Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 4: The Musculoskeletal System - Orthopedics
front 1  Chapter 4.1 Introduction and Overview of the Musculoskeletal System | back 1 no data |
front 2  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Bones | back 2 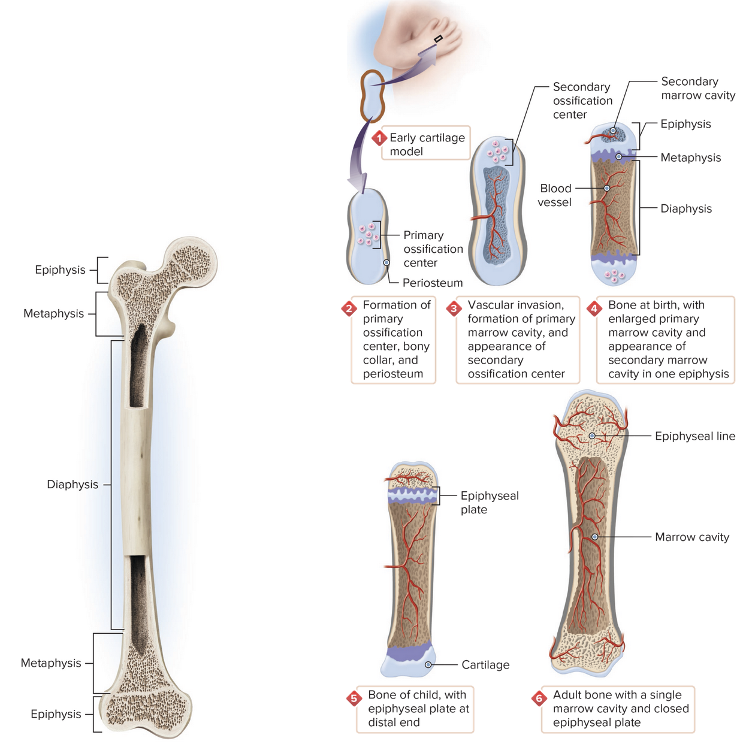 |
front 3  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Bones
| back 3 no data |
front 4  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System The Skeleton | back 4 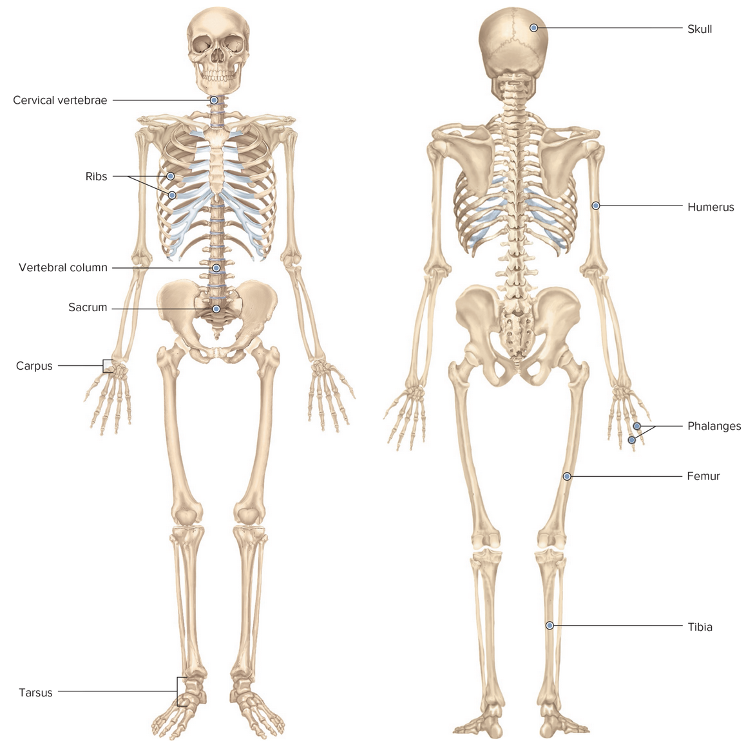 |
front 5  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System The Skeleton
| back 5 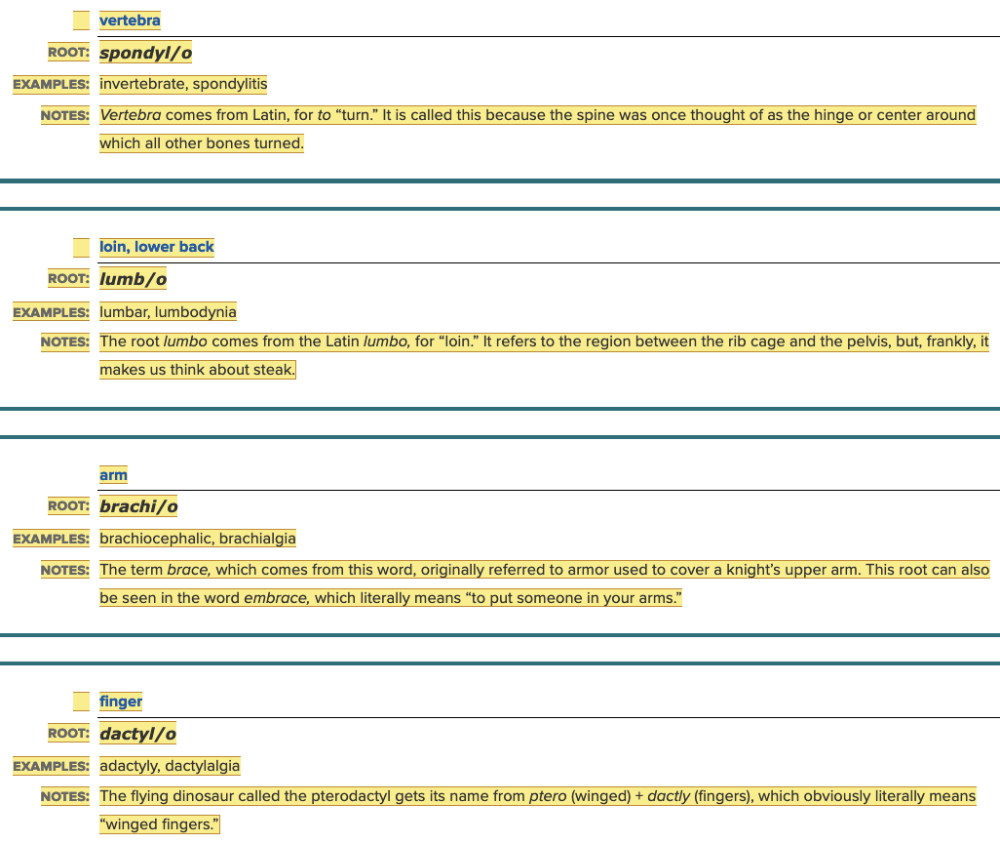 Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System The Skeleton
|
front 6 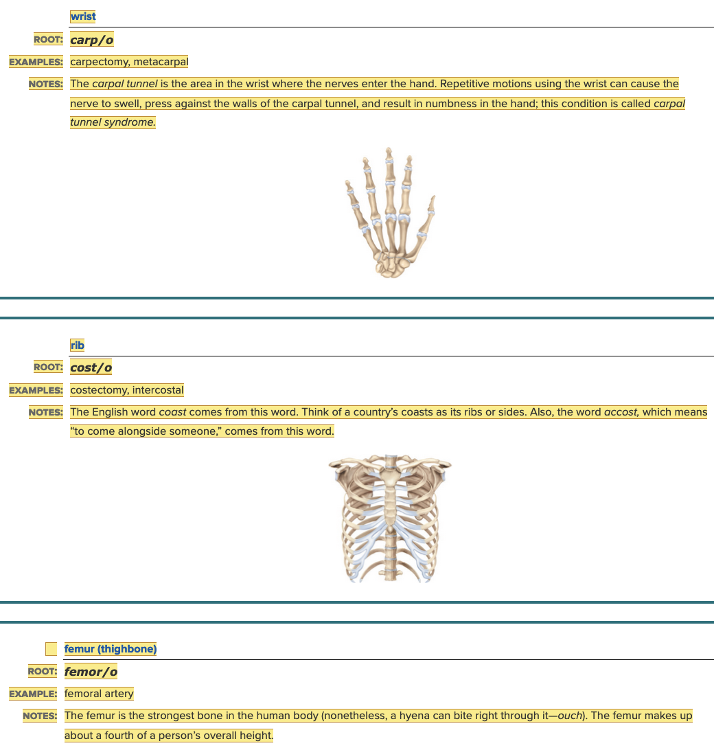 Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System The Skeleton
| back 6  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System The Skeleton
|
front 7  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Joints | back 7  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Joints
|
front 8 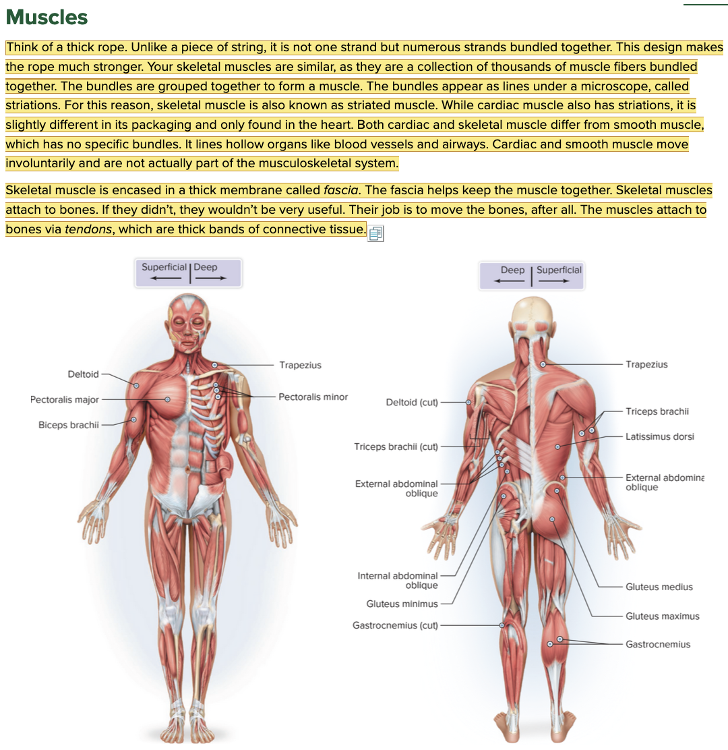 Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Muscles | back 8  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Muscles
|
front 9  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Muscles
| back 9 no data |
front 10  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Motion | back 10  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Motion
|
front 11  Chapter 4.1 Word Parts of the Musculoskeletal System Motion
| back 11 no data |
front 12  Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 12 no data |
front 13  Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4. | back 13 no data |
front 14  Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 5, 6. | back 14 no data |
front 15  Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 7, 8. | back 15 no data |
front 16  Learning Outcome 4.1 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10. | back 16  |
front 17  Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 17 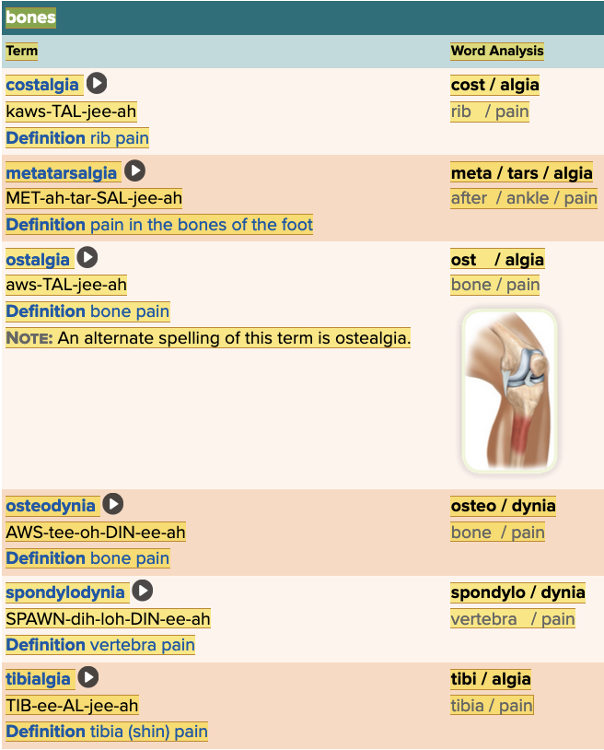 Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 18 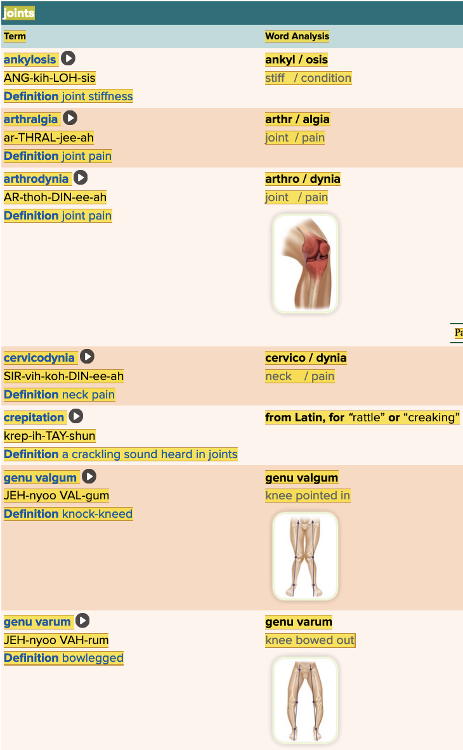 Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 18 no data |
