Which of following is a correct statement about the relationship between ph and the hydrogen-ion concentration of a solution?
a. There are no hydrogen ions present in a solution with a basic pH
b. There are no hydrogen ions present in a solution with a pH of 7
c. The concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution with a pH of 7 is 100 times greater than that in a solution with a pH of 9
d. The concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution with a pH of 5 is twice that than with a pH of 3
c
A controlled experiment is one in which...
A. the experiment is
repeated many times to ensure that the results are accurate.
B.
the experiment proceeds at a slow pace to guarantee that the scientist
can carefully observe all reactions and process all experimental
data.
C. there are at least two groups, one of which does not
receive the experimental treatment.
D. there are at least two
groups, one differing from the other by two or more variables.
E.
there is one group for which the scientist controls all variables.
C
A covalent bond is likely to be polar when...
A. one of the
atoms sharing electrons is much more electronegative than the other
atom.
B. the two atoms sharing electrons are equally
electronegative.
C. the two atoms sharing electrons are of the
same element.
D. it is between two atoms that are both very
strong electron acceptors.
E. the two atoms sharing electrons are
different elements.
A
If the pH of a solution is decreased from 7 to 6, it means that
the...
A. concentration of H+ has decreased to 10 times of what
it was at pH 7.
B. concentration of H+ has increased to 10 times
of what it was a pH 7.
C. concentration of OH- has increased to
10 times what it was at pH 7.
D. concentration of OH- has
decreased to 10 times what it was at pH 7.
E. Both B and D are correct.
E
- The movement of water to the top of a 15-meter tree is best explained by
- A. Transpiration and cohesion
- B. Root and stem pressure
- C. Barometric pressure
- D. Capillary action
- E. Gravitational flow
A
The base composition of DNA varies from one species of bacteria to
another. Which of the following ratios would you expect to remain
constant in the DNA. regardless of the species?
a) pyrimidine +
purine/ deoxyribose
b) adenine/ cytosine
c) adenine +
cytosine/ deoxyribose
d) Pyrimidine/ ribose
A
Analysis of DNA sequences from two individuals of the same species
results in a greater estimate of genetic variability than does
analysis of amino acid sequences from the same individuals
because:
a) different DNA sequences can code for the same amino
acid
b) some amino acid variations cannot be detected by protein
electrophoresis
c) DNA sequencing is a more reliable technique
than protein electrophoresis
d) proteins are more easily damaged
than is DNA
A
Which of the following is a correct statement about
mutations?
a) they are a source of variation for
evolution
b) they drive evolution by creating mutation
pressures
c) they are irreversible
d) they occur in germ
cells but not in somatic cells
A
The working of lac operon is important for which of the following
reasons?
a) It represents a principle means by which genes are
regulated in prokaryotes
b) it represents a principle means by
which genes are regulated in eukaryotes
c) It illustrates the
complexities of rRNA transcription
d) It provided the first clues
to how DNA replication is controlled during the cell cycle
A
Within the cell, many chemical reactions that, by themselves, require
energy input (have a positive free-energy change) can occur because
the reactions
a) may be coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP
b)
take place very slowly
c) take place when the cells are at
unusually high temperatures
d) are catalyzed by enzymes
e)
are aided by various metal ions that act as catalysts
A
Which of the following is true of both mitochondria and
chloroplasts?
(A) They are found in the cells of eukaryotic
autotrophs and heterotrophs.
(B) They include stacks of membranes
that absorb light.
(C) They include compartments where hydrogen
ions are concentrated.
(D) They produce sugars using energy
harvested in the cytoplasm.
(E) They break down sugar to produce
A TP .
C
The tertiary structure and function of a
polypeptide is
principally determined by the
(A) length of the
polypeptide
(B) number of nucleotides present in
the
polypeptide
(C) repeated units of glycerol making up
the
polypeptide
(D) interactions between amino acids
present in
the polypeptide
(E) number of introns within the polypeptide
D
Metabolism of which of the following molecules results in the
greatest net usable energy per gram?
(A) A triglyceride
(B)
A tripeptide
(C) An alpha-linked disaccharide
(D) A
beta-linked disaccharide
(E) Ananabolicsteroid
A
Which of the following can be used to determine the rate of an
enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
- the rate of enzyme used up
-
the rate of substrate used up
the rate of the substrate used up
Which statement is correct about pH?
- Pure water has a neutral
pH of 7 because the concentration of hydrogen ions equals the
concentration of hydroxyl ions.
