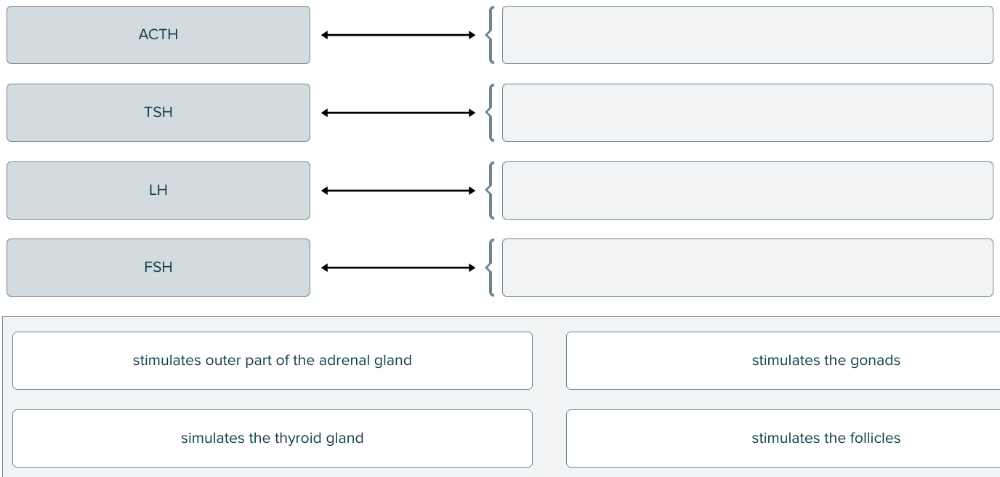
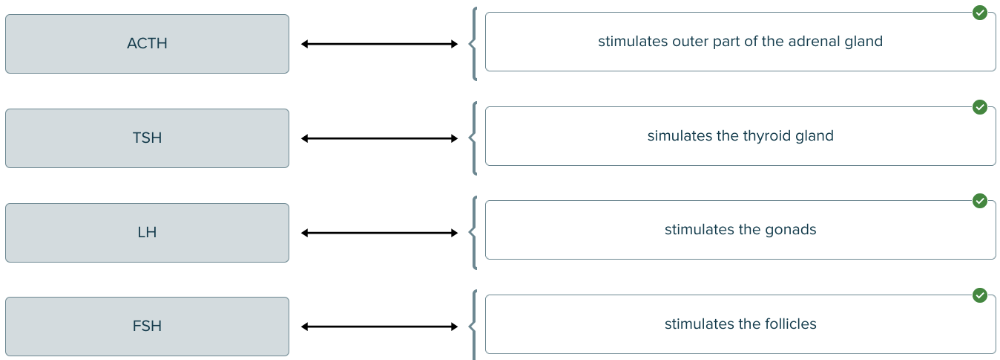
Drag and drop the hormone definition against the corresponding stimulation area.
The presence of ketone bodies is normally a sign of untreated or poorly controlled ______.
Multiple choice question.
- hypoglycemia
- hyperglycemia
- thyrosis
- diabetes
diabetes
The hormone that has the opposite effect as parathyroid hormone is ______.
calcitonin
Select all that apply
What are two types of corticosteroids used in the adrenal glands?
Multiple select question.
- Glucocorticoids
- Epinephrine
- Fructose
- Mineralocorticoids
Glucocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids
The suffix means blood condition is called ______.
-emia
The main form of sugar found in the bloodstream is called ______.
glucose
Match the endocrine term associated with its definition.
Bulging of the eyes due to hyperthyroidism is called ______.
Multiple choice question.
- goiter
- acromegaly
- pituitary gigantism
- exophthalmos
exophthalmos
A substance that increases in the blood as a result of faulty carbohydrate metabolism is called a ______ body.
ketone
Fill in the blank question.
Insulin and glucagon regulate ______ levels in the blood, while calcitonin and parathyroid hormone regulate ______ levels in the blood.
Blank 1: sugar or glucose
Blank 2: calcium
The term that describes constant hunger in patients with diabetes is called ______.
polyphagia
Which suffix means urine condition?
Multiple choice question.
- -crine
- -tropin
- -emia
- -uria
-uria
The suffix -arche indicates beginning. When the glands on top of the kidney begin secreting hormones, it is called ______.
Multiple choice question.
- menarche
- adrenarche
- thelarche
adrenarche
What word means to secrete internally?
