Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Lab Exercises: 7-11
front 1 Microbes that require oxygen to grow but at much lower levels than 20% | back 1 Microaerophile |
front 2 Microbes that can only grow when oxygen is not present | back 2 Obligate anaerobe |
front 3 Microbes that can only grow when oxygen is present | back 3 Obligate aerobe |
front 4 Microbes that can grow in oxygen but do not require oxygen for energy metabolism | back 4 Aerotolerant anaerobe |
front 5 Microbes that are flexible and can grow with or without oxygen | back 5 Facultative anaerobe |
front 6 Which bacteria have optimal growth between -5 to 15°C? | back 6 Psychrophile |
front 7 Which bacteria have optimal growth between 45° to 75°C? | back 7 Thermophile |
front 8 Which bacteria have optimal growth between 25° to 45°C? | back 8 Mesophile |
front 9 Which bacteria have optimal growth above 75°C? | back 9 Hyperthermophile |
front 10 A bacterium that grows at a pH of 10 | back 10 Alkaliphile |
front 11 A bacterium that grows at a pH of 4 | back 11 Acidophile |
front 12 A bacterium that grows at a pH of 7 | back 12 Neutrophile |
front 13 These microbes can grow in excessive sugar concentrations | back 13 Osmophile |
front 14 These microbes require a high concentration of sodium chloride in order to grow | back 14 Obligate halophile |
front 15 These microbes can grow in moderate concentration of sodium chloride | back 15 Halotolerant |
front 16 A cell that has more solutes than the surrounding environment is | back 16 Hypertonic |
front 17 A cell that has fewer solutes than the surrounding environment is | back 17 Hypotonic |
front 18 Water flows (into/out of) a cell that is hypotonic | back 18 Out of |
front 19 Water flows (into/out of) a cell that is hypertonic | back 19 Into |
