Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 7: The Endocrine System - Endocrinology
front 1  Chapter 7 Introduction and Overview of the Endocrine System | back 1 no data |
front 2  Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 1 | back 2 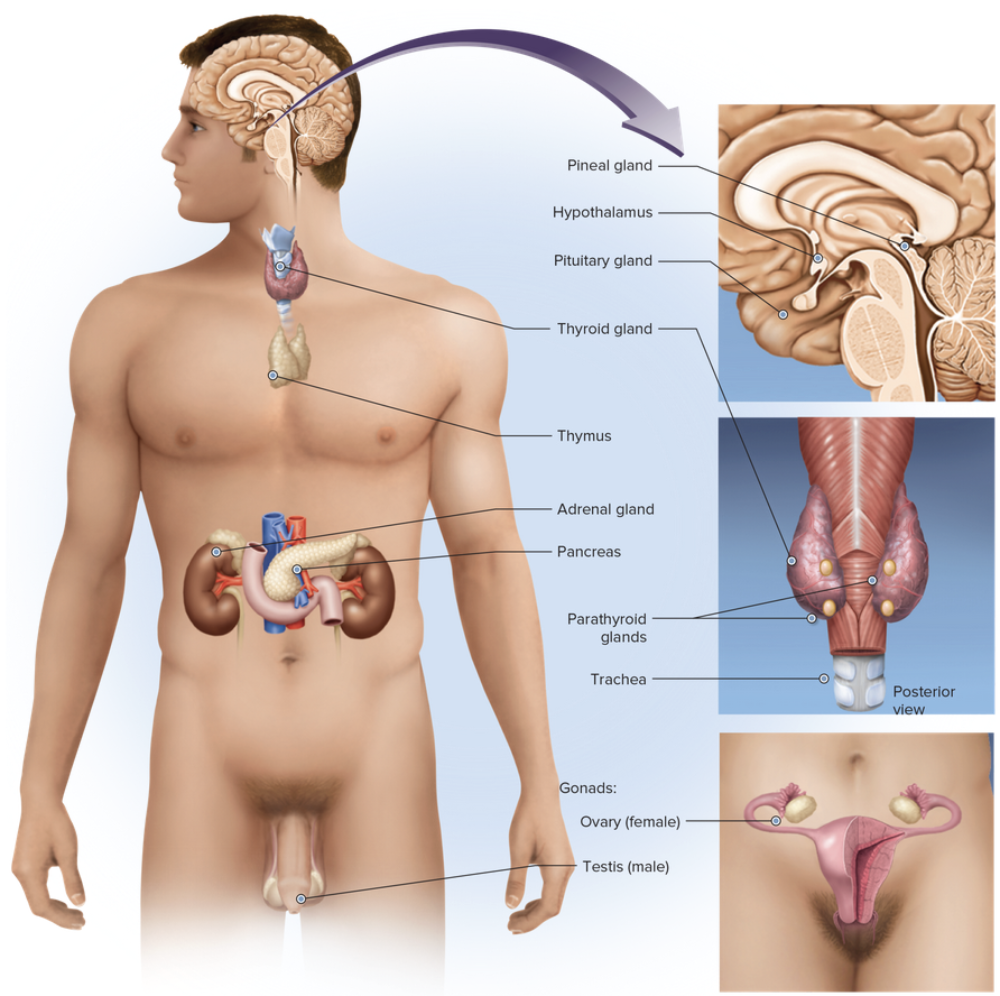 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 2 |
front 3  Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 3 | back 3 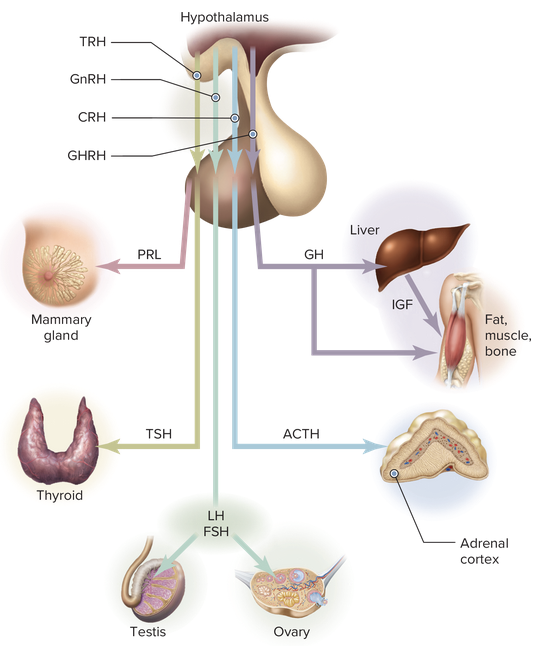 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 4 |
front 4 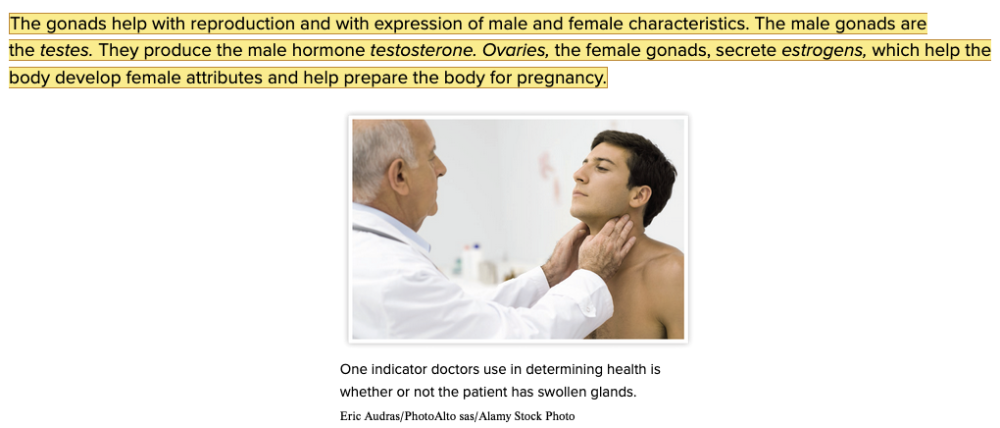 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Part 5 | back 4 no data |
front 5 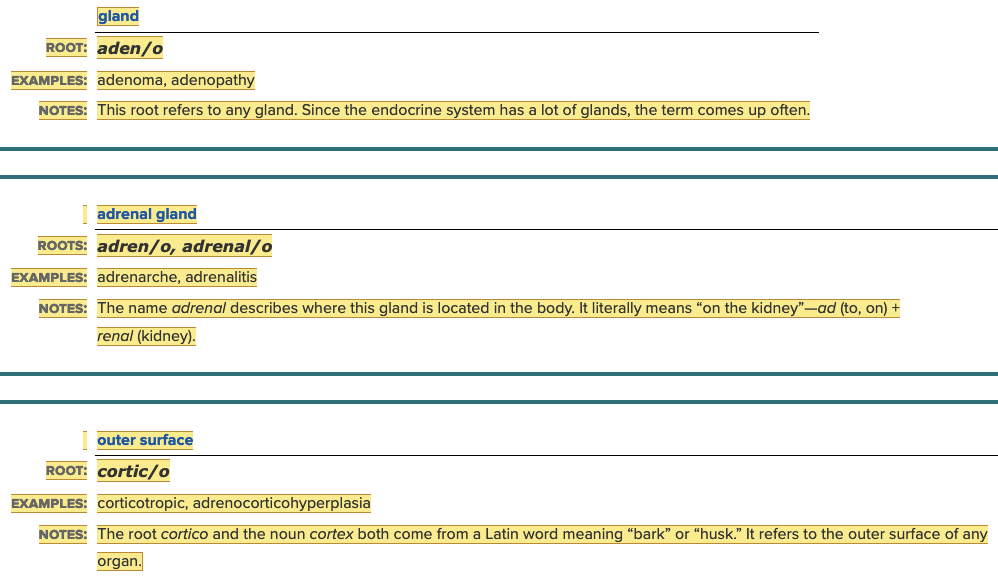 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 1 | back 5 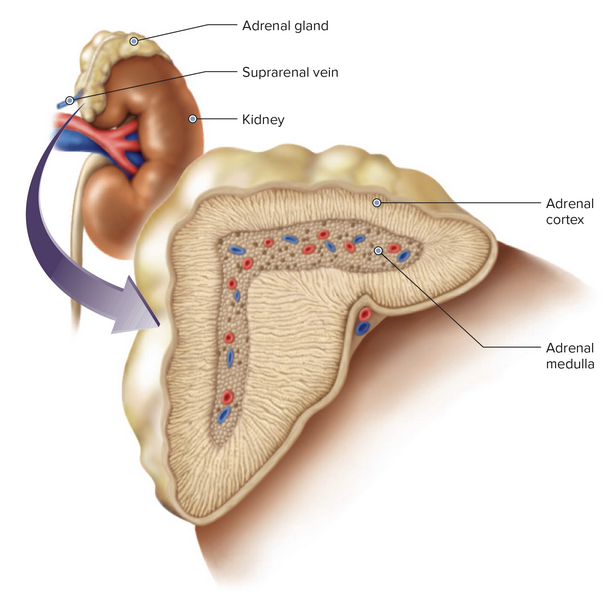 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 2 |
front 6 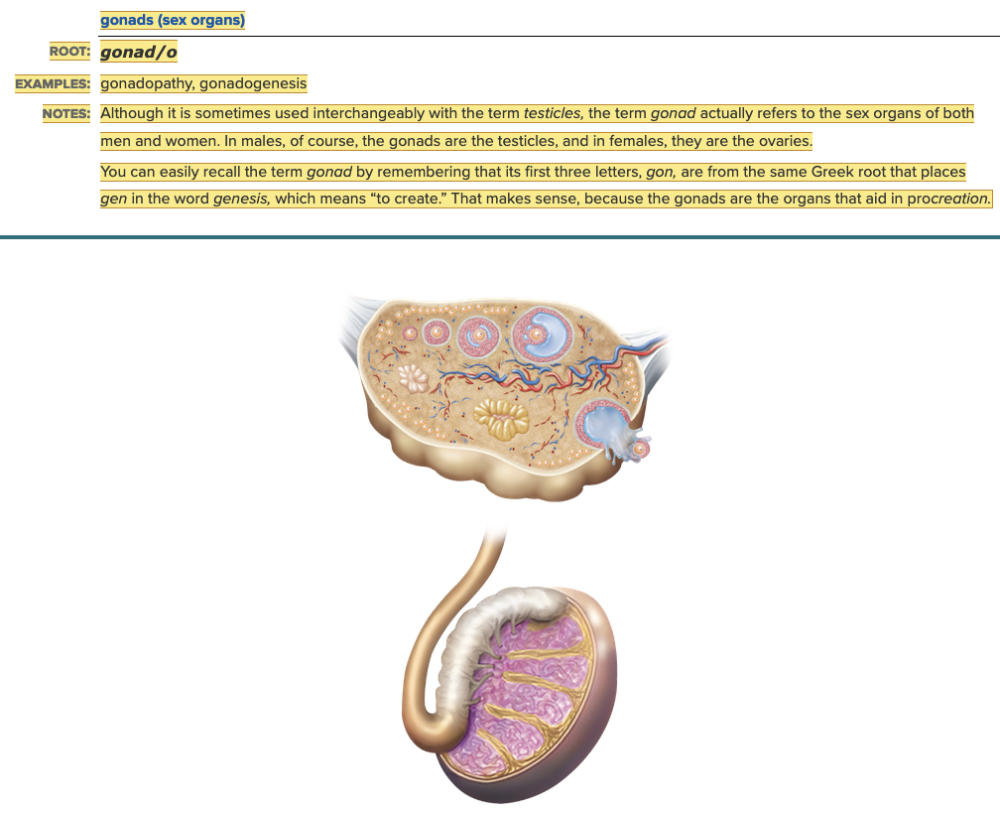 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 3 | back 6 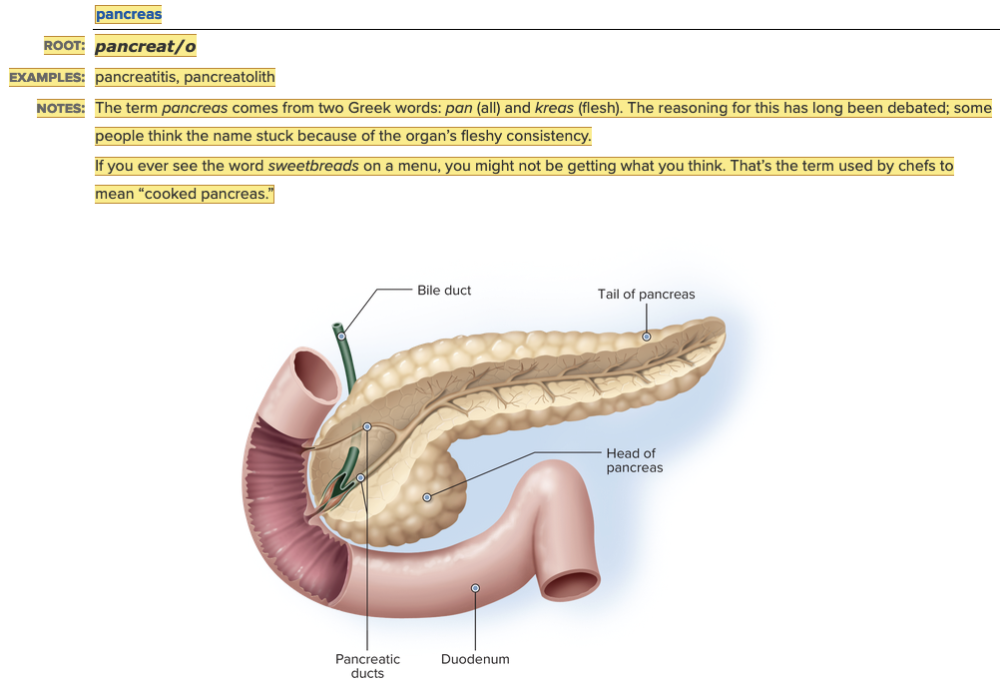 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 4 |
front 7  Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 5 | back 7 no data |
front 8  Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 6 | back 8 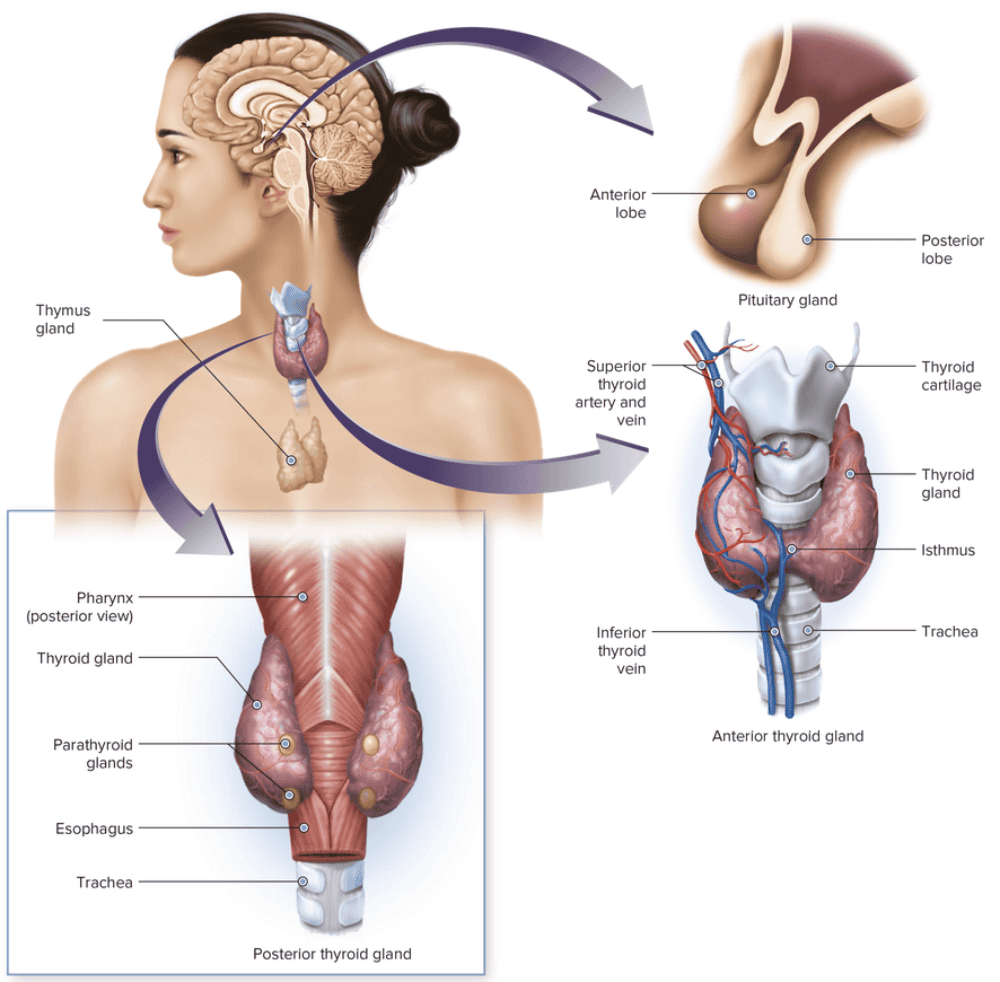 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 7 |
front 9 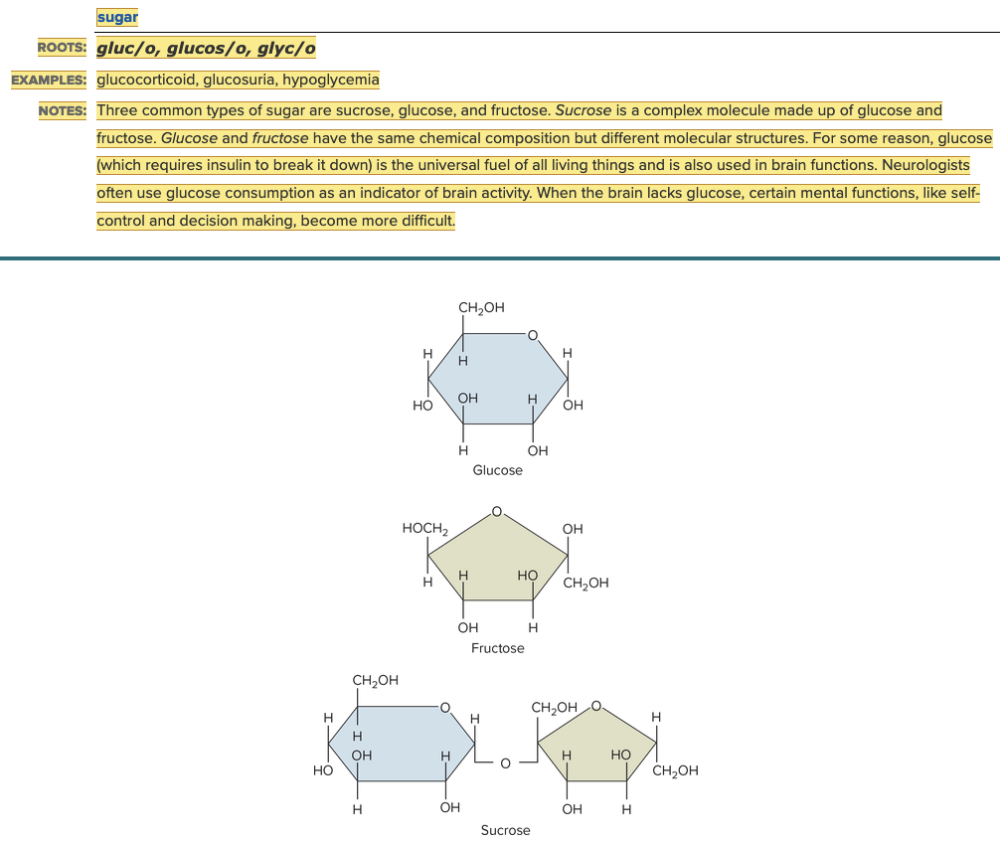 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 8 | back 9  Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Endocrine Gland Table Part 9 |
front 10  Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Part 1 | back 10 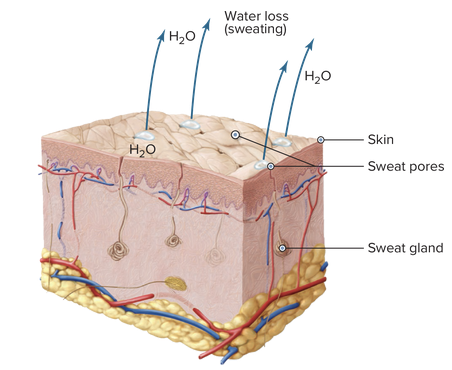 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Part 2 |
front 11  Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Part 3 | back 11 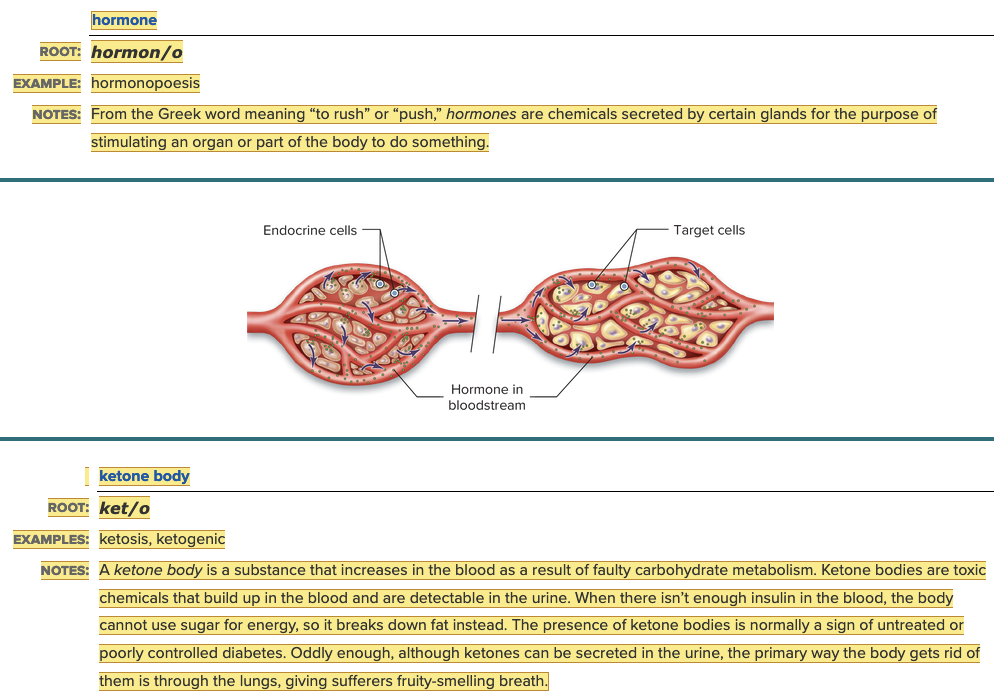 Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Word Roots for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Table |
front 12  Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Suffixes for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Table Part 1 | back 12  Chapter 7.1 Word Parts of the Endocrine System Suffixes for Secretions, Chemicals, and Blood Work Table Part 2 |
front 13  Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 13 no data |
front 14  Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4. | back 14 no data |
front 15  Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 5, 6. | back 15 no data |
front 16  Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 7, 8. | back 16 no data |
front 17  Learning Outcome 7.1 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10. | back 17 no data |
