Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P II Chapters 20 21 and 22 Attendance Quiz 6 and 7 Unit Test 6 Northeast Mississippi Community College
front 1 Possible causes of hypoxia include ________. | back 1 too little oxygen in the atmosphere |
front 2 Which of the choices below is NOT a role of the pleurae? | back 2 aids in blood flow to and from the heart because the heart sits between the lungs |
front 3 Inspiratory capacity is: | back 3 the total amount of air that can be inspired after a tidal expiration |
front 4 Which of the disorders below is characterized by destruction of the walls of the alveoli producing abnormally large air spaces that remain filled with air during exhalation? | back 4 Emohysema |
front 5 Intrapulmonary pressure is the: | back 5 Pressure within the alveoli of the lungs |
front 6 Which of the following maintains the patency (openness) of the trachea? | back 6 C-shaped cartilage rings |
front 7 The amount of air that can be inspired above the tidal volume is called ____________. | back 7 Inspiratory reserve |
front 8 Which of the choices below determines the direction of respiratory gas movement? | back 8 partial pressure gradient |
front 9 Regulatory T cells ___________. | back 9 may function in preventing autoimmune reactions |
front 10 Which immunoglobulin class is attached to the external surface of B cells and acts as an antigen receptorf the B cell? | back 10 igD |
front 11 Activated T cells and macrophages release to mobilize immune cells and attract other leukocytes into the area. | back 11 Cytokines |
front 12 Natural killer (NK) cells __________. | back 12 can kill cancer cells before the immune system is activated |
front 13 T-cell activation requires ________. | back 13 antigen binding and co-stimulation |
front 14 Phagocyte mobilization involves ________. | back 14 mainly neutrophil and macrophage migration into inflamed areas |
