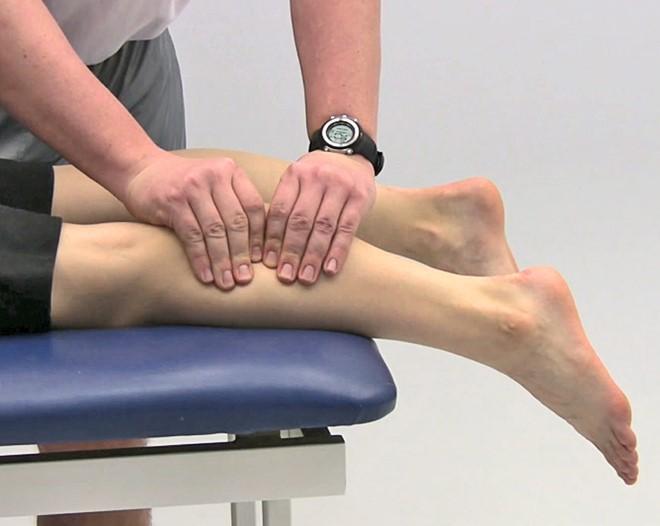
| back 5 - Patient is supine and slowly lifts a leg while keeping the knee extended
- At the end of motion (Max Flexion) dorsiflex the ankle
(+) test: Pain
Indication:
- Pain at 30 degrees indicated hip problem or inflamed
nerve
- Pain from 30-60 degrees indicates sciatic nerve
impingement
- Pain from 70-90 degrees indicates sacroiliac
joint problem
- Pain with dorsiflexion at the end of motion
indicates nerve root impingement or sciatic nerve irritation
|
| back 6 Position:
- Patient flexes the wrists and puts the back of the hands
together
- The position is held for approx 1 minute
(+) Test:
Indication:
|
| back 7 Position:
- Athlete makes a fist with the thumb tucked on the inside
- Wrist is ulnarly deviated
(+) Test:
Indication:
|
front 8 Valgus or Varus Stress Test for Elbow | back 8 Valgus (Ulnar)
- Position:
- Patient’s
elbow flexed to 25°
- One hand supports the lateral elbow
with the fingers reaching behind the joint to palpate the medial
joint line
- The opposite grasps the distal forearm
- Examiner applies valgus torque to the elbow
- (+) Test:
- Increased laxity compared to the opposite
side, and/or
pain - Indication:
- Injury to the ulnar collateral ligament
|
front 9 Valgus or Varus Stress Test for Knee | |
front 10 Test for Lateral Epicondylitis | |
front 11 Test for Medial Epicondylitis | |
| back 12 Position:
- Athlete is sitting or standing
- Athlete makes a fist
and the examiner observes the position of the third metacarpal
(+) Test:
- Third metacarpal is at level with the second and the fourth
metacarpals
Indications:
|
| back 13 Position:
- Patient's shoulder is placed in internal rotation
- While maintaining shoulder internal rotation, examiner passively
flexes the shoulder to end range
(+) test:
- Pain in subacrominal space between 90-180 deg of flexion
Indication:
|
| back 14 Position:
- Patient's shoulder is placed in 90 deg of flexon with elbow
flexed to 90 deg
- While maintaining shoulder flexion,
examiner passively internally rotates the shoulder
(+) test:
- Pain in subacromial space in end range
Indication:
|
| back 15 Position:
- Patient abducts both arms and flexes elbows to 90 deg
flexion
- Patient opens and closes the hands for 3 minutes
(+) Test:
- Inability to maintain testing position or replication of
motor/sensory symptoms
Indication:
|
| back 16 Position:
- Examiner palpates the radial pulse
- Examiner abducts
the patients shoulder and flex the elbow to 90 deg and externally
rotates the arm while asking the patient to rotate the head away
from injured side
(+) test:
- Diminished or disappearance of radial pulse
Indication:
|
| back 17 Position:
• Patient sitting with elbow extended and palm facing forward
•
Examiner resists shoulder flexion while palpating for tenderness over
the bicipital groove.
