Exercise 5-6 in the Lab Manual
A group of similar cells and associated structures(the matrix) that function together to carry out specific activities
Tissue
What are the basic types of tissue in the human body?
Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue
What covers body surfaces and/or lines hollows organs, body cavities, and ducts. It can also form certain types of glands?
Epithelial Tissue
What kind of tissue is often found connecting structures together. It protects and supports the body or specific parts of the body, secures organs to other structures, serves as an energy reserve(fat), provides immunity and transports substances through out the body(blood)?
Connective tissue
What is two or more tissues that function together to perform specific activities?
Organ
Epithelium consisting or one layer of thin flat, scale-like cells.
Simple squamous epithelium
What location do you find simple squamous epithelium cells in the body?
kidneys, blood vessels
What is the function of simple squamous epithelium cells?
Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; secrets lubrication substances in serosae.
composed of one layer of cells with cells that are somewhat cube shaped and are tightly joined together forming tine tubes
simple cuboidal epithelium
line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands
simple cuboidal epithelium
Where is the lumen in a simple cuboidal epithelium
in the center of the cubed cell
what are some locations of simple cuboidal epithelium tissue?
ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface, and kidney
What is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium tissue
secretion and absorption
Epithelium tissue that is longer than it is wide with the nucluei found in the base of the cell; often you will see goblet cells in this tissue
simple columnar epithelium
Where in the body are simple columnar epithelium tissue found?
gallbladder, digestive track and some regions of the uterus
What is the function of simple columnar epithelium tissue?
absorption and secretion of mucus, enzymes; ciliated types propels mucus by ciliated action
Epithelium made up of cells that reach the basement membrane and appear to be stratified because their nuclei are at different levels.
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
What is the function of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
secretion, particularly of mucus, propulsion of mucus by cillary action
Where in the body do you find pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract, and male sperm
The nuclei of the cells can be seen at different levels and not all of the cells seems to reach the surface; However each cell attaches to the basement membrane, so there is only one layer of cells even though there appears to be more
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Epithelium that occurs in layers where the surface cells are squamous in shape
statified ciliated epithelium
Where is stratified ciliated epithelium found in the body?
esophagus, mouth, vagina and epidermis of the skin
What is the function of stratified ciliated epithelium tissue?
Protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasions
In the upper layers of the cell of a stratified squamous epithelium the shape of the nuclei are _________?
squamous or flat like
In the deeper layers of the cell of a stratified squamous epithelium the shape of the nuclei are _________?
Round
A type of loose connective tissue
Areolar connective tissue
________ tissue is composed of a loose arrangement of cells which lie in a matrix that is composed of ground substance and fibers.
Connective Tissue
Collagen, elastic and reticular fibers are found in which type of tissue
Areolar connective tissue
Areolar tissue is prevalently found where?
under epithella of body; mucus membranes; packages organs, and surrounds capillaries
What is the function of Areolar connective tissue?
wraps and cushions organs; holds and conveys tissue fluids
Composed of dense, regular connective tissue.
Tendons
In addition to tendons what other structures are composed of dense connective tissue
most ligaments and aponeuroses
What is the function of dense connective tissue?
Attaches muscle to bone or muscle to muscle
You will find Collagen fibers, and fibroblast in what connective tissue?
dense connective tissue
You will find collagen fibers, fat cells, elastic fibers, fibroblast and ground substance in which connective tissue?
Areolar connective tissue
the gel-like material in which connective tissue cells and fibers are embedded.
ground substance
A connective tissue found along with areolar connective tissue
Adipose connective tissue
Fat cells are called what?
adipocytes
Where in the body to you find adipose tissue?
under skin, around kidneys in the breast
What are some functions of adipose tissue?
reserve food fuel, insulates against heat loss, supports and protects organs
Has more rigidity than other types of connective tissue
Hyaline cartilage
What is chondroitin sulfate?
jelly like material in the ground substance
Where in the body do you find hyaline cartilage?
long bones, embrionic skeleton, costal cartilages of the ribs
What is the function of hyaline cartilage?
supports and reinforces; has resilient cushioning properties
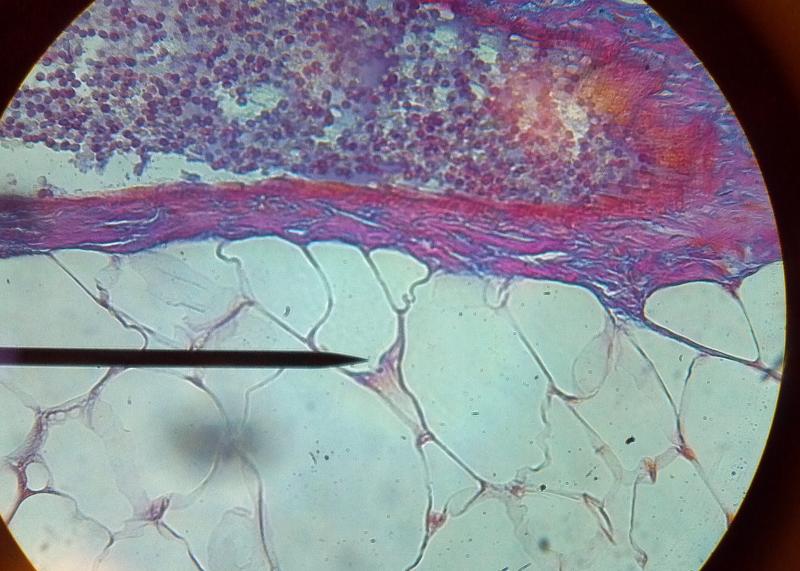
What kind of tissue is this?
Adipose tissue
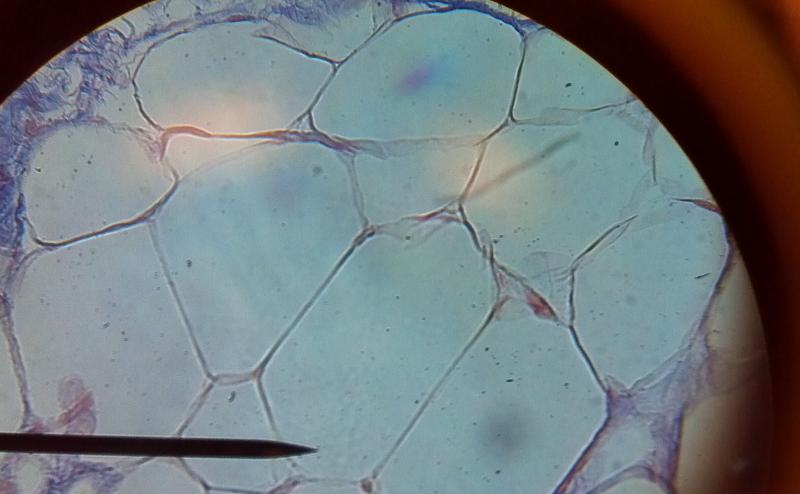
What kind of tissue is this?
Adipose Tissue
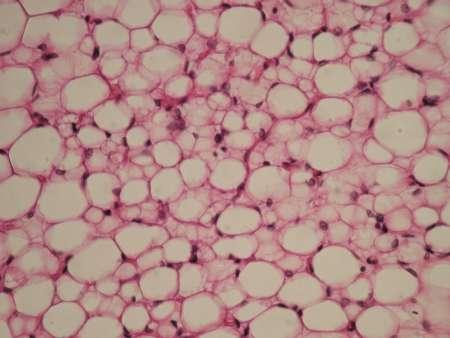
What kind of tissue is this?
Adipose Tissue
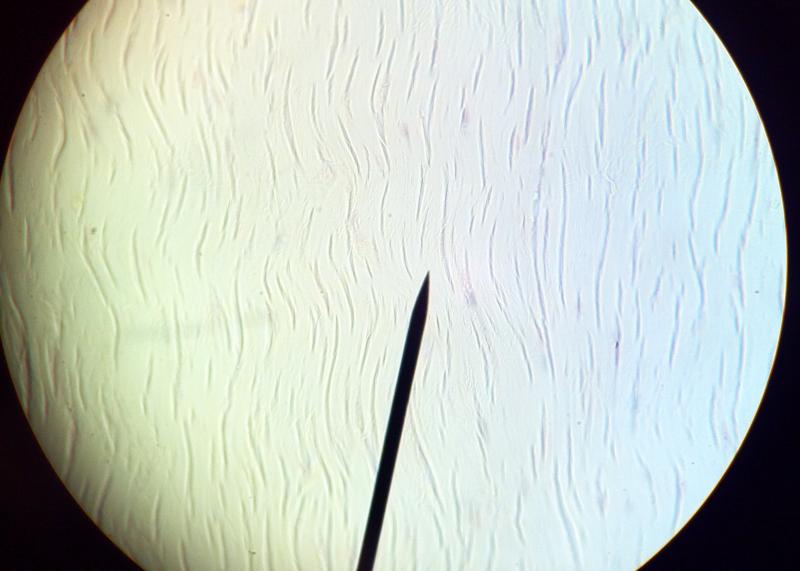
What kind of tissue is this?
Dense regular connective tissue
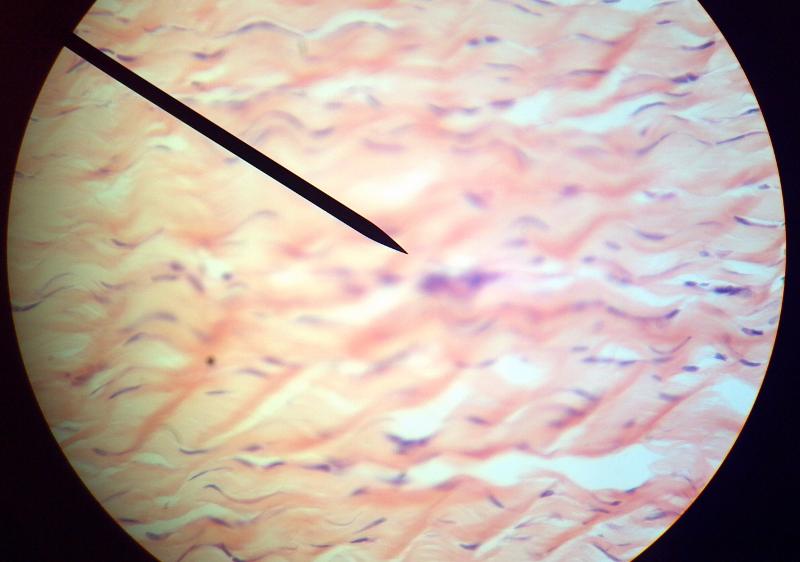
What kind of tissue is this?
Dense regular connective tissue
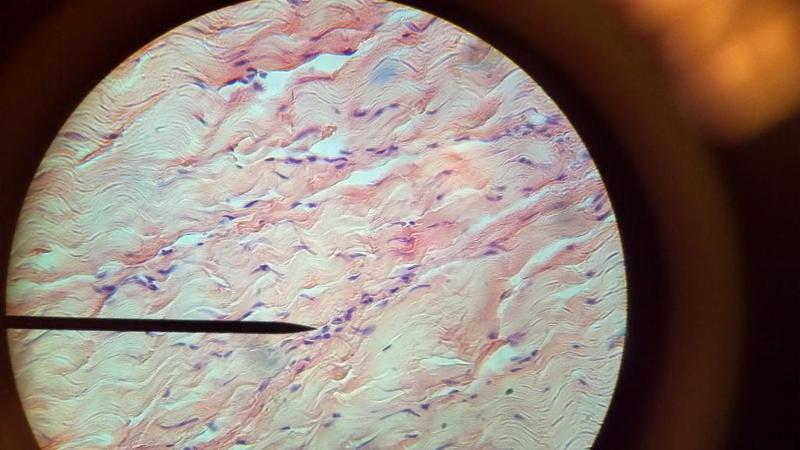
What kind of tissue is this?
