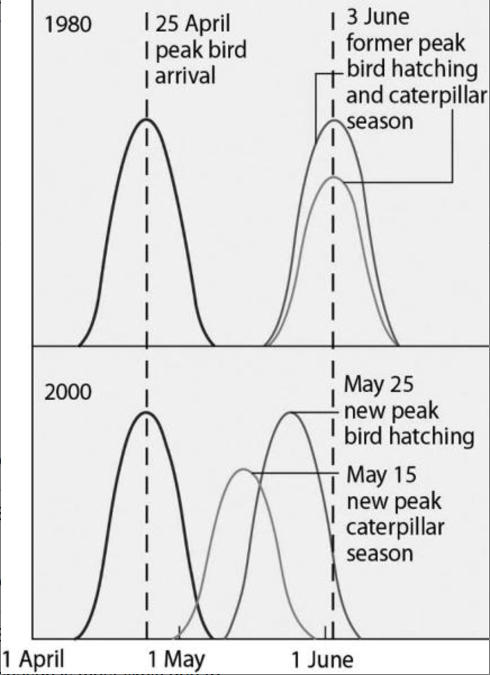
Flycatcher birds that migrate from Africa to Europe feed their nestlings a diet that is almost exclusively moth caterpillars. The graph in Figure 43.3 shows the mean (peak) dates of bird arrival, bird hatching, and caterpillar season for the years 1980 and 2000.
Flycatcher birds that migrate from Africa to Europe feed their nestlings a diet that is almost exclusively moth caterpillars. The graph in Figure 43.3 shows the mean (peak) dates of bird arrival, bird hatching, and caterpillar season for the years 1980 and 2000.
The shift in the peak of caterpillar season is most likely due to
- A) pesticide use.
- B) earlier migration returns of flycatchers.
- C) an innate change in the biological clock of the caterpillars.
- D) global warming.
- E) acid precipitation in Europe.
D

Flycatcher birds that migrate from Africa to Europe feed their nestlings a diet that is almost exclusively moth caterpillars. The graph in Figure 43.3 shows the mean (peak) dates of bird arrival, bird hatching, and caterpillar season for the years 1980 and 2000.
Why were ecologists concerned about the shift in the peak caterpillar season from June 3, 1980 to May 15, 2000?
- A) The caterpillars would have eaten much of the foliage of the trees where flycatchers would have nested, rendering their nests more open to predation.
- B) The earlier hatching of caterpillars would compete with other insect larval forms that the flycatchers would also use to feed their young.
- C) The flycatcher nestlings in 2000 would miss the peak caterpillar season and might not be as well fed, leading to population reductions.
- D) The flycatchers would have to migrate sooner to match their brood-rearing to the time of peak caterpillar season.
C
Agricultural lands frequently require nutrient augmentation because
- A) nitrogen-fixing bacteria are not as plentiful in agricultural soils because of the use of pesticides.
- B) the nutrients that become the biomass of plants are not cycled back to the soil on lands where they are harvested.
- C) land that is available for agriculture tends to be nutrient-poor.
- D) grains raised for feeding livestock must be fortified and thus require additional nutrients.
- E) cultivation of agricultural land inhibits the decomposition of organic matter.
B
Nitrogen is available to plants only in the form of
A)
N2 in the atmosphere.
B) nitrite ions in the soil.
C) uric
acid from animal excretions.
D) amino acids from decomposing
plant and animal proteins.
E) nitrate ions in the soil.
E
In the nitrogen cycle, the bacteria that replenish the atmosphere
with N2 are
A) Rhizobium bacteria.
B) nitrifying
bacteria.
C) denitrifying bacteria.
D) methanogenic
protozoans.
E) nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
C
Denitrifying bacteria convert _____ to _____.
nitrates ...
nitrogen gas
nitrogen gas ... nitrates
nitrogen gas ...
ammonium
ammonium ... nitrogen gas
nitrogen gas ... nitrites
nitrates to nitrogen gas
In terms of nutrient cycling, why does timber harvesting in a
temperate forest cause less ecological devastation than timber
harvesting in tropical rain forests?
A) Trees are generally less
numerous in temperate forests, so fewer nutrients will be removed from
the temperate forest ecosystem during a harvest.
B) Temperate
forest tree species require fewer nutrients to survive than their
tropical counterpart species, so a harvest removes fewer nutrients
from the temperate ecosystem.
C) The warmer temperatures in the
tropics influence rain forest species to assimilate nutrients more
slowly, so tropical nutrient absorption is much slower than in
temperate forests.