front 19 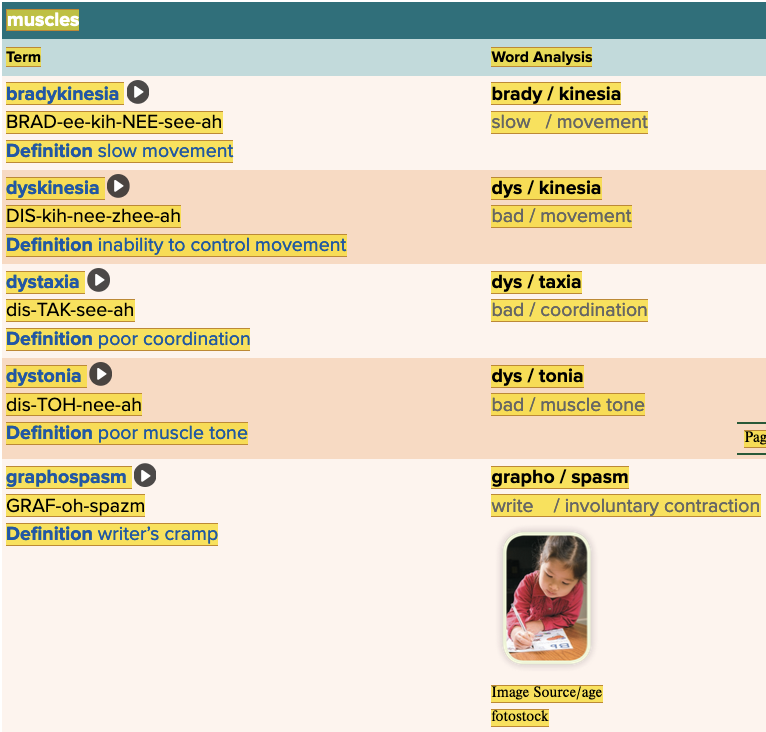 Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 19  Chapter 4.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 20  Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 20 no data |
front 21  Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 21 no data |
front 22  Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 22 no data |
front 23  Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 23 no data |
front 24  Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 24 no data |
front 25  Learning Outcome 4.2 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 25  |
front 26  Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 26  Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 27 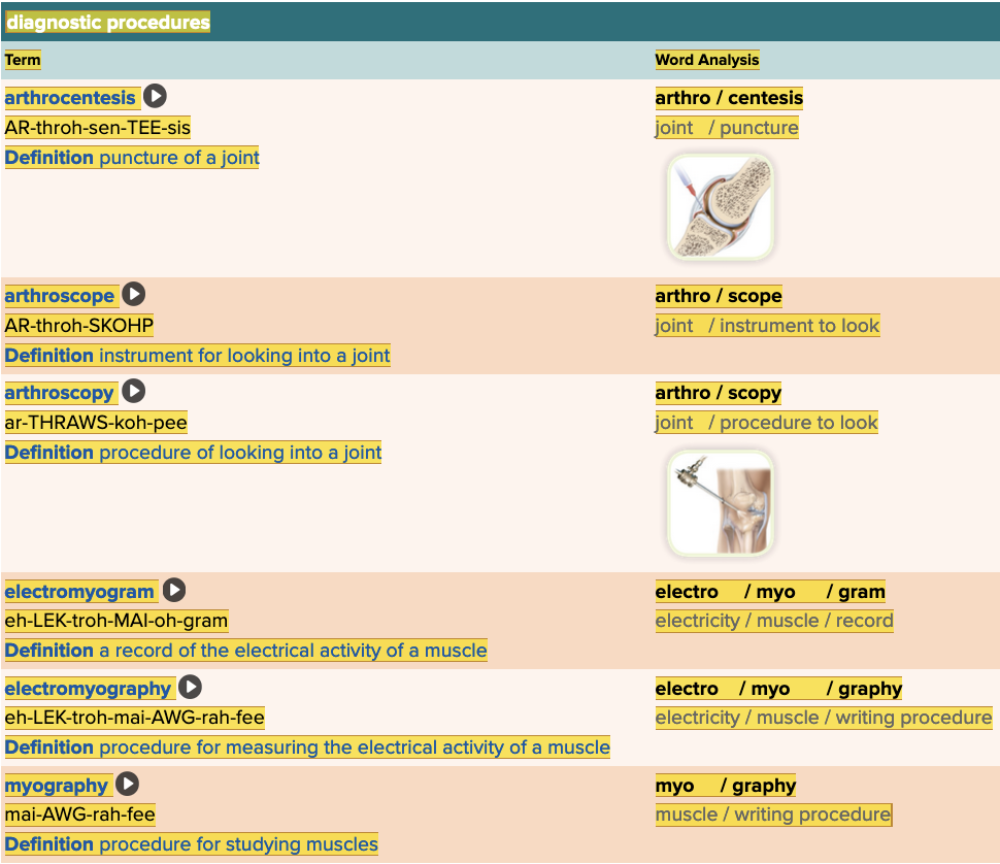 Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 27  Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 28 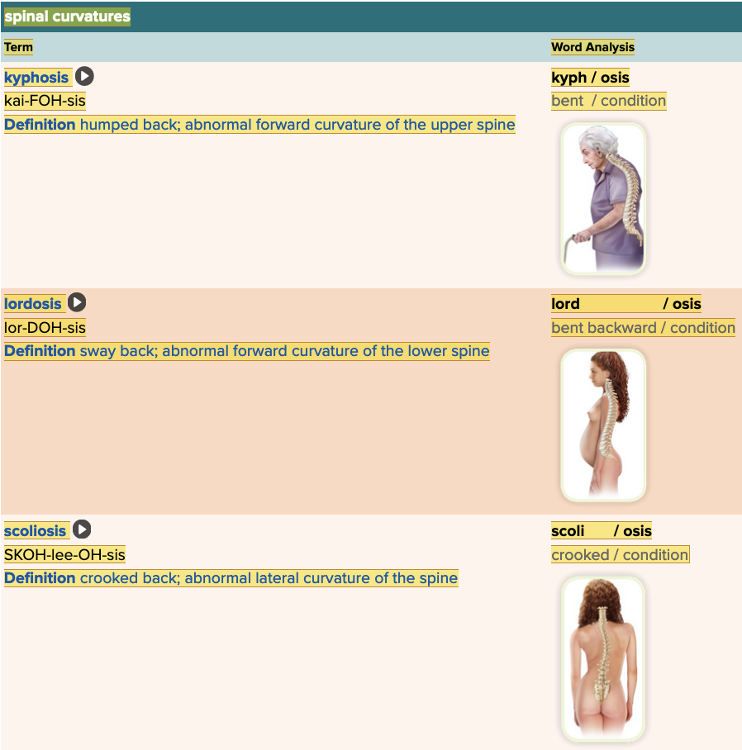 Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 28 no data |
front 29 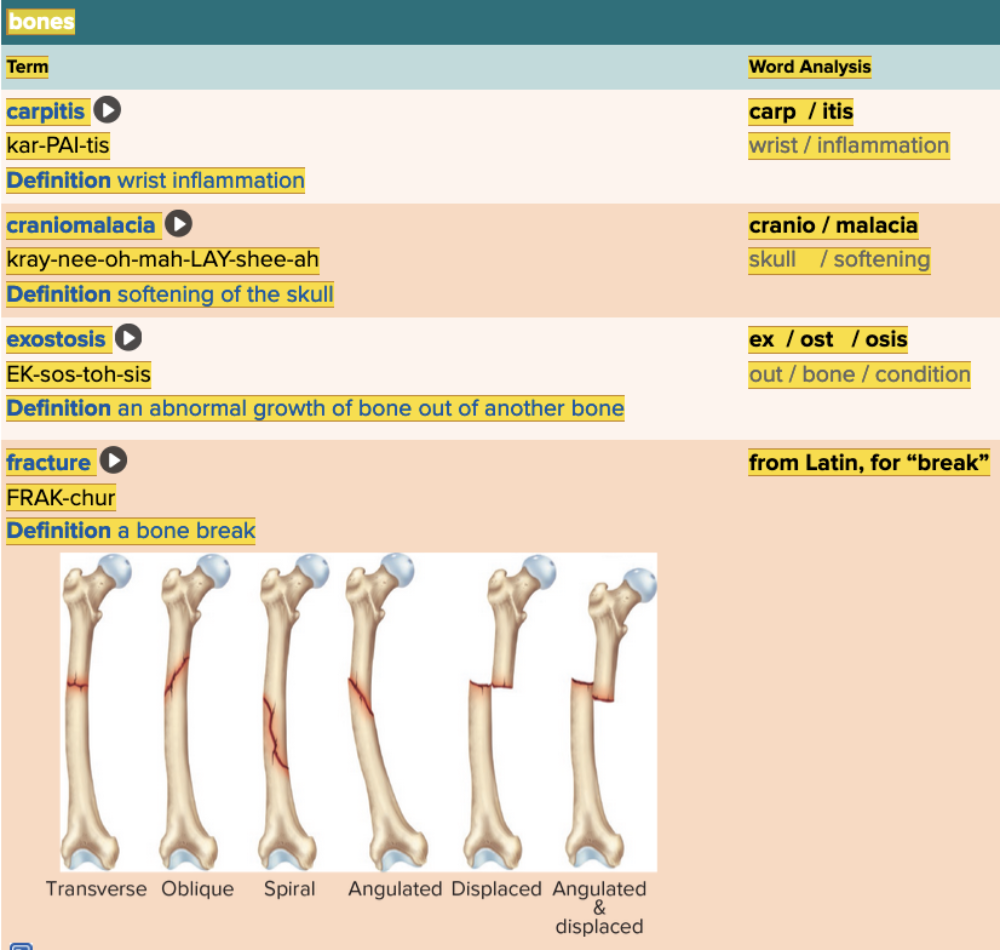 Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 29 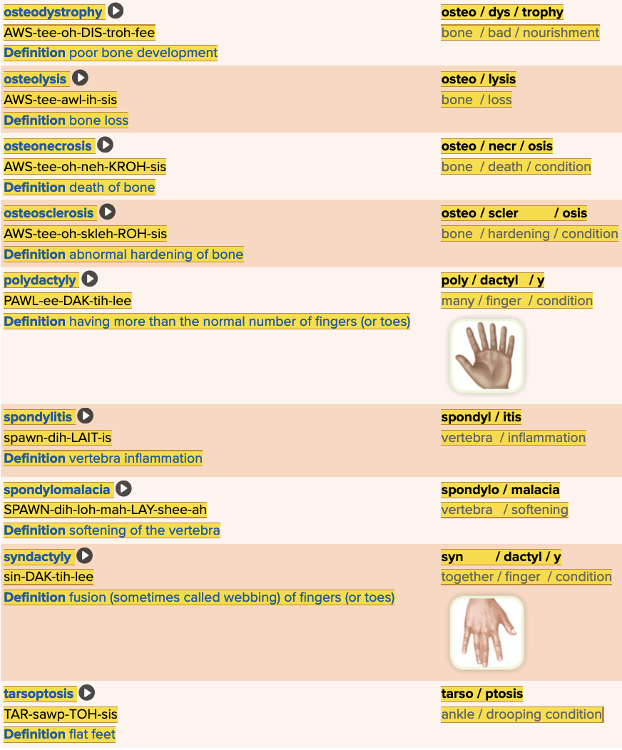 Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 30 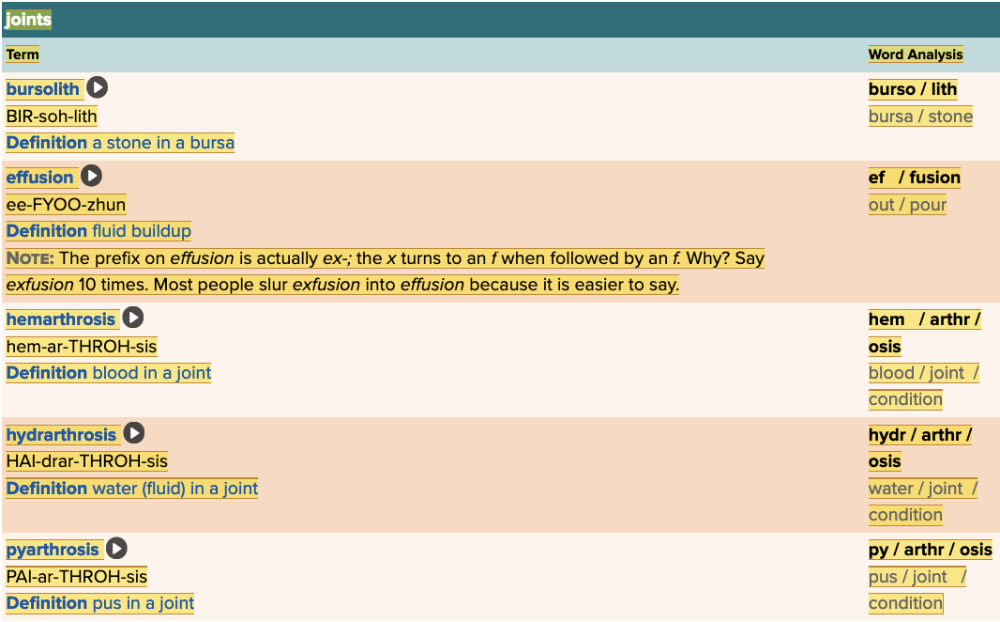 Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 30 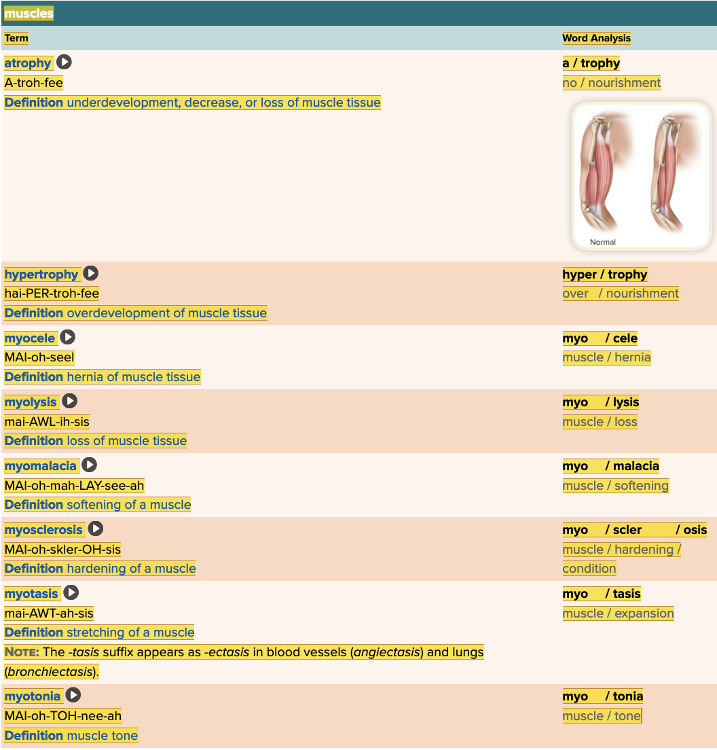 Chapter 4.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 31  Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 31 no data |
front 32  Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 32 no data |
front 33 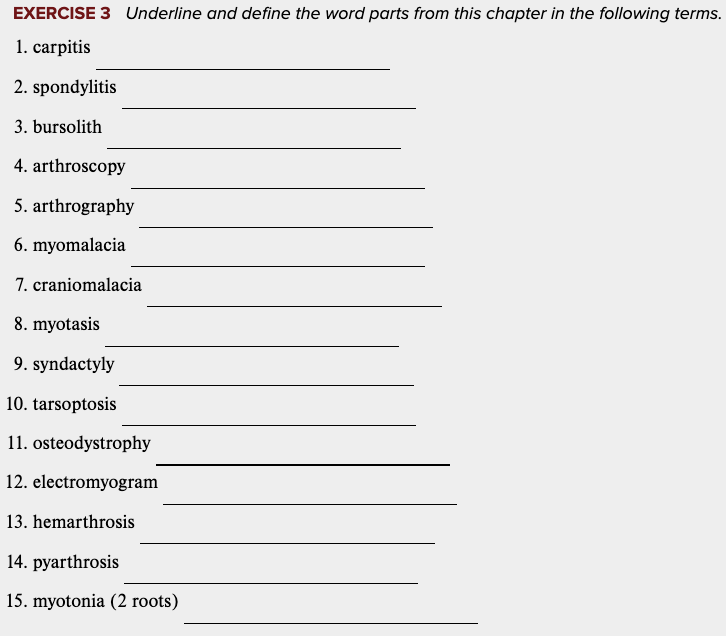 Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 33 no data |
front 34 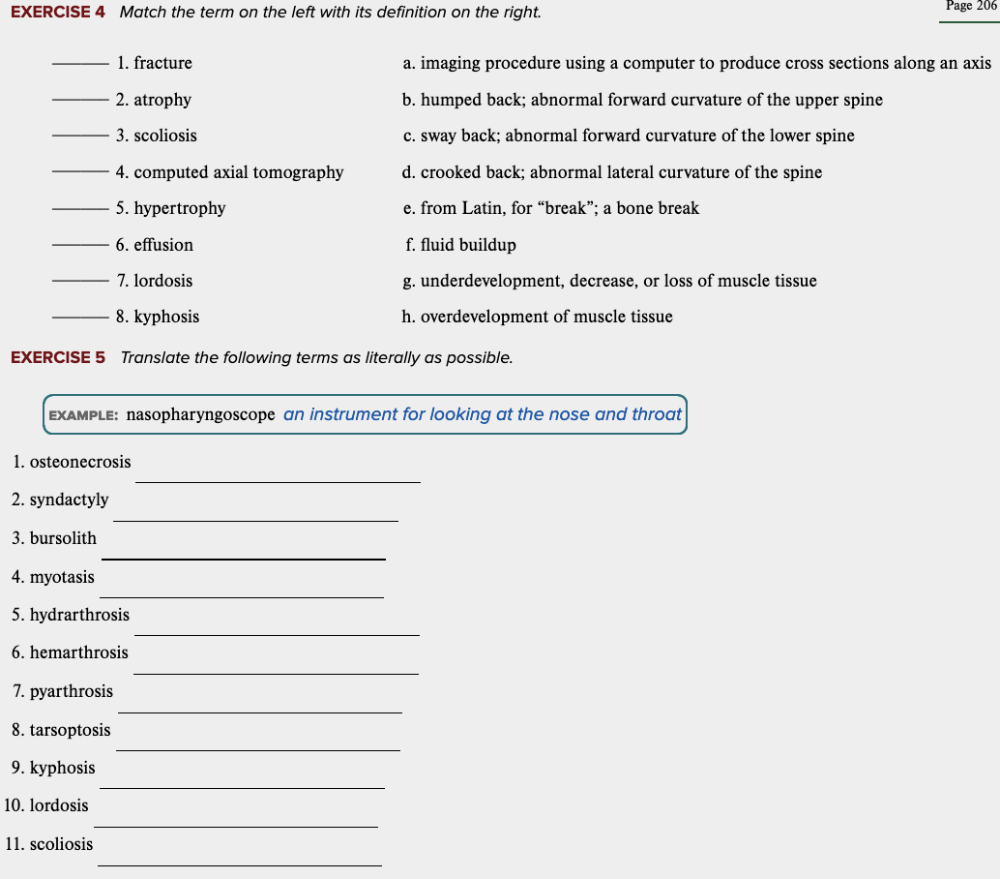 Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 34 no data |
front 35  Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 35 no data |
front 36  Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 36  |
front 37  Learning Outcome 4.3 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 37 no data |
