Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 12: The CNS (Brain and Spinal Cord)
front 1 Development of the Neural Tube from Embryonic Ectoderm | back 1 4 steps: 1-neural plate forms from surface of ectoderm 2-the neural plate invaginates (folds), forming neural groove with neural folds 3-neural fold cells migrate to form neural crest, which forms much of the PNS and many other structures 4-the neural groove becomes the neural tube, which will form CNS structures |
front 2 Embryonic Ectoderm- Neural tube development: Step 1 | back 2 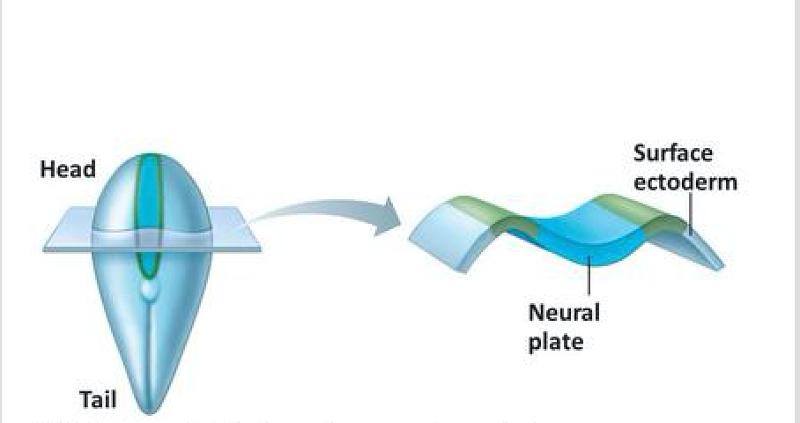 |
front 3 Embryonic Ectoderm- Neural tube development: Step 2 | back 3 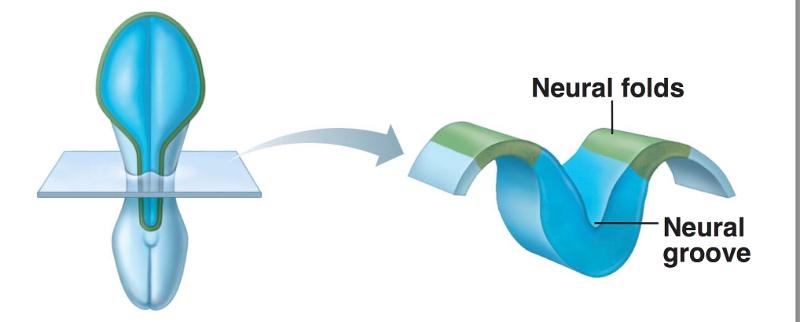 |
front 4 Embryonic Ectoderm- Neural tube development: Step 3 | back 4 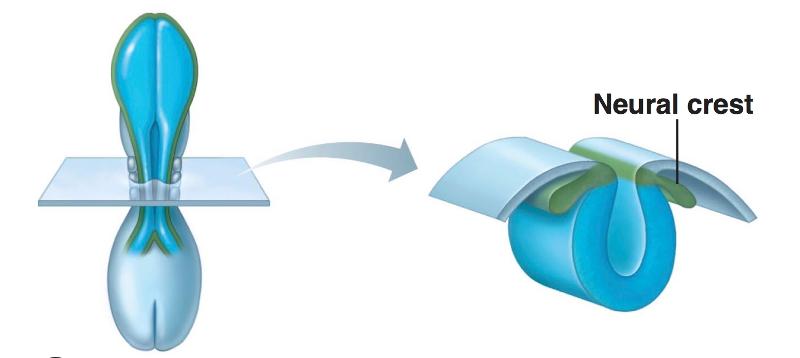 |
front 5 Embryonic Ectoderm- Neural tube development: Step 4 | back 5 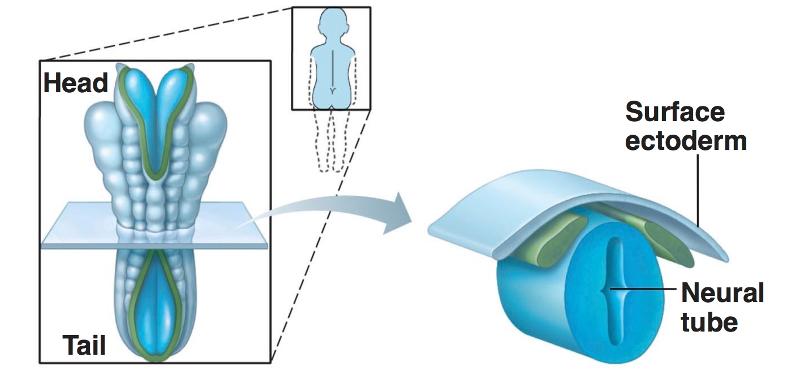 |
front 6 Embryonic Development of Human Brain | back 6 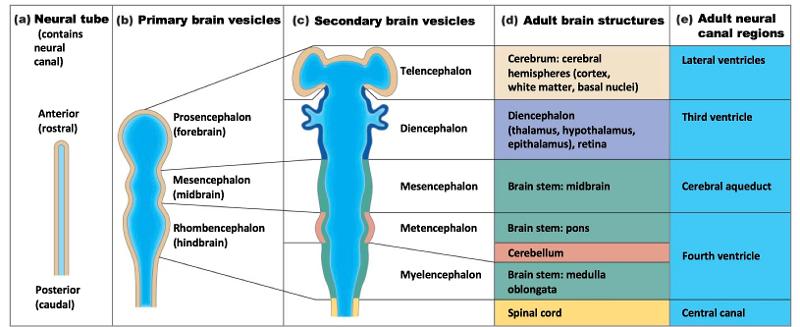 |
front 7 Neural Tube contains what important thing? | back 7 a neural canal has two sides: anterior and posterior |
front 8 Primary Brain Vesicles | back 8 Prosencephalon (forebrain) Mesencephalon (midbrain) Rhombencephalon (hindbrain) |
front 9 Secondary Brain Vesicles | back 9 1-Telencephalon (end brain) 2-Diencephalon (interbrain) 3-Mesencephalon (midbrain) 4-Metencephalon (after brain) 5-Myelencephalon (spinal brain) |
front 10 Telencephalon's Adult Brain Structures | back 10 Cerebrum: cerebral hemispheres (cortex, white matter, basal nuclei) |
front 11 Telencephalon's Adult Neural Region | back 11 Lateral Ventricles |
front 12 Diencephalon's Adult Brain Structures | back 12 Diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus), retina |
front 13 Diencephalon's Adult Neural Canal Region | back 13 Third Ventricle |
front 14 Mesencephalon's Adult Brain Structures | back 14 Brain stem: midbrain |
front 15 Mesencephalon's Adult Neural Canal Region | back 15 Cerebral Aquaduct |
front 16 Metancephalon's Adult Brain Structures | back 16 Brain Stem: pons Cerebellum |
front 17 Metencephalon and Myelencephalon share what neural canal region? | back 17 Fourth Ventricle |
front 18 Myelencephalon's Adult Brain Structure | back 18 Brain Stem: Medulla Oblongata |
front 19 Spinal Cord has what neural canal region? | back 19 Central Canal |
front 20 Effect of Space Restriction on Brain Development: Because the brain grows quicker than the skull... | back 20 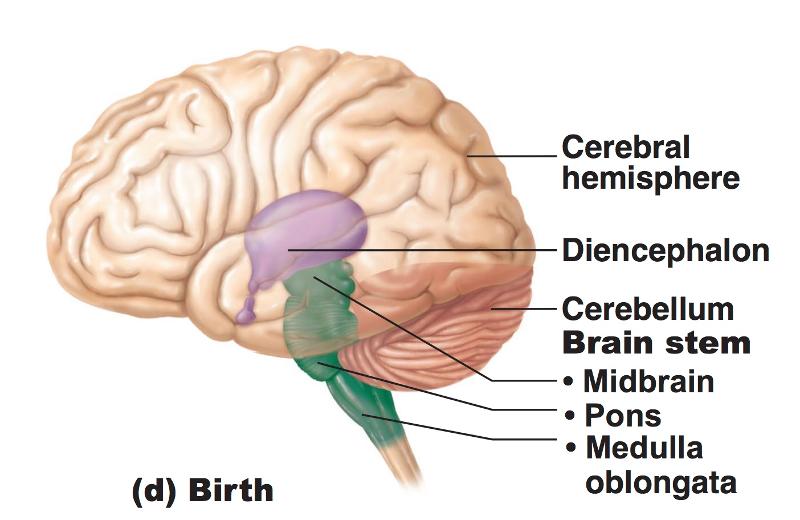 2 flexures develop...the midbrain flexure and the cervical flexure both move the forebrain toward the brain stem |
