This is the mass of tissue from the sternum to the vertebral column between the lungs.
- Epicardium
- Parietal layer
- Pericardial tissue
- Mediastinum
- Fibrous cardium
D
This is the layer that protects the heart.
- Epicardium
- Parietal layer
- Myocardial tissue
- Mediastinum
- Endocardium
A
To which side of the body is the apex pointed?
- At the midline
- To the left
- To the right
- Different for males and females
- Posteriorly
B
Which of the following consists of inelastic dense irregular connective tissue?
- Parietal layer of pericardium
- Serous pericardium
- Fibrous pericardium
- Epicardium
- Pericardial cavity
C
This is used to reduce the friction between membranes of the heart.
- Epicardium
- Endocardium layer
- Pericardium
- Pericardial (serous) fluid
- Pericardial cavity
D
This consists of mesothelium and connective tissue.
- Epicardium
- Myocardium
- Endocardium
- Pericardial cavity
- Fibrous pericardium
A
Which layer consists of cardiac muscle tissue?
- Epicardium
- Pericardium
- Myocardium
- Endocardium
- Hypocardium
C
This is used to increase the capacity of the atrium.
- Ventricle
- Coronary sulcus
- Fossa ovalis
- Interatrial septum
- Auricle.
E
This marks the boundary between the ventricles.
- Coronary sulcus
- Anterior interventricular sulcus
- Posterior interventricular sulcus
- Coronary sulcus and posterior interventricular sulcus
- Anterior and posterior intercentricular sulcus
E
These extend into the auricle.
- Pectinate muscles
- Interatrial septum
- Coronary sulcus
- Ventricle
- Chordae tendinae
A
Through which structure does blood pass from the right atrium to the right ventricle?
- Bicuspid valve
- Interventricular septum
- Tricuspid valve
- Mitral valve
- Ascending aorta
C
What types of tissue comprise the valves of the heart?
- Dense regular connective tissue
- Dense irregular connective tissue
- Areolar connective tissue
- Hyaline cartilage
- Cardiac muscle tissue
B
From the left ventricle, where does blood pass?
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle
- Bicuspid valve
- Aortic semilunar valve
- Pulmonary trunk
D
In a fetus, this structure temporarily shunts blood from the pulmonary trunk into the aorta.
- Fossa ovalis
- Foramen ovale
- Trabeculae carnae
- Descending aorta
- Ductus arteriosus
E
As each ventricle contracts where does blood move?
- Into an artery
- Into the apex
- Into a vein
- Through an atrioventricular valve
- Through the apex
A
As each atrium contracts where does blood move?
- Into an auricle
- Into an artery
- Into a vein
- Through an atrioventricular valve
- Through a semilunar valve
D
Which of the below valves prevents blood from flowing back from the lungs?
- Tricuspid valve
- Bicuspid valve
- Pulmonary valve
- Aortic valve
- Pulmonary vein
C
In this disorder the aortic valve is narrowed.
- Aortic insufficiency
- Rheumatic fever
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Aortic stenosis
- Mitral insufficiency
D
This heart structure carries deoxygenated blood.
- Left atrium and ventricle
- Left atrium only
- Right atrium and ventricle
- Right ventricle only
- Left atrium and right ventricle
C
This vessel distributes oxygenated blood to the myocardium.
- Coronary artery
- Coronary vein
- Right ventricle
- Left auricle
- Myocardial vein
A
Cardiac muscle fibers electrically connect to neighboring fibers by
- Desmosomes
- Intermediate discs
- Gap junctions
- Contractile fibers
- Chordae tendinae
C
Which of the following contains the largest amount of mitochondria?
- Smooth muscle
- Skeletal muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Hepatocytes
- Leukocytes
C
This is a network of specialized cardiac muscle fibers that provide a path for each cycle of cardiac excitation to progress through the heart.
- Pacemaker
- Sinoatrial node
- Purkinje fibers
- Conduction system
- Bundle of His
D
This is a the correct sequence of structures that allows the normal sequence of excitation to progress through the heart.
- Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers, Atrioventricular (AV) node
- Sinoatrial (SA), Purkinje fibers, AV node, Bundle of His
- Purkinje fibers, AV node, SA node, Bundle of His
- SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers
- Bundle of His, SA node, AV node, Purkinje fibers
D
By comparison, cardiac muscle cells have _____________contraction plateau time than skeletal muscle cells.
- a shorter
- a longer
- no difference in
B
This is the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle into the aorta each minute.
- Cardiac output
- Cardiac input
- Stroke volume
- Heart rate
- Auscultation
A
This term refers to the period of time during a cardiac cycle when contraction occurs and blood pressure rises.
- filling
- systole
- repolarization
- diastole
- fibrillation
B
Which of these periods represents greatest cardiac output?
- atrial diastole
- ventricular diastole
- atrial systole
- ventricular systole
D
The second heart sound represents which of the below events?
- Valvular stenosis
- Semilunar valves opening
- Atrioventricular valves closing
- Semilunar valves closing
- Atrioventricular valves opening
D
This part of the heart can initiate a contraction and can set a constant heart rate of about 100 beats per minute.
- Cardiac accelerator nerves
- Chemoreceptors
- Cardiovascular center
- Sinoatrial valve
- Proprioceptors
D
Stimulation of this nerve reduces heart rate.
- Cardiac accelerator nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
- Medulla oblongata nerve
- Vagus nerve
- Phrenic nerve
D
Which of the below reduces heart rate.
- Increased Norepinephrine hormone
- Increased Thyroid hormone
- Increased potassium levels
- Increased calcium levels
- Increased sympathetic stimulation
C
This part of the brain regulates heart rate.
- Cardiac accelerator nerves
- Chemoreceptors
- Medulla oblongata
- Vagus nerve
- Proprioceptors
C
This electrical event represents repolarization of the ventricle.
- R wave
- T wave
- S wave
- P wave
- Q wave
B
Which of the below factors would increase Stroke volume?
- increased preload, increased afterload, increased contractility
- decreased preload, decreased afterload, decreased contractility
- increased preload, decreased afterload, increased contractility
- decreased preload, increased afterload, increased contractility
- increased preload, increased afterload, decreased contractility
C
This electrical event triggers contraction of the atria.
- R wave
- T wave
- S wave
- P wave
- Q wave
D
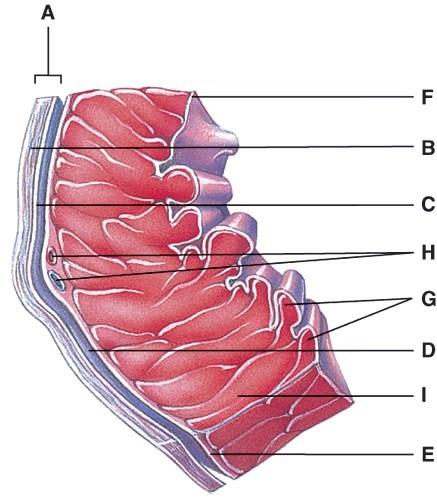
This portion of the heart wall is responsible for the pumping action.
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
E

