Lab Exercises: 7-11
Microbes that require oxygen to grow but at much lower levels than 20%
Microaerophile
Microbes that can only grow when oxygen is not present
Obligate anaerobe
Microbes that can only grow when oxygen is present
Obligate aerobe
Microbes that can grow in oxygen but do not require oxygen for energy metabolism
Aerotolerant anaerobe
Microbes that are flexible and can grow with or without oxygen
Facultative anaerobe
Which bacteria have optimal growth between -5 to 15°C?
Psychrophile
Which bacteria have optimal growth between 45° to 75°C?
Thermophile
Which bacteria have optimal growth between 25° to 45°C?
Mesophile
Which bacteria have optimal growth above 75°C?
Hyperthermophile
A bacterium that grows at a pH of 10
Alkaliphile
A bacterium that grows at a pH of 4
Acidophile
A bacterium that grows at a pH of 7
Neutrophile
These microbes can grow in excessive sugar concentrations
Osmophile
These microbes require a high concentration of sodium chloride in order to grow
Obligate halophile
These microbes can grow in moderate concentration of sodium chloride
Halotolerant
A cell that has more solutes than the surrounding environment is
Hypertonic
A cell that has fewer solutes than the surrounding environment is
Hypotonic
Water flows (into/out of) a cell that is hypotonic
Out of
Water flows (into/out of) a cell that is hypertonic
Into
When the temperature increases past the optimal, the hydrogen bonding in the RNA breaks down and the proteins denature in this structure
Ribsosome
When the temperature increases past the optimal, lipids can be destroyed affecting which structure?
Cell membrane
Which temperature results in white colonies of Serratia?
37°C
When the temperature decreases past the optimal, lipids can freeze affecting which strcuture?
Cell membrane
When the temperature decreases past the optimal, the activity of this molecule will slow down
Enzyme
When the temperature increases past the optimal, these denature
Enzyme
Which temperature results in pinkish/red colonies of Serratia?
25°C
Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does Serratia grow best at?
37°C
Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does E. coli grow best at?
37°C
Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does GST grow best at?
55°C
Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does Serratia grow the worst at?
55°C
Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature, which temperature does E. coli grow the worst at?
55°C
Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does GST grow the worst at?
37°C
Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does E. coli grow best at?
7
Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does S. epidermidis grow best at?
5
Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does does A. faecalis grow best at?
7
Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does E. coli grow the worst at?
3
Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does S. epidermidis grow the worst at?
3
Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does A. faecalis grow the worst at?
3
Antivirals are compounds that kill or inhibit
Viruses
Antifungals are compounds that kill or inhibit
Fungi
Antibiotics are compounds that kill or inhibit
Bacteria
Antiparasitics are compounds that kill or inhibit
Animals
Chemical agents that are applied to inanimate objects to kill microbes are
Disinfectants
Substances that kill or inhibit microorganisms but are gentle enough to apply to tissue are
Antiseptics
What antibiotics target the cell wall of bacteria?
- Penicillin
- Ampicillin
- Bacitracin
Which antibiotics target the DNA and RNA synthesis of bacteria?
- Fluoroquinolones
- Rifamycins
Which antibiotics target the protein synthesis of bacteria?