front 15 Cytotoxic t cells ___________. | back 15 are the only T cells that can directly attack and kill other cells |
front 16 Small molecules that bind with self-proteins to produce antigenic substances are called ________. | back 16 Haptens |
front 17 The primary immune response __________. | back 17 has a lag B period while B cells proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells |
front 18 Monoclonal antibodies are used for the diagnosis of all of the following except | back 18 Juvenile diabetes |
front 19 Which of the following would be classified as a delayed hypersensitivity reaction? | back 19 allergic contact dermatitis |
front 20 Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in phagocytosis? | back 20 chemotaxis, adherence, ingestion, digestion, killing |
front 21 Which of the following is not a normal component of lymph? | back 21 red blood cells |
front 22 Antibodies that act against a particular foreign substance are released by ________. | back 22 plasma cells |
front 23 What is a bubo? | back 23 an infected lymph node |
front 24 A sentinel node is ________. | back 24 the first node to receive lymph from an area suspected to be cancerous |
front 25 Which of the following is not a function of lymph nodes? | back 25 produce lymph fluid and cerebro-spinal fluid |
front 26 Lymph capillaries are absent in all but which of the following? | back 26 digestive organs |
front 27 Select the correct statement about lymphoid tissue. | back 27 Lymphoid tissue is predominantly reticular connective tissue. |
front 28 Which of the following does not influence hemoglobin saturation? | back 28 nitric oxide |
front 29 The respiratory membrane is a combination of ________. | back 29 alveolar and capillary walls and their fused basement membranes |
front 30 The nose serves all the following functions except ________. | back 30 as the direct initiator of the cough reflex |