D) There are far fewer decomposers in
tropical rain forests, so turning organic matter into usable nutrients
is a slower process than in temperate forest ecosystems.
E)
Typical harvests remove up to 75% of the nutrients in the woody trunks
of tropical rain forest trees, leaving nutrient-impoverished soils behind.
E
Aquatic nitrate pollution can result in _____.
a. algal
bloom
b. oxygen depletion
c. fish kills
d.
hypoxia
e. an algal bloom that, when the algae die and are
decomposed by bacteria, leads to hypoxia and the death of fish
e
Use the incomplete diagram below, illustrating some of the steps
involved in eutrophication to answer the following question.
A---> algae grow faster --> algae die -->Dead algae and
plants accumulate-->(B)-->Dissolved oxygen levels
fall-->aquatic animals suffocate and die.
What would be
a likely entry for box B?
Use the incomplete diagram below,
illustrating some of the steps involved in eutrophication to answer
the following question.
What would be a likely entry for
box B?
a. carbon dioxide building up from cellular respiration by
decomposers
b. fish that cannot acclimate to low oxygen
levels
c. warm water holding less oxygen than cold water
d.
plants no longer producing oxygen
e. decomposer population
carries on cellular respiration and uses up oxygen
d
Use the incomplete diagram below, illustrating some of the steps
involved in eutrophication to answer the following question.
A---> algae grow faster --> algae die -->Dead algae and
plants accumulate-->(B)-->Dissolved oxygen levels
fall-->aquatic animals suffocate and die.
What would be a likely entry for A?
A. increased temperature
b. elimination of sunlight
c. increased sunlight
d. fertilizers washed into the lake
e. increased UV radiation
d
The high level of pesicides found in birds of prey is an example of
a. eutrophication
b. predation
c. biological magnification
d. the green world hypothesis
e. chemical cycling through an ecosystem
C
Which of the following causes an increase in the intensity of UV radiation on Earth?
a. depletion of atomospheric ozone
b. turnover
c. biological magnification
d. greenhouse effect
e. eutrophication
a
The biggest difference between the flow of energy and the flow of chemical nutrients in an ecosystem is that __________.
the amount of energy is much greater than the amount of nutrients
energy is recycled, but nutrients are not
organisms always need nutrients, but they don't always need energy
nutrients are recycled, but energy is not
organisms always need energy, but they don't always need nutrients
nutrients are recycled but energy is not
Which of the following best describes a consequence of having no bacteria and fungi in a food web?
a. Grasses will have no direct access to chemical components recycled from dead organisms
b. rabbits will have no direct access to energy absorbed from secondary consumers
c. shrews will have no direct access to matter transferred from tertiary consumers
d. hawks will have no direct access to nitrogen acquired from the atmosphere
c
7) To recycle nutrients, an ecosystem must have, at a minimum,
A) producers.
B) producers and decomposers.
C)
producers, primary consumers, and decomposers.
D) producers,
primary consumers, secondary consumers, and decomposers.
E)
producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, top carnivores, and decomposers.
B
11) If the sun were to suddenly stop providing energy to Earth, most
ecosystems would vanish. Which of the following ecosystems would
likely survive the longest after this hypothetical disaster?
A)
tropical rain forest
B) tundra
C) benthic ocean
D)
grassland
E) desert
C
12) Which of the following is true of detrivores?
A) They
recycle chemical elements directly back to primary consumers.
B)
They synthesize organic molecules that are used by primary producers.
C) They convert organic materials from all trophic levels to
inorganic compounds usable by primary producers.
D) They secrete
enzymes that convert the organic molecules of detritus into CO₂ and
H₂O.
E) Some species are autotrophic, while others are heterotrophic.
C
14) Approximately 1% of the solar radiation that strikes a plant is
converted into the chemical bond energy of sugars. Why is this amount
so low?
A) Approximately 99% of the solar radiation is converted
to heat energy.
B) Only 1% of the wavelengths of visible light
are absorbed by photosynthetic pigments.
C) Most solar energy
strikes water and land surfaces.
D) Approximately 99% of the
solar radiation is reflected.
E) Only the green wavelengths are
absorbed by plants for photosynthesis.