front 18  Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 18 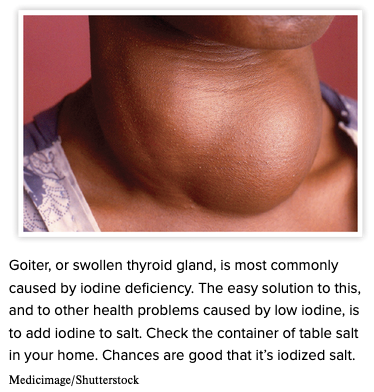 Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 19 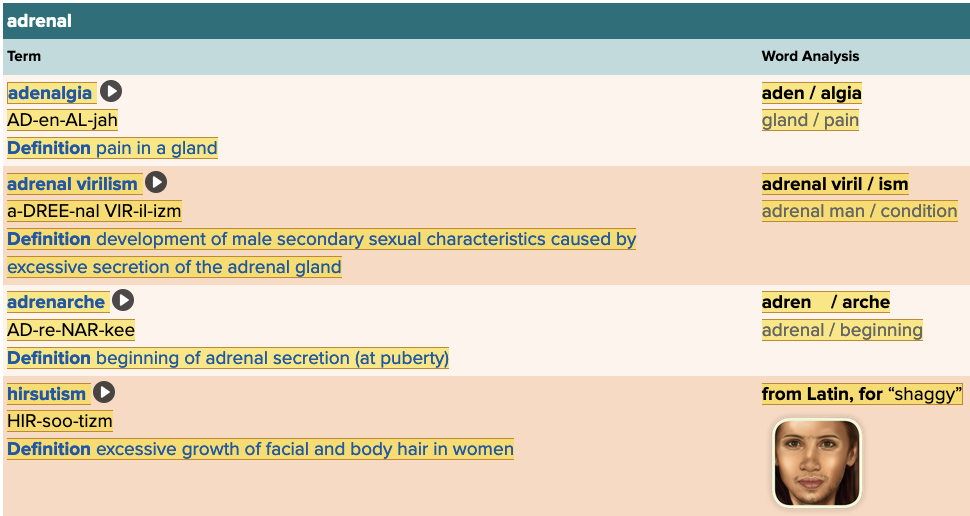 Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 19 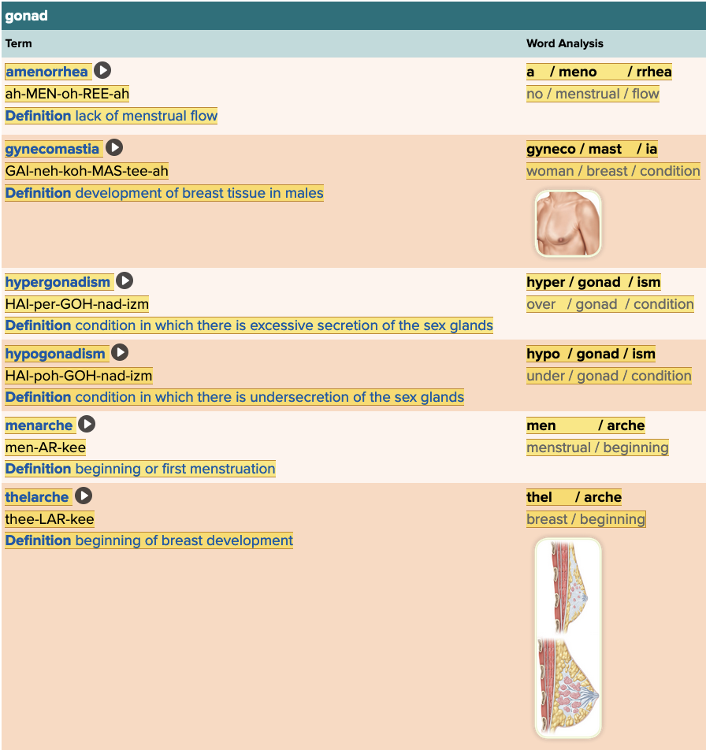 Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 20 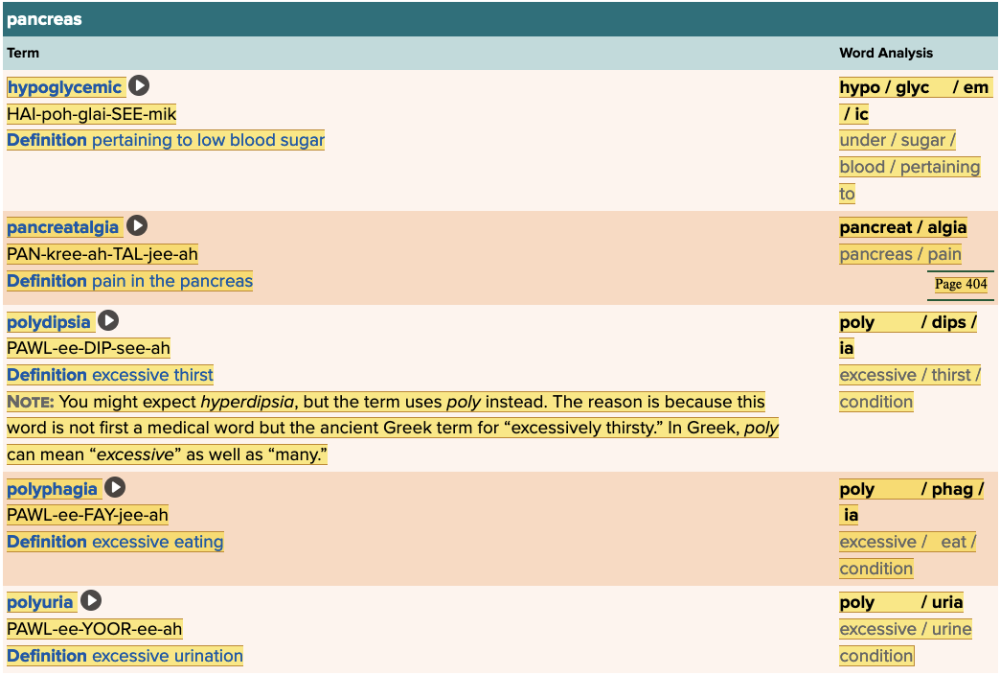 Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 20 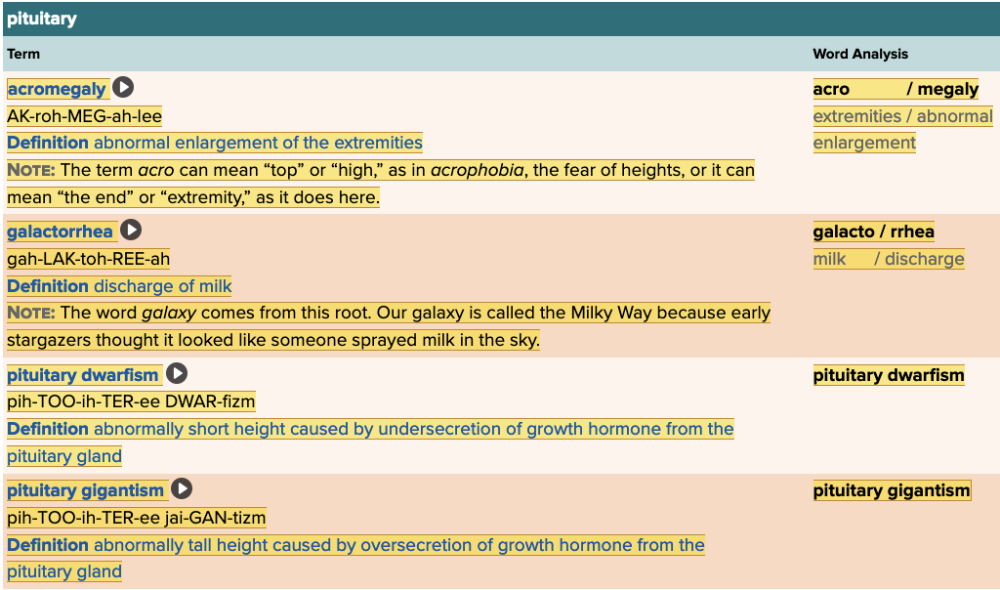 Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 21 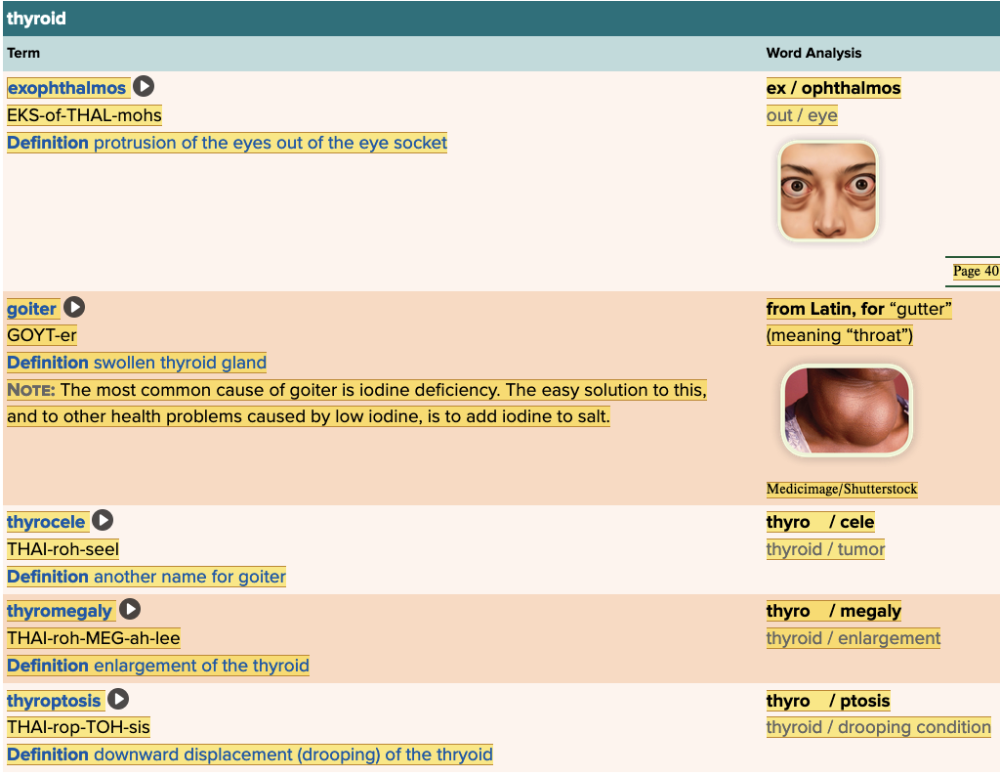 Chapter 7.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 21 no data |
front 22  Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 22 no data |
front 23  Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 23 no data |
front 24  Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4. | back 24 no data |
front 25  Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 25 no data |
front 26  Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 6 Part 1. | back 26  |
front 27  Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 6 Part 2. | back 27 no data |
front 28  Learning Outcome 7.2 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 28 no data |
front 29  Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 29  Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 30 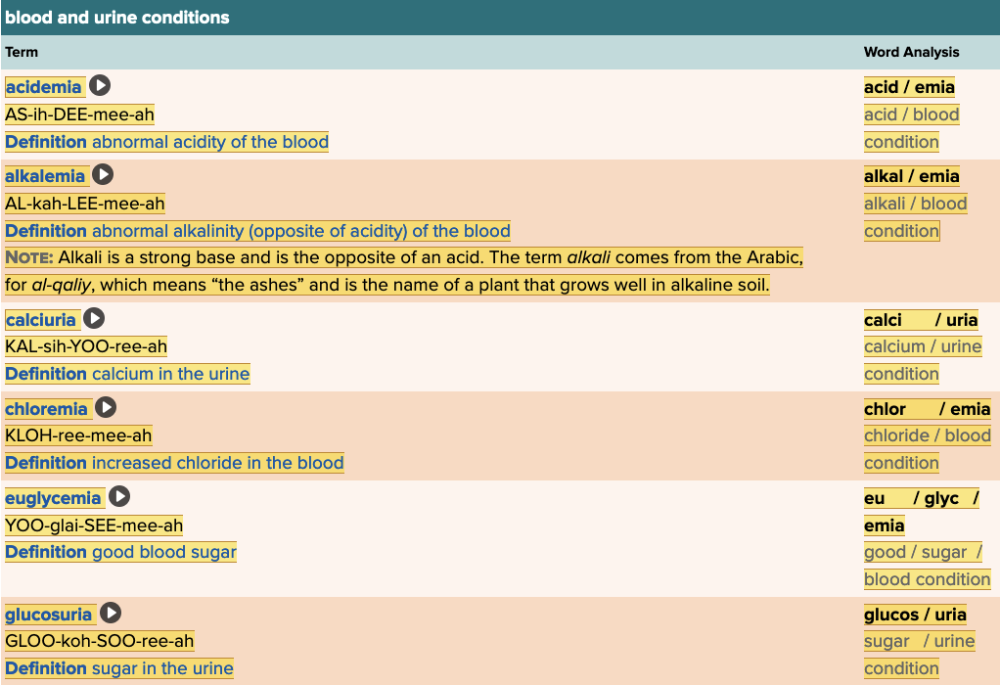 Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 30  Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 31  Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 31  Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 32  Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 32  Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 33  Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 33 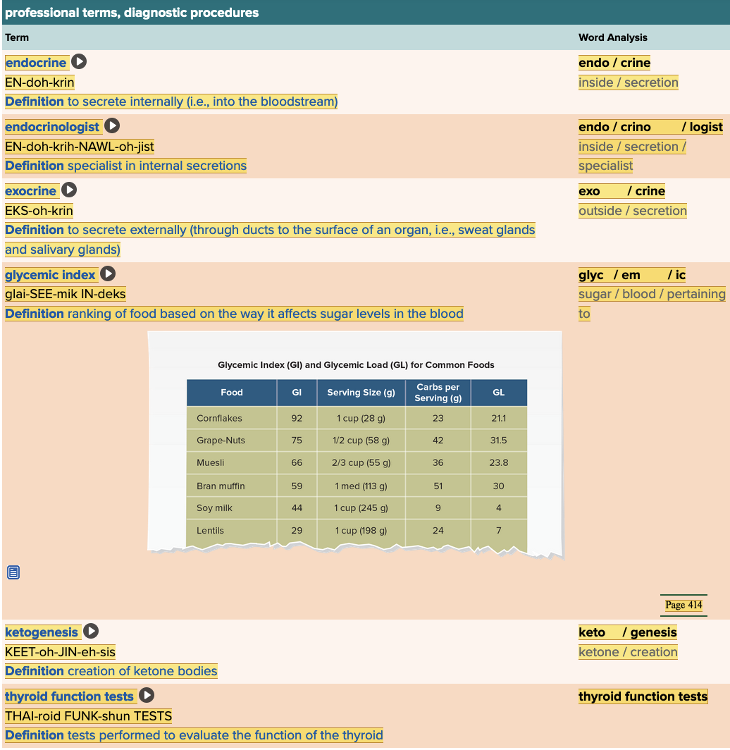 Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 34  Chapter 7.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 34 no data |
front 35  Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 35 no data |
front 36  Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 36 no data |
front 37  Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 37 no data |
front 38  Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 38 no data |
front 39 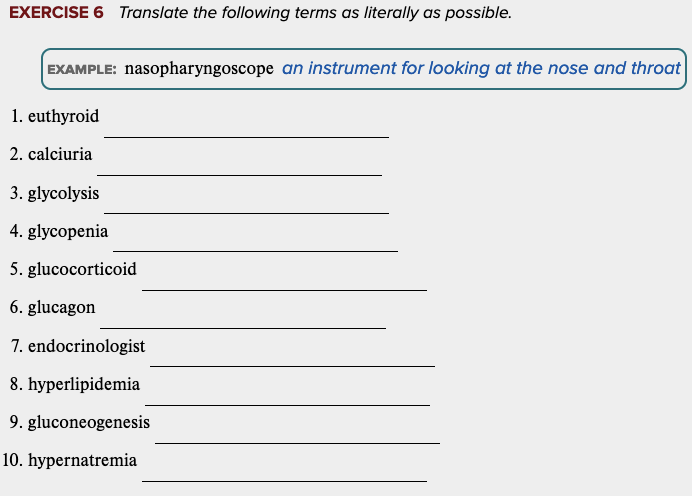 Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 39 no data |
front 40  Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 40 no data |
front 41  Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 41  |