- The concentration of a solution
with a pH of 5 is times more acidic than a solution with pH 1.
pure water has a neutral pH of 7 because the concentration of hydrogen ions equals the concentration of hydroxyl ions
Substrate F can be removed from enzyme G by dialysis. Enzyme G is inactive after removal of F, but can be reactivated by adding F. Substrate F is probably
a. protein molecule
b. DNA molecule
c. starch molecule
d. coenzyme
e. competitive inhibitor
D
If plants are grown for several days in an atmosphere containing 14CO2 in place of 12CO2 one would expect to find
a. very little radioactivity in the growing leaves
b. large amounts of radioactive water released from the stomates
c. a large increase in the 14C in the starch stored in the roots
d. a large decrease in the rate of carbon fixation in the guard cells
a large increase in 14C in the starch stored in the roots.
The end products of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are
ATP, NADPH, O2.
The Calvin cycle is
is a light dependent reaction that requires carbon fixation through RuBisCo enzyme that uses ATP and NADPH from light reactions to produce 3C sugars.
ATP and NADPH are important for photosynthesis. How are the molecules made available for the synthesis of carbohydrates in the second part of photosynthesis?
Chemiosmosis produces these coenzymes. Essentially, this process consists of a rush of protons across a membrane (the thylakoid membrane, in this case), along with the synthesis of ATP molecules.
Which of the following is an important difference between light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
A.The light-dependent reactions occur only during the day; the light-independent reactions occur only during the night.
BThe light-dependent reactions occur in the cytoplasm; the light-independent reactions occur in chloroplasts.
C.The light-dependent reactions utilize CO2 and H2O; the light-independent reactions produce CO2 and H2O.
D.The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH2; the light-independent reactions use energy stored in ATP and NADPH.
D
The light reactions supply the Calvin Cycle with which of the
following
A. Oxygen
B. ATP and NADPH
C. Water
D.
Carbon Dioxide
B
The final product of the Calvin Cycle is
A. G3P
B.
RuBP
C. ATP
D. PGA
A
Carbohydrate-synthesizing reactions of photosynthesis directly
require
A. Light
B. Oxygen and Water
C. Products of
light reactions
D. Chlorophyll and carbon dioxide
products of light reactions
Aerobic respiration and the light dependent phases of photosynthesis
have all of the following characteristics in common except
A. ATP is synthesized in both.
B. they both consume
oxygen.
C. redox reactions take place in both.
D. coenzymes
are reduced in both.
B
Which of the following statements accurately describes the difference
between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
a. Aerobic respiration
uses O2 as the final electron acceptor, whereas anaerobic respiration
uses H2O.
b. Anaerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final
electron acceptor, and aerobic respiration uses either an inorganic
molecule, such as nitrate ions or sulfate ions, or an organic
molecule, such as an acid or alcohol.
c. Aerobic respiration uses
oxygen as the final electron acceptor, and anaerobic respiration uses
either an inorganic molecule, such as nitrate ions or sulfate ions, or
an organic molecule, such as an acid or alcohol.
d. Aerobic
respiration uses an organic molecule as the final electron acceptor,
and anaerobic respiration uses an inorganic molecule as the final
electron acceptor.
B
By using the isotope O18 as a tracer element in studying photosynthesis, it has been possible to show that the O2 released in the process comes from
a. O16
b. sugar
c. carbon dioxide only
d. water only
e. carbon dioxide and water
D
27. Aerobic and anaerobic respiration are alike in all of the following ways except
a. both release energy from glucose
b. Acetaldehyde is converted into ethyl alcohol
c. ADP is changed to ATP
d. CO2 is a product
e. NAD is reduced
B
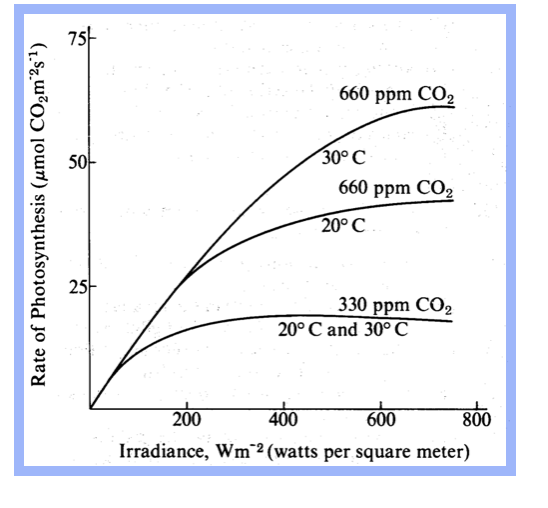
The graph shows the relationship of photosynthetic rate and irradiance (light intensity) influenced by both temperature and carbon dioxide level.