Multiple choice question.
- Autocrine
- Endocrine
- Exocrine
- Paracrine
Endocrine
Lack of menstrual flow is termed ______.
amenorrhea
The thyroid disorder that results in decreased metabolism, weight gain and decreased appetite is called ______.
hypothyroidism
If a patient has low blood sugar, she is ______.
Multiple choice question.
- hyperglycemic
- hypogonadic
- hypoglycemic
- hypoxemic
hypoglycemic
Males that experience breast development have the condition called ______.
gynecomastia
The prefix galacto- means ______.
Multiple choice question.
- milk
- galaxy
- breast
- pituitary
milk
Pain of a gland is called ______.
adenalgia
Which of the following terms would describe thyroptosis?
Multiple choice question.
- Goiter
- Enlargement of the thyroid
- Drooping of the thyroid
- Protrusion of the eye sockets
Drooping of the thyroid
The beginning of breast development in women is termed ______.
Multiple choice question.
- hypogonadism
- menarche
- thelarche
- amenorrhea
- gynecomastia
thelarche
Which of the following is a term often used to describe adrenaline?
Multiple choice question.
- Gluconeogenesis
- Epinephrine
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypoglycemia
Epinephrine
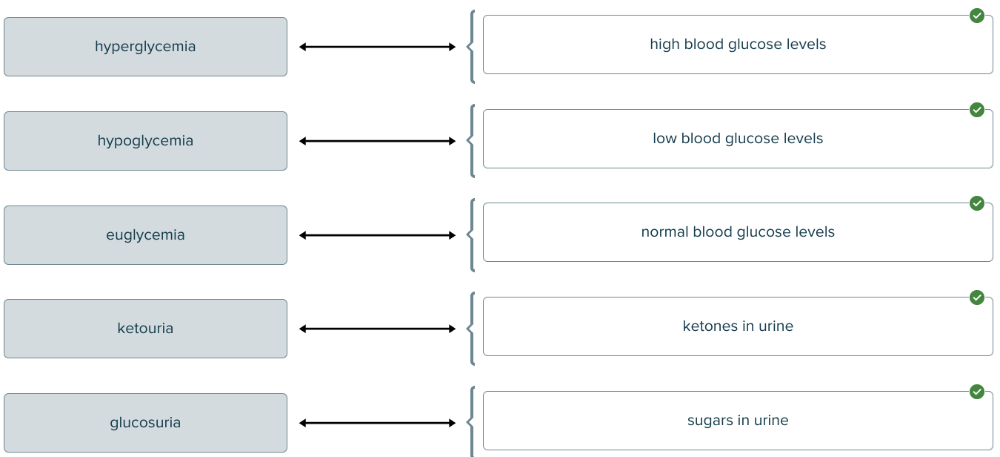
The suffix -emia means blood condition. Drag and drop the definitions against the corresponding blood conditions.
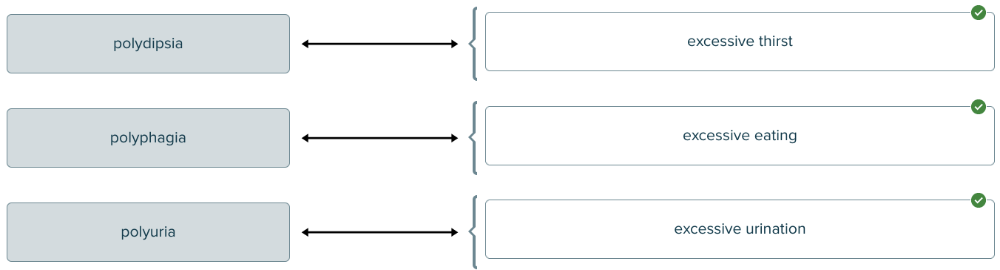
The Greek prefix poly- means excessive. Match each pancreatic disease with its description.
The term that describes having too much base in the blood is ______.
Multiple choice question.
- acidemia
- hyperkalemia
- alkalemia
- euglycemia
alkalemia
Which of the following would be associated with acromegaly?
Multiple choice question.