front 31 Complete the following statement using the choices below. Air moves out of the lungs when the pressure inside the lungs is ________. | back 31 greater than the pressure in the atmosphere |
front 32 Unlike inspiration, expiration is a passive act because no muscular contractions are involved. Expiration, however, depends on two factors. Which of the choices below lists those two factors? | back 32 the recoil of elastic fibers that were stretched during inspiration and the inward pull of surface tension due to the film of alveolar fluid |
front 33 Which of the following counteracts the movement of bicarbonate ions from the RBC? | back 33 chloride shifting |
front 34 In the plasma, the quantity of oxygen in solution is ________. | back 34 only about 1.5% of the oxygen carried in blood |
front 35 Gas emboli may occur because a ________. | back 35 diver holds his breath upon ascent |
front 36 The statement, "in a mixture of gases, the total pressure is the sum of the individual partial pressures of gases in the mixture" paraphrases ________. | back 36 Dalton's law |
front 37 Which of the following statements is true regarding the respiratory rate of a newborn? | back 37 The respiratory rate of a newborn is, at its highest rate, approximately 40-80 respirations per minute. |
front 38 For gas exchange to be efficient, the respiratory membrane must be ________. | back 38 0.5 to 1 micrometer thick |
front 39 The most powerful respiratory stimulus for breathing in a healthy person is ________. | back 39 increase of carbon dioxide |
front 40 The erythrocyte count increases after a while when an individual goes from a low to a high altitude because the ________. | back 40 concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes |
front 41 Surfactant helps to prevent the alveoli from collapsing by ________. | back 41 interfering with the cohesiveness of water molecules, thereby reducing the surface tension of alveolar fluid |