- Chloramphenicol
- Streptomycin
- Tetracycline
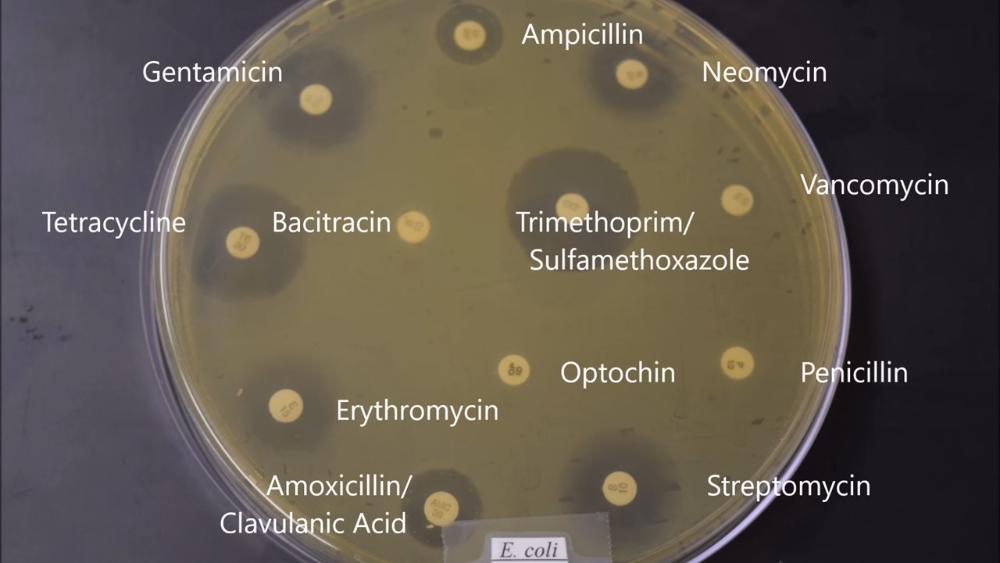
Which antibiotic is E. coli completely resistant to?
- Bacitracin
- Nasitracon
- Optochin
- Penicillin
- Vancomycin
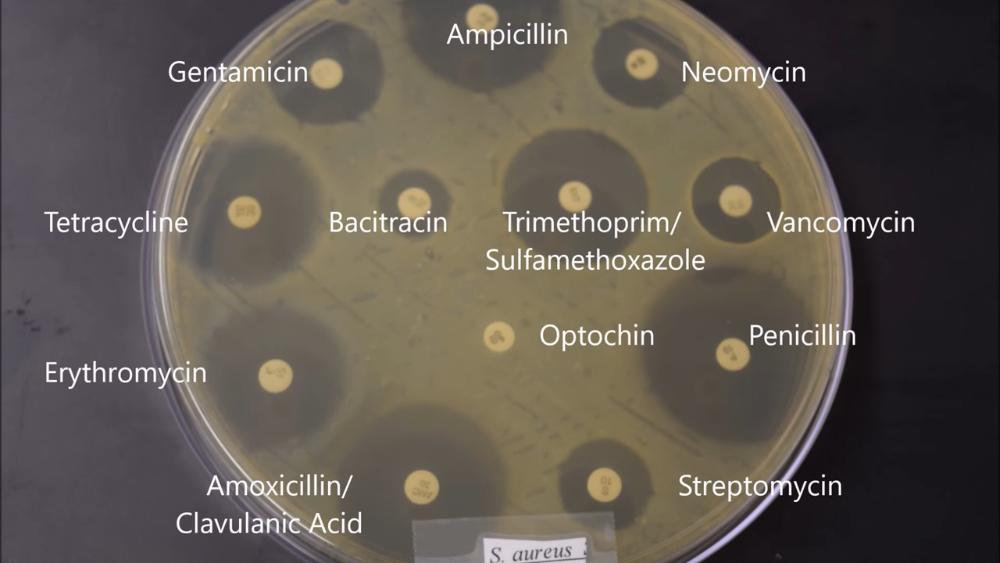
Which antibiotic is S. aureus completely resistant to?
Optochin

Indicate five antibiotics that E. coli is highly susceptible to.
- Streptomycin
- Gentamycin
- Erythomycin
- Trimethoprim
- Tetracycline

Indicate four antibiotics that S. aureus is mildly resistant to.
- Streptomycin
- Neomycin
- Vancomycin
- Bacitracin
Which antibiotic would you not use to treat an infection of E. coli or S. aureus
Optochin
Which two antibiotics would be better to treat both E. coli and S. aureus infections?
- Trimethoprim
- Tetracycline
Fermentation is a form of energy metabolism where the final electron acceptor is
Organic
Anaerobic respiration is a form of energy metabolism where the final electron acceptor is
Inorganic
Aerobic respiration is a form of energy metabolism where the final electron acceptor is
Oxygen
Which molecule is hydrolyzed by proteases?
Casein
Which molecule is hydrolyzed by amylase?