Dense regular connective tissue
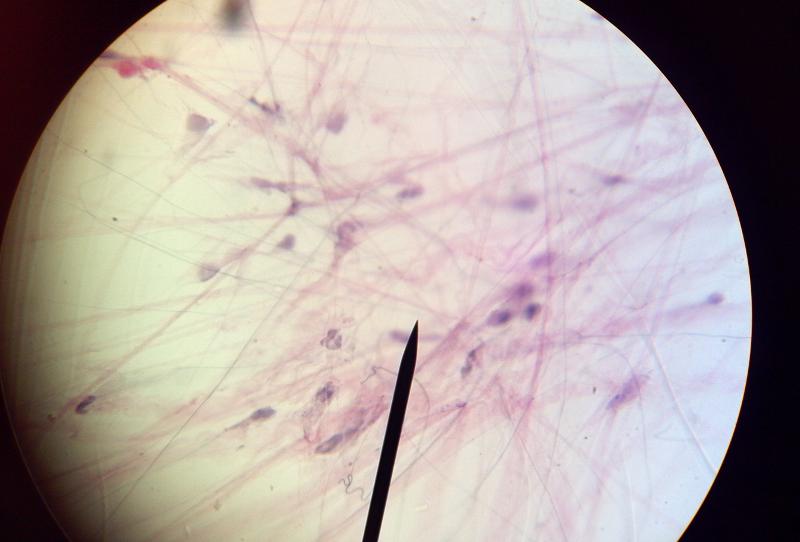
What kind of tissue is this?
Loose Areolar connective tissue
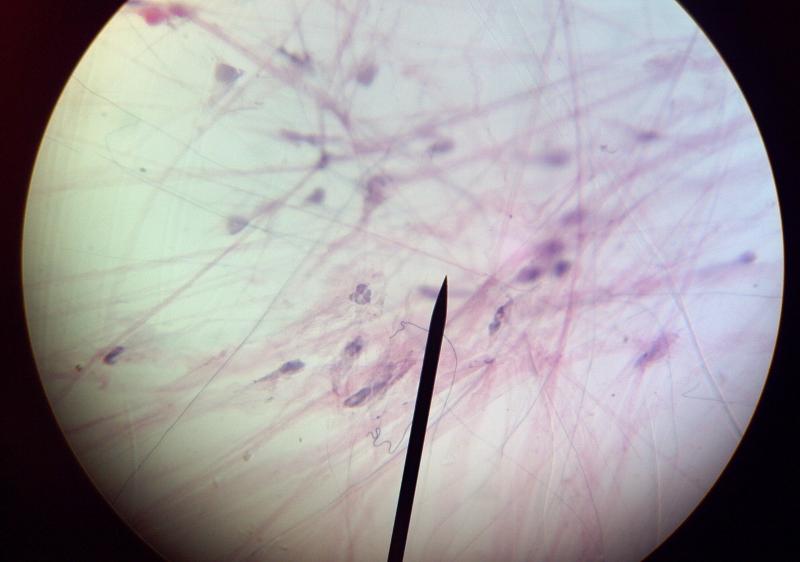
What kind of tissue is this?
Loose Areolar connective tissue
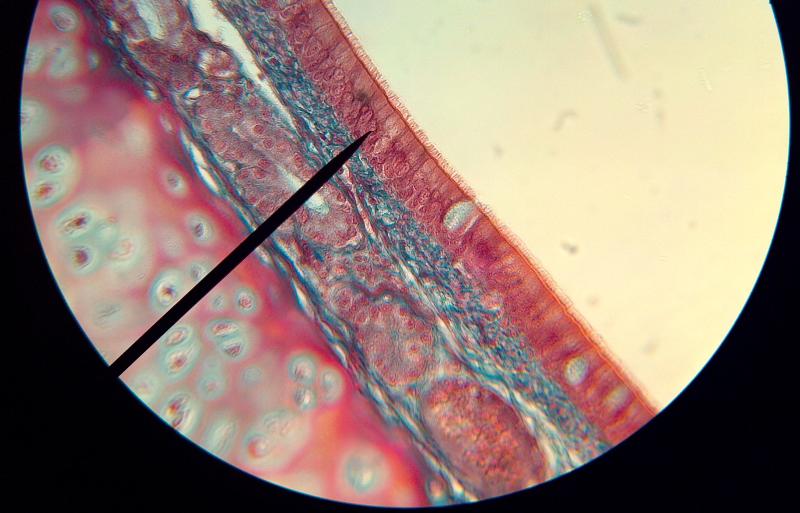
What kind of tissue is this?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar
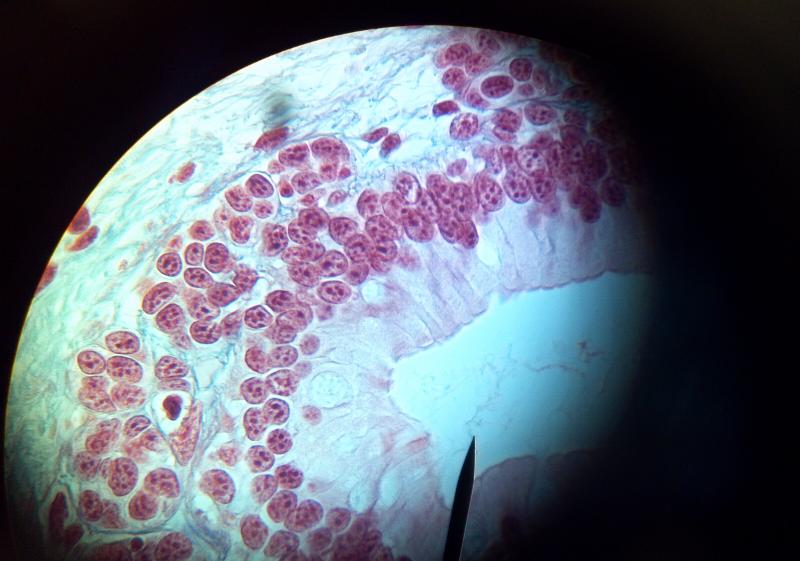
What kind of tissue is this?
Simple Columnar
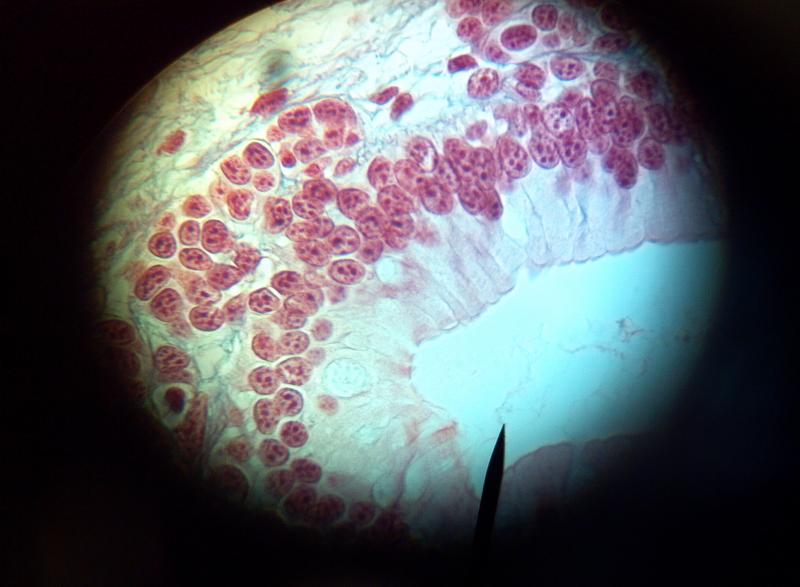
What kind of tissue is this?
Simple Columnar
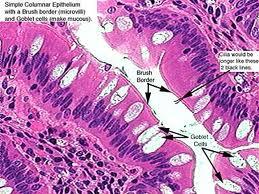
What kind of tissue is this?
Simple Columnar
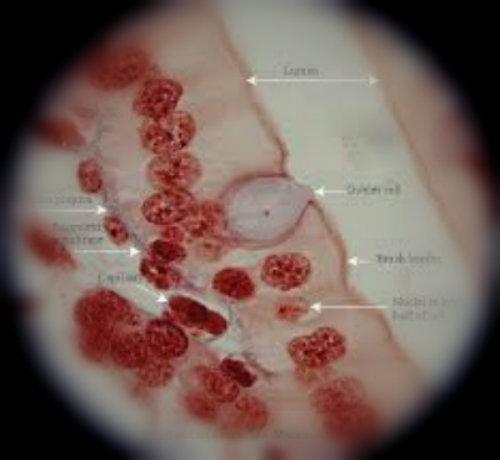
What kind of tissue is this?
Simple Columnar
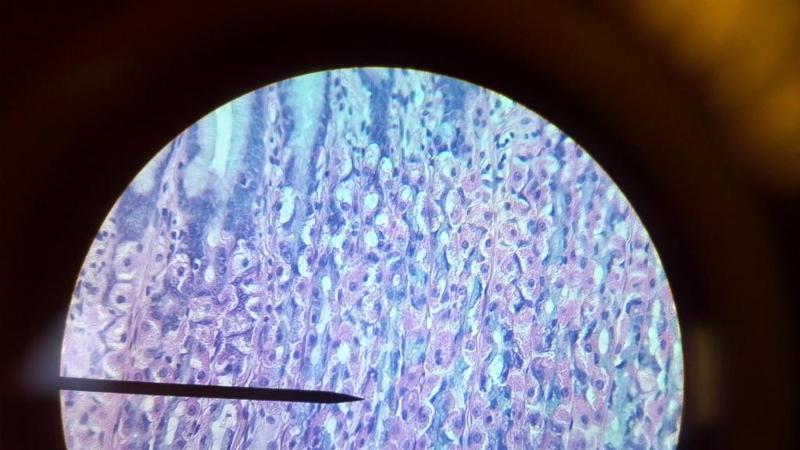
What kind of tissue is this?
Simple columnar
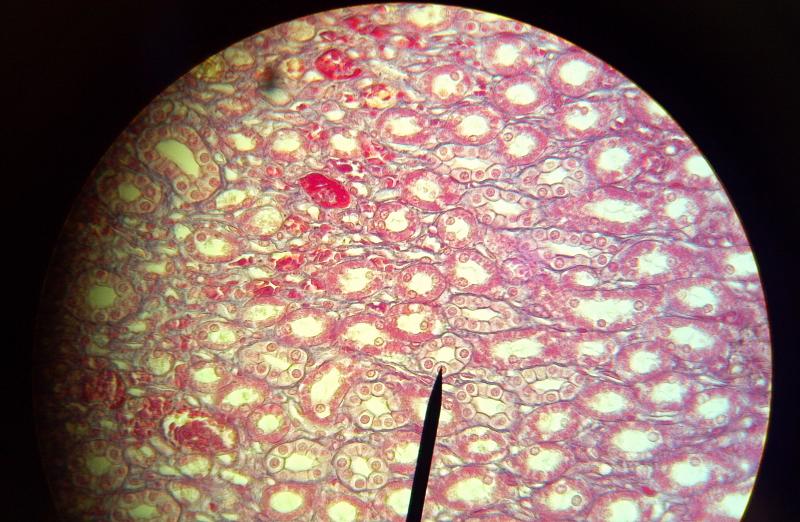
What kind of tissue is this?
