Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 1: The Human Organism - Multiple Choice
front 1 1. Anatomy is | back 1 C |
front 2 2. Which subdivision of anatomy involves the study of organs that
function together? | back 2 C |
front 3 3. Which of the following activities would represent a physiological
study? | back 3 E |
front 4 4. Visual inspection of the appearance of the liver and gallbladder
during surgery is associated with which of the following? | back 4 C |
front 5 5. Microscopic examination of a frozen tissue specimen is an
application of which of the following disciplines? | back 5 A |
front 6 6. Studies at the biochemical and molecular levels would be most
appropriate for learning about the | back 6 C |
front 7 7. Knowledge of the structure of body parts helps us to understand
their function. Which of the following is an accurate example of that
principle? | back 7 C |
front 8 8. An investigator who conducts an experiment to determine how changes in pH affect the function of enzymes on digestion is most likely to be a(n) A. neurologist. | back 8 D |
front 9 9. The study of the structural features and functions of the cell is A. cytology. | back 9 A |
front 10 10. The study of tissues is | back 10 B |
front 11 11. The study of the body's organization by areas is | back 11 B |
front 12 12. The study of the external form of the body and its relationship to deeper structures is A. systemic anatomy. | back 12 E |
front 13 13. Which of the following systems carries necessary compounds like
oxygen and nutrients throughout the body? | back 13 B |
front 14 14. Consider the following structural levels: chemical, organ,
tissue, cell, and organ system. Which level encompasses the other
four? | back 14 B |
front 15 15. A tissue is a | back 15 D |
front 16 16. Organize the following structural levels of the human body from
simplest to most complex. | back 16 C |
front 17 17. Which organ system is the location of blood cell
production? | back 17 B |
front 18 18. Which body system would be affected by degeneration of cartilage
in joints? | back 18 D |
front 19 19. The gallbladder, liver, and stomach are all part of the | back 19 E |
front 20 20. The integumentary system | back 20 A |
front 21 21. Which of the following is NOT the correct name of an organ system? A. integumentary | back 21 E |
front 22 22. A cell is | back 22 C |
front 23 23. An organ is | back 23 B |
front 24 24. An organ system is | back 24 D |
front 25 25. An organelle is | back 25 A |
front 26 26. What system removes nitrogenous waste products from the blood and
regulates blood pH, ion balance, and water balance? | back 26 E |
front 27 27. An organism's ability to use energy in order to swim is an
example of | back 27 A |
front 28 28. The changes an organism undergoes through time is called | back 28 E |
front 29 29. Nerve cells generate electrical signals in response to changes in
the environment. This is an example of | back 29 E |
front 30 30. An increase in the number of cells is | back 30 B |
front 31 31. The change in the shape of tissues or organs is called | back 31 E |
front 32 32. Homeostasis is defined as | back 32 D |
front 33 33. Which of the following is consistent with homeostasis? | back 33 A |
front 34 34. A blood clot stimulating even more blood clotting is an example
of | back 34 B |
front 35 35. Which of the following is most similar to the negative feedback
mechanism in human physiology? | back 35 C |
front 36 36. A researcher discovered a new hormone that raises blood calcium
levels. According to the principles of negative feedback, this hormone
would be secreted when | back 36 B |
front 37 37. In a negative feedback mechanism, the response of the effector
| back 37 A |
front 38 38. Which of the following is most consistent with homeostasis? | back 38 E |
front 39 39. A researcher discovered a sensory receptor that detects
decreasing oxygen concentrations in the blood. According to the
principles of negative feedback, it is likely that stimulation of this
sensory receptor will produce which of the following types of
responses? | back 39 B |
front 40 40. Which of the following is NOT a component of a negative feedback
mechanism? | back 40 B |
front 41 41. Positive-feedback mechanisms are always damaging to the body. A. TRUE | back 41 B |
front 42 42. In the anatomical position, the | back 42 E |
front 43 43. Which of the following sets of directional terms are most
appropriately referred to as opposites? | back 43 A |
front 44 44. The term "dorsal" means | back 44 C |
front 45 45. The anatomical term that means "away from the midline of the
body" is | back 45 D |
front 46 46. The thumb is ___ to the fifth digit (little finger). | back 46 B |
front 47 47. Which of the following describes the position of the nose? | back 47 E |
front 48 48. The shoulder is _____ to the elbow. | back 48 E |
front 49 49. A term that means "toward the attached end of a limb"
is | back 49 E |
front 50 50. Which of the following is most inferior in location? | back 50 A |
front 51 51. While Stacy is in the process of passing over the bar during a
pole vault, her hips are considered to be | back 51 C |
front 52 52. Cephalic means | back 52 C |
front 53 53. Posterior means | back 53 E |
front 54 54. Medial means | back 54 A |
front 55 55. Proximal means | back 55 D |
front 56 56. Deep means | back 56 B |
front 57 57. In the expression "Let your fingers do the walking,"
which of the following anatomical terms could be substituted for
"fingers?" | back 57 C |
front 58 58. The anatomical arm refers to the part of the upper limb from the
| back 58 C |
front 59 59. The lumbar region is the | back 59 C |
front 60 60. The antecubital region is the | back 60 A |
front 61 61. The antebrachial region is the | back 61 E |
front 62 62. The pectoral region is the | back 62 B |
front 63 63. The plantar surface is the | back 63 D |
front 64 64. The brachial region is commonly known as the | back 64 D |
front 65 65. The inguinal region is commonly known as the | back 65 A |
front 66 66. The gluteal region is commonly known as the | back 66 B |
front 67 67. The sternal region is commonly known as the | back 67 C |
front 68 68. The umbilical region is commonly known as the | back 68 E |
front 69 69. The cervical region is the | back 69 D |
front 70 70. The popliteal region is the | back 70 C |
front 71 71. The sural region is the | back 71 A |
front 72 72. The femoral region is the | back 72 E |
front 73 73. The axillary region is the | back 73 B |
front 74 74. What plane divides the body into equal right and left halves?
