Chapter 4: The Musculoskeletal System - Orthopedics

Chapter 4.1
Introduction and Overview of the Musculoskeletal System

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Bones
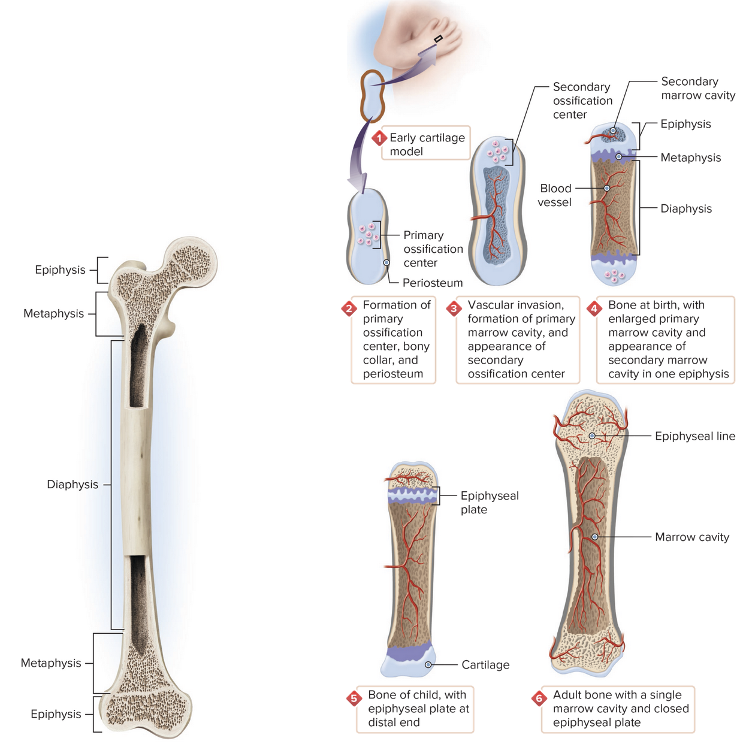

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Bones
- Growth Table: Root Examples

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
The Skeleton
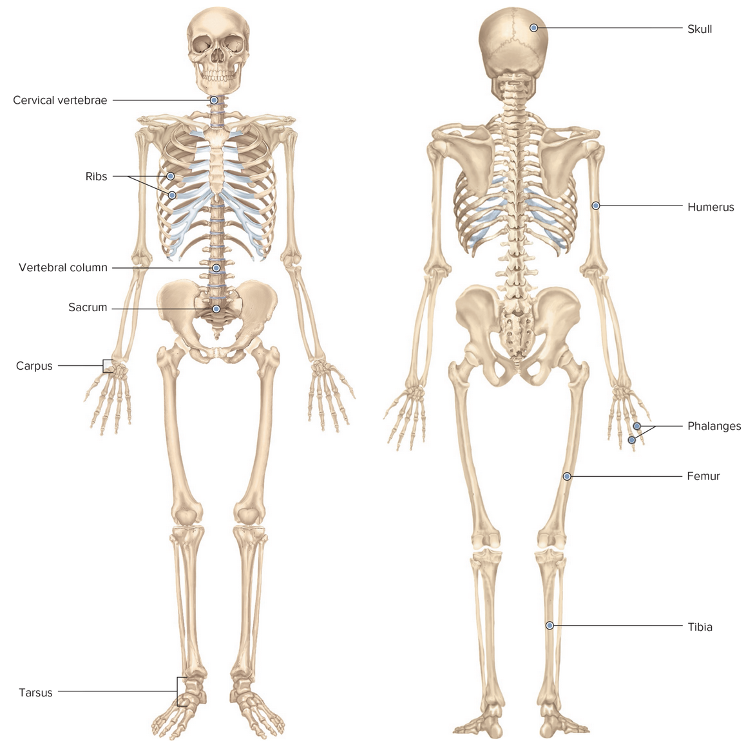

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
The Skeleton
- Parts of Skeleton Table: Root Examples Part 1
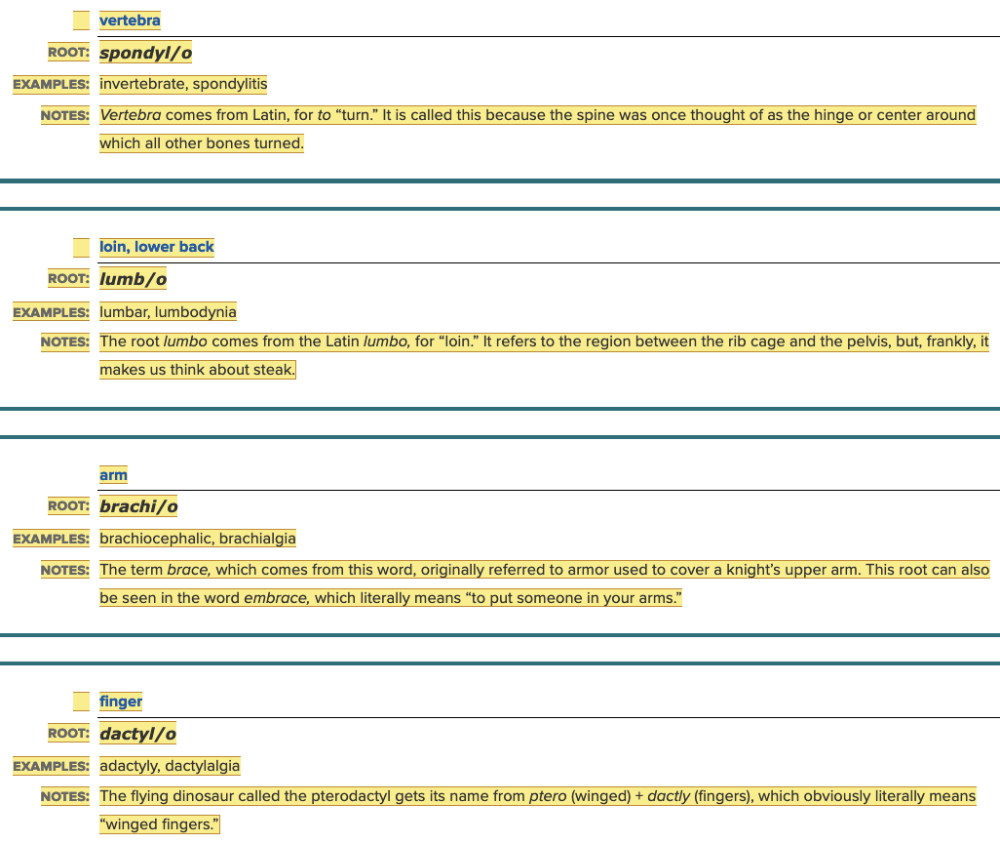
Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
The Skeleton
- Parts of Skeleton Table: Root Examples Part 2
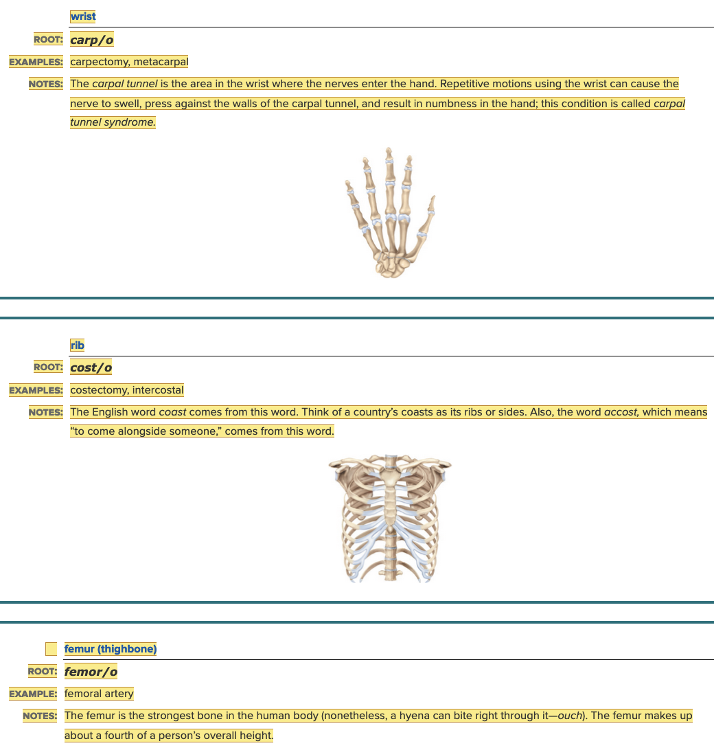
Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
The Skeleton
- Parts of Skeleton Table: Root Examples Part 3
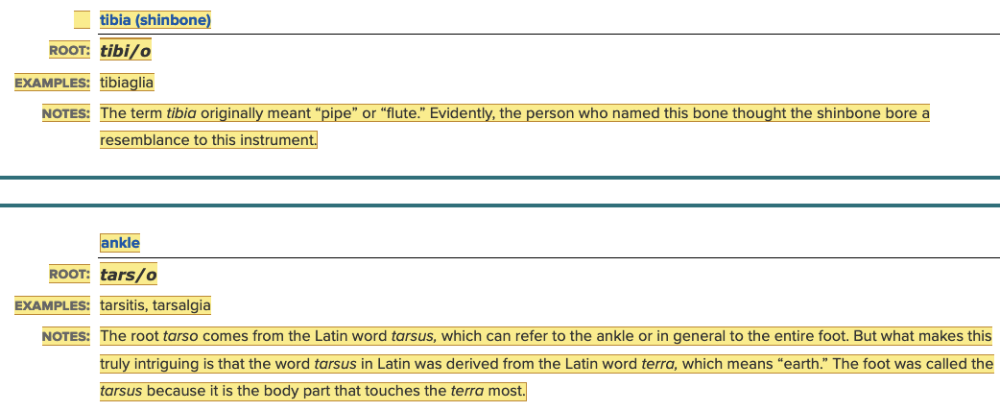
Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
The Skeleton
- Parts of Skeleton Table: Root Examples Part 4

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Joints

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Joints
- Parts of the Joint Table: Root Examples
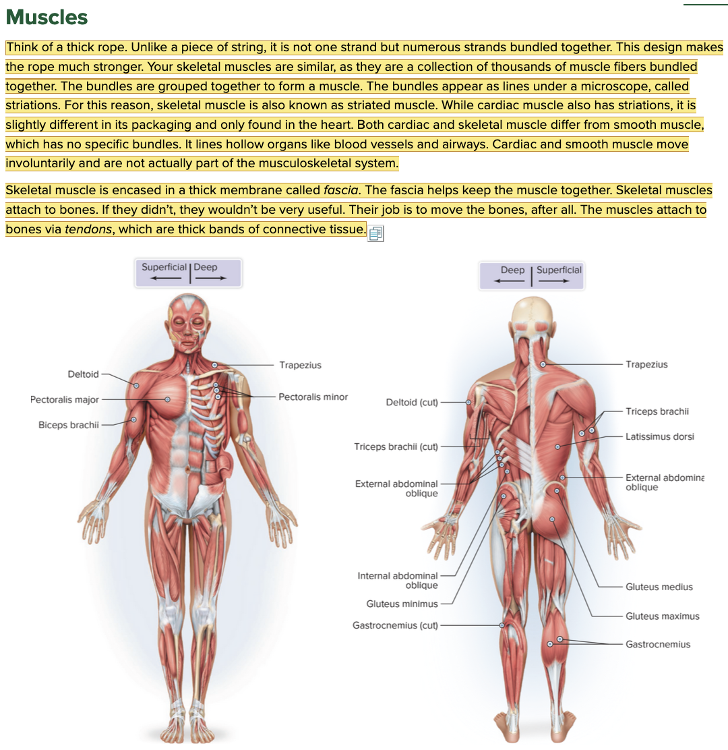
Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Muscles

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Muscles
- Parts of the Muscle Table: Root Examples Part 1
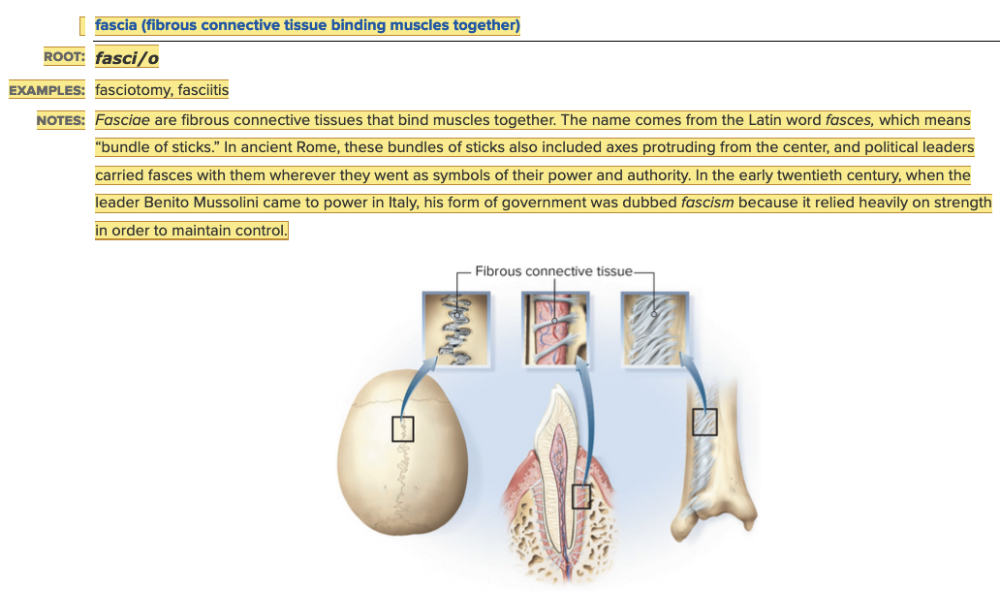
Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Muscles
- Parts of the Muscle Table: Root Examples Part 2

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Motion

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Motion
- Motion Table: Root Examples Part 1

Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System
Motion
- Motion Table: Root Examples Part 2

Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2.
Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4.

Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 5, 6.

Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 7, 8.

Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10.

Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective
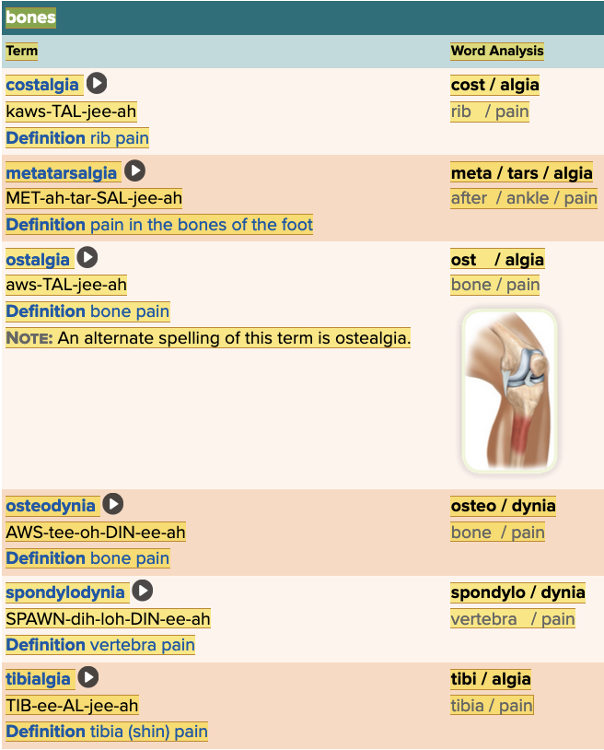
Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective: Bones Table
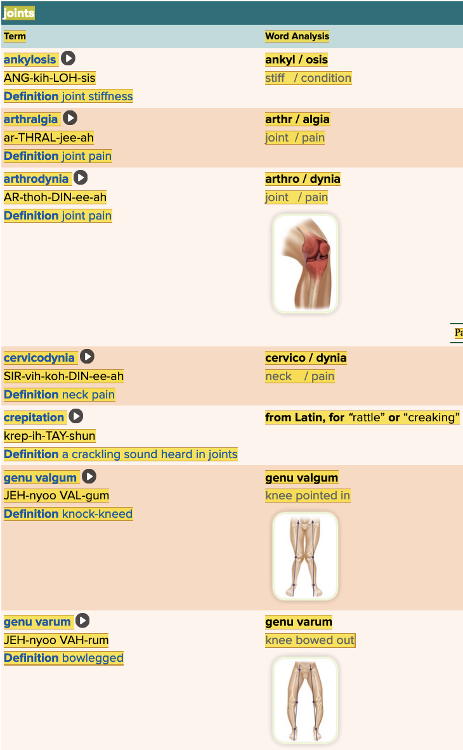
Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective: Joints Table
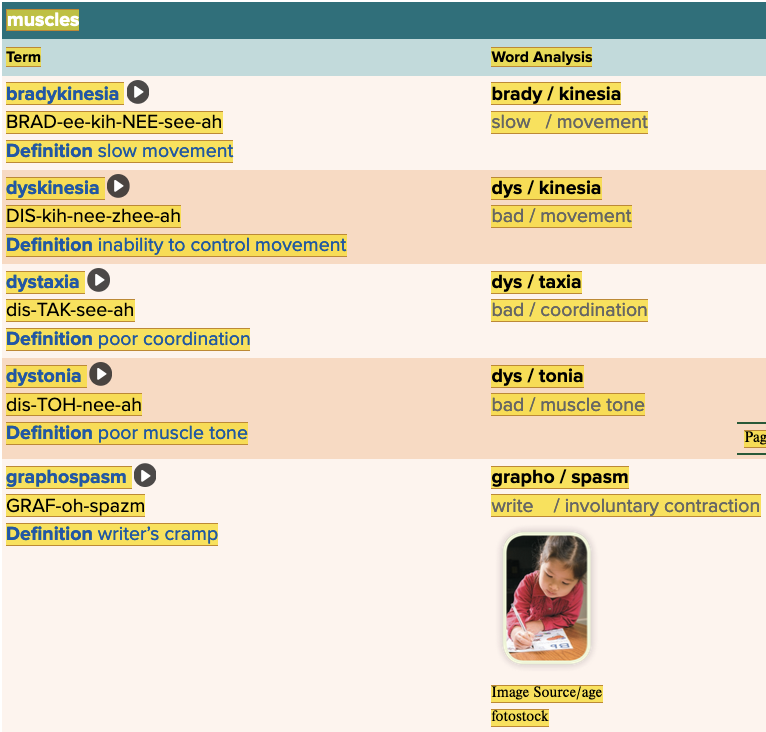
Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective: Muscles Table Part 1
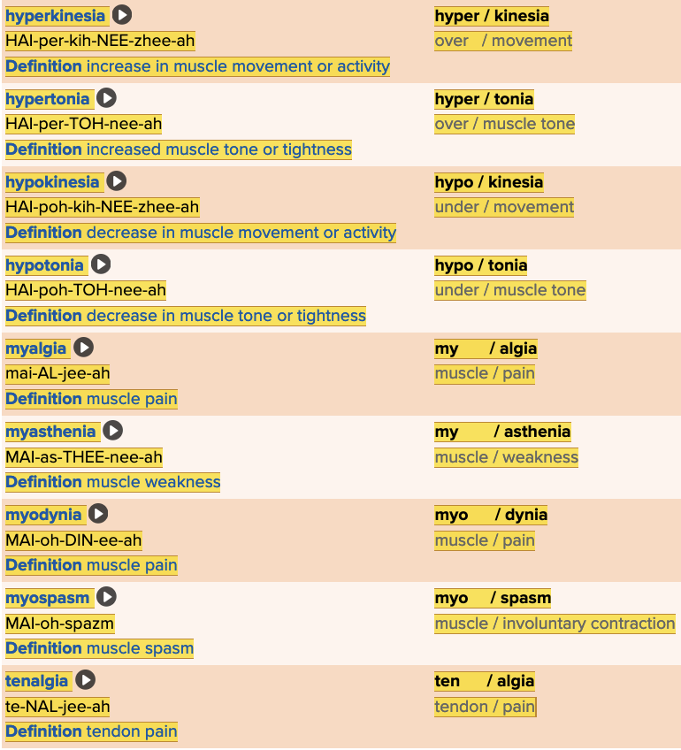
Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
- Subjective: Muscles Table Part 2

Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 1.

Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 2.
Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 3.
Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5.

Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 6.

Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 7.

Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective

Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective
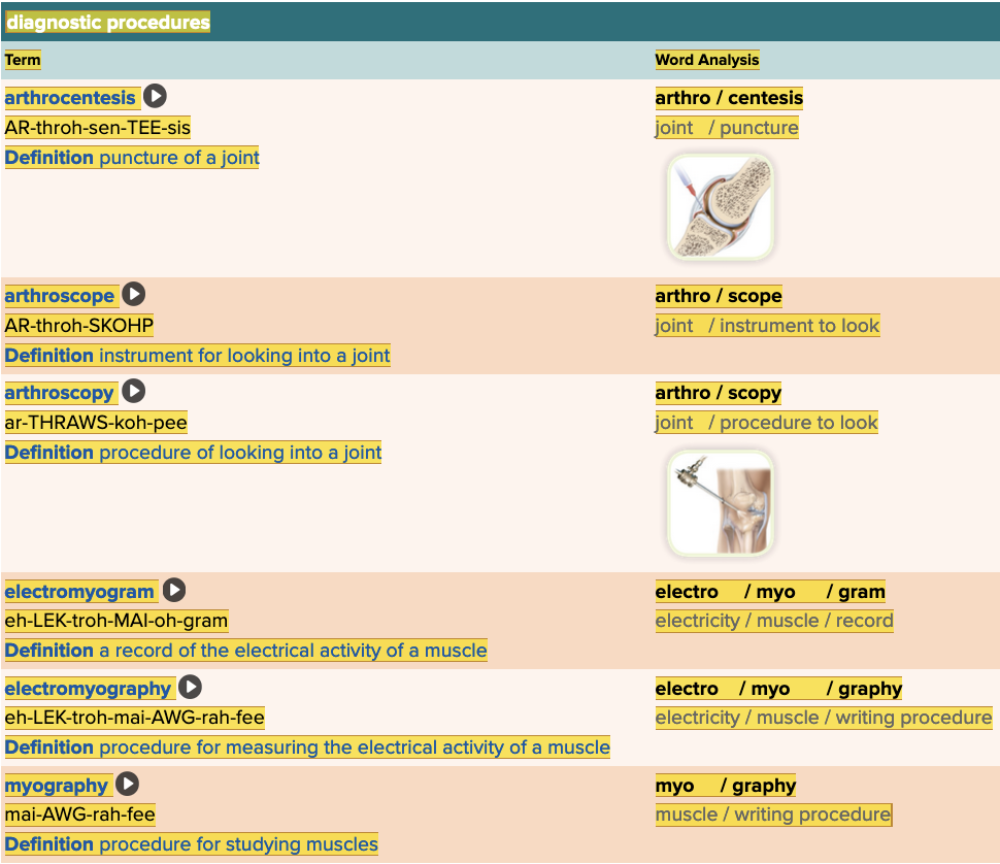
Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Diagnostic Procedures Table
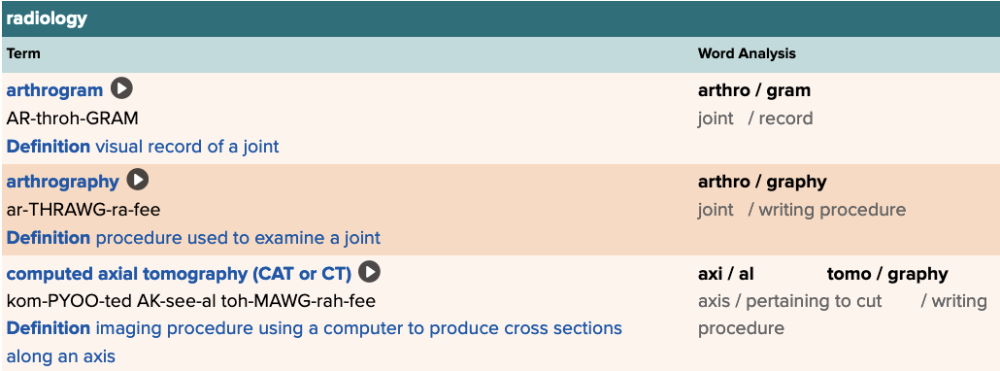
Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Radiology Table
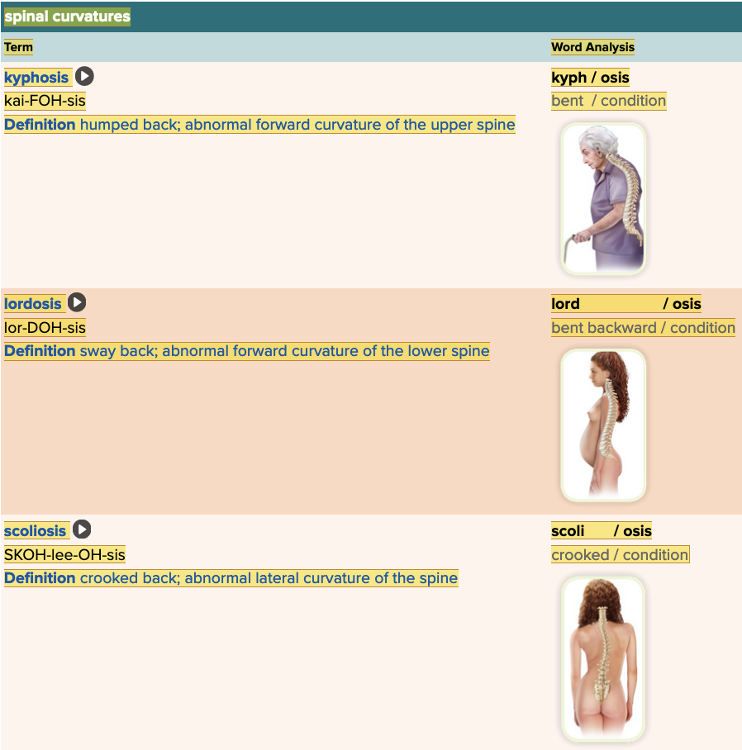
Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Spinal Curvatures Table
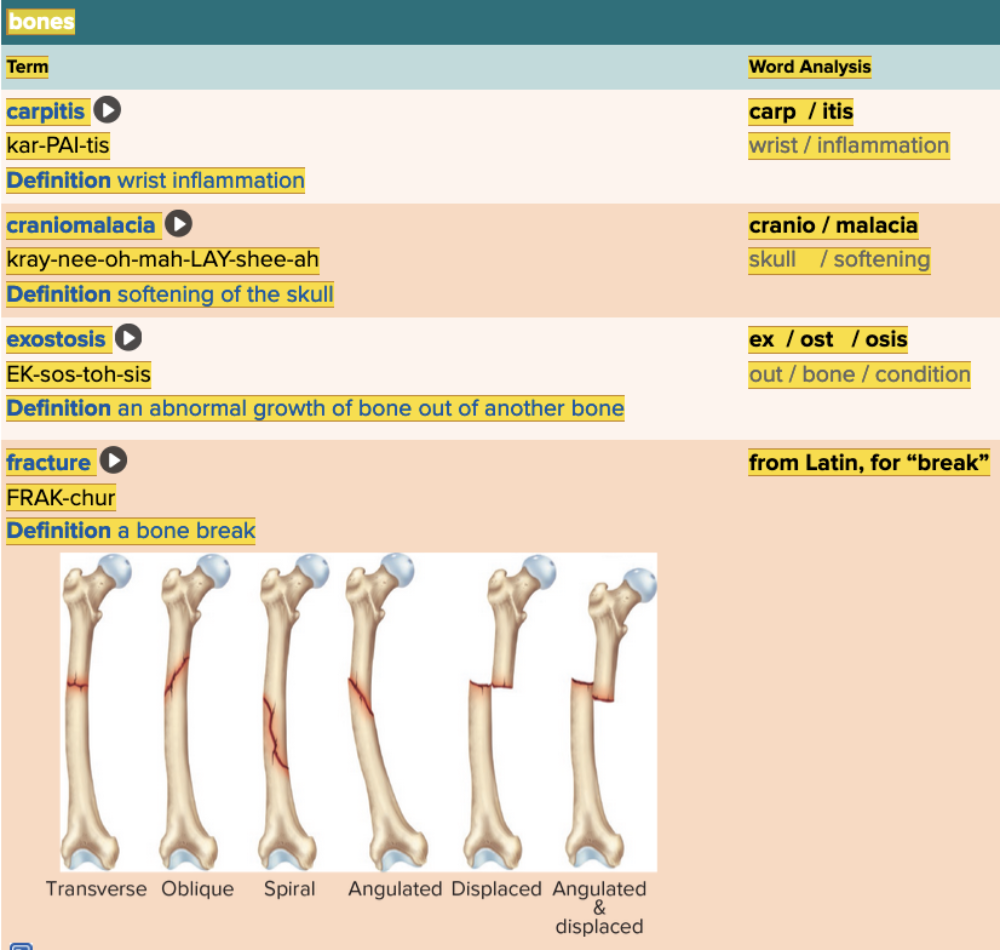
Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Bones Table Part 1
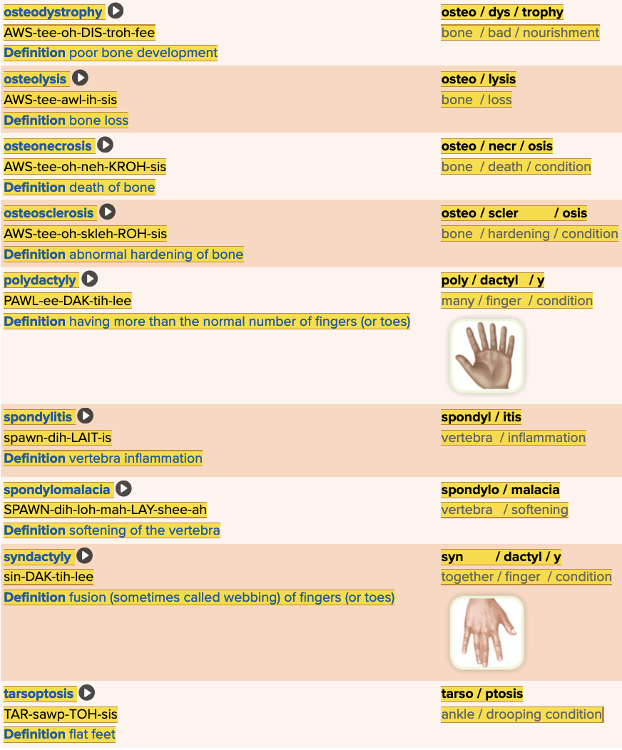
Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Bones Table Part 2
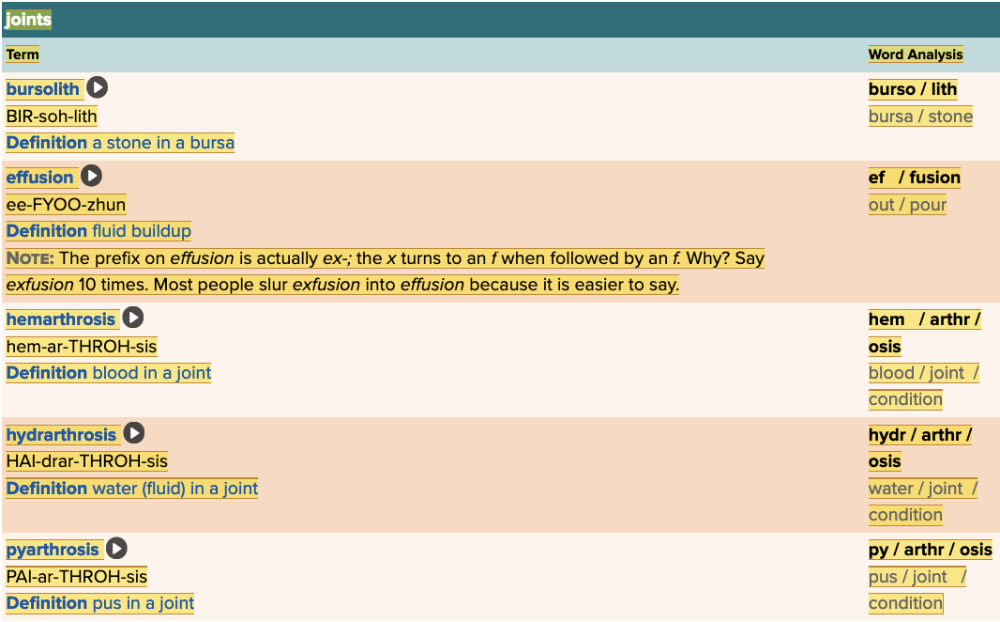
Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Joints Table
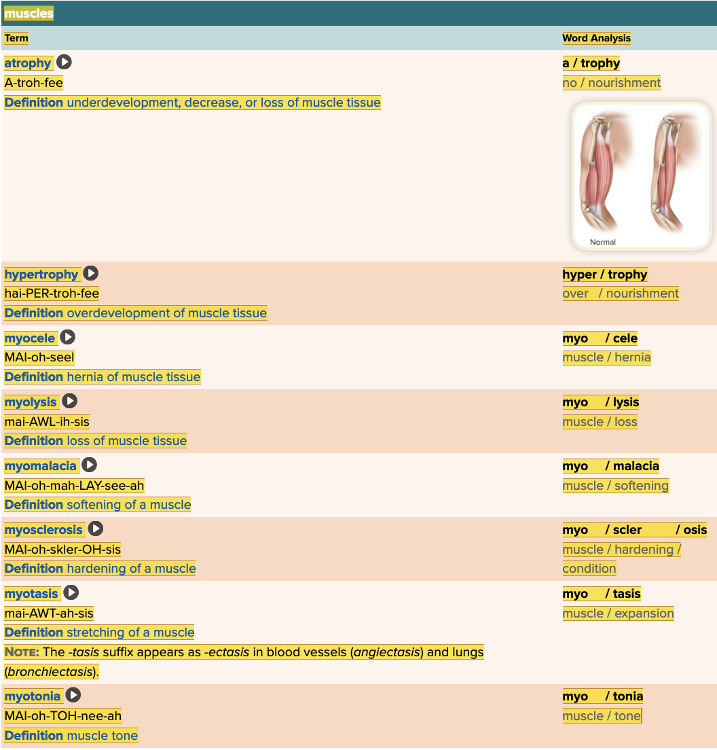
Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
- Objective: Muscles Table

Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 1.
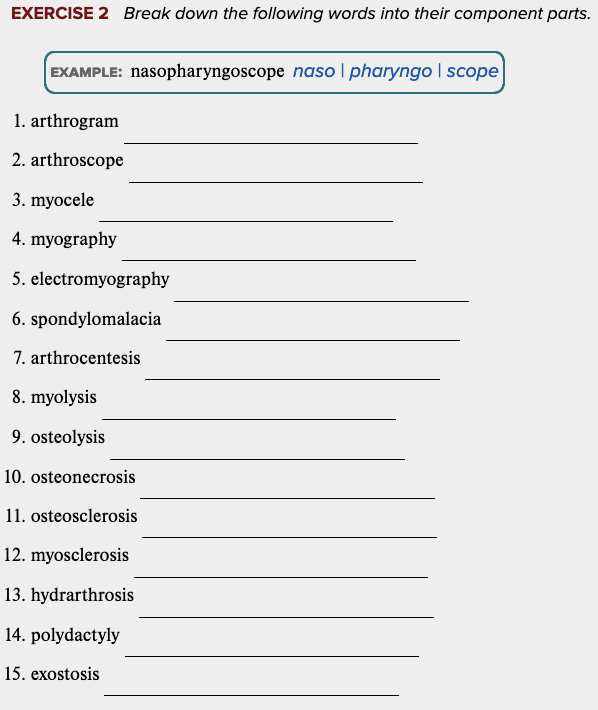
Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 2.
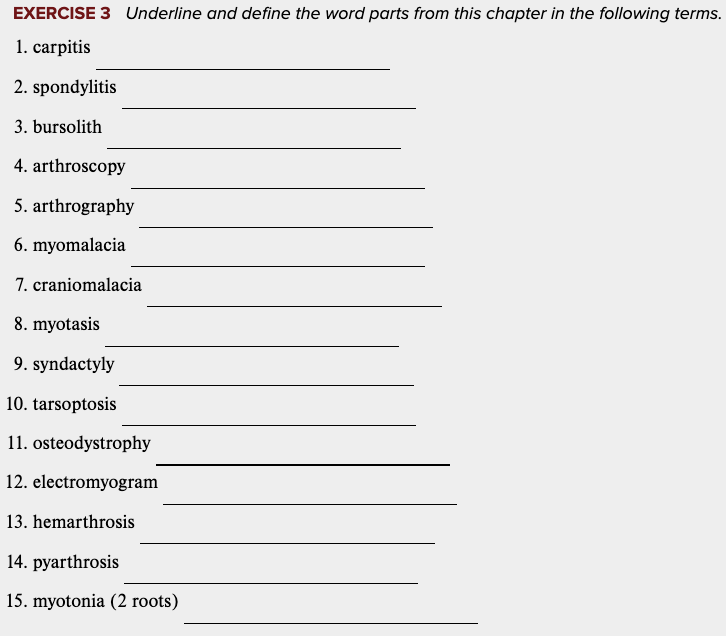
Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 3.
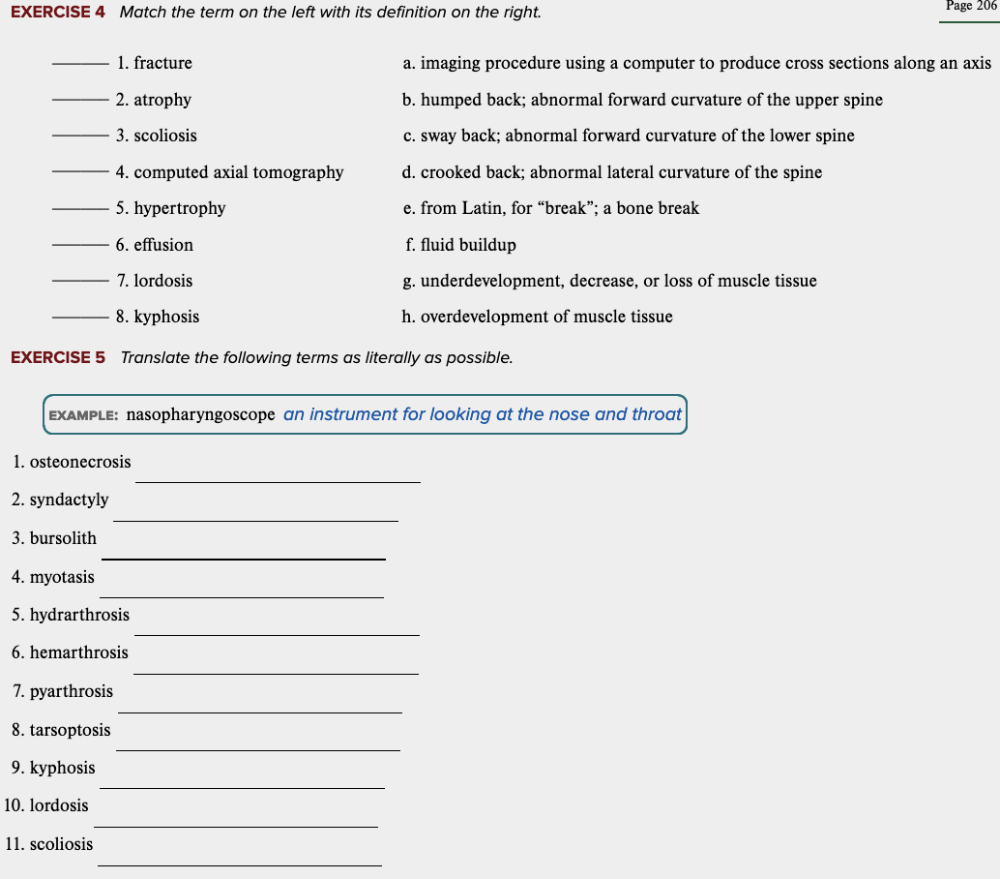
Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5.

Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 6.

Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 7.


Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 8.

Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment

Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment
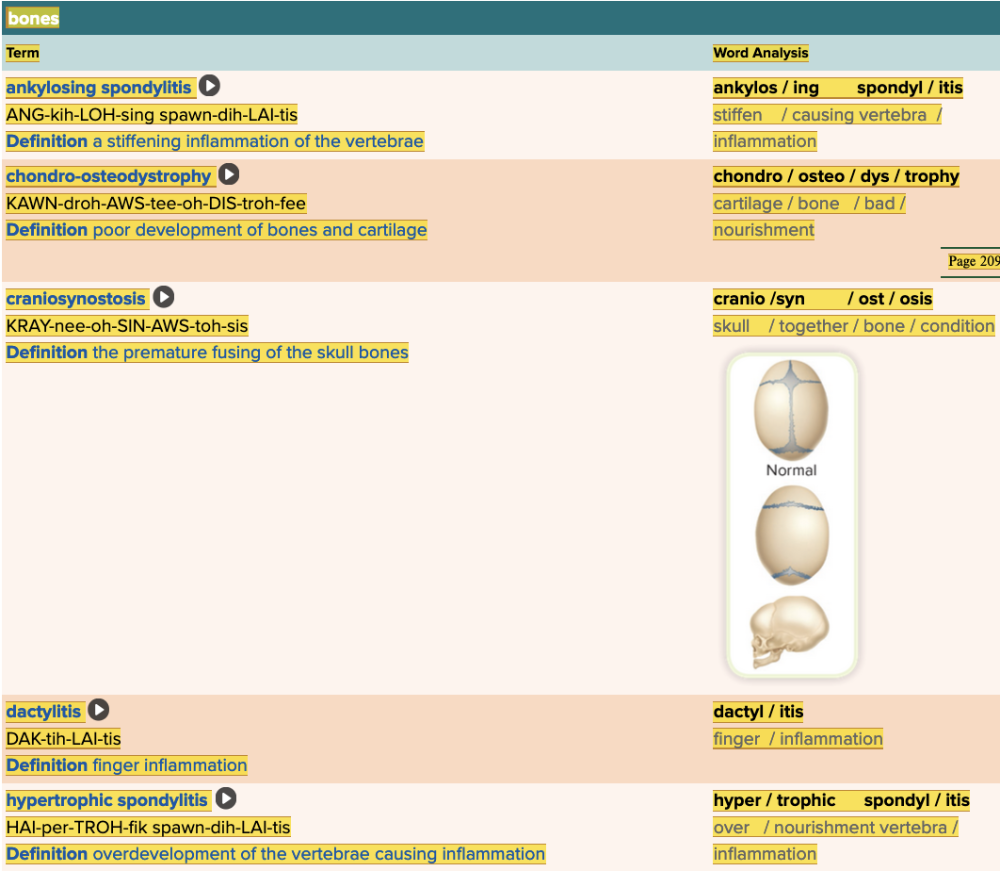
Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Bones Table Part 1
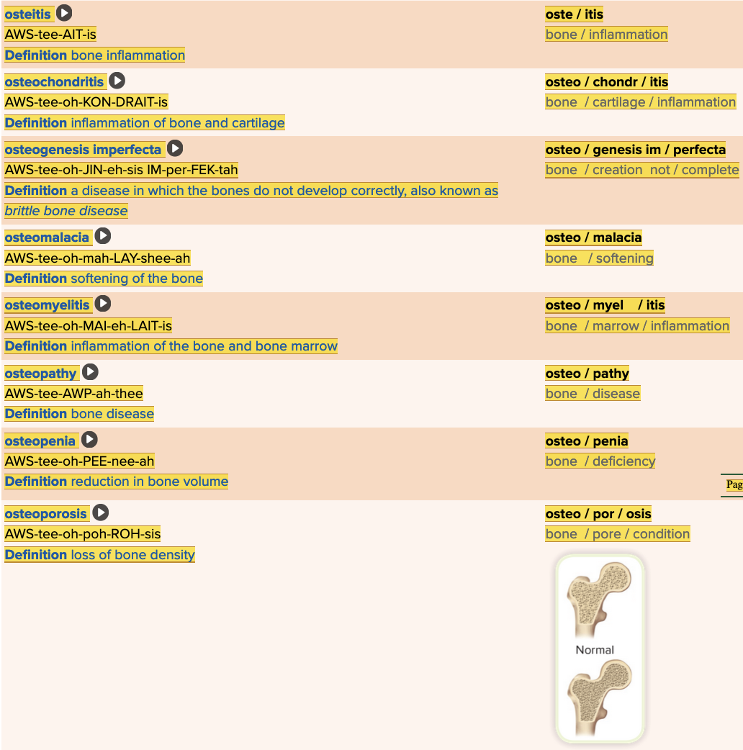
Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Bones Table Part 2
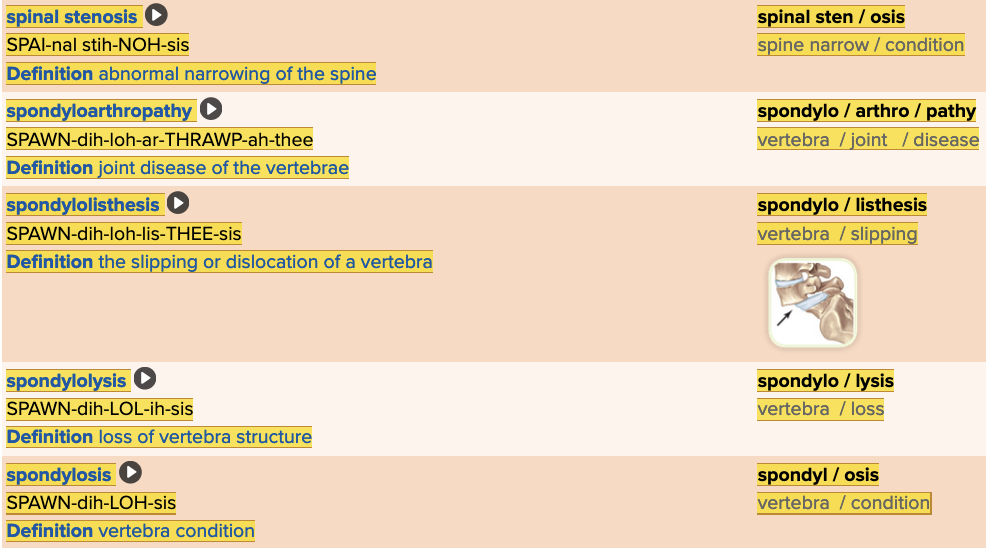
Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Bones Table Part 3
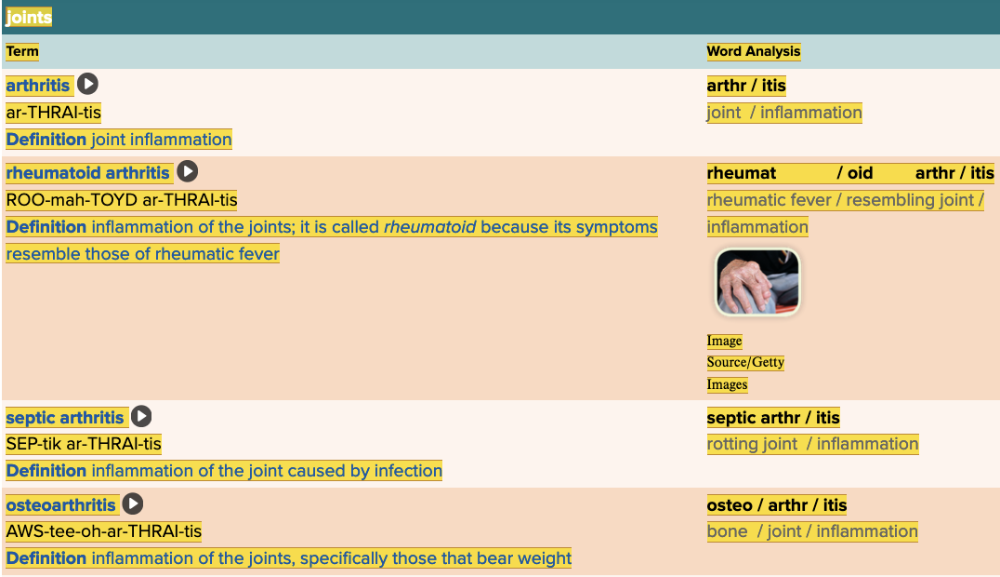
Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Joints Table Part 1
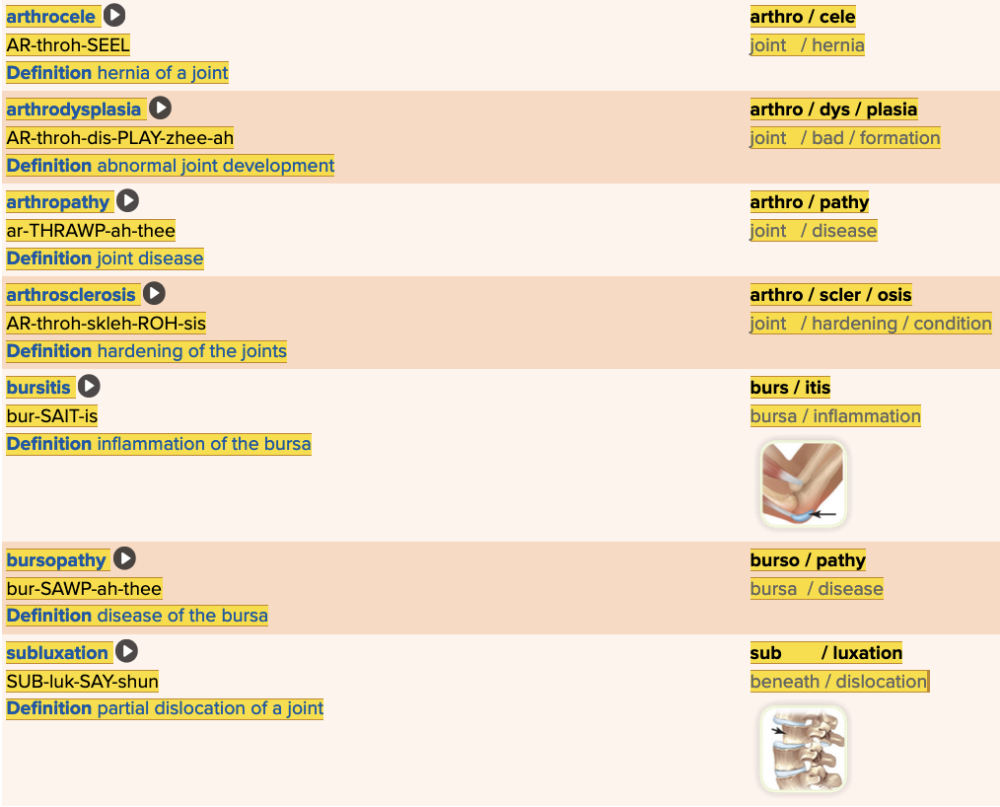
Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Joints Table Part 2
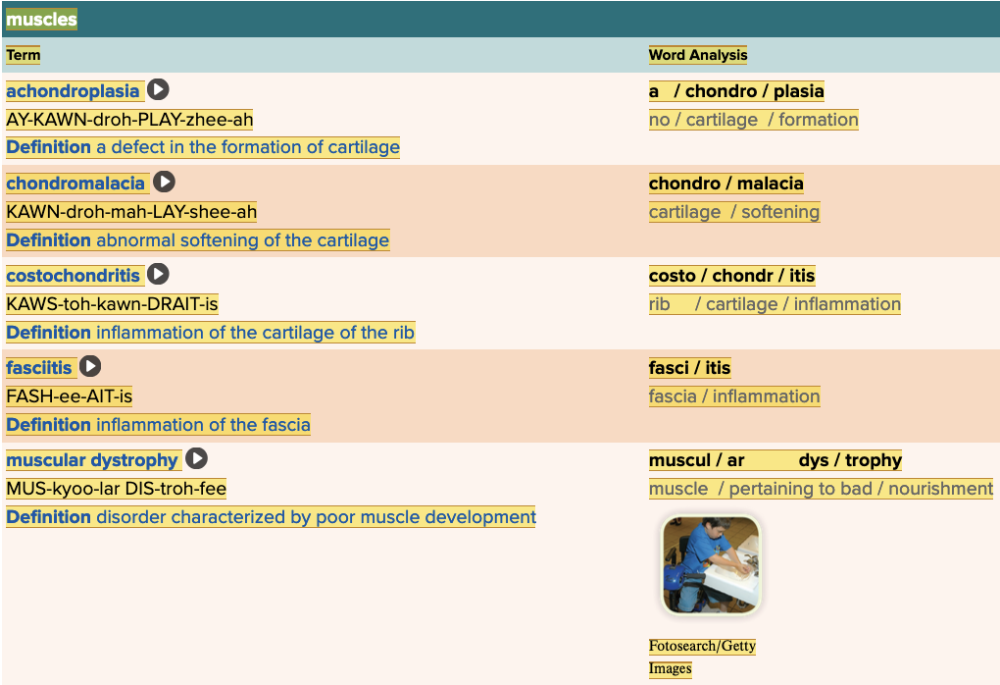
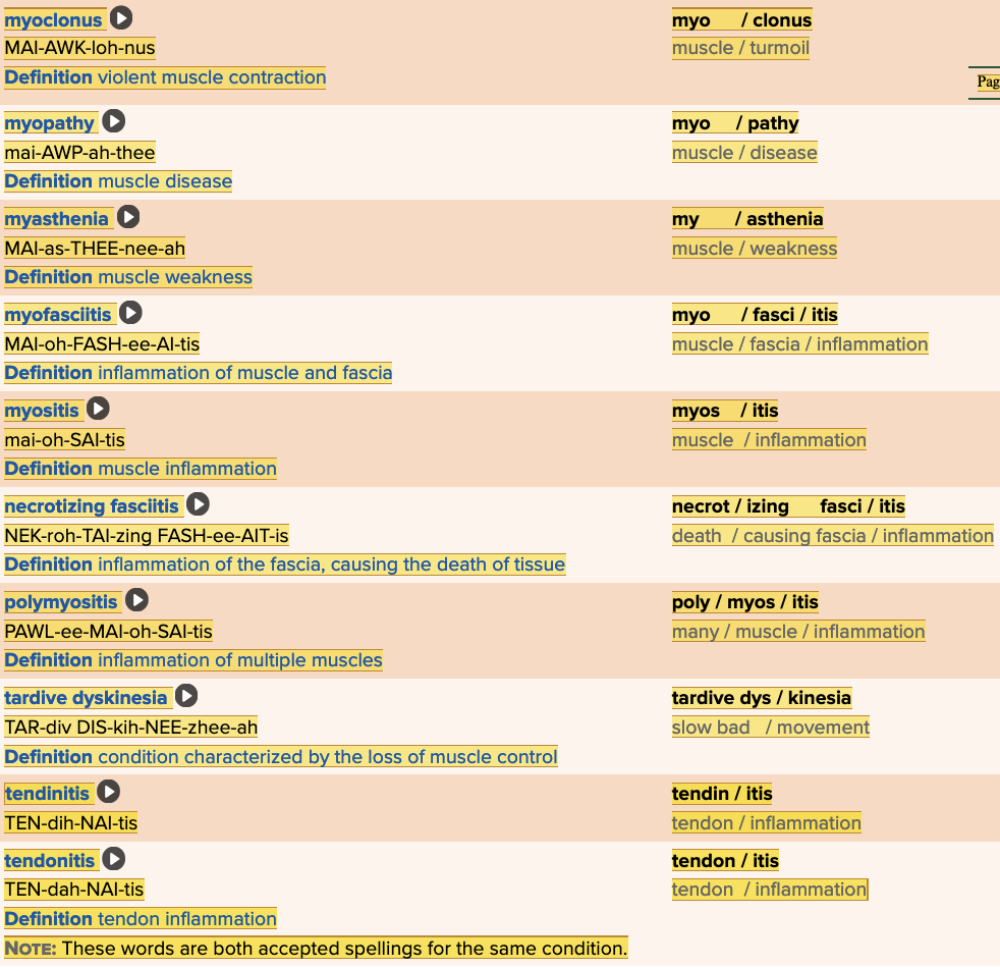
Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Muscles Table Part 1
Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Muscles Table Part 2
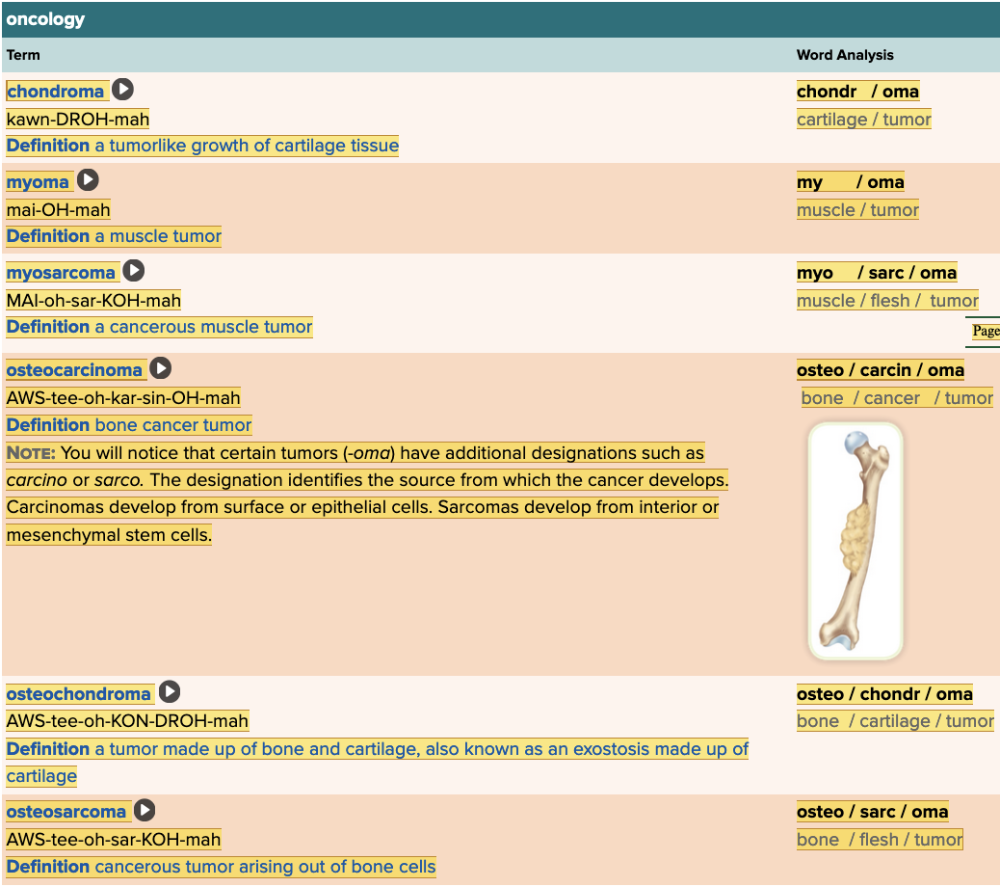
Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
- Assessment: Oncology Table

Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 1.

Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 2.

Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 3.

Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 4.
Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 5.

Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 6.

Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 7.


Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 8, 9.
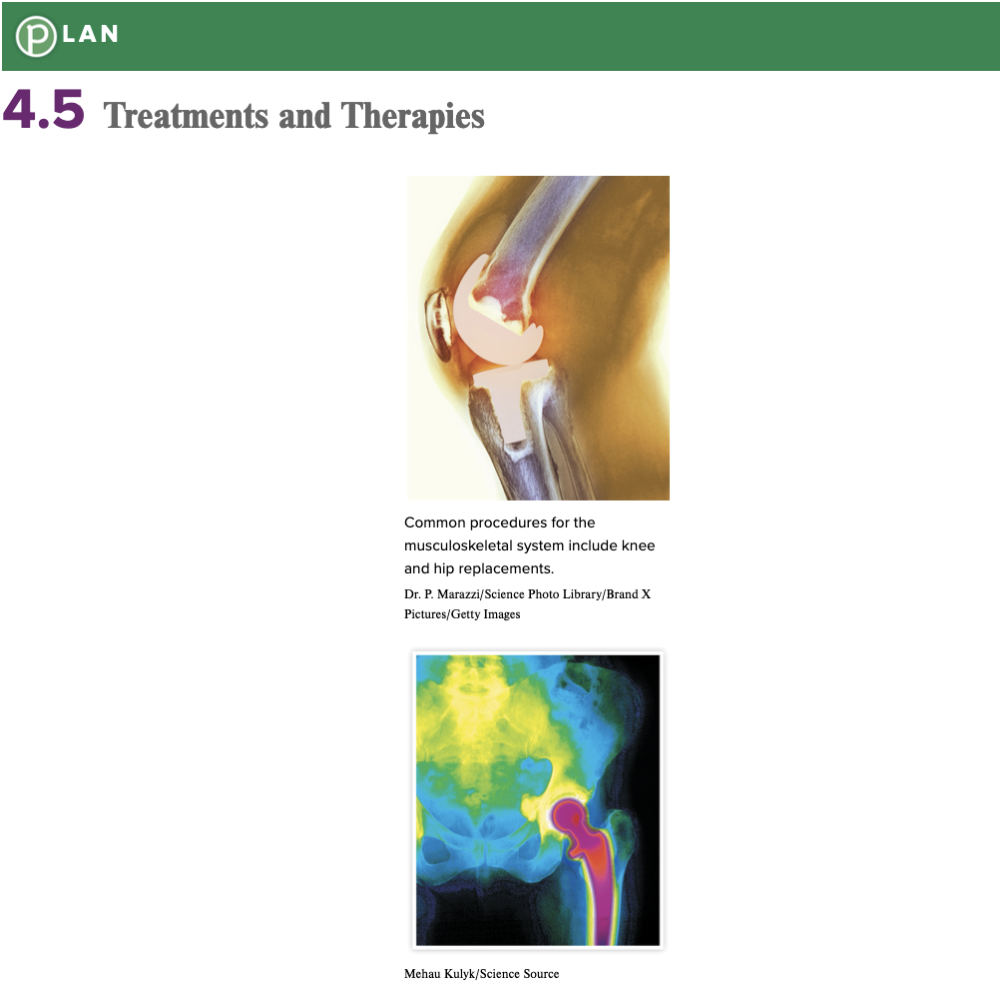
Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan

Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan
Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Pharmacology Table
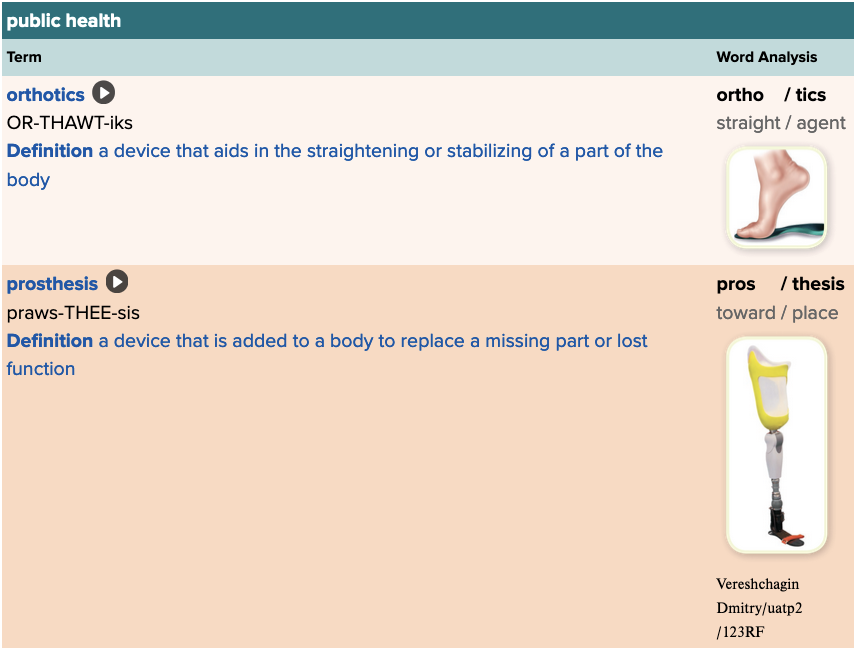
Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Public Health Table
Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Procedures for Joints Table Part 1
Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Procedures for Joints Table Part 2
Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Procedures for Joints Table
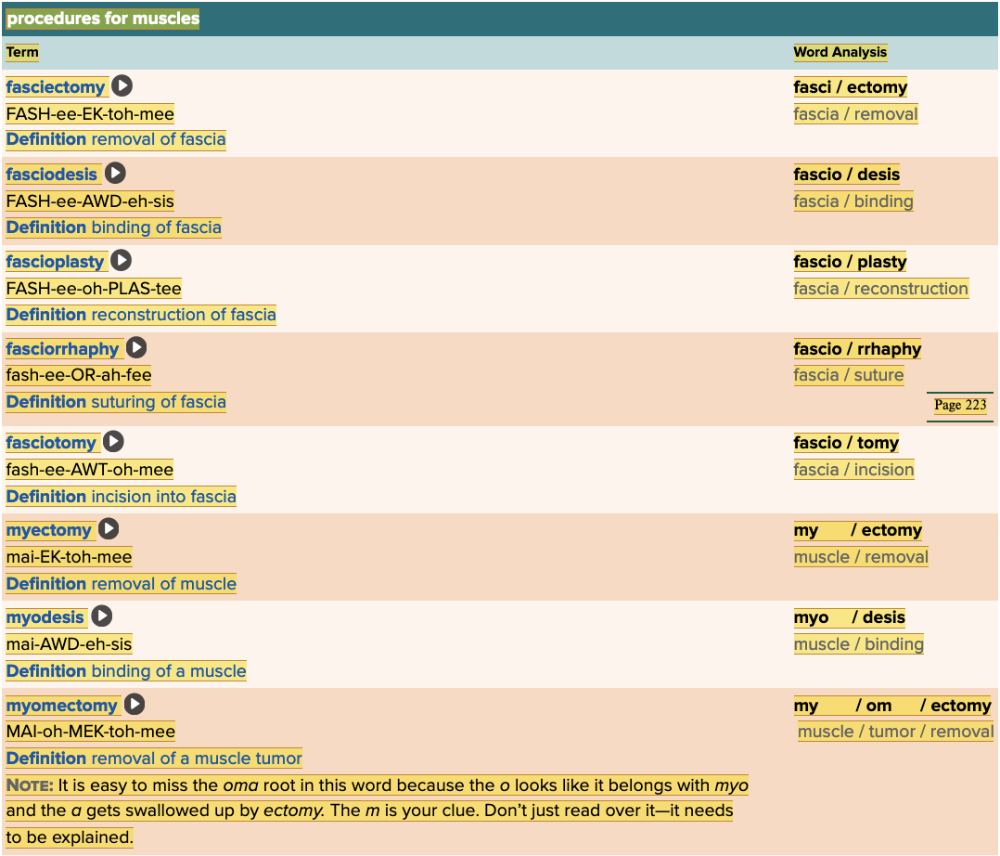
Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Procedures for Muscles Table Part 1
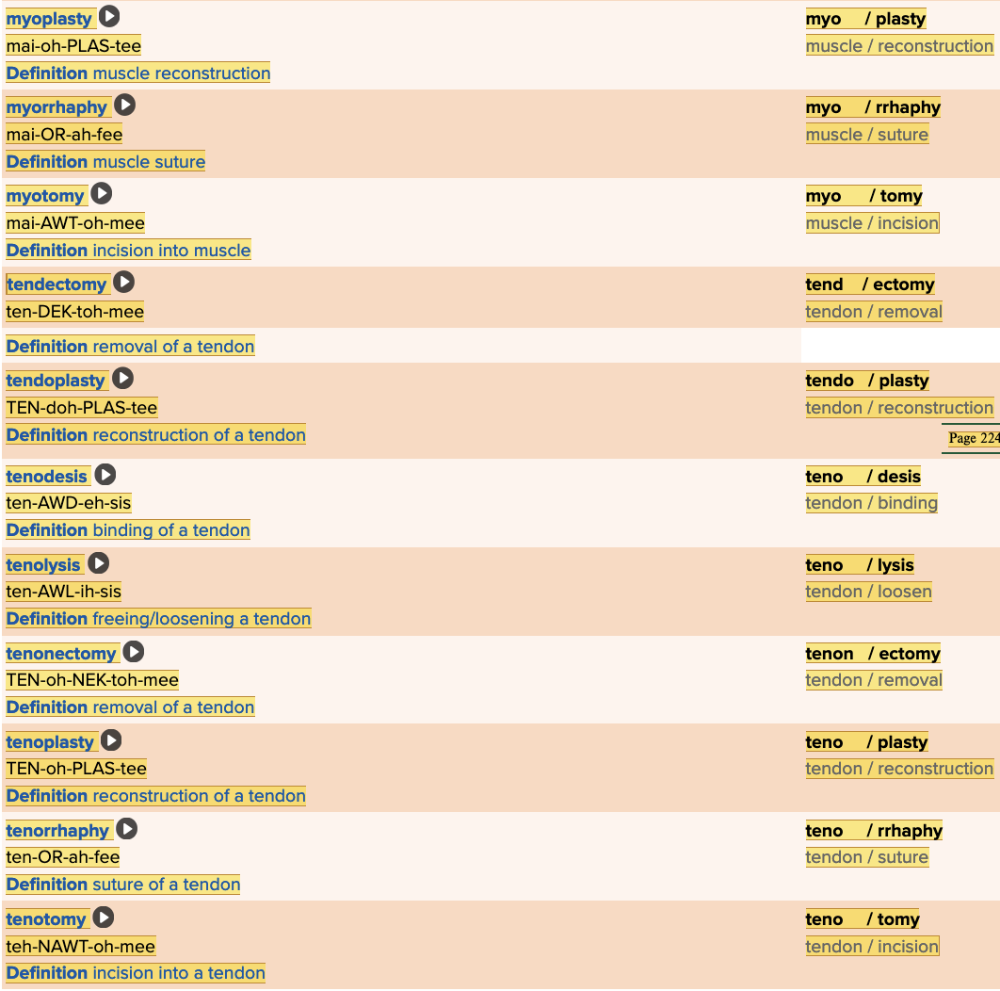
Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
- Plan: Procedures for Muscles Table Part 2

Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 1.
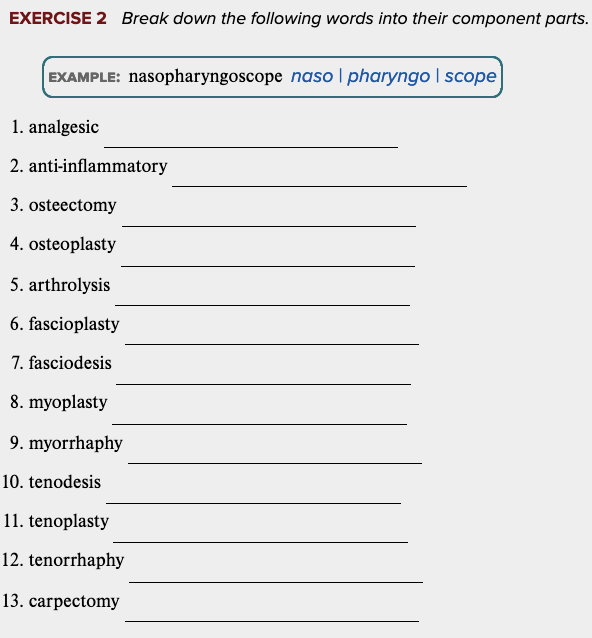
Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 2.
Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 3.

Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 4.

Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 5.

Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 6.

Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 7.
Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 8.
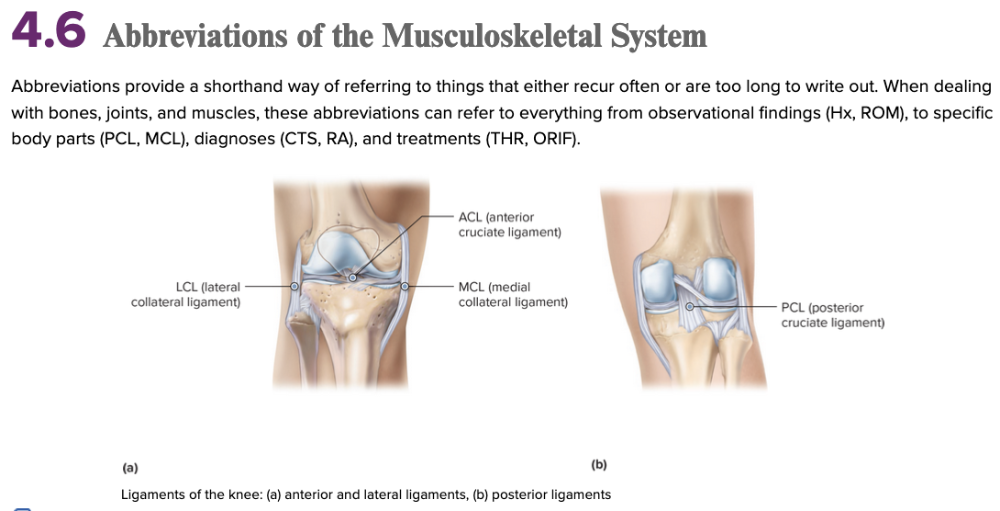
Chapter 4.6 Abbreviations of the Musculoskeletal System
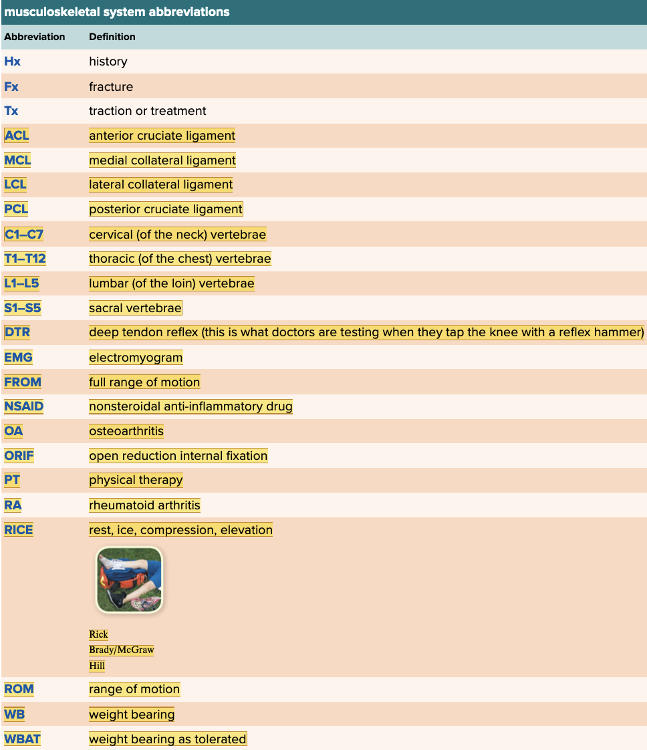
Chapter 4.6 Abbreviations of the Musculoskeletal System
- Musculoskeletal System Abbreviations Table

Learning Outcome 4.6 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2.

Learning Outcome 4.6 Exercises: Exercise 3.


Chapter 4.7 Electronic Health Records
Orthopedic Clinic Note
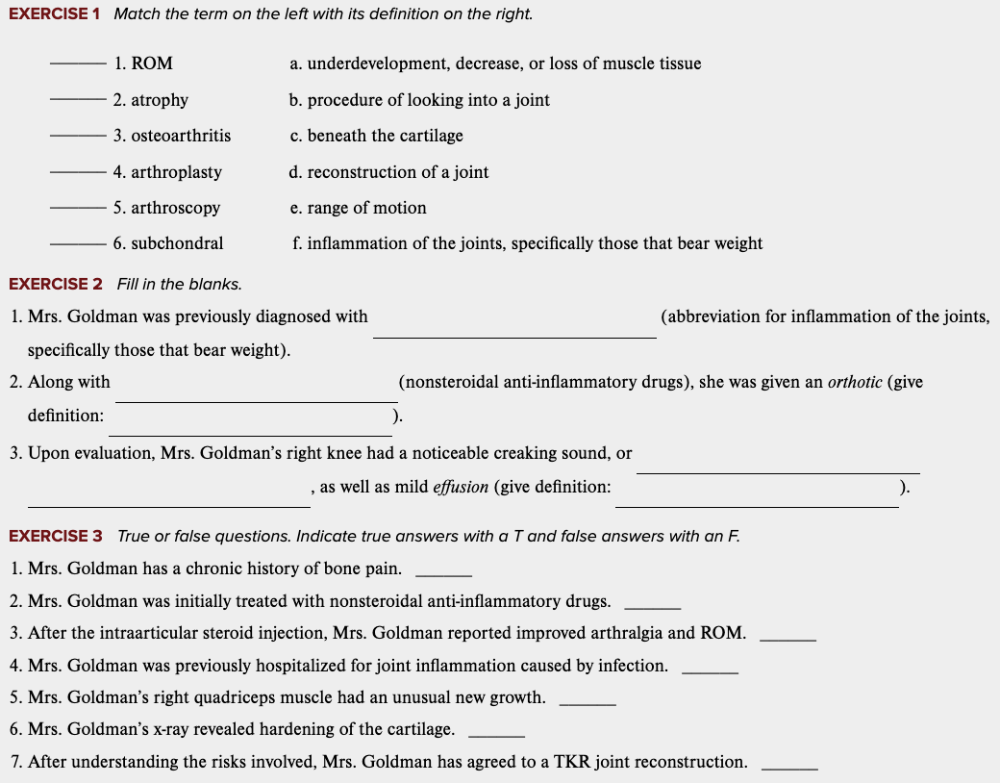
Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2, 3.

Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 4.

Chapter 4.7 Electronic Health Records
Discharge Summary Part 1

Chapter 4.7 Electronic Health Records
Discharge Summary Part 2
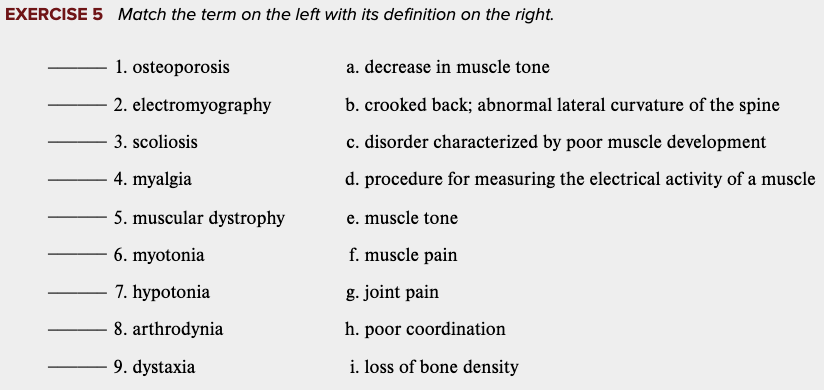
Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 5.
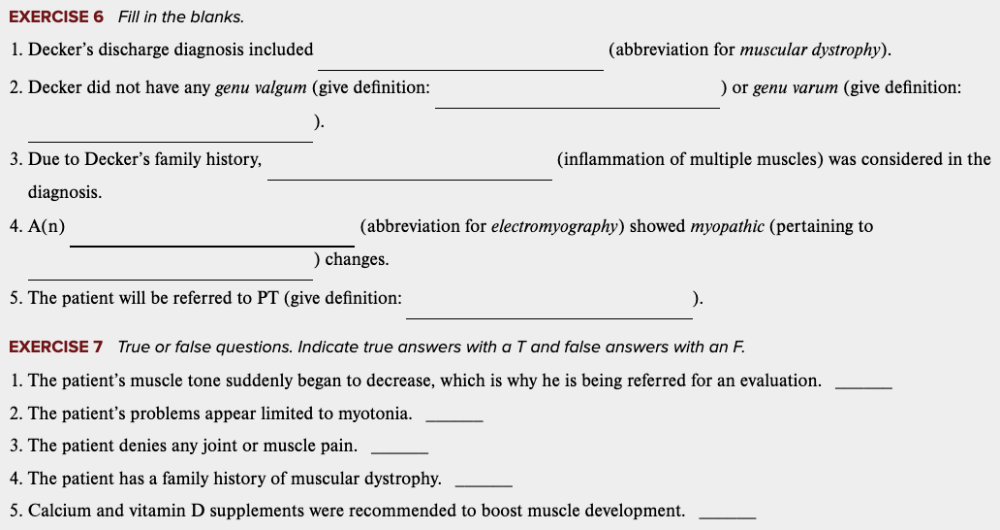
Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 6, 7.

Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 8.


Chapter 4.7 Electronic Health Records
Orthopedic Consult Note
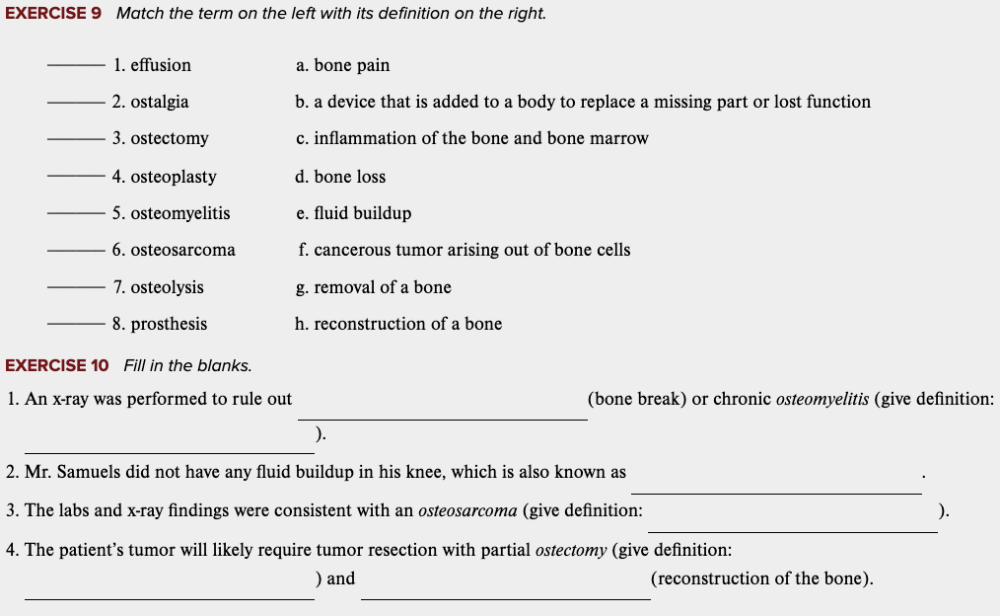
Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10.

Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 11.

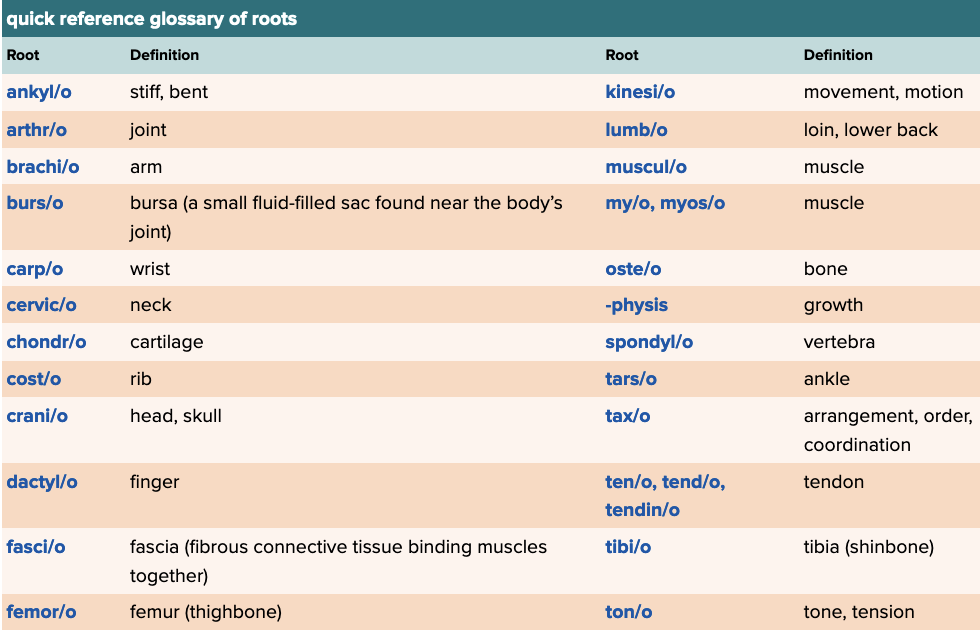
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Quick Reference Glossary of Roots Table
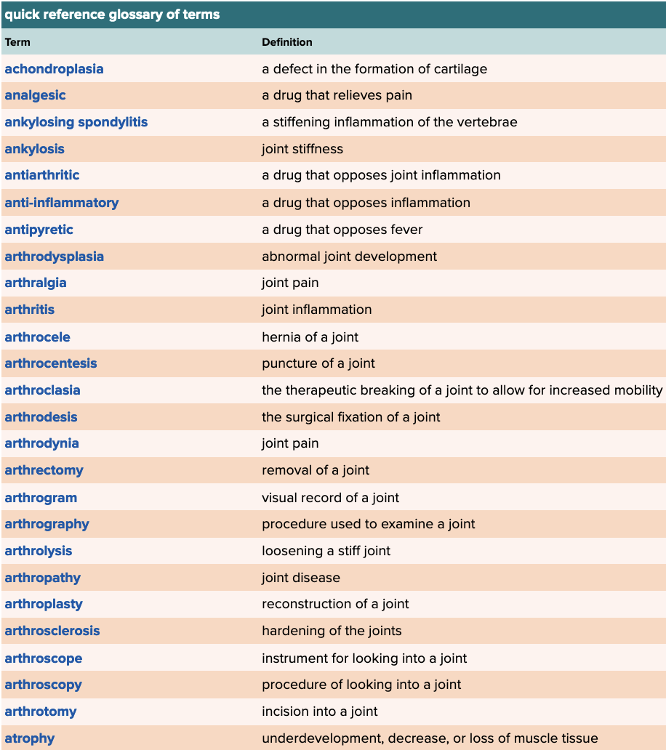
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Quick Reference Glossary of Terms Table Part 1
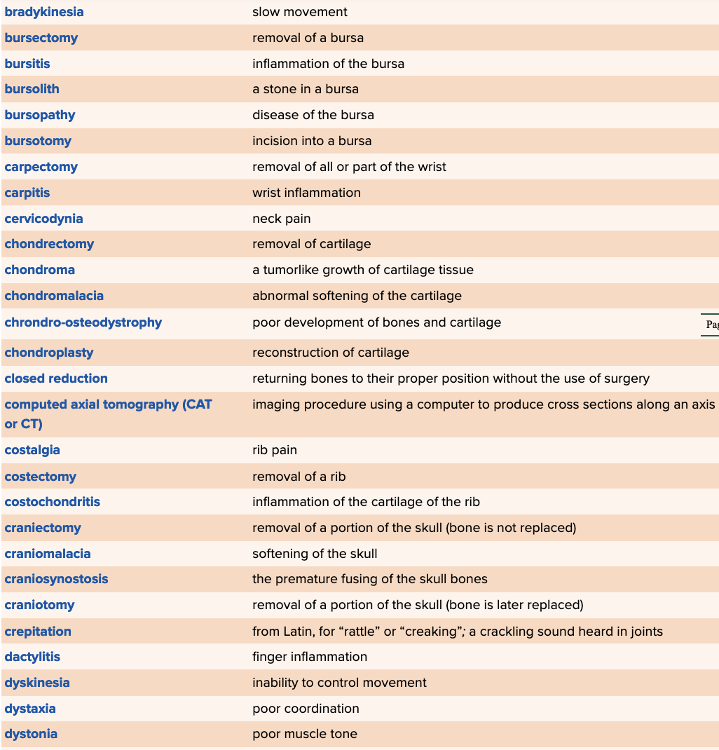
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Quick Reference Glossary of Terms Table Part 2
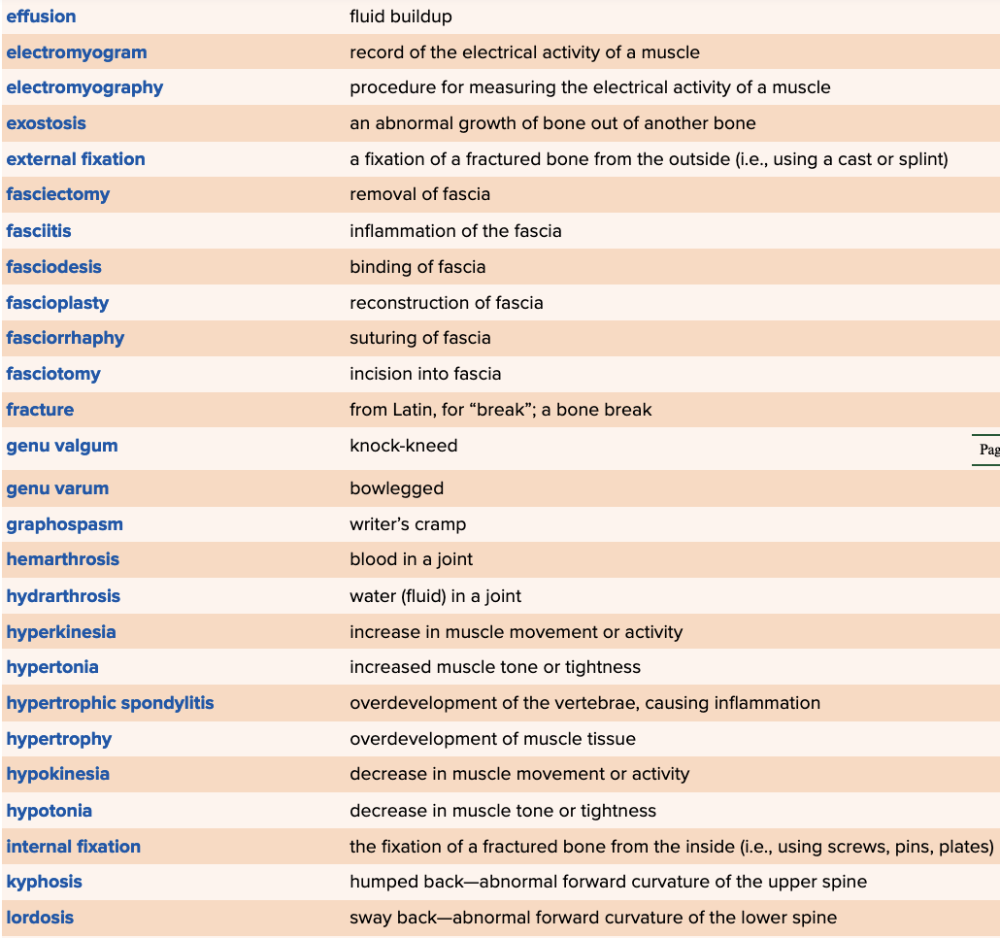
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Quick Reference Glossary of Terms Table Part 3
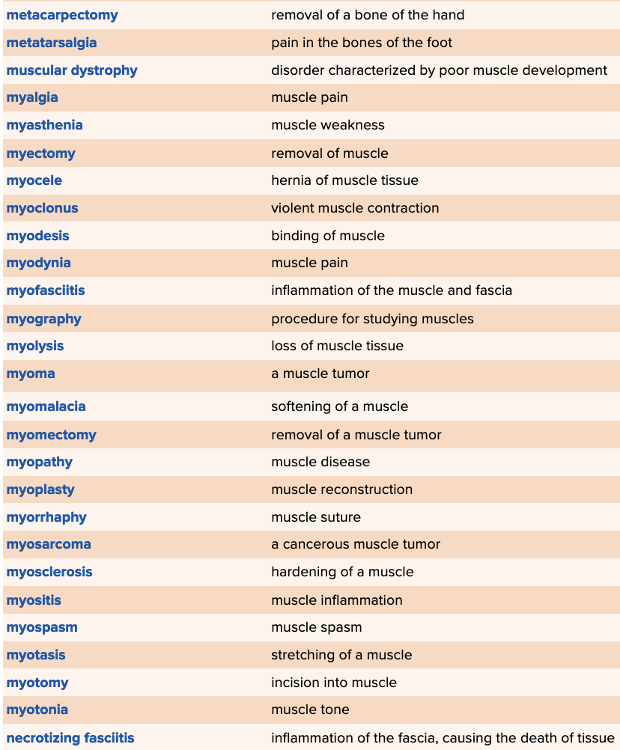
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Quick Reference Glossary of Terms Table Part 4
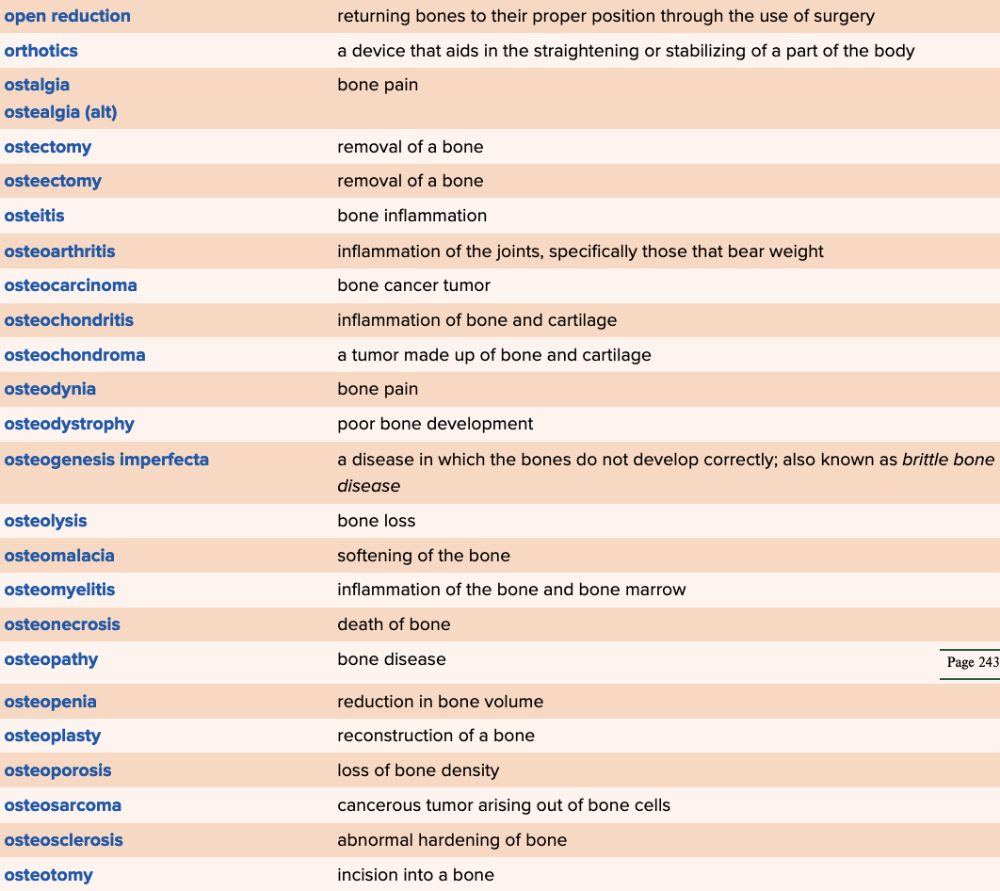
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Quick Reference Glossary of Terms Table Part 5
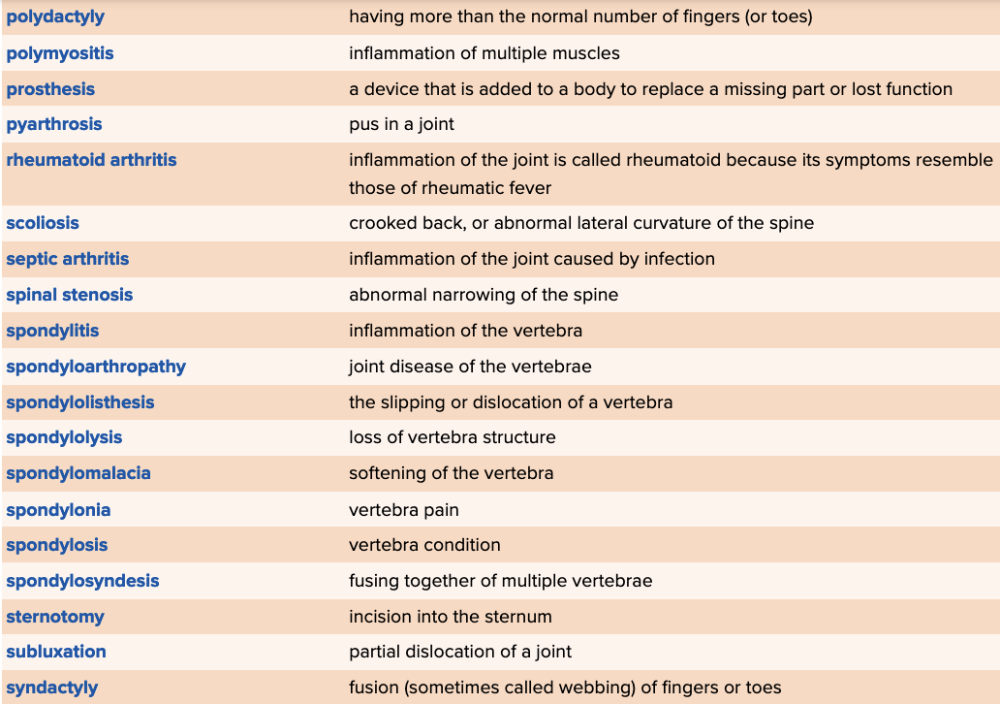
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Quick Reference Glossary of Terms Table Part 6

Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Quick Reference Glossary of Terms Table Part 7
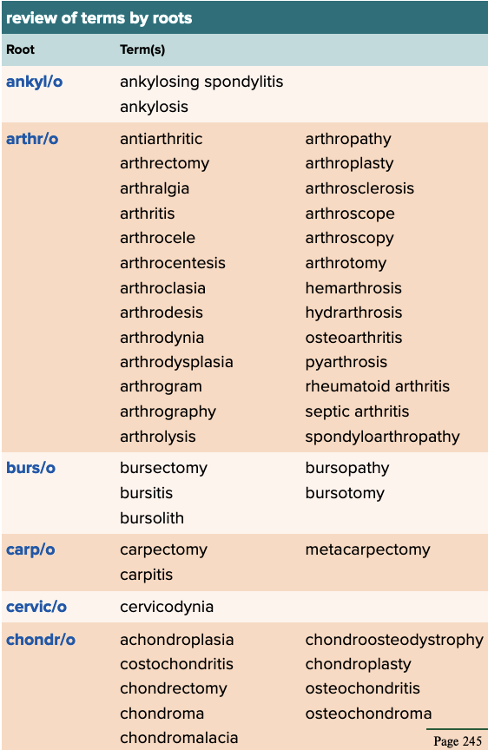
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Review of Terms by Roots Table Part 1
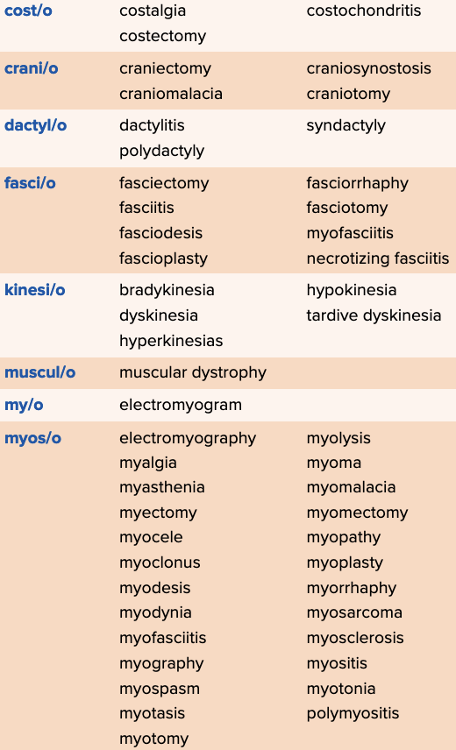
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Review of Terms by Roots Table Part 2
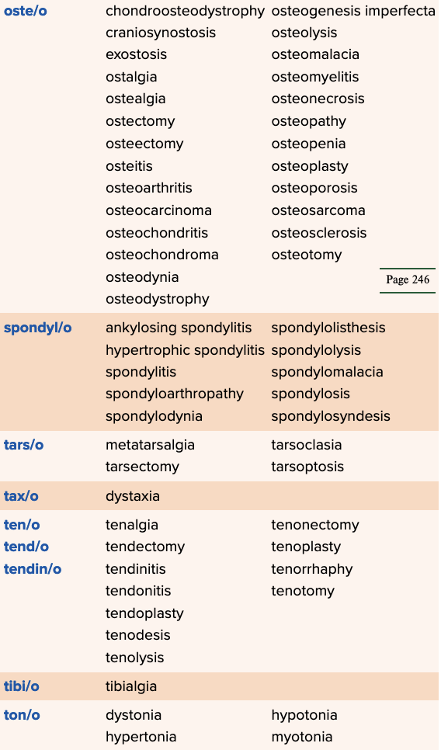
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Review of Terms by Roots Table Part 3
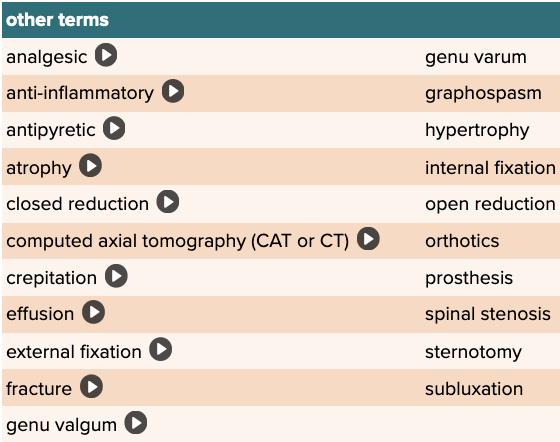
Chapter 4 Quick Reference
- Other Terms Table

Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 1, 2.

Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 3, 4.

Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 5.

Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 6.

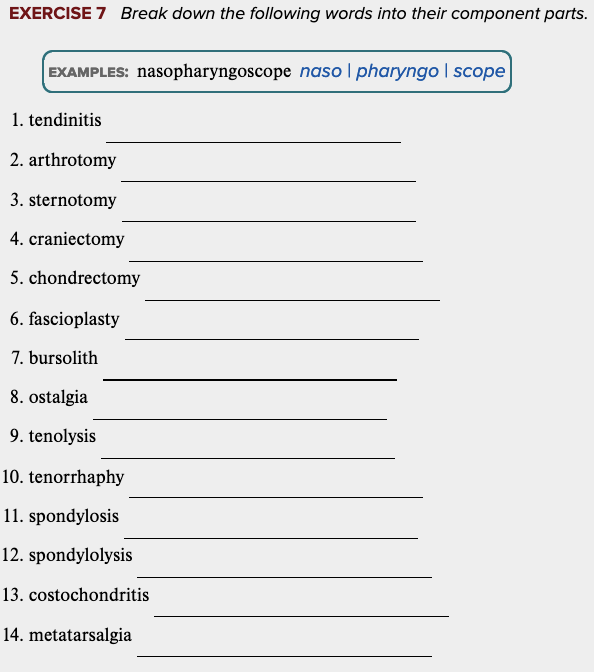
Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 7.
Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 8.

Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 9.
Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 10.


Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 11.

Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 12.

Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 13, 14.
The location of bone growth is known as the ______ plate.
epiphyseal
The suffix -physis in the word epiphysis means
Multiple choice question.
- cell.
- length.
- bone.
- growth.
growth.
Spell the term for more than one vertebra ______.
Vertebrae
Spell the term for the bones of your fingers ______.
phalanges
As a full-grown adult, a human has ______ bones in the body.
Multiple choice question.
- 206
- 210
- 310
- 300
206
In the formation of bone, an initial model is made from ______ and replaced with bone.
Multiple choice question.
- cartilage
- marrow
- blood
- periosteum
cartilage
The area between the rib cage and pelvis is the
Multiple choice question.
- lumbar area.
- mediastinum area.
- thoracic area.
- cranial area.
lumbar area.lumbar area.
______ is the study of matter, energy, and motion.
Physics
Which of the following is the root for arm?
Multiple choice question.
- carp/o
- brachi/o
- cost/o
- dactyl/o
brachi/o
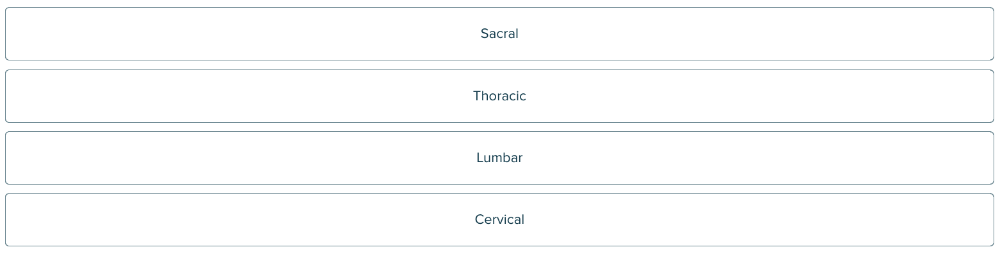
Click and drag on elements in order
List, from top to bottom, the sections of the spine (vertebral column).
1. Cervical
2. Thoracic
3. Lumbar
4. Sacral
Spell the term that means surgical removal of the wrist ______.
carpectomy
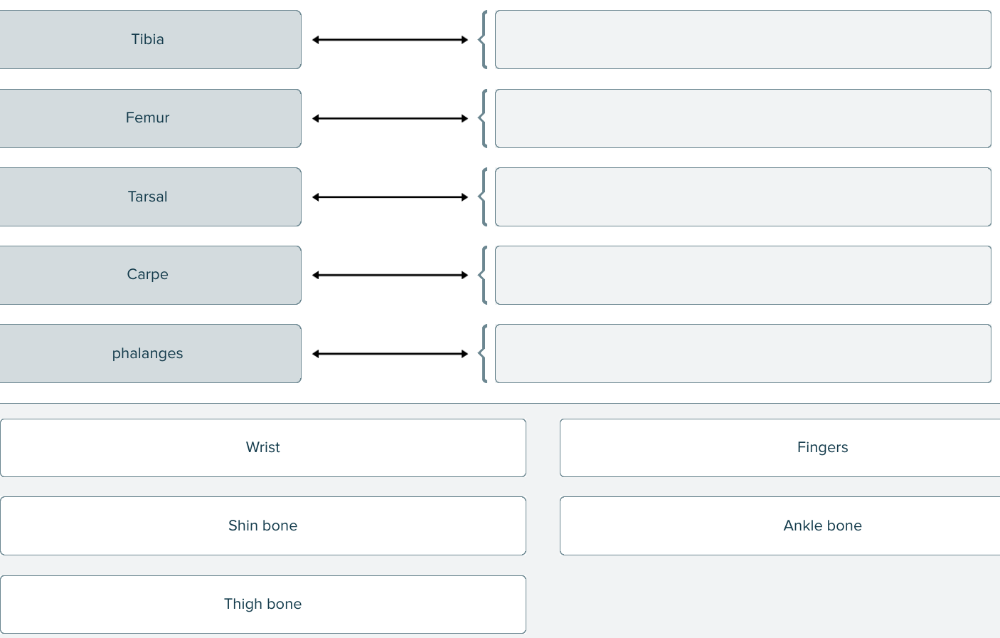
Match the term with its correct body part
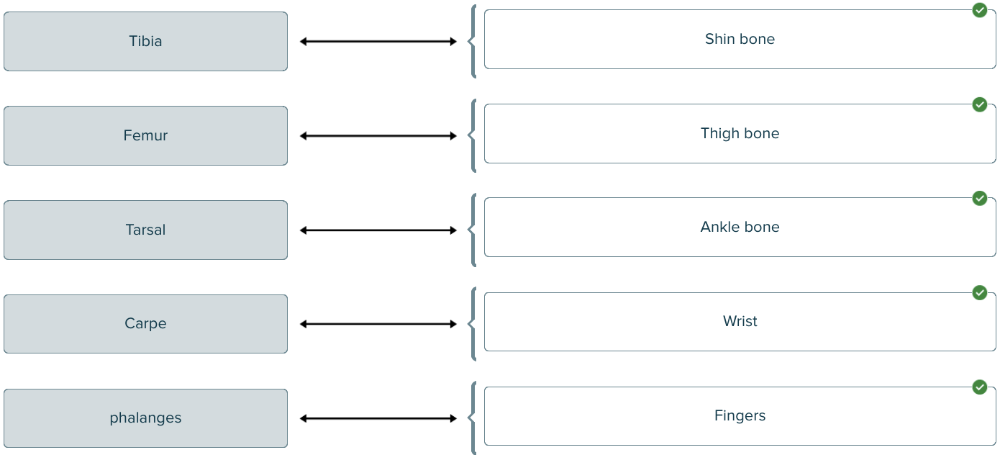
The intercostal muscles are muscles that connect the ______.
Multiple choice question.
- ribs
- vertebrae
- toes
- fingers
ribs
Which bone is present in an adult, but not in a newborn?
Multiple choice question.
- Femur
- Tibia
- Phalanges
- Kneecap
Kneecap
The term for shin bone is called ______.
tibia
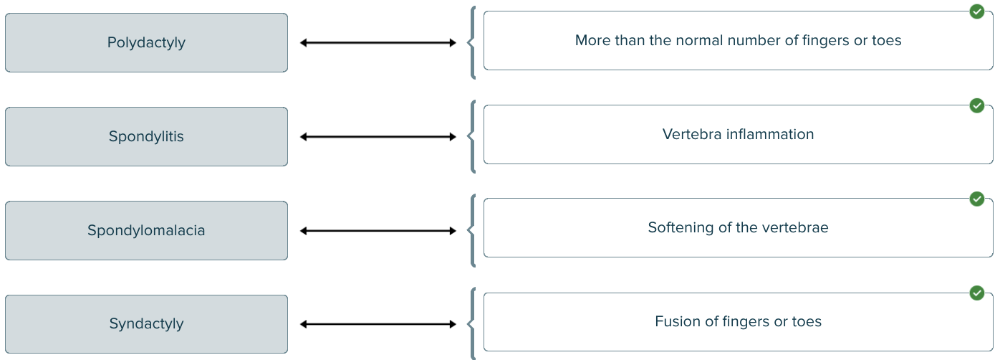
Spondylitis is inflammation of the ______.
Vertebrae
Tarsalgia is a term describing pain in the
Multiple choice question.
- wrist.
- ribs.
- knee.
- ankle.
ankle.
Which of the following is the root for finger?
Multiple choice question.
- lumbodynia
- brachiocephalic
- lumbar
- dactyl/o
dactyl/o
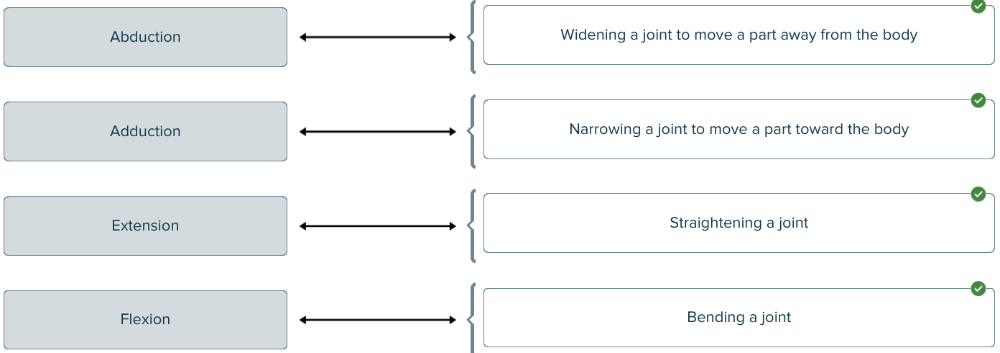
Match each motion to the action described.
Repetitive motions cause the nerve to swell and can result in ______ in the hand, called carpal tunnel syndrome.
numbness
The term for holding bone to bone at joints is ______.
ligaments or ligament
Deconstruct the term costectomy by separating the root from the suffix with a hyphen.
cost-ectomy
Select all that apply
Which term(s) contain the root word that means cartilage?
Multiple select question.
- chondritis
- chondrodynia
- tibiaglia
- epiphysis
- chondritis
- chondrodynia
Which of the following is the term for tibia?
Multiple choice question.
- femor/o
- dactyl/o
- tibi/o
- lumb/o
tibi/o
Inflammation of a joint is called
Multiple choice question.
- chondritis.
- bursitis.
- tarsitis.
- arthritis.
arthritis.
Ex.
bursitis - Reason: The bursa is near the joint but not the joint itself. The joint is where two or more bones come together.
Tarsitis means inflammation of the ______.
ankle
Select all that apply
Bursa comes from the ______ word that means ______.
Multiple select question.
- purse
- Greek
- Latin
- Greek
- purse
The term ______ is used to describe the widening of a joint to move parts away from the body, while the term ______ means the exact opposite; i.e. bringing parts toward the body.
Blank 1: abduction
Blank 2: adduction
Select all that apply
Which of the following muscles belong to the trunk (chest and abdomen, not including shoulder and buttocks)?
Multiple select question.
- Deltoid
- Internal abdominal oblique
- Gluteus maximus
- Gastrocnemius
- Pectoralis major
- Triceps brachii
- Pectoralis minor
- Gluteus medius
- External abdominal oblique
- Gluteus minimus
- Latissimus dorsi
- Biceps brachii
- Internal abdominal oblique
- Pectoralis major
- Pectoralis minor
- External abdominal oblique
- Latissimus dorsi
Spell the term that defines the tissue holding a muscle to a bone ______.
tendon or tendons
A band of connective tissue holding muscle to bone is called a
Multiple choice question.
- fasciae.
- tendon.
- bursa.
- ligament.
tendon.
Chondr/o is the root for the term ______.
Cartilage
The plural form of fascia is
Multiple choice question.
- fascii.
- fascias.
- fasciae.
- fasix.
fasciae.
Spell the term that means inflammation of a joint ______.
arthritis
Which of the following is the definition of the root tax/o?
Multiple choice question.
- stiff
- tone
- motion
- coordination
coordination
Inflammation in a small fluid-filled sac near a joint (named after a purse) is called
Multiple choice question.
- cervicitis.
- arthritis.
- bursitis.
- spondylitis.
bursitis.
The medical term for bowlegged is
Multiple choice question.
- genu varum.
- hypotonia.
- hypertrophy.
- genu valgum.
genu varum.
Which of the following muscles belong to the lower extremity (buttocks, thigh, or leg)?
Multiple choice question.
- Deltoid
- Biceps brachii
- Internal obliques
- Gastrocnemius
Gastrocnemius
Deconstruct the term that means vertebral pain by separating the root from the suffix with a hyphen. Enter hyphens in the appropriate blanks.
______ ______ ______.
Blank 1: spondylo
Blank 2: -
Blank 3: dynia
Select all that apply
Which of the following combining forms mean muscle?
Multiple select question.
- Myc/o
- Myos/o
- Muscul/o
- My/o
- Myos/o
- Muscul/o
- My/o
Bands of connective tissue holding muscles together are called ______.
Multiple choice question.
- fascia
- ligaments
- bursa
- tendons
fascia
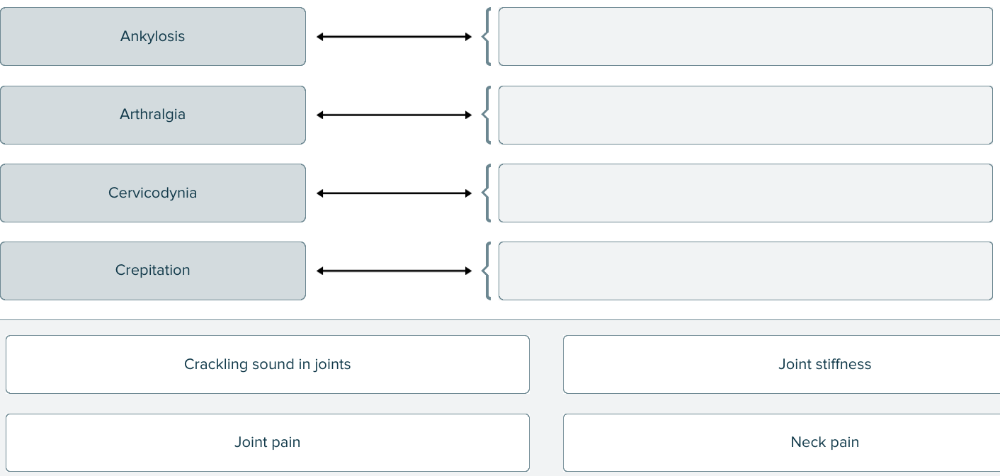
Match each medical term related to joints with its definition.
Hyper- is a prefix meaning over. Hyperkinesia means excess
Multiple choice question.
- coordination.
- stiffness.
- movement.
- tension.
movement.
The suffix -dynia in the word cervicodynia means ______.
pain
The term ataxia indicates a problem with
Multiple choice question.
- stiff joints.
- knock-kneed.
- coordination.
- pain.
coordination.
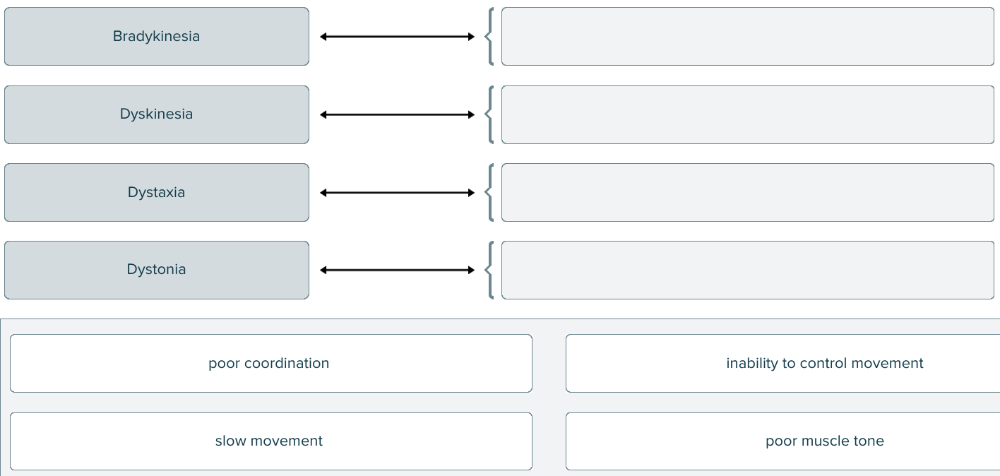
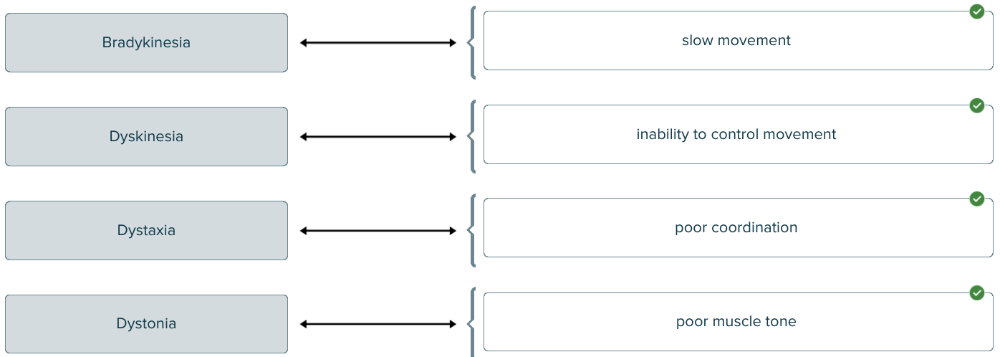
Match the terms associated with the muscle to the correct definitions.
Match each medical term related to bones with its definition.
Spell the term that means increased muscle tone ______.
hypertonia
A band of connective tissue holding muscle to bone is called a
Multiple choice question.
- tendon.
- bursa.
- fasciae.
- ligament.
tendon.
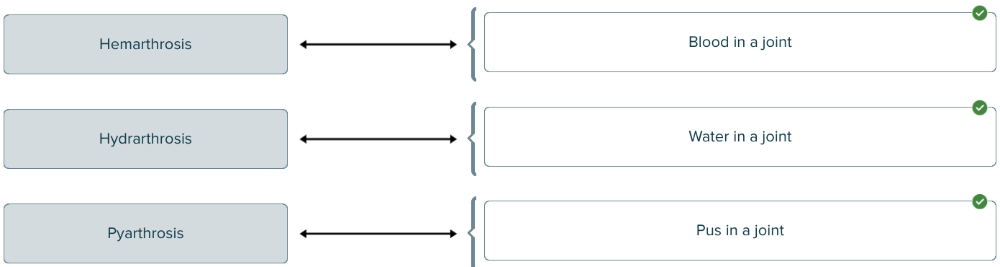
The medical term for pus in a joint is
Multiple choice question.
- arthrocentesis.
- myotonia.
- pyarthrosis.
- hemarthrosis.
pyarthrosis.
Ex.
arthrocentesis. - Reason: Arthr/o means joint, but -centsis means the process of drawing off fluid with a needle.
hemarthrosis. - Reason: Arthr/o means joint, but hem- means blood.
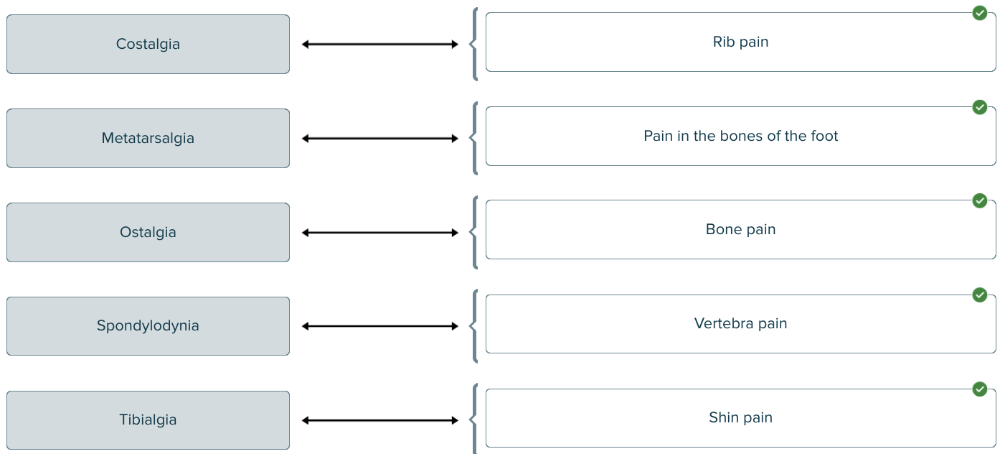
Spell the term that means bone pain ______.
osteodynia, ostalgia, or ostealgia
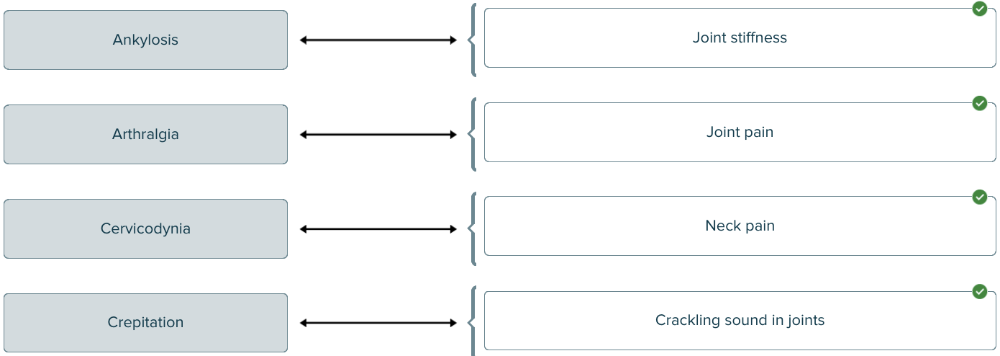
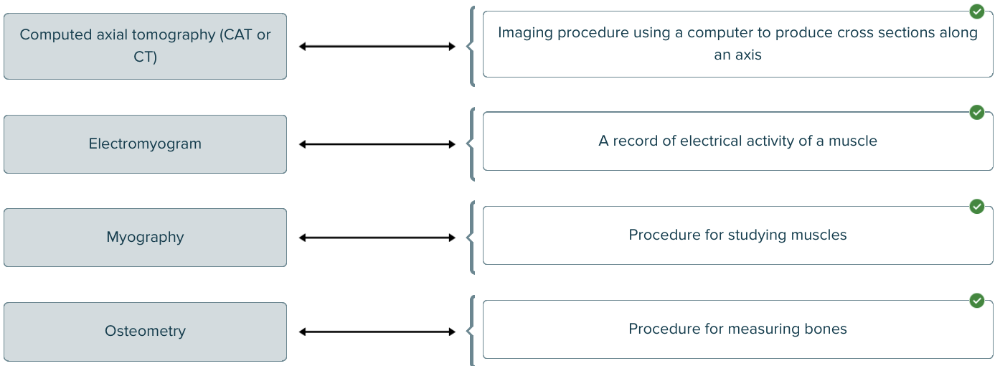
Match the medical term with the definition.
Match each medical term about joints with its definition.
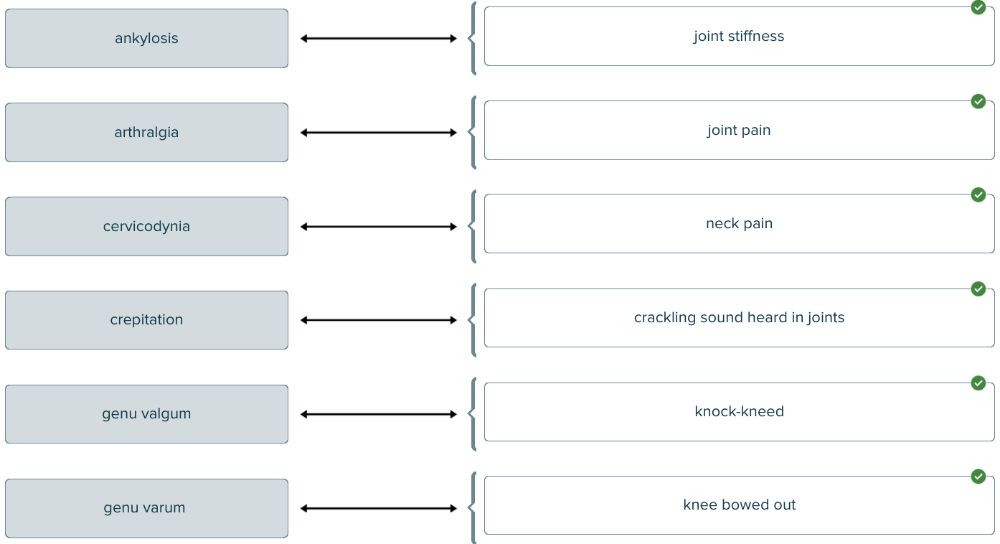
Puncture of a joint (for example, to retrieve a fluid sample for laboratory analysis) is called
Multiple choice question.
- arthroscopy.
- myography.
- arthrocentesis.
- arthrography.
arthrocentesis.
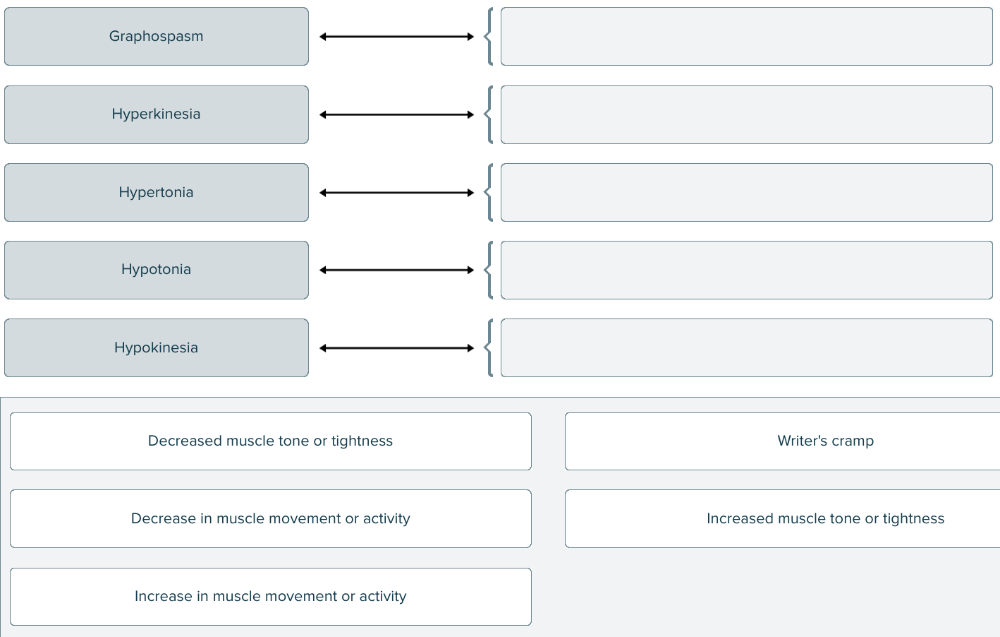
Match the terms related to muscles to their definitions.
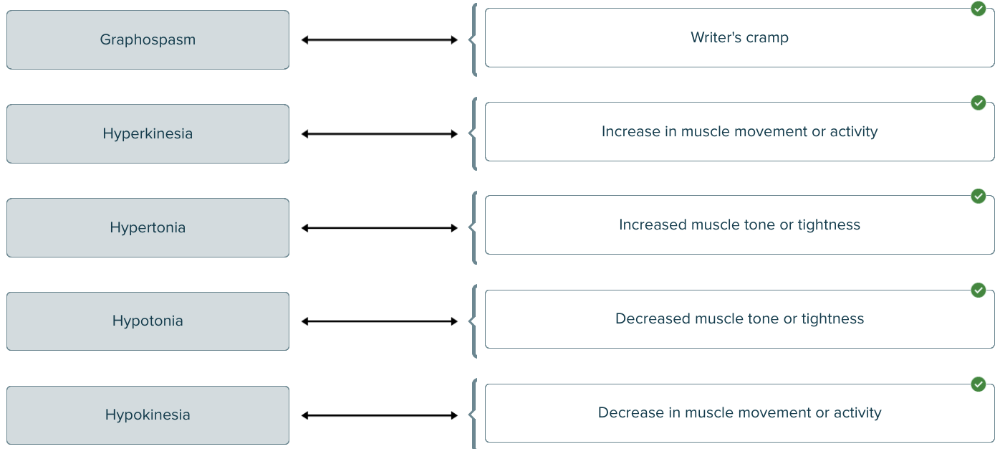
Spell the term that means a sway back or abnormal forward curvature of the lower spine ______.
lordosis
Slow movement is defined by the term ______.
bradykinesia
A drooping condition of the ankle is
Multiple choice question.
- hypertrophy.
- tarsoptosis.
- spondylomalacia.
- polydactyly.
tarsoptosis.
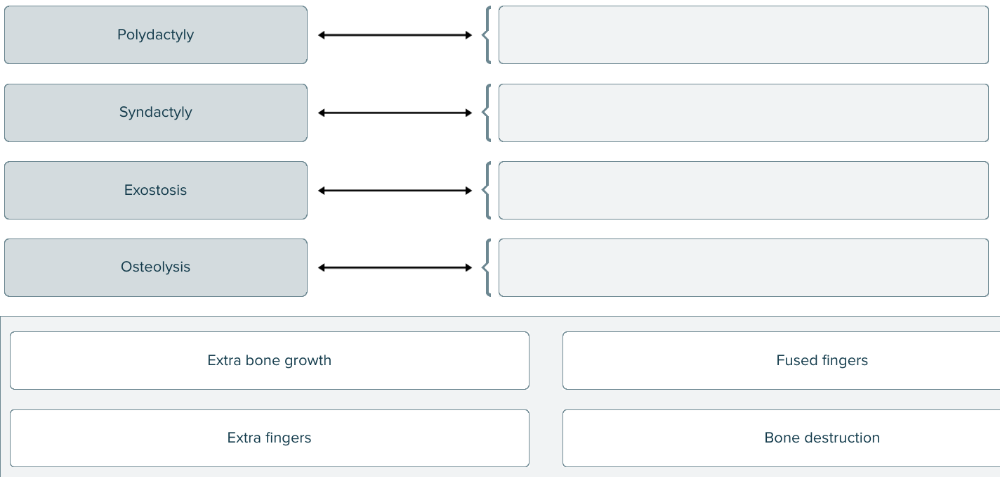
Match the following musculoskeletal terms to the correct definitions.
Spell the term that means abnormal hardening of bone ______.
osteosclerosis
A visual record of a joint is termed a(n) ______.
arthrogram
Match each medical term with the definition.
Which of the following is used as an instrument for looking into a joint?