B
Subtraction of which of the following will convert gross primary productivity into net primary productivity?
a. the energy contained in the standing crop
b. the energy used by heterotrophs in respiration
c. the energy used by autotrophs in respiration
d. the energy fixed by photosynthesis
e. all solar energy
C
The difference between net and gross primary productivity would likely be greatest for
a. phytoplankton in the ocean
b. corn plants in a farmer's field
c. prairie grasses
d. an oak tree in a forest
e. sphagnum moss in a bog
D
Which of these ecosystems accounts for the largest amount of Earth's net primary productivity?
a. tundra
b. savanna
c. salt march
d. open ocean
e. tropical rain forest
d
18) Which of these ecosystems has the highest net primary
productivity per square meter?
A) savanna
B) open ocean
C) boreal forest
D) tropical rain forest
E)
temperate forest
D
Which of the following is a true statement regarding mineral
nutrients in soils and their implication for primary productivity?
A) Globally, phosphorous availability is most limiting to
primary productivity.
B) Adding a nonlimiting nutrient will
stimulate primary productivity.
C) Adding more of a limiting
nutrient will increase primary productivity, indefinitely.
D)
Phosphorous is sometimes unavailable to producers due to leaching.
E) Alkaline soils are more productive than acidic soils.
D
How is it that the open ocean produces the highest net primary
productivity of Earth's ecosystems, yet net primary productivity per
square meter is relatively low?
A) Oceans contain greater
concentrations of nutrients compared to other ecosystems.
B)
Oceans receive a lesser amount of solar energy per unit area.
C)
Oceans have the largest area of all the ecosystems on Earth.
D)
Ocean ecosystems have less species diversity.
E) Oceanic
producers are generally much smaller than oceanic consumers.
C
Why is net primary production (NPP) a more useful measurement to an
ecosystem ecologist than gross primary production (GPP)?
A) NPP
can be expressed in energy/unit of area/unit of time.
B) NPP can
be expressed in terms of carbon fixed by photosynthesis for an entire
ecosystem.
C) NPP represents the stored chemical energy that is
available to consumers in the ecosystem.
D) NPP is the same as
the standing crop.
E) NPP shows the rate at which the standing
crop is utilized by consumers.
C
Which of the following ecosystems would likely have a larger net
primary productivity/hectare and why?
A) open ocean because of
the total biomass of photosynthetic autotrophs
B) grassland
because of the small standing crop biomass that results from
consumption by herbivores and rapid decomposition
C) tropical
rain forest because of the massive standing crop biomass and species
diversity
D) cave due to the lack of photosynthetic autotrophs
E) tundra because of the incredibly rapid period of growth
during the summer season
B
Which statement best describes what ultimately happens to the
chemical energy that is not converted to new biomass in the process of
energy transfer between trophic levels in an ecosystem?
A) It is
undigested and winds up in the feces and is not passed on to higher
trophic levels.
B) It is used by organisms to maintain their
life processes through the reactions of cellular respiration.
C)
Heat produced by cellular respiration is used by heterotrophs to
thermoregulate.
D) It is eliminated as feces or is dissipated
into space as heat in accordance with the second law of
thermodynamics.
E) It is recycled by decomposers to a form that
is once again usable by primary producers.
D
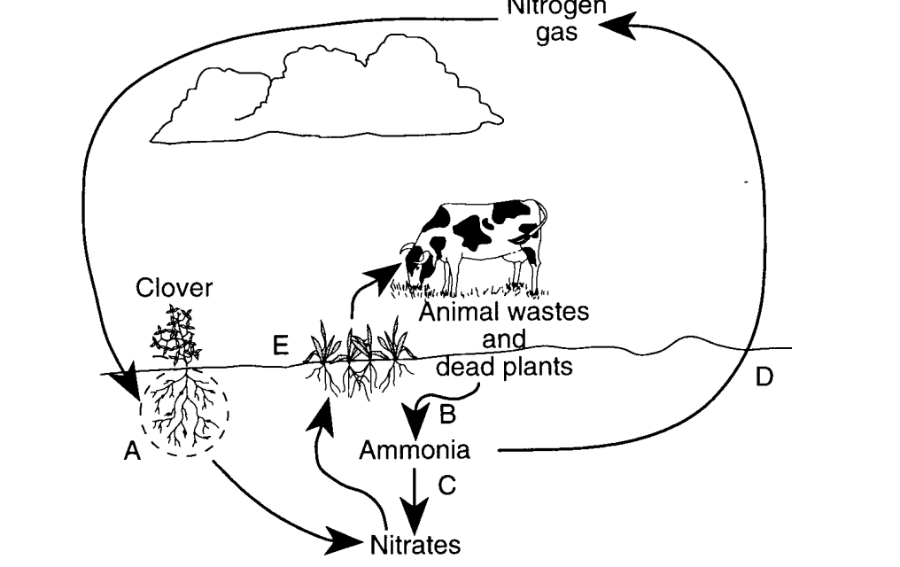
Assimilation of nitrate by photosynthetic eukaryotes
E

Nitrogen fixation by prokaryotes
A

Denitrification by anaerobic prokaryotes
D
Scientists have found that the existing populations of a certain species of amphibian are small in number, lacking in genetic diversity, and separated from each other by wide areas of dry land. Which of the following human actions is most likely to improve the long-term survival of the amphibians?