Simple Cuboidal
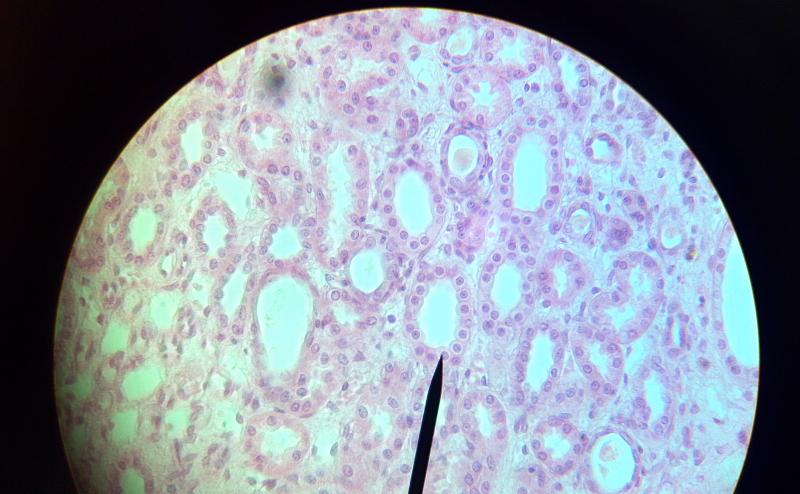
What kind of tissue is this?
Simple Cuboidal
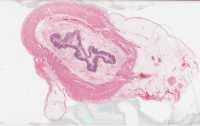
What kind of tissue is this?
Simple Squamous
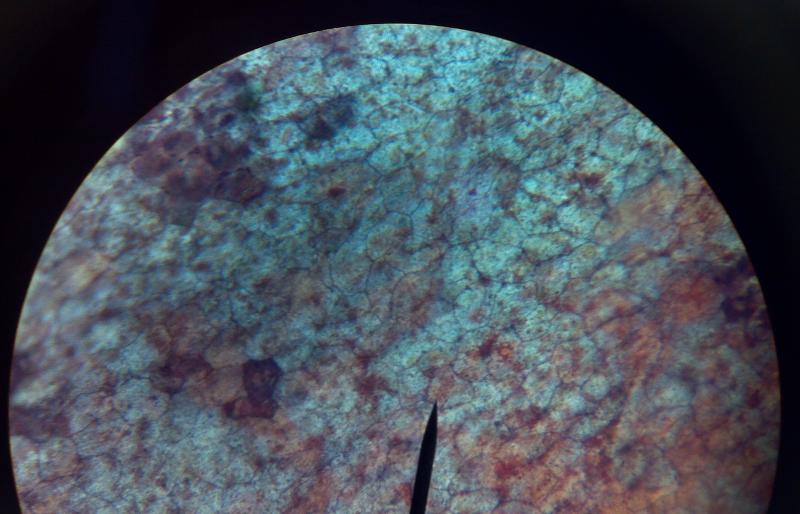
What kind of tissue is this?
Simple Squamous
What kind of tissue is this?
Stratified Squamous
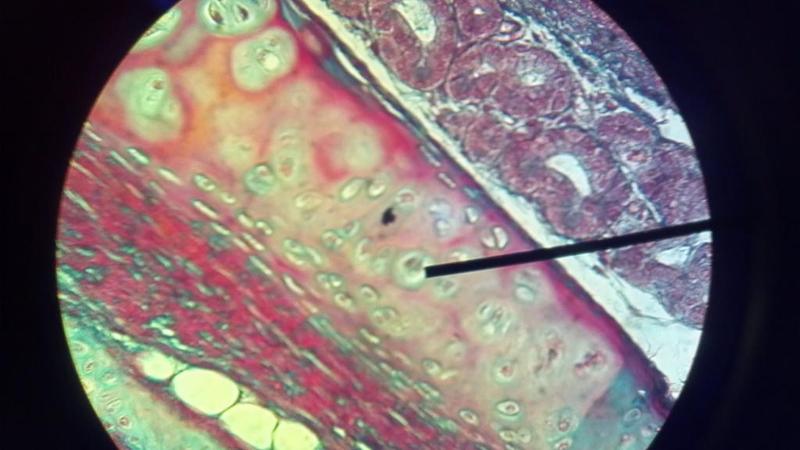
What kind of tissue is this?
Hyaline Cartilage
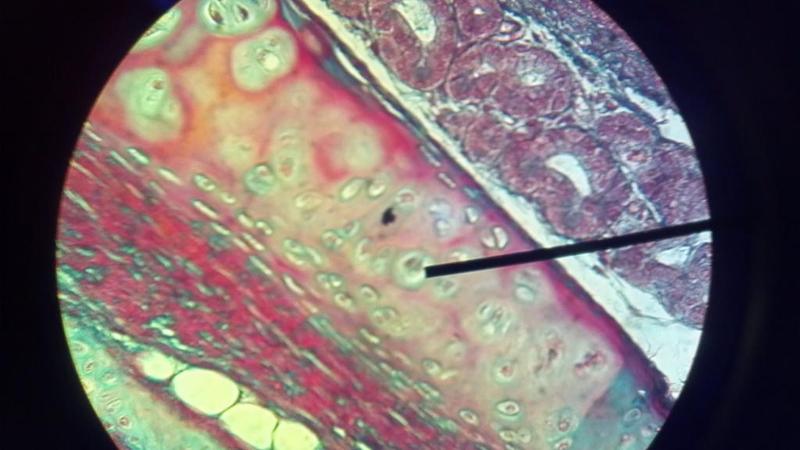
What kind of tissue is this?
Hyaline Cartilage
Name the types of Connective Tissue?
Areolar, Adipose, hyaline, dense regular connective
Name the one layer Epithelium tissue.
Simple Squamous, Simple Cuboidal, Simple Columnar, and Psuedostratified Ciliated Columnar
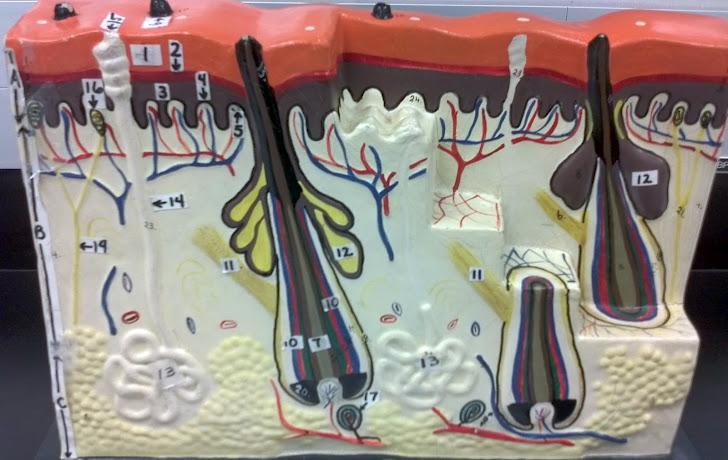
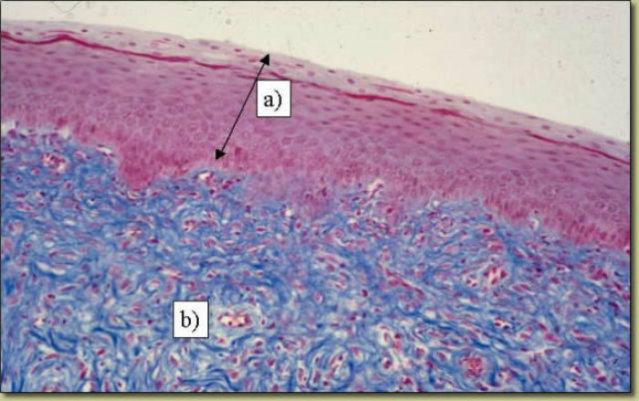
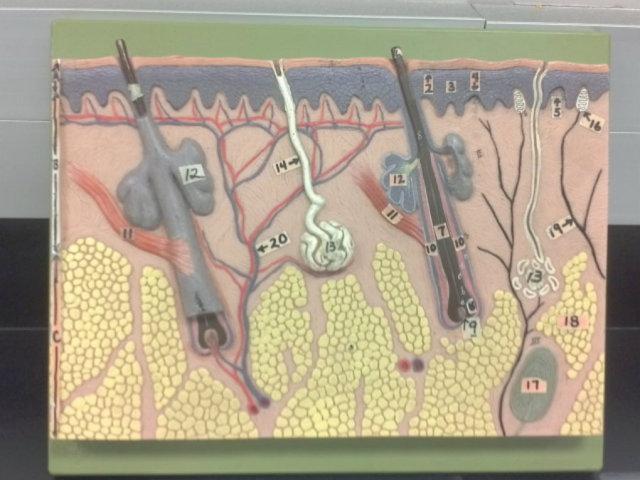
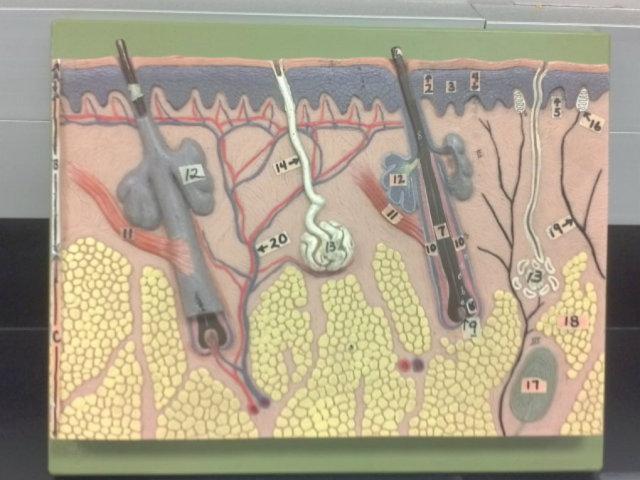
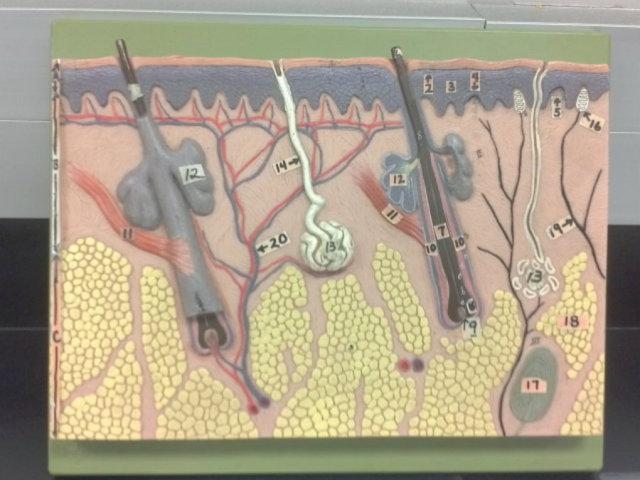
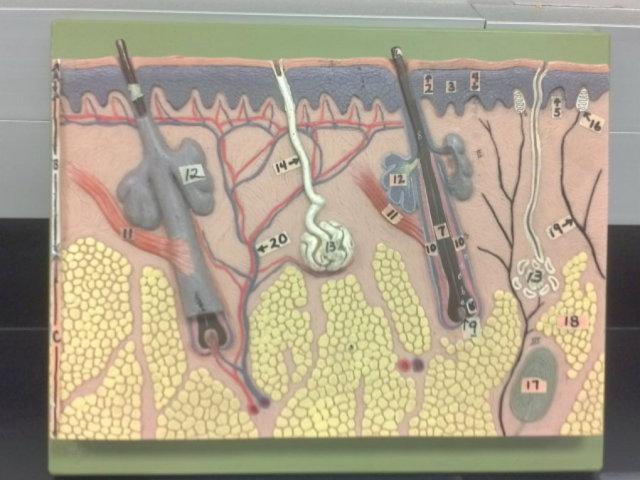
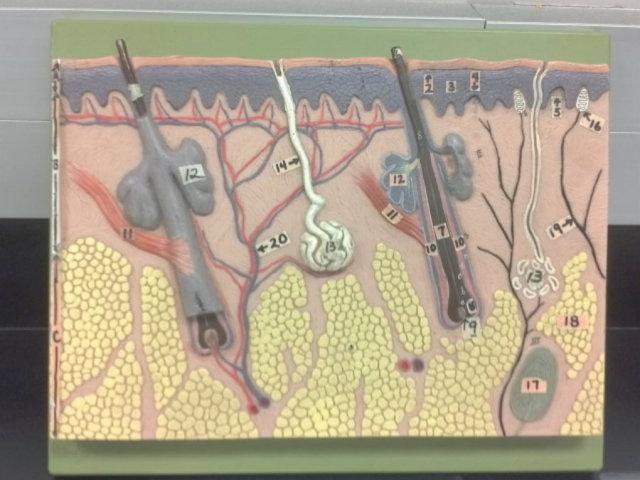
What is A in this picture?