front 21 Effect of Space Restriction on Brain Development: Because the cerebral hemispheres are forced to take a horseshoe-shaped course and grow posteriorly and laterally... | back 21 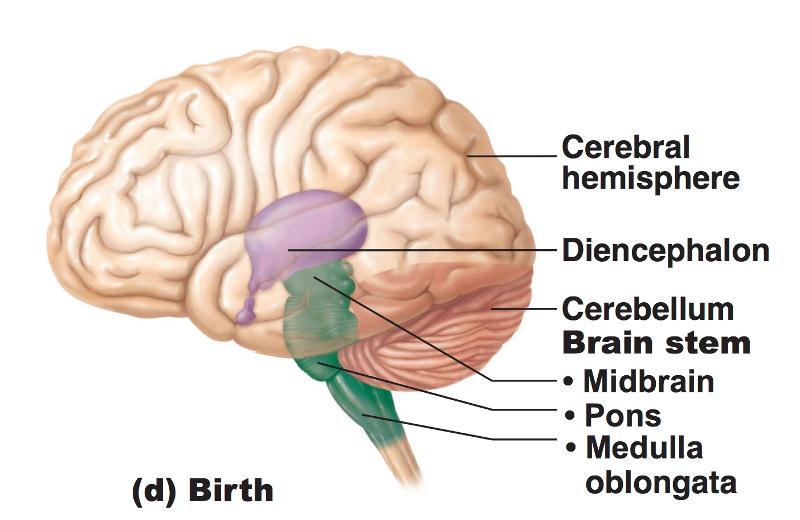 they grow back over and almost completely envelop the diencephalon and midbrain |
front 22 Effect of Space Restriction on Brain Development: By week 26, the further growth of cerebral hemispheres causes their surfaces to crease and fold, producing convolutions and increasing surface area to allow... | back 22 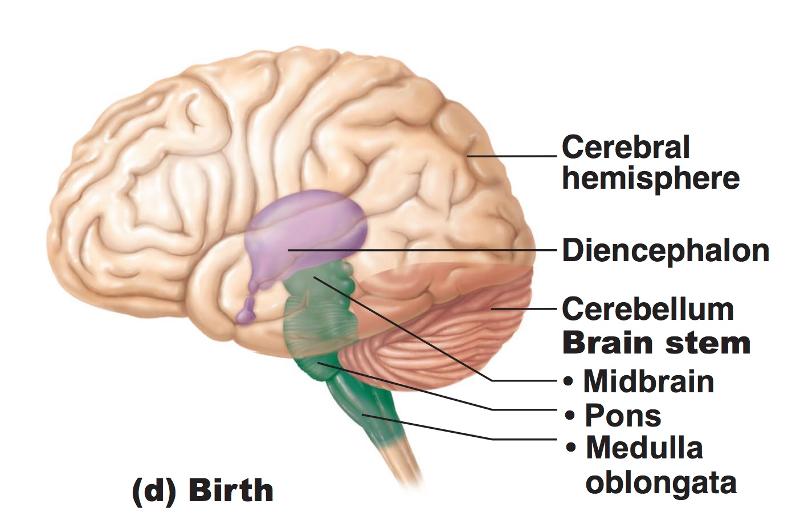 more neurons to occupy the limited space |
front 23 Ventricles in the brain | back 23 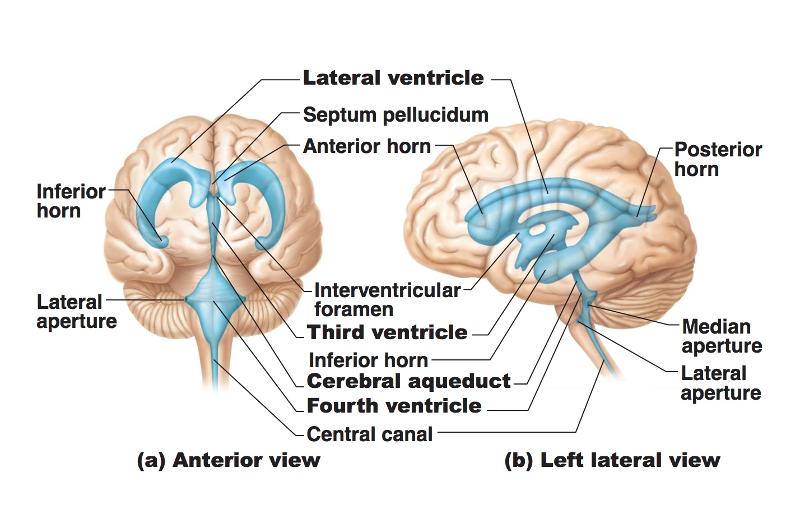 4 of them! Lateral Ventricle Third Ventricle Cerebral Aquaduct Fourth Ventricle |
front 24 Ventricles are lined with... | back 24 Ependymal Cells |
front 25 2 Lateral apertures and a single median aperture in the 4th ventricle are the openings that connect the 4 ventricles to the... | back 25 subarachnoid space |
front 26 The fluid that surrounds the brain, spinal cord, and ventricles is... | back 26 cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) |
front 27 The Cerebral Hemispheres take up... | back 27 85% of total brain mass |
front 28 Ridges/folds of the hemispheres are called... | back 28 Gyri |
front 29 "shallow grooves" are called... | back 29 sulci |
front 30 Sulci divide the brain into 5 hemispheres. What are they? | back 30 Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Insula |
front 31 "deep grooves" are called... | back 31 fissures |
front 32 What jobs do fissures have? | back 32 separate large regions of brain |
front 33 The median longitudinal fissure separates... | back 33 the brain into right and left hemispheres |
front 34 The transverse cerebral fissure separates... | back 34 the cerebral hemisphere from the cerebellum |
front 35 Lobes and Fissures of the Cerebral Hemispheres | back 35 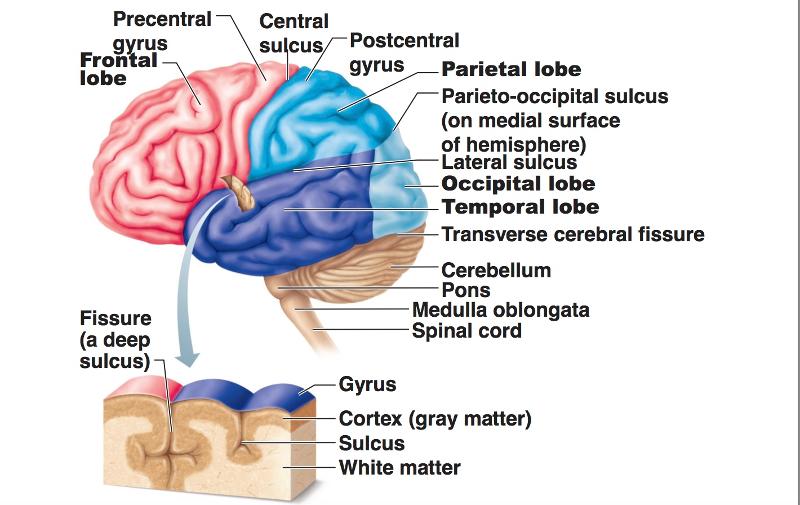 |
front 36 Cerebral Cortex Composition | back 36 outer layer of gray matter neuron cell bodies dendrites neuroglia cells blood vessels NO axon or fiber tracts!!! **billions of neurons arranged in 6 layers..(40% of brain mass) |
front 37 MRI of the cerebral cortex | back 37 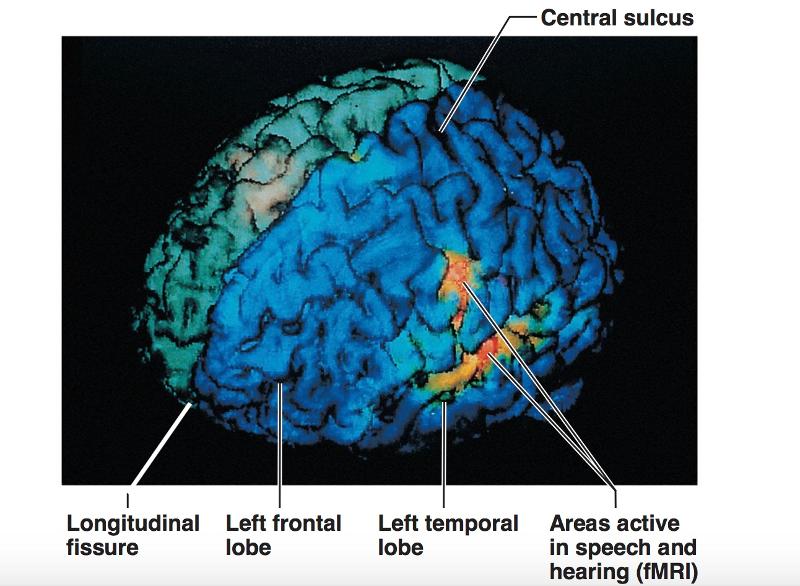 |
front 38 Brain Cortex: 3 kinds of Functional Areas | back 38 Motor areas Sensory areas Association areas |
front 39 All the neurons of the Brain Cortex are... | back 39 interneurons |
