A commensal bacterium
- does not receive any benefit from its host.
- is beneficial to its host.
- may also be an opportunistic pathogen.
- isn't capable of causing disease in its host.
- always causes disease in its host.
C) may also be an opportunistic pathogen.
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Both members are harmed in a symbiotic relationship.
B) Members of a symbiotic relationship cannot live without each other.
C) A parasite is not in symbiosis with its host.
D) Symbiosis always refers to different organisms living together and benefiting from each other.
E) At least one member must benefit in a symbiotic relationship.
E) At least one member must benefit in a symbiotic relationship.
A nosocomial infection is
A) always present, but is inapparent at the time of hospitalization.
B) acquired during the course of hospitalization.
C) always caused by medical personnel.
D) only a result of surgery.
E) always caused by pathogenic bacteria.
B) acquired during the course of hospitalization.
The major significance of Robert Koch's work is that
A) microorganisms are present in a diseased animal.
B) diseases can be transmitted from one animal to another.
C) microorganisms can be cultured.
D) microorganisms cause disease.
E) microorganisms are the result of disease.
D) microorganisms cause disease.
Which of the following is NOT a verified exception in the use of Koch's postulates?
A) Some diseases have poorly defined etiologies.
B) Some pathogens can cause several disease conditions.
C) Some human diseases have no other known animal host.
D) Some diseases are not caused by microbes.
E) Some diseases are noncommunicable.
E) Some diseases are noncommunicable.
Which of the following diseases is NOT spread by droplet infection?
A) botulism
B) tuberculosis
C) measles
D) the common cold
E) diphtheria
A) botulism
Biological transmission differs from mechanical transmission in that biological transmission
A) occurs when a pathogen is carried on the feet of an insect.
B) involves fomites.
C) involves reproduction of a pathogen in an arthropod vector prior to transmission.
D) requires direct contact.
E) works only with noncommunicable diseases.
C) involves reproduction of a pathogen in an arthropod vector prior to transmission.
Which of the following definitions is INCORRECT?
A) endemic: a disease that is constantly present in a population
B) epidemic: a disease that is endemic across the world
C) pandemic: a disease that affects a large number of people in the world in a short time
D) sporadic: a disease that affects a population occasionally
E) incidence: number of new cases of a disease
B) epidemic: a disease that is endemic across the world
Focal infections initially start out as
A) sepsis.
B) bacteremia.
C) local infections.
D) septicemia.
E) systemic infections.
C) local infections.
The rise in herd immunity amongst a population can be directly attributed to
A) increased use of antibiotics.
B) improved handwashing.
C) vaccinations.
D) antibiotic-resistant microorganisms.
E) None of the answers is correct.
C) vaccinations.
Koch observed Bacillus anthracis multiplying in the blood of cattle. What is this condition called?
A) bacteremia
B) focal infection
C) local infection
D) septicemia
E) systemic infection
C) local infection
Which one of the following does NOT contribute to the incidence of nosocomial infections?
A) antibiotic resistance
B) lapse in aseptic techniques
C) gram-negative cell walls
D) lack of handwashing
E) lack of insect control
C) gram-negative cell walls
Transient microbiota differ from normal microbiota in that transient microbiota
A) cause diseases.
B) are found in a certain location on the host.
C) are always acquired by direct contact.
D) are present for a relatively short time.
E) never cause disease.
D) are present for a relatively short time.
Which of the following statements about nosocomial infections is FALSE?
A) They occur in compromised patients.
B) They may be caused by opportunists.
C) They may be caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
D) They may be caused by normal microbiota.
E) The patient was infected before hospitalization.
E) The patient was infected before hospitalization.
One effect of washing regularly with antibacterial agents is the removal of normal microbiota. This can result in
A) body odor.
B) fewer diseases.
C) increased susceptibility to disease.
D) normal microbiota returning immediately.
E) no bacterial growth because washing removes their food source.
D) normal microbiota returning immediately.
Which of the following is NOT a reservoir of infection?
A) a sick person
B) a healthy person
C) a sick animal
D) a hospital
E) None of the answers is correct; all of these can be reservoirs of infection.
E) None of the answers is correct; all of these can be reservoirs of infection.
Which of the following is NOT a communicable disease?
A) malaria
B) AIDS
C) tuberculosis
D) tetanus
E) typhoid fever
D) tetanus
Which of the following is a fomite?
A) water
B) droplets from a sneeze
C) pus
D) insects
E) a hypodermic needle
E) a hypodermic needle
Which of the following statements about biological transmission is FALSE?
A) The pathogen reproduces in the vector.
B) The pathogen may enter the host in the vector's feces.
C) Houseflies are an important vector.
D) The pathogen may be injected by the bite of the vector.
E) The pathogen may require the vector as a host.
C) Houseflies are an important vector.
Which of the following definitions is INCORRECT?
A) acute: a short-lasting primary infection
B) inapparent: infection characteristic of a carrier state
C) chronic: a disease that develops slowly and lasts for months
D) primary infection: an initial illness
E) secondary infection: a long-lasting illness
E) secondary infection: a long-lasting illness
Symptoms of disease differ from signs of disease in that symptoms
A) are changes felt by the patient.
B) are changes observed by the physician.
C) are specific for a particular disease.
D) always occur as part of a syndrome.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) are changes felt by the patient.
The science that deals with when diseases occur and how they are transmitted is called
A) ecology.
B) epidemiology.
C) communicable disease.
D) morbidity and mortality.
E) public health.
B) epidemiology.
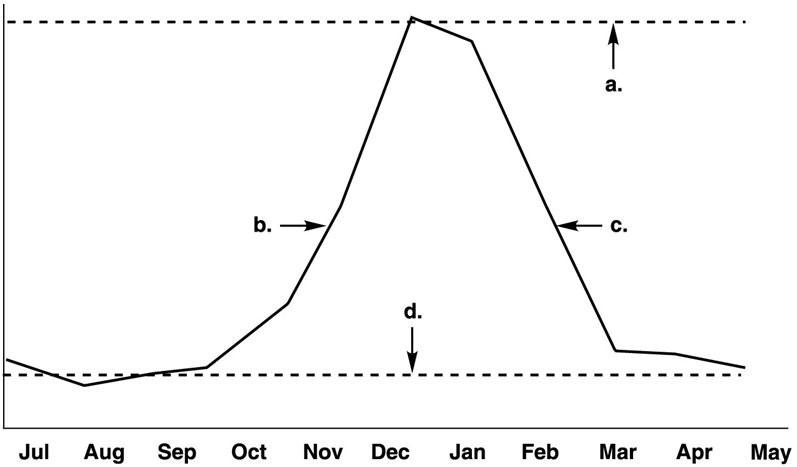
Figure 14.1 shows the incidence of influenza during a typical year. Which letter on the graph indicates the endemic level?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
D) d
Emergence of infectious diseases can be attributed to all of the following EXCEPT
A) antibiotic resistance.