front 42 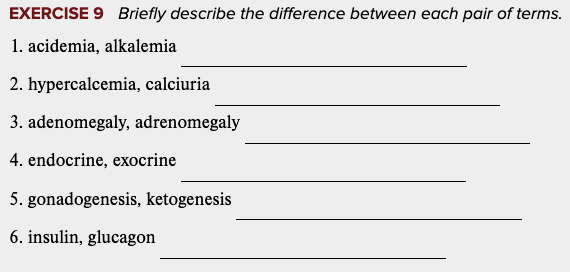 Learning Outcome 7.3 Exercises: Exercise 9. | back 42 no data |
front 43  Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 43  Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 44 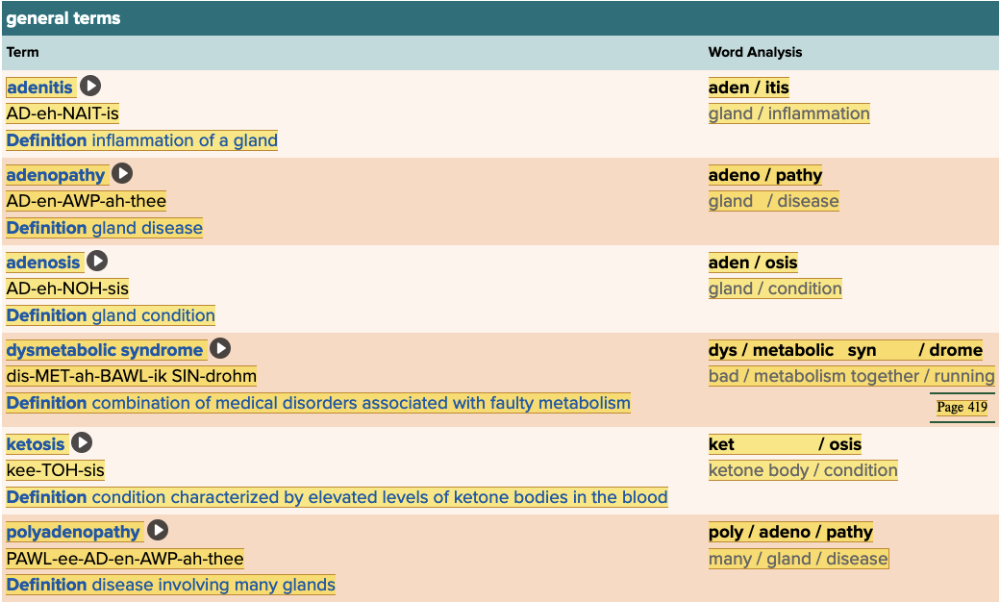 Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 44 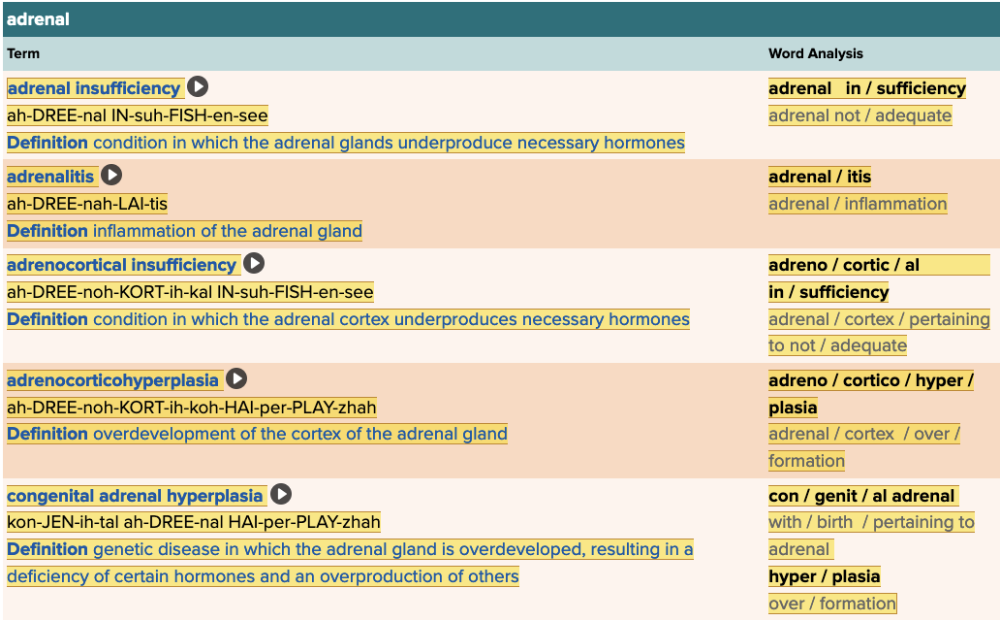 Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 45 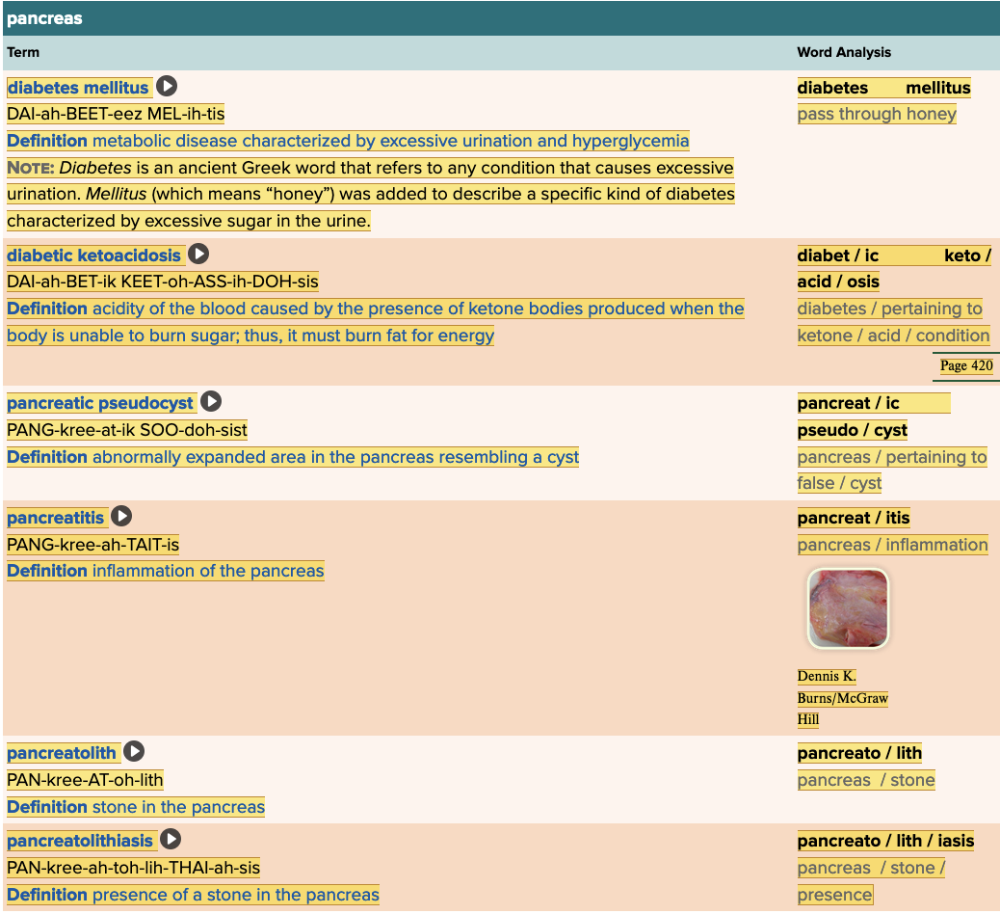 Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 45  Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 46 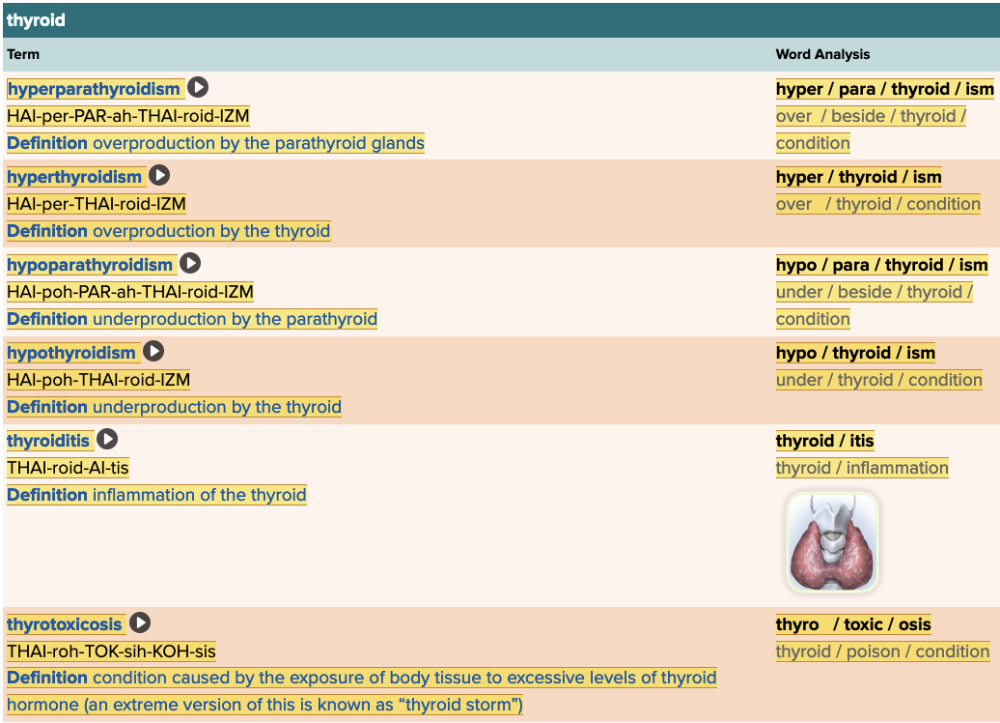 Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 46 no data |
front 47  Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 47 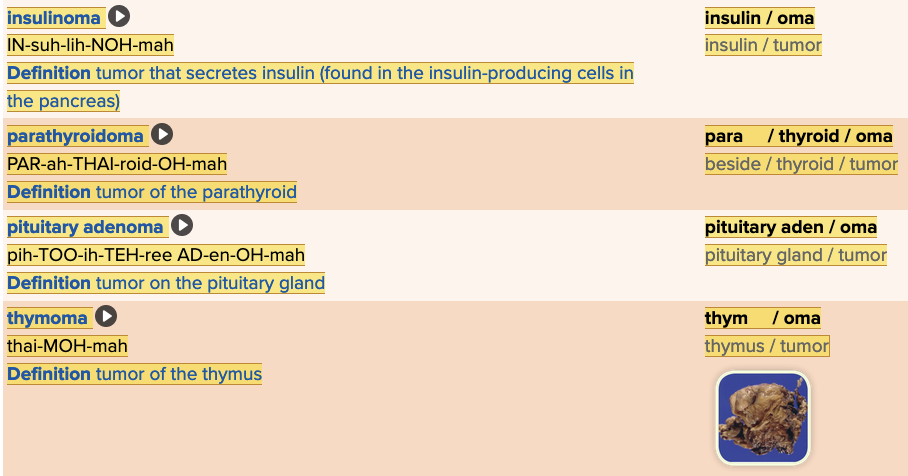 Chapter 7.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 48  Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 48 no data |
front 49  Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 49 no data |
front 50  Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 50 no data |
front 51  Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 4. | back 51 no data |
front 52  Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 52 no data |
front 53  Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 53 no data |
front 54  Learning Outcome 7.4 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 54 no data |
front 55  Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 55  Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 56  Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 56  Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 57 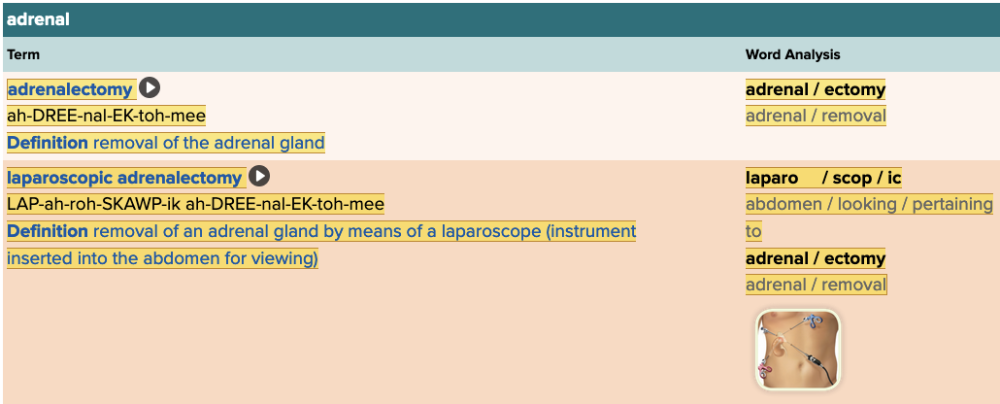 Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 57 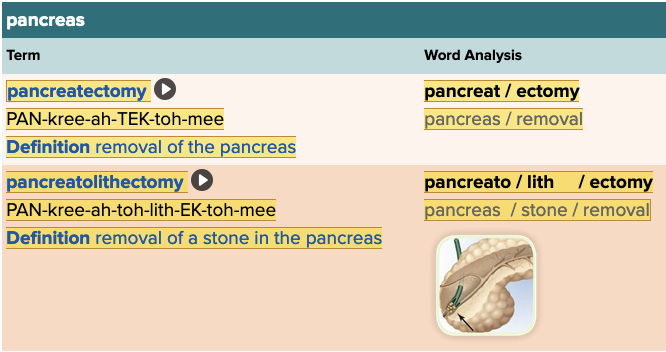 Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 58 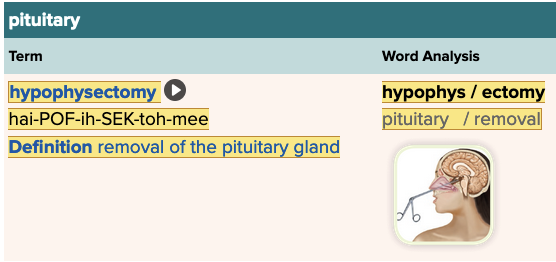 Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 58 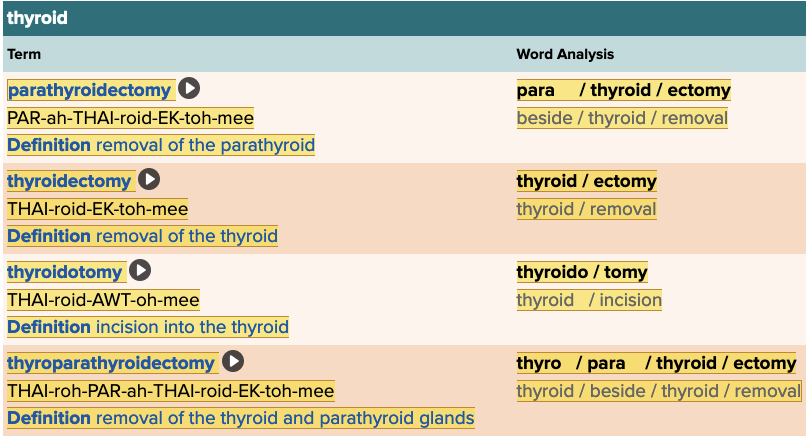 Chapter 7.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 59  Learning Outcome 7.5 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 59 no data |
front 60 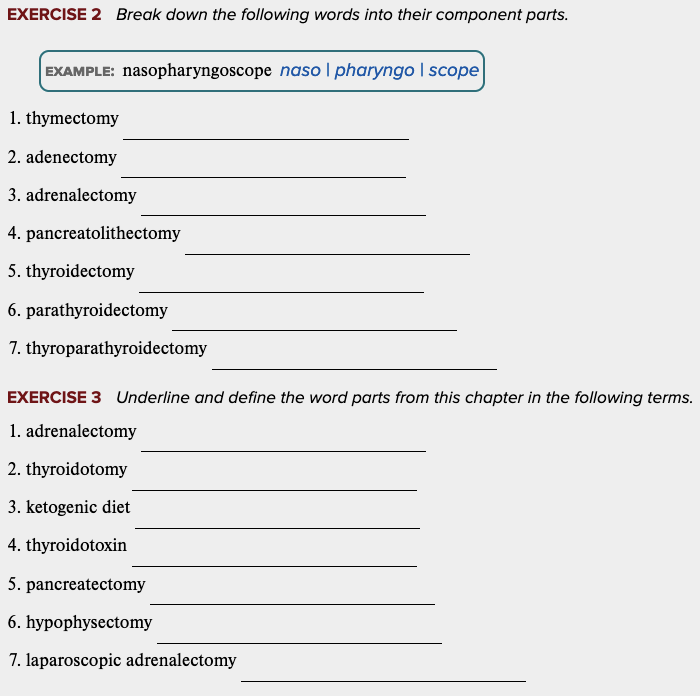 Learning Outcome 7.5 Exercises: Exercise 2, 3. | back 60 no data |
front 61  Learning Outcome 7.5 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 61 no data |
front 62  Learning Outcome 7.5 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 62 no data |
front 63  Chapter 7.6 Abbreviations | back 63 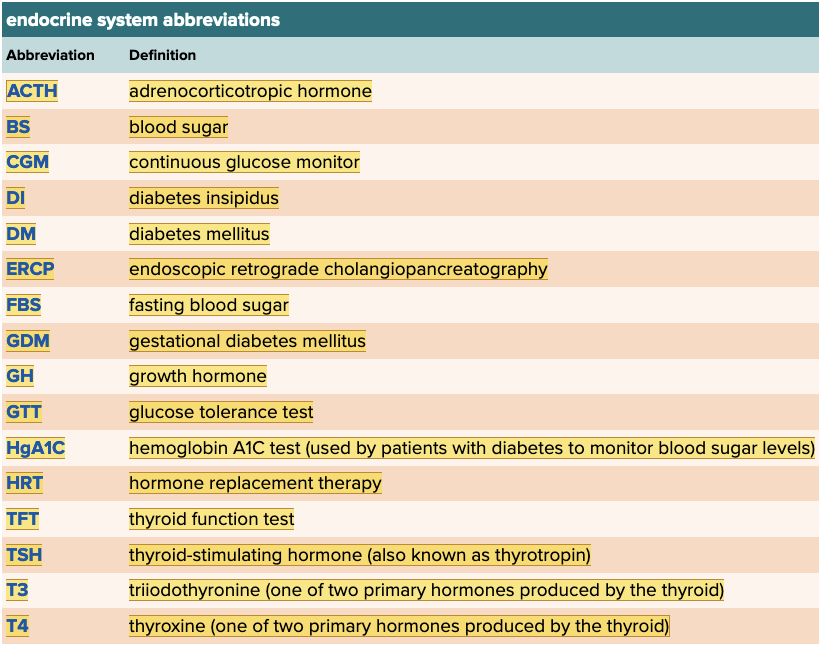 Chapter 7.6 Abbreviations
|
