The haploid human genome is 3 Gbp long (3x10^9 bp). How long would the genomic DNA in a single diploid cell in your body be if it were stretched out end to end?
~2 m
The haploid human genome is 3 Gbp long (3x10^9 bp). There are approximately 50 trillion cells in the human body. How long would all of the human genomic DNA in your body be if it were stretch out end to end?
100 billion Km
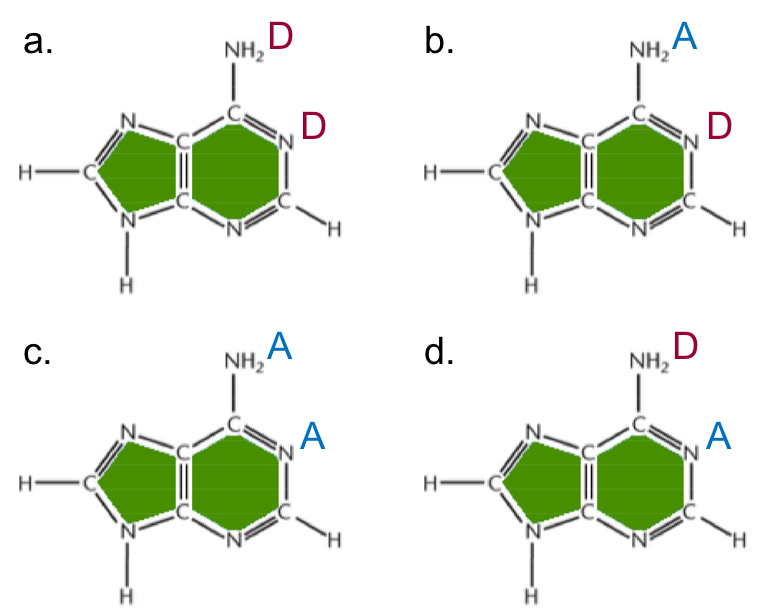
Which shows the correct hydrogen bond potential for adenine?
Picture d
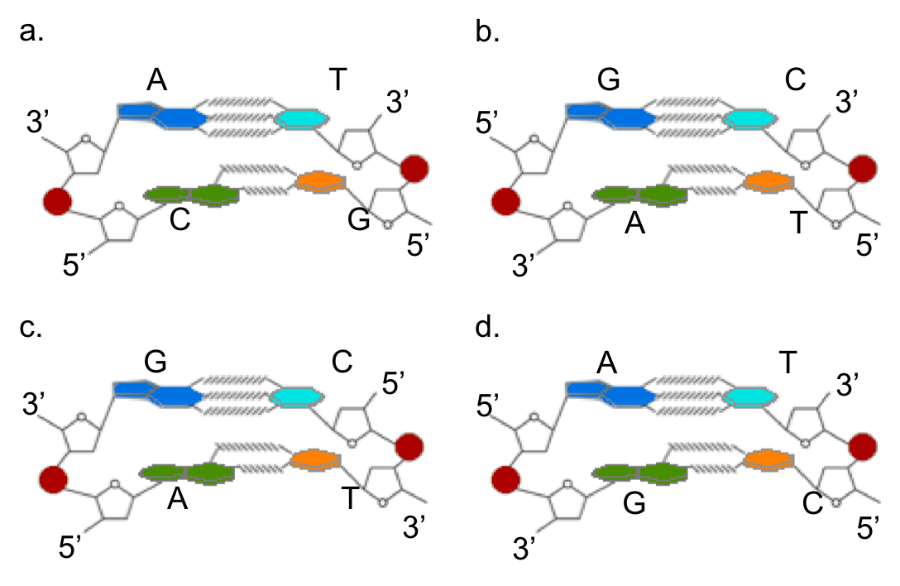
Which of the DNA structures is correct?
Figure b
If there are 6 C’s in the DNA sequence, how many G’s are there?
6

Which sequence would you predict for the 13-mer DNA that melts to initiate DNA replication?
Sequence b
What kind of enzyme is primase?
DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Which of the following components is not involved during the formation of the replication fork?
