Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
DECISION 2.1 Modelling with graphs
front 1 graph | back 1 Points (called vertices or nodes) which are connected by lines (edges or arcs) |
front 2 weighted graph/network | back 2 if a graph has a number associated with each edge (usually called its weight) then it is a weighted graph or a network |
front 3 vertex set | back 3 list of all the nodes on a graph e.g. A,B,C,D,E |
front 4 edge set | back 4 list of all the edges in a graph (AB, AC, etc...) |
front 5 subgraph | back 5 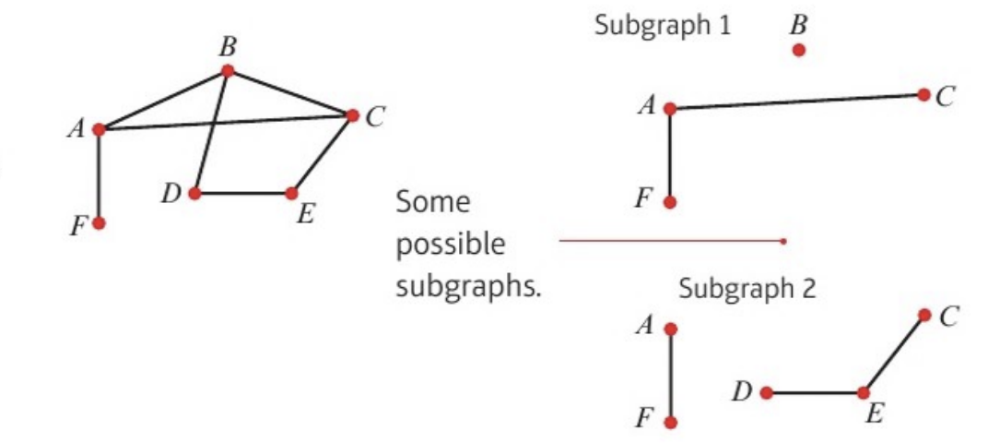 A subgraph of (e.g.) graph G is a graph where each of whose vertices belongs to G - it is simply a part of the original graph (graph on left is graph G, graphs on right are subgraphs of graph G) |
front 6 degree/valency/order of a vertex | back 6 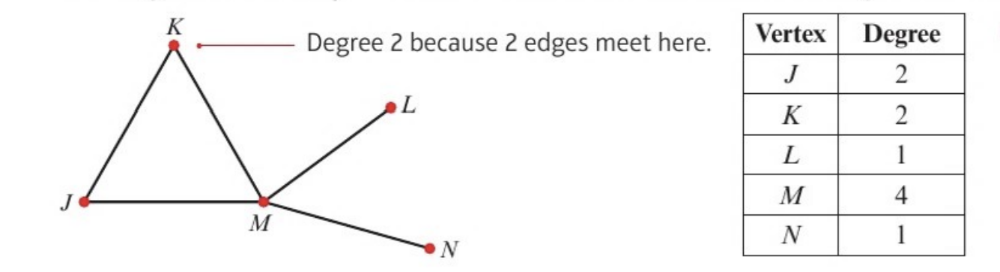 number of edges incident to that vertex if a vertex has even degree we say it is even and if it has odd degree we say it is an odd vertex |
front 7 walk | back 7 a route through a graph along edges from one vertex to the next |
front 8 path | back 8 a walk in which no vertex is visited more than once |
front 9 trail | back 9 a walk in which no edge is visited more than once |
front 10 cycle | back 10 a walk in which the end vertex is the same as the start vertex and no other vertex is visited more than once |
front 11 Hamiltonian cycle | back 11 a cycle* which includes every vertex *cycle=a walk in which the end vertex is the same as the start vertex and no other vertex is visited more than once |
front 12 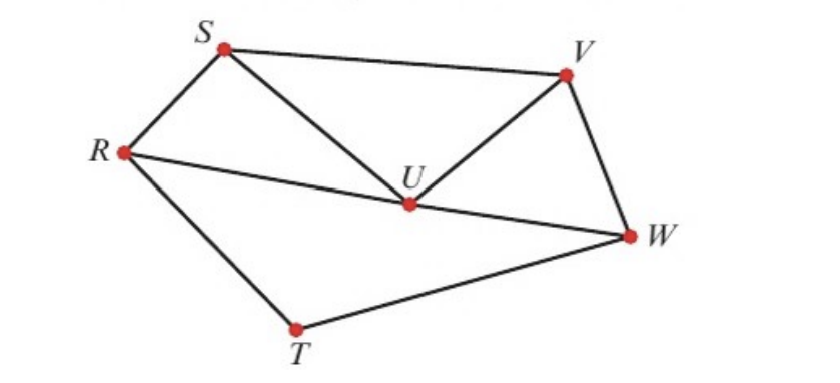 in terms of the diagram, give examples of: 1. a walk 2. a path 3. a trail 4. a cycle 5. an hamiltonian cycle | back 12 walk: e.g. RSUWVU, SUV, etc path: RSUVW, RUVW, etc trail: RUSVUW cycle: RSUR hamiltonian cycle: RSUVWTR |
front 13 connected vs unconnected graphs | back 13 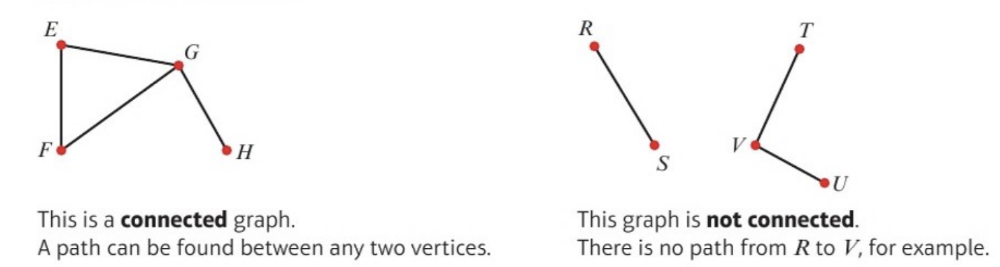 Two vertices are connected if there is a path between them. a graph is connected if all its vertices are connected |
front 14 loop | back 14  an edge that starts and finishes at the same vertex |
front 15 simple graph | back 15  graph in which there are no loops and there is at most one edge connecting any pair of vertices |
front 16 digraph | back 16 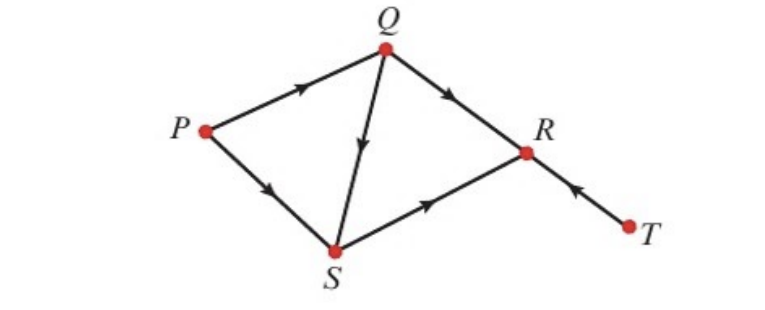 if the edges of a graph have a direction associated with them they are known as directed edges and the graph is known as a directed graph (digraph) |
front 17 Euler's handshaking lemma | back 17 In any undirected graph, the sum of the degrees of the vertices is equal to 2x the number of edges. Therefore, the number of odd vertices must always be even (including possibly zero). This result is known as Euler's handshaking lemma. |