Starch
Which molecule is hydrolyzed by lipases?
Fat
Which molecule is deaminated into phenylpyruvic acid and ammonia?
Phenylalanine
Which molecule is degraded in indole, ammonia, and pyruvic acid?
Tryptophan
Which molecule splits in carbon dioxide and ammonia when it's hydrolyzed?
Urea
The mixed acid fermentation test uses which reagent to indicate a positive reaction?
Urea
Which enzyme is tested for with hydrogen peroxide?
Catalase
The 2,3-butanediol fermentation test uses which reagent to indicate a positive reaction?
Barritt
Which enzyme is tested for in an oxidation test?
Oxidase
Name one of the tests that must be completed under anaerobic conditions in the API20E.
LDC
Name one of the tests that examines carbon utilization in the API20E.
MAN
Name one of the tests that examines nitrogen utilization in the API20E.
URE
Name one of the tests that examines protein utilization in the API20E.
IND
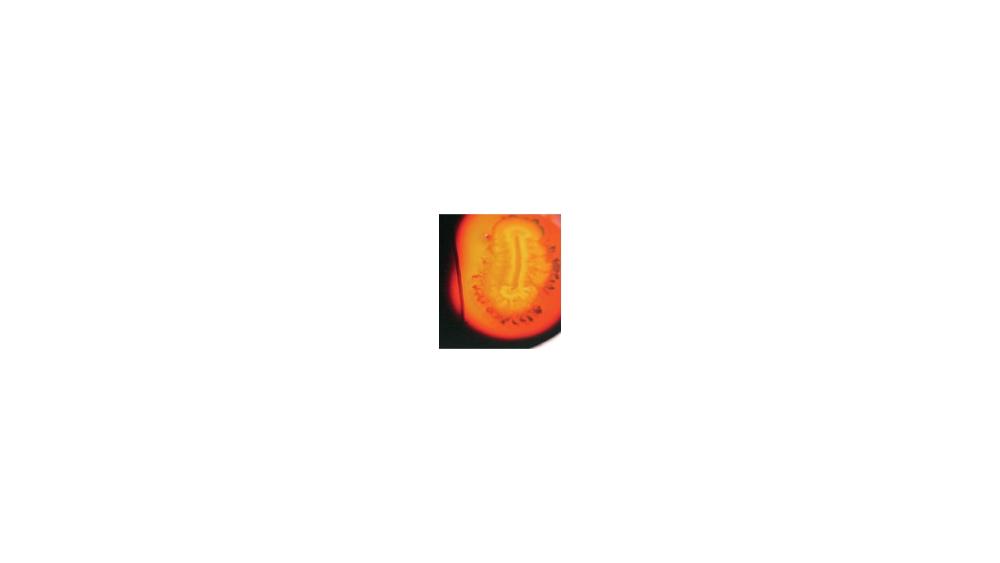

For the starch hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response.
Positive

For the starch hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response.
Negative
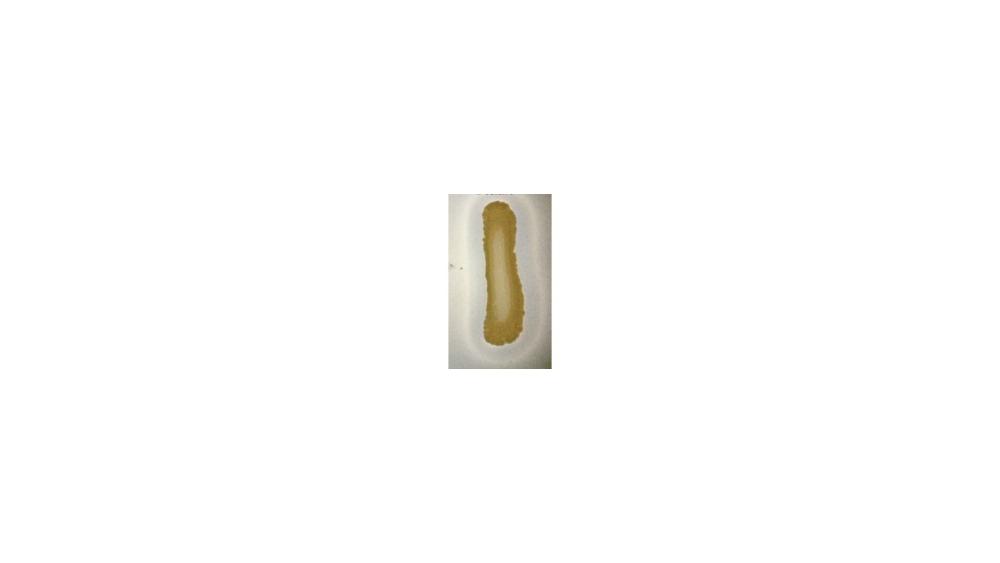

For the casein hydrolysis test, the image shoes a ____ response.