Ligase
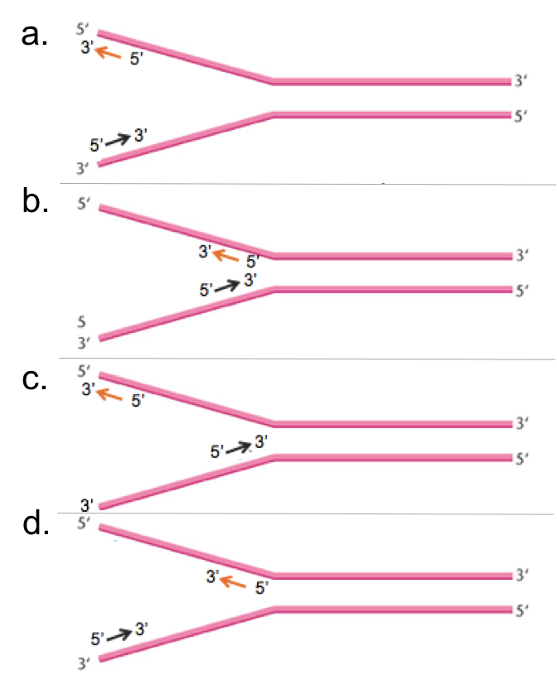
If you were primase where would you lay down primers to replicate the melted DNA?
As indicated in d
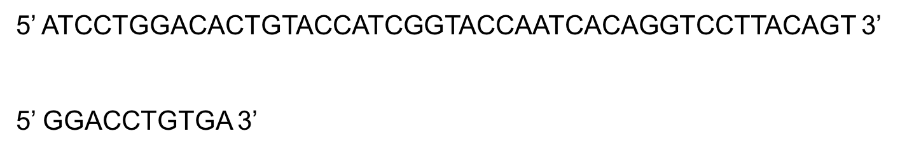
If the two oligonucleotides are allowed to anneal and the DNA polymerase and all substrates (4 dNTPs, etc.) are added to the mix, what will the first nucleotide incorporated in the DNA be?
T
In what cells would you expect to see telomerase activity?
Cancer cells. Pluripotent stem cells. Adult B lymphocytese.
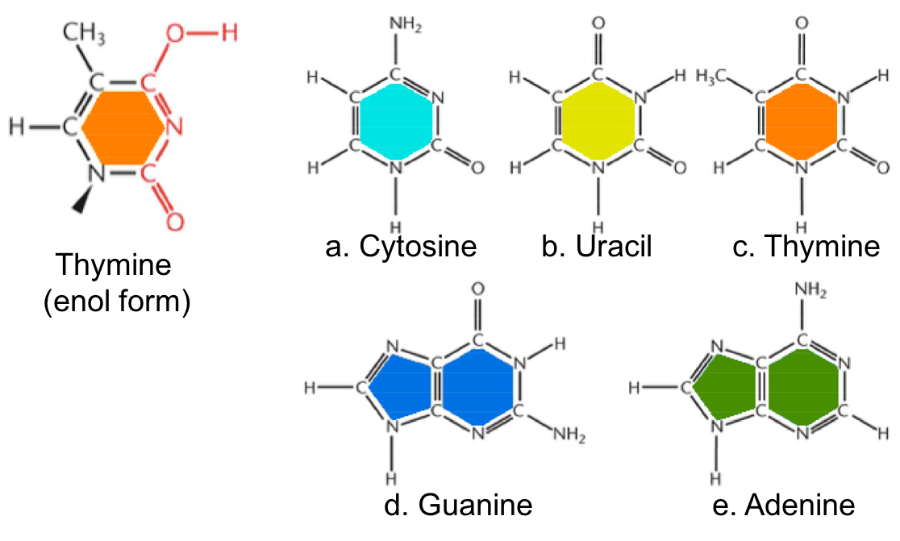
Which base will thymine (enol) pair with in DNA?
Guanine
A tautomeric shift may result in:
A transition mutation
How many mutations would you expect to see in the human genome if mismatches could not be repaired?
600,000
Proofreading removes approximately 99% of mismatches before DNA replication moves on. After proofreading what is the mutation rate for DNA replication in humans?
10^-6 mutations/base pair
Proofreading removes approximately 99% of mismatches before DNA replication moves on. How many mutations would you expect to see in the human genome if mismatches can be repaired by proofreading?