5. According to the graph, the greatest rate of photosynthesis occurs when CO2 is present at
- high concentrations and low temperatures
- low concentrations and high temperatures
- high concentrations and low irradiance levels
- high concentrations and high irradiance levels
3

26. From the data in the graph, which of the following conclusions is most reasonable?
- The rate of photosynthesis is inversely proportional to light intensity.
- The rate of photosynthesis at 660 ppm CO2 is more dependent on temperature than the rate at 330 ppm CO2.
- There is no theoretical maximum for the rate of photosynthesis.
- Attempts to increase the photosynthetic yield in field crops should involve the lowering of CO2 levels.
2

Which of the following seems most likely from the data?
- Light produces heat, which causes increases in the rates of photosynthesis.
- Light causes the saturation of cytochrome oxidase, which then limits the use of CO2.
- The photosynthetic rate could be increased further by decreasing the CO2 concentration.
- Increasing irradiance levels above 800 Wm–2 would have less effect on the rate of photosynthesis than would increasing the CO2 concentration.
A
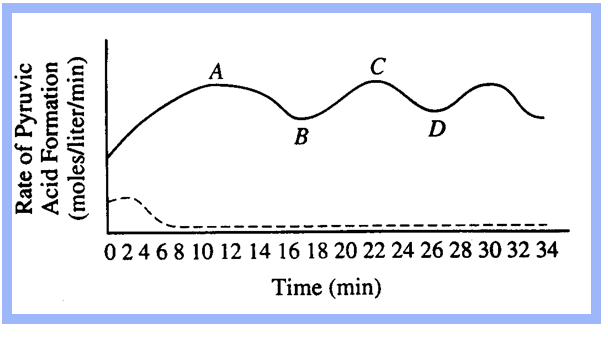
A tissue culture of vertebrate muscle was provided with a constant excess supply of glucose under anaerobic conditions starting at time zero and the amounts of pyruvic acid and ATP produced were measured. The solid line in the graph above represents the pyruvic acid produced in moles per liter per minute. ATP levels were also found to be highest at points A and C, lowest at B and D. A second culture was set up under the same conditions, except that substance X was added, and the results are indicated by the dotted line.
8. The rate of pyruvic acid formation fluctuates because
- all glucose has reacted
- all enzymes have been used up
- the reaction is accelerated by positive feedback
- the reaction is affected by negative feedback
4

Which of the following best accounts for the shape of the solid line between points A and D?
- After ten minutes the cellular enzymes became ineffective.
- Respiration became uncontrolled.
- ATP acted as an allosteric inhibitor on one or more of the enzymes.
- The measurements of pyruvic acid were unreliable.
3

It is most reasonable to hypothesize that, in the breakdown of glucose, substance X is
- an activator
- an inhibitor
- a substrate
- a coenzyme
2

Which of the following is most likely to result if oxygen is added to the tissue culture?
- Lactic acid formation will increase.
- For each glucose molecule consumed, more ATP will be formed.
- The levels of ATP produced will decrease.
- Ethyl alcohol will be produced.
2
[17] Which of the following organelles is correctly matched with its
function?
-----------------------------------------------
[A]
Lysosome . . lipid hydrolysis
[B] Nucleolus . . protein
synthesis
[C] Ribosome . . carbohydrate synthesis
[D] Mitochondrion . . Calvin cycle
[E] Endoplasmic
reticulum . . transcription
A
Which of the following is TRUE of C (subscript 4), plants such as
corn?
-----------------------------------------------
[A]
The Calvin cycle is confined to the bundle sheath cells.
[B] The plants are classified as cacti.
[C] The
stomates open at night rather than during the day.
[D]
They will not grow in climates where the temperature exceeds
70°F.
[E] They have an anatomy that is found only in gymnosperms.