front 42 The factors responsible for holding the lungs to the thorax wall are ________. | back 42 surface tension from pleural fluid and negative pressure in the pleural cavity |
front 43 Which respiratory-associated muscles would contract if you were to blow up a balloon? | back 43 internal intercostals and abdominal muscles would contract |
front 44 The loudness of a person's voice depends on the ________. | back 44 force with which air rushes across the vocal folds |
front 45 Select the correct statement about the pharynx. | back 45 The auditory tube drains into the nasopharynx. |
front 46 Factors that influence the rate and depth of breathing include ________. | back 46 voluntary cortical control |
front 47 Which of the choices below is not a factor that promotes oxygen binding to and dissociation from hemoglobin? | back 47 number of red blood cells |
front 48 With the Bohr effect, more oxygen is released because a(n) ________. | back 48 decrease in pH (acidosis) weakens the hemoglobin-oxygen bond |
front 49 Which of the choices below describes the forces that act to pull the lungs away from the thorax wall and thus collapse the lungs? | back 49 the natural tendency for the lungs to recoil and the surface tension of the alveolar fluid |
front 50 The major nonelastic source of resistance to air flow in the respiratory passageways is ________. | back 50 friction |
front 51 Which of the following determines lung compliance? | back 51 alveolar surface tension |
front 52 Which of the statements below does not describe antigens? | back 52 Antigens only come from microbes |
front 53 Which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones? | back 53 lymphocytes |
front 54 Select the correct statement about lymph transport. | back 54 Lymph transport depends on the movement of adjacent tissues, such as skeletal muscles. |
front 55 Lymphoid tissue that appears as a swelling of the mucosa in the oral cavity is called a(n) ________. | back 55 tonsil |