front 40 More Facts of Brain Cortex Function | back 40 each hemisphere controls the sensory and motor functions of the opposite side of the body some functions of the brain are mostly found in one side of the brain no functional area of the cortex acts alone conscious behavior involves the entire cortex in one way or another |
front 41 Functional and Structural Areas of the Cerebral Cortex | back 41 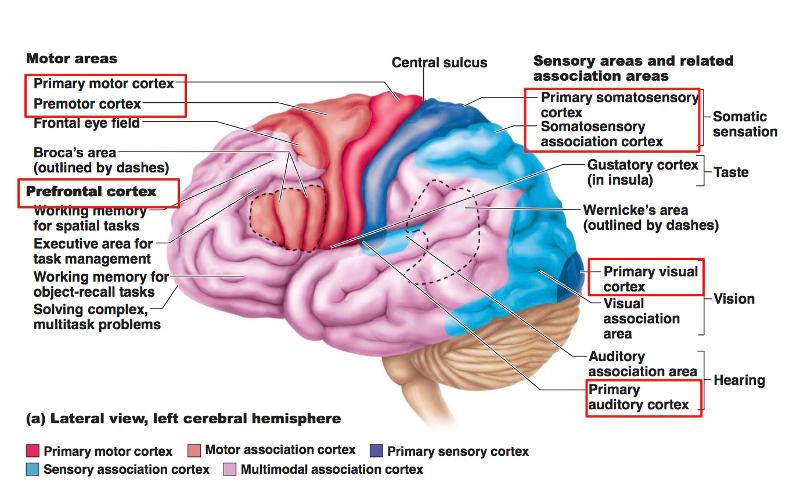 |
front 42 Cool map to help remember the important areas for structure and function | back 42 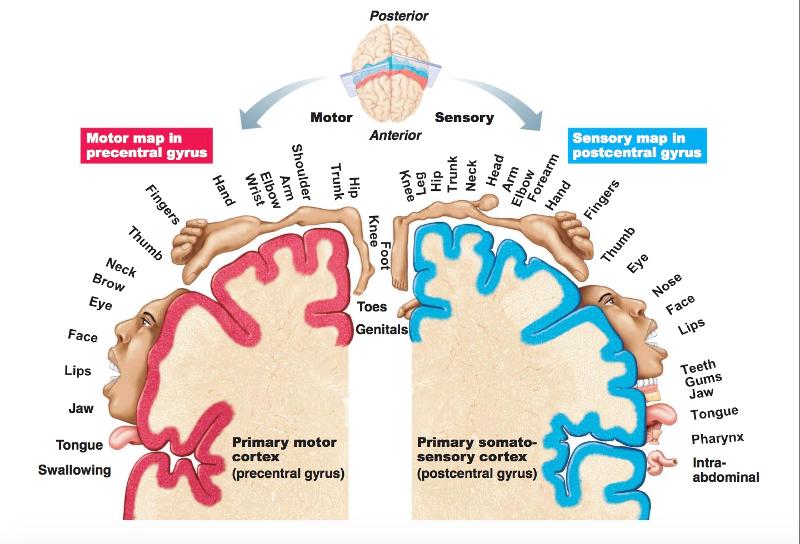 |
front 43 Primary Motor Cortex Location | back 43 pre central gyrus of frontal lobe |
front 44 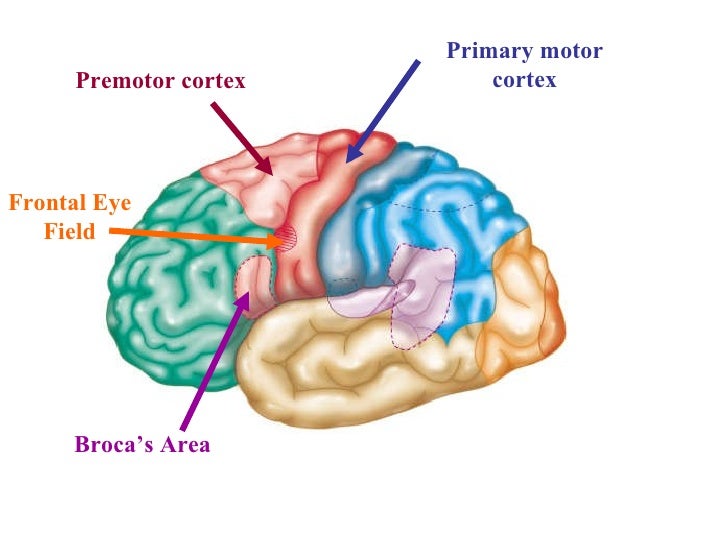 The Primary Motor Cortex has... | back 44 large neurons called pyramidal cells |
front 45 Pyramidal cells allow... | back 45 conscious control of muscles |
front 46 Pyramidal cells' long axons form... | back 46 motor tracts called pyramidal tracts (corticospinal tracts) in the spinal cord where innervation is contralateral (as in taking place on opposite sides) |
front 47 The kind of mapping where pyramidal cells controlling specific body parts are grouped together... | back 47 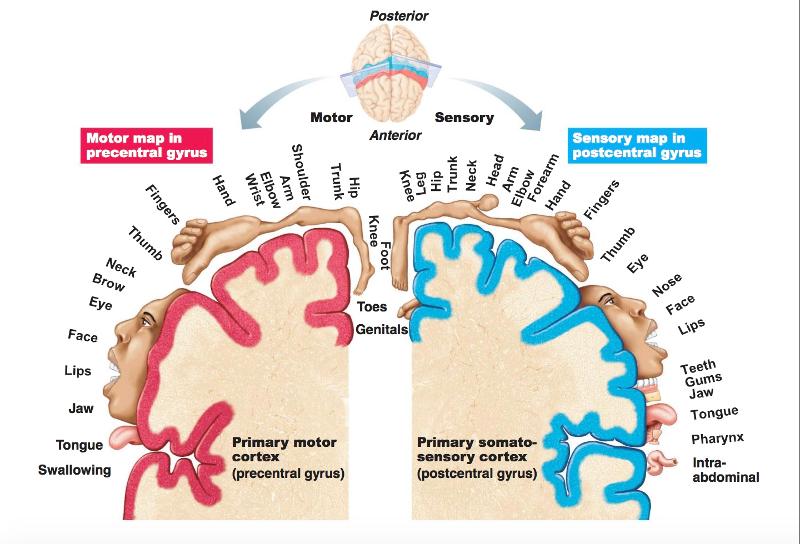 somatotopy |
front 48 Somatotopy's way of distorting the size of a figure to show how much gyrus is devoted to the body part is... | back 48 motor homunculi |
front 49 Premotor Cortex Location | back 49 just anterior to the precentral gyrus in the frontal lobe |
front 50  Premotor Cortex Job | back 50 Controls learned motor skills of a repetitious or patterned nature (ex: typing, piano, driving) |
front 51 Broca's Area Location | back 51 anterior to the inferior region of the premotor area present only in the left hemisphere |
front 52  Broca's Area Job | back 52 special motor speech |
front 53 Frontal Eye Field Location | back 53 partially in and anterior to the premotor cortex and superior to the Broca's Area |
front 54 Frontal Eye Field Job | back 54 controls voluntary movement of eyes |
front 55  Stroke Symptoms by Stroke Location: stroke to primary motor cortex | back 55 loss of voluntary control (paralysis) of muscle reflexes intact |
front 56  Stroke Symptoms by Stroke Location: stroke to premotor cortex | back 56 loss of muscle motor memory retain voluntary muscle control, but have to learn activities all over again reflexes intact |
front 57 Primary Somatosensory Cortex Location | back 57 in the post central gyrus of parietal lobe |
front 58 2 Groups of neurons that supply the Primary Somatosensory Cortex | back 58 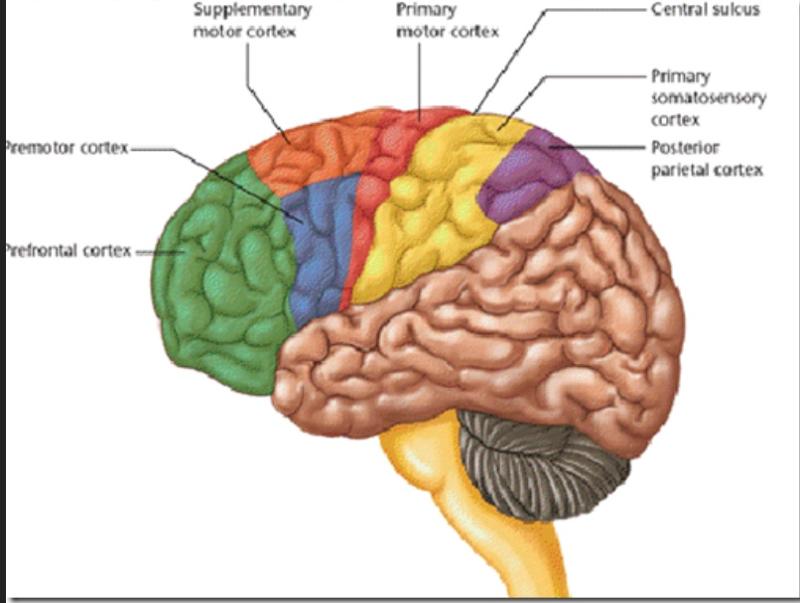 sensory skin receptors (touch) proprioceptors (position sense receptors) **give a sense of spatial discrimination and represented graphically by the somatosensory homunculus |