- Lack of development
- Enlargement of the extremities
- Secretion of milk
- Abnormal hair growth
Enlargement of the extremities
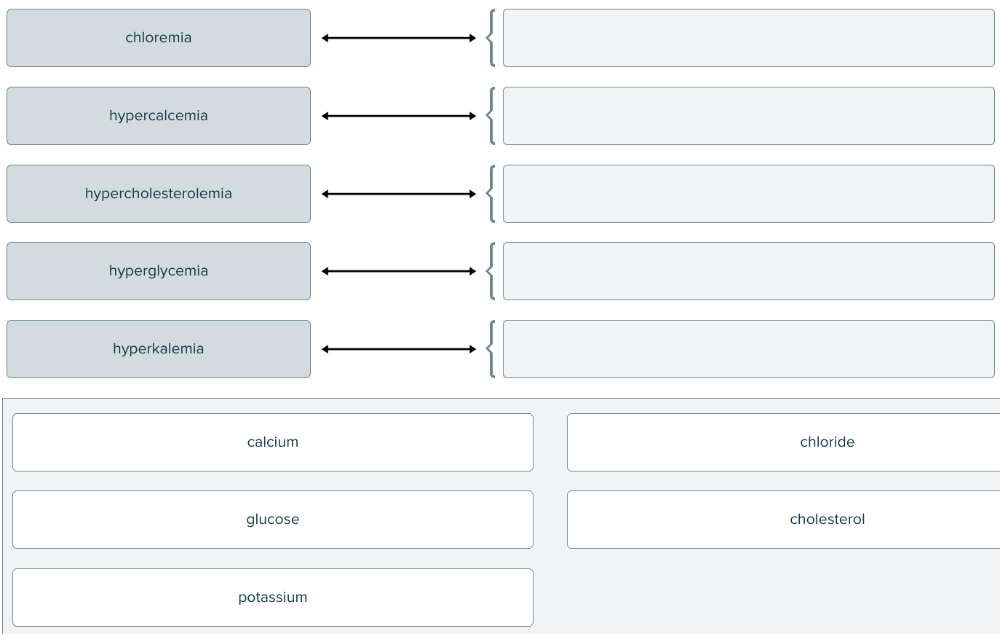
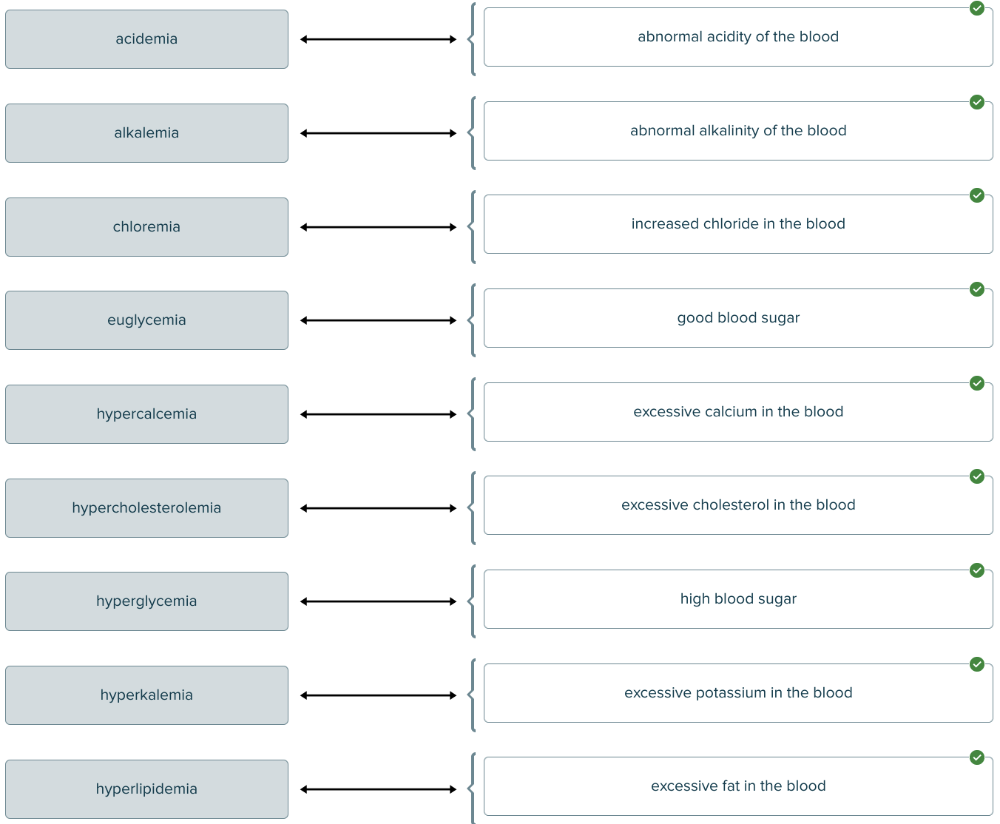
Match the blood condition with abnormal compound in the blood.