B) climatic changes.
C) new strains of previously known agents.
D) ease of travel.
E) The emergence of infectious diseases can be attributed to all of these.
E) The emergence of infectious diseases can be attributed to all of these.
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) malaria — vector
B) salmonellosis — vehicle transmission
C) syphilis — direct contact
D) influenza — droplet infection
E) None of the pairs is mismatched.
E) None of the pairs is mismatched.
Which of the following can contribute to postoperative infections?
A) using syringes more than once
B) normal microbiota on the operating room staff
C) errors in aseptic technique
D) antibiotic resistance
E) All of the answers are correct.
E) All of the answers are correct.
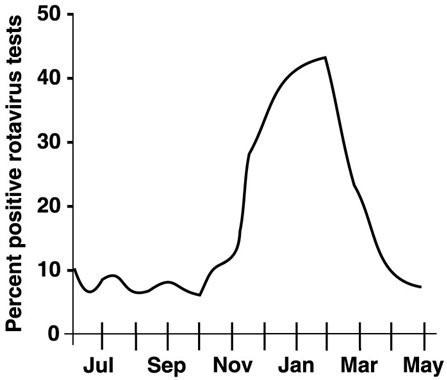
In Figure 14.2, when is the prevalence the highest?
A) July
B) January
C) February
D) March
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
C) February
A cold transmitted by a facial tissue is an example of
A) direct contact.
B) droplet transmission.
C) fomite.
D) vector.
E) vehicle transmission.
E) vehicle transmission.
A researcher has performed a prospective study on a disease. To which specific kind of epidemiological study is this referring?
A) analytical
B) case control
C) descriptive
D) experimental
E) prodromal
C) descriptive
The CDC is located in
A) Atlanta, GA.
B) Washington, DC.
C) New York City, NY.
D) Los Angeles, CA.
E) Chicago, IL.
A) Atlanta, GA.
A disease in which the causative agent remains inactive for a time before producing symptoms is referred to as
A) subacute.
B) subclinical.
C) latent.
D) zoonotic.
E) acute.
C) latent.
A needlestick is an example of
A) direct contact.
B) droplet transmission.
C) indirect contact transmission by fomite.
D) direct biological transmission by vector.
E) vehicle transmission.
C) indirect contact transmission by fomite.
Which of the following is NOT a predisposing factor of disease?
A) lifestyle
B) genetic background
C) climate
D) occupation
E) All of these are predisposing factors of disease.
E) All of these are predisposing factors of disease.
In which of the following diseases can gender be considered a viable predisposing factor?
A) urinary tract infections
B) pneumonia
C) salmonellosis
D) tetanus
E) anthrax
A) urinary tract infections
In which of the following patterns of disease does the patient experience no signs or symptoms?
A) prodromal
B) decline
C) convalescence
D) incubation
E) both incubation and convalescence
E) both incubation and convalescence
Situation 14.1
During a six-month period, 239 cases of pneumonia occurred in a town of 300 people. A clinical case was defined as fever ≥ 39°C lasting >2 days with three or more symptoms (i.e., chills, sweats, severe headache, cough, aching muscles/joints, fatigue, or feeling ill). A laboratory-confirmed case was defined as a positive result for antibodies against Coxiella burnetii. Before the outbreak, 2000 sheep were kept northwest of the town. Of the 20 sheep tested from the flock, 15 were positive for C. burnetii antibodies. Wind blew from the northwest, and rainfall was 0.5 cm compared with 7 to 10 cm during each of the previous three years.
36) Situation 14.1 is an example of
A) human reservoirs.
B) a zoonosis.
C) a nonliving reservoir.
D) a vector.
E) a focal infection.
B) a zoonosis.
The etiologic agent of the disease in Situation 14.1 is
A) sheep.
B) soil.
C) Coxiella burnetii.
D) pneumonia.
E) wind.
C) Coxiella burnetii.
The method of transmission of the disease in Situation 14.1 was
A) direct contact.
B) droplet.
C) indirect contact.
D) vector-borne.
E) vehicle.
E) vehicle.
Which of the following is NOT an example of microbial antagonism?
A) acid production by bacteria
B) bacteriocin production
C) bacteria occupying host receptors
D) bacteria causing disease
E) bacteria producing vitamin K
D) bacteria causing disease
The yeast Candida albicans does not normally cause disease because of
A) symbiotic bacteria.
B) antagonistic bacteria.
C) parasitic bacteria.
D) commensal bacteria.
E) other fungi.
B) antagonistic bacteria.
If a prodromal period exists for a certain disease, it should occur prior to
A) incubation.
B) illness.
C) decline.
D) convalescence.
B) illness.
Which one of the following is NOT a zoonosis?
A) cat-scratch disease
B) Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
C) rabies
D) tapeworm
E) All of these are zoonoses.
E) All of these are zoonoses.
Pseudomonas bacteria colonized the bile duct of a patient following his liver transplant surgery. This is an example of a
A) communicable disease.
B) latent infection.
C) nosocomial infection.
D) sporadic disease.
E) None of the answers is correct.
C) nosocomial infection.
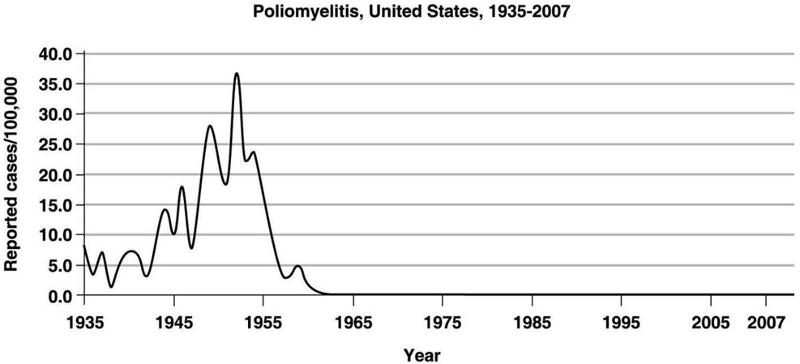
The graph in Figure 14.3 shows the incidence of polio in the United States. The period between 1945 and 1955 indicates a(n)
A) endemic level.
B) epidemic level.
C) sporadic infection.
D) communicable disease.
E) pandemic.
B) epidemic level.
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Antimicrobial therapy for hemodialysis-associated infections increases antibiotic resistance.
B) aureus is differentiated from other mannitol+ cocci by the coagulase test.
C) The M in MRSA stands for mannitol.
D) The USA100 strain accounts for most hospital-acquired MRSA.
E) The USA300 strain accounts for most community-acquired MRSA.
C) The M in MRSA stands for mannitol.
For a particular disease at a specific time period, morbidity rates should always be equal or greater than mortality rates.
True/False
Answer: TRUE
Testing the effectiveness of a new drug for anthrax would be best performed as an experimental study.
True/False
Answer: TRUE
MMWR is a publication by the CDC that reports on only emerging diseases.