front 64  Learning Outcome 7.6 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 64 no data |
front 65  Learning Outcome 7.6 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 65 no data |
front 66  Learning Outcome 7.6 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 66  |
front 67 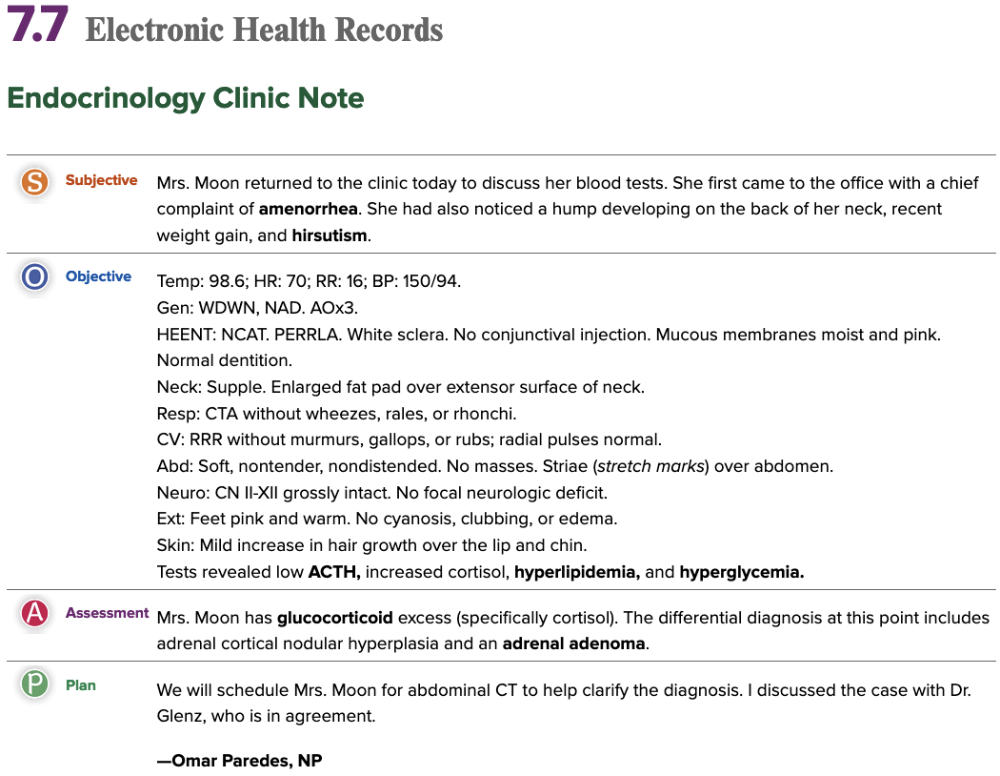 Chapter 7.7 Electronic Health Records Endocrinology Clinic Note | back 67 no data |
front 68  Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2, 3. | back 68 no data |
front 69  Chapter 7.7 Electronic Health Records Emergency Department Visit | back 69 no data |
front 70  Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 70 no data |
front 71  Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 6, 7. | back 71 no data |
front 72  Chapter 7.7 Electronic Health Records Surgery Follow-Up Note | back 72 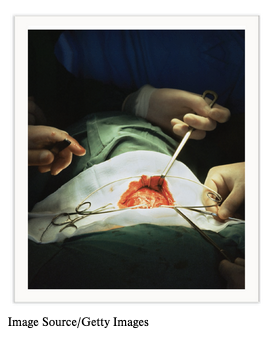 |
front 73  Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 8, 9. | back 73 no data |
front 74  Learning Outcome 7.7 Exercises: Exercise 10, 11. | back 74 no data |
front 75 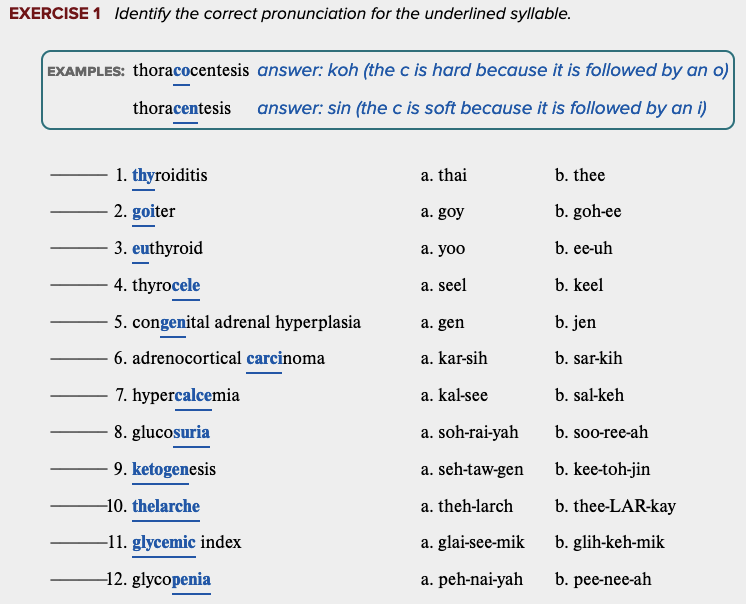 Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 75 no data |
front 76  Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 2, 3. | back 76 no data |
front 77  Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 77 no data |
front 78  Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 78 no data |
front 79  Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 79  |
front 80 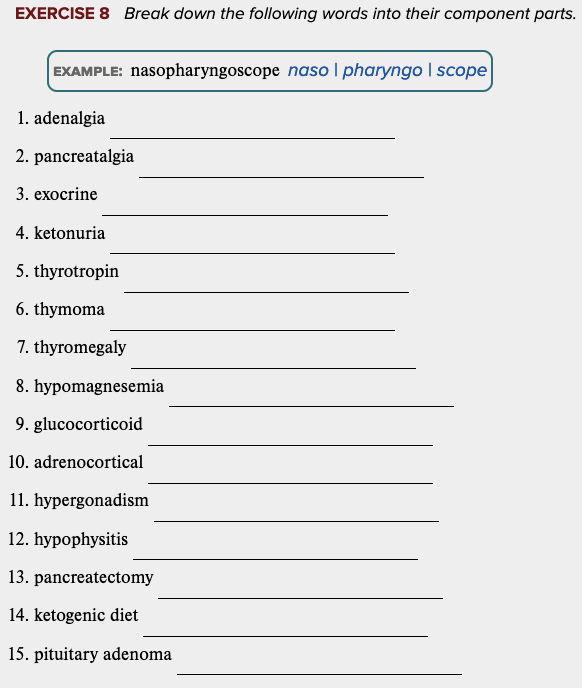 Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 80 no data |
front 81  Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 9. | back 81 no data |
front 82 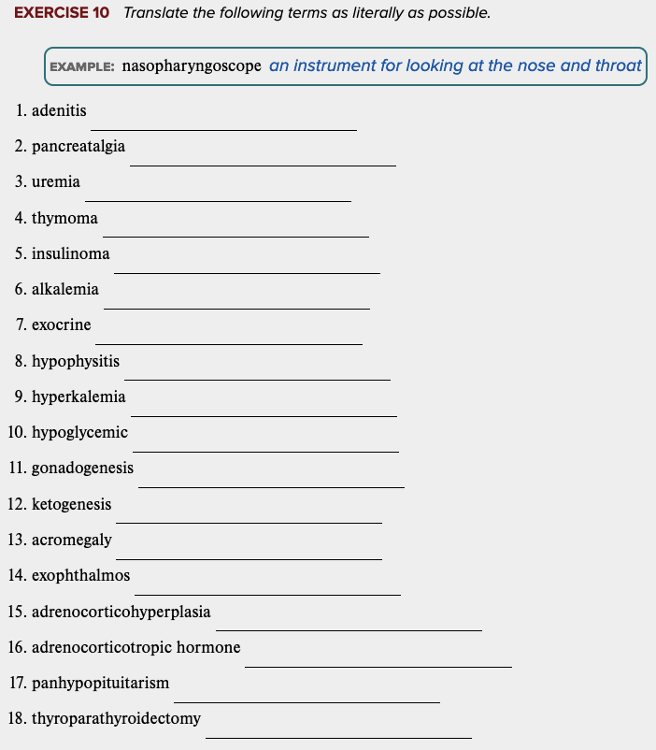 Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 10. | back 82 no data |
front 83  Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 11, 12. | back 83 no data |
front 84  Chapter 7 Review Exercises: Exercise 13, 14, 15. | back 84 no data |
front 85 Hormones generally cause ______ changes to their target cells than the nervous system. Multiple choice question.
| back 85 slower |
front 86 The thyroid gland and parathyroid gland release hormones that ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 86 keep critical minerals like calcium and sodium in balance |
front 87 Select all that apply Identify all the glands associated with the endocrine system. Multiple select question.
| back 87
|
front 88 The main function of the hypothalamus is to direct the activity of the ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 88 pituitary gland |
front 89 What does thyroid hormone refer to? Multiple choice question.