front 20 When the temperature increases past the optimal, the hydrogen bonding in the RNA breaks down and the proteins denature in this structure | back 20 Ribsosome |
front 21 When the temperature increases past the optimal, lipids can be destroyed affecting which structure? | back 21 Cell membrane |
front 22 Which temperature results in white colonies of Serratia? | back 22 37°C |
front 23 When the temperature decreases past the optimal, lipids can freeze affecting which strcuture? | back 23 Cell membrane |
front 24 When the temperature decreases past the optimal, the activity of this molecule will slow down | back 24 Enzyme |
front 25 When the temperature increases past the optimal, these denature | back 25 Enzyme |
front 26 Which temperature results in pinkish/red colonies of Serratia? | back 26 25°C |
front 27 Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does Serratia grow best at? | back 27 37°C |
front 28 Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does E. coli grow best at? | back 28 37°C |
front 29 Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does GST grow best at? | back 29 55°C |
front 30 Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does Serratia grow the worst at? | back 30 55°C |
front 31 Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature, which temperature does E. coli grow the worst at? | back 31 55°C |
front 32 Based on the absorbance readings, which temperature does GST grow the worst at? | back 32 37°C |
front 33 Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does E. coli grow best at? | back 33 7 |
front 34 Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does S. epidermidis grow best at? | back 34 5 |
front 35 Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does does A. faecalis grow best at? | back 35 7 |
front 36 Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does E. coli grow the worst at? | back 36 3 |