front 59 Somatosensory Association Cortex Location | back 59 just posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex |
front 60 Somatosensory Association Cortex Job | back 60 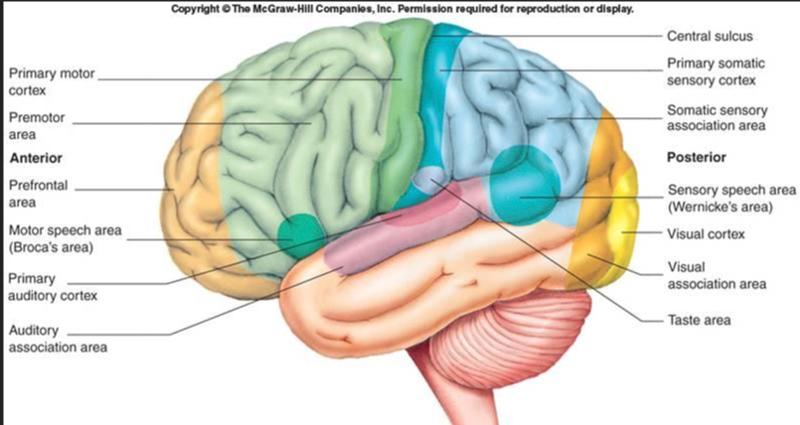 integrate sensory inputs as in temperature, pressure, texture, size, memory used when you pick up an object in your pocket without looking at it/feeling for something in the dark |
front 61 Visual Areas of the Cortex Location | back 61 on the extreme posterior tip of the occipital lobe buried deep in the calcarine sulcus |
front 62 Visual Areas of the Cortex Job | back 62 receives visual info from the retinas |
front 63 Visual Association Area Location | back 63 surrounds primary visual cortex and covers much of the occipital lobe |
front 64 Visual Association Area Job | back 64 uses past visual experiences to interpret visual stimuli enables us to recognize and appreciate what we see |
front 65 Primary Auditory Cortex Location | back 65 each one is located in the superior margin of the temporal lobe abutting the lateral sulcus |
front 66 Primary Auditory Cortex Job | back 66 interprets pitch, loudness, location |
front 67 Auditory Association Area Job | back 67 permits perception of sound stimulus: understanding what we hear storing memories of sound Wernick's Area includes parts of the Auditory Cortex |
front 68 Primary Olfactory (smell) Cortex Location | back 68 on the medial aspect of the temporal lobe |
front 69 Primary Olfactory Cortex Job | back 69 makes us aware of different odors |
front 70 Gustatory Cortex Location | back 70 in the insula, deep in the temporal lobe |
front 71 Gustatory Cortex Job | back 71 involved in the perception of taste |
front 72 Visceral Sensory Area Location | back 72 in cortex of insula, posterior to gustatory cortex |
front 73 Visceral Sensory Area Job | back 73 perception of visceral sensations: upset stomach, full bladder, constipation.. |
front 74 Vestibular (Equilibrium) Cortex Location | back 74 posterior insula, deep in the Temporal Lobe |
front 75 Vestibular (Equilibrium) Cortex Job | back 75 helps with conscious awareness of balance, head position |
front 76 Multimodal Association Areas: sensory information flow in the brain (direction) | back 76 1st-to the primary sensory cortex (you can see the words on the test) 2nd-to the sensory association cortex (you recognize the words as something you read) 3rd-to the multimodal association cortex (the words you read have meaning, based on memory) |