(A) Cloning the largest individuals to counteract the effects of aggressive predation
(B) Reducing the population size by one-fifth to decrease competition for limited resources
(C) Constructing a dam and irrigation system to control flooding
(D) Building ponds in the areas of dry land to promote interbreeding between the separated populations
D
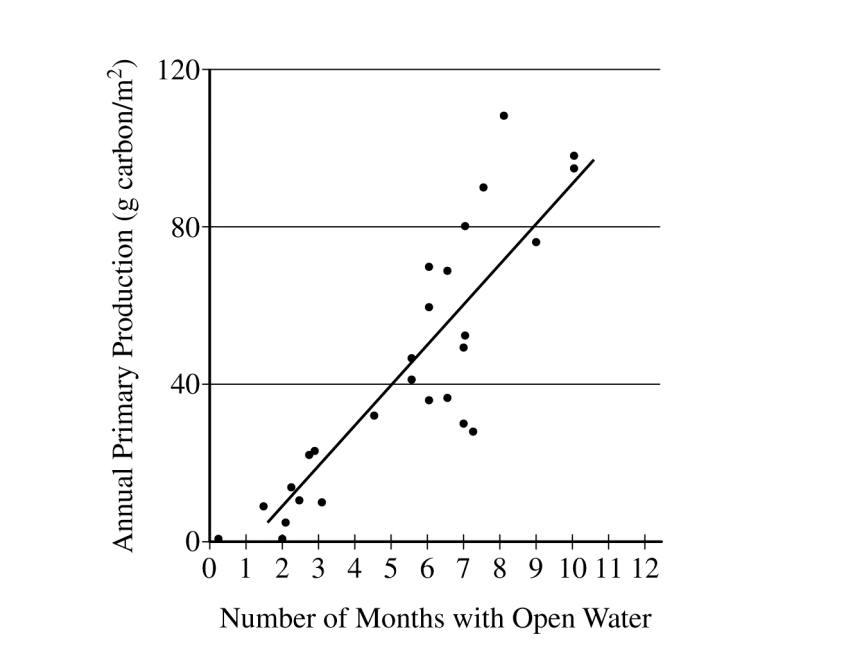
. In the Arctic Ocean, the predominant primary producers are phytoplankton. Phytoplankton are consumed by zooplankton, which in turn are eaten by codfish. In years when there is more open water (less ice coverage), there are more zooplankton and fish than in years with less open water (more ice coverage). Based on the graph above, the difference is most likely because (A) when there is less open water, light is blocked from the zooplankton, so they cannot produce as much food for the fish
(B) when there is more open water, the temperature is warmer, so the zooplankton and fish populations increase in size
(C) the ice blocks the light, so in years with more ice coverage, there is less photosynthesis by the phytoplankton
(D) the ice increases the light available for photosynthesis, so primary production increases and zooplankton populations increase in size
C
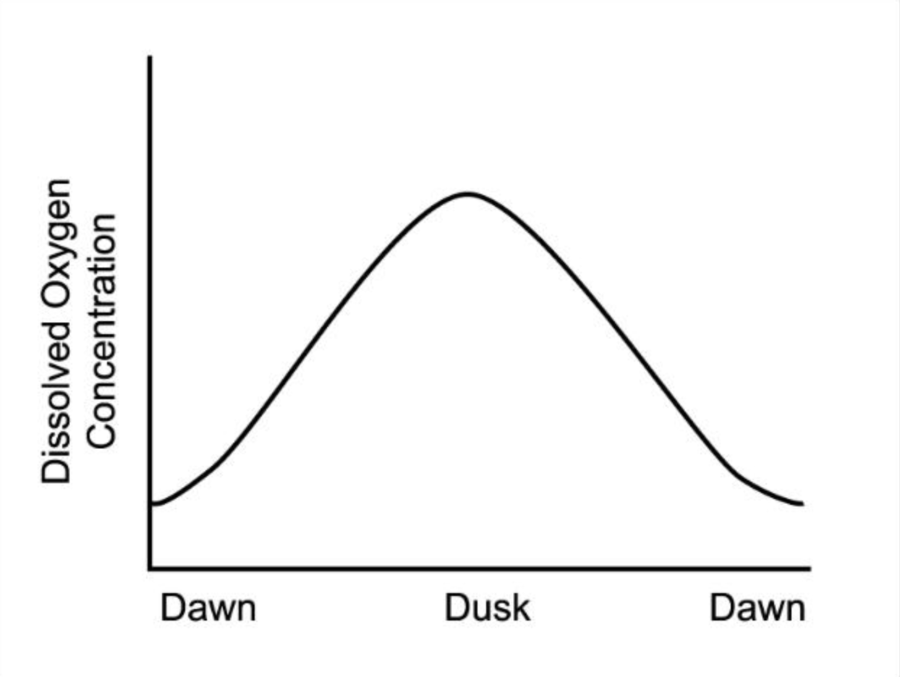
What most likely causes the trends in oxygen concentration shown in the graph above?