front 38  Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 38  Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 39 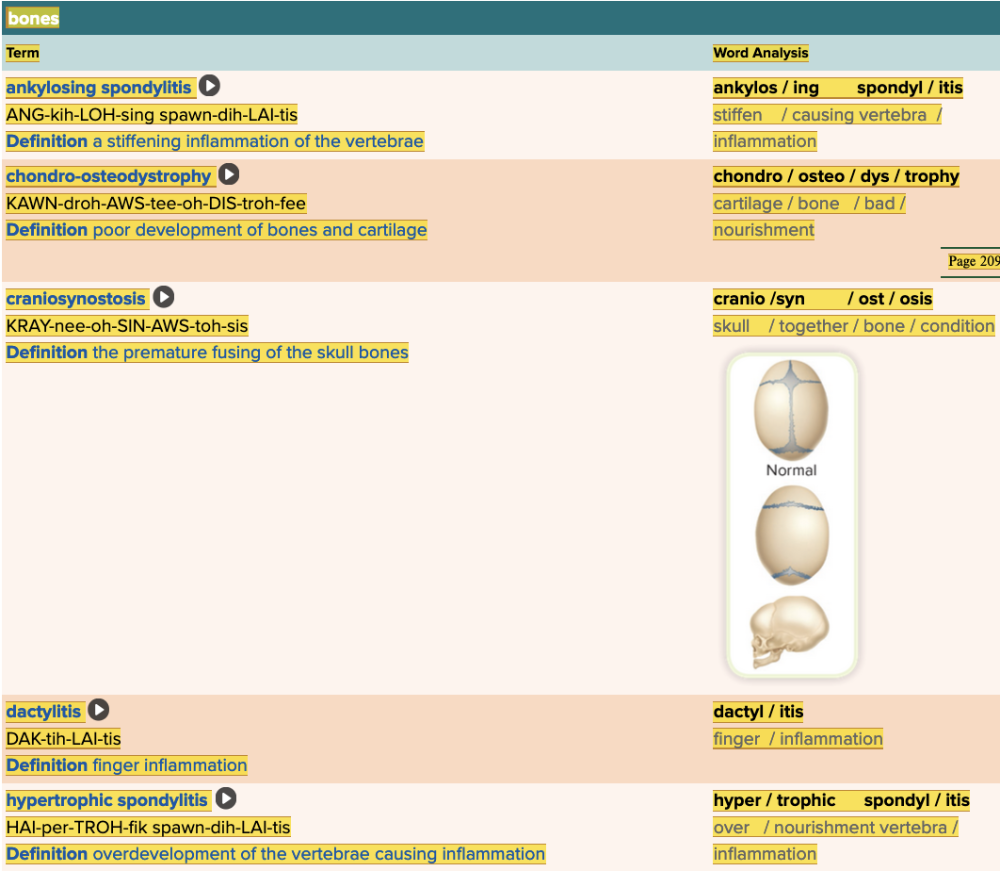 Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 39 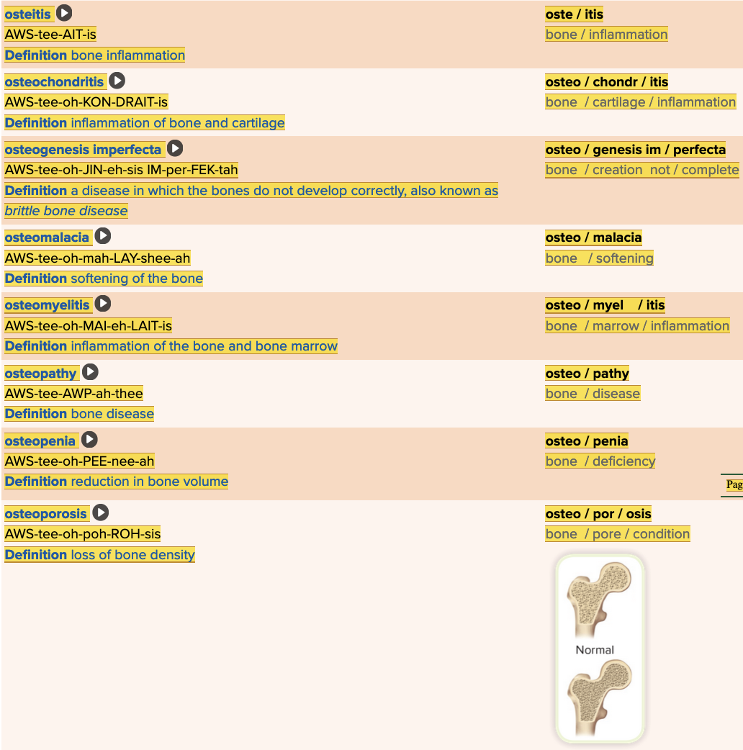 Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 40 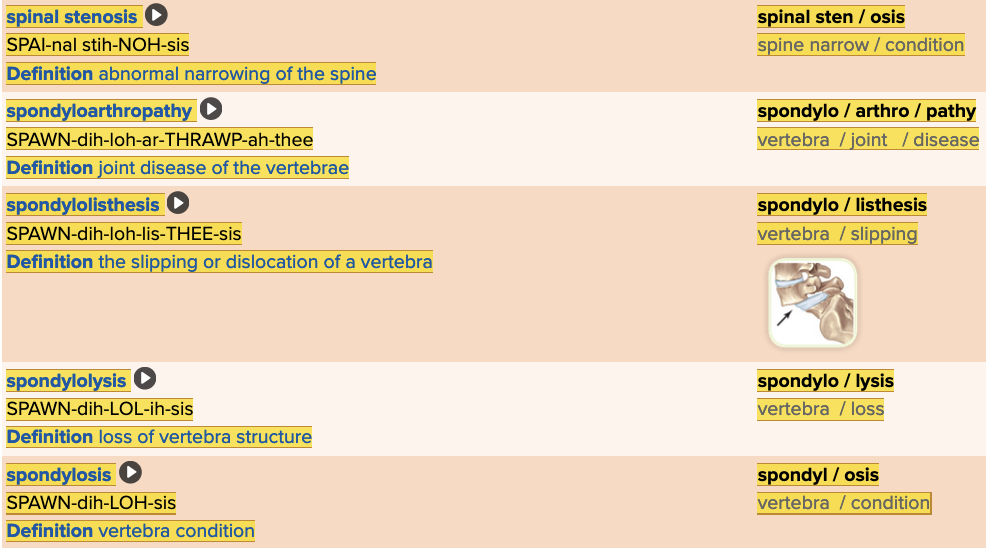 Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 40 no data |
front 41 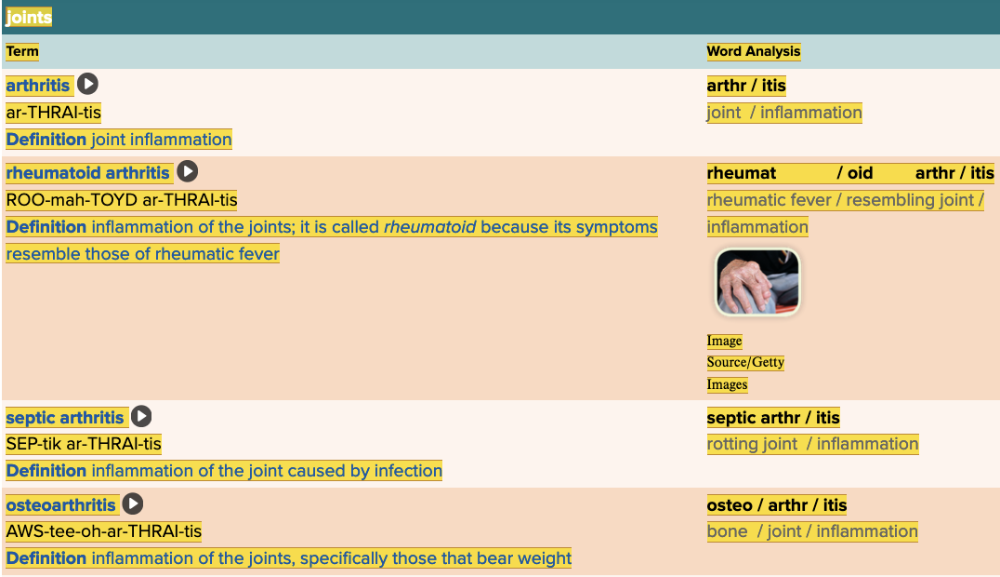 Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 41 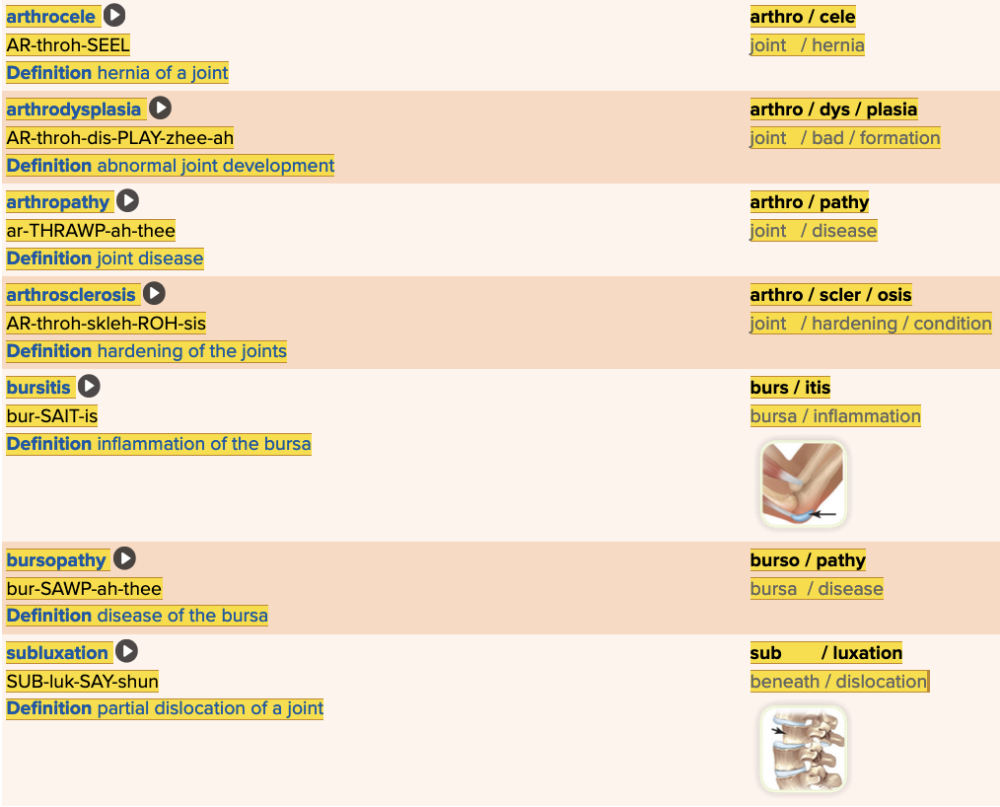 Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 42 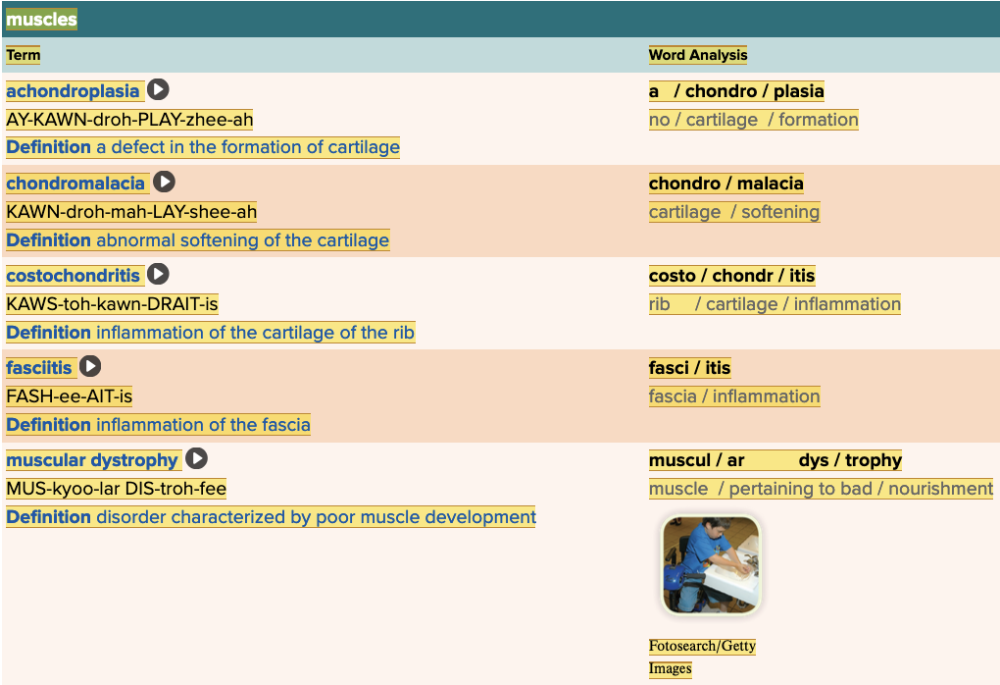 Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 42 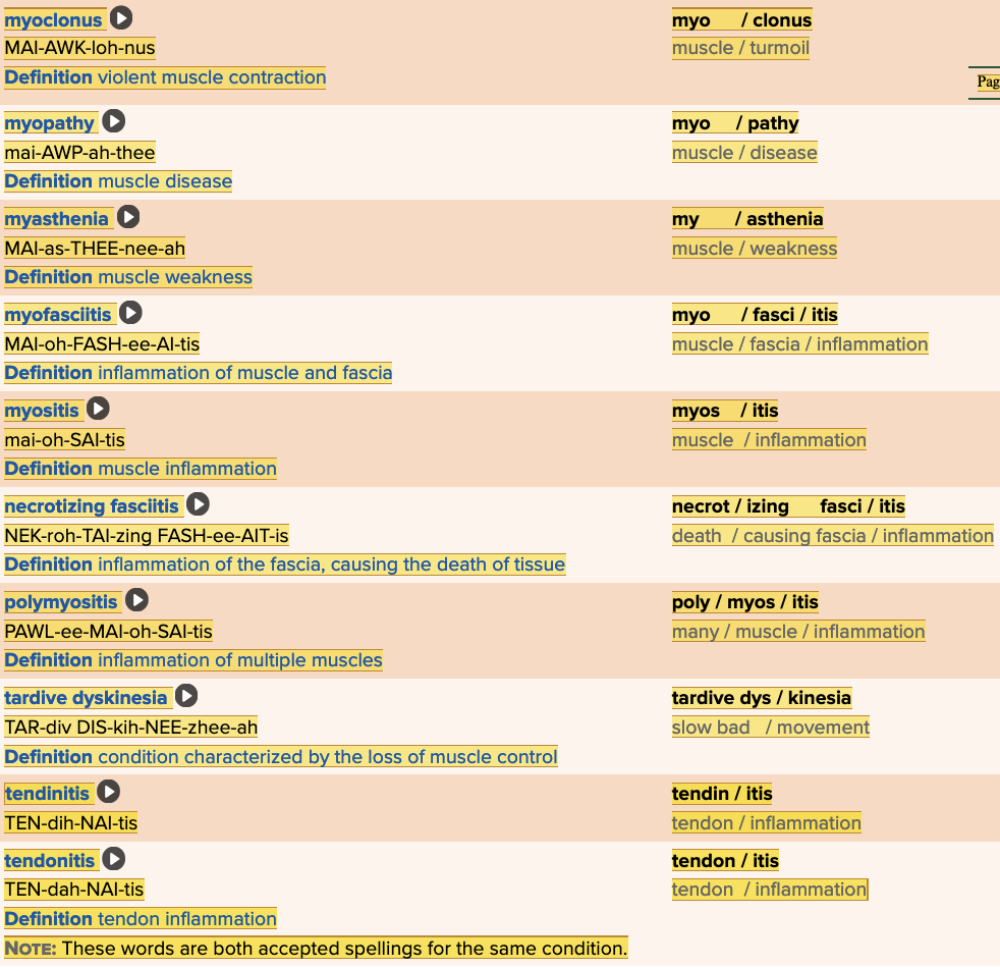 Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 43 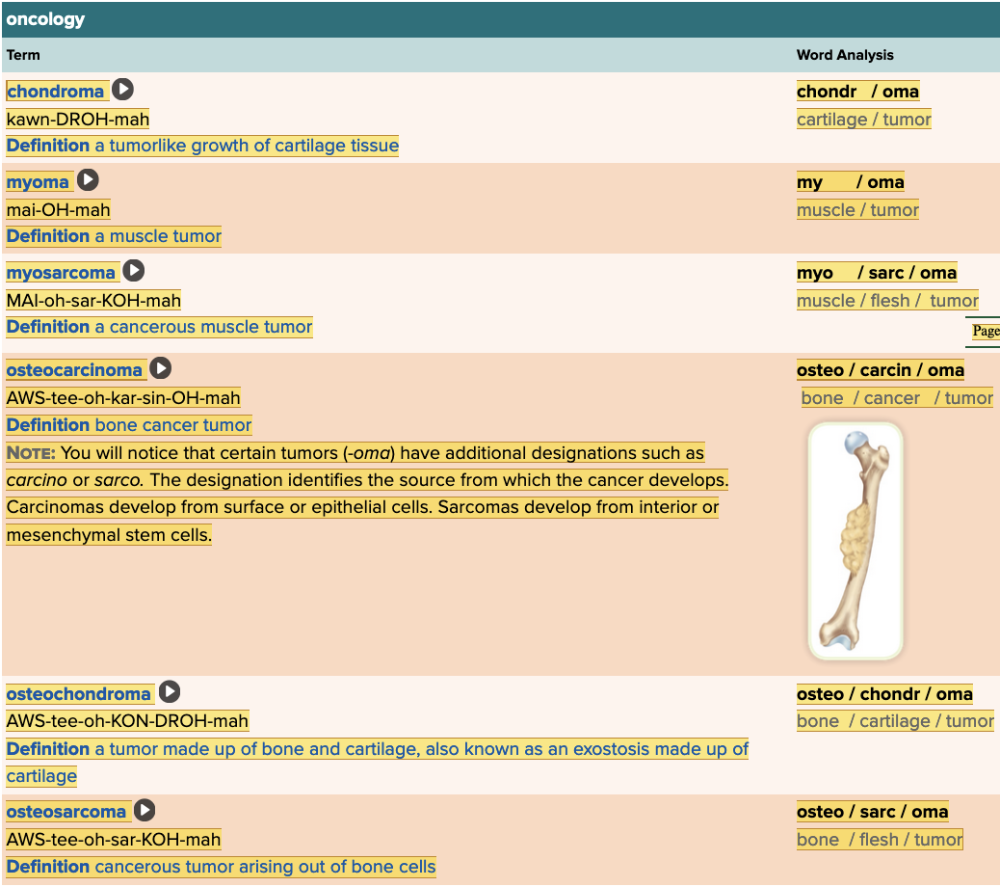 Chapter 4.3 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 43 no data |
front 44  Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 44 no data |
front 45  Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 45 no data |
front 46  Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 46 no data |
front 47  Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 4. | back 47 no data |
front 48 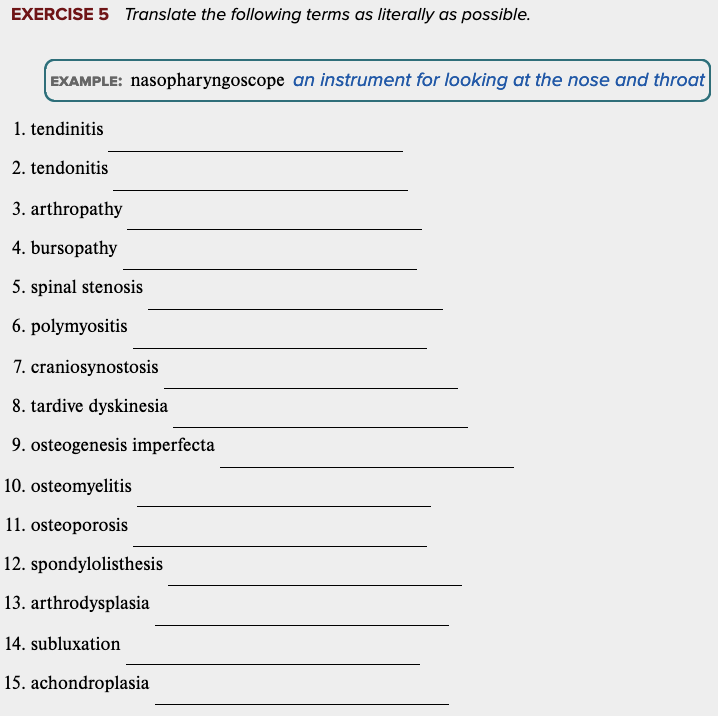 Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 48 no data |
front 49  Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 49 no data |
front 50  Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 50  |
front 51  Learning Outcome 4.4 Exercises: Exercise 8, 9. | back 51 no data |
front 52 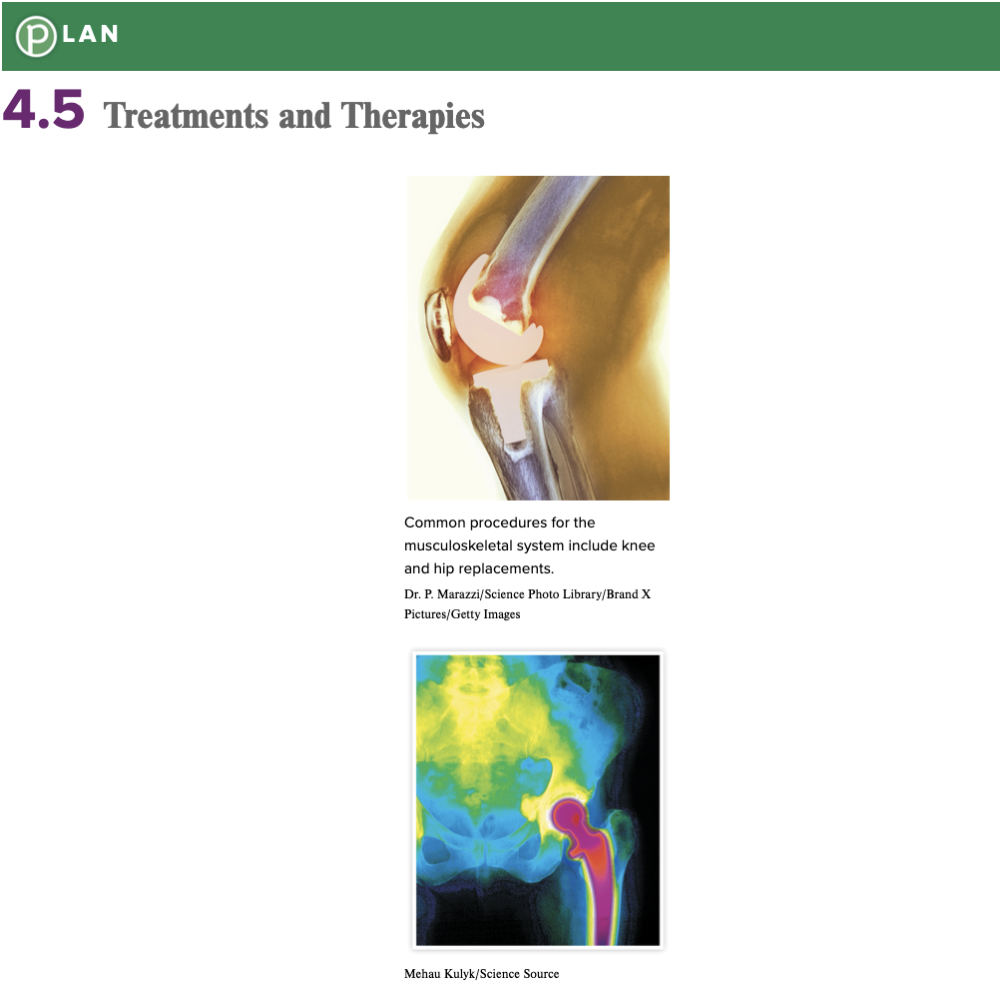 Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 52  Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 53  Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 53  Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 54  Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 54  Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 55 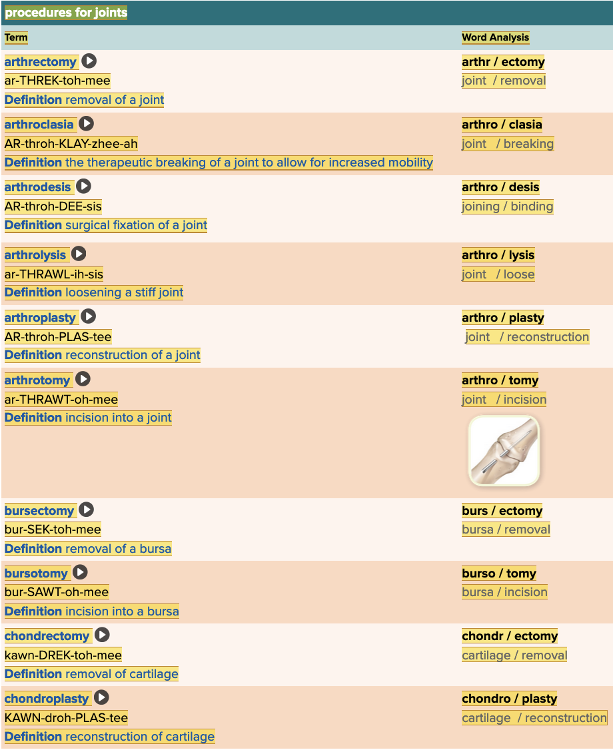 Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 55 no data |
front 56 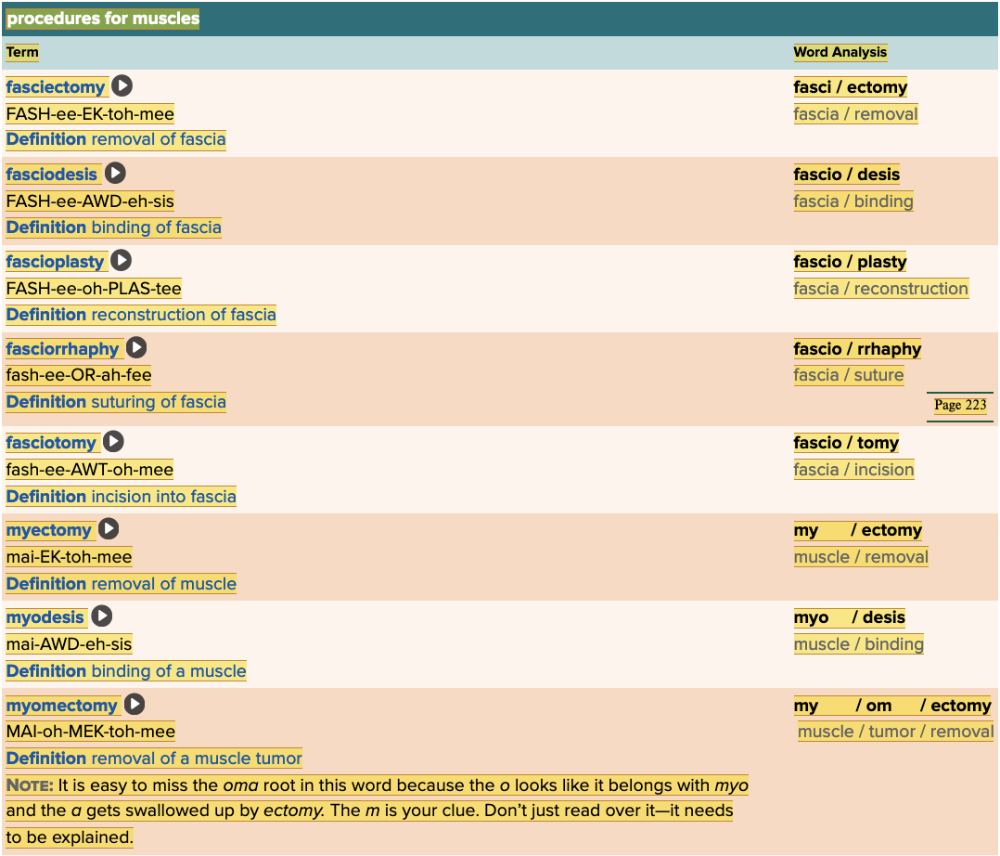 Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 56 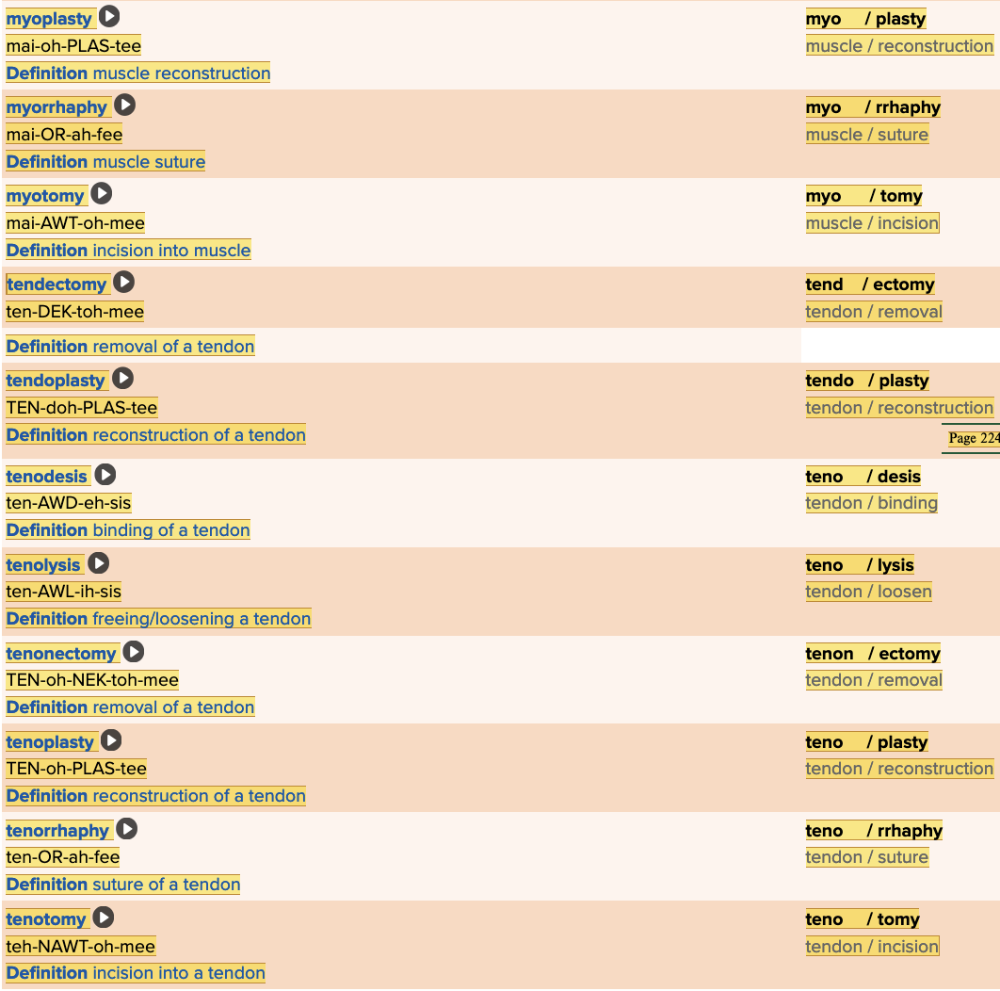 Chapter 4.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 57  Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 57 no data |
front 58  Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 58 no data |