front 37 Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does S. epidermidis grow the worst at? | back 37 3 |
front 38 Based on the absorbance readings, which pH does A. faecalis grow the worst at? | back 38 3 |
front 39 Antivirals are compounds that kill or inhibit | back 39 Viruses |
front 40 Antifungals are compounds that kill or inhibit | back 40 Fungi |
front 41 Antibiotics are compounds that kill or inhibit | back 41 Bacteria |
front 42 Antiparasitics are compounds that kill or inhibit | back 42 Animals |
front 43 Chemical agents that are applied to inanimate objects to kill microbes are | back 43 Disinfectants |
front 44 Substances that kill or inhibit microorganisms but are gentle enough to apply to tissue are | back 44 Antiseptics |
front 45 What antibiotics target the cell wall of bacteria? | back 45 - Penicillin - Ampicillin - Bacitracin |
front 46 Which antibiotics target the DNA and RNA synthesis of bacteria? | back 46 - Fluoroquinolones - Rifamycins |
front 47 Which antibiotics target the protein synthesis of bacteria? | back 47 - Chloramphenicol - Streptomycin - Tetracycline |
front 48 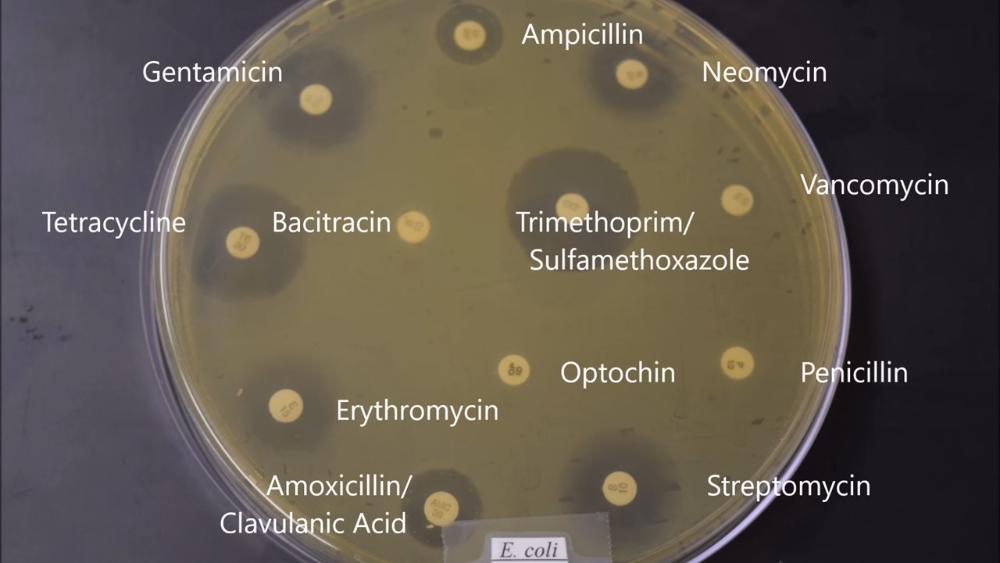 Which antibiotic is E. coli completely resistant to? | back 48 - Bacitracin - Nasitracon - Optochin - Penicillin - Vancomycin |
front 49 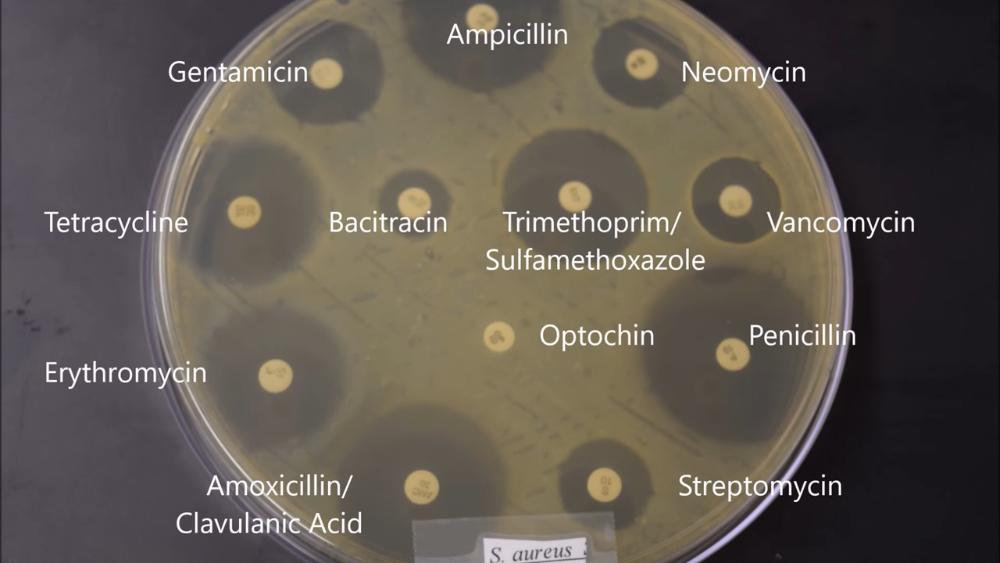 Which antibiotic is S. aureus completely resistant to? | back 49 Optochin |
front 50  Indicate five antibiotics that E. coli is highly susceptible to. | back 50 - Streptomycin - Gentamycin - Erythomycin - Trimethoprim - Tetracycline |
front 51  Indicate four antibiotics that S. aureus is mildly resistant to. | back 51 - Streptomycin - Neomycin - Vancomycin - Bacitracin |
front 52 Which antibiotic would you not use to treat an infection of E. coli or S. aureus | back 52 Optochin |