a. the water becomes colder at night and holds more oxygen
b. respiration in most organisms increases at night
c. more organisms are respiring at night than during the day
d. photosynthesis produces more oxygen than is consumed by respiration during the day
d
Estimates of current rates of extinction
A) indicate that we
have reached a state of stable equilibrium in which speciation rates
equal extinction rates.
B) suggest that one-half of all animal
and plant species may be gone by the year 2100.
C) indicate that
rates may be greater than the mass extinctions at the close of the
Cretaceous period.
D) indicate that only 1% of all of the
species that have ever lived on Earth are still alive.
E)
suggest that rates of extinction have decreased globally
C
Extinction is a natural phenomenon. It is estimated that 99% of all
species that ever lived are now extinct. Why then do we say that we
are now experiencing an extinction (loss of biodiversity) crisis?
A) Humans are ethically responsible for protecting endangered
species.
B) Scientists have finally identified most of the
species on Earth and are thus able to quantify the number of species
becoming extinct.
C) The current rate of extinction is high and
human activities threaten biodiversity at all levels.
D) Humans
have greater medical needs than at any other time in history, and many
potential medicinal compounds are being lost as plant species become
extinct.
E) Most biodiversity hot spots have been destroyed by
recent ecological disasters.
C
Although extinction is a natural process, current extinctions are of
concern to environmentalists because
A) more animals than ever
before are going extinct.
B) most current extinctions are caused
by introduced species.
C) the rate of extinction is unusually
high.
D) current extinction is primarily affecting plant
diversity.
E) None of the options are correct.
C
Which of the following terms includes all of the others?
A)
species diversity
B) biodiversity
C) genetic diversity
D) ecosystem diversity
E) species richness
B
The use of DDT as an insecticide in the United States has been
outlawed since 1971, yet is still a problem for certain top-level
carnivores in the United States. Which of the following choices best
explains this apparent incongruity?
A) DDT is still used for
mosquito control in tropical countries, and certain migratory
predators can be affected by a seasonal biomagnification.
B) DDT
is persistent in the environment and all of the pre-1971 DDT is still
available in toxic form to poison top-level carnivores.
C)
Pre-1971 DDT has been deposited in certain habitats, particularly
wetlands and estuaries, so predators in these ecosystems are
vulnerable to biomagnifications of DDT.
D) Whereas most
DDT-susceptible species have become resistant to persistent DDT,
others are still vulnerable.
E) All of the options are correct.
A
What is the term for a top predator that contributes to the maintenance of species diversity among its animal prey
a. keystone species
b. keystone mutualist
c. landscape species
d. primary consumer
e. tertiary consumer
a
Which of the following is the most direct threat to biodiversity ?
a. increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide
b. the depletion of the ozone layer
c. overexploitation of species
d. habitat destruction
e. zoned reserves
d
How is habitat fragmentation related to biodiversity loss?
A)
Less carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants in fragmented habitats.
B) In fragmented habitats, more soil erosion takes place.
C) Populations of organisms in fragments are smaller and, thus,
more susceptible to extinction.
D) Animals are forced out of
smaller habitat fragments.
E) Fragments generate silt that
negatively affects sensitive river and stream organisms.