True/False
Answer: FALSE
A researcher only needs to select a cohort group when implementing an analytical epidemiological study.
True/False
Answer: FALSE
Diseases that are referred to as emerging infectious diseases have only been discovered in the past fifty years.
True/False
Answer: FALSE
Compromised hosts are always suffering from suppressed immune systems.
True/False
Answer: FALSE
A host is not considered diseased until an infection changes one's state of health.
True/False
Answer: TRUE
Reservoirs of infections are always animate objects.
True/False
Answer: FALSE
Urinary tract infections are the most common forms of nosocomial infections.
True/False
Answer: FALSE
Both normal and transient flora can become opportunistic pathogens.
True/False
Answer: TRUE
The most frequently used portal of entry for pathogens is the
A) mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
B) mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
C) skin.
D) parenteral route.
E) All of these portals are used equally.
A) mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
The ability of some microbes, such as Trypanosoma or Giardia to alter their surface molecules and evade destruction by the host's antibodies is called
A) antigenic variation.
B) lysogenic conversion.
C) virulence.
D) cytopathic effect.
E) cytocidal effect.
A) antigenic variation.
Most pathogens that gain access through the skin
A) can penetrate intact skin.
B) just infect the skin itself.
C) enter through hair follicles and sweat ducts.
D) must adhere first while their invasive factors allow them to penetrate.
E) must be injected.
C) enter through hair follicles and sweat ducts.
The ID50 is
A) a measure of pathogenicity.
B) the dose that will cause an infection in 50 percent of the test population.
C) the dose that will kill some of the test population.
D) the dose that will cause an infection in some of the test population.
E) the dose that will kill 50 percent of the test population.
B) the dose that will cause an infection in 50 percent of the test population.
All of the following contribute to a pathogen's invasiveness EXCEPT
A) toxins.
B) capsules.
C) cell wall components.
D) hyaluronidase.
E) coagulases.
A) toxins.
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Leukocidins destroy neutrophils.
B) Hemolysins lyse red blood cells.
C) Hyaluronidase breaks down substances between cells.
D) Kinase destroys fibrin clots.
E) Coagulase destroys blood clots.
E) Coagulase destroys blood clots.
Which of the following statements about exotoxins is generally FALSE?
A) They are more potent than endotoxins.
B) They are composed of proteins.
C) They are resistant to heat.
D) They have specific methods of action.
E) They are produced by gram-positive bacteria.
C) They are resistant to heat.
Endotoxins are
A) associated with gram-positive bacteria.
B) molecules that bind nerve cells.
C) part of the gram-negative cell wall.
D) excreted from the cell.
E) A-B toxins.
C) part of the gram-negative cell wall.
Which of the following is NOT a membrane-disrupting toxin?
A) A-B toxin
B) hemolysin
C) leukocidin
D) streptolysin O
E) streptolysin S
A) A-B toxin
Cytopathic effects are changes in host cells due to
A) viral infections.
B) protozoan infections.
C) fungal infections.
D) bacterial infections.
E) helminthic infections.
A) viral infections.
Which of the following does NOT contribute to the symptoms of a fungal disease?
A) capsules
B) toxins
C) allergic response of the host
D) cell walls
E) metabolic products
D) cell walls
All of the following are methods of avoiding host antibodies EXCEPT
A) antigenic changes.
B) IgA proteases.
C) invasins.
D) membrane-disrupting toxins.
E) inducing endocytosis.
D) membrane-disrupting toxins.
Siderophores are bacterial proteins that compete with the host's
A) antibodies.
B) red blood cells.
C) iron-transport proteins.
D) white blood cells.
E) receptors.
C) iron-transport proteins.
The fimbriae of Neisseria gonorrhea and enteropathogenic E. coli are examples of
A) adhesins.
B) ligands.
C) receptors.
D) adhesins and ligands.
E) adhesins, ligands, and receptors.
D) adhesins and ligands.
All of the following are examples of entry via the parenteral route EXCEPT
A) injection.
B) bite.
C) surgery.
D) hair follicle.
E) skin cut.
D) hair follicle.
Superantigens produce intense immune responses by stimulating lymphocytes to produce
A) endotoxins.
B) exotoxins.
C) cytokines.
D) leukocidins.
E) interferons.
C) cytokines.
Botulism is caused by ingestion of a proteinaceous exotoxin; therefore, it can easily be prevented by
A) boiling food prior to consumption.
B) administering antibiotics to patients.
C) not eating canned food.
D) preventing fecal contamination of food.
E) filtering food.
A) boiling food prior to consumption.
All of the following organisms produce exotoxins EXCEPT
A) Salmonella typhi.
B) Clostridium botulinum.
C) Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
D) Clostridium tetani.
E) Staphylococcus aureus.
A) Salmonella typhi.
Which of the following cytopathic effects is cytocidal?
A) inclusion bodies
B) giant cells
C) antigenic changes
D) transformation
E) release of enzymes from lysosomes
E) release of enzymes from lysosomes
All of the following are used by bacteria to attach to host cells EXCEPT
A) M protein.
B) ligands.
C) fimbriae.
D) capsules.
E) A-B toxins.
E) A-B toxins.
Symptoms of protozoan and helminthic diseases are due to
A) tissue damage due to growth of the parasite on the tissues.
B) waste products excreted by the parasite.
C) products released from damaged tissues.
D) tissue damage due to growth of the parasite on the tissues and waste products excreted by the parasite.
E) tissue damage due to growth of the parasite on the tissues, waste products excreted by the parasite, and products released from damaged tissues.
E) tissue damage due to growth of the parasite on the tissues, waste products excreted by the parasite, and products released from damaged tissues.
Which of the following statements about staphylococcal enterotoxin is FALSE?
A) It causes vomiting.
B) It causes diarrhea.
C) It is an exotoxin.
D) It is produced by Staphylococcus aureus growing in the host's intestines.
E) It is a superantigen.
D) It is produced by Staphylococcus aureus growing in the host's intestines.
Which of the following contributes to the virulence of a pathogen?
A) numbers of microorganisms that gain access to a host
B) evasion of host defenses
C) toxin production
D) numbers of microorganisms that gain access to a host and evasion of host defenses
E) numbers of microorganisms that gain access to a host, evasion of host defenses, and toxin production
E) numbers of microorganisms that gain access to a host, evasion of host defenses, and toxin production
Lysogenic bacteriophages contribute to bacterial virulence because bacteriophages
A) give new gene sequences to the host bacteria.
B) produce toxins.
C) carry plasmids.
D) kill the bacteria, causing release of endotoxins.
E) kill human cells.
A) give new gene sequences to the host bacteria.
Twenty-five people developed symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea three to six hours after attending a church picnic where they ate a ham and green bean casserole with cream sauce. The most likely cause of this case of food intoxication is
A) botulinum toxin.
B) aflatoxin.
C) staphylococcal enterotoxin.
D) erythrogenic toxin.