Positive
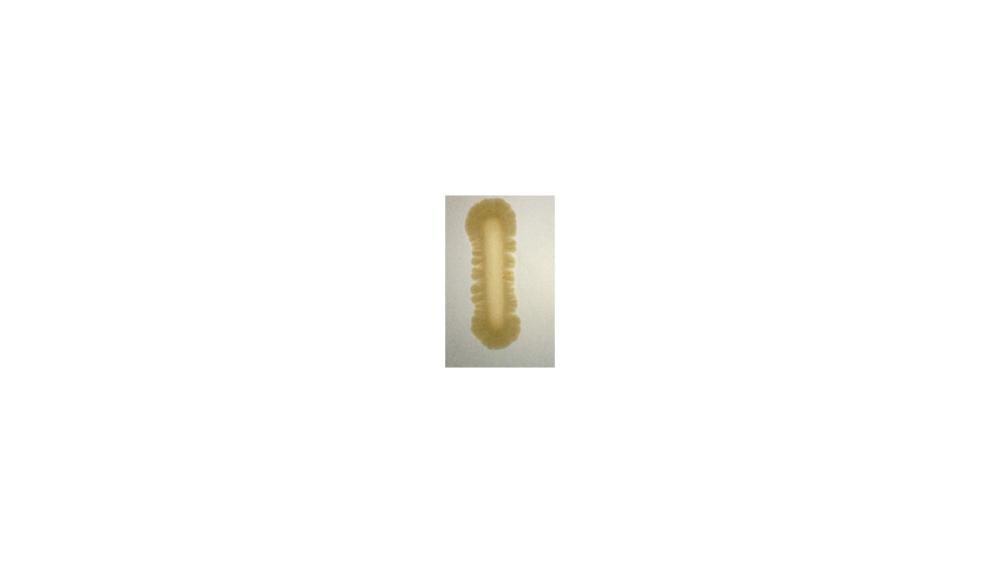
For the casein hydrolysis test, the image shoes a ____ response.
Negative

For the fat hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response.
Negative
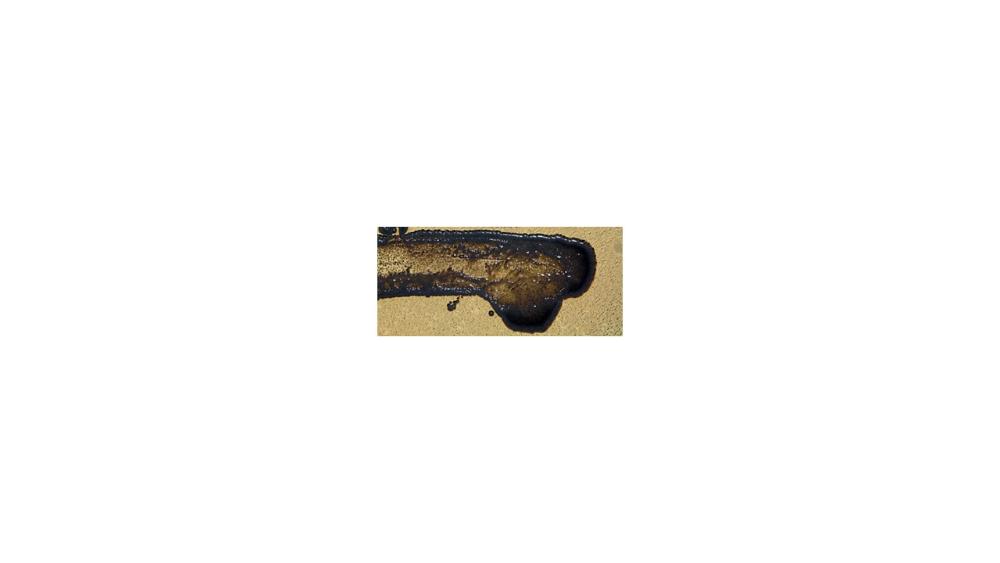

For the fat hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response.