front 59  Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 59 no data |
front 60  Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 4. | back 60 no data |
front 61  Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 61 no data |
front 62  Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 62 no data |
front 63  Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 63 no data |
front 64  Learning Outcome 4.5 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 64 no data |
front 65 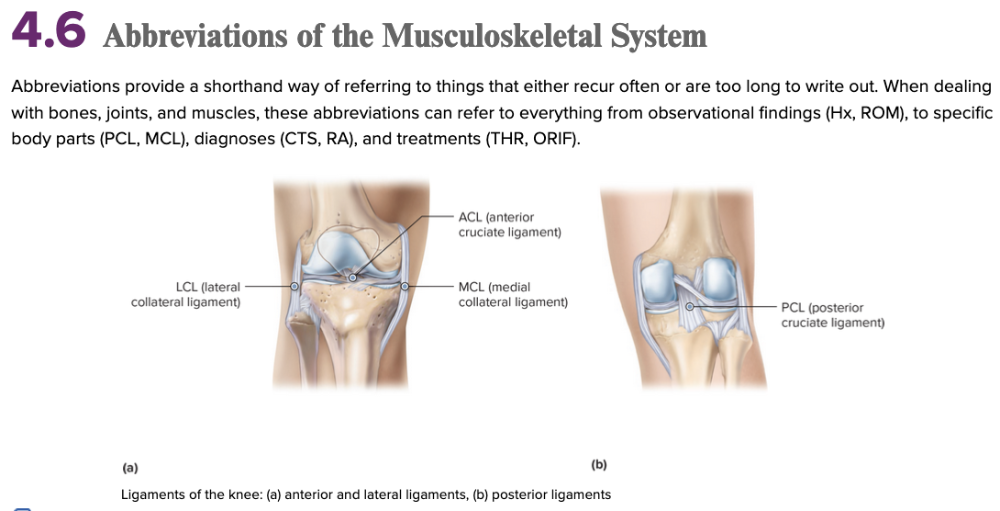 Chapter 4.6 Abbreviations of the Musculoskeletal System | back 65 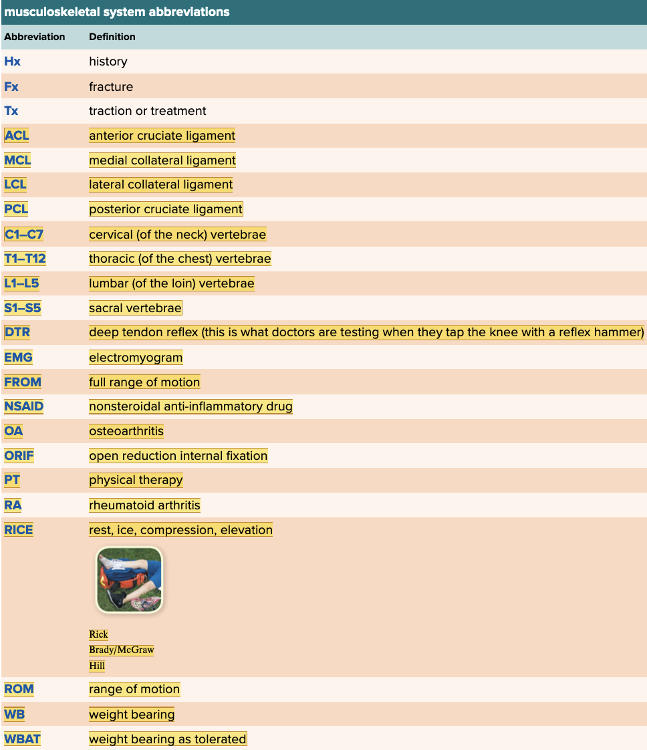 Chapter 4.6 Abbreviations of the Musculoskeletal System
|
front 66  Learning Outcome 4.6 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 66 no data |
front 67  Learning Outcome 4.6 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 67  |
front 68  Chapter 4.7 Electronic Health Records Orthopedic Clinic Note | back 68 no data |
front 69 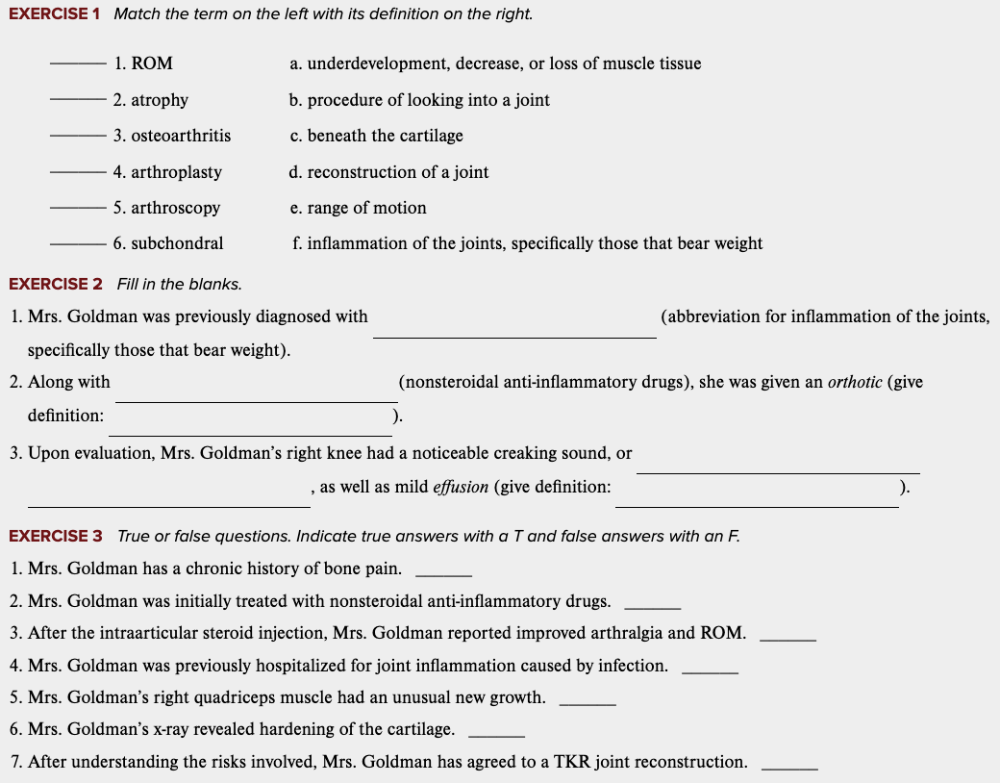 Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2, 3. | back 69 no data |
front 70  Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 4. | back 70 no data |
front 71  Chapter 4.7 Electronic Health Records Discharge Summary Part 1 | back 71  Chapter 4.7 Electronic Health Records Discharge Summary Part 2 |
front 72 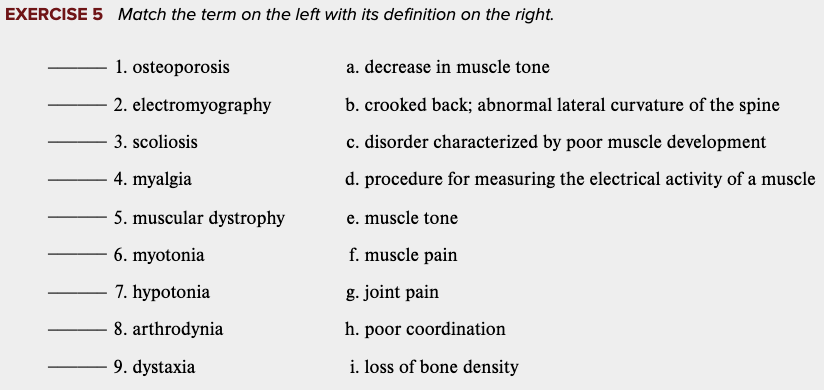 Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 72 no data |
front 73 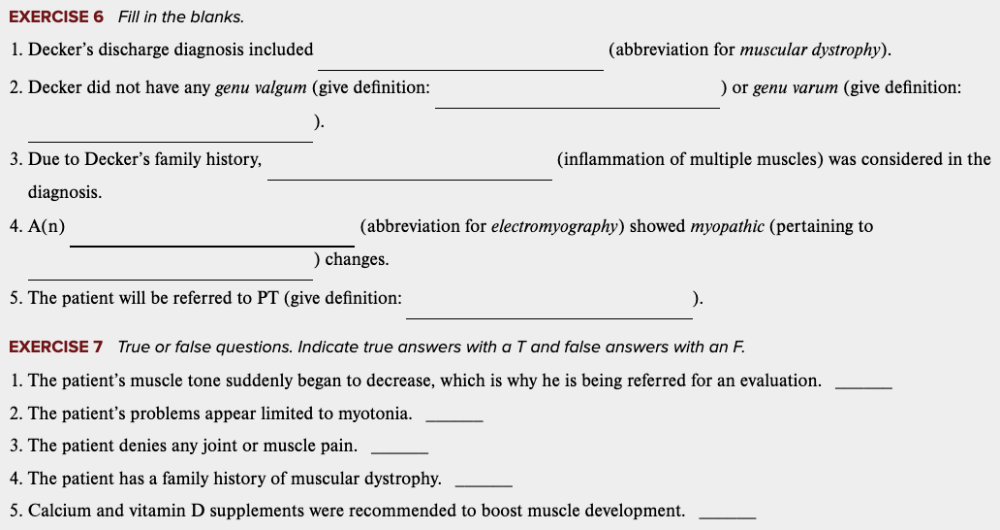 Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 6, 7. | back 73 no data |
front 74  Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 74  |
front 75  Chapter 4.7 Electronic Health Records Orthopedic Consult Note | back 75 no data |
front 76 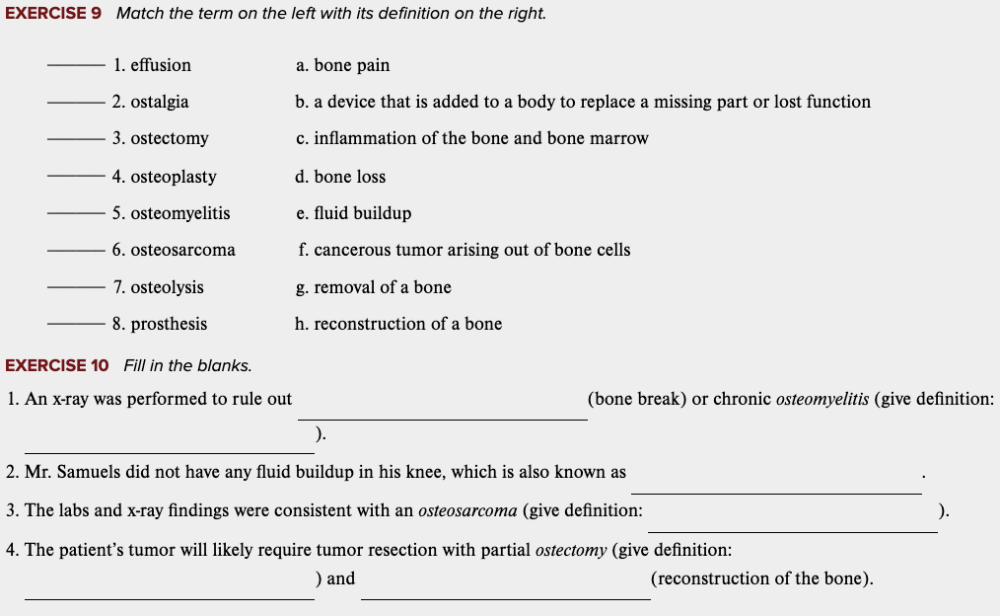 Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10. | back 76 no data |
front 77  Learning Outcome 4.7 Exercises: Exercise 11. | back 77  |
front 78 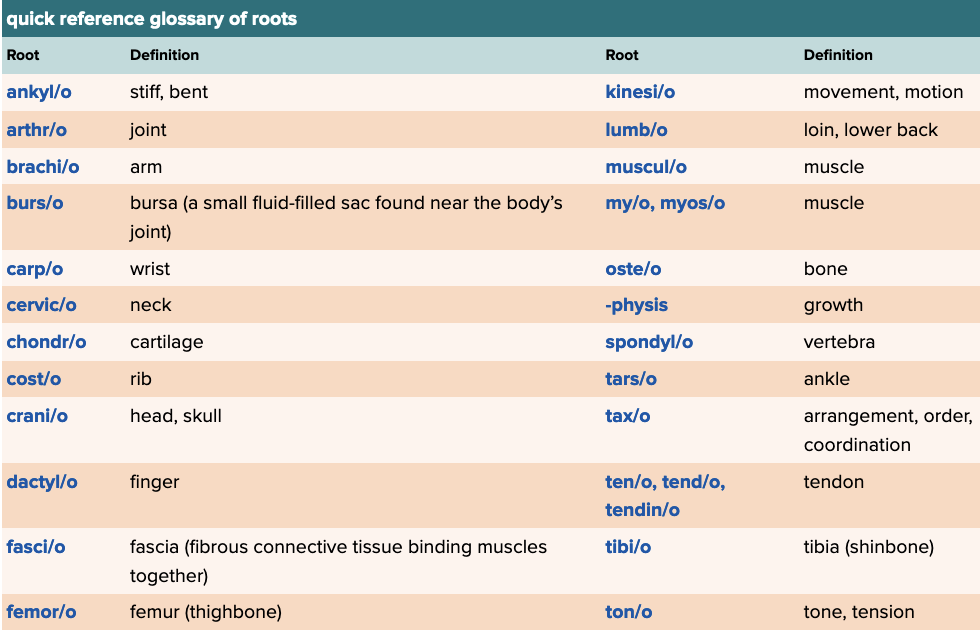 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
| back 78 no data |
front 79 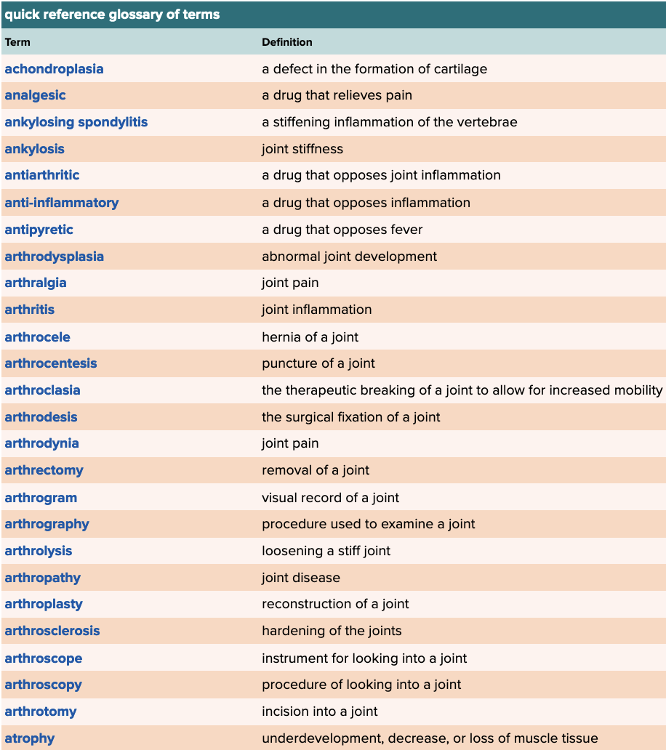 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
| back 79 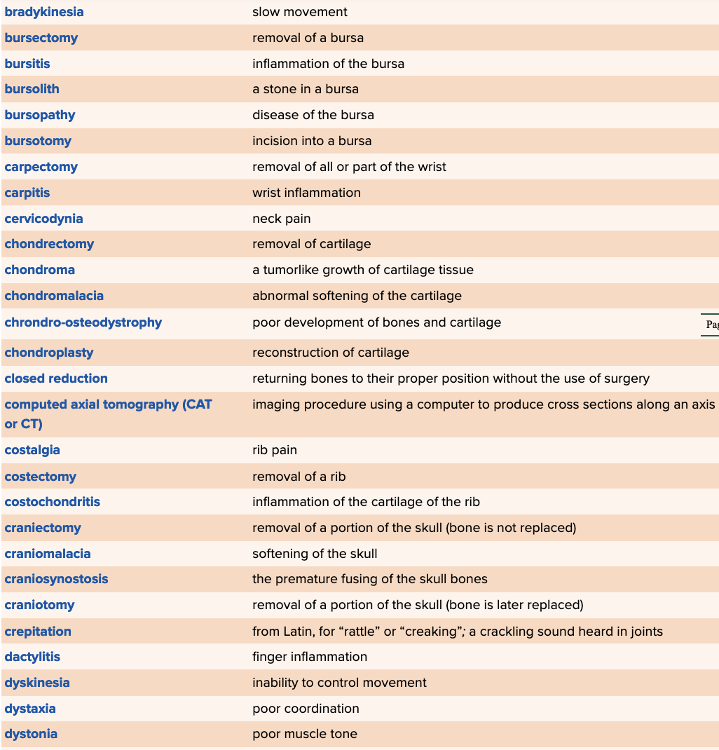 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