E) cholera toxin.
D) erythrogenic toxin.
Which of the following statements about M protein is FALSE?
A) It is found on Streptococcus pyogenes.
B) It is found on fimbriae.
C) It is heat- and acid-resistant.
D) It is readily digested by phagocytes.
E) It is a protein.
D) It is readily digested by phagocytes.
Symptoms of intense inflammation and shock occur in some gram-positive bacterial infections due to
A) A-B toxins.
B) lipid A.
C) membrane-disrupting toxins.
D) superantigens.
E) erythrogenic toxin.
D) superantigens.
Which of the following is an example of direct damage due to bacterial infection?
A) the uncontrolled muscle contractions in Clostridium tetani infection
B) the invasion and lysis of intestinal cells by coli
C) the hemolysis of red blood cells in a staphylococcal infection
D) the fever, nausea, and low blood pressure in a Salmonella infection
E) the excessive secretion of fluids in a Vibrio cholera infection
B) the invasion and lysis of intestinal cells bycoli
Polio is transmitted by ingestion of water contaminated with feces containing polio virus. What portal of entry does polio virus use?
A) skin only
B) parenteral only
C) mucous membranes only
D) skin and parenteral
E) skin, parenteral, and mucous membranes
C) mucous membranes only
All of the following bacteria release endotoxin EXCEPT
A) Clostridium botulinum.
B) Salmonella typhi.
C) Neisseria meningitidis.
D) Proteus vulgaris.
E) Haemophilus influenzae.
A) Clostridium botulinum.
Cholera toxin polypeptide A binds to surface gangliosides on target cells. If the gangliosides were removed,
A) polypeptide A would bind to target cells.
B) polypeptide A would enter the cells.
C) polypeptide B would not be able to enter the cells.
D) Vibrio would not produce cholera toxin.
E) Vibrio would bind to target cells.
C) polypeptide B would not be able to enter the cells.
Bacteria such as E. coli and Salmonella produce invasins that bind host cells, thus causing the cells to
A) release TNF.
B) produce iron-binding proteins.
C) engulf the bacteria.
D) destroy the bacteria.
E) release cytokines.
C) engulf the bacteria.
Which of the following mechanisms is used by gram-negative bacteria to cross the blood-brain barrier?
A) producing fimbriae
B) inducing endocytosis
C) producing toxins
D) inducing TNF
E) antigenic variation
D) inducing TNF
Injectable drugs are tested for endotoxins by
A) the Limulus amoebocyte lysate test.
B) counting the viable bacteria.
C) filtering out the cells.
D) looking for turbidity.
E) culturing bacteria.
A) the Limulus amoebocyte lysate test.
Endotoxins in sterile injectable drugs could cause
A) infection.
B) septic shock symptoms.
C) giant cell formation.
D) nerve damage.
E) no damage, because they are sterile.
B) septic shock symptoms.
Gram-negative septic shock results from the following events. What is the second step?
A) Body temperature is reset in the hypothalamus.
B) Fever occurs.
C) IL-1 is released.
D) LPS is released from gram-negative bacteria.
E) Phagocytes ingest gram-negative bacteria.
D) LPS is released from gram-negative bacteria.
Antibiotics can lead to septic shock if used to treat
A) viral infections.
B) gram-negative bacterial infections.
C) gram-positive bacterial infections.
D) protozoan infections.
E) helminth infestations.
B) gram-negative bacterial infections.
Which of the following is NOT a cytopathic effect of viruses?
A) cell death
B) host cells fusing to form multinucleated syncytia
C) inclusion bodies forming in the cytoplasm or nucleus
D) increased cell growth
E) toxin production
E) toxin production
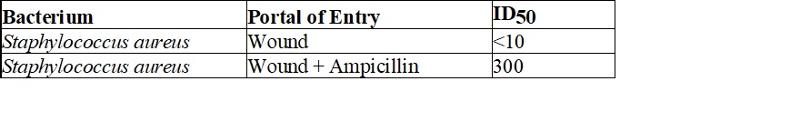
Table 15.1 shows the ID50 for Staphylococcus aureus in wounds with and without the administration of ampicillin before surgery. Based on the data, the administration of ampicillin before surgery
A) decreases the risk of staphylococcal infection.
B) increases the risk of staphylococcal infection.
C) has no effect on risk of infection.
D) replaces tetracycline.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
A) decreases the risk of staphylococcal infection.
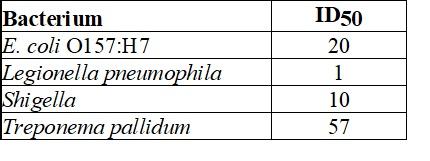
Which organism in Table 15.2 most easily causes an infection?
A) coli O157:H7
B) Legionella pneumophila
C) Shigella
D) Treponema pallidum
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
B) Legionella pneumophila
Which organism in Table 15.2 causes the most severe disease?
A) coli O157:H7
B) Legionella pneumophila
C) Shigella
D) Treponema pallidum
E) It cannot be determined from the information provided.
E) It cannot be determined from the information provided.
Bacteria that cause periodontal disease have adhesins for receptors on streptococci that colonize on teeth. This indicates that
A) streptococci get bacterial infections.
B) streptococcal colonization is necessary for periodontal disease.
C) bacteria that cause periodontal disease adhere to gums and teeth.
D) bacteria that cause periodontal disease adhere to teeth.
E) streptococci cause periodontal disease.
B) streptococcal colonization is necessary for periodontal disease.
Nonpathogenic Vibrio cholerae can acquire the cholera toxin gene by
A) phagocytosis.
B) transduction.
C) conjugation.
D) transformation.
E) infecting a pathogenic Vibrio cholerae.
B) transduction.
In response to the presence of endotoxin, phagocytes secrete tumor necrosis factor. This causes
A) the disease to subside.
B) a decrease in blood pressure.
C) a fever.
D) a gram-negative infection.
E) an increase in red blood cells.
B) a decrease in blood pressure.
Patients developed inflammation a few hours following eye surgery. Instruments and solutions were sterile, and the Limulus assay was positive. The patients' inflammation was due to
A) bacterial infection.
B) viral infection.
C) endotoxin.
D) exotoxin.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided
C) endotoxin.
In general, the LD50 for exotoxins is much greater than the LD50 for endotoxins.
True/False
FALSE
Biofilms provide pathogens with an adhesion mechanism and aid in resistance to antimicrobial agents.
True/False
TRUE
The M protein enhances the virulence of Streptococcus by preventing phagocytosis.
True/False
TRUE
In A-B exotoxins, the A component binds to the host cell receptor so that the B component can enter the cell.
True/False
FALSE
The Limulus amoebocyte assay is used to detect minute amounts of endotoxin in drugs and medical devices.
True/False
TRUE
Cytopathic effects, such as inclusion bodies and syncytium formation, are the visible signs of viral infections.