Epidermis
What is B in this picture?
Dermis
What is C in this picture?
Hypodermis
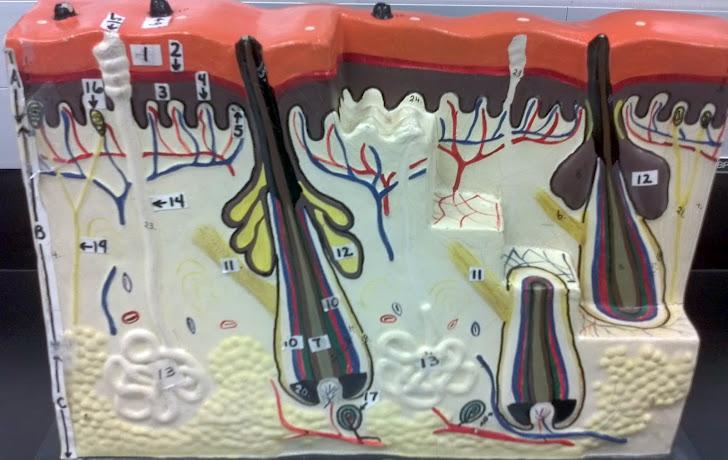
What is 1 in this picture?
Stratum Corneum
What is 2 in this picture?
Stratum Granulosum
What is 3 in this picture?
Stratum Spinosum
What is 4 in this picture?
Stratum Basale
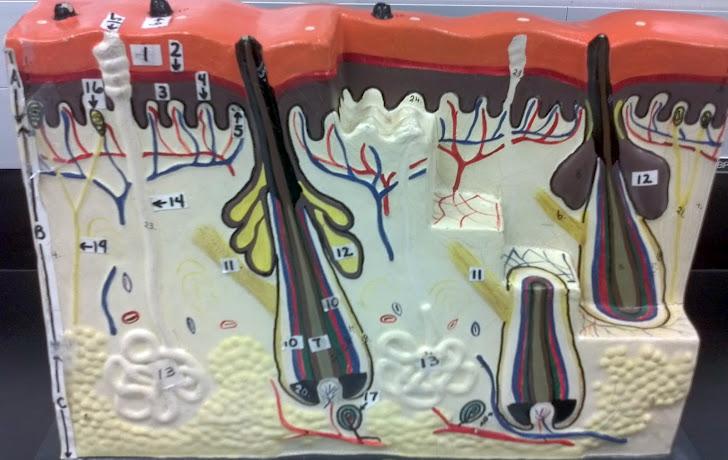
What is 5 in this picture?
Dermal Papilla

What is 6 in this picture?
Hair Shaft
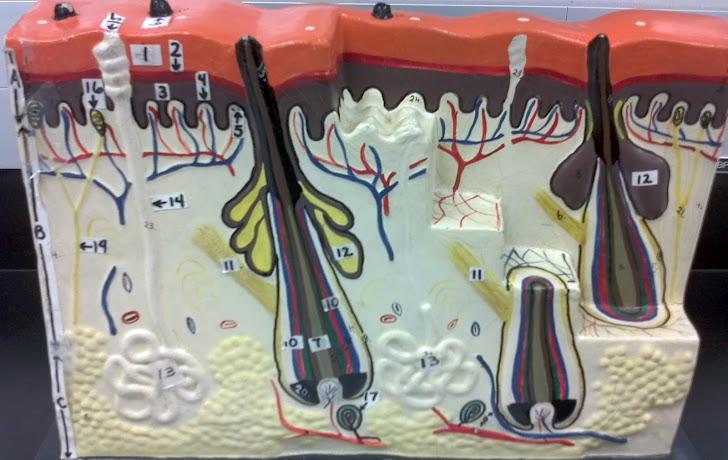
What is 7 in this picture?
Hair Root

What is 8 in this picture?
Hair Bulb
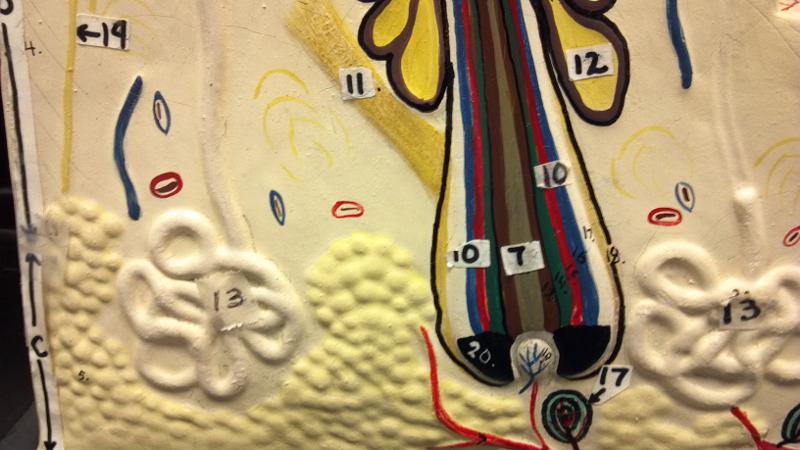

What is 9 in this picture?
Hair Papilla
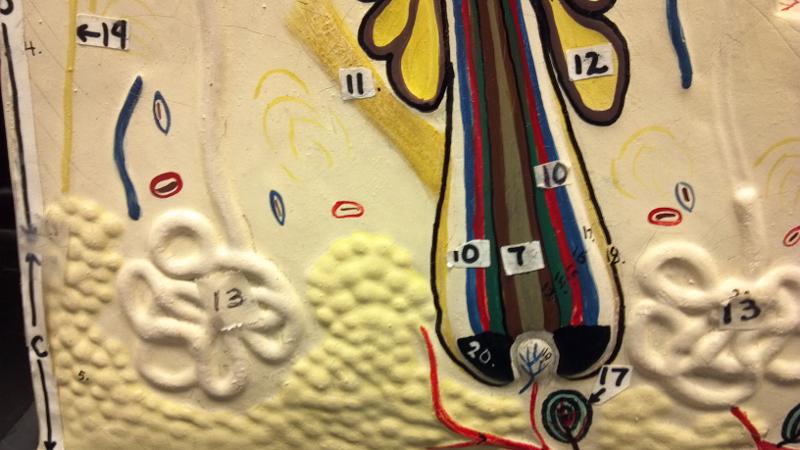

What is 10 in this picture?
Hair Follicle
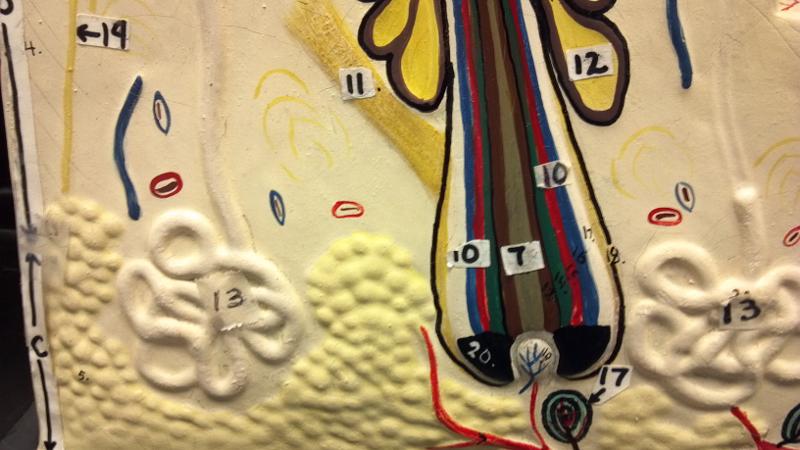

What is 11 in this picture?
Arrector Pili muscle
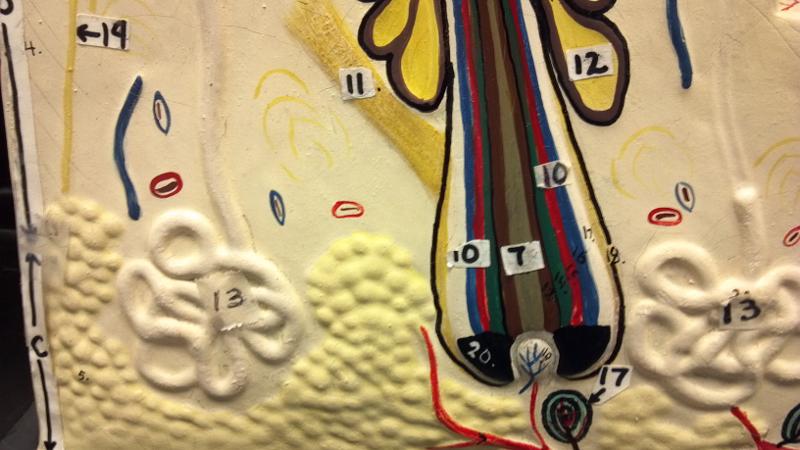

What is 12 in this picture?