Multiple choice question.
- Arthroscope
- Cervicodynia
- Electromyogram
- Arthrocentesis
Arthroscope
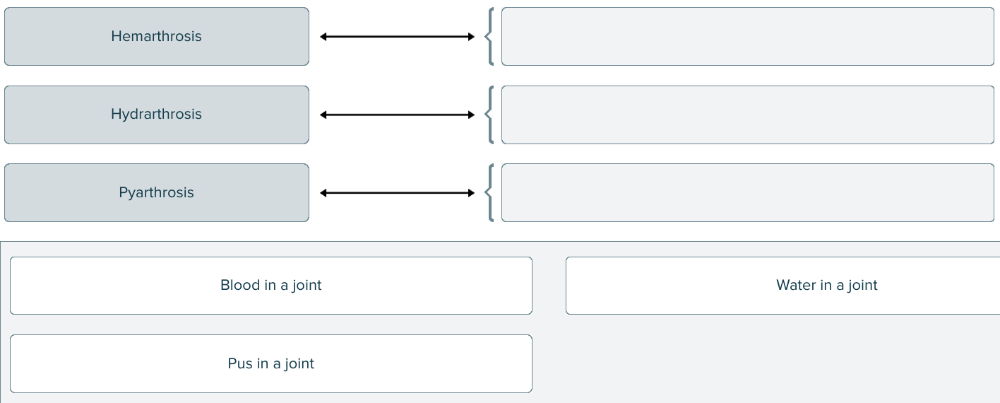
Match each medical term with the material found in a joint.
A humped back or abnormal forward curvature of the upper spine is called
Multiple choice question.
- kyphosis.
- spondylosis.
- lordosis.
- scoliosis.
kyphosis.
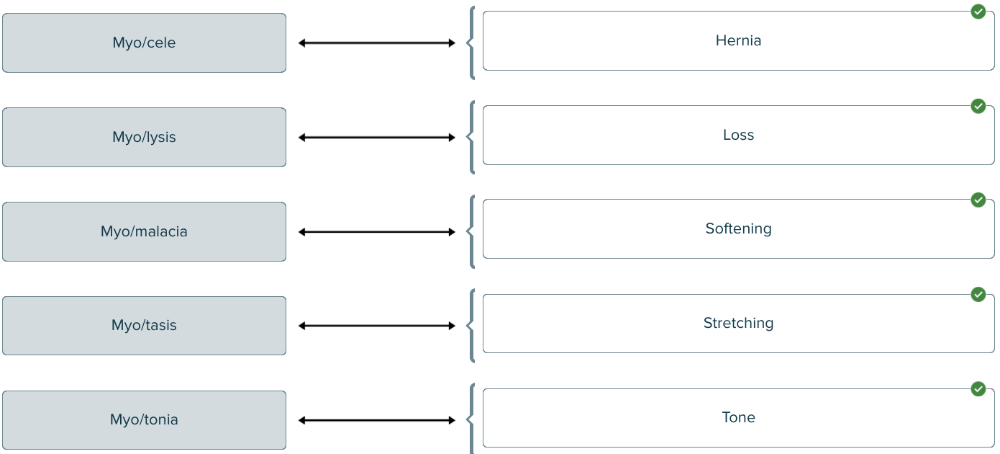
Match each combining form of my/o and suffix with the correct meaning as it relates to muscle.
The medical term for fusion of the fingers or toes is
Multiple choice question.
- tarsoptosis.
- syndactyly.
- spondylomalacia.
- atrophy.
syndactyly.
Overdevelopment of muscle tissue is termed ______.
hypertrophy
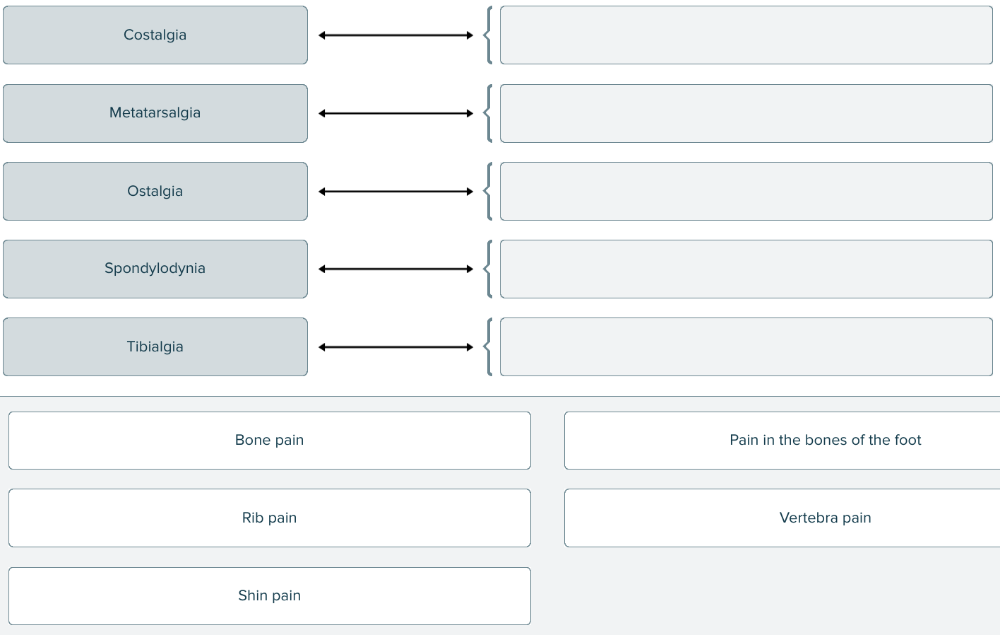
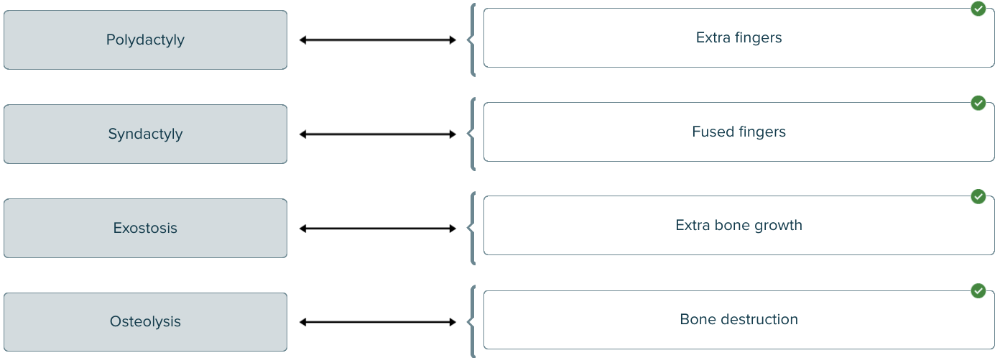
Match each medical term related to bones with its definition.
Poor development of bones and cartilage is termed ______.
chondrosteodystrophy
The suffix -ptosis means a drooping condition. Tarsoptosis is the medical word for
Multiple choice question.
- ankle inflammation.
- fractured ankle.
- flat feet.
- softening of the vertebrae.
flat feet.
When the spinal canal narrows abnormally, the condition is called
Multiple choice question.
- osteoporosis.
- spinal stenosis.
- osteomalacia.
- dactylitis.
spinal stenosis.
The medical term for a stone in a small fluid-filled sac found near a joint is
Multiple choice question.
- effusion.
- hydrarthrosis.
- bursolith.
- pyarthrosis.
bursolith.
The term osteochondroma means
Multiple choice question.
- bone cancer.
- cancer of the joint.
- inflammation of the joint.
- bone and cartilage tumor.
bone and cartilage tumor.
Sclerosis can be used as a root or as a suffix meaning hardening condition. Myosclerosis is a condition of hardening of a
Multiple choice question.
- bone.
- muscle.
- connective tissue band.
- joint.
muscle.
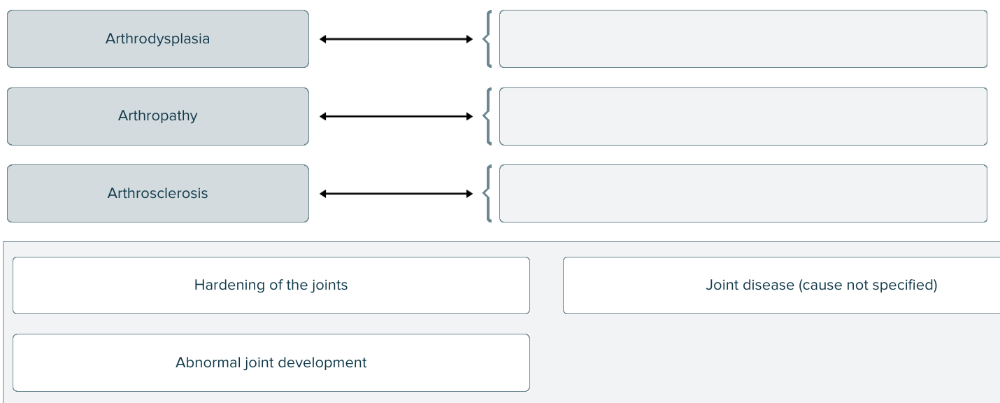
Arthro- is a root or prefix meaning joint. Match each disease of the joints with its definition.
Which of the following terms means loss of muscle tissue?
Multiple choice question.
- Myomalacia
- Myosclerosis
- Myotonia
- Myolysis
The suffix -trophy in the word hypertrophy means
Multiple choice question.
- head.
- muscle.
- nourishment.
- appetite.
nourishment.
When a joint herniates, it is called a(n)
Multiple choice question.
- arthrocele.
- arthrodysplasia.
- arthrosclerosis.
- bursopathy.
arthrocele.
Spell the term than indicates the condition where the bones of the skull are fused together ______.
craniosynostosis
Select the definition for the term Myopathy.
Multiple choice question.
- Muscle contractions
- Muscle Disease
- Muscle spasms
- Muscle weakness
Muscle Disease
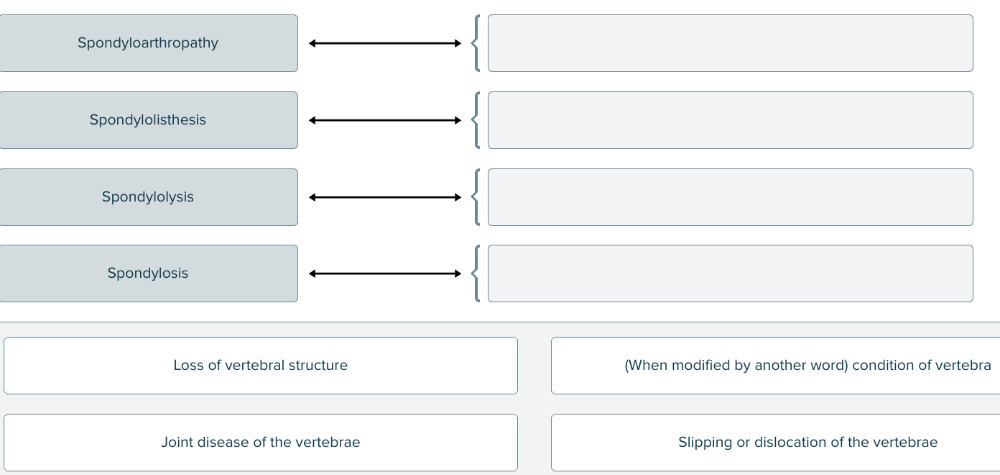
Spondylo- is a root that means vertebra. Match each medical term with its definition.
In tendinitis, the suffix -itis means
Multiple choice question.
- weakness.
- pain.
- tumor.
- inflammation.
inflammation.
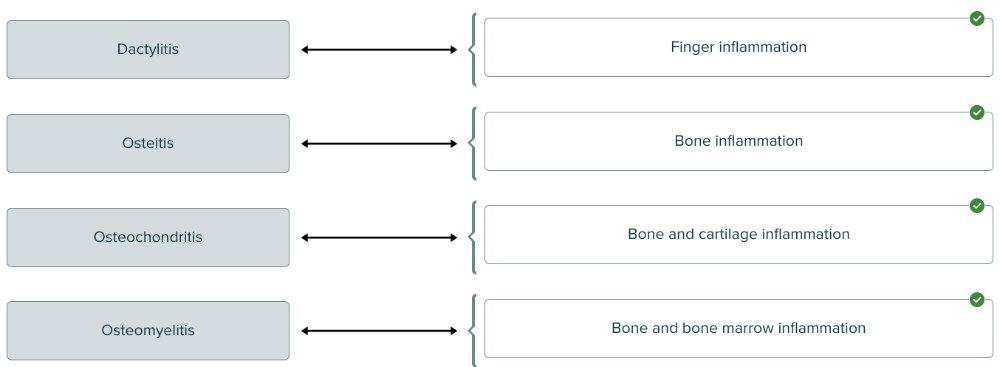
The suffix -itis means inflammation. Match each medical term with the location of inflammation.
Which of the following is the term for a muscle tumor?
Multiple choice question.
- Myosarcoma
- Osteocarcinoma
- Myoma
- Chondroma
Myoma
The term arthritis means inflammation of a joint. Spell the term that means inflammation of joints, but specifically those that bear weight ______. (Hint: a root for "bone" is in the word.)
osteoarthritis
A drug that opposes fever is called an
Multiple choice question.
- antiarthritic.
- analgesic.
- antipyretic.
- anti-inflammatory.
antipyretic.
Ex.
- analgesic.
Reason: Analgesics oppose the pain associated with fever but not (necessarily) the fever itself.
- anti-inflammatory.
Reason: Anti-inflammatories oppose all four signs of inflammation but not fever specifically.
Spell the term for abnormal joint development ______.
arthrodysplasia
(arthro= joint / dys= bad / plasia=formation)
Spell the term that means surgical excision of part of the skull ______.
craniectomy
Which of the following terms means violent muscle contractions?
Multiple choice question.
- Myofascitis
- Myopathy
- Myasthenia
- Myoclonus
Myoclonus
Returning broken or displaced bones to their proper position through the use of surgery is called ______ reduction.
open
Select all that apply
Choose the correct spelling of the term that means inflammation of the tendon.
Multiple select question.
- Tendenitis
- Tindonitis
- Tendinitis
- Tendonitis
- Tendinitis
- Tendonitis
The use of screws, pins, and plates to hold a fractured bone in place from the inside is called
Multiple choice question.
- open reduction.
- osteoclasia.
- external fixation.
- internal fixation.
internal fixation.
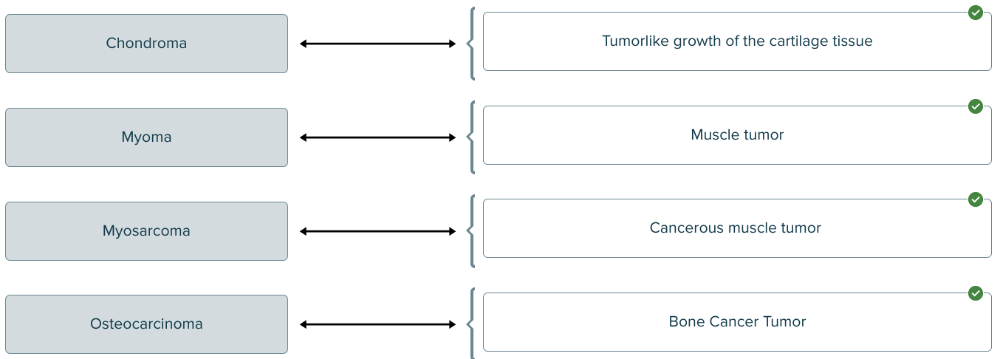
Match the oncology term to the correct definition.
To correct clubfoot, often surgical fracture of the ankle bone is required. This procedure is called ______.
tarsoclasia
A drug that opposes inflammation throughout the body is called an:
Multiple choice question.
- analgesic
- antipyretic
- anti-inflammatory
- antiarthritic
anti-inflammatory
Ex.
- antipyretic
Reason: Fever is only one aspect of inflammation.
- antiarthritic
Reason: Anti-arthritics are specific to joint inflammation.
The term arthrolysis means
Multiple choice question.
- loosening a stiff joint.
- surgical fixation of a joint.
- removal of a joint.
- reconstruction of a joint.
loosening a stiff joint.
The difference between a craniotomy and a craniectomy is that in a craniotomy, the piece of skull is
Multiple choice question.
- transplanted into a donor.
- incinerated.
- left in place.
- replaced after it is removed.
replaced after it is removed.
The meaning of the root in the word myectomy is ______.
muscle
(root= my-)
Which of the following is the procedure for removing a rib?
Multiple choice question.
- Craniotomy
- Costectomy
- Craniectomy
- Carpectomy
Costectomy
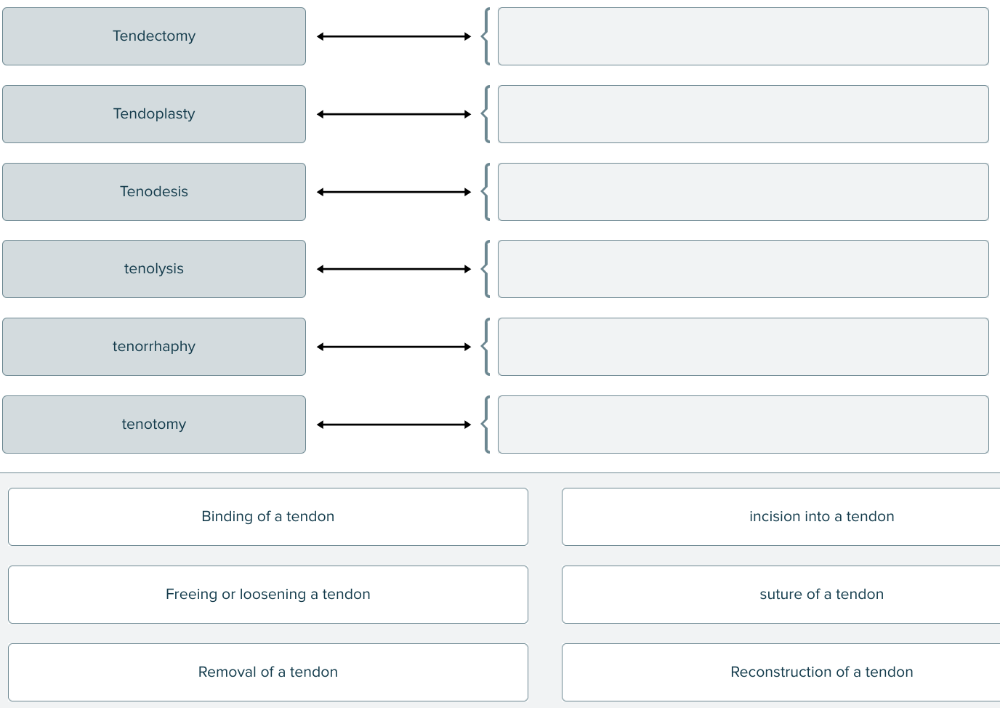
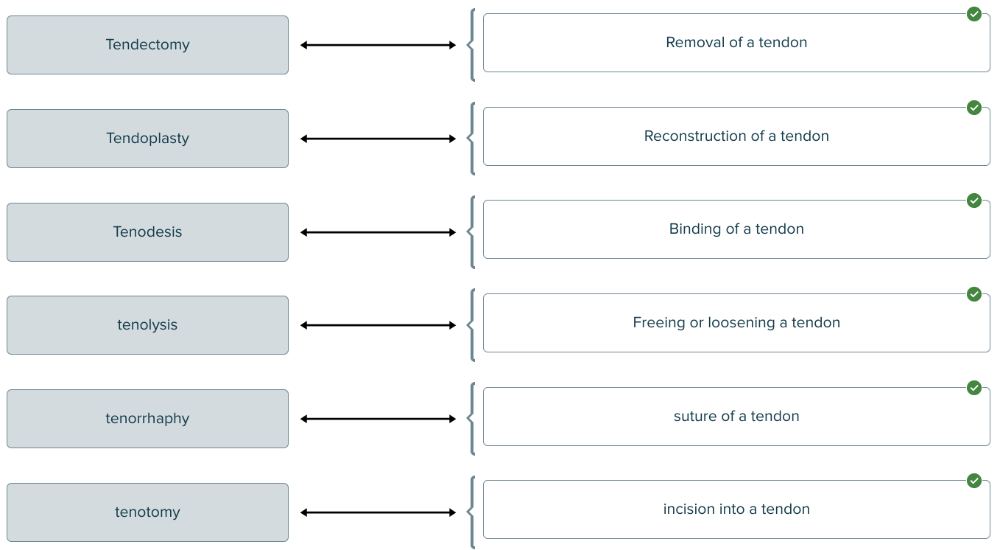
Match each medical term for tendon treatment or therapy with its description.
The use of casts, splints, and stabilizers to hold a fractured bone in place from the outside is termed ______ fixation.
external
The abbreviation LCL stands for lateral collateral ligament (of the knee). The abbreviation MCL stands for:
Multiple choice question.
- muscular collateral ligament
- major collateral ligament
- medial collateral ligament
- minor collateral ligament
medial collateral ligament
Select all that apply
Identify the terms that mean removal of a bone.
Multiple select question.
- Osteectomy
- Ostectomy
- Osteoplasty
- Osteoclasia
- Osteectomy
- Ostectomy
In the abbreviation T12, the letter represents
Multiple choice question.
- tibial.
- talipes.
- thoracic.
- tarsal.
thoracic.
An incision into a joint is termed ______.
arthrotomy
The abbreviation ORIF stands for
Multiple choice question.
- over reduction in fascia.
- open resection in fascia.
- open reduction internal fixation.
- open re-suture internal fixation.
open reduction internal fixation.
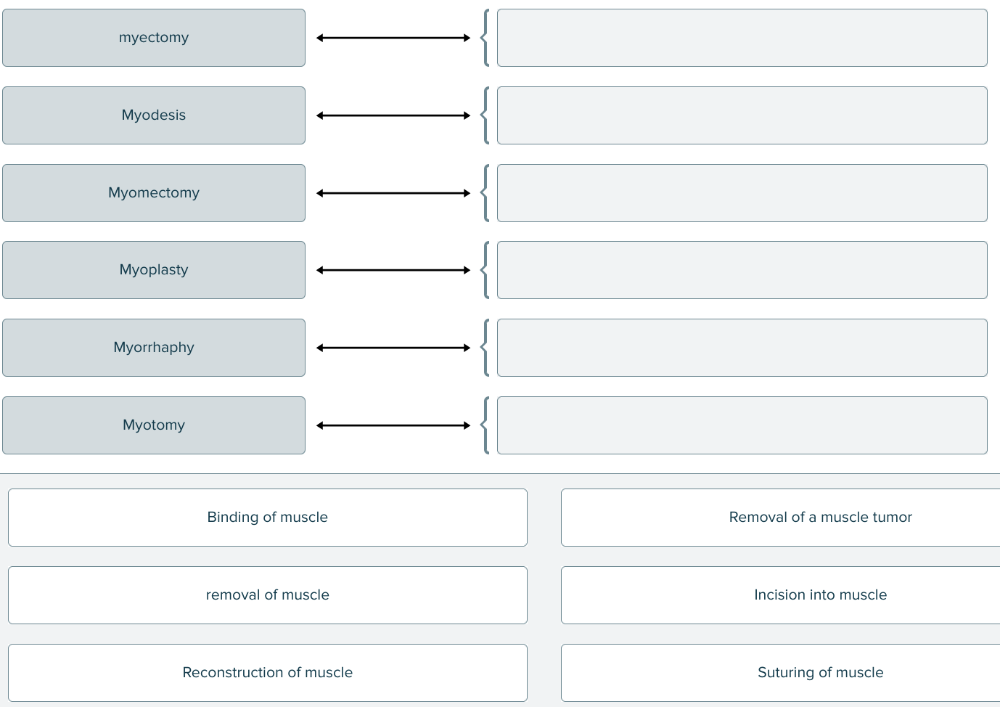
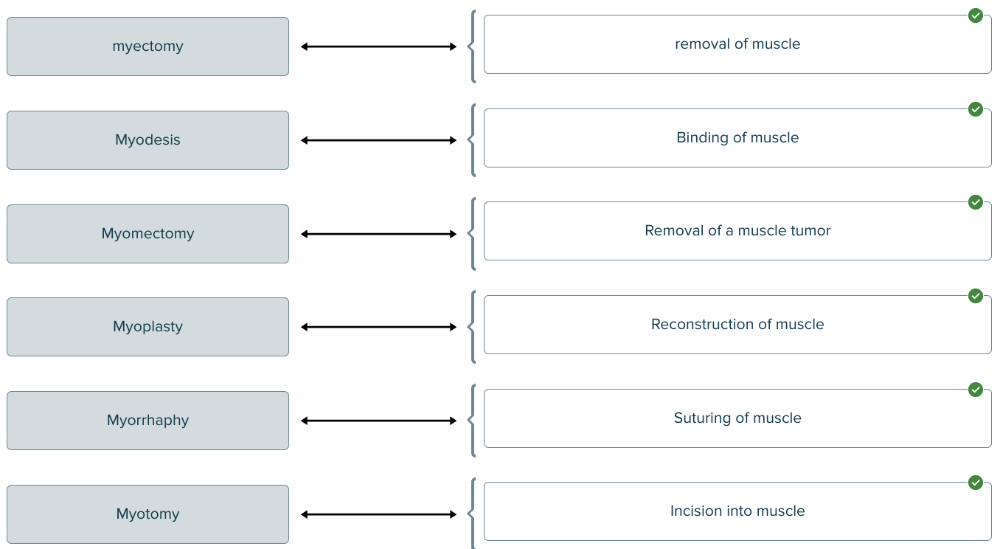
Match each term for treatments and therapies of muscle with its description.
Select all that apply
Identify the terms for removal of a tendon.
Multiple select question.
- Tenodesis
- Tendoplasty
- Tenonectomy
- Tendectomy
- Tenonectomy
- Tendectomy
In the abbreviations ACL and PCL used for the knee joint, the letter C stands for ______.
cruciate
Ex.
ACL - anterior cruciate ligament
PCL - posterior cruciate ligament
Click and drag on elements in order
Place the abbreviations in the proper order, starting with the superior (topmost) set.
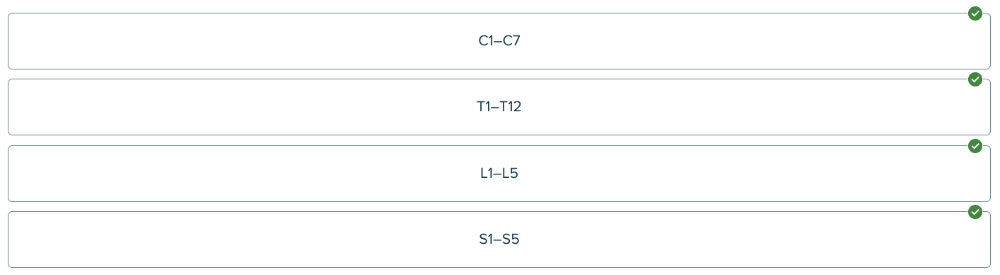
Ex.
C - cervical (of the neck) vertebrae
T - thoracic (of the chest) vertebrae
L - lumbar (of the loin)
vertebrae
S - sacral vertebrae
The acronym RICE stands for
Multiple choice question.
- rest, ice, cold, elevation.
- rest, iron, cold, elevation.
- rest, ice, compression, elevation.
- rest, inflammation, compression, elevation.
rest, ice, compression, elevation.