True/False
TRUE
Ergot and aflatoxin are toxins sometimes found in grains contaminated with fungi.
True/False
TRUE
Most symptoms of endotoxins can be treated with administration of anti-endotoxin antibodies.
True/False
FALSE
Infections with some viruses may induce chromosomal changes that alter the growth properties of host cells.
True/False
TRUE
Many pathogens use the same portal for entry and exit from the body.
True/False
TRUE
Innate immunity
A) is slower than adaptive immunity in responding to pathogens.
B) is nonspecific and present at birth.
C) involves a memory component.
D) involves T cells and B cells.
E) provides increased susceptibility to disease.
B) is nonspecific and present at birth.
All of the following protect the skin and mucous membranes from infection EXCEPT
A) multiple layers of cells.
B) tears.
C) saliva.
D) HCl.
E) the "ciliary escalator."
D) HCl.
The function of the "ciliary escalator" is to
A) propel inhaled dust and microorganisms toward the mouth, away from the lower respiratory tract.
B) remove microorganisms from the gastrointestinal tract.
C) remove microorganisms from the lower respiratory tract.
D) trap microorganisms in mucus in the upper respiratory tract.
E) trap inhaled dust and microorganisms in mucus and propel it away from the lower respiratory tract.
E) trap inhaled dust and microorganisms in mucus and propel it away from the lower respiratory tract.
Which of the following exhibits the highest phagocytic activity?
A) eosinophils
B) erythrocytes
C) macrophages
D) basophils
E) neutrophils
C) macrophages
TLRs attach to all of the following EXCEPT
A) AMPs.
B) flagellin.
C) LPS.
D) PAMPs.
E) peptidoglycan.
A) AMPs.
A differential cell count is used to determine each of the following EXCEPT
A) the total number of white blood cells.
B) the numbers of each type of white blood cell.
C) the number of red blood cells.
D) leukocytosis.
E) leukopenia.
C) the number of red blood cells.
The complement protein cascade is the same for the classical pathway, alternative pathway, and lectin pathway after the point in the cascade where the activation of ________ takes place.
A) C1
B) C2
C) C3
D) C5
E) C6
C) C3
All of the following increase blood vessel permeability EXCEPT
A) kinins.
B) prostaglandins.
C) lysozymes.
D) histamine.
E) leukotrienes.
C) lysozymes.
A child falls and suffers a deep cut on her leg. The cut went through her skin and she is bleeding. Which of the following defense mechanisms will participate in eliminating contaminating microbes?
A) mucociliary escalator
B) normal skin flora
C) phagocytosis in the inflammatory response
D) acidic skin secretions
E) lysozyme
C) phagocytosis in the inflammatory response
Margination refers to
A) the adherence of phagocytes to microorganisms.
B) the chemotactic response of phagocytes.
C) adherence of phagocytes to the lining of blood vessels.
D) dilation of blood vessels.
E) the movement of phagocytes through walls of blood vessels.
C) adherence of phagocytes to the lining of blood vessels.
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) All three types of interferons have the same effect on the body.
B) Alpha interferon promotes phagocytosis.
C) Gamma interferon causes bactericidal activity by macrophages.
D) Alpha interferon acts against specific viruses.
E) Beta interferon attacks invading viruses.
C) Gamma interferon causes bactericidal activity by macrophages.
Which of the following is found normally in serum?
A) complement
B) interferon
C) histamine
D) leukocytosis-promoting factor
E) TLRs
A) complement
Each of the following is an effect of complement activation EXCEPT
A) interference with viral replication.
B) bacterial cell lysis.
C) opsonization.
D) increased phagocytic activity.
E) increased blood vessel permeability.
A) interference with viral replication.
Which of the following is an effect of opsonization?
A) increased adherence of phagocytes to microorganisms
B) increased margination of phagocytes
C) increased diapedesis of phagocytes
D) inflammation
E) cytolysis
A) increased adherence of phagocytes to microorganisms
Normal microbiota provide protection from infection in each of the following ways EXCEPT
A) they produce antibacterial chemicals.
B) they compete with pathogens for nutrients.
C) they make the chemical environment unsuitable for nonresident bacteria.
D) they produce lysozyme.
E) they change the pH of the environment.
D) they produce lysozyme.
Each of the following provides protection from phagocytic digestion EXCEPT
A) M protein.
B) capsules.
C) formation of phagolysosomes.
D) leukocidins.
E) biofilms.
C) formation of phagolysosomes.
The antimicrobial effects of AMPs include all of the following EXCEPT
A) inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
B) lysis of bacterial cells.
C) destruction of nucleic acids.
D) pore formation in bacterial membranes.
E) inhibition of phagocytosis.
E) inhibition of phagocytosis.
The swelling associated with inflammation decreases when the fluid
A) returns to the blood.
B) goes into lymph capillaries.
C) is excreted in urine.
D) is lost as perspiration.
E) is transported into macrophages.
B) goes into lymph capillaries.
Which of the following statements about fixed macrophages is FALSE?
A) They are found in certain tissues and organs.
B) They develop from neutrophils.
C) They are cells of the mononuclear phagocytic system.
D) They are mature monocytes.
E) They gather at sites of infection.
B) They develop from neutrophils.
Phagocytes utilize all of the following to optimize interaction with (getting to and getting hold of) microorganisms EXCEPT
A) trapping a bacterium against a rough surface.
B) opsonization.
C) chemotaxis.
D) lysozyme.
E) complement.
D) lysozyme.
All of the following are effects of histamine EXCEPT
A) vasodilation.
B) fever.
C) swelling.
D) redness.
E) pain.
B) fever.
All of the following are effects of histamine EXCEPT
A) destruction of an injurious agent.
B) removal of an injurious agent.
C) isolation of an injurious agent.
D) repair of damaged tissue.
E) production of antibodies.
E) production of antibodies.
A chill is a sign that
A) body temperature is falling.
B) body temperature is rising.
C) body temperature is not changing.
D) the metabolic rate is decreasing.
E) blood vessels are dilating.
B) body temperature is rising.
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) There are at least thirty complement proteins.
B) All of the complement proteins are constantly active in serum.
C) Factors B, D, and P cause cytolysis.
D) Complement activity is antigen-specific.
E) Complement increases after immunization.
A) There are at least thirty complement proteins.
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) diapedesis — movement of leukocytes between capillary walls cells out of blood and into tissue
B) chemotaxis — chemical degradation inside a phagolysosome
C) abcess — a cavity created by tissue damage and filled with pus
D) pus — tissue debris and dead phagocytes in a white or yellow fluid
E) scab — dried blood clot over injured tissue
B) chemotaxis — chemical degradation inside a phagolysosome
All of the following are part of the mechanism of action of alpha and beta interferons EXCEPT
A) they bind to the surface of uninfected cells.
B) they are effective for long periods.
C) they initiate manufacture of antiviral proteins.
D) they disrupt stages of viral multiplication.
E) they initiate transcription.
B) they are effective for long periods.