| back 74 C |
front 75 75. Which of the following abdominal regions would contain the
appendix? | back 75 B |
front 76 76. Which of the following is NOT found in the epigastric region?
| back 76 C |
front 77 77. A vertical plane that separates the body into right and left
portions is called a _____ plane. | back 77 A |
front 78 78. "Cutting off your nose" would be a section in the _____
plane. | back 78 A |
front 79 79. Amputation of a foot at the ankle would involve a cut in the
_____ plane. | back 79 C |
front 80 80. The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity by the
| back 80 B |
front 81 81. A bullet enters the left lung and collapses it. Which cavity has
been entered? | back 81 C |
front 82 82. The cavity of the body immediately inferior to the diaphragm is
the _____ cavity. | back 82 E |
front 83 83. The suffix "-itis" means inflammation. Which of the
following terms means inflammation of the membrane lining the body
cavity that contains the liver? | back 83 B |
front 84 84. Which of the following organs is retroperitoneal in location?
| back 84 D |
front 85 85. The wall of the abdominopelvic cavity is lined by a serous
membrane called the | back 85 B |
front 86 86. The visceral pleura is | back 86 B |
front 87 87. The parietal peritoneum is | back 87 C |
front 88 88. The mesentery is | back 88 A |
front 89 89. The pleural cavity is the | back 89 D |
front 90 90. The parietal pericardium is | back 90 E |
front 91 91. A major limitation of radiographs is that they A. can only visualize bone. | back 91 B |
front 92 92. An anatomic image created from sound waves is a | back 92 D |
front 93 93. A CT scan allows for a three-dimensional image to be generated. A. TRUE | back 93 A |
front 94 94. What technique creates a three-dimensional dynamic image of blood
vessels? | back 94 A |
front 95 95. Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the movement of | back 95 C |
front 96 96. The delivery of a radioactive compound to the body to study the
metabolism of tissues is called | back 96 B |
front 97 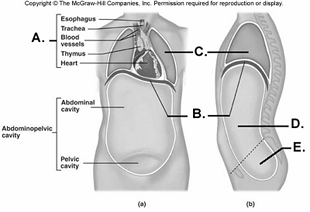 97. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other
structures. What does "A" represent? | back 97 B |
front 98 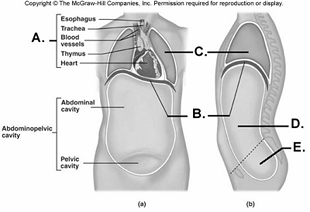 98. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other
structures. What does "B" represent? | back 98 A |
front 99 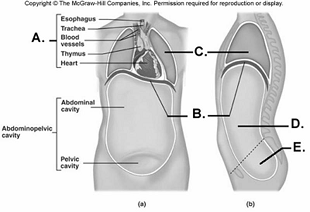 99. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other
structures. What does "C" represent? | back 99 D |
front 100 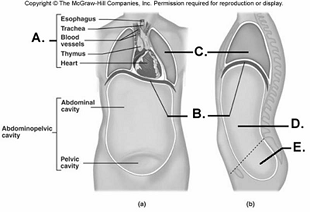 100. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other
structures. What does "D" represent? | back 100 E |
front 101 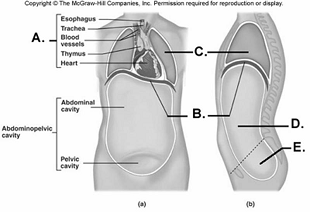 101. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other structures. What does "E" represent? A. diaphragm | back 101 C |
front 102 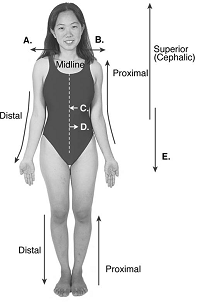 102. Directional terms are important in the study of anatomy. What
does "A" represent? | back 102 B |
front 103 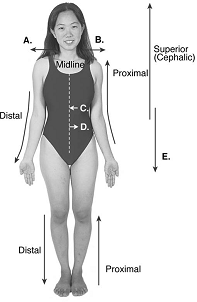 103. Directional terms are important in the study of anatomy. What
does "B" represent? | back 103 C |
front 104 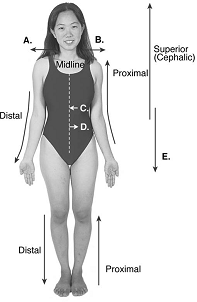 104. Directional terms are important in the study of anatomy. What does "C" represent? A. median | back 104 A |
front 105 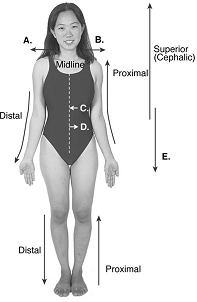 105. Directional terms are important in the study of anatomy. What does "D" represent? A. median | back 105 E |
front 106 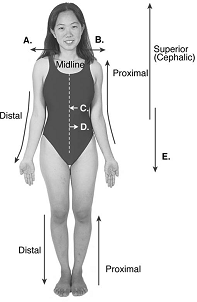 106. Directional terms are important in the study of anatomy. What
does "E" represent? | back 106 D |
front 107 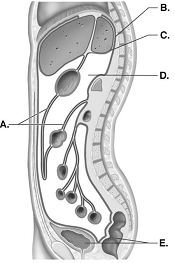 107. This is a sagittal section through the abdominopelvic cavity.
What structure does "A" represent? | back 107 B |
front 108 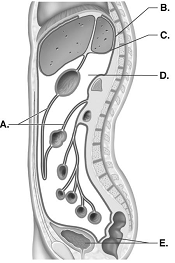 108. This is a sagittal section through the abdominopelvic cavity.
What serous membrane does "B" represent? | back 108 C |
front 109 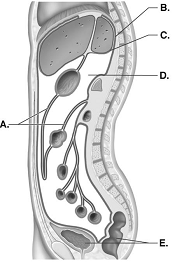 109. This is a sagittal section through the abdominopelvic cavity.