A
Typical of prokaryotic celis after fission
[Match]
-----------------------------------------------
[A]
Unpaired unreplicated linear chromosomes
[B] Unpaired
replicated linear chromosomes
[C] Paired replicated linear
chromosomes
[D] Circular chromosomes
[E]
Extra-chromosomal circular DNA
D
[70] Eukaryotic cells at prophase of mitosis
[Match]
-----------------------------------------------
[A]
Unpaired unreplicated linear chromosomes
[B] Unpaired
replicated linear chromosomes
[C] Paired replicated linear
chromosomes
[D] Circular chromosomes
[E]
Extra-chromosomal circular DNA
B
[71] Eukaryotic cells at metaphase I
[Match]
-----------------------------------------------
[A]
Unpaired unreplicated linear chromosomes
[B] Unpaired
replicated linear chromosomes
[C] Paired replicated linear
chromosomes
[D] Circular chromosomes
[E]
Extra-chromosomal circular DNA
C
[72] Plasmid exchanged by conjugating bacteria
[Match]
-----------------------------------------------
[A]
Unpaired unreplicated linear chromosomes
[B] Unpaired
replicated linear chromosomes
[C] Paired replicated linear
chromosomes
[D] Circular chromosomes
[E]
Extra-chromosomal circular DNA
E
Describe the difference between the two processes in cellular respiration that produce ATP: oxidative phosphorylation and substrate-level phosphorylation
Most of the ATP produced in cellular respiration come from oxidative
phosphorylation, in which the energy released from redox reactions in
an electron transport chain is used to produce ATP.
In
substrate level phosphorylation, an enzyme dirctly transfers a
phosphate group to ADP fro an intermediate substrate. All ATP
production in glycolysis occurs by substrate-level phosphorylation,
this form of ATP production also occurs at one step in the citric acid cycle.
Which of the following occurs in both fermentation and aerobic cellular respiration
a. osygen and carbon dioxide are consumed
b. FAD is reduced, driving ATP synthesis
c. Proton gradients are produced across membranes
d. ATP is synthesized from ADP and inorganic phosphate
e. most of the energy from glucose is released as carbon dioxide
D
Metabolism of which of the following molecules results in the
greatest net usable energy per gram?
(A) A triglyceride
(B)
A tripeptide
(C) An alpha-linked disaccharide
(D) A
beta-linked disaccharide
(E) Ananabolicsteroid
A
Which of the following best describes allosteric inhibition of an
enzyme?
(A) The inhibitor binds to the mRNA to prevent
translation of the enzyme.
(B) The inhibitor binds to the enzyme
substrate.
(C) The inhibitor binds to the enzyme but not
at
its active site.
(D) The inhibitor binds to the enzyme at
its active site.
(E) The inhibitor binds to the gene that encodes
for the enzyme.
C
Production of ATP occurs in all of the following processes
EXCEPT
(A) glycolysis
(B) Krebs cycle
(C) electron
transport system and chemiosmosis (D) light-dependent reactions of
photosynthesis (E) light-independent reactions of photosynthesis
E
The flow of which of the following into the mitochondrial matrix
provides the chemiosmotic energy for the synthesis of ATP?
(A)
Inorganic phosphate (B) ADP
(C) Glucose
(D) Protons
(E) Electrons
D
Which of the following causes the rapid change of membrane polarity
during an action potential?
(A) Diffusion of neurotransmitters
such as acetylcholine
(B) Diffusion of positively charged ions
across the cell membrane
(C) Release of electrons from inside the
cell
(D) Release of protons from inside the cell (E) Active
transport of cations by the sodium-potassium pump
B
Which of the following is NOT associated with nuclear division and cell division in animals?
a. formation of spindles
b. constriction of the dividing cells
c. duplication of chromosomes
d. separation of chromosomes
e. formation of cell plates
E
Crossing-over is a process that involves
a. exchange of genetic material between chromosomes that are not homologous
b. random segregation of genes on different chromosomes
c. continued maintenance of genetic stability
d. exchange of genetic material between chromosomes that are homologous
e. random segregation of genes on homologous chromosomes
D
if 2n=48 for a particular cell, then the chromosome number in each cell after meiosis would be
24
All of the following are true statements about meiosis in mammals
EXCEPT:
a) It produces cells with the haploid number of
chromosomes.
b) It follows DNA replication.
c) It occurs
only in reproductive structures.
d) It produces four genetically
identical gametes.
e) It serves as a factor in bringing about
variation among offspring.
D
Which term describes centrioles beginning to move apart in animal cells
Prophase
Which term describes centromeres uncoupling, sister chromatids separating, and the two new chromosomes moving to opposite poles of the cell
Anaphase
f cells in process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the functioning of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested
Metaphase
Imagine looking through a microscope at a squashed onion root tip. The chromosomes of many of the cells are plainly visible. In some cells, replicated chromosomes are aligned along the center of the cell. These particular cells are in which stage of mitosis
metaphase