front 77 3 Parts of the Multimodal Association Cortex | back 77 Anterior Association Area (prefrontal cortex) Posterior Association Area Limbic Association Area |
front 78 Anterior Association Area (prefrontal cortex) Location | back 78 frontal lobe |
front 79 Anterior Association Area (prefrontal cortex) Job | back 79 intellect, complex learning, recall, personality, working memory, abstract ideas, judgment, reasoning, persistence, planning heavily dependent on positive and negative feedback from one's social environment |
front 80 Posterior Association Area Location | back 80 temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes |
front 81 Posterior Association Area Job | back 81 role in recognizing patterns, faces, localization, binding sensory inputs, understanding written and spoken language way to remember: mmm..look at that guy's posterior! |
front 82 Limbic Association Area Location | back 82 cingulate gyrus, hippocampus areas |
front 83 Limbic Association Area Job | back 83 provides the emotional impact of a scene |
front 84 Lateralization means that... | back 84 each hemisphere has some unique abilities |
front 85 in 90%, the left hemisphere is dominant for... | back 85 language, math, logic |
front 86 in 90%, the right hemisphere is dominant for... | back 86 visual-spacial, intuition, emotion, art, music |
front 87 90% of people with left hemisphere dominance tend to be... | back 87 right-handed |
front 88 In 10% of people, the roles of the hemispheres... | back 88 are reversed or share functions equally |
front 89 Cerebral White Matter consists largely of... | back 89 myelinated fibers bundled into large tracts |
front 90 Tract Name Classification is determined by... | back 90 the direction in which they run |
front 91 The 3 Tract Classification Names | back 91 Commissural Tracts Association Fibers Projection Fibers |
front 92 Commissural Tract Example | back 92 corpus callosum--it connects the right and left hemispheres |
front 93 Association Fibers Job | back 93 Connect different parts of the same hemisphere |
front 94 Projection Fibers Job | back 94 connect the cerebral hemispheres to the lower brain and spinal cord |
front 95 Basal Nuclei are... | back 95 spots deep in the brain where large groups of neuron cell bodies are located |
front 96 The 3 groups of basal nuclei/neuron cell bodies | back 96 Caudate nucleus Putamen Globus Pallidus |
front 97 Basal Nuclei Job | back 97 important in starting, stopping, and monitoring the intensity of movements executed by the cortex, especially if they are slow or stereotyped ex: swinging arms when walking AND inhibit unwanted movements ex: absent in Huntington's Chorea and Parkinson's Dz--Chorea (dance) |