|
front 80 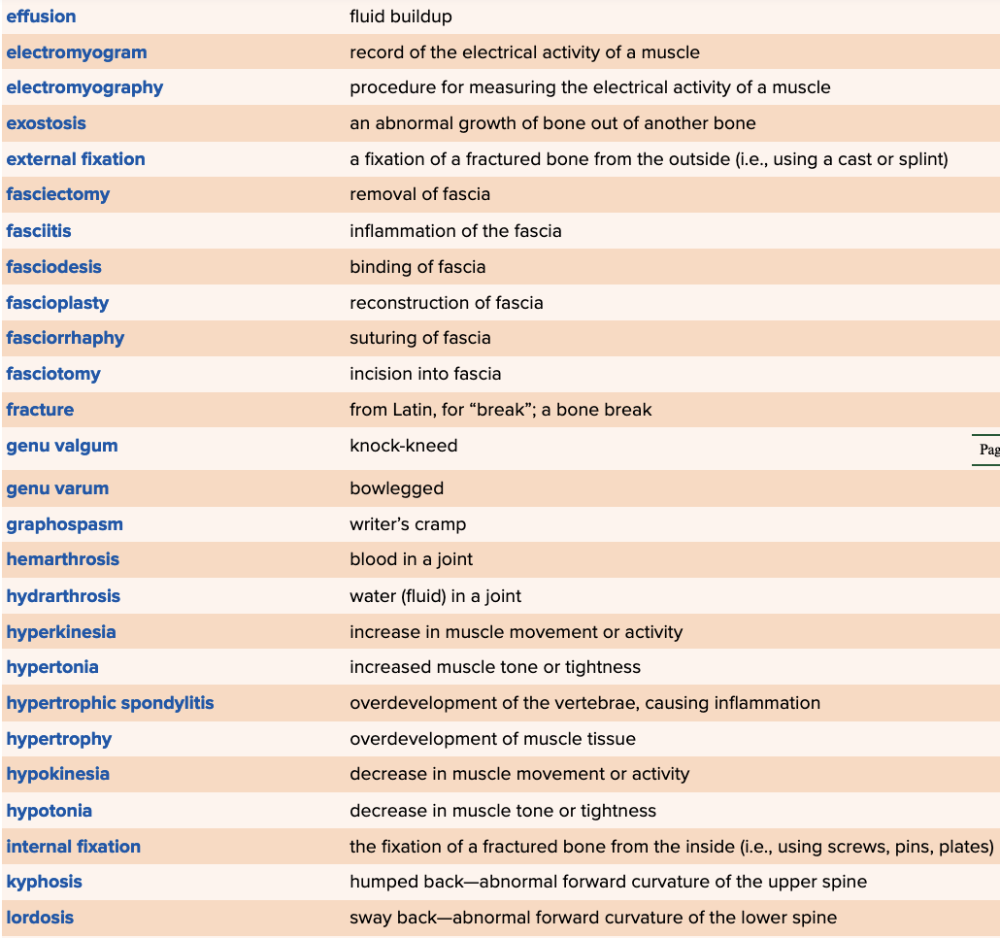 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
| back 80 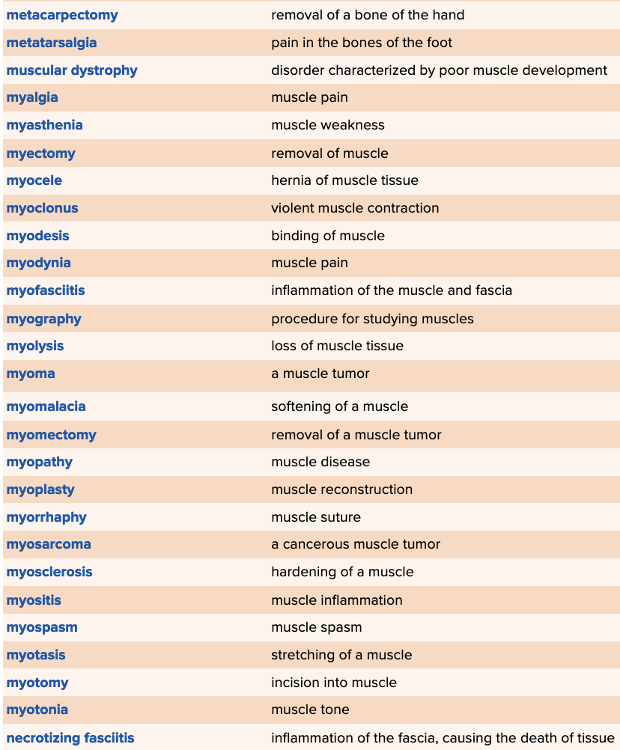 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
|
front 81 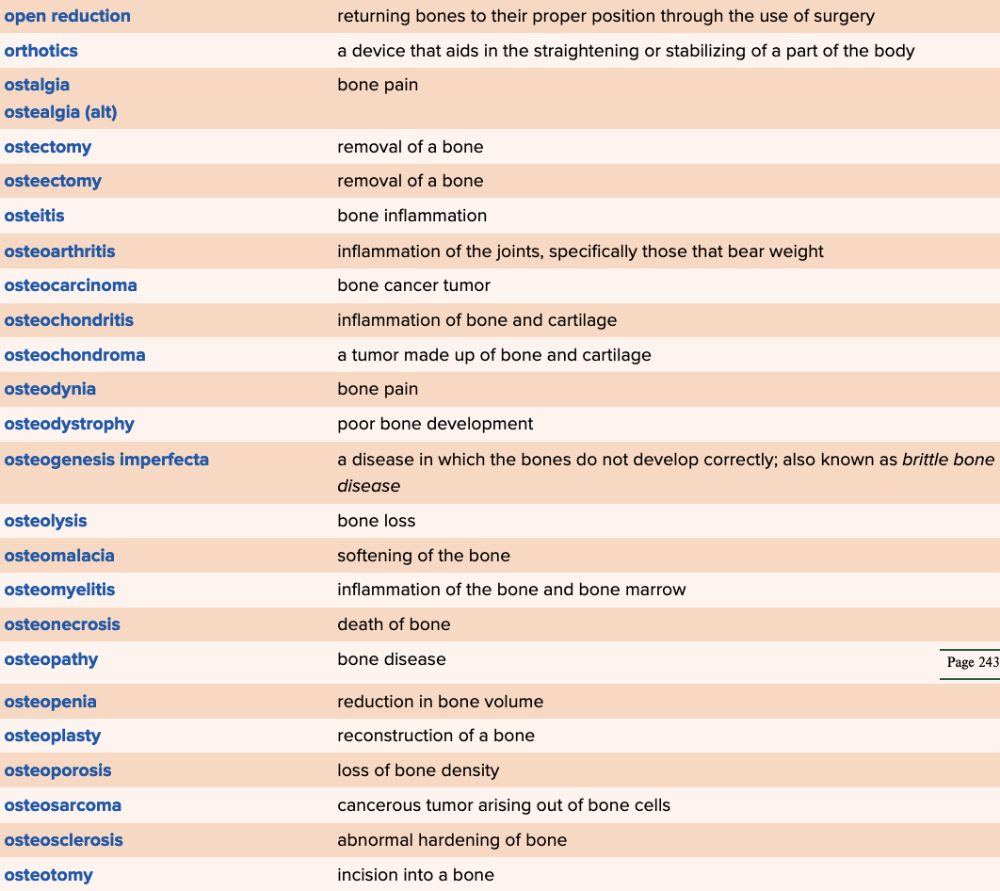 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
| back 81 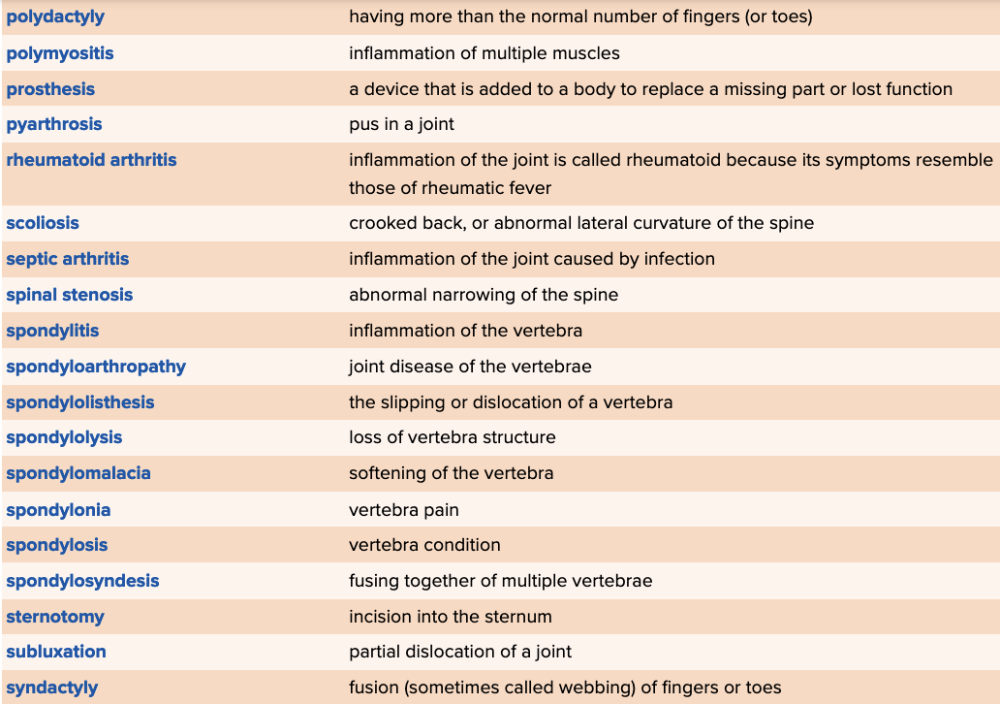 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
|
front 82  Chapter 4 Quick Reference
| back 82 no data |
front 83 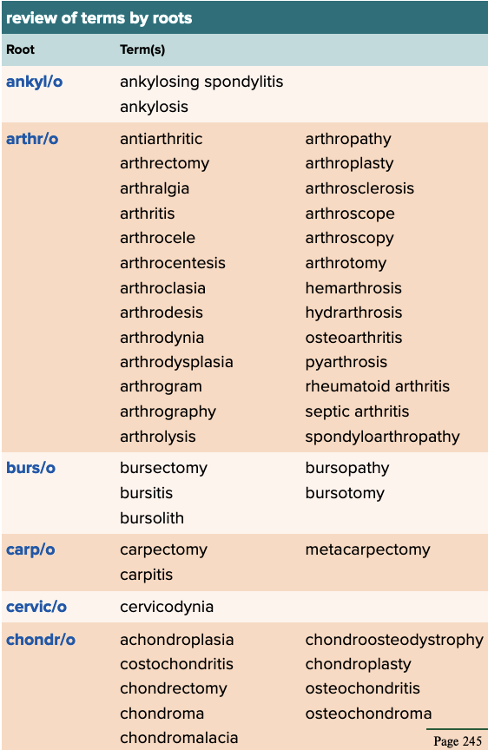 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
| back 83 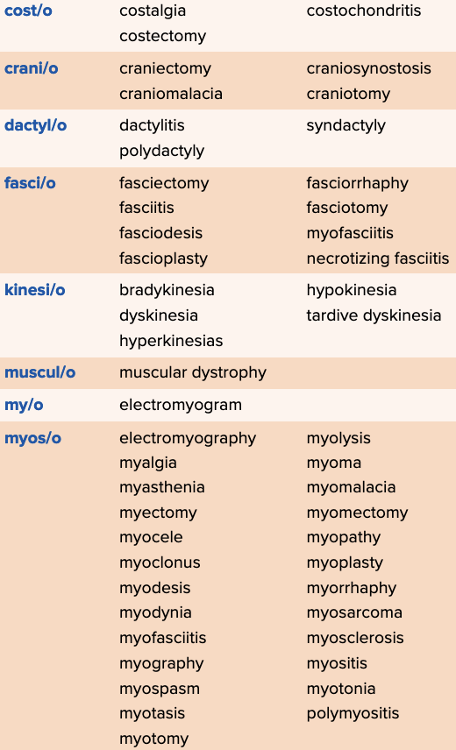 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
|
front 84 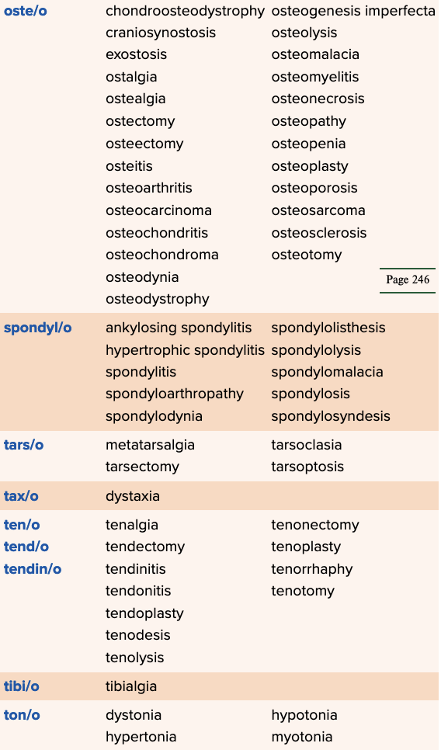 Chapter 4 Quick Reference
| back 84  Chapter 4 Quick Reference
|
front 85  Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 85 no data |
front 86  Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 3, 4. | back 86 no data |
front 87  Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 87 no data |
front 88  Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 88  |
front 89 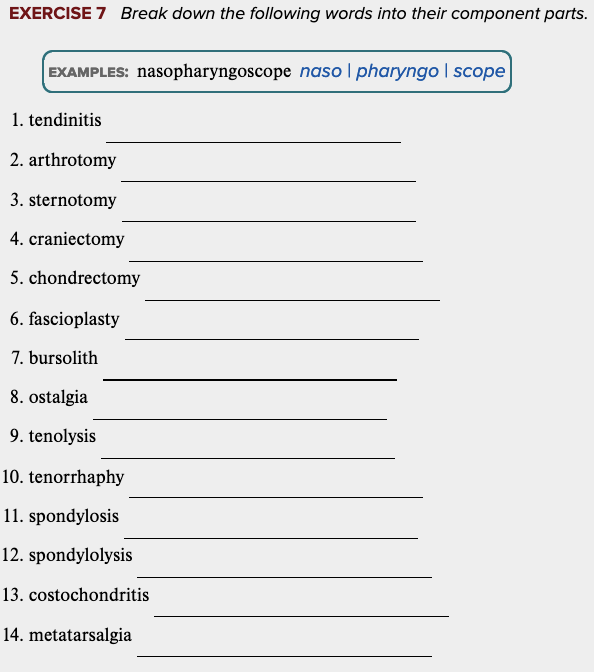 Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 89 no data |
front 90 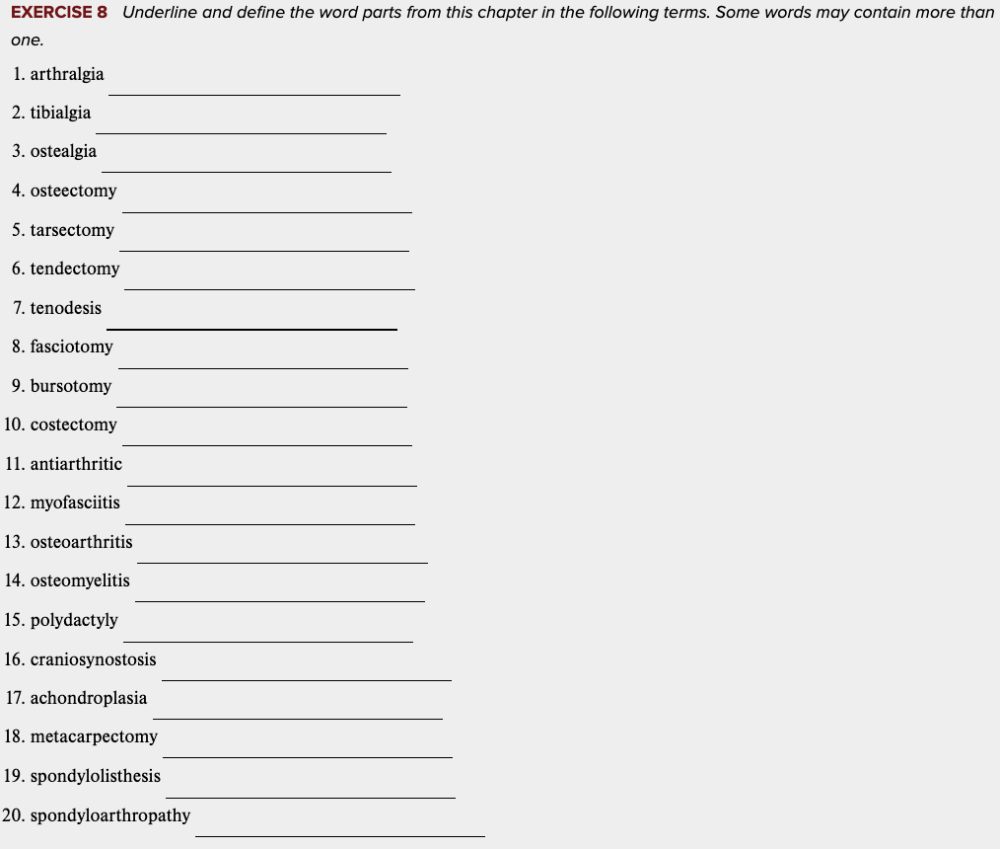 Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 90 no data |
front 91  Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 9. | back 91 no data |
front 92 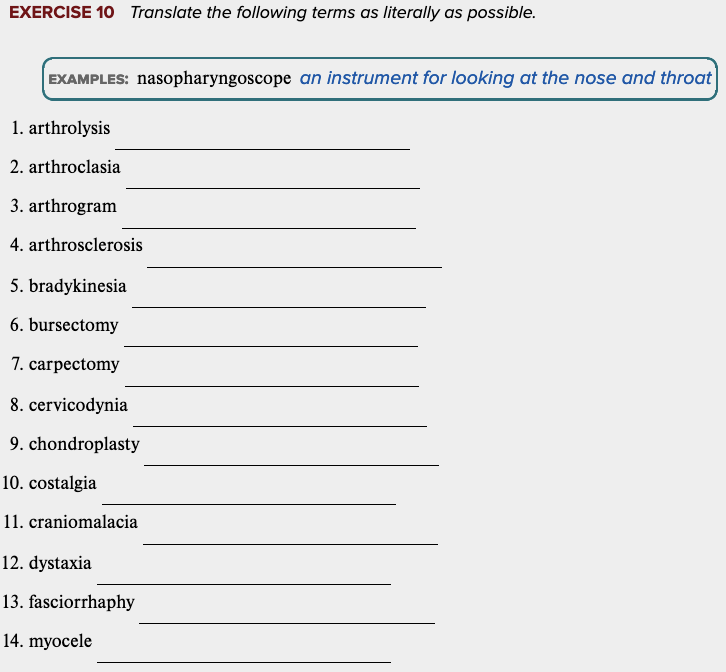 Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 10. | back 92  |
front 93  Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 11. | back 93 no data |
front 94  Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 12. | back 94 no data |
front 95  Chapter 4 Review Exercises: Exercise 13, 14. | back 95 no data |
front 96 The location of bone growth is known as the ______ plate. | back 96 epiphyseal |
front 97 The suffix -physis in the word epiphysis means Multiple choice question.
| back 97 growth. |
front 98 Spell the term for more than one vertebra ______. | back 98 Vertebrae |
front 99 Spell the term for the bones of your fingers ______. | back 99 phalanges |
front 100 As a full-grown adult, a human has ______ bones in the body. Multiple choice question.