What serous membrane does "C" represent? | back 109 A |
front 110 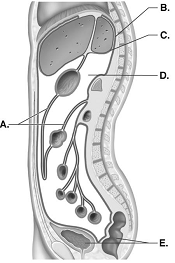 110. This is a sagittal section through the abdominopelvic cavity.
What cavity does "D" represent? | back 110 E |
front 111 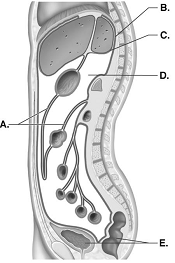 111. This is a sagittal section through the abdominopelvic cavity. What structures does "E" represent? A. visceral peritoneum (covers organs) | back 111 D |
front 112 Anatomy deals with the | back 112 A |
front 113 Physiology deals with the | back 113 B |
front 114 Which of the following statements about anatomy and physiology is
true? | back 114 D |
front 115 Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology originated from
which of the following languages? | back 115 C |
front 116 Information about human cells can be obtained by studying | back 116 D |
front 117 The first human anatomical illustrations, published by ___________,
allowed for the correction of centuries of mistakes in
textbooks. | back 117 B |
front 118 Biochemical and molecular explanations provide a better understanding
of | back 118 C |
front 119 Knowledge of the structure of body parts helps in understanding their
function. Which of the following is an accurate example of that
principle? | back 119 D |
front 120 The location and description of bones in the skeletal system will be
covered under | back 120 B |
front 121 Which of the following statements about physiology is true? | back 121 B |
front 122 Magnetic resonance imaging makes use of | back 122 B |
front 123 The study of the microscopic structure of the tissues and organs is
called | back 123 D |
front 124 Magnetic resonance imaging might be used to | back 124 D |
front 125 The smallest structures that are considered to be alive are | back 125 B |
front 126 Cells contain structures called _________, which can perform specific
activities like energy production, and digestion. | back 126 C |
front 127 To understand the structure and function of an organism we also need
to understand the structure and properties of | back 127 A |
front 128 To understand the structure of complex body systems we start from the
structure of the atom and progress to the structure of the organ
systems. This concept is called | back 128 D |
front 129 Which of the following lists is in the order of increasing levels of
complexity? | back 129 C |
front 130 Tissues are formed by a group of ________ that perform similar
functions. | back 130 A |
front 131 The heart is an example of a(n) | back 131 B |
front 132 To maintain life all living organisms depend on | back 132 B |
front 133 As one of the characteristic of Life, development includes | back 133 C |
front 134 Which of the following activities is not necessary to maintain
life? | back 134 A |
front 135 To avoid extinction of a species, living organisms need to | back 135 C |
front 136 Which of the following carries necessary compounds like nutrients and
hormones throughout the body? | back 136 C |
front 137 What organ system is responsible for the production of blood
cells? | back 137 B |
front 138 The ability of an organism to sense changes that take place within
its body is an example of | back 138 A |
front 139 Homeostasis is defined as the | back 139 C |
front 140 Which of the following is NOT an example of a homeostatic
mechanism? | back 140 B |
front 141 A blood clot stimulating formation of more blood clotting is an
example of | back 141 C |
front 142 The function of ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) is to conserve water by
decreasing urine output. According to the negative feedback mechanism,
ADH will be secreted when the | back 142 A |
front 143 A ______ section separates the body into right and left
portions. | back 143 D |
front 144 Amputation of a foot at the ankle would involve a cut in the
___________ plane. | back 144 C |
front 145 Which of the following sets of directional terms are most
appropriately referred to as opposite? | back 145 A |
front 146 The three major anatomical planes are | back 146 C |
front 147 Which of the following does NOT belong to the axial part of the