| back 89 T3 and T4 |
front 90 Which of the following organ is not an endocrine organ? Multiple choice question.
| back 90 liver |
front 91 The gland that is both an endocrine gland and a gastrointestinal organ is the ______. | back 91 pancreas |
front 92 Growth hormone functions to ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 92 help the body grow to adult height |
front 93 The inner layer of the adrenal gland makes the fight-or-flight hormone called ______. | back 93 adrenaline or epinephrine |
front 94 The signal makers and senders of the endocrine system are called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 94 glands |
front 95 The male gonads are the ______ and the female gonads are the ______. | back 95 Blank 1: testes, teste, testicles, or testicle Blank 2: ovaries or ovary |
front 96 The chemical signals used by the hypothalamus to affect the function of the pituitary are called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 96 releasing hormones |
front 97 In the words corticotropic and adrenocorticohyperplasia, the root cortic (combining form cortic/o) means ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 97 outer surface |
front 98 Select all that apply What two glands help to regulate calcium levels in the blood? Multiple select question.
| back 98
|
front 99 The suffix -pathy means disease. A disease of the sex organs is called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 99 gonadopathy |
front 100 Select all that apply The pancreas functions to ______. Multiple select question.
| back 100
|
front 101 The suffix -lith means stone. A stone in the pancreas is called a(n) ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 101 pancreatolith |
front 102 Select all that apply The outer cortex of the adrenal gland functions to ______. Multiple select question.
| back 102
|
front 103 What endocrine organ is named for its resemblance to a shield and lies in the throat region? Multiple choice question.
| back 103 Thyroid |
front 104 Select all that apply What hormones are secreted by the gonads? Multiple select question.
| back 104
|
front 105 Select all that apply Which of the following are examples of glands used for excessive exocrine responses? Multiple select question.
| back 105
|
front 106 In the words adenoma and adenopathy, the root aden (combining form aden/o) means ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 106 gland |
front 107 In the term gonadogenesis, the word genesis means ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 107 to create |
front 108 Which of the following is a term used for secretion? Multiple choice question.