6,000
The initial mechanism for repairing nucleotide errors in DNA is ________.
DNA polymerase proofreading
What types of mutations can intercalating agents lead to?
Frameshift mutations
Which of the following is the type of DNA repair in which thymine dimers are directly broken down by the enzyme photolyase?
Direct repair
The graph shows the results of an Ames test to identify the the effect of several concentrations of Aflatoxin B using a couple of his- Salmonella strains (TA 100 and TA 1538). While TA 100 is a strain sensitive to reversion mutations by base substitutions, TA 1538 is sensitive to frameshift mutations. Based on the results, what kind of mutations can Aflatoxin B1 lead to?
All except frameshift mutations
Which of the following regarding the Ames test is true?
It is used to identify mutants with restored biosynthetic activity.
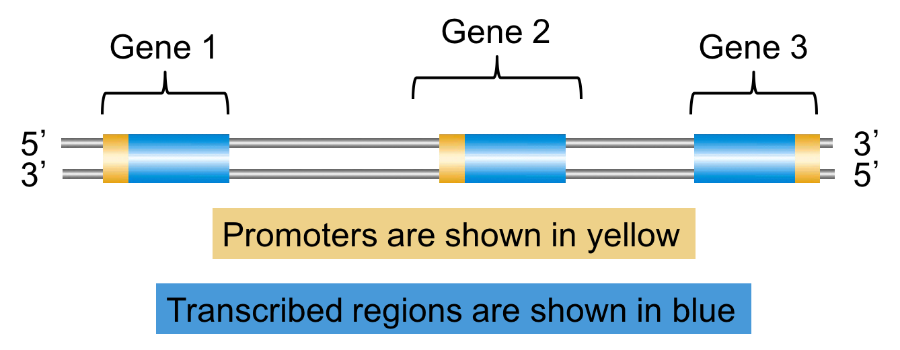
In a given chromosome, both strands are used as templates, but in any one gene, only one strand is used. For the 3 genes shown above, what are the template strands?
Lower, lower, upper.
Which sequence would you predict to be at a promoter site?
TATAAT
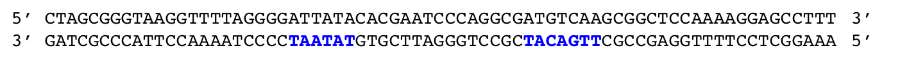
For the prokaryotic DNA sequence above, which direction does the transcription proceeds? Note: -35 and -10 consensus sequences are in blue.
Right to left
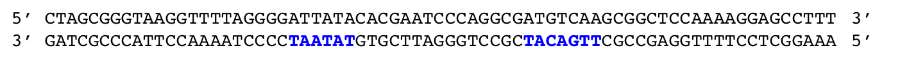
For the prokaryotic DNA sequence above, which strand is the coding (non-template) strand?
Bottom
What is the sequence of the 5’ end of the mRNA transcribed from this prokaryotic gene?
UAGA
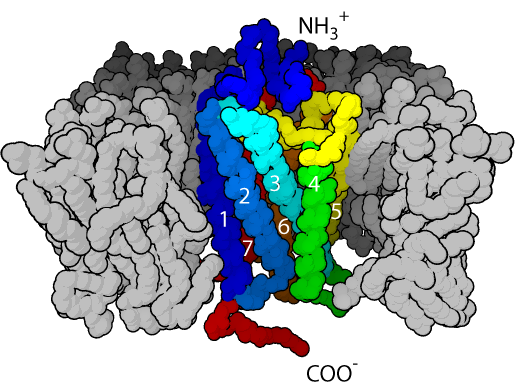
Which amino acid would you expect to be part of an alpha-helix from the GPCR signaling protein?
Leucine

What is the sequence of the protein made from this prokaryotic nucleic acid sequence?