body? | back 147 D |
front 148 The anterior medial thoracic region is called the _____
region. | back 148 D |
front 149 The groin is also known as the ______ region. | back 149 B |
front 150 The spleen is in the _______ of the abdomen. | back 150 A |
front 151 A view of the heart showing the interior of all four chambers would
be a ______ section. | back 151 B |
front 152 A ______ plane passes through the breast, hip, and knee on only one
side of the body. | back 152 D |
front 153 The antecubital (cubital fossa) region of the body most resembles
what other body region? | back 153 C |
front 154 The cranial cavity is _______ to the thoracic cavity. | back 154 D |
front 155 Most of the esophagus is in the | back 155 B |
front 156 The axial portion of the body includes | back 156 C |
front 157 The upper midportion of the abdomen is called the ______
region. | back 157 D |
front 158 When the body is placed in the anatomical position, which of the
following is NOT true? | back 158 C |
front 159 A parietal membrane _______, whereas a visceral membrane
_______. | back 159 B |
front 160 Which of the following organs is located in the abdominopelvic
cavity? | back 160 D |
front 161 The thoracic cavity lies where in relationship to the abdominopelvic
cavity? | back 161 C |
front 162 The membrane on the surface of a lung is called the | back 162 A |
front 163 The dorsal cavity includes which of the following smaller
cavities? | back 163 A |
front 164 The ankle is _______ to the knee. | back 164 D |
front 165 The acromial region is the | back 165 C |
front 166 The _______ contains a portion of the inguinal region. | back 166 A |
front 167 The urinary bladder is in the ________ region. | back 167 D |
front 168 Examples of serous membranes include | back 168 D |
front 169 All of the following are retroperitoneal EXCEPT the | back 169 A |
front 170 The anus is in the ____ region. | back 170 A |
front 171 The carpus is distal to the | back 171 D |
front 172 The concept of anatomical position stipulates all of the following
EXCEPT the | back 172 D |
front 173 The breast is in the ______ region. | back 173 C |
front 174 All of the following are found in the thoracic cavity EXCEPT
the | back 174 C |
front 175 Which of the following is NOT the name of an organ system? | back 175 A |
front 176 _____________ investigates the body's structure, whereas __________
investigates the processes or functions of living things. | back 176 E |
front 177 Ultrasound, X-rays, CT, and MRI are all examples of | back 177 A |
front 178 A group of cells with similar structure and function, together with
the extracellular substances located between them, form a(n) | back 178 C |
front 179 The basic living unit of all plants and animals is the | back 179 A |
front 180 Which organ system removes substances from the blood, combats
disease, maintains tissue fluid balance, and absorbs fat from the
digestive tract? | back 180 C |
front 181 Which organ system consists of skin, hair, nails, and sweat
glands? | back 181 B |
front 182 Which organ system consists of hormone-secreting glands, such as the
pituitary and thyroid glands? | back 182 A |
front 183 Which of these characteristics of life helps maintain homeostasis
when environmental conditions change? | back 183 E |
front 184 Development is a process that begins with fertilization and ends
with | back 184 E |
front 185 Given these terms related to negative(--)feedback: 1. control center
2. effector 3. receptor 4. response 5. stimulus Arrange them in the
correct order as they operate to maintain homeostasis. | back 185 E |
front 186 A body temperature of 98.6 degrees F (37 degrees C) is the __________
for body temperature. | back 186 D |
front 187 Which of these processes illustrates positive-feedback? | back 187 D |
front 188 Failure of negative-feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis | back 188 A |
front 189 According to the concept of negative feedback, a slight increase in
blood pressure causes | back 189 B |
front 190 To maintain homeostasis, the normal range of values for a
variable | back 190 B |