| back 100 206 |
front 101 In the formation of bone, an initial model is made from ______ and replaced with bone. Multiple choice question.
| back 101 cartilage |
front 102 The area between the rib cage and pelvis is the Multiple choice question.
| back 102 lumbar area.lumbar area. |
front 103 ______ is the study of matter, energy, and motion. | back 103 Physics |
front 104 Which of the following is the root for arm? Multiple choice question.
| back 104 brachi/o |
front 105 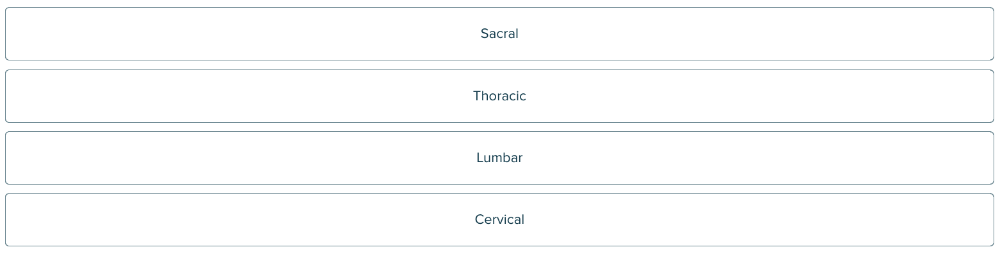 Click and drag on elements in order List, from top to bottom, the sections of the spine (vertebral column). | back 105 1. Cervical 2. Thoracic 3. Lumbar 4. Sacral |
front 106 Spell the term that means surgical removal of the wrist ______. | back 106 carpectomy |
front 107 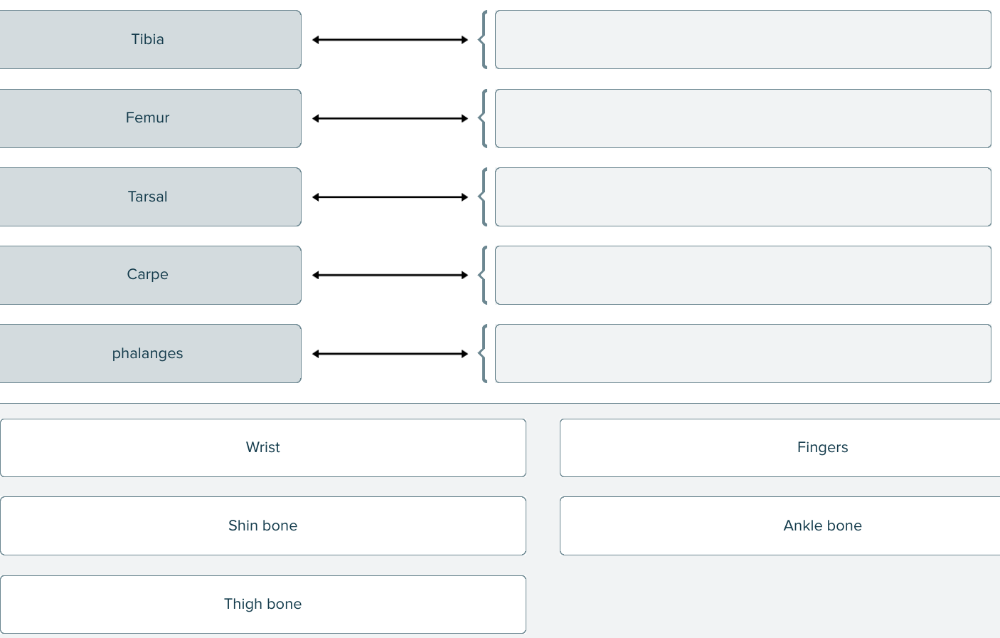 Match the term with its correct body part | back 107 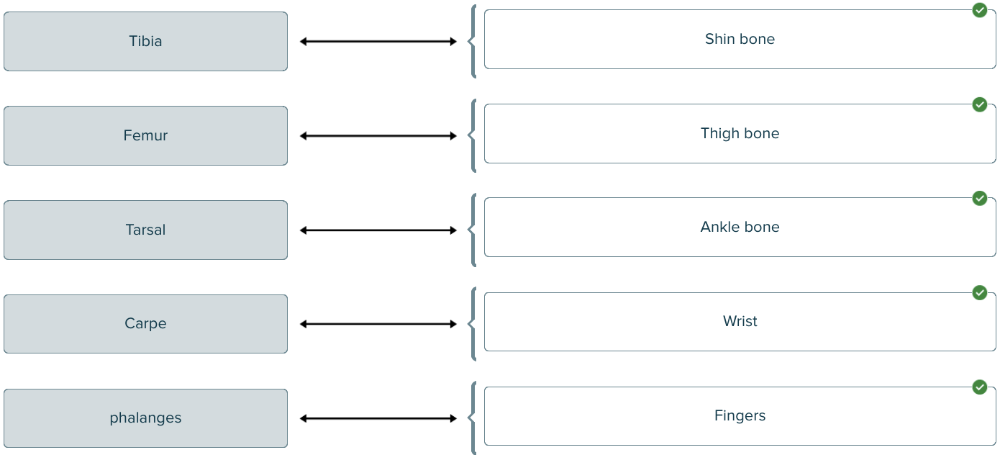 |
front 108 The intercostal muscles are muscles that connect the ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 108 ribs |
front 109 Which bone is present in an adult, but not in a newborn? Multiple choice question.
| back 109 Kneecap |
front 110 The term for shin bone is called ______. | back 110 tibia |
front 111 Spondylitis is inflammation of the ______. | back 111 Vertebrae |
front 112 Tarsalgia is a term describing pain in the Multiple choice question.
| back 112 ankle. |
front 113 Which of the following is the root for finger? Multiple choice question.
| back 113 dactyl/o |
front 114  Match each motion to the action described. | back 114 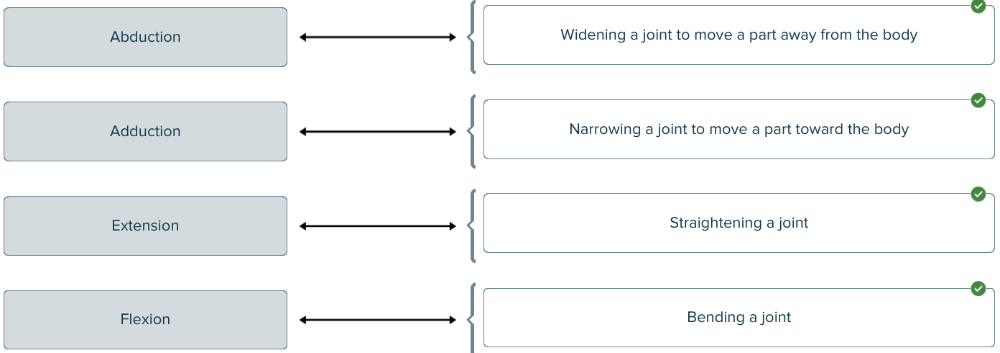 |
front 115 Repetitive motions cause the nerve to swell and can result in ______ in the hand, called carpal tunnel syndrome. | back 115 numbness |
front 116 The term for holding bone to bone at joints is ______. | back 116 ligaments or ligament |
front 117 Deconstruct the term costectomy by separating the root from the suffix with a hyphen. | back 117 cost-ectomy |
front 118 Select all that apply Which term(s) contain the root word that means cartilage? Multiple select question.
| back 118
|
front 119 Which of the following is the term for tibia? Multiple choice question.
| back 119 tibi/o |
front 120 Inflammation of a joint is called Multiple choice question.
| back 120 arthritis. Ex. bursitis - Reason: The bursa is near the joint but not the joint itself. The joint is where two or more bones come together. |
front 121 Tarsitis means inflammation of the ______. | back 121 ankle |
front 122 Select all that apply Bursa comes from the ______ word that means ______. Multiple select question.
| back 122
|
front 123 The term ______ is used to describe the widening of a joint to move parts away from the body, while the term ______ means the exact opposite; i.e. bringing parts toward the body. | back 123 Blank 1: abduction Blank 2: adduction |
front 124 Select all that apply Which of the following muscles belong to the trunk (chest and abdomen, not including shoulder and buttocks)? Multiple select question.
| back 124
|
front 125 Spell the term that defines the tissue holding a muscle to a bone ______. | back 125 tendon or tendons |
front 126 A band of connective tissue holding muscle to bone is called a Multiple choice question.
| back 126 tendon. |
front 127 Chondr/o is the root for the term ______. | back 127 Cartilage |
front 128 The plural form of fascia is Multiple choice question.
| back 128 fasciae. |
front 129 Spell the term that means inflammation of a joint ______. | back 129 arthritis |
front 130 Which of the following is the definition of the root tax/o? Multiple choice question.
| back 130 coordination |
front 131 Inflammation in a small fluid-filled sac near a joint (named after a purse) is called Multiple choice question.
| back 131 bursitis. |
front 132 The medical term for bowlegged is Multiple choice question.
| back 132 genu varum. |
front 133 Which of the following muscles belong to the lower extremity (buttocks, thigh, or leg)? Multiple choice question.
| back 133 Gastrocnemius |
front 134 Deconstruct the term that means vertebral pain by separating the root from the suffix with a hyphen. Enter hyphens in the appropriate blanks. ______ ______ ______. | back 134 Blank 1: spondylo Blank 2: - Blank 3: dynia |
front 135 Select all that apply Which of the following combining forms mean muscle? Multiple select question.
| back 135
|
front 136 Bands of connective tissue holding muscles together are called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 136 fascia |
front 137 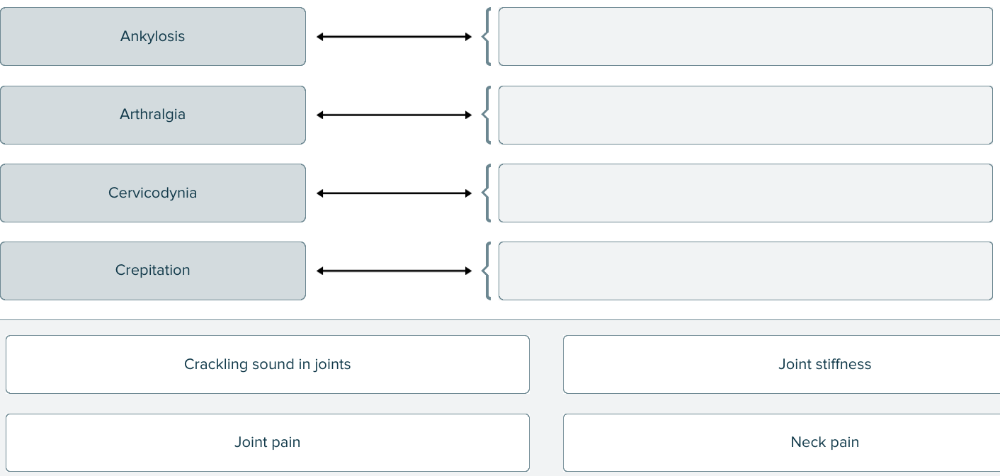 Match each medical term related to joints with its definition. | back 137 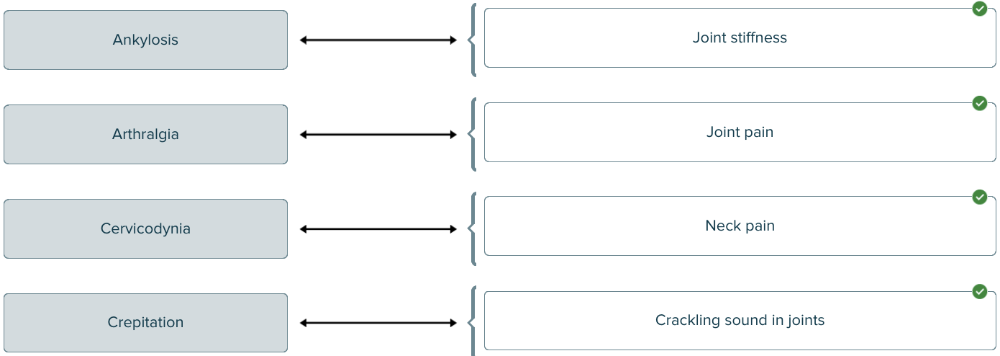 |
front 138 Hyper- is a prefix meaning over. Hyperkinesia means excess Multiple choice question.
| back 138 movement. |
front 139 The suffix -dynia in the word cervicodynia means ______. | back 139 pain |
front 140 The term ataxia indicates a problem with Multiple choice question.
| back 140 coordination. |
front 141 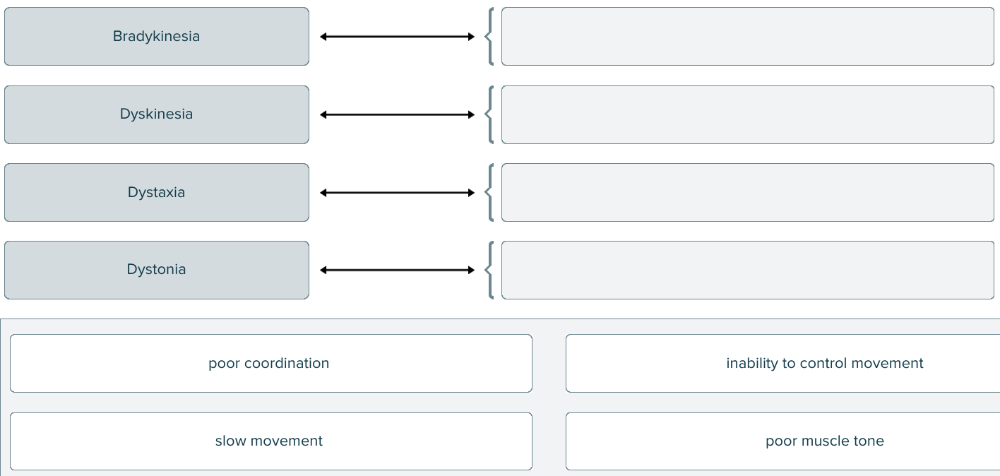 Match the terms associated with the muscle to the correct definitions. | back 141 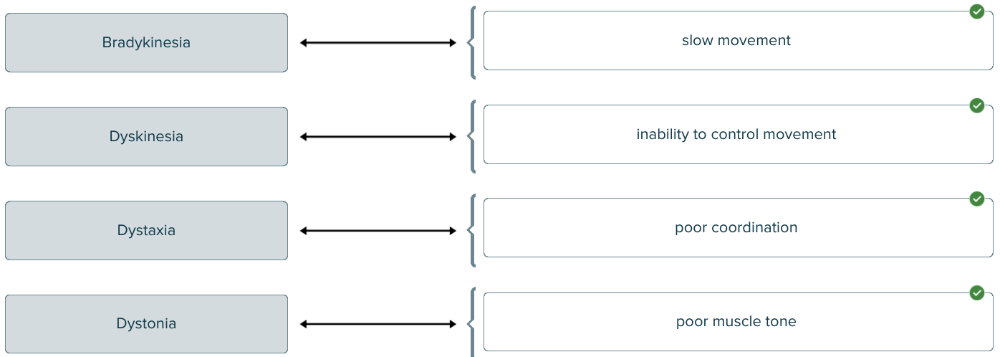 |
front 142 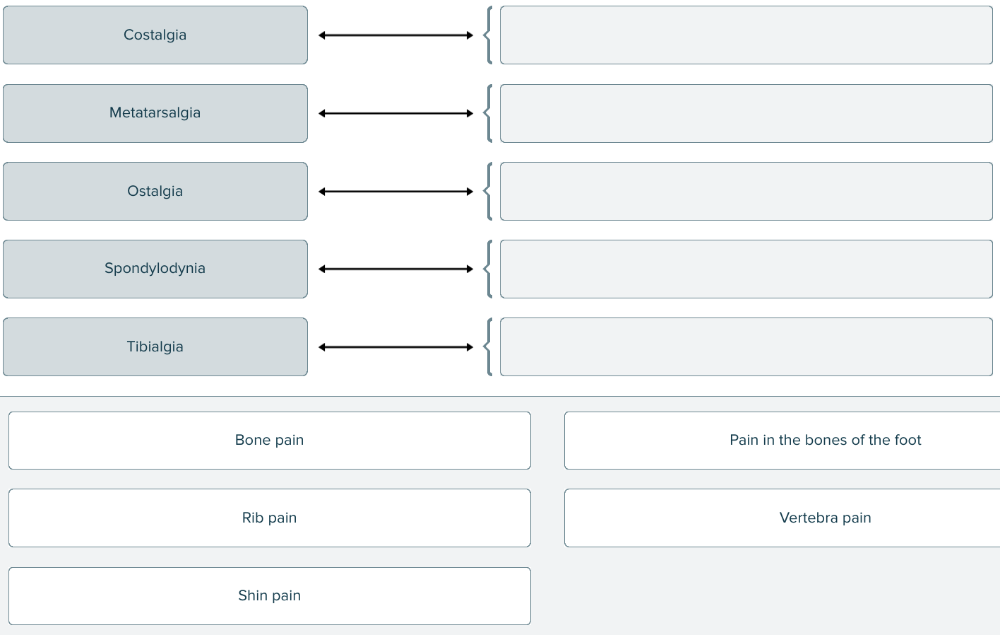 Match each medical term related to bones with its definition. | back 142 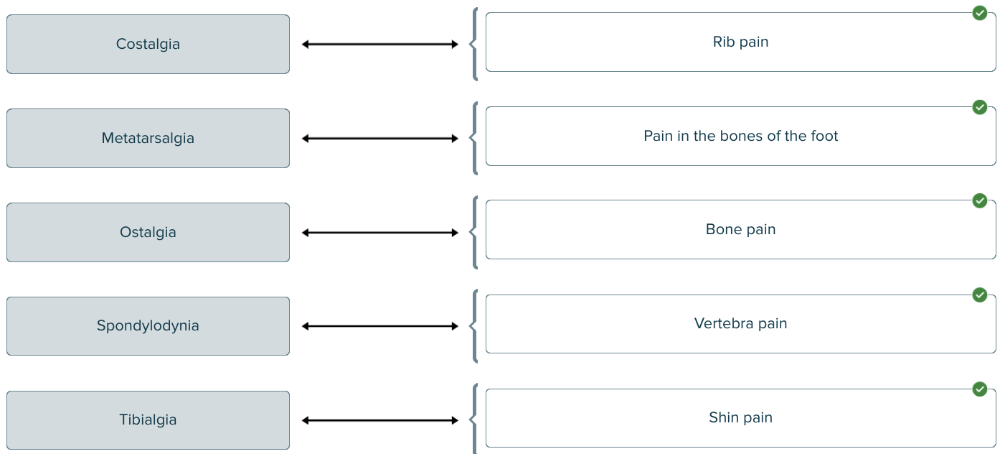 |
front 143 Spell the term that means increased muscle tone ______. | back 143 hypertonia |
front 144 A band of connective tissue holding muscle to bone is called a Multiple choice question.
| back 144 tendon. |
front 145 The medical term for pus in a joint is Multiple choice question.