N-Met-Asn-Ser-C
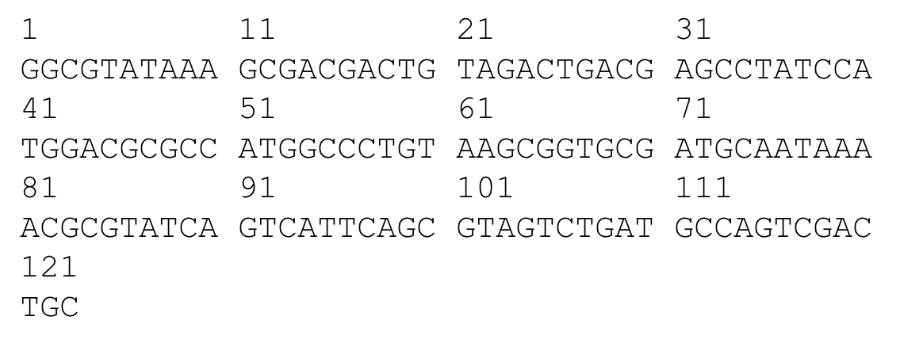
For the eukaryotic DNA sequence shown, what region of the DNA will be transcribed into mRNA?
41-101
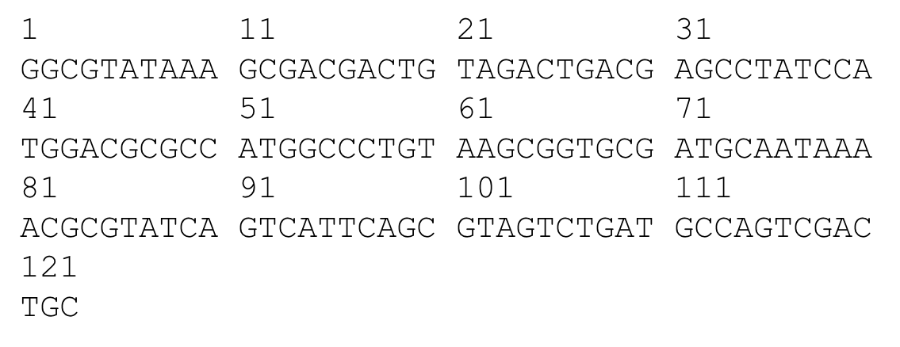
For the eukaryotic DNA sequence shown, what region of the mRNA contains the open reading frame that will be translated into protein?
51-59
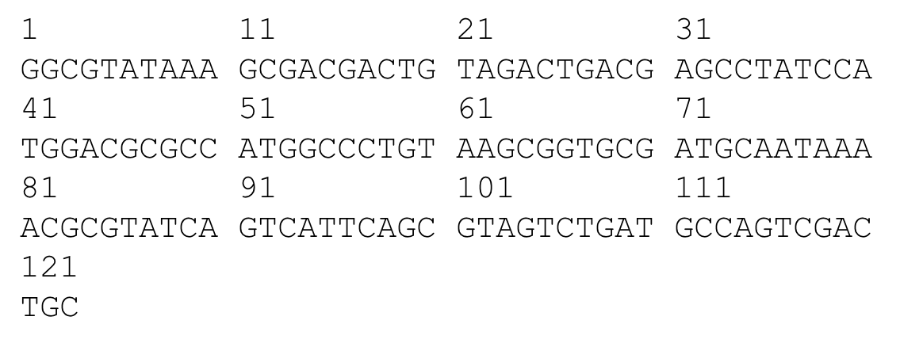
For the eukaryotic DNA sequence shown below, where is the 3’ UTR?

63-101
An operon of genes encoding enzymes in a biosynthetic pathway is likely to be which of the following?
Repressible
Which of the following conditions leads to maximal expression of the lac operon?
lactose present, glucose absent
What does the wild-type lacI protein do?
Acts as a repressor (inhibits transcription from the lac operon).
Lactose (actually allolactose) binds to the lacI protein and regulates its ability to bind to the operator. Lactose binding to lacI protein:
Prevents lacI protein from binding to the operator (acts as an inducer).
Which of the following are true of epigenetic changes?
Allow DNA to be transcribed. Move histones to open or close a chromosomal region. Are temporary
The PCR step during which the double-stranded template molecule separates into two strands is called _____________.
denaturation
In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA will be attracted to the negative electrode.
T/F
False
Which of the following are true about DNA and gel electrophoresis?
DNA is negatively charged. Small bands travel more quickly than large bands. The size of a DNA fragment is measured in base pairs
Regarding Sanger's sequencing method, why does the incorporation of a ddNTP in the growing complementary strand terminates the process of DNA replication?