(+) Test:
• Pain over LH biceps tendon
Indication:
• LH biceps tendinopathy |
| back 18 Position:
• Patient’s shoulders elevated 90° in a scapular plane
(30° anterior to the frontal plane)
• With patient’s thumb
pointing down (i.e. empting the can), examiner applies downward
pressure at the wrist
(+) Test:
• Weakness or pain
accompanying the movement
Indication:
• Supraspinatus
pathology (ex. impingement, RC tear, tendinopathy) |
| back 19 Position:
• Patient’s shoulder in 90° flexion and 15° horizontal
adduction
• With patient’s thumb pointing down ( = shoulder IR),
examiner applies downward pressure at the wrist
• Repeats this
with palm facing up ( = shoulder ER)
(+) Test:
• Pain or
clicking within the GH joint experienced with the arm
internally rotated but is decreased during external
rotation
Indication:
• Labral pathology
*Note that pain at AC joint may indicate AC joint injury |
front 20 Anterior Drawer Test of the Knee | back 20 Position:
- Patient is supine with knee flexed to 90°, muscles
relaxed
- Examiner stabilizes the foot (can sit on the foot),
and pulls the proximal tibia anterior
(+) Test:
- Forward movement of the tibia that is greater than the normal
side
Indication:
- Damage to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament
|
| back 21 Position:
- Patient supine with knee flexed to 30°, muscles relaxed
- Examiner grasps the patient's femur with 1 hand, and proximal
tibia with another, and pulls the proximal tibia anterior while
stabilizing the femur
(+) Test:
- Forward movement of the tibia that is greater than the normal
side
Indication:
- Damage to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament
|
| back 22 Position:
- Examiner places one hand on top of the knee with thumb over
one joint line and index and middle finger on the other joint
line
- From full flexion, move the knee into extension
while:
- Maintaining tibial external rotation and applying
varus torque (stresses medial meniscus)
- Maintaining tibial
internal rotation and applying valgus torque (stresses lateral
meniscus)
(+) Test:
- Popping, clicking, or locking of the knee
Indication:
|
| back 23 Position:
- Patient is supine of a treatment table
- Examiner
supports the patient's legs in a 90/90 position
(+) Test:
- Posterior sagging of the tibia
Indication:
- Damage to the posterior cruciate ligament
|
| back 24 Leg Special Test
Position:
- Examiner squeezes the patient's calf muscles, while the foot
is extended off the table
(+) Test:
- Absence of foot movement (plantar flexion)
Indication:
|
| back 25 Position:
- Patient's ankle in 90 degree dorsiflexion
- Examiner
cups a hand around the calcaneous and inverts the foot while
palpating the lateral ligaments]
(+) test:
- Excessive motion and/or clunking sound as it reaches the end
point
Indication:
- Damage to the calcaneofibular (CF) ligament (primarily) and
other lateral structures
|
| back 26 Position:
- Patient's ankle in 90° dorsiflexion
- Examiner cups a
hand around the calcaneous and everts the foot while
palpating the deltoid
ligaments
(+) Test:
- Excessive motion and/or clunking sound as it reaches the end
point
Indication:
- Damage to the deltoid ligaments
|
| back 27 Position:
- Examiner stabilizes the distal leg, while grasping the
patient's foot and passively moving the ankle into dorsiflexion and
external rotation
(+) Test:
Indication:
- Damage to the deltoid ligament, distal ankle syndesmosis,
anterior/posterior distal tibiofibular ligaments. and interosseous
membrane
|
| back 28 Position:
- Patient sitting with elbow flexed 90° and forearm
pronated
- Examiner resists elbow flexion and supination
- (+) Test:
• Pain or snapping in the bicipital groove
- Indication:
• LH biceps tendinopathy |
front 29 Appley's Compression Test (Pulling upwards) | back 29 Position:
- Patient is prone with knee flexed 90°
- Examiner
applies axial loading to the leg while rotating tibia (foot) into
internal and external rotation
(+) Test:
Indication:
|
front 30 Appley's Distraction Test (Pushing downwards) | back 30 Position:
- Patient is prone with knee flexed 90°
-
Examiner applies distraction to the leg while
rotating tibia (foot) into internal and external rotation
(+) Test:
Indication:
- Possible injury to the ligament or joint capsule
- No
pain if meniscal injury is present
|