The term that means to have swollen thyroid glands is ______.
goiter or thyrocele
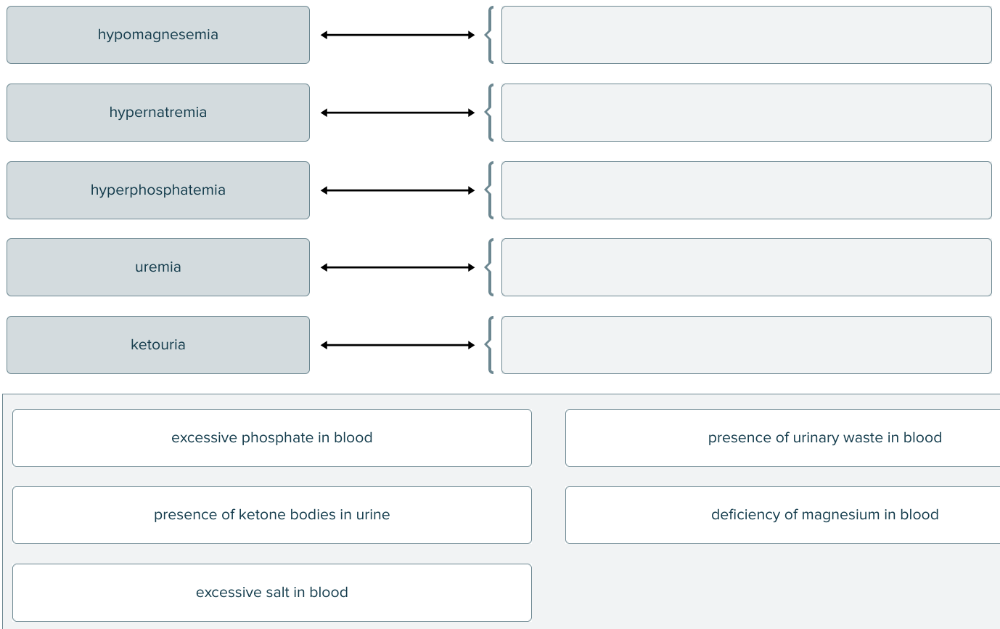
Match each blood and urine condition with the abnormal compound(s) found.
Select all that apply
Select the tests below used for endocrinology testing.
Multiple select question.
- Elevation in blood sugar
- Decrease in blood sugar
- Effect of hormones in blood
- Levels of hormone in blood
- Effect of hormones in blood
- Levels of hormone in blood
Adrenaline and ______ are the same thing.
epinephrine
Which of the following is the term used for excessive potassium in the blood?
Multiple choice question.
- Ketonuria
- Hyperkalemia
- Polyuria
- Chloremia
Hyperkalemia
Which hormone is secreted by the pancreas and controls the metabolism and uptake of sugar and fats?
Multiple choice question.
- Glucocorticoid
- Insulin
- Gonadotropin
- Thyrotropin
Insulin
An abnormal acidity in the blood is termed ______.
acidemia
Which of the following would describe a deficiency of sugar in the body?
Multiple choice question.
- Adenomegaly
- Gonadogenesis
- Glycopenia
- Euthyroid
Glycopenia
Ex.
- Adenomegaly
Reason: This is the abnormal enlargement of a gland
- Gonadogenesis
Reason: This is a creation of gonads
- Euthyroid
Reason: This is the normal function of thyroid
Which term means good blood sugar?
Multiple choice question.
- euglycemia
- glucosuria
- hyperglycemia
- hypoglycemia
euglycemia
The term that describes the breakdown of matter into energy for the human body is ______.
metabolism
Excessive urination is called ______.