This is comprised of a thin layer of endothelium overlying a thin layer of connective tissue.
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
D

Which layer of the pericardium consists of dense irregular connective tissue?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
B

In the diagram, where is the trabeculae carnae?
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
D
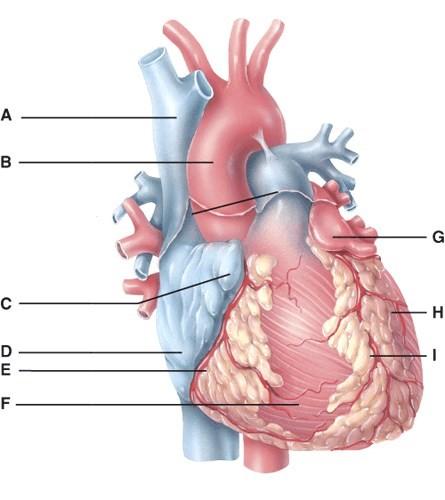
In the diagram, where is the coronary sulcus?
- C
- E
- G
- H
- I
B

In the diagram, where is the left auricle of left atrium?
- C
- F
- G
- H
- I
C

In the diagram, where is the ascending aorta?
- A
- B
- D
- F
- H
B

In the diagram, these contain coronary blood vessels and a variable amount of fat.
- F and H
- A and B
- C and G
- E and I
- D and F
D
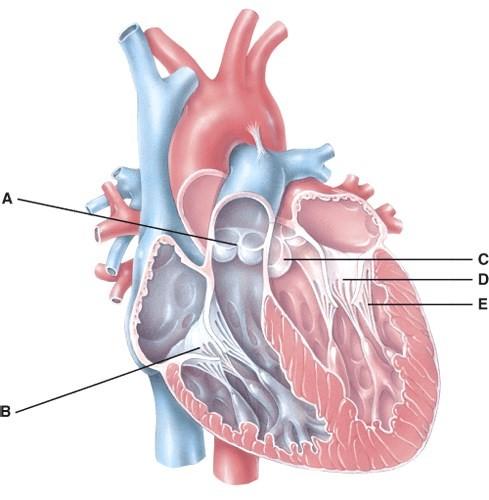
In the diagram, where does the blood pass from the right atrium into the right ventricle?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
B

In the diagram, which labeled structure is the pulmonary semilunar valve?
- B
- D
- E
- A
- None of the above
D