Positive
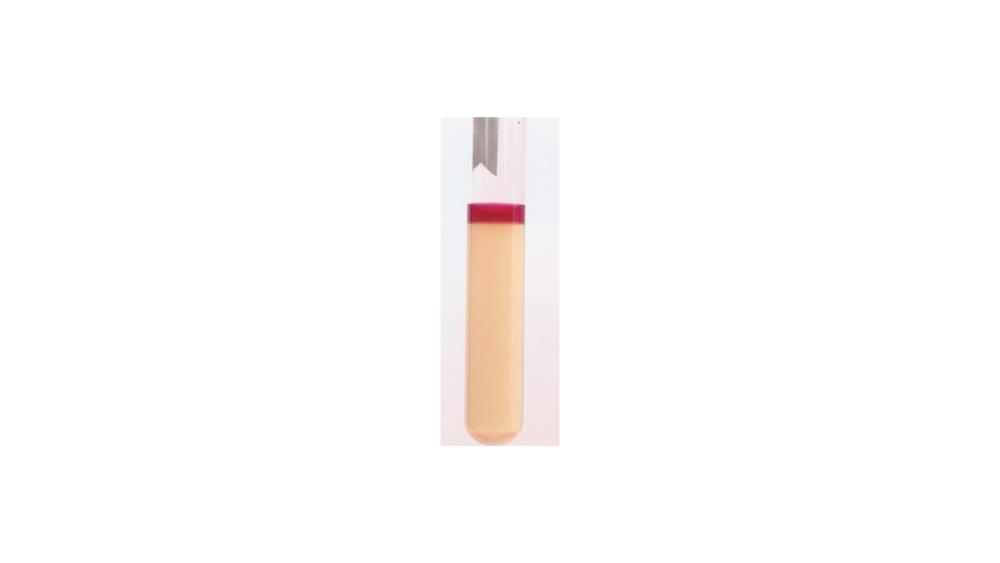

For the tryptophan hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response.
Positive
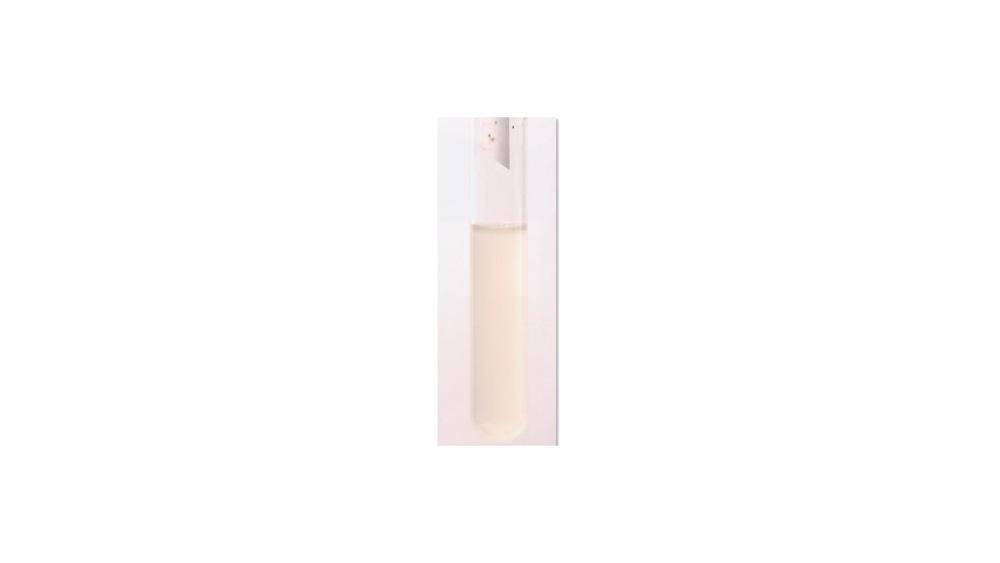

For the tryptophan hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response.