Because the ddNTP cannot form a phosphodiester bond with the sugar from a newly recruited dNTP due to the missing hydroxyl group (–OH).
Insulin produced by molecular cloning:
is a recombinant protein
All of the following are processes used to introduce DNA molecules into bacterial cells except:
transcription
Which of the following is required for repairing the phosphodiester backbone of DNA during molecular cloning?
DNA ligase
In blue-white screening, what do blue colonies represent?
Cells containing empty plasmid vectors.
In the reproductive cloning of an animal, the genome of the cloned individual comes from ________.
a body cell
How are genomic libraries created?
There are multiple methods - the main one uses molecular cloning to amplify fragments of genomes for further study and addition to a collection (the genomic library).
Personal genomics is relatively __________.
new, as recent discoveries and genome mapping efforts have made genetic information more readily available.
What led to the commercialization of personal genomic products?
The increase in understanding of genetics and decrease in price of mapping a genome.
Why are personal genomics products potentially dangerous?
Results are limited and consumers may make incorrect medical decisions based on their results. Genetic discrimination may also occur.
What is genetic discrimination?
Discrimination against people by their employers, health care providers, insurance companies because of genetic indicators of health.
Epigenetics is best described as ________________.
additions to changes in a sequence, like "tags" that sit on the main nucleotide sequence.
Epigenetics creates noticeable effects by _________________.
histone modifications, which alter gene expression.
What kind of traits does epigenetics affect?
Widespread, multi-cellular traits like cancer and inherited disorders.
What factors influence epigenetics?
Both environmental and genetic factors.
An expectant mother is exposed to secondhand smoke for the duration of her pregnancy. Who in the situation is affected?
All three generations - the mother, developing baby, and subsequent generations.
Cytosines and guanines are paired by 2 hydrogen bonds, while adenines and thymines are paired by 3 hydrogen bonds.
T/F
False
The correct order of steps in a PCR cycle is:
Denaturation, annealing, extension
At which temperature does a DNA double helix denature?
95
The goal of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is to:
Amplify a small amount of DNA sequence
RNA differs from DNA in that it:
contains ribose sugar
contains uracil
is usually found as a single-stranded molecule in cells
What are the 3 main components of a DNA nucleotide?
A phosphate group, a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose
Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds. During PCR, hydrogen bonds are broken during the denaturation step.
T/F
True
Which of the following is incorrect?
-Two strands of DNA double helix are held together by covalent bonds
-Adenine pairs with Thymine
-Nucleotides in DNA consist of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
-Cytosine pairs with Guanine
Two strands of DNA double helix are held together by covalent bonds
Which of the following amino acids are frequently found at the transcription start site in eukaryotes?
Methionine
Although DNA and RNA synthesis have many shared features, there is a distinctive property in RNA synthesis which is absent in DNA. Which of the following is this?
RNA polymerase can begin synthesis of a new RNA strand by first adding nucleoside triphosphate; DNA polymerase requires a primer sequence
Choose the pair of molecules that are most alike in their nucleotide sequence:
mRNA and DNA coding strand
Given DNA sequence: 5’ TCCGATTGG 3’. Which of the answers below represents the correct type and complementary sequence in the correct direction for this sequence?
DNA; 3’ AGGCTAACC 5’
What is the term used to represent a set of bacterial genes under coordinate control?
Operon
What effect on transcription of the structural genes of the lac operon is observed when glucose is absent and lactose present in high levels?
Transcription is induced
The main role of cAMP in transcriptional regulation of lac operon is:
Activates activator protein
What happens when E.coli is grown in environment that contains both glucose and lactose in terms of lac operon regulation?
Neither CAP or lac repressor are bound to DNA
Genetic engineering has been used to do which of the following:
Make bacteria that produce human proteins
Make plants more resistant to disease
Improve the nutritional quality of plants
The mechanism of intake of DNA fragments from the surrounding medium by a cell is called
Transformation
When ‘sticky ends’ are paired they can be covalently joined by:
DNA Ligase
In the lab, DNA can be cut at a specific sequence in rDNA technology using:
Restriction Endonuclease