front 56 Which of the following determine(s) what specific foreign substances our adaptive immune system will be able to recognize and resist? | back 56 Our genes |
front 57 Antibody functions include all of the following except ________. | back 57 cross-linking cell-bound antigens on red blood cells when blood types are properly matched |
front 58 B lymphocytes develop immunocompetence in the ________. | back 58 bone marrow |
front 59 B cells respond to the initial antigen challenge by ________. | back 59 producing progeny cells that include plasma cells and memory cells |
front 60 Which of the following is not a method by which antibodies work? | back 60 direct cell lysis |
front 61 Which of the following does not contain a mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue? | back 61 thymus |
front 62 Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system? | back 62 transporting respiratory gases |
front 63 Select the correct statement about lymphocytes. | back 63 B cells produce plasma cells, which secrete antibodies into the blood. |
front 64 Which of the following is not a part of the lymphatic system? | back 64 erythrocytes |
front 65 Which of the following statements is a false or incorrect statement? | back 65 After becoming immunocompetent, the naive T cells and B cells are exported to the bone marrow where the encounters with antigens occur. |
front 66 Which of the following cells predominate at the sites of chronic infections? | back 66 Macrophages |
front 67 Which of the following is not a function of the inflammatory response? | back 67 replaces injured tissues with connective tissue |
front 68 Interferons ________. | back 68 interfere with viral replication within cells |
front 69 The tonsils located at the base of the tongue are the ________. | back 69 lingual tonsils |
front 70 Functions of the spleen include all of those below except ________. | back 70 forming crypts that trap bacteria |