front 53 Which two antibiotics would be better to treat both E. coli and S. aureus infections? | back 53 - Trimethoprim - Tetracycline |
front 54 Fermentation is a form of energy metabolism where the final electron acceptor is | back 54 Organic |
front 55 Anaerobic respiration is a form of energy metabolism where the final electron acceptor is | back 55 Inorganic |
front 56 Aerobic respiration is a form of energy metabolism where the final electron acceptor is | back 56 Oxygen |
front 57 Which molecule is hydrolyzed by proteases? | back 57 Casein |
front 58 Which molecule is hydrolyzed by amylase? | back 58 Starch |
front 59 Which molecule is hydrolyzed by lipases? | back 59 Fat |
front 60 Which molecule is deaminated into phenylpyruvic acid and ammonia? | back 60 Phenylalanine |
front 61 Which molecule is degraded in indole, ammonia, and pyruvic acid? | back 61 Tryptophan |
front 62 Which molecule splits in carbon dioxide and ammonia when it's hydrolyzed? | back 62 Urea |
front 63 The mixed acid fermentation test uses which reagent to indicate a positive reaction? | back 63 Urea |
front 64 Which enzyme is tested for with hydrogen peroxide? | back 64 Catalase |
front 65 The 2,3-butanediol fermentation test uses which reagent to indicate a positive reaction? | back 65 Barritt |
front 66 Which enzyme is tested for in an oxidation test? | back 66 Oxidase |
front 67 Name one of the tests that must be completed under anaerobic conditions in the API20E. | back 67 LDC |
front 68 Name one of the tests that examines carbon utilization in the API20E. | back 68 MAN |
front 69 Name one of the tests that examines nitrogen utilization in the API20E. | back 69 URE |
front 70 Name one of the tests that examines protein utilization in the API20E. | back 70 IND |
front 71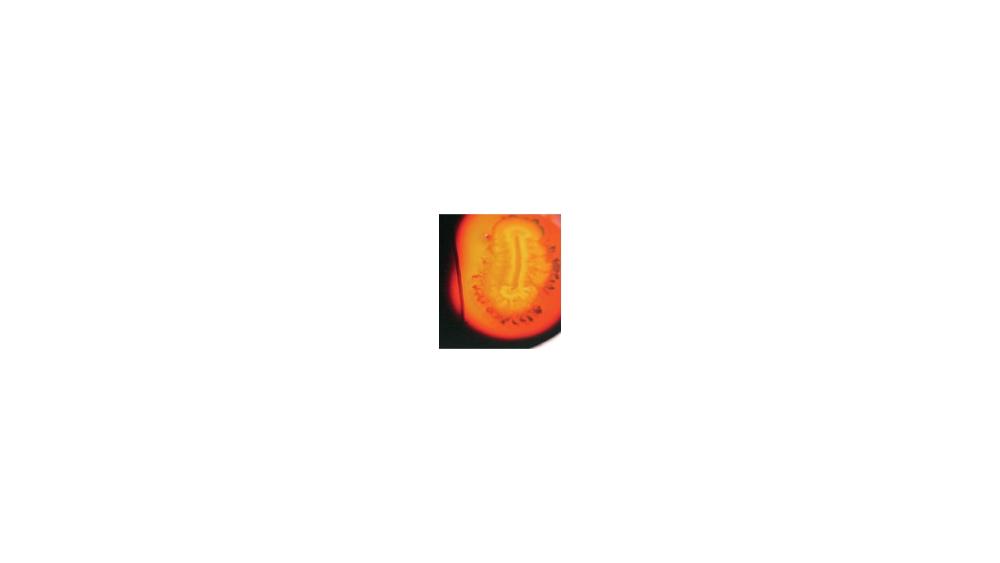  For the starch hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 71 Positive |