Sebaceous gland(sweat)
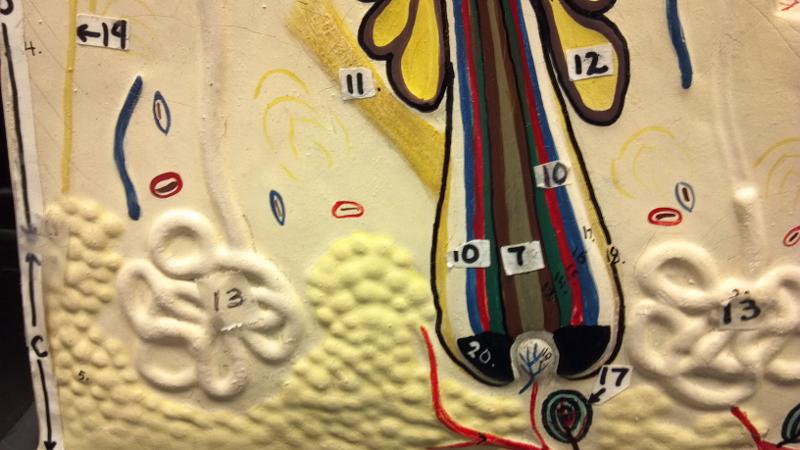

What is 13 in this picture?
Sudoriferous gland(oil)
What is 14 in this picture?
Duct of the Sudoriferous gland

What is 15 in this picture?
Pore of the Sudoriferous
What is 16 in this picture?
meissner's corpuscle(touch, light pressure)
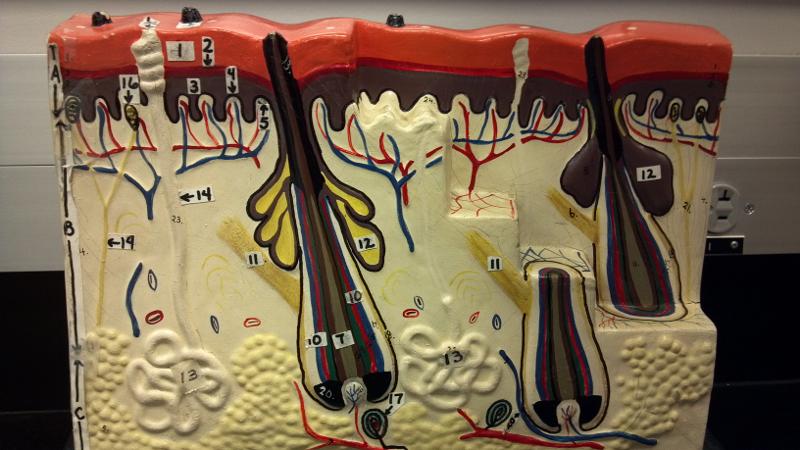
What is 17 in this picture?
pacinian corpuscle(heavy pressure)

What is 18 in this picture?
Adipose Tissue
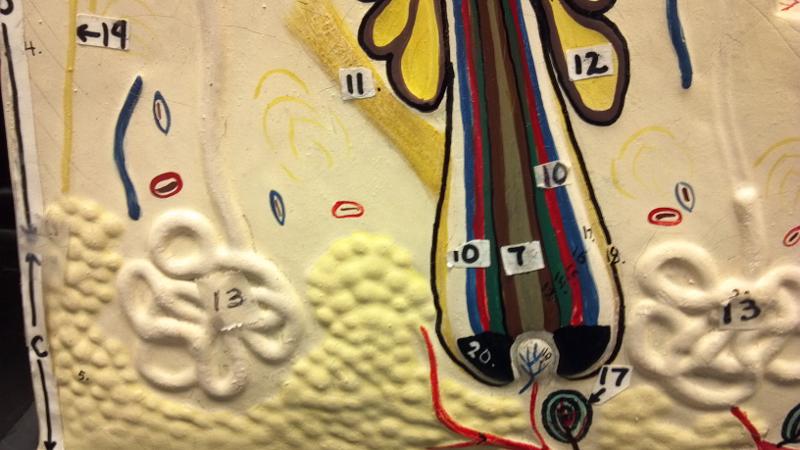

What is 19 in this picture?
Nerve
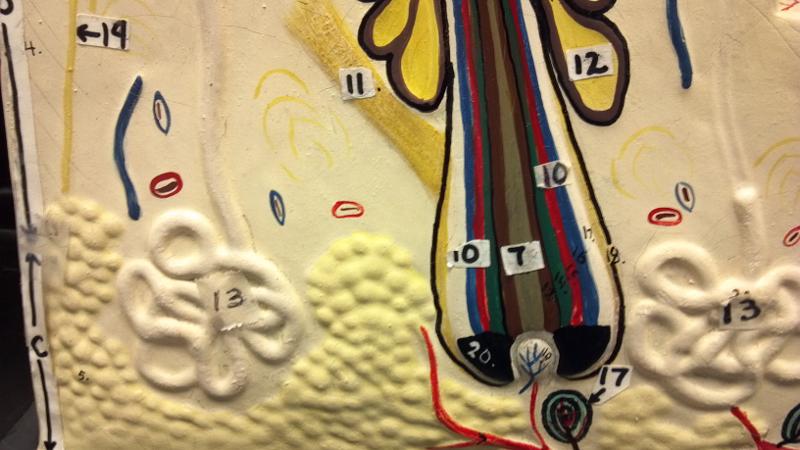

What is 20 in this picture?
blood vessels(red and blue)
Is the largest and most versatile organ in the body
Skin
What kind of tissue is skin composed of?
stratified squamous epithelium, dense connective tissue, areolar connective tissue, adipose connective tissue
A group of organs that function for a common purpose
system
What is the primary function of skin?
Protection
A chemical that helps waterproof skin is called?
keratin
What is the most superficial layer of the epidermis?
sratum corneum
What is the deepest layer of the epidermis?
Stratum basale(germinativum)
Where does an arrector pili muscle attach?
hair follicle
What is the function of stratum corneum?
barrier function of the skin
What is the function of stratum gerinativum (basale)
skin regeneration
What is the function of keratin?
strengthens skin and helps waterproof
What is the function of the papilla?
holds capillaries that provide nutrients to growing hair follicles
What is the function of sudoriferous glands
body temp regulation