| back 108 crino |
front 109 Select all that apply Which of the following are the Greek terms for pancreas? Multiple select question.
| back 109
|
front 110 Select all that apply The hormones produced by the pancreas include ______. Multiple select question.
| back 110 glucagon insulin |
front 111 What root (combining form) is used to describe the pituitary?
| back 111 Hypophys/o |
front 112 Which of the following is a hormones produced in the gonads of the male? Multiple choice question.
| back 112 Testosterone |
front 113 What word means to secrete internally? Multiple choice question.
| back 113 Endocrine |
front 114 In the words corticotropic and adrenocorticohyperplasia, the root cortic (combining form cortic/o) means ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 114 outer surface |
front 115 When the level of glucose is measured as high the patient would be diagnosed as having ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 115 hyperglycemia |
front 116 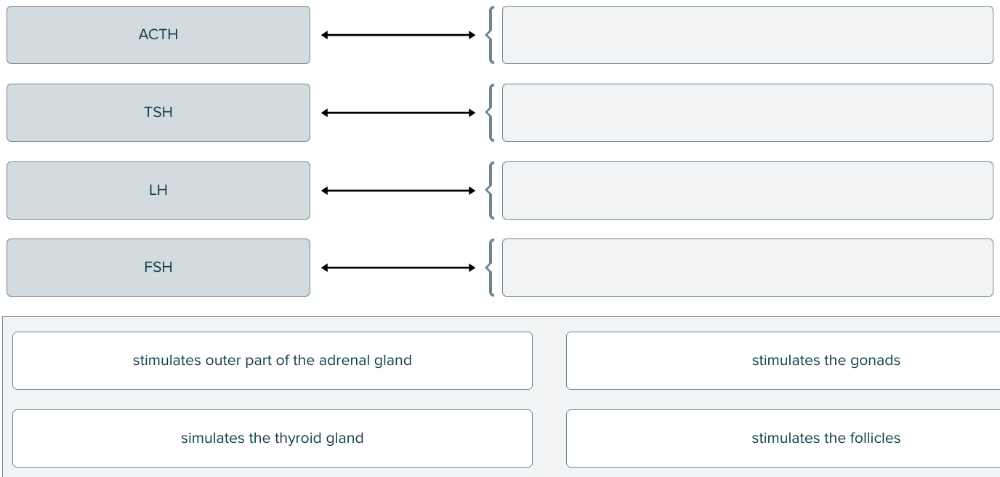 Drag and drop the hormone definition against the corresponding stimulation area. | back 116 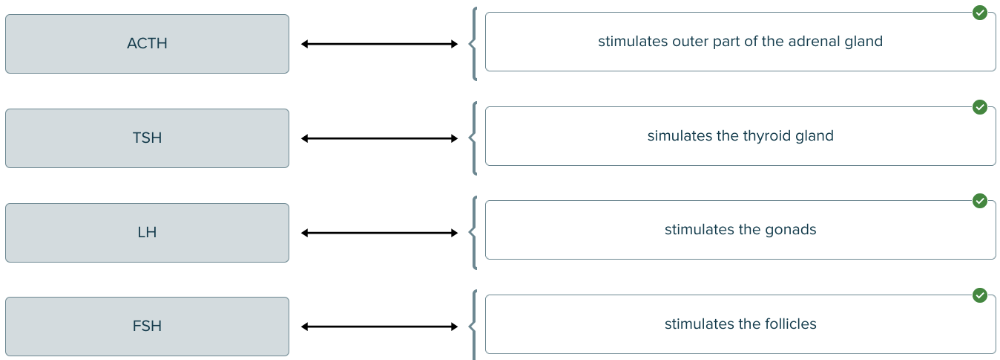 |
front 117 The presence of ketone bodies is normally a sign of untreated or poorly controlled ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 117 diabetes |
front 118 The hormone that has the opposite effect as parathyroid hormone is ______. | back 118 calcitonin |
front 119 Select all that apply What are two types of corticosteroids used in the adrenal glands? Multiple select question.
| back 119 Glucocorticoids Mineralocorticoids |
front 120 The suffix means blood condition is called ______. | back 120 -emia |
front 121 The main form of sugar found in the bloodstream is called ______. | back 121 glucose |
front 122 Match the endocrine term associated with its definition. | back 122 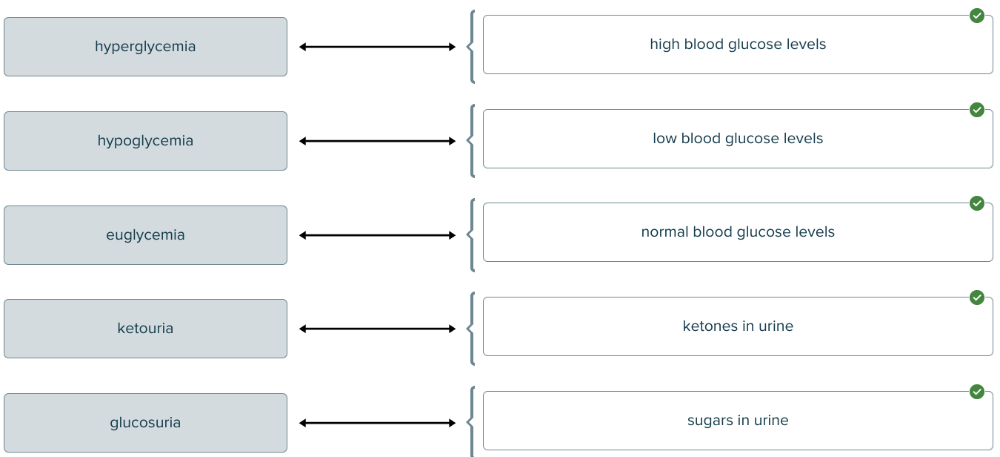 |
front 123 Bulging of the eyes due to hyperthyroidism is called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 123 exophthalmos |
front 124 A substance that increases in the blood as a result of faulty carbohydrate metabolism is called a ______ body. | back 124 ketone |
front 125 Fill in the blank question. Insulin and glucagon regulate ______ levels in the blood, while calcitonin and parathyroid hormone regulate ______ levels in the blood. | back 125 Blank 1: sugar or glucose Blank 2: calcium |
front 126 The term that describes constant hunger in patients with diabetes is called ______. | back 126 polyphagia |
front 127 Which suffix means urine condition? Multiple choice question.