polyuria
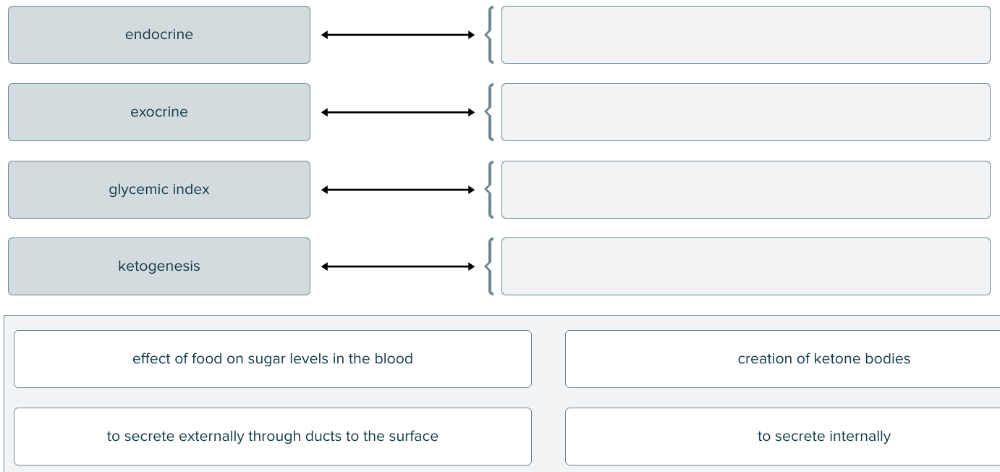
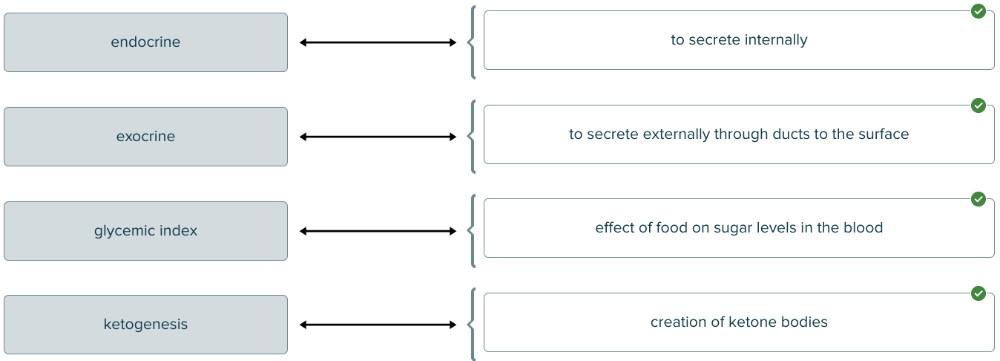
Which of the definitions below would describe a glycemic index?
Multiple choice question.
- Specialist in internal secretions
- To secrete internally
- Ranking of food based on the way it affects sugar levels in the blood.
- To secrete externally through ducts, organs, of glands.
Ranking of food based on the way it affects sugar levels in the blood.
Which hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland and stimulates the cortex of the adrenal gland?
Multiple choice question.
- Glucagon
- Adrenaline
- Epinephrine
- Corticotropin
Corticotropin
Ex.
Shorter name for the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
The procedure that examines the bile ducts and pancreas is ______.
Multiple choice question.
- adrenocorticotropic
- ketogenesis
- cholanglopancreatography
- endocrinologist
cholanglopancreatography
Ex.
- adrenocorticotropic
Reason: hormone secreted by the pituitary gland
- ketogenesis
Reason: creation of ketone bodies
- endocrinologist
Reason: specialist in internal secretions
The hormone that stimulates the gonads is ______.
gonadotropin
Pituitary infarction refers to ______.
Multiple choice question.
- insufficiency of the pituitary gland
- bleeding into the pituitary gland
- tumor of the pituitary gland
- inflammation of the pituitary gland
- death of the pituitary gland
death of the pituitary gland
In the laboratory result euthyroid, the prefix eu- means ______.
Multiple choice question.