front 71 Large clusters of lymph nodes occur in all of the following locations except the ________. | back 71 lower extremities |
front 72 Which of the following would not be classified as a lymphatic structure? | back 72 pancreas |
front 73 The thymus is most active during ________. | back 73 childhood |
front 74 Which of the following is not a role of activated complement? | back 74 prevention of immediate hypersensitivity reactions |
front 75 Which of the following statements regarding NK cells is a false or incorrect statement? | back 75 NK cells are a type of neutrophil. |
front 76 Which of the following is characteristic of antibodies? | back 76 composed of heavy and light polypeptide chains |
front 77 Select the correct statement about the function of antibodies. | back 77 Complement fixation is the main mechanism by which antibodies provide protection. |
front 78 The antibody molecule is held together by ________ bonds. | back 78 disulfide |
front 79 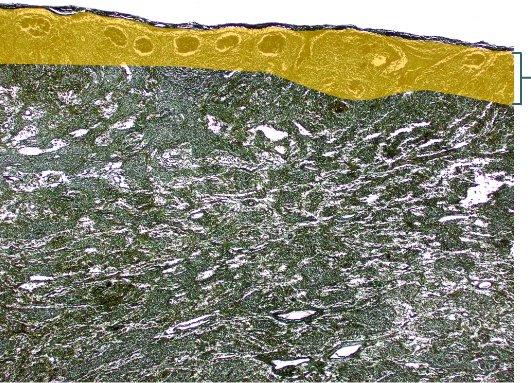 Which structure is highlighted? | back 79 cortex |
front 80 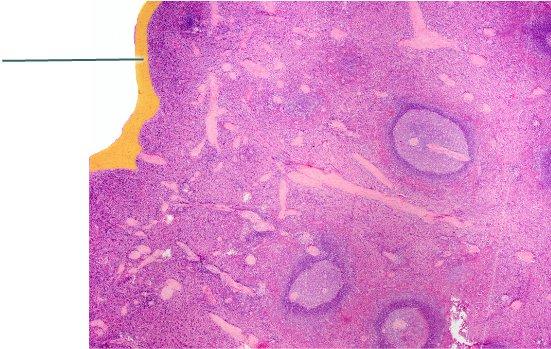 Which structure is highlighted? | back 80 capsule |
front 81 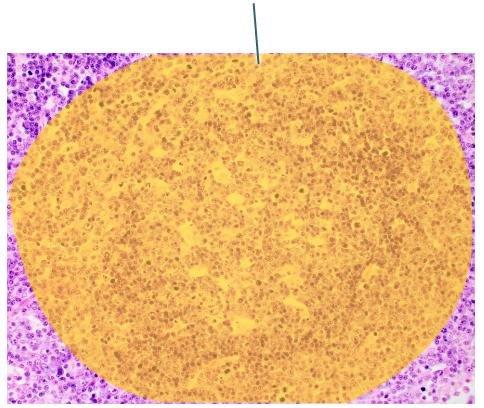 Which structure is highlighted? | back 81 lymphoid follicle |
front 82  Which structure is highlighted? | back 82 medulla |
front 83 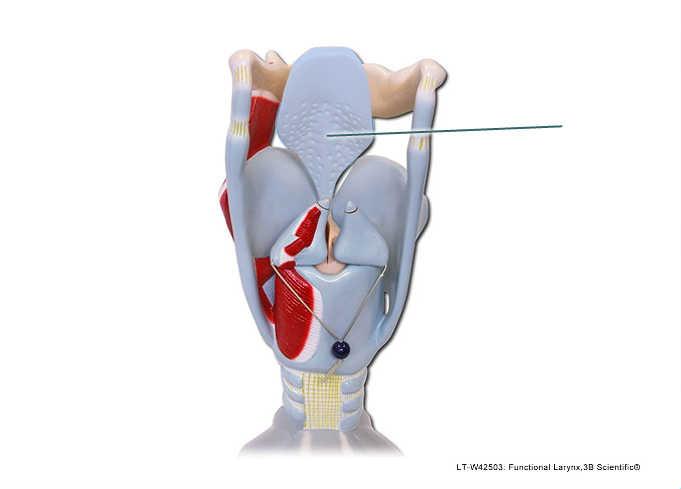 The highlighted structure is composed of what type of cartilage? | back 83 elastic |
front 84 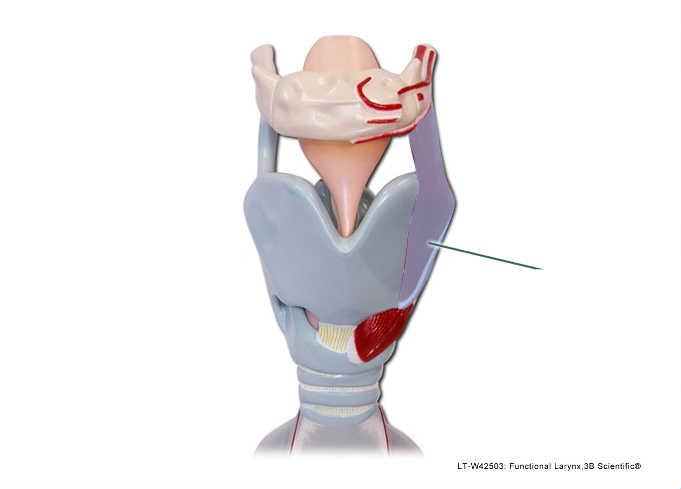 Which two structures are connected by the highlighted muscle? | back 84 thyroid cartilage and hyoid bone |
front 85 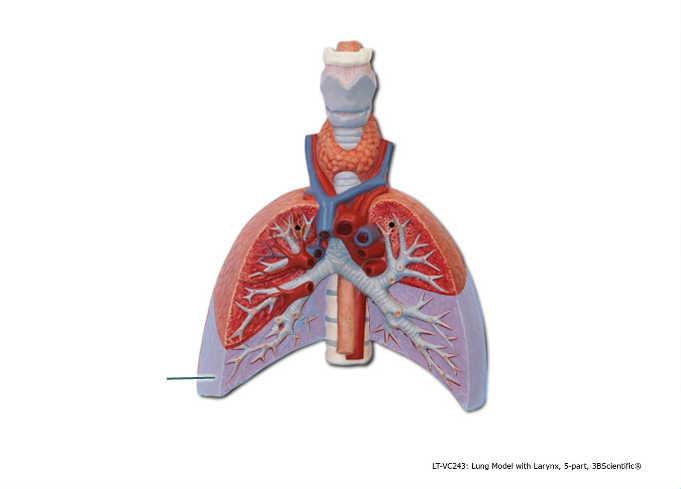 Which lobe is highlighted? | back 85 inferior |
front 86 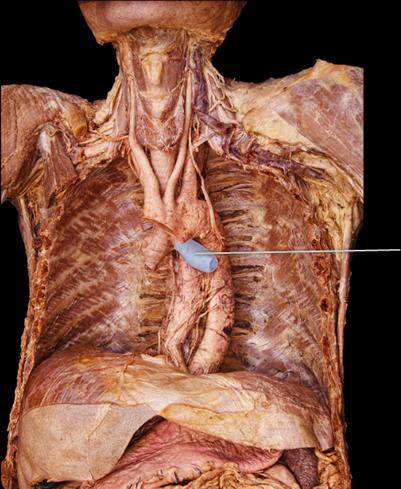 Which structure is highlighted? | back 86 left main bronchus |
front 87  Which cartilage is highlighted? | back 87 thyroid |
front 88 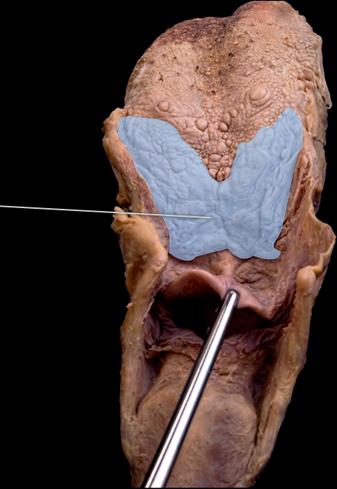 Which structure is highlighted? | back 88 lingual tonsil |