What is the function of sebaceous glands?
oil secretion
What is the function of Arrector pili?
raise hair when cold or frightened
The dermis contains what layers?
hypodermis
What kind of connective tissue is in the hypodermis?
areolar and adipose connective tissue
The outermost cells of the epidermis is?
stratum corneum
The bottom layer of epidermis that constantly makes new cells and pushes them toward the top surface is?
stratum basale(germinativum)
The three major layers of the skin are?
epidermis, dermis and hypodermis
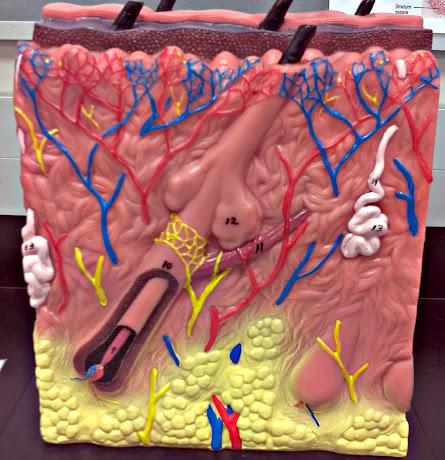
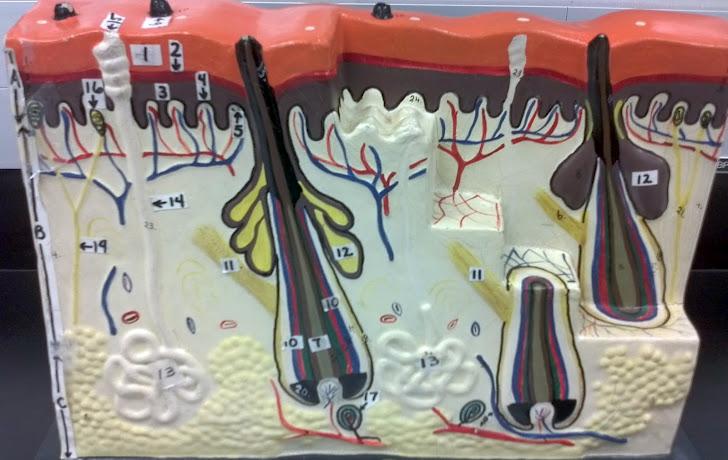
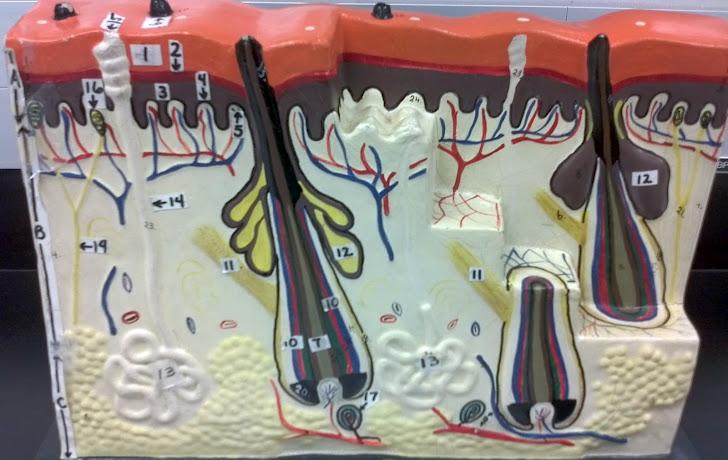
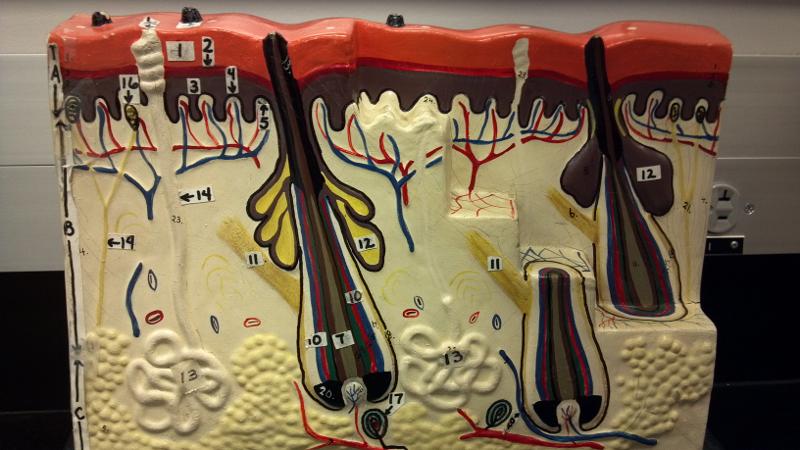
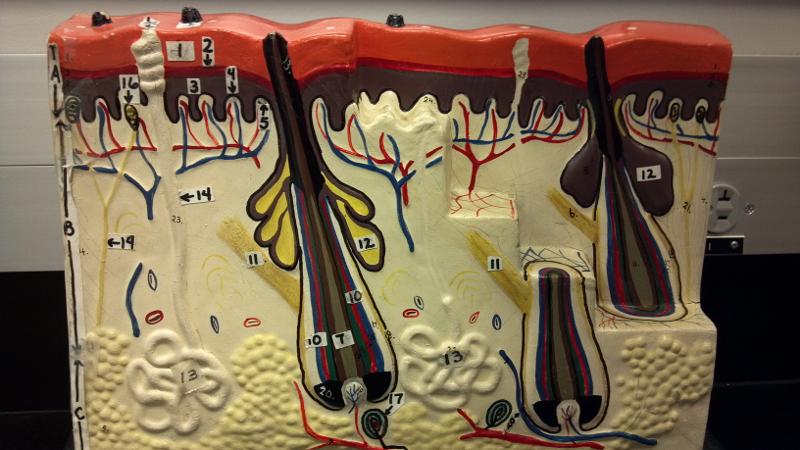
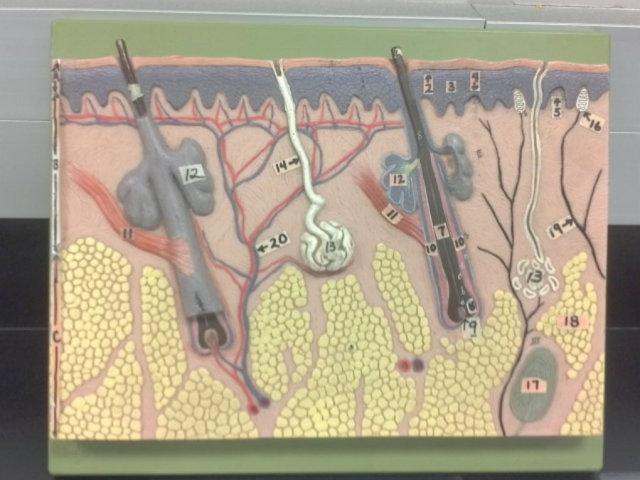
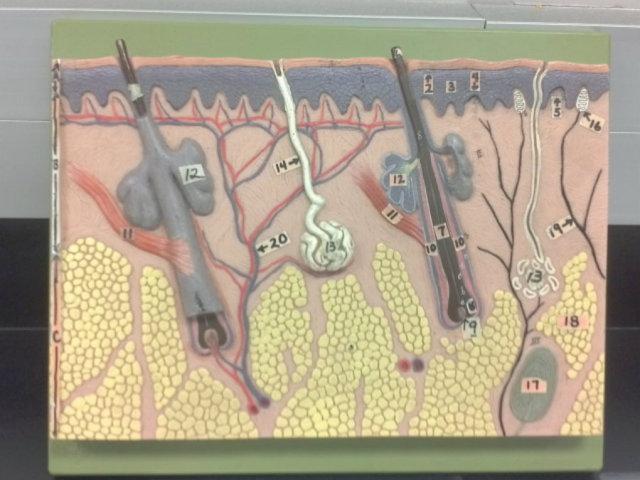
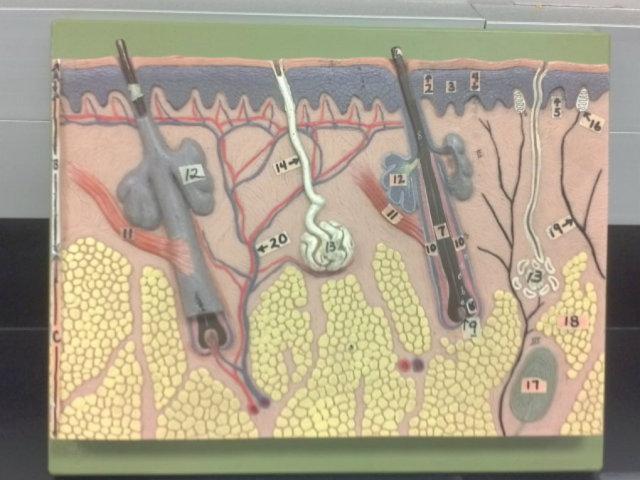
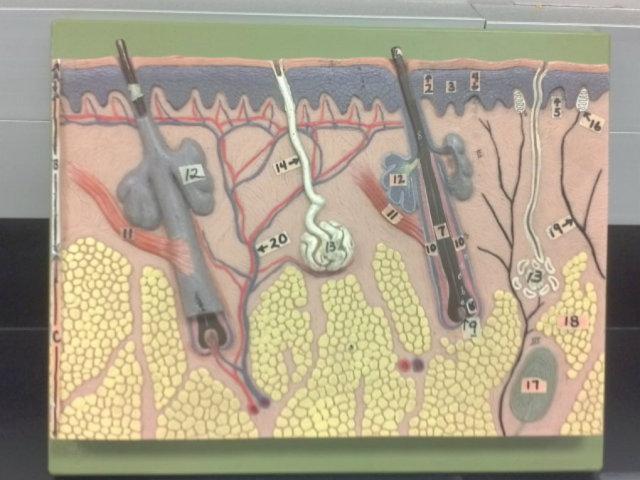
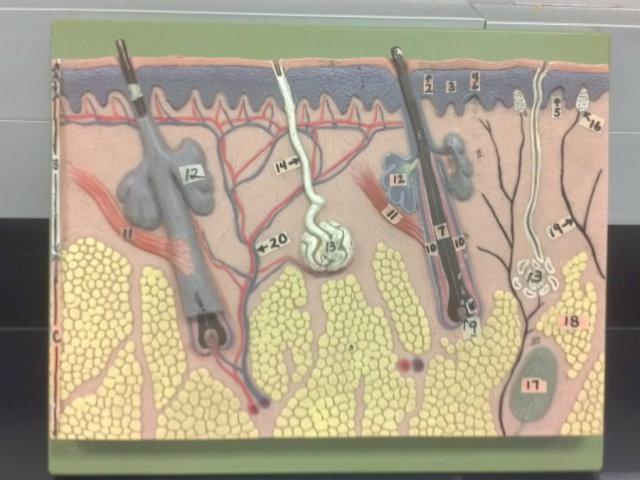
What is 9 in this picture?
Hair papilla
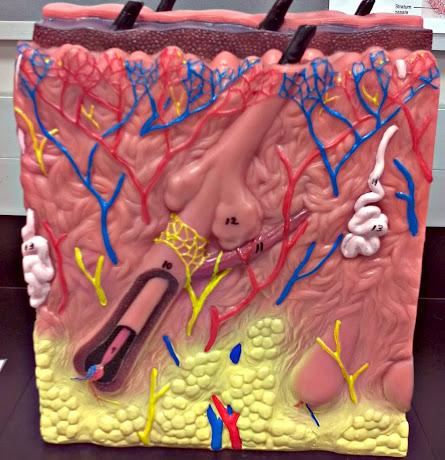
What is 10 of this picture?
Hair follicle
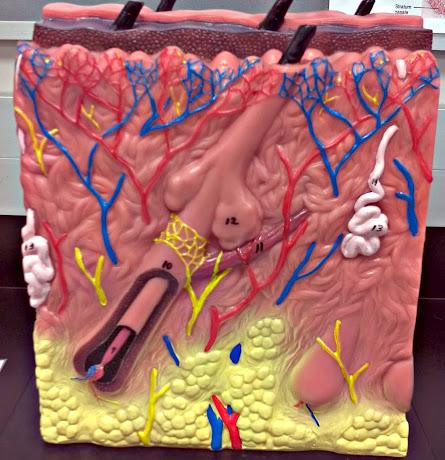
What is 11 in this picture?
arrector pillae muscle
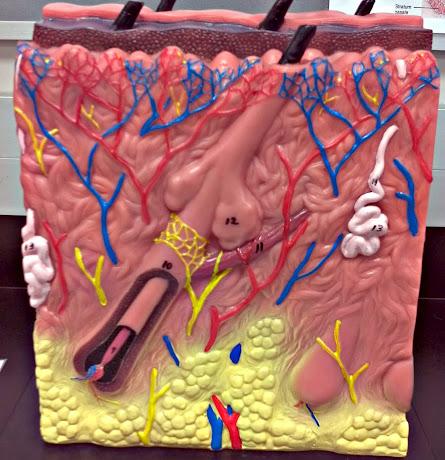
What is 12 in this picture?
sebaceous gland
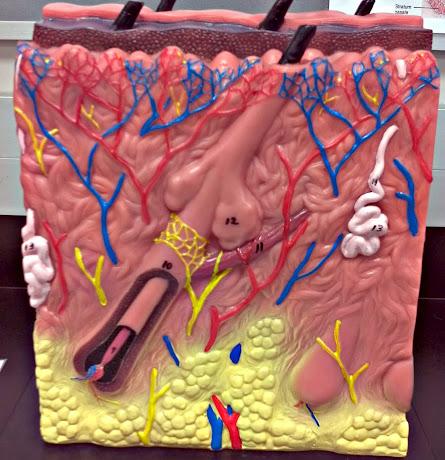
What is 13 in this picture?
sudoriferous gland
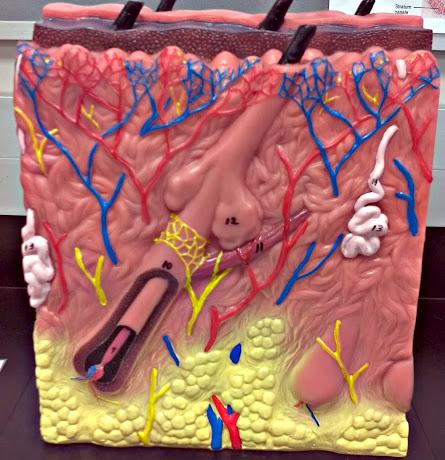
What is 14 in this picture?
duct of sudoriferous gland
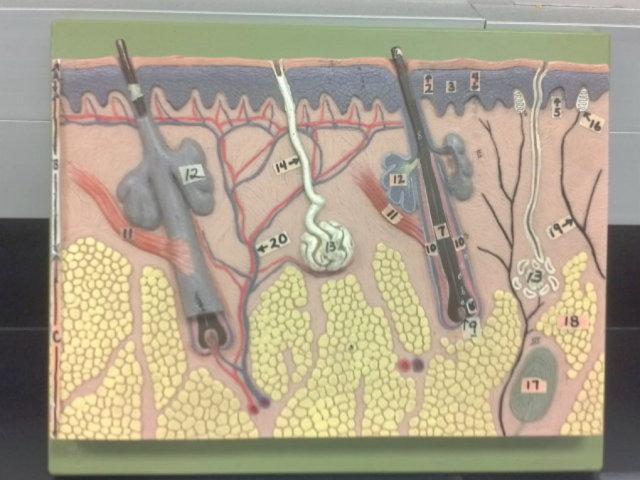
What is A in this picture?
Epidermis
What is B in this picture?
Dermis
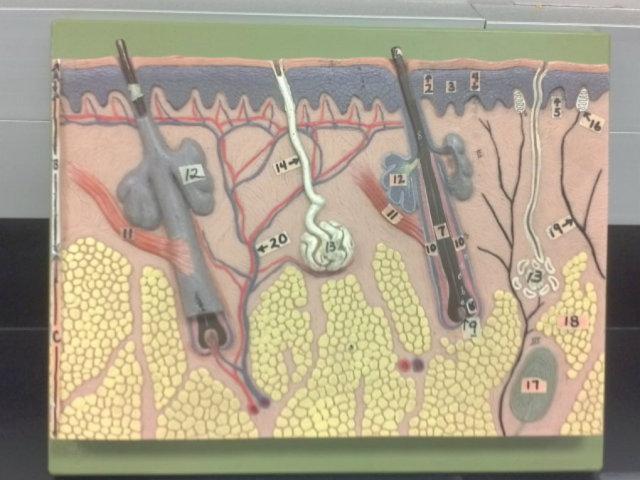
What is C in this picture?