front 98 The Thalamus is... | back 98 one of the Diencephalon brain structures composed of multiple separate nuclei 2 egg-shaped collections of nuclei in the center of the brain with a small space between them called the 3rd ventricle |
front 99 3rd Ventricle | back 99 a space between 2 egg-shaped collections of nuclei inside the thalamus |
front 100 Interthalamic adhesion (intermediate mass) is a.. | back 100 small connection between the 2 egg-shaped collections of nuclei inside the thalamus |
front 101 Thalamus Jobs | back 101 sorting and editing information processing touch, pressure, pain directing information to appropriate locations |
front 102 Hypothalamus is... | back 102 below the thalamus |
front 103 Hypothalamus composition | back 103 mammillary bodies infundibulum |
front 104 Mammillary bodies are... | back 104 relay stations in the olfactory pathway |
front 105 The infundibulum is... | back 105 the connecting stalk of pituitary |
front 106 Hypothalamus Jobs (multiple) | back 106 autonomic control center center for emotional response body temp regulation regulation of food intake regulation of water balance and thirst regulation of sleep-wake cycles control of endocrine system functioning |
front 107 Epithalamus Location | back 107 most dorsal part of the diencephalon forms the roof of the third ventricle pineal gland is located here |
front 108 Pineal Gland (body) Jobs | back 108 secretes the hormone melatonin to regulate the sleep-wake cycle |
front 109 Brain Stem Composition | back 109 midbrain pons medulla oblongata |
front 110 10 of the 12 cranial nerves come out of the... | back 110 Brain Stem |
front 111 Midbrain Location | back 111 between the diencephalon and the pons |
front 112 Cerebral Aquaduct Location | back 112 in the middle of the midbrain joining the 3rd and 4th ventricles |
front 113 surrounding the Cerebral Aqueduct is the... | back 113 periaquaductal gray matter |
front 114 periaquaductal gray matter jobs | back 114 involved in pain suppression and serves as a link for the fight-flight response |
front 115 The 3rd and 4th cranial nerves are located here... | back 115 Midbrain |
front 116 Pons Location | back 116 in between the midbrain and medulla oblangata |
front 117 Behind the pons is the... | back 117 4th ventricle |
front 118 Nuclei for CN V, CN VI, and CN VII are here... | back 118 Pons |
front 119 Medulla Oblongata Location | back 119 between the pons and the spinal cord |