front 72  For the starch hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 72 Negative |
front 73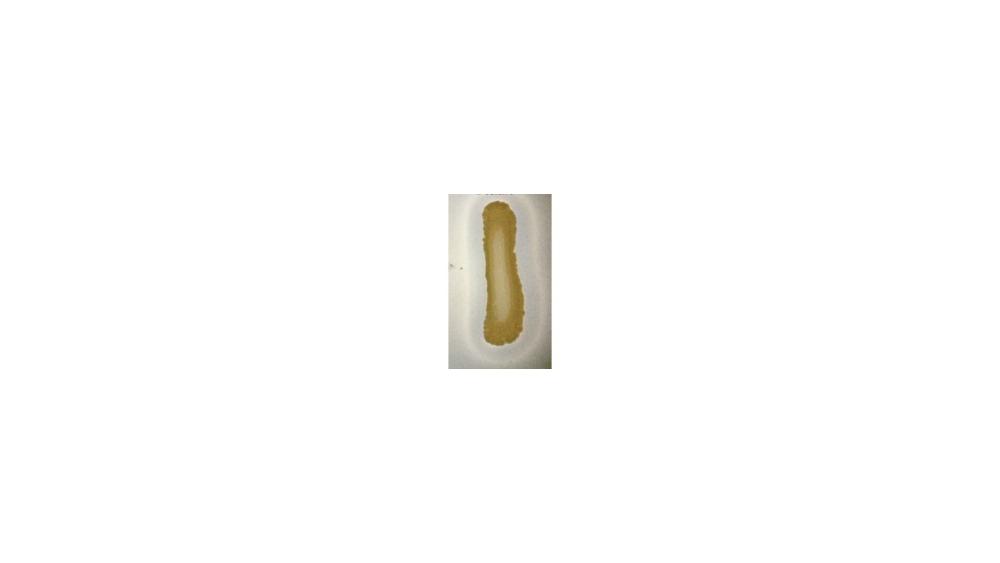  For the casein hydrolysis test, the image shoes a ____ response. | back 73 Positive |
front 74 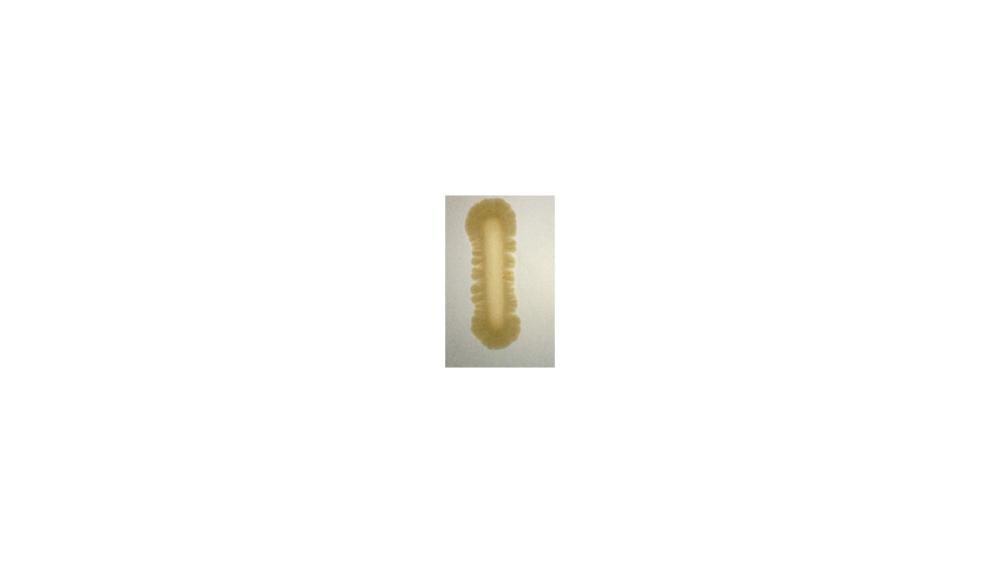 For the casein hydrolysis test, the image shoes a ____ response. | back 74 Negative |
front 75  For the fat hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 75 Negative |
front 76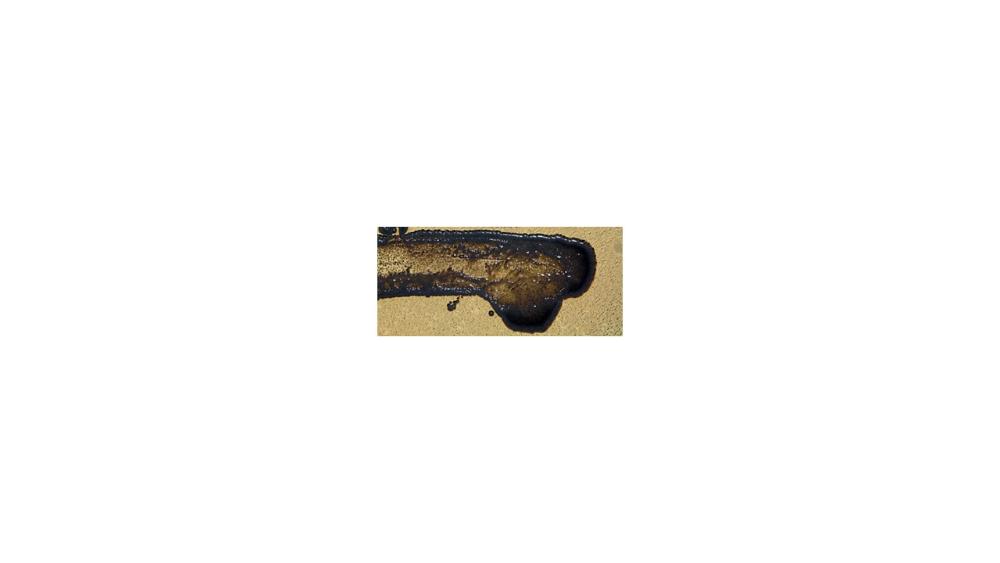  For the fat hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 76 Positive |
front 77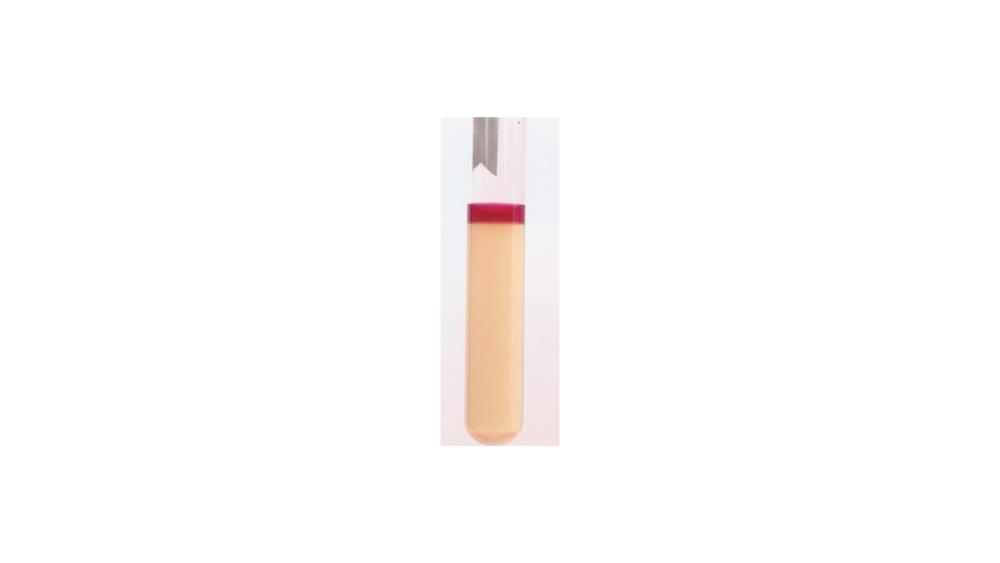  For the tryptophan hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 77 Positive |
front 78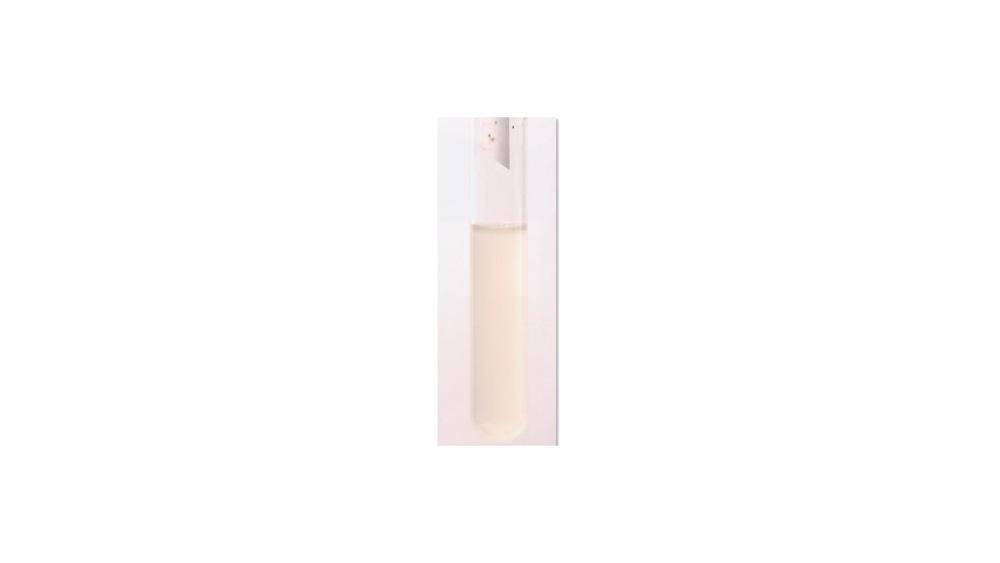  For the tryptophan hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 78 Negative |
front 79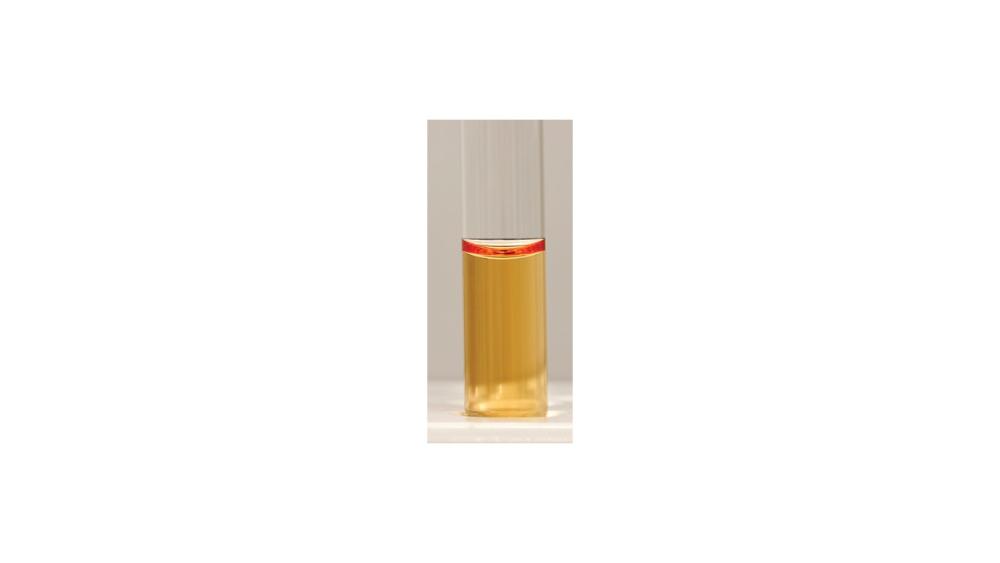  For the urea hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 79 Negative |
front 80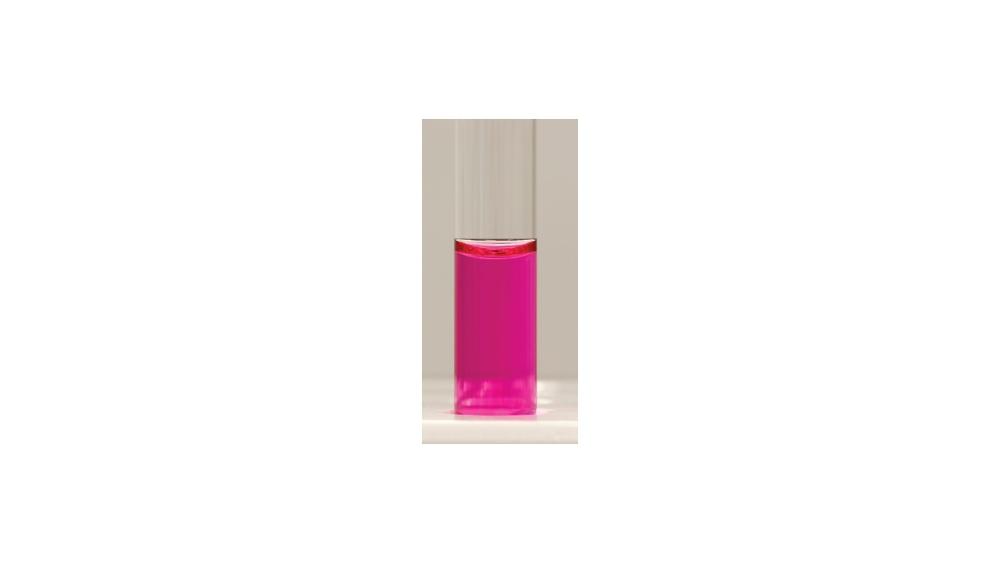  For the urea hydrolysis test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 80 Positive |
front 81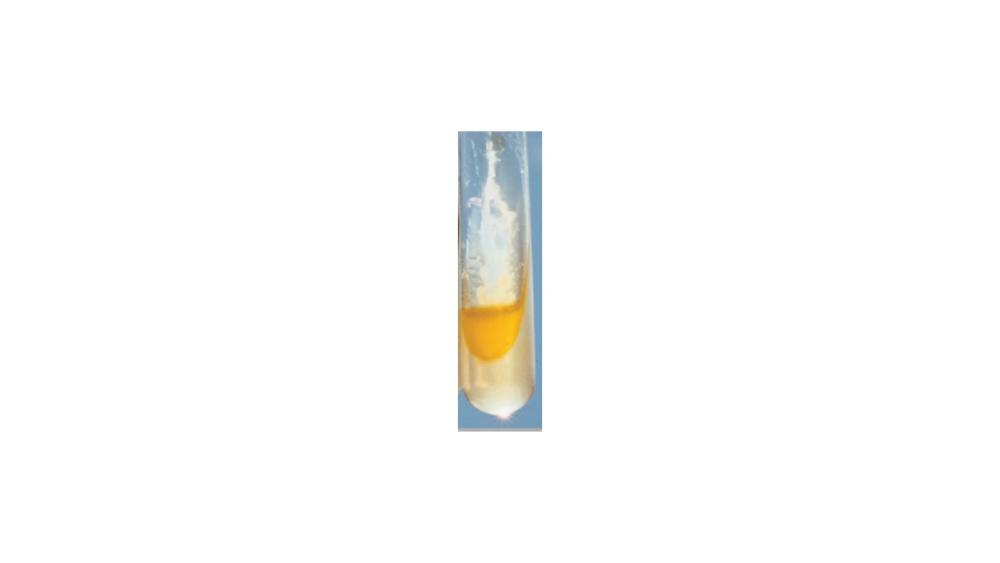  For the phenylalanine deamination test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 81 Negative |
front 82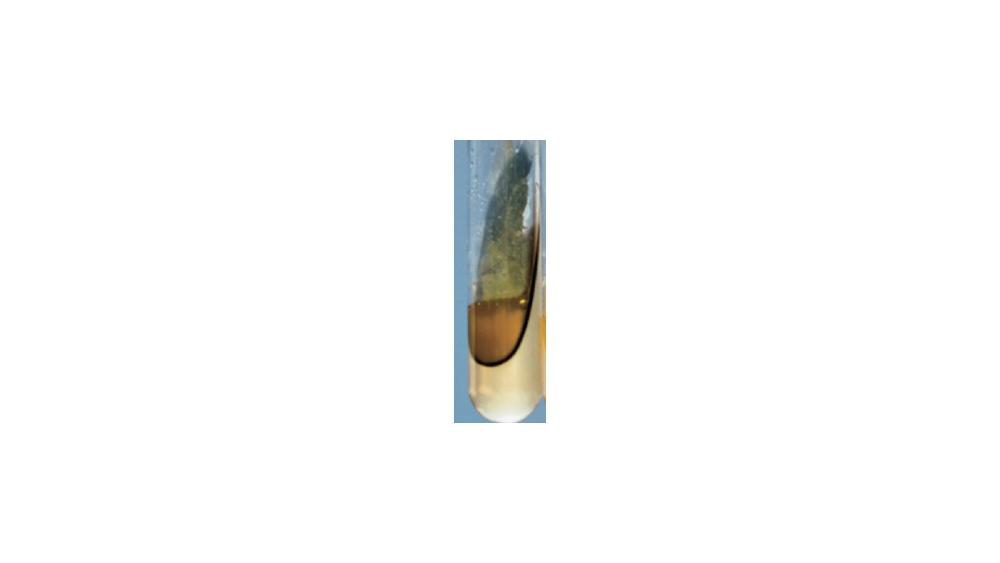  For the phenylalanine deamination test, the image shows a ____ response. | back 82 Positive |
front 83 Which of the following is the most widely used molecular tool in biology? | back 83 PCR |
front 84 Which of the following is the most widely used bioinformatic tool in biology? | back 84 BLAST |
front 85 Which genetic locus is typically used to identify bacteria and archaea? | back 85 16s rRNA |
front 86 Which genetic loci is typically used to identify fungi and other eukaryotes? | back 86 - ITS - CO1 |