front 89 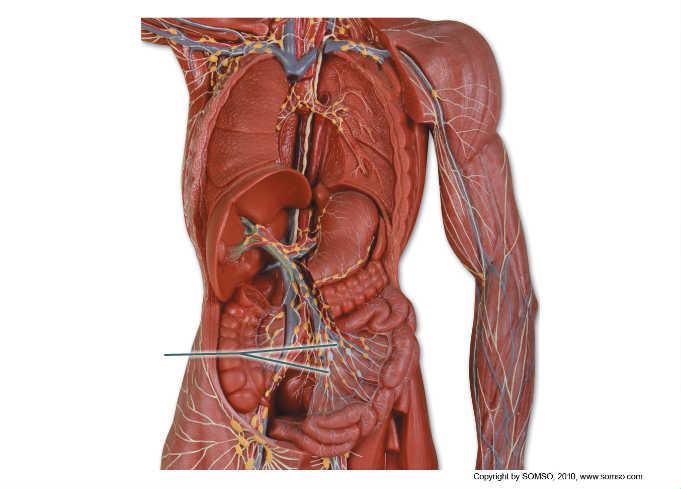 Which nodes are highlighted? | back 89 mesenteric |
front 90 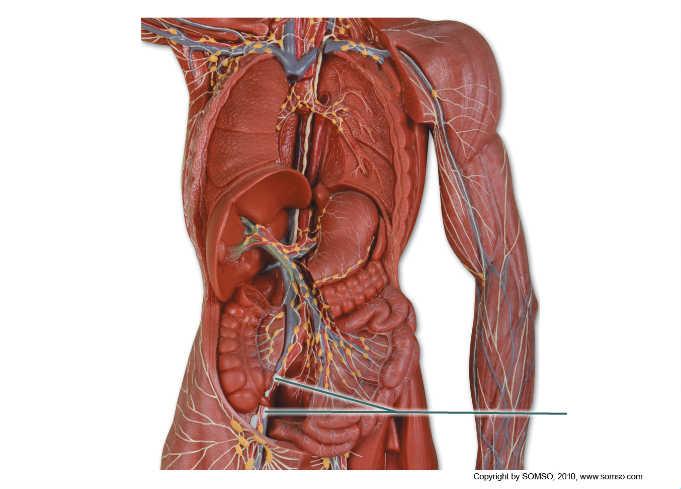 Which nodes are highlighted? | back 90 iliac |
front 91 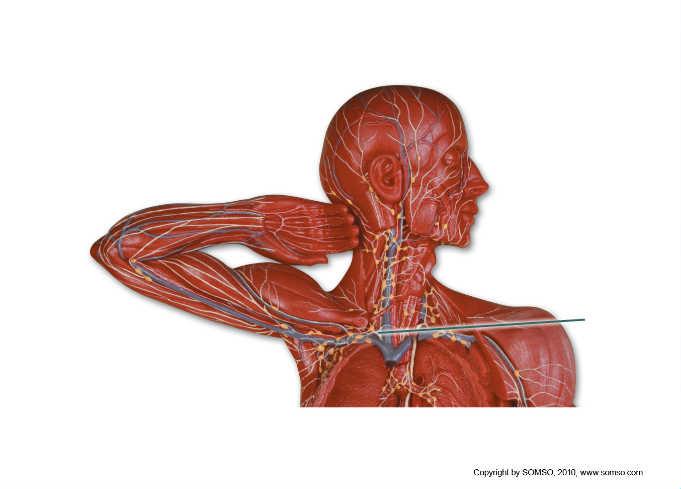 Which structure is highlighted? | back 91 right lymphatic duct |
front 92 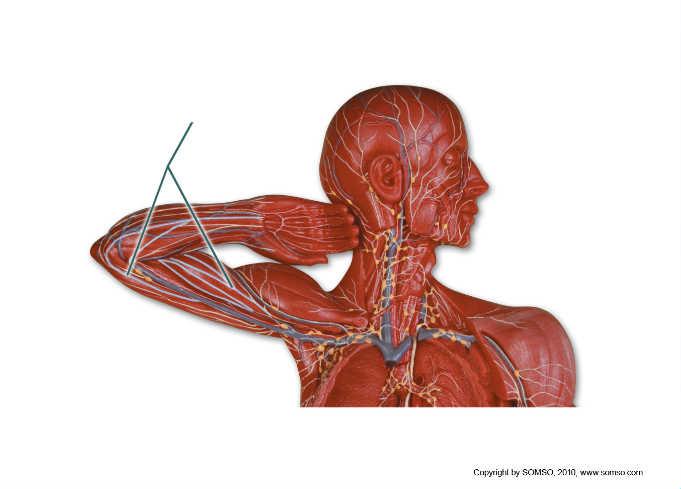 Which structures are highlighted? | back 92 lymphatic collecting vessels |
front 93 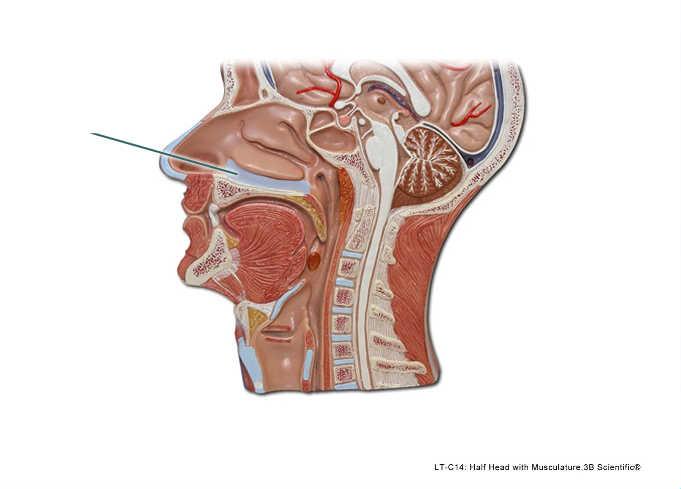 Which structure is highlighted? | back 93 inferior meatus |
front 94 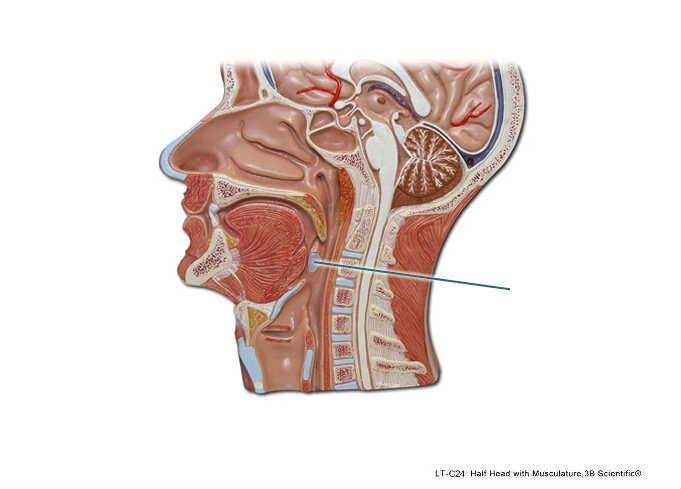 Which structure is highlighted? | back 94 palatine tonsil |
front 95  Which lymph nodes are highlighted? | back 95 axillary |
front 96 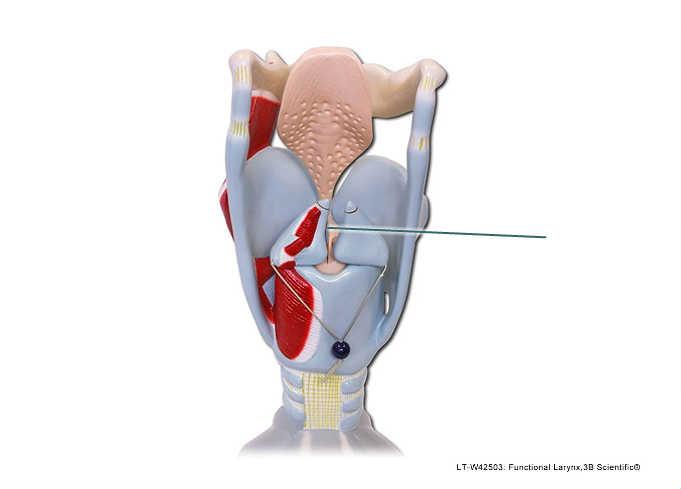 Which structure is highlighted? | back 96 rima glottidis |
front 97 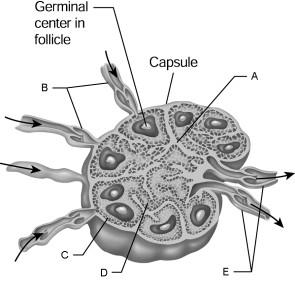 Medulla. | back 97 D |
front 98  Efferent vessels. | back 98 E |
front 99  Cortex. | back 99 C |
front 100  Afferent vessels. | back 100 B |
front 101  Trabecula. | back 101 A |
front 102 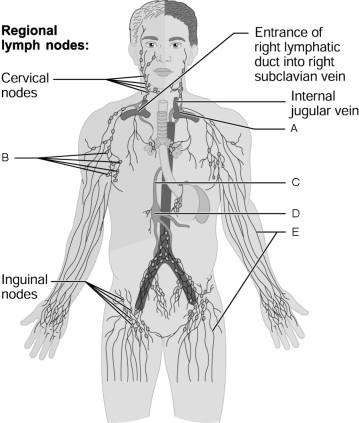 Lymphatic collecting vessels. | back 102 E |
front 103  Axillary node. | back 103 B |
front 104  Cisterna chyli. | back 104 D |
front 105  Entrance of thoracic duct into subclavian vein. | back 105 A |
front 106  Thoracic duct. | back 106 C |
front 107 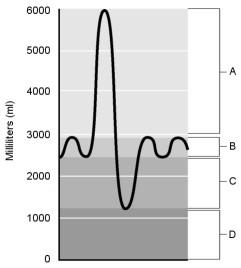 Inspiratory reserve volume. | back 107 A |
front 108  Tidal volume. | back 108 B |
front 109  Expiratory reserve volume. | back 109 C |
front 110  Residual volume | back 110 D |
front 111  Air that does not participate in the exchange of gases. | back 111 D |
front 112 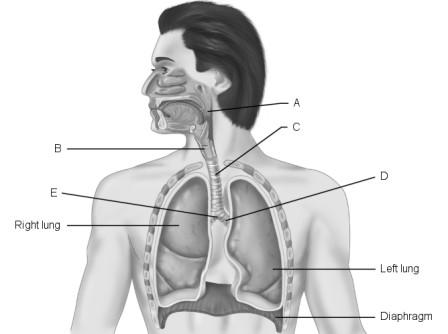 Main (primary) bronchus. | back 112 D |
front 113  Pharynx. | back 113 A |
front 114  Larynx. | back 114 B |
front 115  Carina of trachea. | back 115 E |
front 116  Trachea. | back 116 C |