- thyroid
- good
- sugar
- gland
good
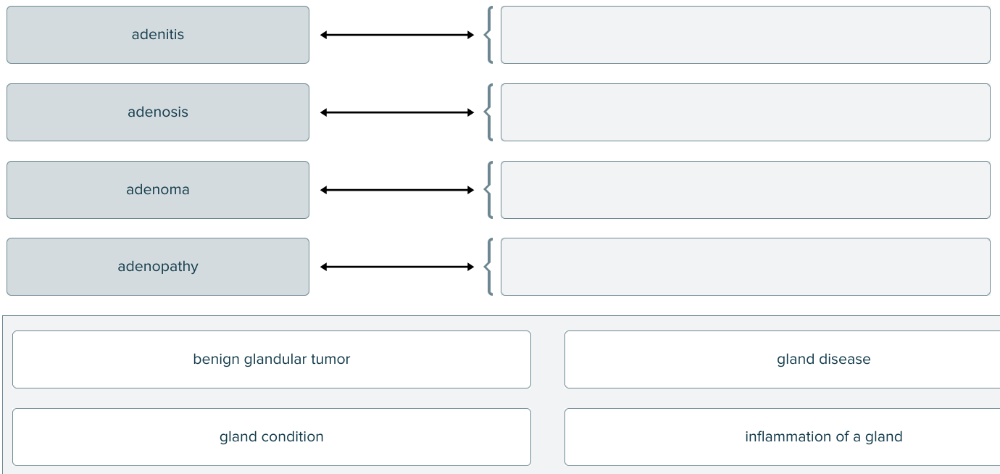
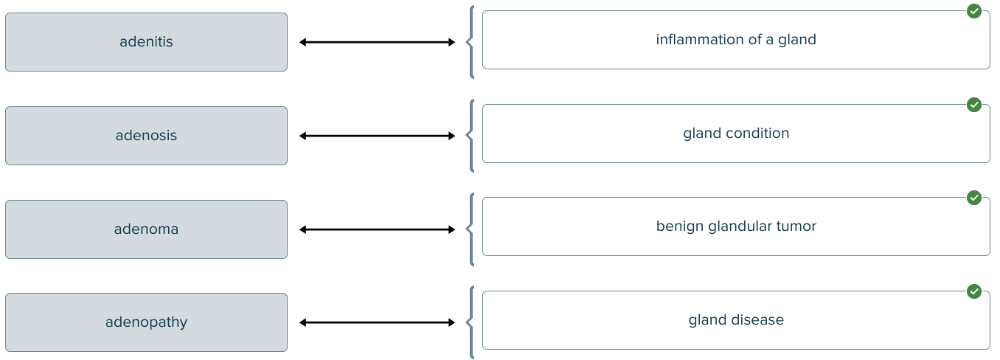
The root aden (and combining form aden/o) means gland. Match each term pertaining to a gland with its definition.
Which suffix means formation?
Multiple choice question.
- -bol
- -gonad
- -genesis
- -ism
-genesis
Which of the following would describe the inflammation of the adrenal gland?
Multiple choice question.
- Adenosis
- Polyadenopathy
- Adrenalitis
- Ketosis
Adrenalitis
Ex.
- Adenosis
Reason: gland disease
- Polyadenopathy
Reason: disease involving many glands
- Ketosis
Reason: condition characterized by elevated levels of ketone bodies in the blood
Match each professional and diagnostic term associated with the endocrine system to its description.
Excessive sugar in urine is characteristic of ______.
Multiple choice question.
- pancreatolithiasis
- pancreatitis
- diabetes mellitus
- diabetic ketoacidosis
diabetes mellitus
Select all that apply
Which of the following are the root for the term cholangiopancreatography?
Multiple select question.
- pancreato
- angio
- chol
- graphy
- pancreato
- angio
- chol
Ex.
- pancreato
Reason: pancreas
- angio
Reason: vessel
- chol
Reason: bile
- graphy
Reason: suffix
Inflammation of the pituitary gland is termed ______.
Multiple choice question.
- panhypopituitarism
- hyperpituitarism
- hypopituitarism
- hypophysitis
hypophysitis
What is the condition when a thyroid gland is producing too much hormone?
Multiple choice question.
- Hyperthyroidism
- Adenitis
- Adenopathy
- Hypothyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Ex.
- Adenitis
Reason: inflammation of a gland
- Adenopathy
Reason: gland disease
- Hypothyroidism
Reason: too low
If the function of the entire pituitary gland is defective or absent, it is termed ______.
Multiple choice question.
- hypophysitis
- panhypopituitarism
- pituitary adenoma
- hyperpituitarism
panhypopituitarism
When a patient has a combination of medical disorders, all of which are associated with faulty metabolism, she is said to have ______.
Multiple choice question.