In the diagram, where is the atrioventricular valve?
- B
- D
- A
- B and D
- B,D, and A
D
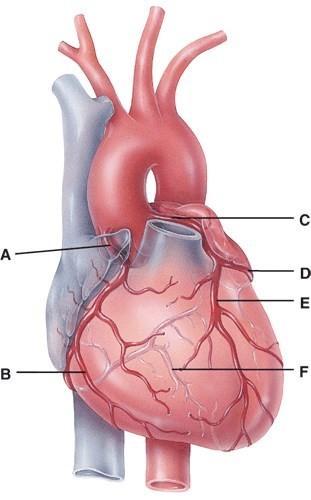
In the diagram, which labeled structure is the anterior interventricular branch of the left coronary artery?
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
D

In the diagram, this supplies the walls of the ventricles with oxygenated blood.
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
E

In the diagram, all of the following carry oxygenated blood.
- A
- B
- F
- E
- All of the above
E

In the diagram, where is the marginal branch of the right coronary artery?
- A
- B
- D
- E
- F
B

In the diagram, which labeled structure is the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery?
- B
- D
- E
- F
- C
B

In the diagram, where is the posterior interventricular branch?
- B
- D
- E
- F
- C
D
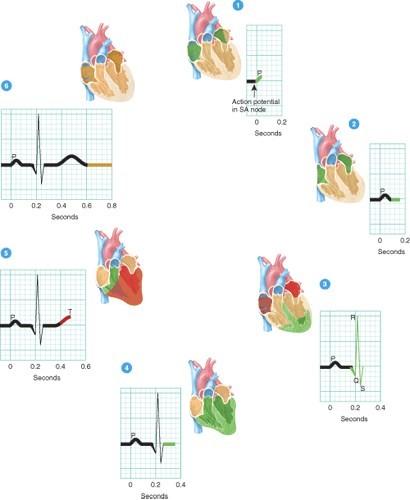
Which phases of a heartbeat shown in the diagram involve repolarization of the heart’s four chambers?
- 1 and 4
- 2 and 4
- 4 and 6
- 1, 3, and 5
- 1, 2, 4 and 6
- 3 and 5
F

Where in the figure does depolarization events occur?
- 2 and 4
- 1 and 3
- 2,4 and 6
- 1,3, and 5
- 4 and 6
B
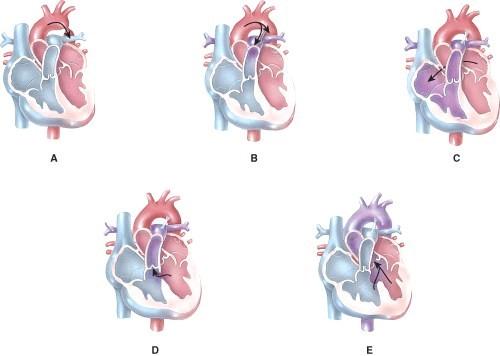
Which of the following represents coarctation of the aorta?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
A

Which of the following represents an atrial septal defect?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
C
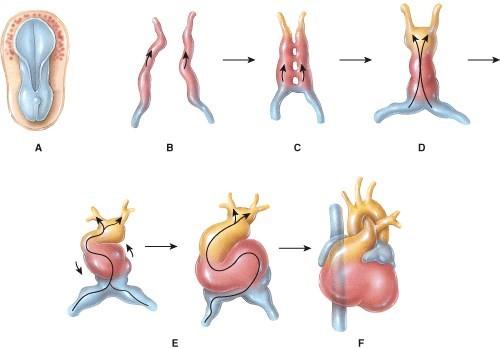
Which of the following represents the formation of the primitive heart tube?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
C

Which of the following represents formation of the endocardial tubes?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
B
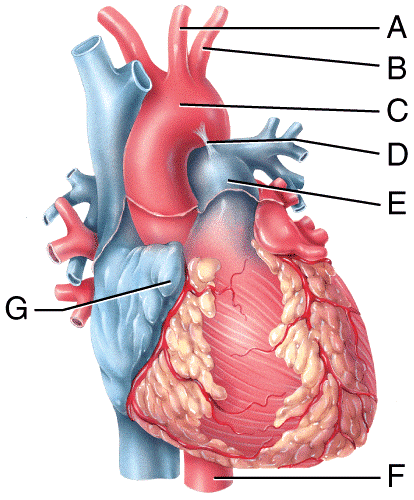
Which blood vessel shown in the figure carries oxygenated blood to the lower thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity of the body?
- A
- B
- E
- F
- H
D

Which labeled structure shown in the diagram is a remnant of fetal circulation that is not directly involved in adult circulation?
- A
- B
- H
- D
- E
D

Which labeled blood vessel in the diagram is an artery carrying deoxygenated blood?
- A
- B
- C
- E
- I
D

Which labeled blood vessel in the diagram is the left common carotid artery?
- A
- B
- E
- F
- H
A