front 87 In DNA extraction the first step is to ____ | back 87 Break the cells open to expose the DNA |
front 88 In DNA extraction the second step is to ____ | back 88 Remove the lipids and proteins |
front 89 In DNA extraction the third step is to ____ | back 89 Precipitate the DNA with alcohol |
front 90 Which reagent of PCR stabilizes the molecular reactions? | back 90 Buffer |
front 91 Which reagent of PCR creates covalent bonds to make the new DNA strand? | back 91 Taq polymerase |
front 92 Which reagent of PCR hybridizes with the DNA at the location where amplification will occur? | back 92 Primers |
front 93 Which reagent of PCR is the building blocks of the new DNA? | back 93 dNTPs |
front 94 Which type of PCR is used to quantify how much RNA is being produced? | back 94 Reverse transcriptase PCR |
front 95 Which type of PCR is used to amplify a large amount of a DNA target and then sequenced? | back 95 Conventional PCR |
front 96 Which type of PCR is used as a diagnostic to distinguish between different microbes? | back 96 Real-time PCR |
front 97 Which phase of PCR allows for the primases to form hydrogen bonds with the single stranded DNA? | back 97 Annealing |
front 98 Which phase of PCR raises the temperature to break the DNA into single strands? | back 98 Denaturation |
front 99 Which phase of PCR uses the Taq polymerase to add complementary nucleotides to the single strand of DNA? | back 99 Extention |
front 100 Which phase of PCR has an optimal temperature at 72°C? | back 100 Extension |
front 101 Which phase of PCR has an optimal temperature at 95°C? | back 101 Denaturation |
front 102 Which phase of PCR has an optimal temperature at 50-60°C? | back 102 Annealing |
front 103 This BLAST result is used as a comparison between searches. | back 103 Max or total score |