front 120 Pyramids are located at the lowest part of the... | back 120 Medulla Oblangata |
front 121 Pyramids are... | back 121 a collection of longitudinal fibers |
front 122 Decussation of the pyramids | back 122 fibers that cross from left to right and vice versa (the cross-over point) |
front 123 CN nuclei located in the medulla oblongata are... | back 123 CN VIII, CN IX, CN X, CN XI, CN XII |
front 124 Medulla Oblongata Jobs | back 124 Cardiovascular center (for heart rate) Respiratory center (for rate of breathing) vomiting, hiccuping, swallowing, sneezing, coughing (reflexes) |
front 125 Cerebellum means | back 125 "small brain" |
front 126 Cerebellum Location | back 126 behind the pons and medulla below the transverse cerebral fissure |
front 127 Cerebellum Jobs | back 127 precise contraction of skeletal muscles for smooth, coordinated movements (as in driving, typing, sports) all of these functions are subconscious |
front 128 Limbic System Jobs | back 128 emotional or affective feelings helps recognize facial expressions helps assess danger elicits fear response |
front 129 Psychosomatic Illness | back 129 a connection with an emotion that can induce an illness (like anxiety) |
front 130 Reticular Formation Location | back 130 extends through the core of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain |
front 131 Reticular Activating System Job | back 131 sends continuous stream of impulses to the cerebral cortex to keep it alert and enhance excitability can filter out familiar or weak signals so you can focus on new things |
front 132 Why can you ignore background noise while doing something? | back 132 The Reticular Activating System* |
front 133 Meninges Location | back 133 layers around the brain |
front 134 3 Layers of Meninges | back 134 Dura mater Arachnoid mater Pia mater |
front 135 Falx Cerebri Falx Cerebelli Tentorium Cerebelli | back 135 are partitions that subdivide the cranial cavity of the dura mater |
front 136 Falx Cerebri location | back 136 between right and left hemispheres |
front 137 Falx Cerebelli location | back 137 between right and left cerebellum |
front 138 Tentorium Cerebelli location | back 138 separates the cerebrum and cerebellum |
front 139 Arachnoid mater contains the... | back 139 subdural space and subarachnoid space |
front 140 Subarachnoid space is between...and is filled with... | back 140 the arachnoid mater and pia mater CSF |
front 141 The Pia mater is... | back 141 directly attached to the brain |
front 142 Dural Septa and Dural Venous Sinuses | back 142 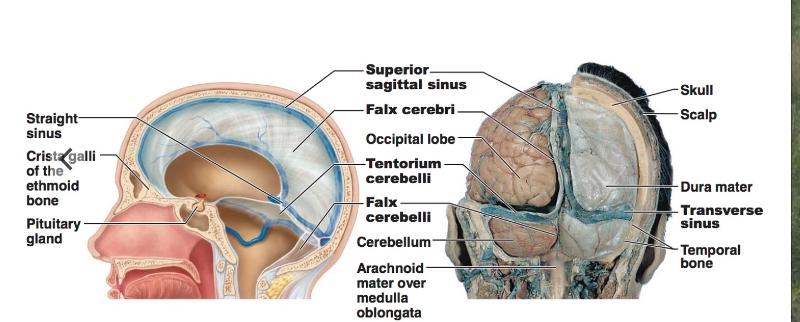 ex: falx cerebri, falx cerebelli, tentorium cerebelli |