C
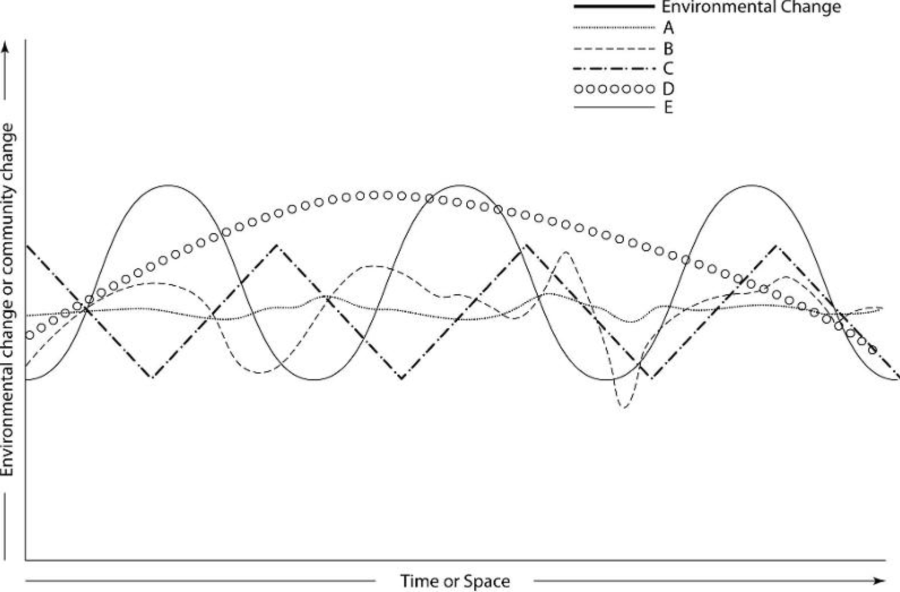
Based on what you know about ecosystem stability and the information
provided in the graph, which community (A-E) would likely support the
most biodiversity?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
A
Introduced species can have deleterious effects on biological
communities by A) preying on native species. B) competing with native
species for food or light. C) displacing native species.
D)
competing with native species for space or breeding/nesting habitat.
E) All of the options are correct.
E
Overexploitation encourages extinction and is most likely to
a. animals that occupy a broad ecological niche
b. large animals with low intrinsic reproductive rates
c. most organisms that live in the oceans
d. terrestrial organisms more than aquatic organisms
e. edge adapted species
b
Assuming a wildfire would reduce the ground cover in a an ecosystem, how is that likely to affect ground temperature?
a. Ground temperature would be colder all year long
b. Ground temperature would be warmer all year long
c. Ground temperature would be colder in the winter, but warmer in the spring through summer as insects begin to emerge
d. there is no relationship between ground cover and ground temperature
c
Yellow-billed cuckoos typically hatch in mid-July. Emerging cicadas are a primary food source for nesting cuckoos. Wildfires typically destroy ground coverage which raises the ground temperature and encourages Cicada nymphs to hatch earlier. Which of the following best predicts the effect of wildfires on yellow-billed cuckoo populations?
a. the yellow-billed cuckoo population will decline because the decreased ground cover will allow lizards to prey on cuckoo nests.
b. the yellow-billed cuckoo population will decline because cicadas will emerge before the hatching season begins
c. the yellow-billed cuckoo population will grow because the adults will more easily see and eat the cicada nymphs
d. the yellow billed cuckoo population will remain unchanged because cuckoos do not nest in areas affected by wildfires
C
Aisha wants to conduct an experiment to determine whether sun and
shade varieties of the same plant species prefer the same wavelengths
of light. She plans to measure rates of photosynthesis. Which design
would be best for her experiment?
A.1 plant of the sun variety
tested under blue light only, and 1 plant of the shade variety tested
under blue light only.
B.4 plants of the sun variety: 1 tested
under blue light, 1 under green, 1 under red, and 1 under yellow
light, and 4 plants of the shade variety:1 tested under blue light, 1
under green, 1 under red, and 1 under yellow light
C.10 plants of
the sun variety tested under blue light only; and 10 plants of the
shade variety tested under blue light only
D.40 plants of the sun
variety: 10 tested under blue light, 10 under green, 10 under red, and
10 under yellow light, and 40 plants of the shade variety: 10 tested
under blue light, 10 under green, 10 under red, and 10 under yellow light.