front 104 This BLAST result illustrates how much of the inputted sequence is used in the alignment. | back 104 Percent query coverage |
front 105 This BLAST result is the number of alignments that occur by chance. | back 105 Expect value |
front 106 This BLAST result illustrates how well the inputted sequence matches to sequences in the databse. | back 106 Percent similarity |
front 107 Mutations create variation in which microbial organisms? | back 107 - Bacteria - Archaea - Eukaryotes |
front 108 Horizontal gene transfer creates variation in which microbial organisms? | back 108 - Bacteria - Archaea |
front 109 Crossing over and independent assortment create variation in which microbial organisms? | back 109 Eukaryotes |
front 110 This type of mutation changes the DNA and changes the protein by shortening or truncating it. | back 110 Nonsense |
front 111 This type of mutation changes the DNA but does not change the protein. | back 111 Silent |
front 112 This type of mutation changes the DNA and the protein by adding or subtracting DNA nucleotides. | back 112 Indel |
front 113 The synonymous substitution rate is used to determine the mutation rate. Which type of mutation results in synonymous substitutions? | back 113 Silent |
front 114 This type of mutation changes the DNA and changes the protein by replacing one amino acid with another. | back 114 Missense |
front 115 This type of mutation causes frameshifts. | back 115 Indel |
front 116 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer typically occurs between bacteria of the same species or more directly related. | back 116 Transformation |
front 117 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer indicates direct contact between two cells. | back 117 Conjugation |
front 118 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer requires a dead bacterial cell that leaves behind DNA. | back 118 Transformation |
front 119 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer involves naked DNA. | back 119 Transformation |
front 120 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer requires a lysed bacterial cell. | back 120 Transuction |
front 121 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer includes indirect contact between two cells and any gene can be transferred between the cells via a virus. | back 121 Generalized transduction. |
front 122 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer involves a virus. | back 122 Transduction |
front 123 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer typically occurs between bacteria of the same strain within a species. | back 123 Transduction |
front 124 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer involves a plasmid. | back 124 Conjugation |
front 125 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer includes indirect contact between two cells and only specific genes can be transferred between the cells via a virus. | back 125 Specialized transduction |
front 126 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer requires two living bacterial cells. | back 126 Conjugation |
front 127 This form of bacterial horizontal gene transfer typically occurs between bacteria with the same cell wall type (Gram positive or Gram negative). | back 127 Conjugation |
front 128 Growth on all the plates indicates which gene is on the plasmid? | back 128 Streptomycin resistance gene |
front 129 Growth on all the plates except the one with nalidixic acid (LB + nal) indicates which gene is on the plasmid? | back 129 Ampicillin resistance gene |
front 130 Growth on all the plates except the two with ampicillin (LB + amp, LB + amp + str) indicates which gene is on the plasmid? | back 130 Nalidixic acid resistance gene |