Negative
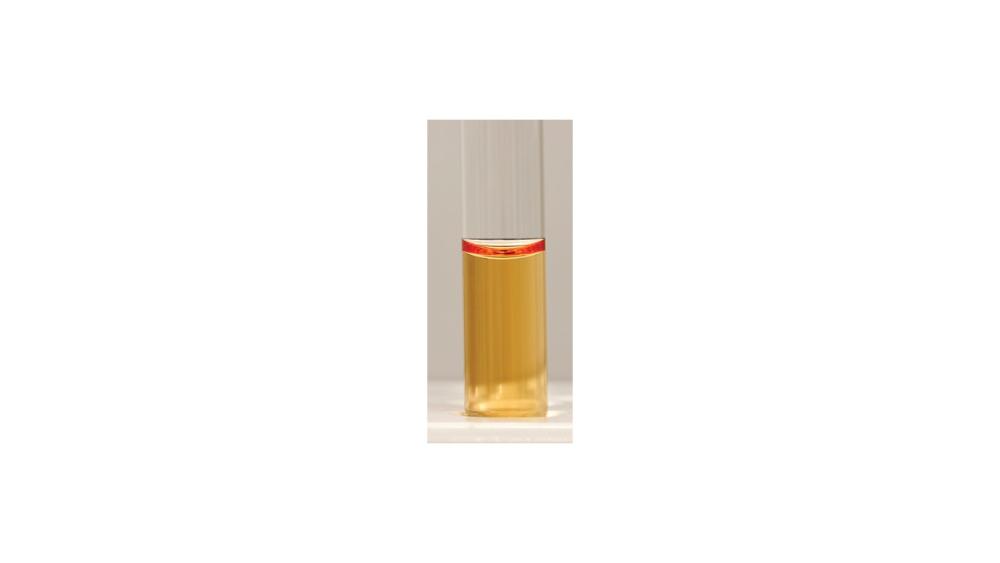

For the urea hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response.
Negative
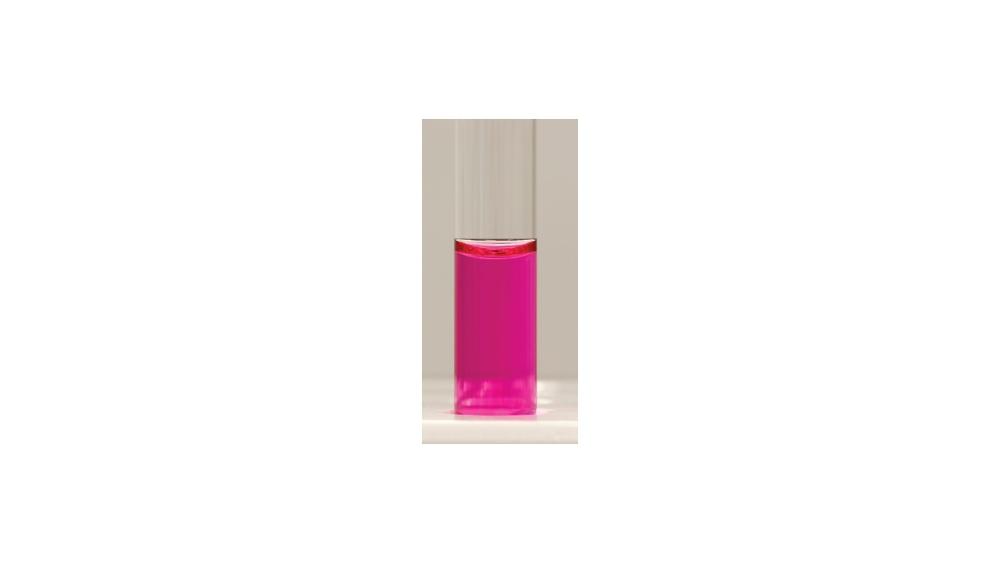

For the urea hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response.