The alternative pathway for complement activation is initiated by
A) lipid-carbohydrate complexes and C3.
B) C5-C9.
C) antigen-antibody reactions.
D) factors released from phagocytes.
E) factors released from damaged tissues.
A) lipid-carbohydrate complexes and C3.
The classical pathway for complement activation is initiated by
A) lipid-carbohydrate complexes and C3.
B) C5-C9.
C) antigen-antibody reactions.
D) factors released from phagocytes.
E) factors released from damaged tissues.
C) antigen-antibody reactions.
Activation of C3a results in
A) acute inflammation.
B) increased blood vessel permeability.
C) opsonization.
D) attraction of phagocytes.
E) cell lysis.
A) acute inflammation.
Neutrophils with defective lysosomes are unable to
A) undergo chemotaxis.
B) migrate.
C) produce toxic oxygen products.
D) attach to microorganisms and other foreign material.
E) engulf microorganisms and other foreign material.
C) produce toxic oxygen products.
Innate immunity includes all of the following EXCEPT
A) phagocytosis.
B) inflammation.
C) production of antibody.
D) production of interferon.
E) activation of complement.
C) production of antibody.
After ingesting a pathogen, lysosomal enzymes produce all of the following EXCEPT
A) complement.
B) O2-.
C) H2O2.
D) OH.
E) HOCl.
A) complement.
Activation of C5-C9 results in
A) activation of C3.
B) fixation of complement.
C) lysis of microbial cells.
D) phagocytosis.
E) inflammation.
C) lysis of microbial cells.
All of the following are true regarding NK cells EXCEPT
A) they are a type of lymphocyte.
B) they are found in tissues of the lymphatic system.
C) they have the ability to kill infected body cells and some tumor cells.
D) they destroy infected body cells by phagocytosis.
E) they release toxic substances that cause cell lysis or apoptosis.
D) they destroy infected body cells by phagocytosis.
Which of the following is involved in resistance to parasitic helminths?
A) basophils
B) eosinophils
C) lymphocytes
D) monocytes
E) neutrophils
B) eosinophils
Macrophages arise from which of the following?
A) basophils
B) eosinophils
C) lymphocytes
D) monocytes
E) neutrophils
D) monocytes
All of the following pertain to fever EXCEPT that it
A) accelerates microbial growth by increasing iron absorption from the digestive tract.
B) stimulates T lymphocyte activity.
C) is caused by interleukin-1 and TNF-alpha coming into contact with the hypothalamus.
D) intensifies the effect of antiviral interferons.
E) can be initiated by specific types of pathogens.
A) accelerates microbial growth by increasing iron absorption from the digestive tract.
All of the following are iron-binding proteins found in humans EXCEPT
A) lactoferrin.
B) transferrin.
C) hemoglobin.
D) siderophorin.
E) ferritin.
D) siderophorin.
All of the following occur during inflammation. What is the first step?
A) diapedesis
B) margination
C) phagocyte migration
D) repair
E) vasodilation
E) vasodilation
The lectin pathway for complement action is initiated by
A) mannose on host membranes.
B) mannose on the surface of microbes.
C) lectins of the microbe.
D) gram-negative cell walls.
E) gram-positive cell walls.
B) mannose on the surface of microbes.
All of the following are components of the inflammatory process EXCEPT
A) dilation of blood vessels.
B) release of histamines and prostaglandins.
C) chemotaxis.
D) diapedesis.
E) antibody synthesis.
E) antibody synthesis.
Several inherited deficiencies in the complement system occur in humans. Which of the following would be the MOST severe?
A) deficiency of C3
B) deficiency of C5
C) deficiency of C6
D) deficiency of C7
E) deficiency of C8
A) deficiency of C3
Which of the following statements about the classical pathway of complement activation is FALSE?
A) C1 is the first protein activated in the classical pathway.
B) The C1 protein complex is initiated by antigen-antibody complexes.
C) C3 is not involved in the classical pathway.
D) Cleaved fragments of some of the proteins act to increase inflammation.
E) C3b causes opsonization.
C) C3 is not involved in the classical pathway.
Lysozyme and the antibiotic penicillin have similar mechanisms of action in that they both cause damage to the bacterial
A) cell membrane.
B) capsule.
C) cell wall.
D) DNA.
E) ribosomes.
C) cell wall.
Which non-specific defense mechanism is mismatched with its associated body structure or body fluid?
A) lysozyme — tears and saliva
B) mucociliary escalator — intestines
C) very acidic pH — stomach
D) keratin and tightly packed cells — skin
E) cerumen and sebum — ear
B) mucociliary escalator — intestines
The dermis is composed of connective tissue and serves the primary purpose of providing direct protection from the external environment.
True/False
FALSE
Microorganisms that are members of the normal microbiota are also known to cause disease.
True/False
TRUE
Maturation of stem cells into mature blood cells occurs in the red bone marrow.
True/False
TRUE
The inflammatory response can only be triggered by an infection.
True/False
FALSE
Histamine and kinins cause increased blood flow and capillary permeability.
True/False
TRUE
Aspirin alleviates pain, inflammation, and fever by inhibiting prostaglandins.
True/False
TRUE
Complement proteins in their intact and unactivated form act as opsonins by binding to microorganisms and promoting phagocytosis.
True/False
FALSE
Digestion of microorganisms occurs in phagosomes.
True/False
FALSE
An example of a TLR would be peptidoglycan found in the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria.
True/False
FALSE
Ingestion of certain lactic acid bacteria (LABs) has been shown to be beneficial for function and health of the intestinal tract.
True/False
TRUE
What type of immunity results from vaccination?
A) innate immunity
B) naturally acquired active immunity
C) naturally acquired passive immunity
D) artificially acquired active immunity
E) artificially acquired passive immunity
D) artificially acquired active immunity
What type of immunity results from transfer of antibodies from one individual to a susceptible individual by means of injection?
A) innate immunity
B) naturally acquired active immunity
C) naturally acquired passive immunity
D) artificially acquired active immunity
E) artificially acquired passive immunity
E) artificially acquired passive immunity
What type of immunity results from recovery from mumps?
A) innate immunity
B) naturally acquired active immunity
C) naturally acquired passive immunity
D) artificially acquired active immunity
E) artificially acquired passive immunity
B) naturally acquired active immunity
Which of the following is the best definition of epitope?
A) specific regions on antigens that interact with T-cell receptors
B) specific regions on antigens that interact with MHC class molecules
C) specific regions on antigens that interact with haptens
D) specific regions on antigens that interact with antibodies
E) specific regions on antigens that interact with perforins
D) specific regions on antigens that interact with antibodies
Newborns' immunity due to the transfer of antibodies across the placenta is an example of
A) innate immunity.
B) naturally acquired active immunity.
C) naturally acquired passive immunity.
D) artificially acquired active immunity.
E) artificially acquired passive immunity.
C) naturally acquired passive immunity.
