Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
exercise 17
front 1 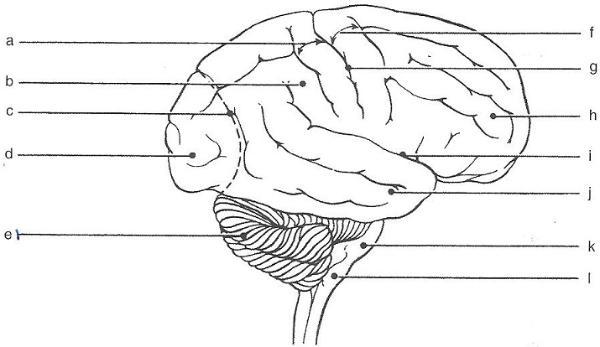 | back 1 a. postcentral gyrus b. parietal lobe c. parieto-occipital d. occopital lobe e. cerebellum f. precentral gyrus g. centeral sulcus h. frontal lobe i. lateral sulcus j. temporal lobe k. pons l. medulla |
front 2 In which of the cerebral lobes is the functional area found? Auditory cortex: | back 2 Temporal |
front 3 In which of the cerebral lobes is the functional area found? Primary motor cortex: | back 3 Frontal |
front 4 In which of the cerebral lobes is the functional area found? Primary sensory cortex: | back 4 Parietal |
front 5 In which of the cerebral lobes is the functional area found? Olfactory cortex: | back 5 Temporal |
front 6 In which of the cerebral lobes is the functional area found? Visual cortex: | back 6 Occipital |
front 7 In which of the cerebral lobes is the functional area found? Broca's area: | back 7 Frontal |
front 8 which of the following structures are not part of the brain stem? ( circle all that apply) cerebral hemispheres pons midbrain cerebellum medulla diencephalon | back 8 cerebral hemispheres cerebellum diencephalon |
front 9 A(n)________ is an elevated rdige of cerebral tissue | back 9 gyrus |
front 10 The convolutions seen in the cerebrum are important because they increase the___________. | back 10 surface area |
front 11 Gray matter is composed of __________. | back 11 neuron cell body |
front 12 White matter is composed of ________. | back 12 axon |
front 13 a fiber tract that provides for communcation between different parts of the same cerebral hemisphere is called a(n)___________. | back 13 association tract |
front 14 whereas one that carries impulses from the cerebrum to lower CNS areas is called a(n) __________ tract. | back 14 projection tract |
front 15 the caudate,putamen,and globus pallidus are collectively called the ________. | back 15 basal nuclei |
front 16 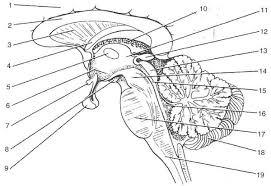 | back 16 1. cerebrall hemisphere 2. corpus callosum 3. septum pellucidum 4. fornix 5.interthalamic adhesion 6. hypothalamus 7. optic chiasma 8.mammillary bodies 9. pituitary gland 10. choroid plexus 11. thalamus 12. pineal gland 13. corpora quadrigemina 14. cerebral peduncle 15. cerbral aqueduct 16. fourth ventricle 17. pons 18. cerebellum 19. medulla oblongata |
front 17 site of regulation of body temperature and water balance; most important autonomic center | back 17  hypothalamus |
front 18 consciousness depends on the function of this part of the brain | back 18  choroid plexus |
front 19 located in the midbrain; contains reflex centers of vision and audition | back 19  copora quadrigemina |
front 20 responsible for regulation of posture and coordination of complex muscular movements | back 20 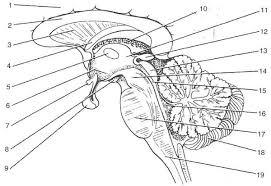 cerebellum |
front 21 important synapse site for afferent fibers traveling to the sensory cortex | back 21 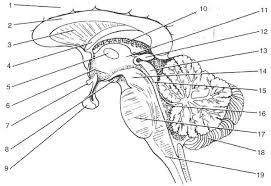 thalamus |
front 22 contains autonomic centers regulating blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rhythm, as well as coughing, sneezing, and swallowing centers | back 22 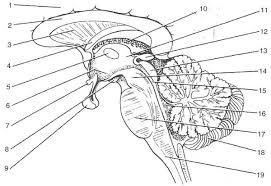 medulla oblongata |
front 23 large commissure connecting the cerebral hemispheres | back 23 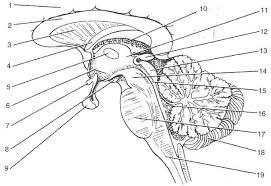 corpus callosum |
front 24 fibers tract involved with olfaction | back 24 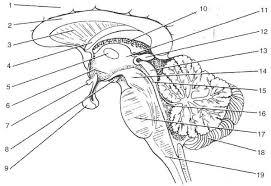 fornix |
front 25 connects the third and fourth ventricles | back 25 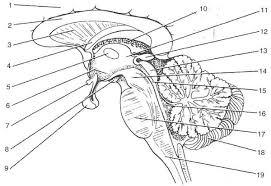 cerebral aqueduct |
front 26 encloses the third ventricle | back 26 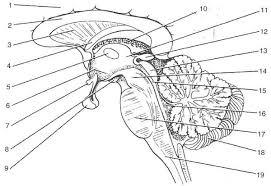 thalamus |
front 27 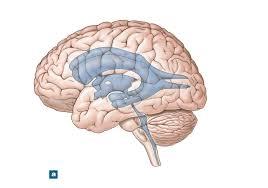 | back 27 interventricular |
front 28 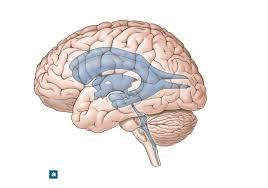 | back 28 lateral ventricle |
front 29 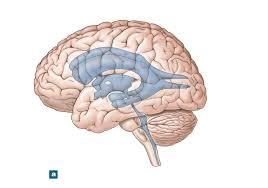 | back 29 third ventricle |
front 30  | back 30 cerebral aqueduct |
front 31 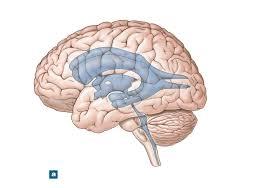 | back 31 median aperture |
front 32 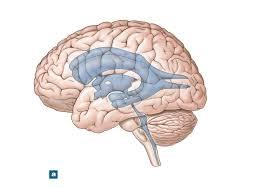 | back 32 lateral aperture |
front 33 cerebrospinal fluid flows from the fourth ventricle into the ________ space surrounding the brain and spinal cord. | back 33 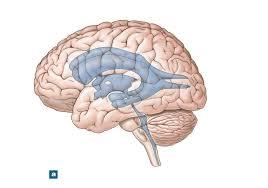 subarachnoid space |
front 34 from this space it drains throught ________ into the ________. | back 34 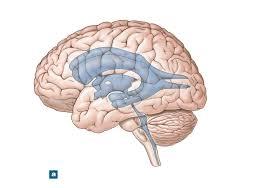 arachnoid villi, dural sinsuses |