- adenosis
- polyadenopathy
- dysmetabolic syndrome
- ketosis
dysmetabolic syndrome
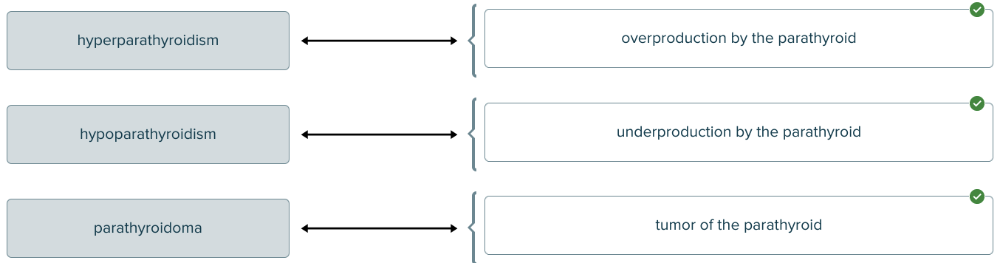
Match each parathyroid-related medical term with its definition.
A condition in which the adrenal cortex underproduces necessary hormones is ______.
Multiple choice question.
- adrenocortical insufficiency
- adrenocorticohyperplasia
- congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- adrenalitis
adrenocortical insufficiency
Select all that apply
Which of the following word roots are associated with the term adrenocortical carcinoma?
Multiple select question.
- Adrenal
- Cortex
- Beside
- Oma
- Adrenal
- Cortex
Which of the following pancreas terms would be defined as a stone in the pancreas?
Multiple choice question.
- Pancreatolithiasis
- Pancreatolith
- Pancreatitis
- Ketosis
Pancreatolith
When a patient's hormone levels are too low they are given ______.
Multiple choice question.
- enzyme replacement therapy
- thyroid replacement therapy
- gland replacement therapy
- hormone replacement therapy
hormone replacement therapy
Overfunctioning of the pituitary gland is termed ______.
Multiple choice question.
- hypopituitarism
- gigantism
- hyperpituitarism
- hypophysitis
hyperpituitarism
Ex.
- gigantism
Reason: Gigantism can be caused by overfunctioning of the pituitary gland, but it's a sign associated with the disease, not the disease name itself.
Select all that apply
Which of the following word parts are associated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion?
Multiple select question.
- Process
- Gland
- Insulin
- Skin
- Process
- Insulin
- Skin
Death of the pituitary gland is termed ______.
Multiple choice question.
- pituitary infarction
- pituitary adenoma
- hypophysitis
- hypopituitarism
pituitary infarction
The surgical term for the removal of a gland in the endocrine system is ______.
adenectomy
Which of the following is caused by a underproduction of the parathyroid?
Multiple choice question.
- Thyroiditis
- Thyrotoxixosis
- Hypoparathroidism
- Adenoma
Hypoparathroidism
Select all that apply
Which of the following are terms used for the term adrenalectomy?
Multiple select question.
- Removal
- Adrenal
- Lith
- Scope
- Removal
- Adrenal
Which of the following conditions is a tumor of the thymus?
Multiple choice question.
- Adenoma
- Hypophysitis
- Thymoma
- Insulinoma
Thymoma
In the term pancreatolithectomy, the word part that means stone is ______.
Multiple choice question.
- lith
- pancreato
- pan
- ectomy
lith
Select all that apply
What are the routes used for delivering supplemental hormones to patients?
Multiple select question.
- Topical
- Oral
- Injection
- Surgical
- Topical
- Oral
- Injection
In the term hypophysectomy, the root word means ______.
Multiple choice question.
- hypothalamus
- pituitary
- parathyroid
- gland
pituitary
A substance poisonous to the thyroid gland is called a ______.
thyroidotoxin
In the term ketogenic diet, the suffix -genic means ______.
Multiple choice question.
- removal of
- creating
- inflammation
- looking
creating
The term thyroidotomy means ______.
Multiple choice question.
- incision into the thyroid
- substance poisonous to the thyroid gland
- tests performed to evaluate the function of the thyroid
- removal of the thyroid
incision into the thyroid
Removal of the adrenal gland using an instrument inserted into the abdomen for viewing is called ______.
Multiple choice question.
- laparoscopic thymectomy
- laparoscopic adenectomy
- laparoscopic adrenalectomy
- laparoscopic pancreatectomy
laparoscopic adrenalectomy
The abbreviation for glucose tolerance test is ______.
GTT
Which of the following means removal of the pancreas?
Multiple choice question.
- Pancreatolithectomy
- Thyroidectomy
- Hypophysectomy
- Pancreatectomy
Pancreatectomy
The removal of the pituitary gland is termed ______.
hypophysectomy
The removal of the thyroid gland is termed ______.
thyroidectomy
The abbreviation GDM means ______ ______ ______
Blank 1: gestational
Blank 2: diabetes
Blank 3: mellitus