Which of the following statements is NOT a possible outcome of antigen-antibody reaction?
A) clonal deletion
B) activation of complement
C) opsonization
D) ADCC
E) agglutination
A) clonal deletion
Which of the following cells is NOT an APC?
A) dentritic cells
B) macrophages
C) mature B cells
D) natural killer cells
E) None of the answers is correct; all of these are APCs.
D) natural killer cells
When an antibody binds to a toxin, the resulting action is referred to as
A) agglutination.
B) opsonization.
C) ADCC.
D) apoptosis.
E) neutralization.
E) neutralization.
CD4+ T cells are activated by
A) interaction between CD4+and MHC II.
B) interaction between TCRs and MHC II.
C) cytokines released by dendritic cells.
D) cytokines released by B cells.
E) complement.
A) interaction between CD4+and MHC II.
Which of the following recognizes antigens displayed on host cells with MHC II?
A) TCcell
B) B cell
C) THcell
D) natural killer cell
E) basophil
C) THcell
The specificity of an antibody is due to
A) its valence.
B) the H chains.
C) the L chains.
D) the constant portions of the H and L chains.
E) the variable portions of the H and L chains.
E) the variable portions of the H and L chains.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of B cells?
A) They originate in bone marrow.
B) They have antibodies on their surfaces.
C) They are responsible for the memory response.
D) They are responsible for antibody formation.
E) They recognize antigens associated with MHC I.
E) They recognize antigens associated with MHC I.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of cellular immunity?
A) The cells originate in bone marrow.
B) Cells are processed in the thymus gland.
C) It can inhibit the immune response.
D) B cells make antibodies.
E) T cells react with antigens.
D) B cells make antibodies.
Plasma cells are activated by a(n)
A) antigen.
B) T cell.
C) B cell.
D) memory cell.
E) APC.
A) antigen.
The antibodies found in mucus, saliva, and tears are
A) IgG.
B) IgM.
C) IgA.
D) IgD.
E) IgE.
C) IgA.
The antibodies found almost entirely and only on the surface of B cells (not secreted from them), and which always exist as monomers, are
A) IgG.
B) IgM.
C) IgA.
D) IgD.
E) IgE.
D) IgD.
The antibodies that can bind to large parasites are
A) IgG.
B) IgM.
C) IgA.
D) IgD.
E) IgE.
E) IgE.
In addition to IgG, the antibodies that can fix complement are
A) IgM.
B) IgA.
C) IgD.
D) IgE.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) IgM.
Large antibodies that agglutinate antigens are
A) IgG.
B) IgM.
C) IgA.
D) IgD.
E) IgE.
B) IgM.
The most abundant class of antibodies in serum is
A) IgG.
B) IgM.
C) IgA.
D) IgD.
E) IgE.
A) IgG.
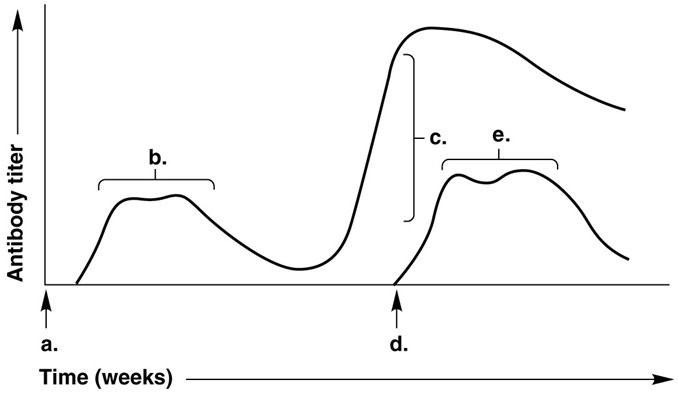
In Figure 17.1, which letter on the graph indicates the patient's secondary response to a repeated exposure with the identical antigen?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
C) c
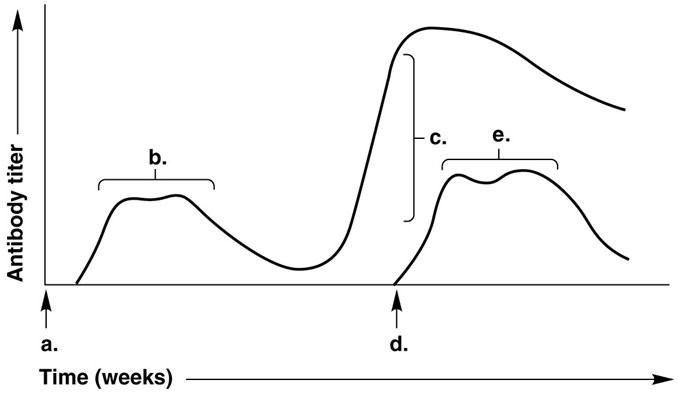
In Figure 17.1, which letter on the graph indicates the highest antibody titer during the patient's response to a second and distinct/different antigen?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
E) e
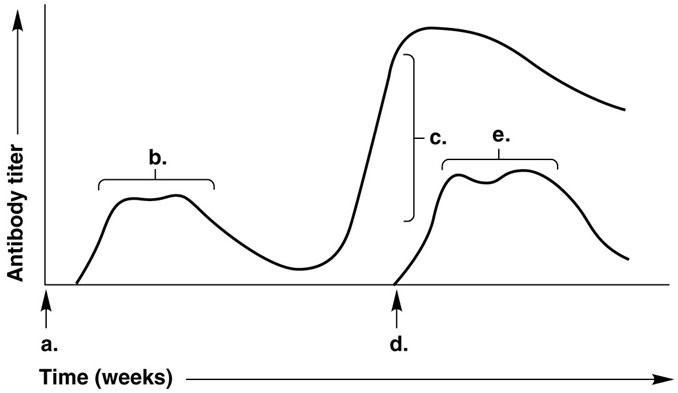
In Figure 17.1, the arrow at time (c) indicates
A) the time of exposure to the same antigen as at time (a).
B) the secondary response.
C) the primary response.
D) exposure to a new antigen.
E) the T-cell response.
B) the secondary response.
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The variable region of a heavy chain is partially responsible for binding with antigen.
B) The variable region of a light chain is partially responsible for binding with antigen.
C) The Fc region attaches to a host cell.
D) The constant region of a heavy chain is the same for all antibodies.
E) All of the answers are correct.
D) The constant region of a heavy chain is the same for all antibodies.
Which of the following is the best definition of antigen?
A) something foreign in the body
B) a chemical that elicits an antibody response and can combine with these antibodies
C) a chemical that combines with antibodies
D) a pathogen
E) a protein that combines with antibodies
B) a chemical that elicits an antibody response and can combine with these antibodies
Which of the following WBCs are NOT lymphocytes?
A) cytotoxic T cells
B) helper T cells
C) NK cells
D) M cells
E) B cells
D) M cells
The following events elicit an antibody response. What is the third step?
A) Antigen-digest goes to surface of APC.