Positive
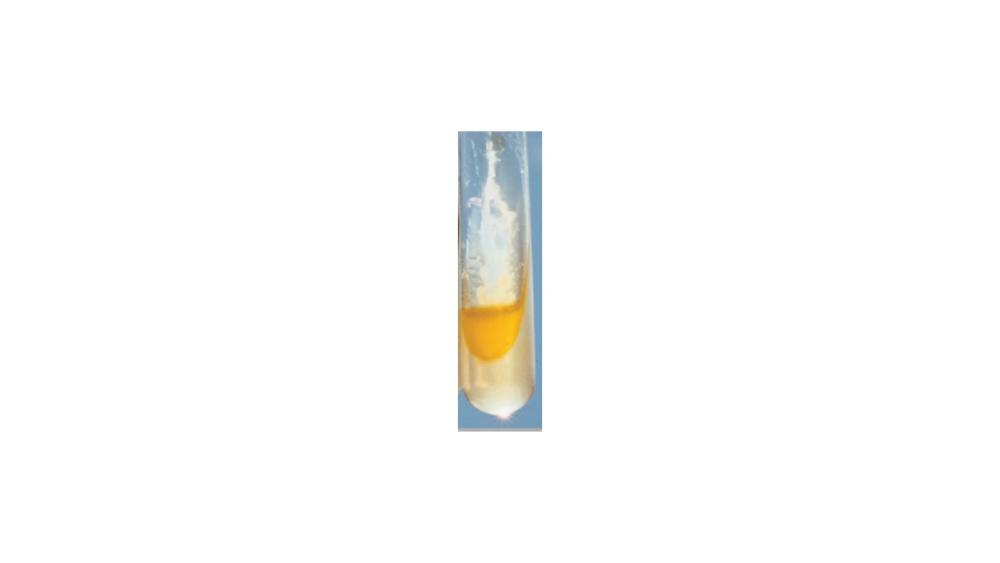

For the phenylalanine deamination test, the image shows a ____ response.
Negative
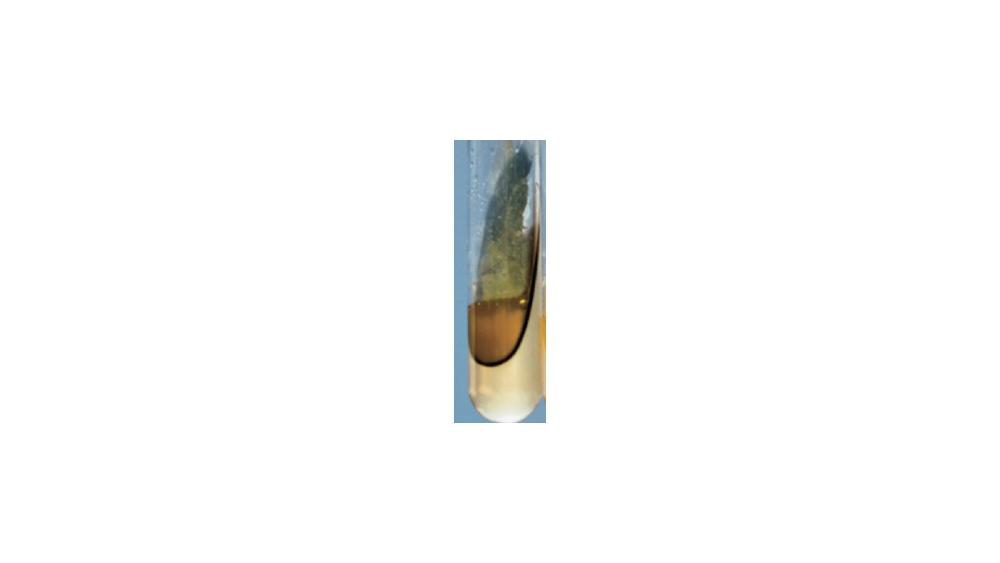

For the phenylalanine deamination test, the image shows a ____ response.