front 143 Cerebrospinal Fluid Location | back 143 in and around spinal cord and brain |
front 144 CSF Jobs | back 144 protects brain and spinal cord |
front 145 Choroid Plexus is found... It is... | back 145 in the roof of each ventricle a bunch of capillaries where CSF is released |
front 146 CSF is constantly... | back 146 being formed and reabsorbed replaced every 8 hours about 500 ml is formed per day |
front 147 Circulation of CSF | back 147 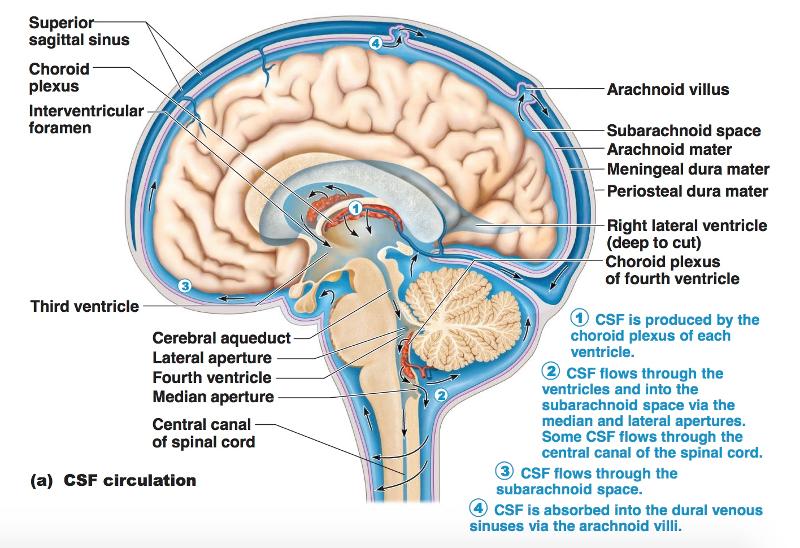 lateral ventricles --> foramen of Monro/third ventricle --> aqueduct of Sylvius --> fourth ventricle --> foramina of Magendie and Luschka --> subarachnoid space over brain and spinal cord --> reabsorption into venous sinus blood via arachnoid granulations |
front 148 Hydrocephalus | back 148 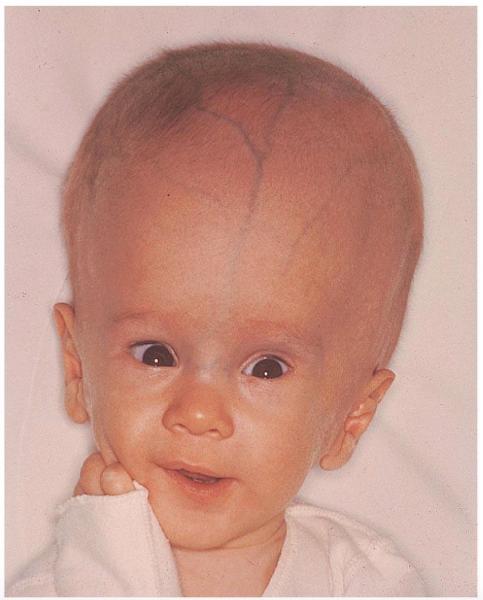 CSF accumulation |
front 149 The Spinal Cord is protected by the... | back 149 spinal dura mater and CSF and an epidural space is exterior to the spinal dura mater |
front 150 Spinal Cord tip ends at about | back 150 L1 or L2 |
front 151 Cone-shaped end of the spinal cord is the... | back 151 conus medullaris |
front 152 Cauda equina is... | back 152 a bunch of sacral nerve fibers that come out of the conus medullaris like a horse tail |
front 153 What is the best area to do a lumbar spinal tap? | back 153 the cauda equina |
front 154 Spinal cord Cross-Sectional Anatomy | back 154 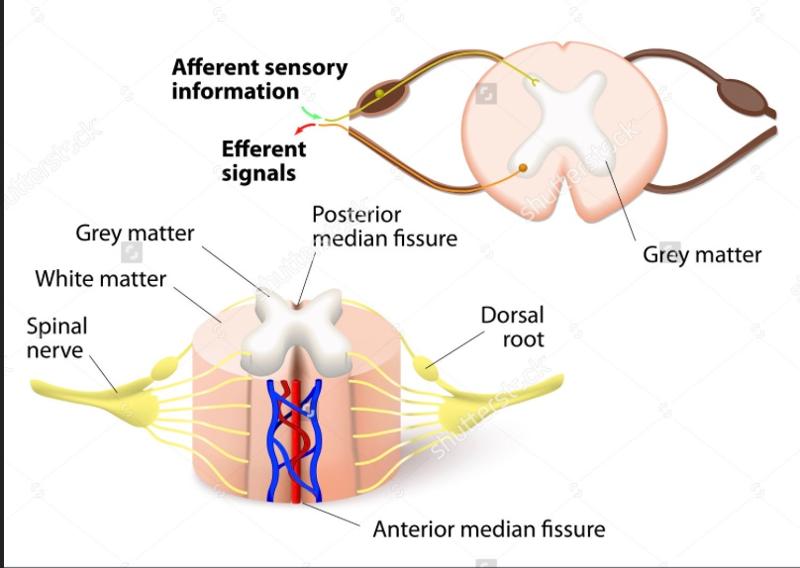 The gray matter of the spinal cord looks like the letter "H" or like a "butterfly" central canal |
front 155 The middle of the spinal cord is the... | back 155 central canal |
front 156 2 posterior projections of the spinal cord's gray matter are... | back 156 the dorsal horns |
front 157 Dorsal Horns Jobs | back 157 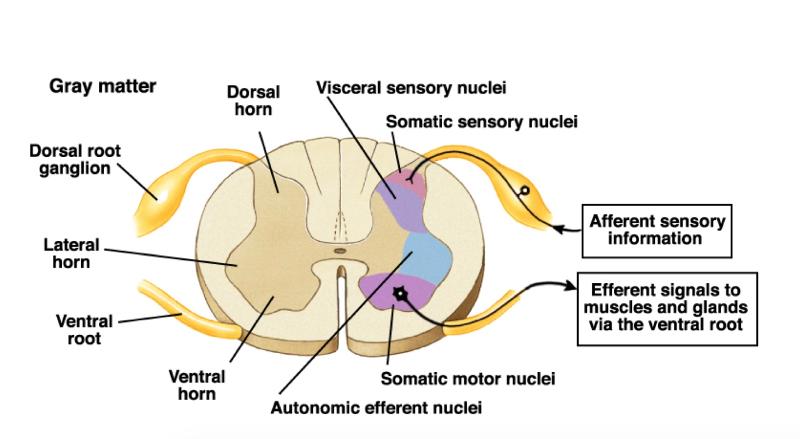 where afferent fibers bring info into the spinal cord where a dorsal root ganglion is part of the entering nerve ex: nerve fiber stretched by reflex hammer |
front 158 2 anterior projections of the spinal cord's gray matter are... | back 158 the ventral horns |
front 159 Ventral Horns Jobs | back 159 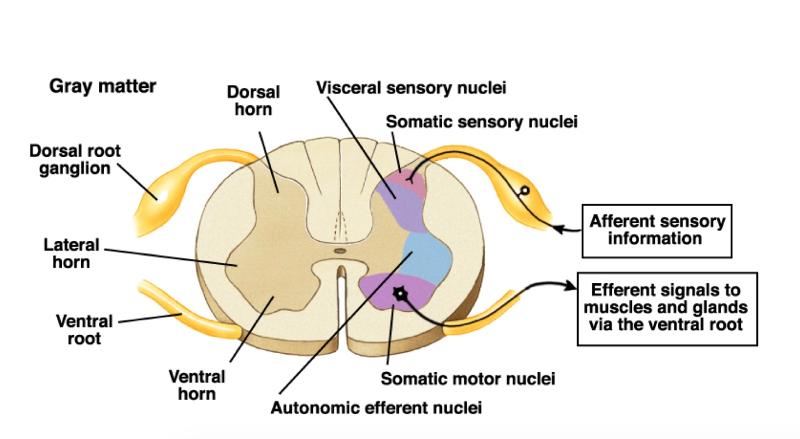 where efferent fibers project information out of the spinal cord ex: muscle is stimulated by nerve to contract |
front 160 Lumbar Tap Puncture | back 160 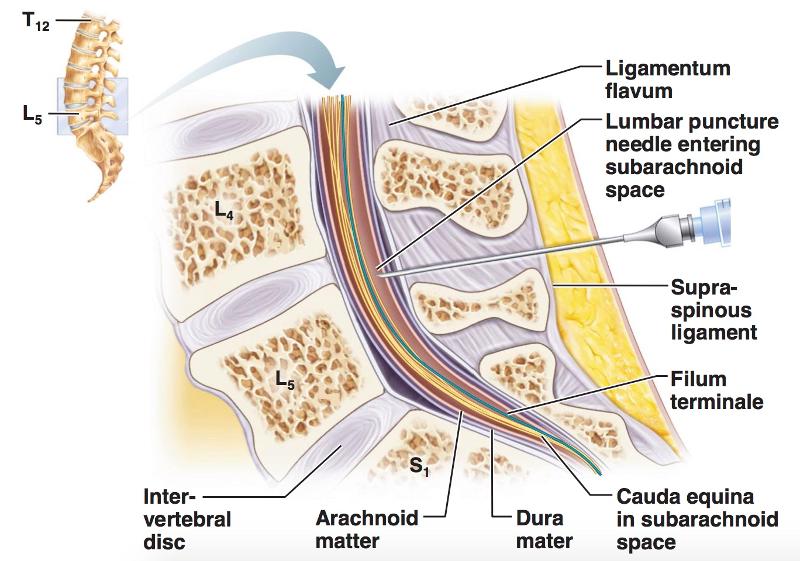 |
front 161 Organization of the Gray Matter of the Spinal Cord | back 161 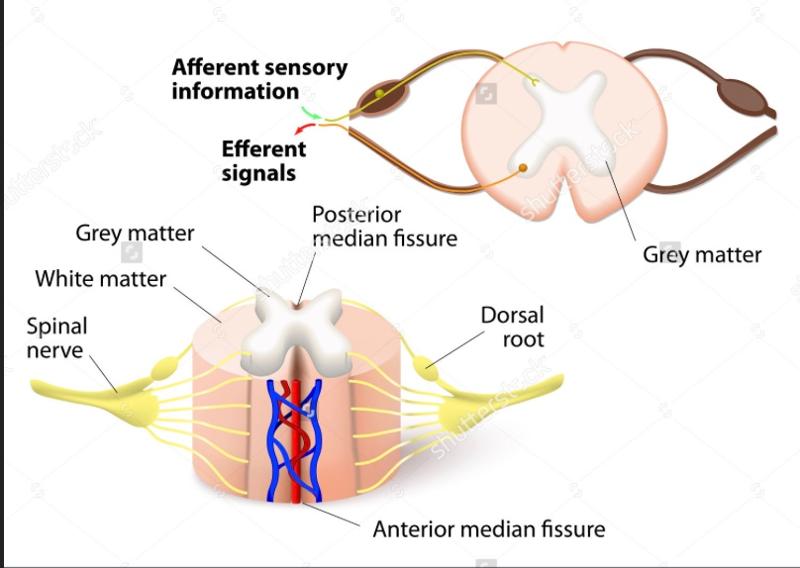 |
front 162 Lumbar Myelomeningocele/Spina Bifita | back 162 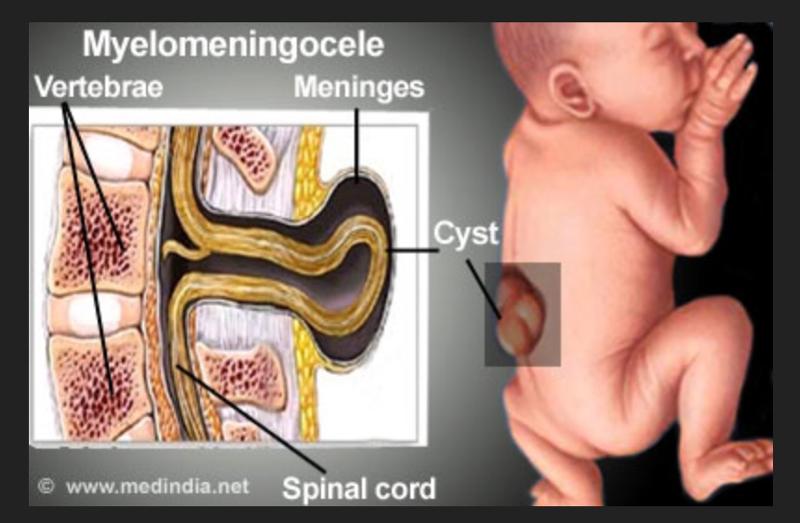 |