Hypodermis
What is 1 in this picture?
Stratum corneum
What is 2 in this picture?
Stratum granulosum
What is 3 in this picture?
Stratum spinosum
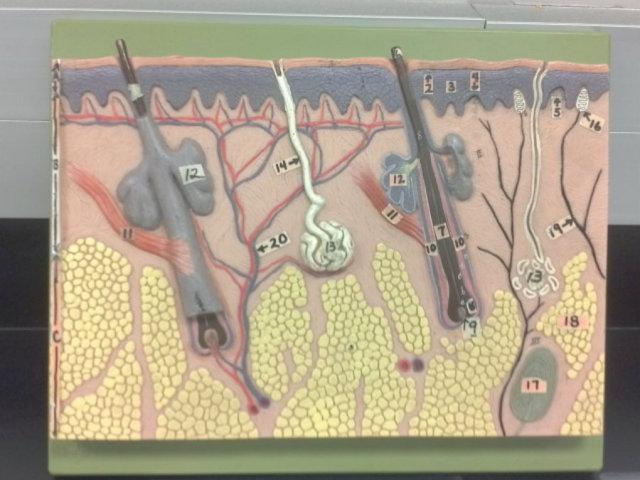
What is 4 in this picture?
Stratum basale
What is 5 in this picture?
Dermal Papilla
What is 6 in this picture?
hair shaft
What is 7 in this picture?
hair root
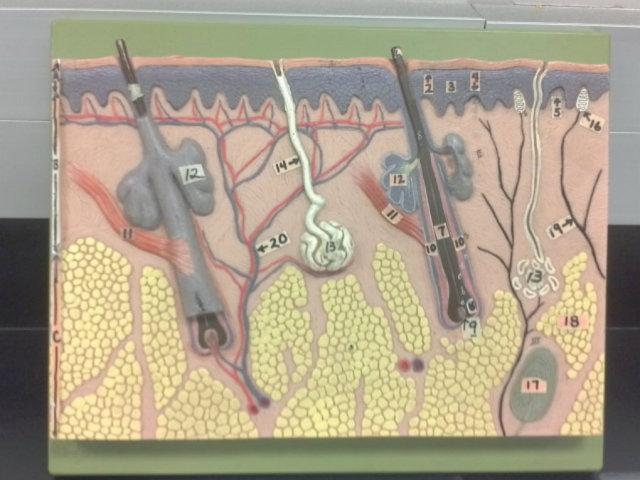
What is 8 in this picture?
hair bulb
What is 9 in this picture?
hair papilla
What is 10 in this picture?
Hair follicle
What is 11 in this picture?
Arrector Pilli muscle
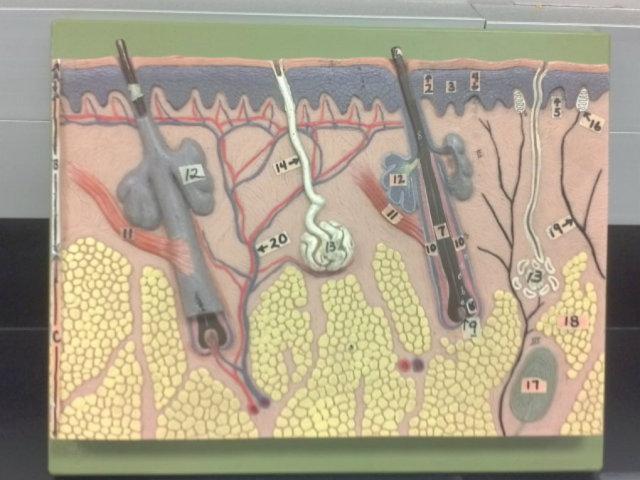
What is 12 in this picture?
Sebaceous gland(oil)
What is 13 in this picture?
sudoriferous gland(sweat)
What is 14 in this picture?
duct of sudoriferous
What is 16 in this picture?
meissner's corpuscle
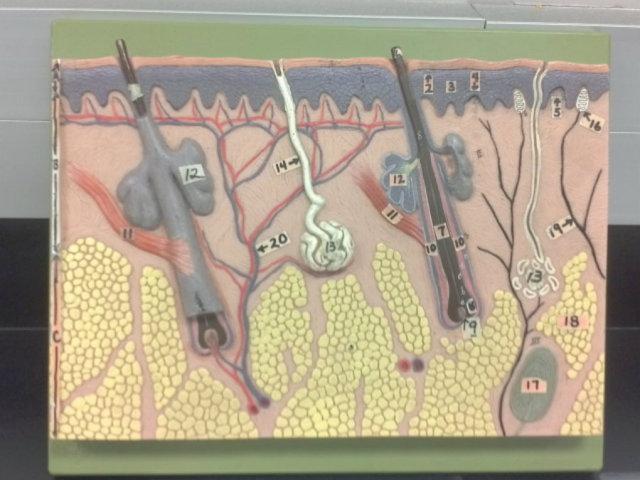
What is 17 in this picture?
pacinian corpuscle
What is 18 in this picture?
adipose tissue
What is 19 in this picture?
Nerve
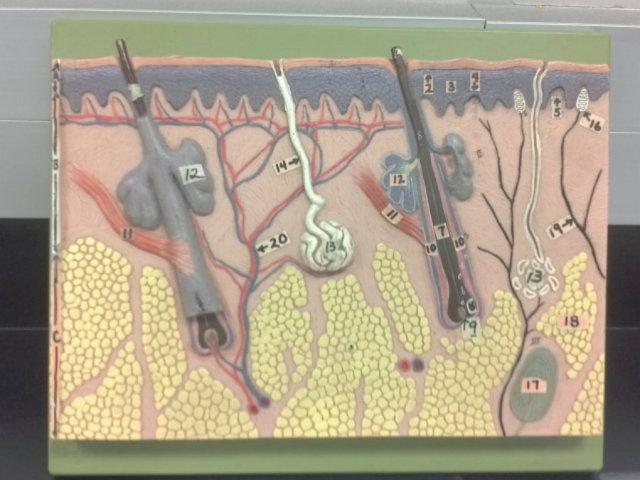
What is 20 in this picture?
Blood vessel