Positive
Which of the following is the most widely used molecular tool in biology?
PCR
Which of the following is the most widely used bioinformatic tool in biology?
BLAST
Which genetic locus is typically used to identify bacteria and archaea?
16s rRNA
Which genetic loci is typically used to identify fungi and other eukaryotes?
- ITS
- CO1
In DNA extraction the first step is to ____
Break the cells open to expose the DNA
In DNA extraction the second step is to ____
Remove the lipids and proteins
In DNA extraction the third step is to ____
Precipitate the DNA with alcohol
Which reagent of PCR stabilizes the molecular reactions?
Buffer
Which reagent of PCR creates covalent bonds to make the new DNA strand?
Taq polymerase
Which reagent of PCR hybridizes with the DNA at the location where amplification will occur?
Primers
Which reagent of PCR is the building blocks of the new DNA?
dNTPs
Which type of PCR is used to quantify how much RNA is being produced?
Reverse transcriptase PCR
Which type of PCR is used to amplify a large amount of a DNA target and then sequenced?
Conventional PCR
Which type of PCR is used as a diagnostic to distinguish between different microbes?
Real-time PCR
Which phase of PCR allows for the primases to form hydrogen bonds with the single stranded DNA?
Annealing
Which phase of PCR raises the temperature to break the DNA into single strands?
Denaturation
Which phase of PCR uses the Taq polymerase to add complementary nucleotides to the single strand of DNA?
Extention
Which phase of PCR has an optimal temperature at 72°C?
Extension
Which phase of PCR has an optimal temperature at 95°C?
Denaturation
Which phase of PCR has an optimal temperature at 50-60°C?
Annealing
This BLAST result is used as a comparison between searches.
Max or total score
This BLAST result illustrates how much of the inputted sequence is used in the alignment.
Percent query coverage
This BLAST result is the number of alignments that occur by chance.
Expect value
This BLAST result illustrates how well the inputted sequence matches to sequences in the databse.
Percent similarity
Mutations create variation in which microbial organisms?
- Bacteria
- Archaea
- Eukaryotes
Horizontal gene transfer creates variation in which microbial organisms?
- Bacteria
- Archaea
Crossing over and independent assortment create variation in which microbial organisms?
Eukaryotes
This type of mutation changes the DNA and changes the protein by shortening or truncating it.
Nonsense
This type of mutation changes the DNA but does not change the protein.
Silent
This type of mutation changes the DNA and the protein by adding or subtracting DNA nucleotides.
Indel
The synonymous substitution rate is used to determine the mutation rate. Which type of mutation results in synonymous substitutions?
Silent
This type of mutation changes the DNA and changes the protein by replacing one amino acid with another.
Missense
This type of mutation causes frameshifts.
Indel
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer typically occurs between bacteria of the same species or more directly related.
Transformation
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer indicates direct contact between two cells.
Conjugation
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer requires a dead bacterial cell that leaves behind DNA.
Transformation
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer involves naked DNA.
Transformation
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer requires a lysed bacterial cell.
Transuction
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer includes indirect contact between two cells and any gene can be transferred between the cells via a virus.
Generalized transduction.
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer involves a virus.
Transduction
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer typically occurs between bacteria of the same strain within a species.
Transduction
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer involves a plasmid.
Conjugation
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer includes indirect contact between two cells and only specific genes can be transferred between the cells via a virus.
Specialized transduction
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer requires two living bacterial cells.
Conjugation
This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer typically occurs between bacteria with the same cell wall type (Gram positive or Gram negative).
Conjugation
Growth on all the plates indicates which gene is on the plasmid?
Streptomycin resistance gene
Growth on all the plates except the one with nalidixic acid (LB + nal) indicates which gene is on the plasmid?
Ampicillin resistance gene
Growth on all the plates except the two with ampicillin (LB + amp, LB + amp + str) indicates which gene is on the plasmid?
Nalidixic acid resistance gene