| back 145 pyarthrosis. Ex. arthrocentesis. - Reason: Arthr/o means joint, but -centsis means the process of drawing off fluid with a needle. hemarthrosis. - Reason: Arthr/o means joint, but hem- means blood. |
front 146 Spell the term that means bone pain ______. | back 146 osteodynia, ostalgia, or ostealgia |
front 147  Match the medical term with the definition. | back 147 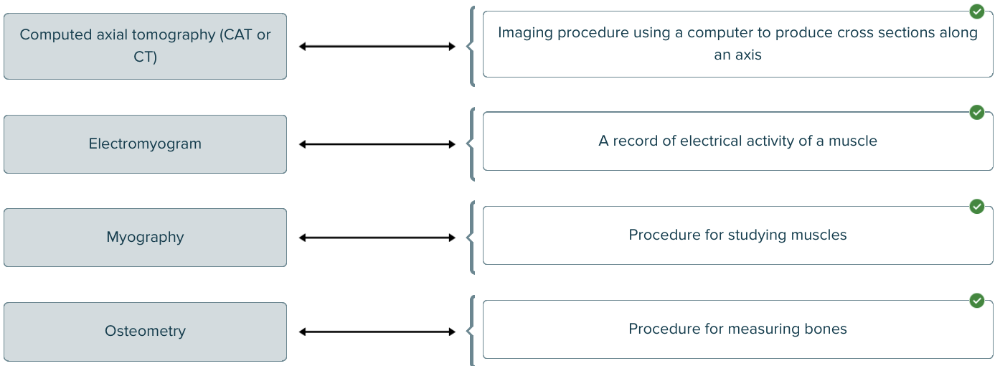 |
front 148  Match each medical term about joints with its definition. | back 148 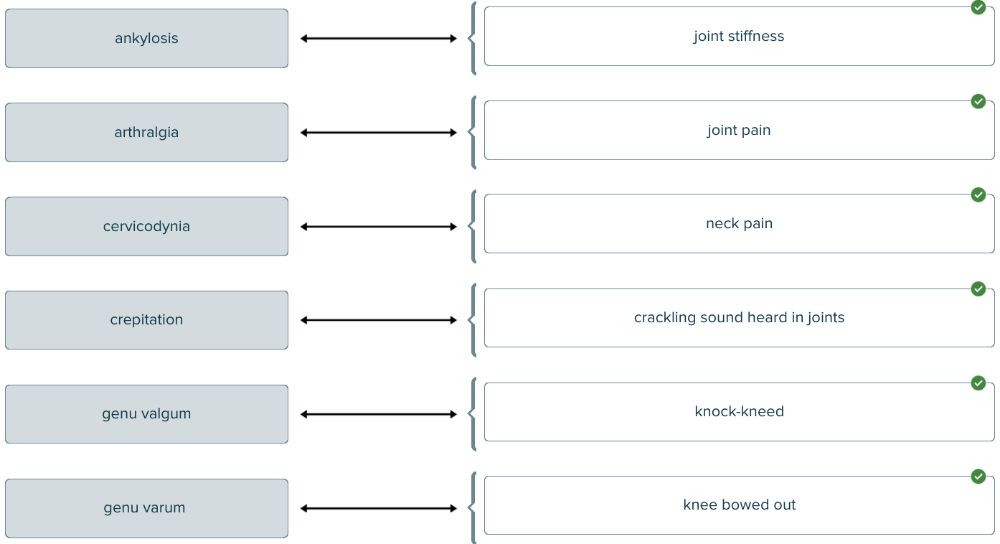 |
front 149 Puncture of a joint (for example, to retrieve a fluid sample for laboratory analysis) is called Multiple choice question.
| back 149 arthrocentesis. |
front 150  Match the terms related to muscles to their definitions. | back 150 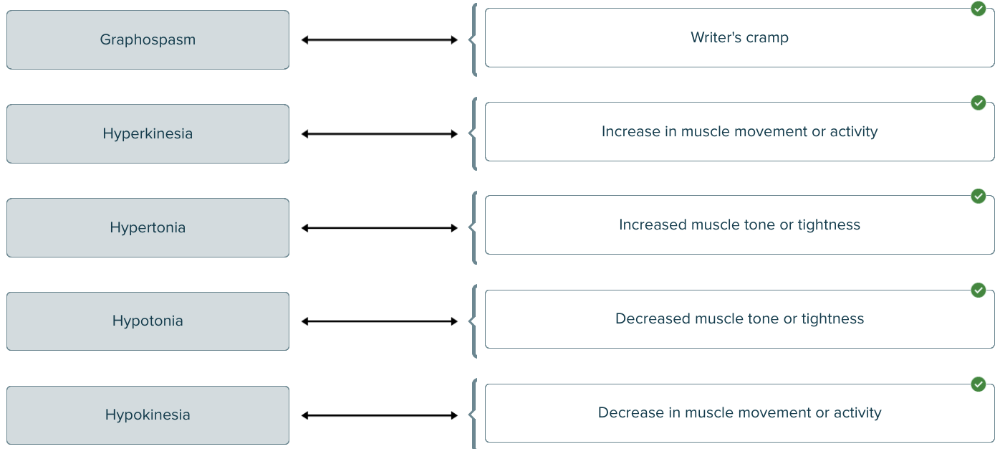 |
front 151 Spell the term that means a sway back or abnormal forward curvature of the lower spine ______. | back 151 lordosis |
front 152 Slow movement is defined by the term ______. | back 152 bradykinesia |
front 153 A drooping condition of the ankle is Multiple choice question.
| back 153 tarsoptosis. |
front 154 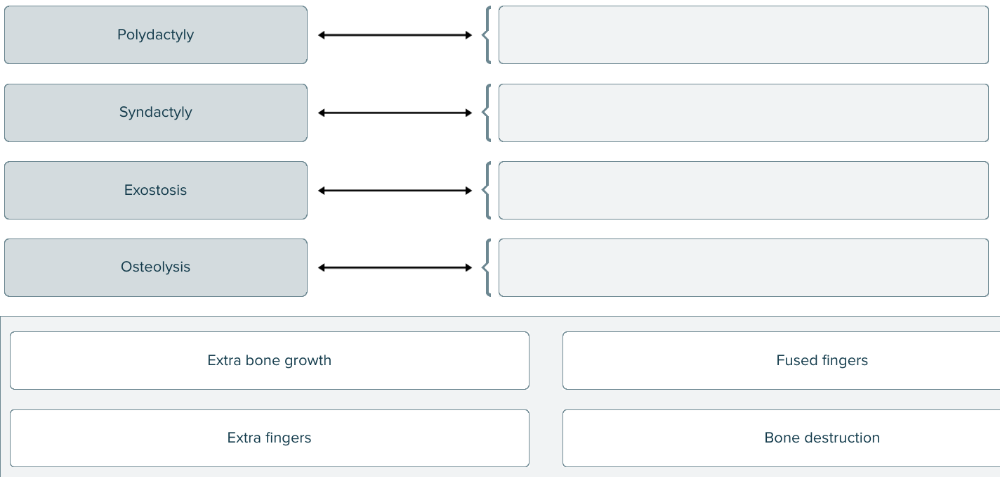 Match the following musculoskeletal terms to the correct definitions. | back 154 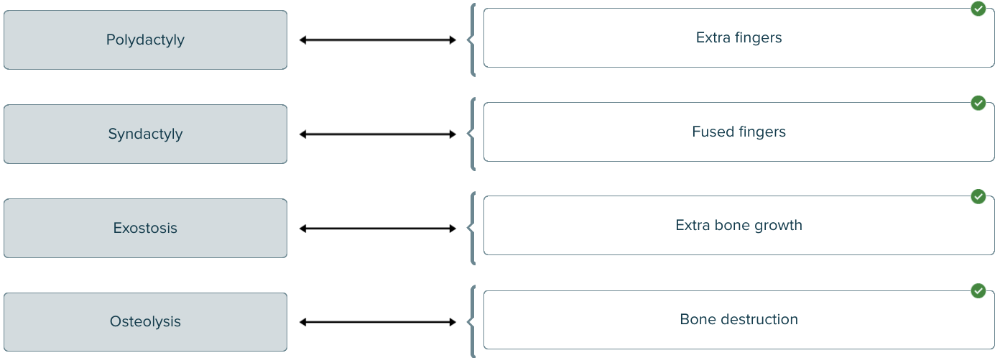 |
front 155 Spell the term that means abnormal hardening of bone ______. | back 155 osteosclerosis |
front 156 A visual record of a joint is termed a(n) ______. | back 156 arthrogram |
front 157  Match each medical term with the definition. | back 157 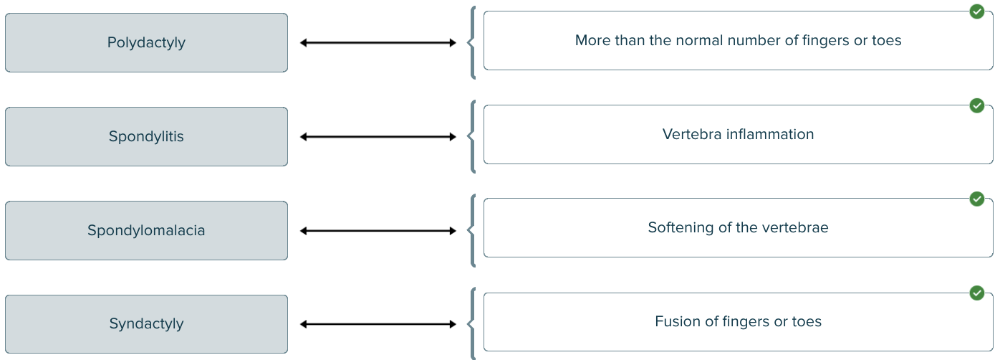 |
front 158 Which of the following is used as an instrument for looking into a joint? Multiple choice question.
| back 158 Arthroscope |
front 159 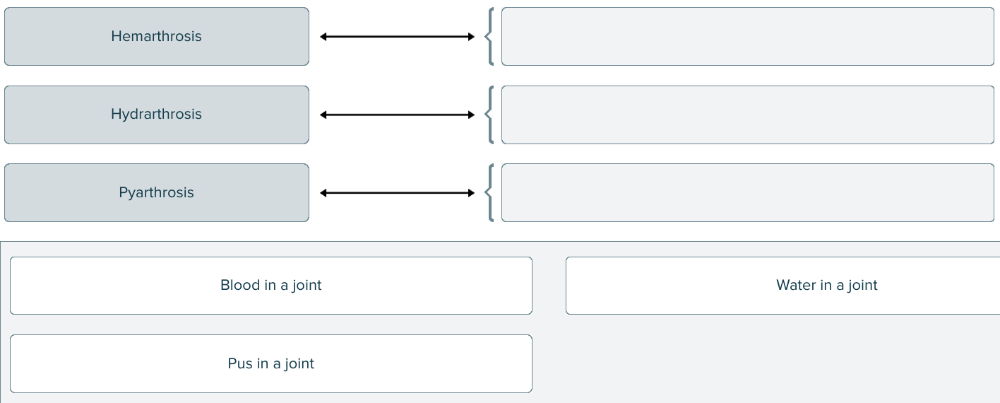 Match each medical term with the material found in a joint. | back 159 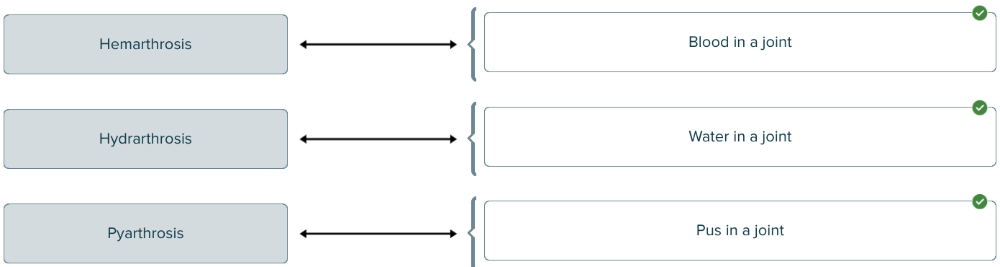 |
front 160 A humped back or abnormal forward curvature of the upper spine is called Multiple choice question.
| back 160 kyphosis. |
front 161 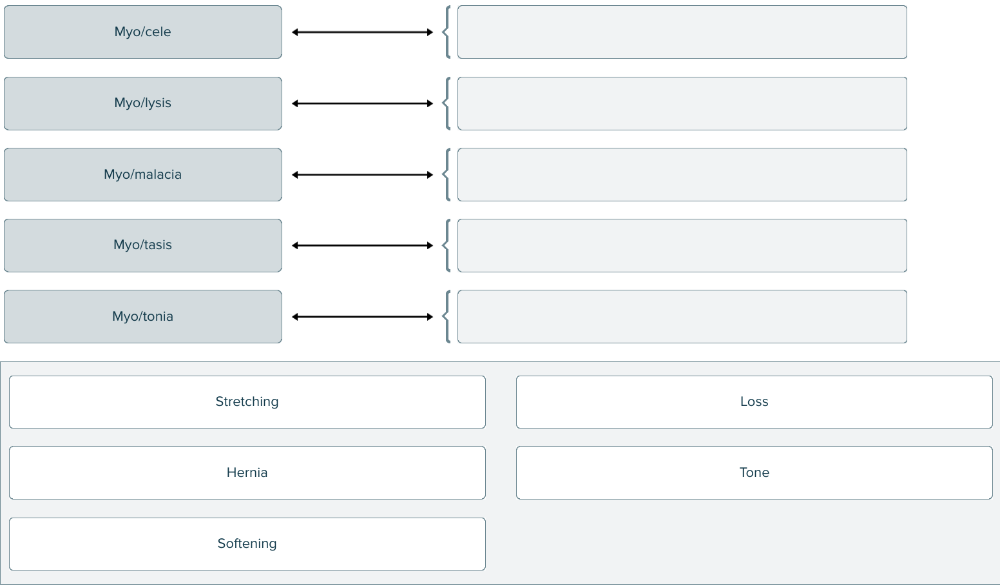 Match each combining form of my/o and suffix with the correct meaning as it relates to muscle. | back 161 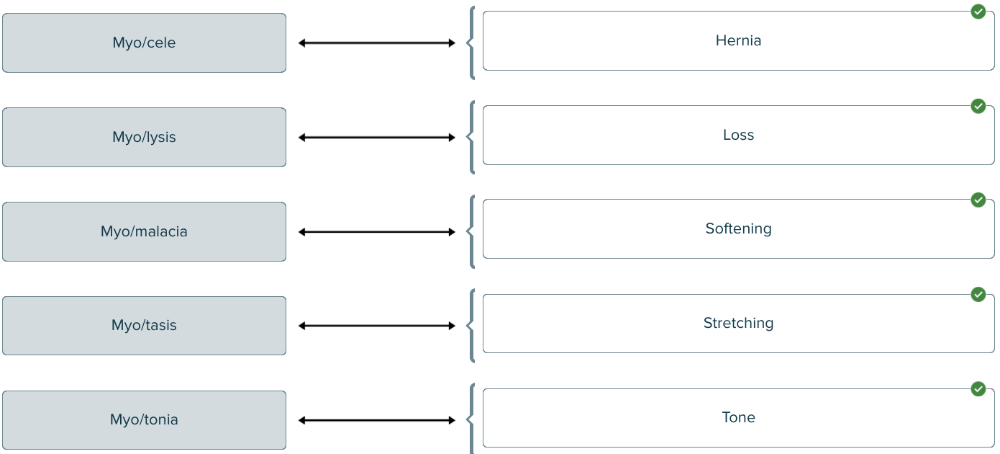 |
front 162 The medical term for fusion of the fingers or toes is Multiple choice question.
| back 162 syndactyly. |
front 163 Overdevelopment of muscle tissue is termed ______. | back 163 hypertrophy |
front 164 Match each medical term related to bones with its definition. | back 164 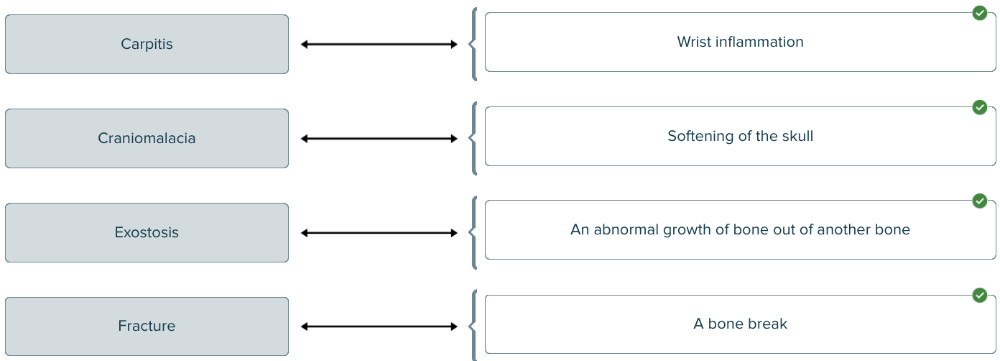 |
front 165 Poor development of bones and cartilage is termed ______. | back 165 chondrosteodystrophy |
front 166 The suffix -ptosis means a drooping condition. Tarsoptosis is the medical word for Multiple choice question.
| back 166 flat feet. |
front 167 When the spinal canal narrows abnormally, the condition is called Multiple choice question.
| back 167 spinal stenosis. |
front 168 The medical term for a stone in a small fluid-filled sac found near a joint is Multiple choice question.
| back 168 bursolith. |
front 169 The term osteochondroma means Multiple choice question.
| back 169 bone and cartilage tumor. |
front 170 Sclerosis can be used as a root or as a suffix meaning hardening condition. Myosclerosis is a condition of hardening of a Multiple choice question.
| back 170 muscle. |
front 171 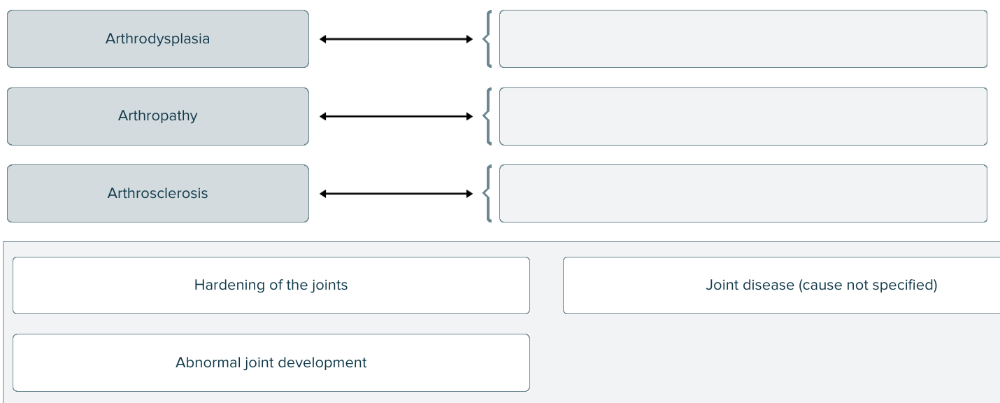 Arthro- is a root or prefix meaning joint. Match each disease of the joints with its definition. | back 171 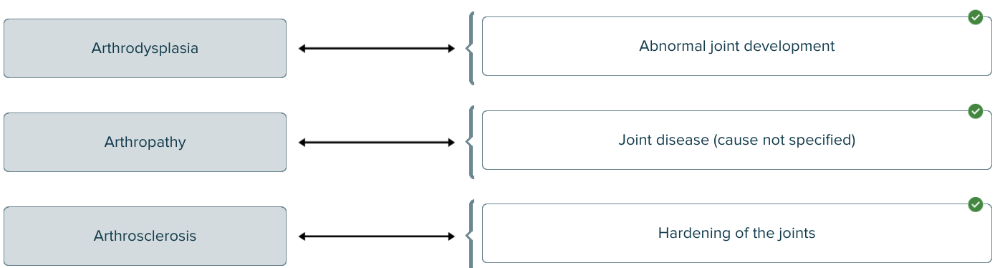 |
front 172 Which of the following terms means loss of muscle tissue? Multiple choice question.
| back 172 no data |
front 173 The suffix -trophy in the word hypertrophy means Multiple choice question.
| back 173 nourishment. |
front 174 When a joint herniates, it is called a(n) Multiple choice question.
| back 174 arthrocele. |
front 175 Spell the term than indicates the condition where the bones of the skull are fused together ______. | back 175 craniosynostosis |
front 176 Select the definition for the term Myopathy. Multiple choice question.