D
Why is an increasing pH often an indication that photosynthesis has occurred in an experiment?
a. As CO2 is released, carbonic acid is created and the pH will rise
b. As CO2 is absorbed, carbonic acid is reduced and the pH will rise
c. As O2 is released, Oxalic acid is created and the pH will rise
A
A student is attempting to study whether or not an organism is capable of performing both photosynthesis and respiration in an aquatic environment. Which of the following would be the preferred experimental setup?
a. a plant placed in a lighted aquatic tank and dark aquatic tank. pH levels monitored as an indication of CO2 levels
b. a plant placed in a lighted aquatic tank and a fish placed in a lighted aquatic tank. pH levels monitored as indication of CO2 levels
c. a fish placed in a lighted aquatic tank and a dark aquatic tank. pH levels monitored as an indication of CO2 levels
d. a fish placed in a lighted aquatic tank and a plant placed in a dark aquatic tank. pH levels monitored as an indication of CO2 levels
A
If an aquatic tank seemingly containing only water was monitored under both lit and unlit conditions, what might a changing pH level indicate about this experiment?
a. Does aquarium glass affect light reaching water samples
b. Is the availability of carbon dioxide a limiting factor in aquatic ecosystems
c. Does light change the chemical composition of CO2
d. Does the aquarium water contain living microorganisms
D
Two students conducted studies to determine the amount of bacteria in
hamburgers cooked to different internal temperatures. The students
cooked 3 hamburgers: 1 rare, 1 medium, and 1 well-done. The students
then took a core from the center of each hamburger and placed each
core in a separate petri dish with nutrient agar. Each dish was
incubated until colonies formed. The students hypothesized that the
rare hamburger core would generate the most bacteria colonies.
Eight hundred colonies grew in the dish containing the rare
hamburger core, 400 colonies grew in the dish containing the medium
hamburger core, and 0 colonies grew in the dish containing the
well-done hamburger core. What is the most appropriate next step for
the students to take in this study?
A. Accept the results; one
trial is all that is necessary to test a hypothesis.
B. Accept
the results; the results of this experiment support their hypothesis.
C. Perform more trials using a different type of meat, under the
same conditions as the first experiment.
D. Perform more trials
using the same type of meat, under the same conditions as the first experiment.
D
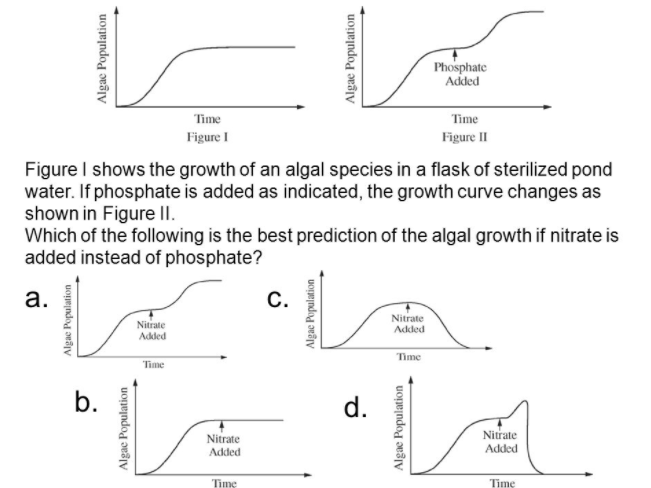
B
The area covered by tropical rain forest is reduced by millions of hectares per year due to agriculture and logging. which of the following best describes a likely result of tropical rain forest deforestation?
a. populations of plants and animals will decrease as more rain forest disappears leading to a decrease in biodiversity
b. an increase of soil moisture will lead to a rapid increase in new vegetation coverage
c. an increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide will lead to higher levels of UV radiation reaching the surface of Earth
d. more oxygen will be available to other organisms as plant numbers decrease
A
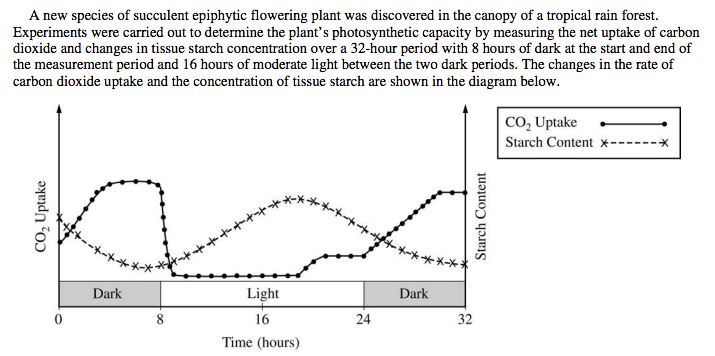
Which of the following is consistent with the data?
a. the highest rate of carbon dioxide uptake occurs at the beginning of the light period
b. the highest rate of carbon dioxide uptake occurs at the beginning of the dark period
c. the highest rate of carbon dioxide uptake occurs near the end of the dark period
d. the highest starch concentration occurs at the beginning of the light period
e. the lowest starch concentration occurs at the end of the light period
B
The photosynthetic pattern of this plant species is unusual for which of the following reasons?