Which labeled blood vessel in the diagram is the right common carotid artery?
- A
- B
- E
- F
- not shown in the diagram
E

Which labeled blood vessel in the diagram is the left subclavian artery?
- A
- B
- E
- F
- H
B

Which labeled structure shown in the diagram is a pouch-like extension that serves to slightly increase the capacity of an atrium?
- F
- E
- G
- I
- D
C

What labeled structure in the figure is the ligamentum arteriosum?
- A
- B
- C
- D
D

Which labeled structure in the figure receives deoxygenated blood from the blood vessel labeled A?
- G
- C
- D
- I
- F
C

What labeled structure in the figure divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries to carry blood to the lungs?
- E
- A
- D
- G
A

Which structure in the figure is labeled B?
- left common carotid artery
- left subclavian artery
- left pulmonary vein
- mitral valve
B

Which structure in the figure is labeled C?
- arch of aorta
- pulmonary trunk
- tricuspid valve
- aortic valve
A

Which structure in the figure is labeled A?
- left common carotid artery
- left subclavian artery
- left pulmonary vein
- mitral valve
A
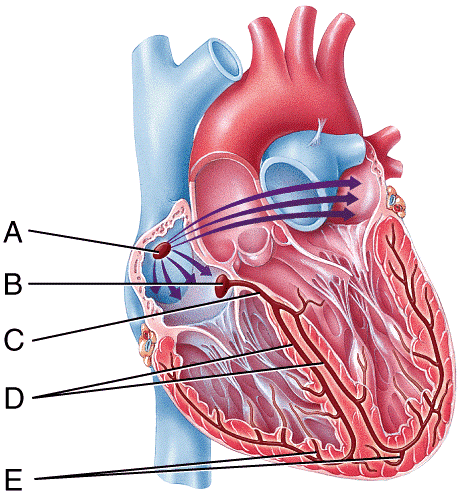
Which labeled structure in the figure acts as the natural pacemaker of the heart?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
A

Which labeled structure in the figure is the AV node?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
B

Which labeled structure in the figure represents the only potential pathway for conducting action potentials from the atria to the ventricles?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
C

Which labeled structure in the figure carries the cardiac action potential directly into the contractile fibers of the ventricular myocardium?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
E
Cardiac output is the volume of blood ejected from the _____________ ventricle into the _____________ each minute.
- left, aorta
- right, aorta
- left or right, aorta or pulmonary trunk
- right, pulmonary trunk
- both left and right aorta are correct
C
The difference between a person’s maximum cardiac output and resting cardiac output is called the
- stroke volume.
- peripheral resistance.
- afterload.
- cardiac reserve.
- venous return.
D
What is the function of foramen ovale during fetal life?
- Allowing blood to flow directly from the right atrium into the left atrium.
- Allowing blood to flow directly from the right ventricle into the left ventricle.
- Serves as a valve in the vena cava to regulate venous blood flow.
- Prevents back flow of blood from aorta into the left ventricle.
- Prevents back flow of blood from pulmonary trunk into the right ventricle.
A
Isovolumetric contraction is the phase of the cardiac cardiac cycle in which
- the semilunar valves are open.
- ventricular repolarization occurs.
- atrial depolarization occurs.
- oxygenated blood leaves the heart into the systemic circulation.
- ventricular pressure increases and ventricular volume remains the same.
E
Which of the following chambers of the heart is surrounded by the thickest layer of myocardium?
- right atrium
- left atrium
- right ventricle
- left ventricle
- right auricle
D
The process of listening to heart sounds using a stethoscope is referred to as
- palpitation.
- palpation.
- auscultation.
- fibrillation.
- echocardiography.
C
Heart murmurs are often heard in individuals with abnormalities in the of the heart.
- valves
- myocardium
- SA node
- AV node
- endocardium
A
Which of the following conditions would lead to an increase in the afterload for the ventricles thus lowering stroke volume and cardiac output?
- hypotension
- hypertension
- increased venous return
- decreased venous return
- positive inotropic agents
B
In comparison to a sedentary individual, a well-trained athlete will usually have all the following characteristics EXCEPT
- a higher cardiac reserve.
- a higher resting cardiac output.
- a higher stroke volume.
- hypertrophy of the heart.
- resting bradycardia.
B
During heart transplants, the nerves are severed resulting in a faster resting heart rate (approximately 100 beats per minute) after the transplant.
- glossopharyngeal
- cardiac accelerator
- vagus
- phrenic
- cervical spinal
C
A corrective cardiac procedure in which a large piece of a patient’s own latissimus dorsi muscle is wrapped around the heart and stimulated by an implanted pacemaker to assist the pumping action of a damaged heart.
- myocardial infarction
- tetrology of Fallot
- cardiomyopathy
- cardiomegaly
- cardiomyoplasty
E