| back 176 Muscle Disease |
front 177 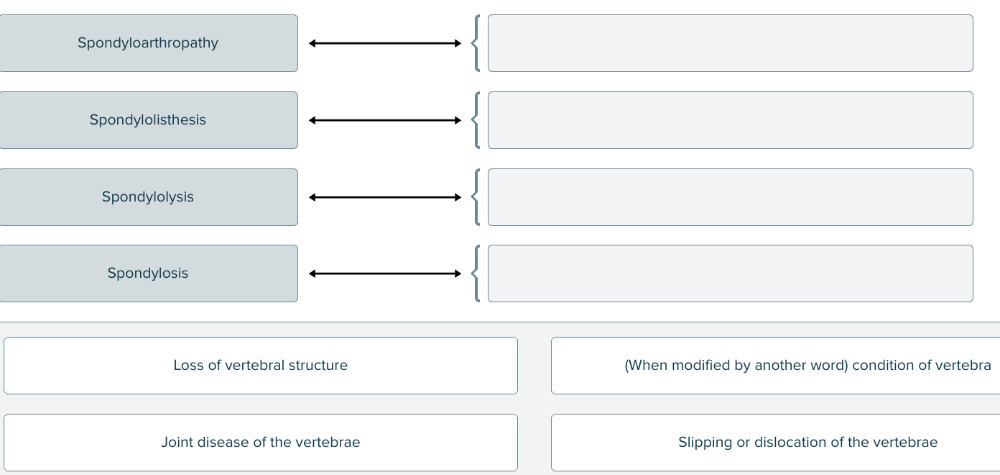 Spondylo- is a root that means vertebra. Match each medical term with its definition. | back 177 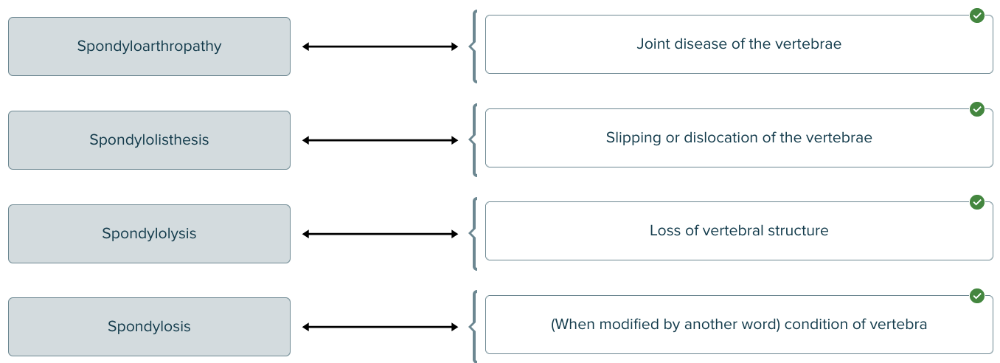 |
front 178 In tendinitis, the suffix -itis means Multiple choice question.
| back 178 inflammation. |
front 179 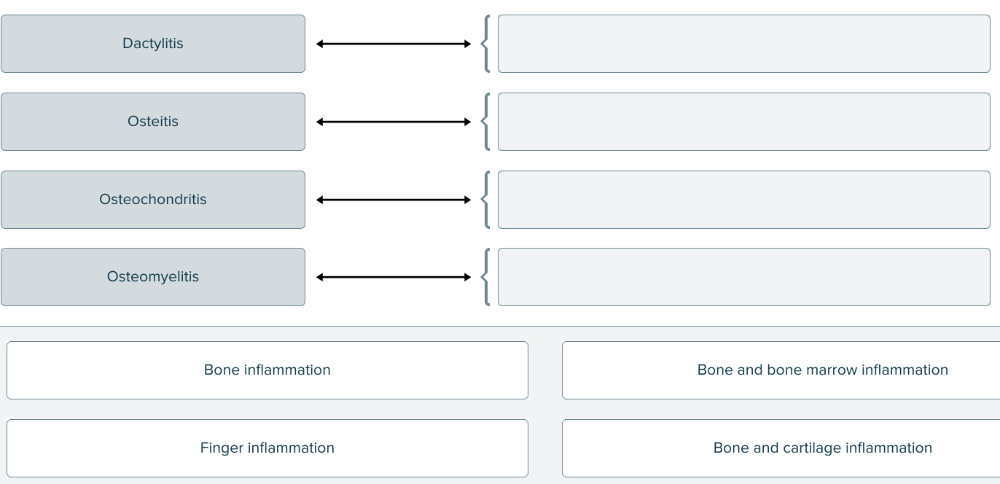 The suffix -itis means inflammation. Match each medical term with the location of inflammation. | back 179 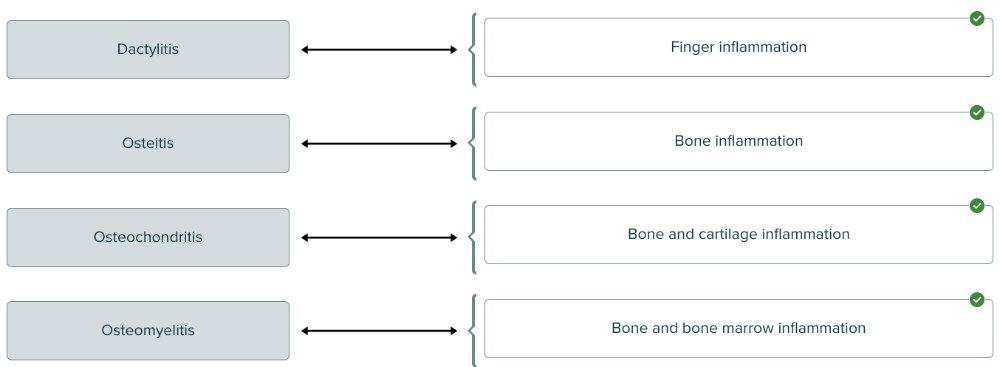 |
front 180 Which of the following is the term for a muscle tumor? Multiple choice question.
| back 180 Myoma |
front 181 The term arthritis means inflammation of a joint. Spell the term that means inflammation of joints, but specifically those that bear weight ______. (Hint: a root for "bone" is in the word.) | back 181 osteoarthritis |
front 182 A drug that opposes fever is called an Multiple choice question.
| back 182 antipyretic. Ex.
Reason: Analgesics oppose the pain associated with fever but not (necessarily) the fever itself.
Reason: Anti-inflammatories oppose all four signs of inflammation but not fever specifically. |
front 183 Spell the term for abnormal joint development ______. | back 183 arthrodysplasia (arthro= joint / dys= bad / plasia=formation) |
front 184 Spell the term that means surgical excision of part of the skull ______. | back 184 craniectomy |
front 185 Which of the following terms means violent muscle contractions? Multiple choice question.
| back 185 Myoclonus |
front 186 Returning broken or displaced bones to their proper position through the use of surgery is called ______ reduction. | back 186 open |
front 187 Select all that apply Choose the correct spelling of the term that means inflammation of the tendon. Multiple select question.
| back 187
|
front 188 The use of screws, pins, and plates to hold a fractured bone in place from the inside is called Multiple choice question.
| back 188 internal fixation. |
front 189 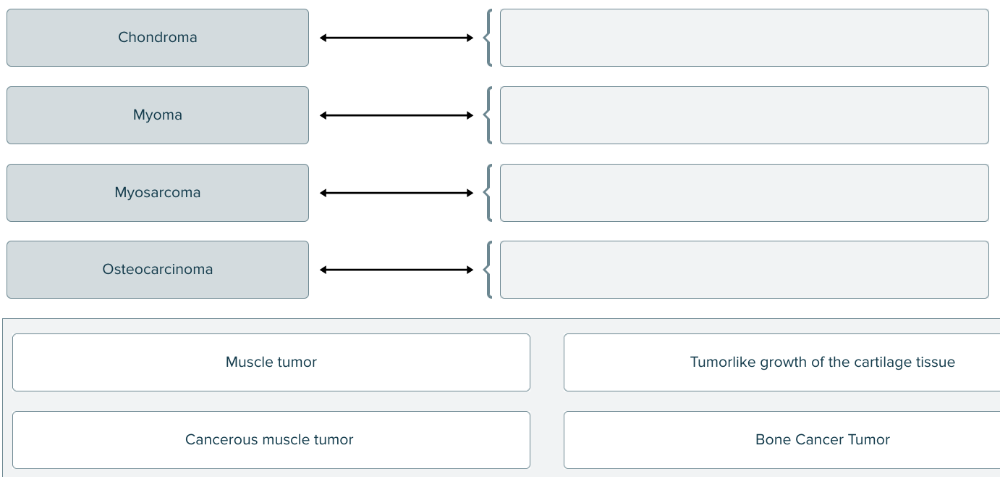 Match the oncology term to the correct definition. | back 189 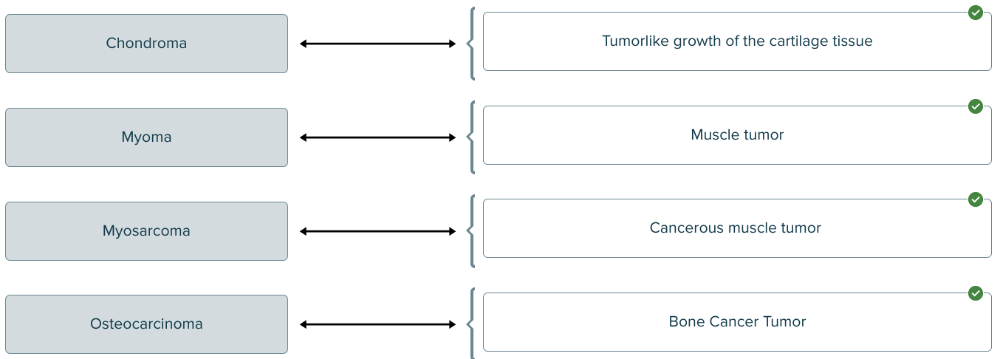 |
front 190 To correct clubfoot, often surgical fracture of the ankle bone is required. This procedure is called ______. | back 190 tarsoclasia |
front 191 A drug that opposes inflammation throughout the body is called an: Multiple choice question.
| back 191 anti-inflammatory Ex.
Reason: Fever is only one aspect of inflammation.
Reason: Anti-arthritics are specific to joint inflammation. |
front 192 The term arthrolysis means Multiple choice question.
| back 192 loosening a stiff joint. |
front 193 The difference between a craniotomy and a craniectomy is that in a craniotomy, the piece of skull is Multiple choice question.
| back 193 replaced after it is removed. |
front 194 The meaning of the root in the word myectomy is ______. | back 194 muscle (root= my-) |
front 195 Which of the following is the procedure for removing a rib? Multiple choice question.
| back 195 Costectomy |
front 196 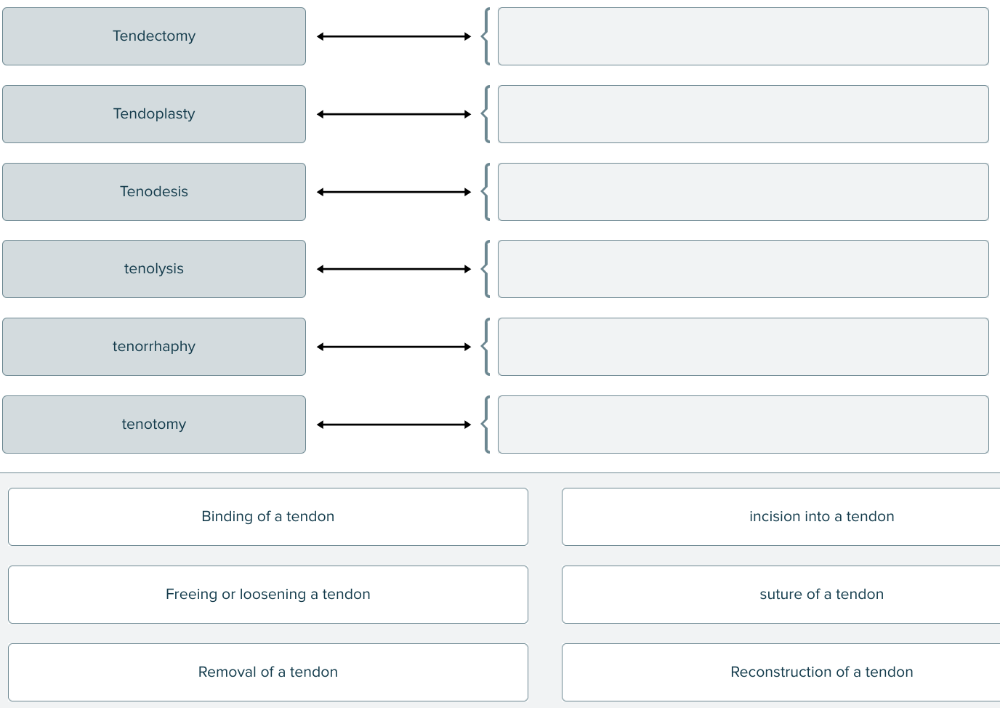 Match each medical term for tendon treatment or therapy with its description. | back 196 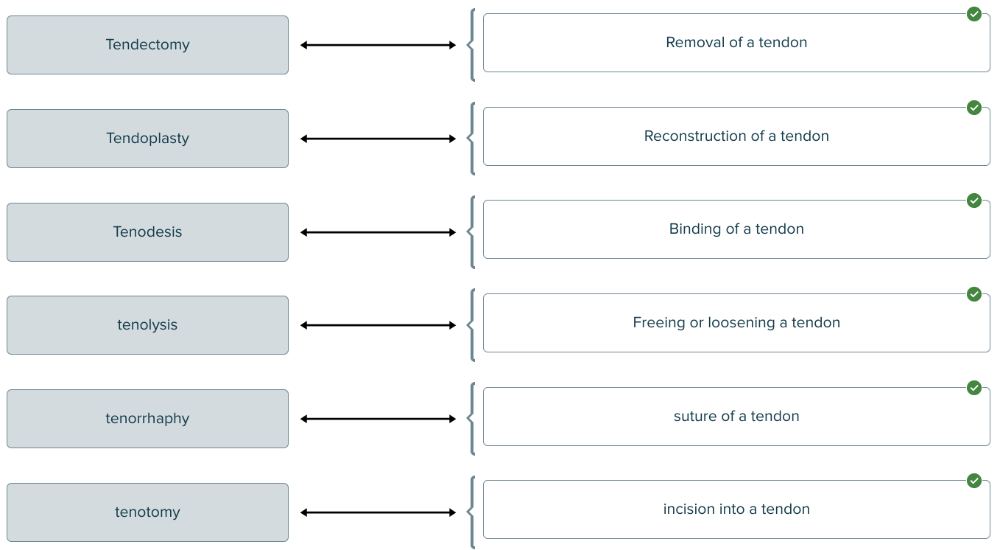 |
front 197 The use of casts, splints, and stabilizers to hold a fractured bone in place from the outside is termed ______ fixation. | back 197 external |
front 198 The abbreviation LCL stands for lateral collateral ligament (of the knee). The abbreviation MCL stands for: Multiple choice question.
| back 198 medial collateral ligament |
front 199 Select all that apply Identify the terms that mean removal of a bone. Multiple select question.
| back 199
|
front 200 In the abbreviation T12, the letter represents Multiple choice question.
| back 200 thoracic. |
front 201 An incision into a joint is termed ______. | back 201 arthrotomy |
front 202 The abbreviation ORIF stands for Multiple choice question.
| back 202 open reduction internal fixation. |
front 203 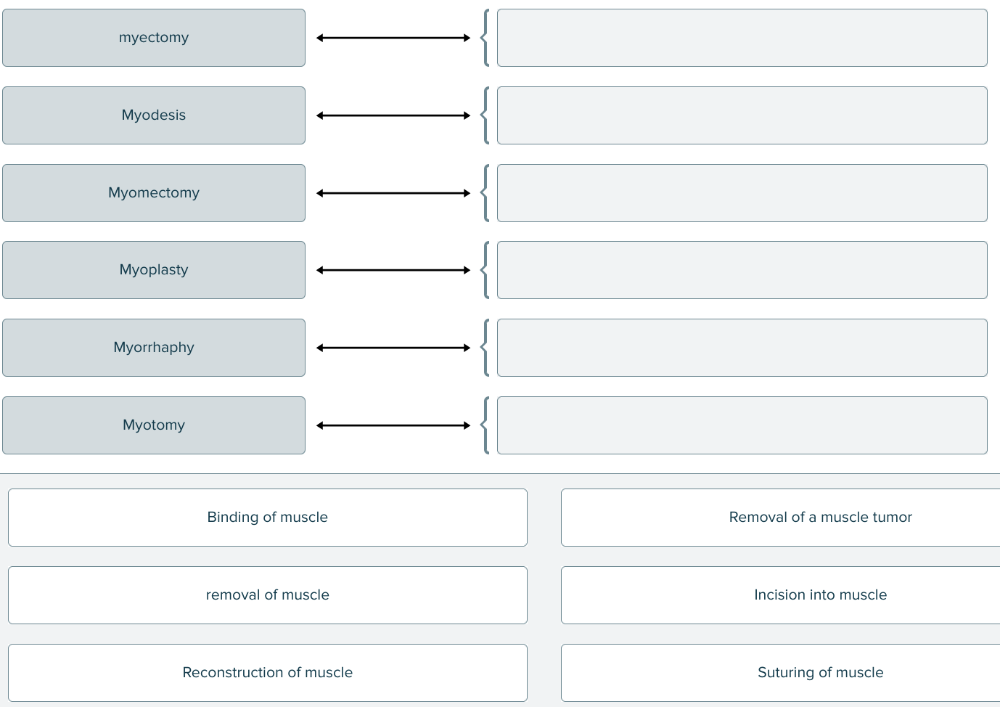 Match each term for treatments and therapies of muscle with its description. | back 203 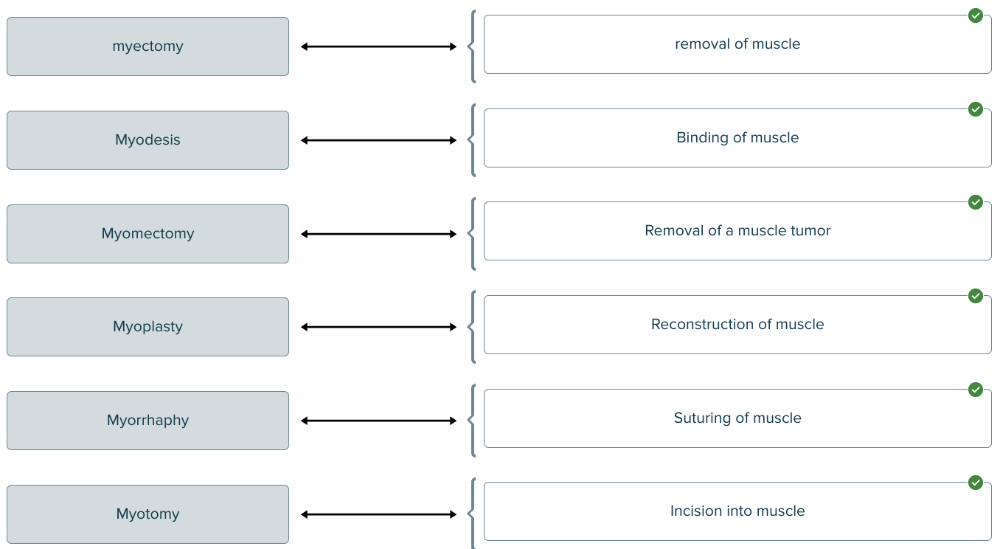 |
front 204 Select all that apply Identify the terms for removal of a tendon. Multiple select question.
| back 204
|
front 205 In the abbreviations ACL and PCL used for the knee joint, the letter C stands for ______. | back 205 cruciate Ex. ACL - anterior cruciate ligament PCL - posterior cruciate ligament |
front 206 Click and drag on elements in order Place the abbreviations in the proper order, starting with the superior (topmost) set. | back 206 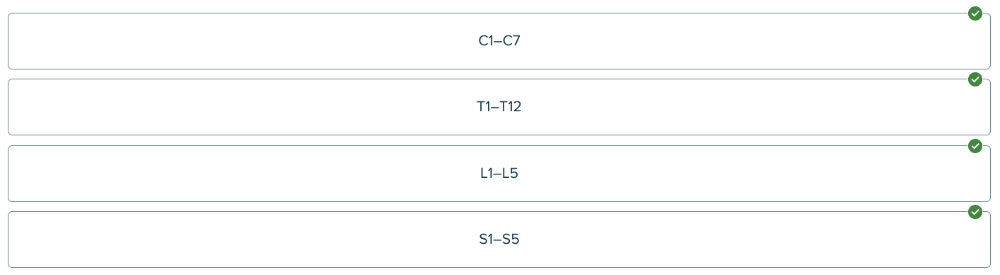 Ex. C - cervical (of the neck) vertebrae T - thoracic (of the chest) vertebrae |
front 207 The acronym RICE stands for Multiple choice question.
| back 207 rest, ice, compression, elevation. |