I. It has a higher rate of carbon dioxide uptake during the light period than the dark period
II. It has a higher rate of carbon dioxide uptake during the dark period than during the light period
III. There is a positive correlation between the rate of carbon dioxide uptake and tissue starch concentration
IV. There is an inverse correlation between the rate of carbon dioxide uptake and tissue starch concentration
a. I only
b. II only
c. IV only
d. I and III
e. II and IV
E
A useful control for the experiment would have included which of the following?
I. Expose the plant to 32 hours of continuous moderate light and measure rates of carbon dioxide uptake and tissue starch concentration
II. Expose the plant to 32 hours of continuous dark and measure rates of carbon dioxide uptake and tissue starch concentration
III. Measure the chlorophyll concentration in the plant's leaf tissue
a. I only
b. II only
c. III only
d. I and II only
e. I, II and III
D
The most likely adaptive significance of this photosynthetic mechanism is to
a. minimize water loss by taking up carbon dioxide at night
b. maximize the production of starch at night
c. maximize the ability to use bright light to take up carbon dioxide
d. maximize water loss during the day so starch can be made
e. minimize starch production during the day
A
What is the fundamental difference between matter and energy?
A) Matter is cycled through ecosystems; energy is not.
B)
Energy is cycled through ecosystems; matter is not.
C) Energy
can be converted into matter; matter cannot be converted into energy.
D) Matter can be converted into energy; energy cannot be
converted into matter.
E) Matter is used in ecosystems; energy
is not
A
Which of the following are responsible for most of the conversion of
organic materials into CO2, which can be utilized in primary
production?
A) autotrophs
B) herbivores
C) primary consumers
D) detrivores
E) carnivores
D
Which of the following describes the role of bacteria or fungi in an arid ecosystem?
a. it coverts radiant energy into chemical energy
b. it directly provides a source of nutrition for animals
c. it is a saprophytic agent restoring inorganic material to the environment
d. it consumes live plants and animals
c
When are two species said to be in direct competition?
a. when they are competing for the same resource without easy alternatives
b. when they are competing for similar resources
c. when the are competing for the same resource whether or not their are alternative resources available
a
A scientist measured the water content of leaves from two different
groups of oak trees on three different summer days. One group of
leaves, the T group, came from trees that had been defoliated by gypsy
moths the previous year. The other leaves, the C group, came from
trees which had not been defoliated. The results, in milliliters of
water per gram of dry weight, are shown in the table below.
.............June 10 June 30 July 28
T Group 26.8.....
20.4..... 12.7
C Group 32.5.... 28.7...... 22.7
All of the following are valid interpretations of these data
EXCEPT:
(A) C leaves typically contain more water than do T
leaves
(B) Both C and T leaves show declines in water content as
the summer goes on.
(C) T leaves show greater declines in water
content than do C leaves.
(D) Defoliation by gypsy moths has no
effect on the water content of next year’s leaves.
(E)
Differences in the water content between C and T leaves grow greater
as the summer goes on
D
Species that utilize the same source of nutrition within a food web can best be described as
a. providing double links in a food chain
b. being homeothermic relative to energy flow
c. occupying the same trophic level
d. being secondary consumers with a complex food web
e. being autotrophs, heterotrophs, or omnivores
c
Carbon dioxide is passed into a solution of bromthymol blue indicator
until the acid solution turns
yellow. A sprig of elodea is then
placed into this yellow solution. After a few hours in the
sunlight,
the yellow solution turns blue. The purpose of this
experiment is to show that
(A) oxygen is given off during
photosynthesis
(B) carbon dioxide is used during
photosynthesis
(C) carbon dioxide is given off as a by-product of
photosynthesis
(D) bromthymol blue changes to bromthymol yellow
under acid conditions
(E) chlorophyll acting as a photocatalyst
is necessary for photosynthesis
B
Eutrophication in lakes is frequently the direct result of
a. nutrient enrichment
b. industrial poisons
c. a diminished supply of nitrates
d. an increase in predators
a