front 191 A term that means "away from the midline" is: | back 191 B |
front 192 Which of these descriptions does NOT apply correctly to a person in
the anatomic position? | back 192 E |
front 193 The scapula (shoulder blade) is __________ to the lung. | back 193 D |
front 194 The elbow is __________ to the wrist. | back 194 E |
front 195 The nose is __________ and __________ to the ears. | back 195 D |
front 196 Which of the paired terms below are opposites? | back 196 E |
front 197 Pancreatitis describes | back 197 A |
front 198 A person lying flat on his back is said to be in the __________
position. | back 198 C |
front 199 Given these directional terms: 1. caudal 2. cephalic 3. distal 4.
inferior 5. proximal Which of these directional terms correctly
describes the relationship of the ankle to the knee? | back 199 D |
front 200 Which of these anatomical terms refers to the ankle? | back 200 E |
front 201 Which of these anatomical terms refers to the shoulder? | back 201 A |
front 202 The only plane that can divide the body into equal halves is
the | back 202 C |
front 203 A(n) __________ plane divides the body into superior and inferior
portions. | back 203 D |
front 204 A cut across the long axis of an organ made at other than a right
angle is called a(n) | back 204 C |
front 205 In which quadrant of the abdomen would stomach pain most likely be
felt? | back 205 C |
front 206 Which of these structures is NOT found in the mediastinum? | back 206 A |
front 207 Which of these statements concerning body regions is correct? | back 207 B |
front 208 The cavity surrounded by the rib cage and bounded inferiorly by the
diaphragm is the | back 208 C |
front 209 The lungs are separated by the | back 209 A |
front 210 Serous membranes | back 210 B |
front 211 The serous membrane on the surface of the lungs is called | back 211 D |
front 212 Which of these organs is NOT retroperitoneal? | back 212 D |
front 213 Given these serous membranes: 1. parietal pericardium 2. visceral
pericardium 3. parietal peritoneum 4. visceral peritoneum 5. parietal
pleura 6. visceral pleura | back 213 C |
front 214 You are doing a handstand. Your head is __________ to your
neck. | back 214 A |
front 215 Physiology | back 215 A |
front 216 The endocrine system | back 216 A |
front 217 The integumentary system | back 217 C |
front 218 The lymphatic system | back 218 D |
front 219 The muscular system | back 219 E |
front 220 The nervous system | back 220 A |
front 221 The urinary system | back 221 B |
front 222 The characteristic of life that is defined as "all the chemical
reactions taking place in an organism" is | back 222 C |
front 223 Negative-feedback mechanisms | back 223 D |
front 224 The following events are part of a negative-feedback
mechanism. Choose the arrangement that lists the events in the order they
occur. | back 224 D |
front 225 Which of these statements concerning positive feedback is
correct? | back 225 C |
front 226 The clavicle (collarbone) is _____________ to the nipple of the
breast. | back 226 D |
front 227 A term that means nearer the attached end of a limb is | back 227 D |
front 228 Which of these directional terms are paired most appropriately as
opposites? | back 228 A |
front 229 The part of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist is called
the | back 229 B |
front 230 A patient with appendicitis usually has pain in the _____________
quadrant of the abdomen. | back 230 B |
front 231 A plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts is
a | back 231 A |
front 232 The pelvic cavity contains the | back 232 E |
front 233 The lungs are | back 233 C |
front 234 Given these characteristics: Which of the characteristics describe serous membranes? | back 234 A |
front 235 Given these organ and cavity combinations: Which of the organs is correctly paired with a space that surrounds
that organ? | back 235 B |
front 236 Which of these membrane combinations are found on the surface of the
diaphragm? | back 236 A |
front 237 Mesenteries | back 237 B |
front 238 Which of the following organs is not retroperitoneal? | back 238 E |