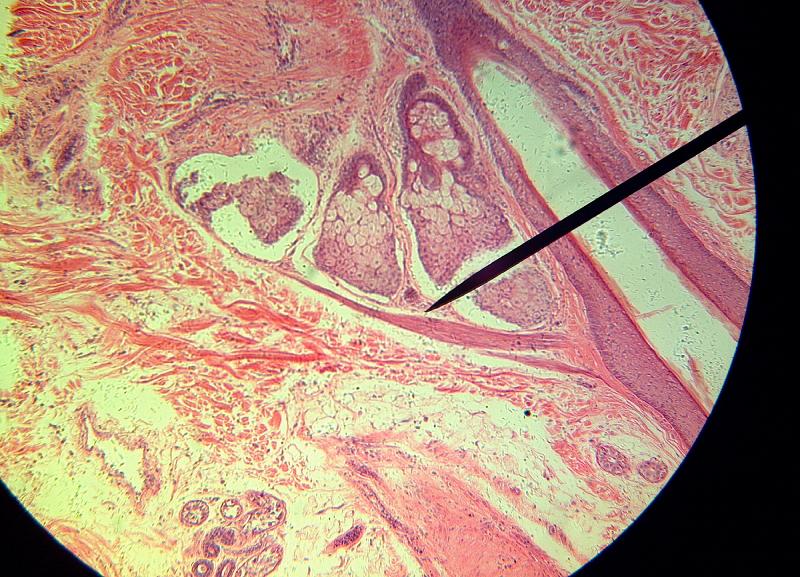
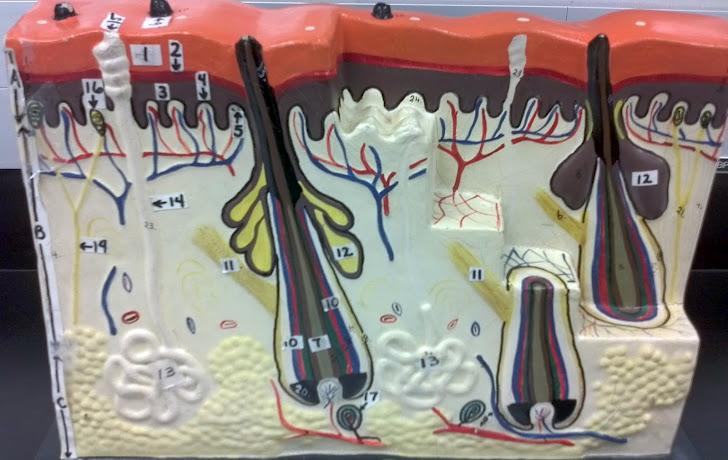
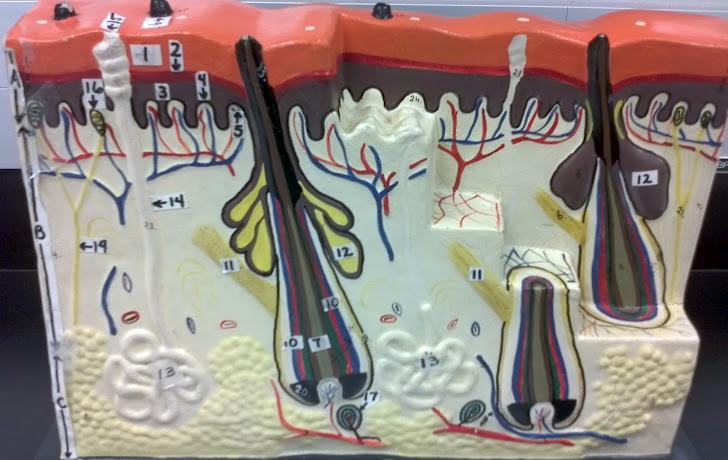
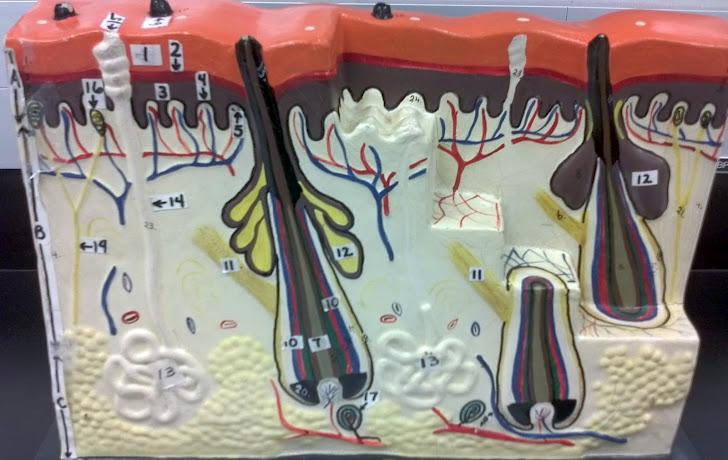
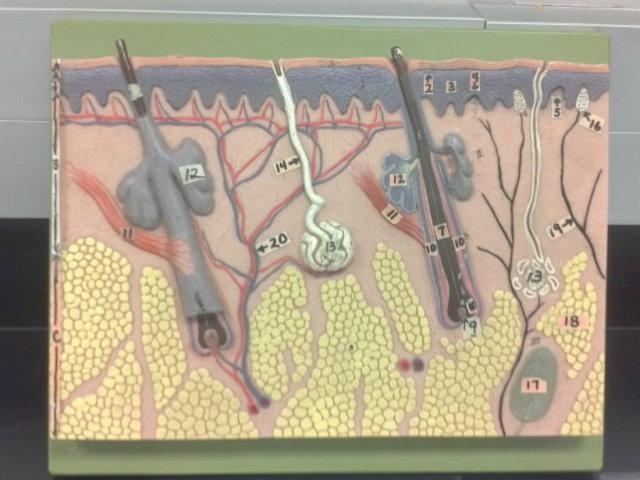
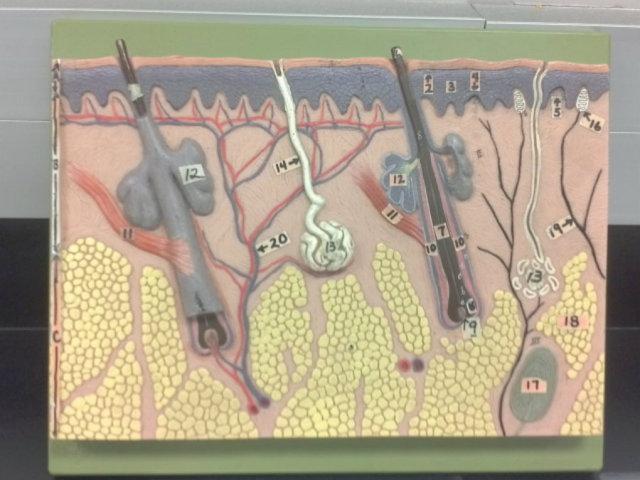
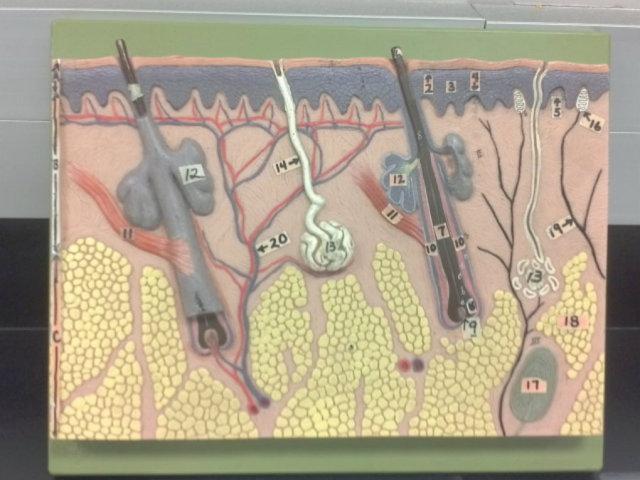
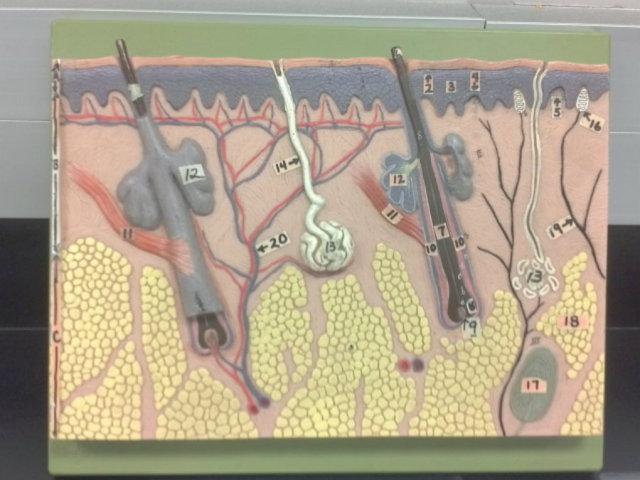
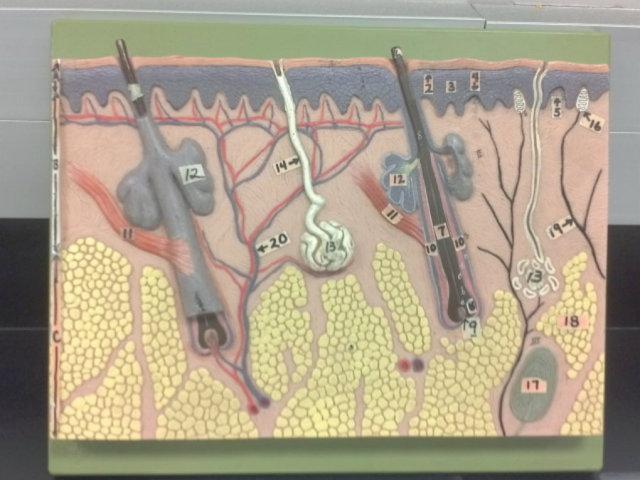
What is the pointer on in this picture?
Arrector Pillae
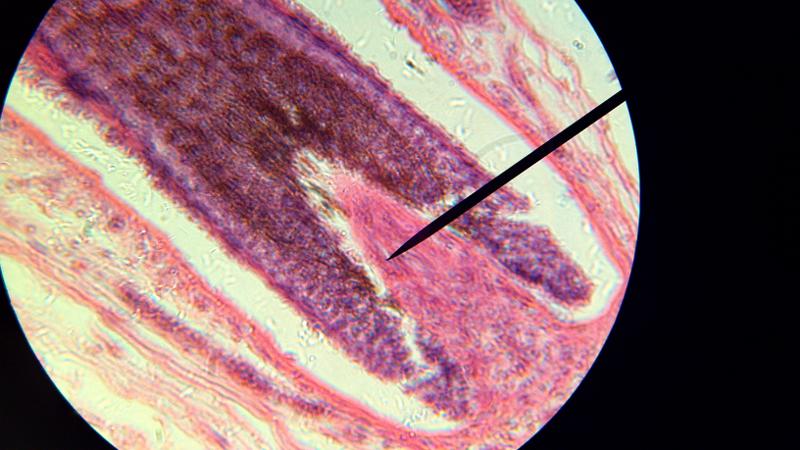
What is the pointer on in this picture?
Hair bulb/ Papilla
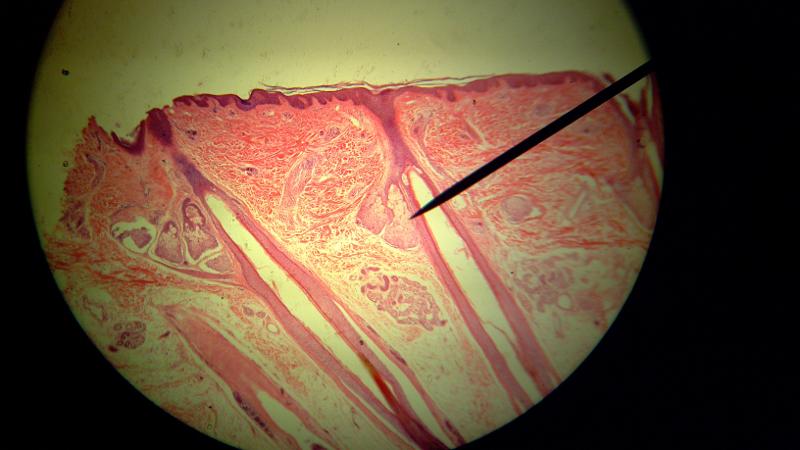
What is the pointer on in this picture?
Sebaceous gland
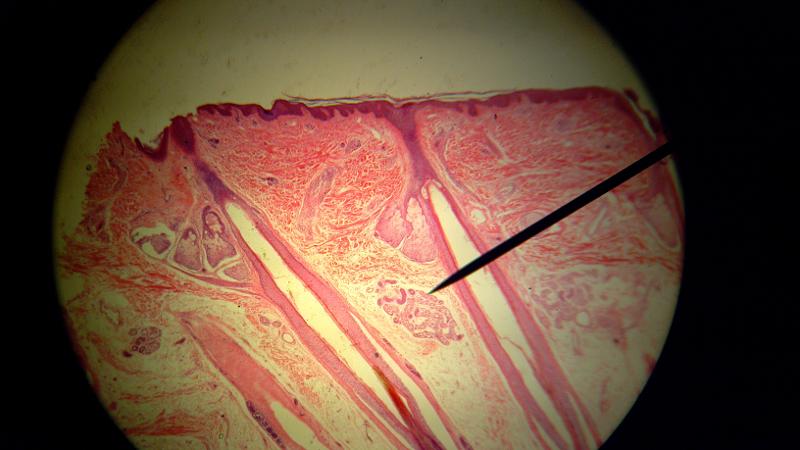
What is the pointer on in this picture?
Sudorifereous (sweat) gland
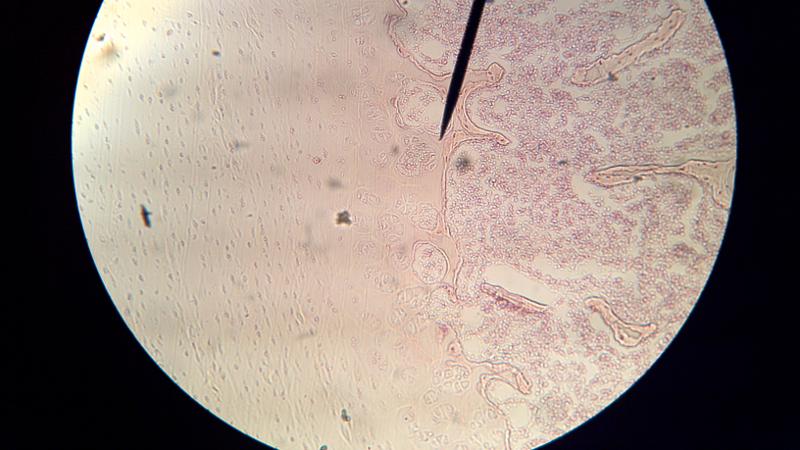
What is to the left of the pointer in this picture?
Hyaline cartilage
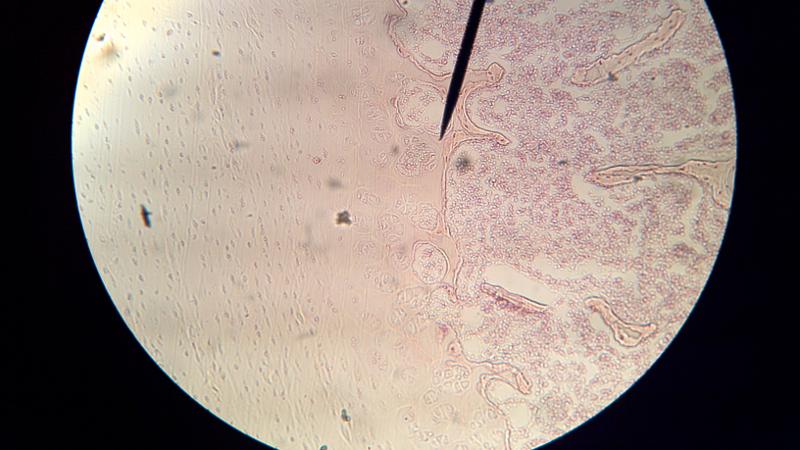
What is to the right of this picture?
Spongy bone

What are the arrows pointing to in this picture?
Epiphyseal plate

What is the thick white stuff in this picture?
Articular(hyaline) cartilage