Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy- Cells
front 1 What is the definition of a cell? (write out) | back 1 The smallest part of a living thing. |
front 2 Cell membrane | back 2 like a skin that surrounds the cell separates inside of cell from everything on the outside. Does not Contain Chromatin Has phospholipid bilayer controls what goes in and out of the cell. surrounds both plant and animal cells |
front 3 Cytoplasm | back 3 jelly-like liquid that fills the cell |
front 4 DNA | back 4 The cells instruction matter; tells the cell what to do Genetic material Located in the nucleus |
front 5 Two main types of cells: Eukaryotic Cells | back 5 Complex, found in plants and animals Have organelles (tiny organs) |
front 6 Do Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus? | back 6 Yes, they have a distinct nucleus |
front 7 Eukaryotic cell's nucleus | back 7 Control center of the eukaryotic cell. Inside is DNA which is organized into structures called chromosomes when the cell is ready to divide. contains Nucleolus, where ribosomes are made |
front 8 Ribosomes | back 8 Little factories that make proteins Float freely in the cytoplasm can attach to the Endoplasmic Reticulum |
front 9 endoplasmic reticulum | back 9 a network of passages that helps move materials around the cell |
front 10 What are the two types of Endoplasmic Reticulum? | back 10 Rough ER Smooth ER |
front 11 Rough ER | back 11 Has ribosomes attached involved in making proteins |
front 12 Smooth ER | back 12 Doesn't have ribosomes attached involved in making fats and detoxifying the cell |
front 13 Golgi Apparatus or Golgi body | back 13 receives proteins and other materials from the ER, modifies them, and packages them up to be sent to where they are needed. |
front 14 Vacuoles | back 14 like storage sacs in plants cells, there's often a large central one that stores water. In animal cells, they are usually smaller and have various storage functions. they are larger in plant cells |
front 15 Lysosomes | back 15 they contain enzymes that break down waste materials and old cell parts Like a cell's recycling center. |
front 16 Mitochondria | back 16 perform cellular respiration which creates energy in the form of ATP that the cell needs to function converts glucose to ATP cells that need more energy have more mitochondria. |
front 17 Cytoskeleton | back 17 the cell's internal scaffolding. made of protein fibers that give the cell its shape, help it move, and support its internal structures |
front 18 Chloroplasts (green) | back 18 in plants cells only responsible for photosynthesis makes glucose they are green because they contain a pigment called chlorophyll. |
front 19 Cell Wall | back 19 In plants cells only the extra layer outside their cell membrane provides extra support, structure, and protection |
front 20 Prokaryotic Cells | back 20 simple cells No nucleus or membrane-enclosed organelles DNA floats in cytoplasm |
front 21 Are Prokaryotic cells always single-celled organisms? | back 21 yes, they are made up of just one cell. |
front 22 Flagella | back 22 some prokaryotic cells have this whip-like tails that help them move around Example: sperm cells |
front 23 All cells have ___ ________, ___________, and ________ ________ (DNA) | back 23 cell membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material. |
front 24 What does DNA stand for? | back 24 Deoxyribonucleic acid |
front 25 What part of the cell contains DNA? | back 25 The eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells |
front 26 What are the 4 nucleotides? | back 26 adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine Adenine - Thymine Cytosine - Guanine |
front 27 What is the shape of DNA? | back 27 A double helix, two spirals twisting around each other |
front 28 what breaks down the cell membrane? | back 28 salt and detergent |
front 29 Phospholipid: ____________ head, ________________ tail | back 29 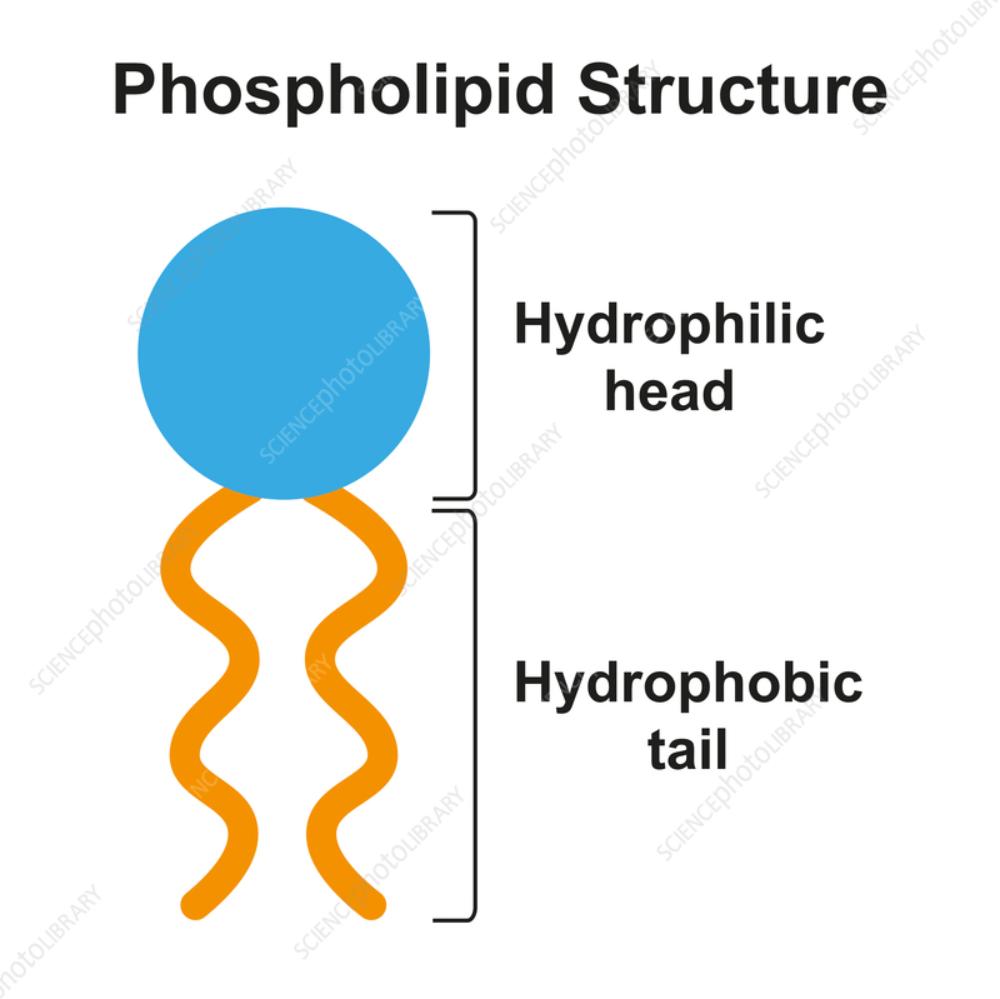 |
front 30 Hydrophilic | back 30 water - loving head of a phospholipid |
front 31 Hydrophobic | back 31 water - fearing tail of a phospholipid |
front 32 list 4 substances that can easily cross the cell membran ewithout the use of cellular energy: | back 32 gases, dust, liquids, solids/ |
front 33 What do cells use glycoproteins for? | back 33 to identify and attach to other cells |
front 34 | back 34 know this. |
front 35 | back 35 |