| back 127 -uria |
front 128 The suffix -arche indicates beginning. When the glands on top of the kidney begin secreting hormones, it is called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 128 adrenarche |
front 129 What word means to secrete internally? Multiple choice question.
| back 129 Endocrine |
front 130 Lack of menstrual flow is termed ______. | back 130 amenorrhea |
front 131 The thyroid disorder that results in decreased metabolism, weight gain and decreased appetite is called ______. | back 131 hypothyroidism |
front 132 If a patient has low blood sugar, she is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 132 hypoglycemic |
front 133 Males that experience breast development have the condition called ______. | back 133 gynecomastia |
front 134 The prefix galacto- means ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 134 milk |
front 135 Pain of a gland is called ______. | back 135 adenalgia |
front 136 Which of the following terms would describe thyroptosis? Multiple choice question.
| back 136 Drooping of the thyroid |
front 137 The beginning of breast development in women is termed ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 137 thelarche |
front 138 Which of the following is a term often used to describe adrenaline? Multiple choice question.
| back 138 Epinephrine |
front 139 The suffix -emia means blood condition. Drag and drop the definitions against the corresponding blood conditions. | back 139 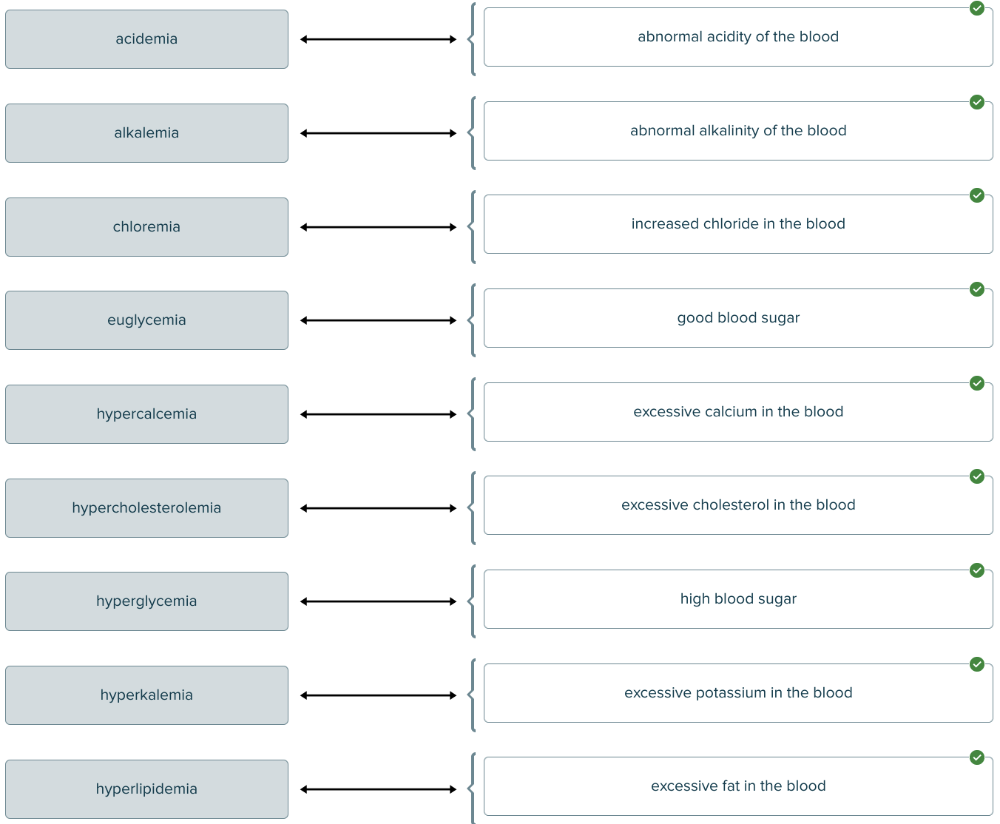 |
front 140 The Greek prefix poly- means excessive. Match each pancreatic disease with its description. | back 140 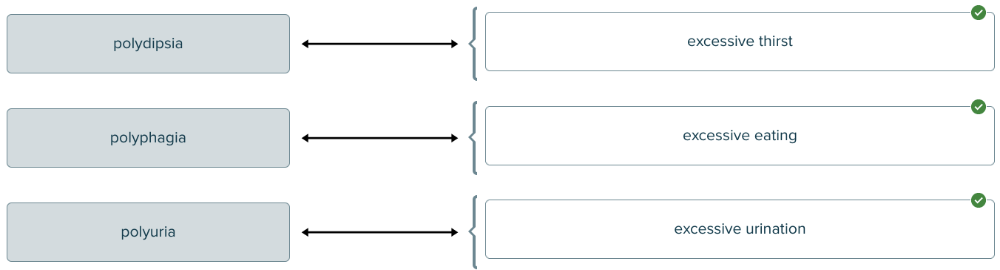 |
front 141 The term that describes having too much base in the blood is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 141 alkalemia |
front 142 Which of the following would be associated with acromegaly? Multiple choice question.
| back 142 Enlargement of the extremities |
front 143 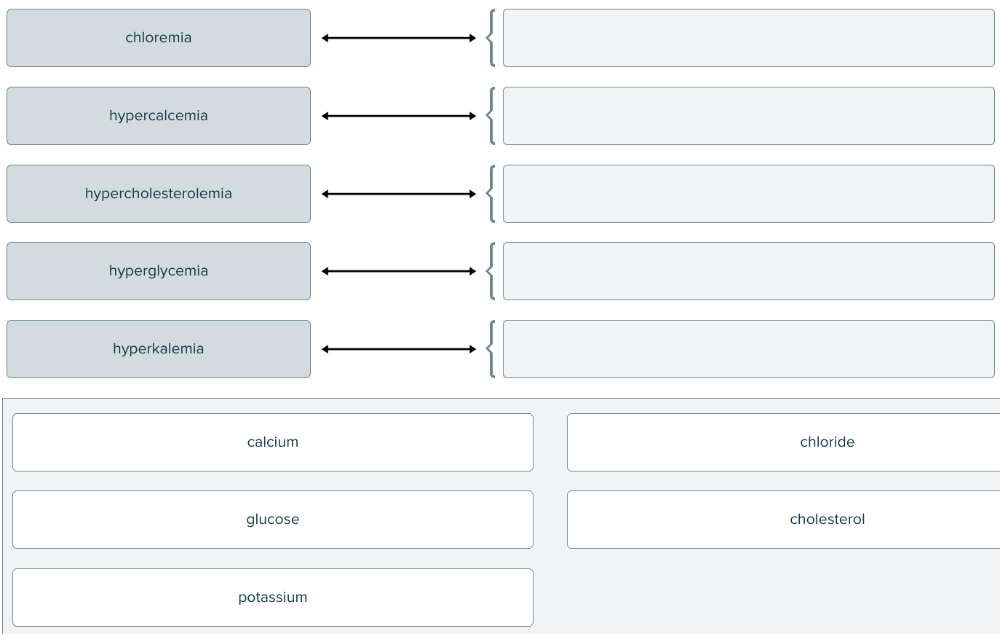 Match the blood condition with abnormal compound in the blood. | back 143 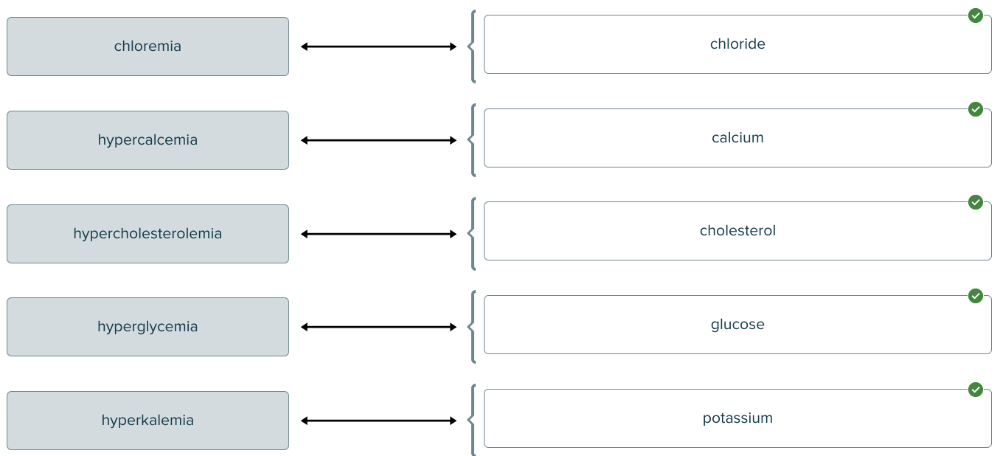 |
front 144 The term that means to have swollen thyroid glands is ______. | back 144 goiter or thyrocele |
front 145 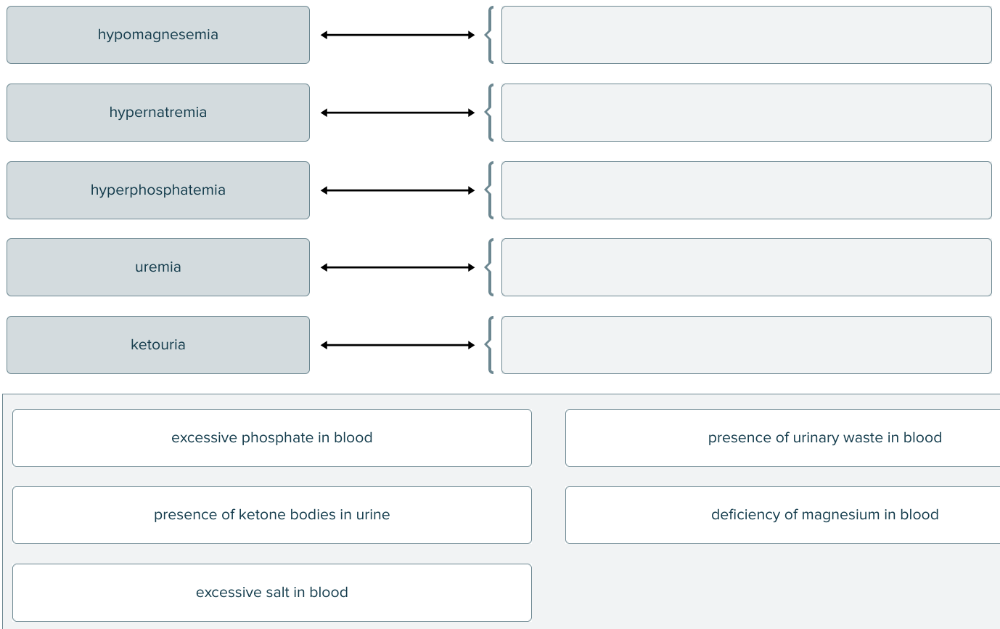 Match each blood and urine condition with the abnormal compound(s) found. | back 145 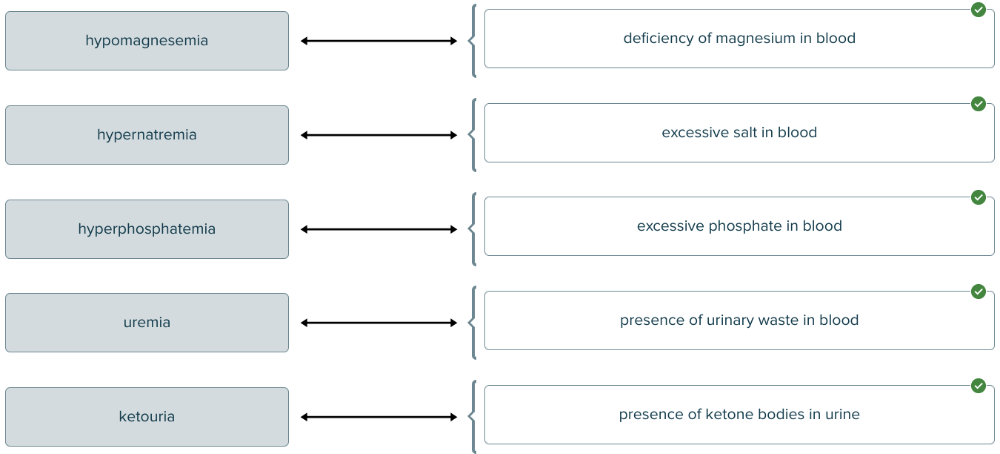 |
front 146 Select all that apply Select the tests below used for endocrinology testing. Multiple select question.
| back 146
|
front 147 Adrenaline and ______ are the same thing. | back 147 epinephrine |
front 148 Which of the following is the term used for excessive potassium in the blood? Multiple choice question.
| back 148 Hyperkalemia |
front 149 Which hormone is secreted by the pancreas and controls the metabolism and uptake of sugar and fats? Multiple choice question.
| back 149 Insulin |
front 150 An abnormal acidity in the blood is termed ______. | back 150 acidemia |
front 151 Which of the following would describe a deficiency of sugar in the body? Multiple choice question.
| back 151 Glycopenia Ex.
Reason: This is the abnormal enlargement of a gland
Reason: This is a creation of gonads
Reason: This is the normal function of thyroid |
front 152 Which term means good blood sugar? Multiple choice question.
| back 152 euglycemia |
front 153 The term that describes the breakdown of matter into energy for the human body is ______. | back 153 metabolism |
front 154 Excessive urination is called ______. | back 154 polyuria |
front 155 Which of the definitions below would describe a glycemic index? Multiple choice question.
| back 155 Ranking of food based on the way it affects sugar levels in the blood. |
front 156 Which hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland and stimulates the cortex of the adrenal gland? Multiple choice question.
| back 156 Corticotropin Ex. Shorter name for the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). |
front 157 The procedure that examines the bile ducts and pancreas is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 157 cholanglopancreatography Ex.
Reason: hormone secreted by the pituitary gland
Reason: creation of ketone bodies
Reason: specialist in internal secretions |
front 158 The hormone that stimulates the gonads is ______. | back 158 gonadotropin |
front 159 Pituitary infarction refers to ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 159 death of the pituitary gland |
front 160 In the laboratory result euthyroid, the prefix eu- means ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 160 good |
front 161 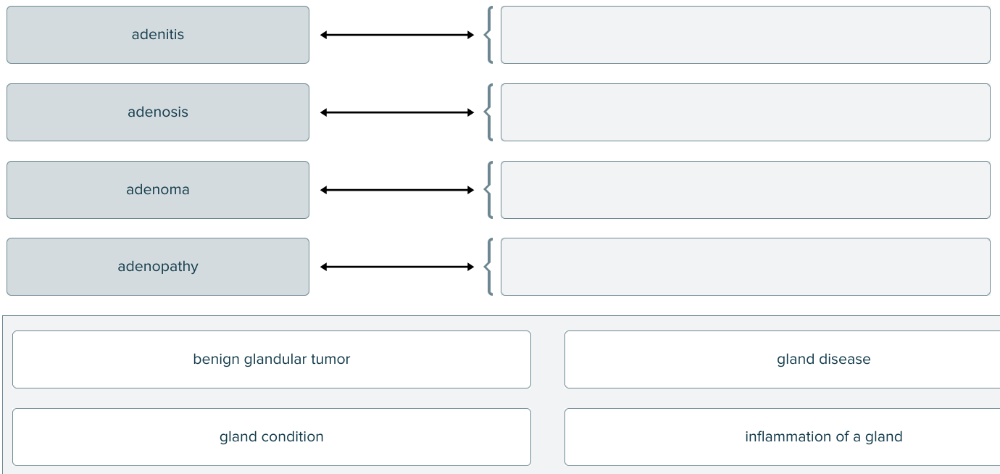 The root aden (and combining form aden/o) means gland. Match each term pertaining to a gland with its definition. | back 161 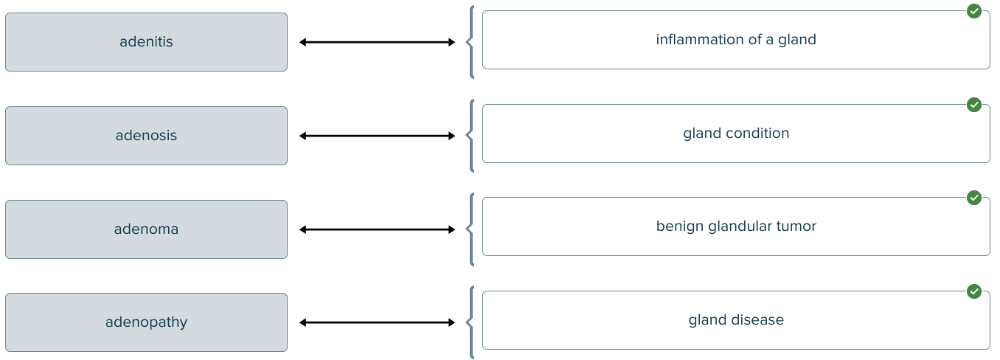 |
front 162 Which suffix means formation? Multiple choice question.
| back 162 -genesis |
front 163 Which of the following would describe the inflammation of the adrenal gland? Multiple choice question.
| back 163 Adrenalitis Ex.
Reason: gland disease
Reason: disease involving many glands
Reason: condition characterized by elevated levels of ketone bodies in the blood |
front 164 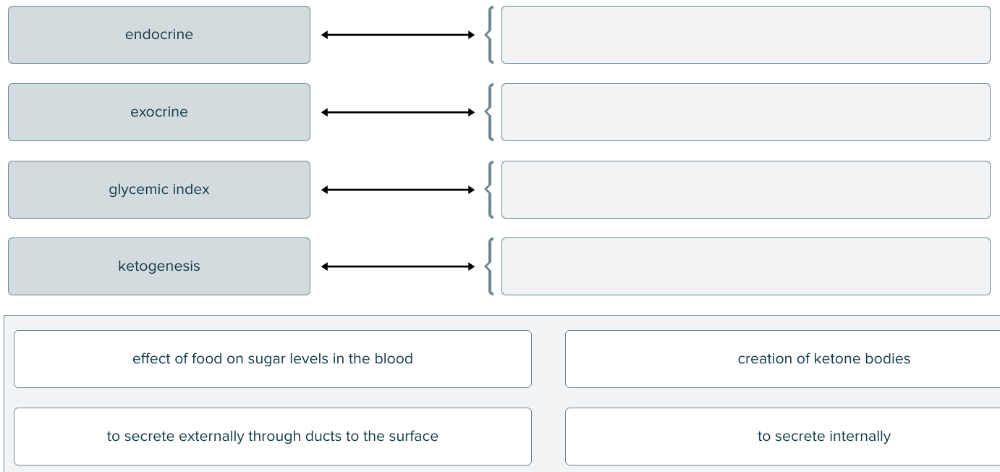 Match each professional and diagnostic term associated with the endocrine system to its description. | back 164 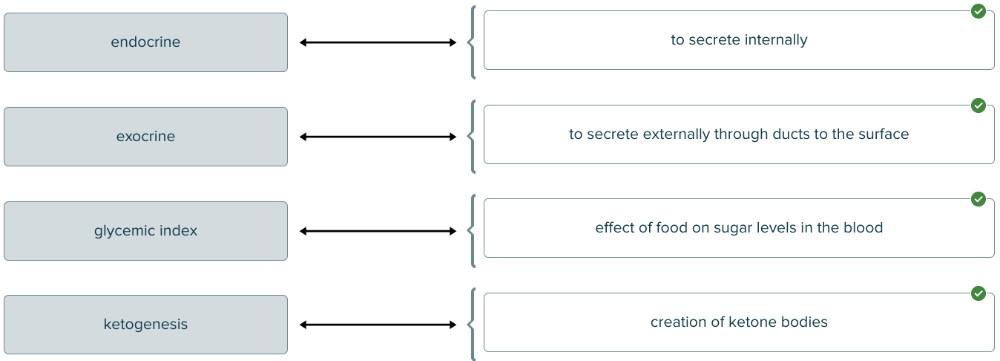 |
front 165 Excessive sugar in urine is characteristic of ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 165 diabetes mellitus |
front 166 Select all that apply Which of the following are the root for the term cholangiopancreatography? Multiple select question.
| back 166
Ex.
Reason: pancreas
Reason: vessel
Reason: bile
Reason: suffix |
front 167 Inflammation of the pituitary gland is termed ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 167 hypophysitis |
front 168 What is the condition when a thyroid gland is producing too much hormone? Multiple choice question.
| back 168 Hyperthyroidism Ex.
Reason: inflammation of a gland
Reason: gland disease
Reason: too low |
front 169 If the function of the entire pituitary gland is defective or absent, it is termed ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 169 panhypopituitarism |
front 170 When a patient has a combination of medical disorders, all of which are associated with faulty metabolism, she is said to have ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 170 dysmetabolic syndrome |
front 171 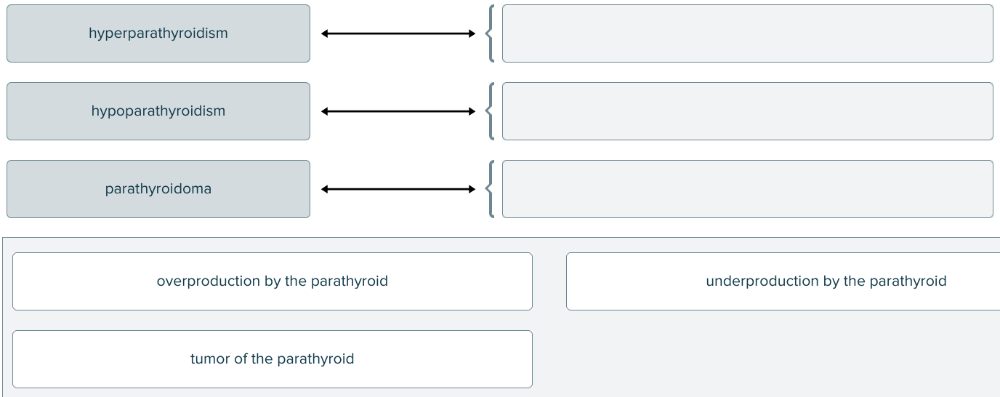 Match each parathyroid-related medical term with its definition. | back 171 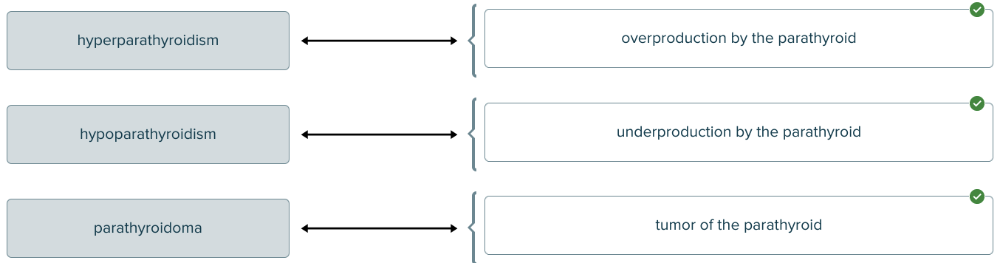 |
front 172 A condition in which the adrenal cortex underproduces necessary hormones is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 172 adrenocortical insufficiency |
front 173 Select all that apply Which of the following word roots are associated with the term adrenocortical carcinoma? Multiple select question.
| back 173
|
front 174 Which of the following pancreas terms would be defined as a stone in the pancreas? Multiple choice question.
| back 174 Pancreatolith |
front 175 When a patient's hormone levels are too low they are given ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 175 hormone replacement therapy |
front 176 Overfunctioning of the pituitary gland is termed ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 176 hyperpituitarism Ex.
Reason: Gigantism can be caused by overfunctioning of the pituitary gland, but it's a sign associated with the disease, not the disease name itself. |
front 177 Select all that apply Which of the following word parts are associated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion? Multiple select question.
| back 177
|
front 178 Death of the pituitary gland is termed ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 178 pituitary infarction |
front 179 The surgical term for the removal of a gland in the endocrine system is ______. | back 179 adenectomy |
front 180 Which of the following is caused by a underproduction of the parathyroid? Multiple choice question.
| back 180 Hypoparathroidism |
front 181 Select all that apply Which of the following are terms used for the term adrenalectomy? Multiple select question.
| back 181
|
front 182 Which of the following conditions is a tumor of the thymus? Multiple choice question.
| back 182 Thymoma |
front 183 In the term pancreatolithectomy, the word part that means stone is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 183 lith |
front 184 Select all that apply What are the routes used for delivering supplemental hormones to patients? Multiple select question.
| back 184
|
front 185 In the term hypophysectomy, the root word means ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 185 pituitary |
front 186 A substance poisonous to the thyroid gland is called a ______. | back 186 thyroidotoxin |
front 187 In the term ketogenic diet, the suffix -genic means ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 187 creating |
front 188 The term thyroidotomy means ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 188 incision into the thyroid |
front 189 Removal of the adrenal gland using an instrument inserted into the abdomen for viewing is called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 189 laparoscopic adrenalectomy |
front 190 The abbreviation for glucose tolerance test is ______. | back 190 GTT |
front 191 Which of the following means removal of the pancreas? Multiple choice question.
| back 191 Pancreatectomy |
front 192 The removal of the pituitary gland is termed ______. | back 192 hypophysectomy |
front 193 The removal of the thyroid gland is termed ______. | back 193 thyroidectomy |
front 194 The abbreviation GDM means ______ ______ ______ | back 194 Blank 1: gestational Blank 2: diabetes Blank 3: mellitus |