B) APC phagocytizes antigen.
C) B cell is activated.
D) THcell recognizes antigen-digest and MHC II.
E) THcell produces cytokines.
D) THcell recognizes antigen-digest and MHC II.
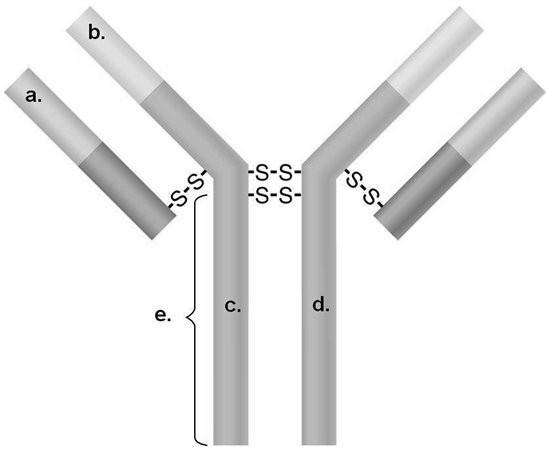
) In Figure 17.2, which areas are similar for all IgG antibodies?
A) a and b
B) a and c
C) b and c
D) c and d
E) b and d
D) c and d
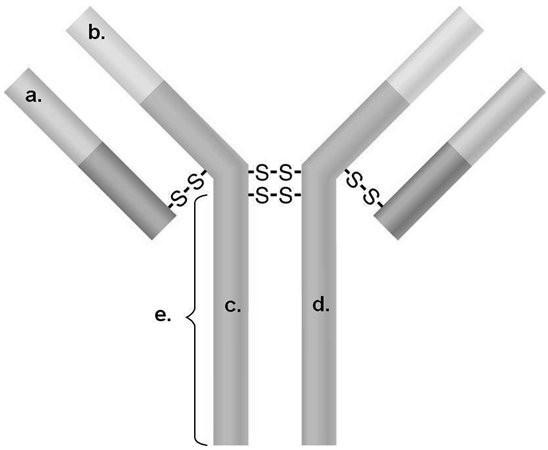
In Figure 17.2, which areas are different for all IgM antibodies?
A) a and b
B) a and c
C) b and c
D) c and d
A) a and b
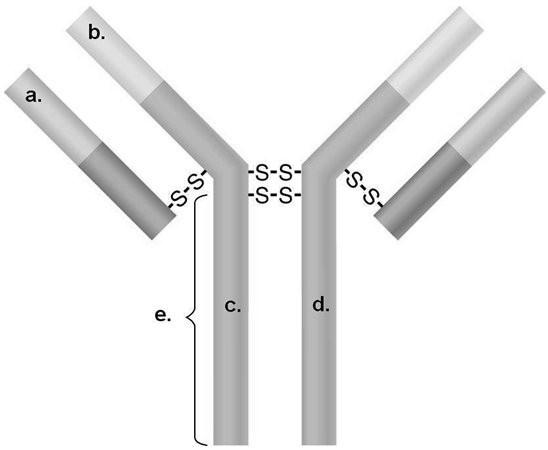
In Figure 17.2, which areas represent antigen-binding sites?
A) a and b
B) a and c
C) b and c
D) c and d
E) b and d
A) a and b
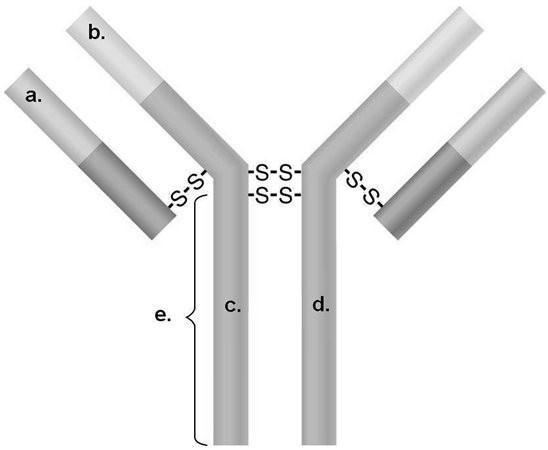
In Figure 17.2, what portion will typically attach to a host cell?
A) a and c
B) b
C) b and c
D) a and d
E) e
E) e
Which of the following bacterial components would most likely result in B cell stimulation by T-independent antigens?
A) capsule
B) flagellum
C) pili
D) ribosome
E) plasmid
A) capsule
The presence of which of the following indicates a current infection rather than a previous infection or vaccination?
A) IgA
B) IgG
C) IgM
D) IgD
E) IgE
C) IgM
Which of the following destroys virus-infected cells?
A) CTL
B) Treg
C) TH
D) dendritic cells
E) B cells
A) CTL
The following events occur in cellular immunity, leading to a response from TH cells. What is the third step?
A) Antibodies are produced.
B) Dendritic cell takes up antigen.
C) Antigen enters M cell.
D) THcell produces cytokines.
E) THcells proliferate.
E) THcells proliferate.
Cytokines released by TH1 cells
A) activate CD8+cells to CTLs.
B) convert TH1 cells to TH2 cells.
C) convert TH2 cells to TH1 cells.
D) kill parasites.
E) convert B cells to T cells.
A) activate CD8+cells to CTLs.
Which one of the following causes transmembrane channels in target cells?
A) granzymes
B) hapten
C) IL-1
D) IL-2
E) perforin
E) perforin
At a minimum, the human immune system is capable of recognizing approximately how many different antigens?
A) 105
B) 1010
C) 1015
D) 1020
E) 1025
C) 1015
Thymic selection
A) destroys T cells that do not recognize self-molecules of MHC.
B) destroys B cells that make antibodies against self.
C) destroys MHC molecules.
D) destroys CD4+cells that attack self.
E) activates B cells.
A) destroys T cells that do not recognize self-molecules of MHC.
Which of the following statements about natural killer cells is FALSE?
A) They destroy virus-infected cells.
B) They destroy tumor cells.
C) They destroy cells lacking MHC I.
D) They are stimulated by an antigen.
E) None of the answers are correct; all of these statements are true.
D) They are stimulated by an antigen.
An antibody's Fc region can be bound by
A) antibodies.
B) macrophages.
C) T helper cells.
D) B cells.
E) CTLs.
B) macrophages.
A Treg cell deficiency could result in
A) increased number of viral infections.
B) increased number of bacterial infections.
C) autoimmunity.
D) increased severity of bacterial infections.
E) transplant rejection.
C) autoimmunity.
ADCC is a process that is most effective in destroying
A) eukaryotic pathogens.
B) prions.
C) extracellular viruses.
D) bacterial pathogens.
E) bacterial toxins.
A) eukaryotic pathogens.
IL-2, produced by TH cells,
A) activates macrophages.
B) stimulates THcell maturation.
C) causes phagocytosis.
D) activates antigen-presenting cells.
E) activates TCcells to CTLs.
B) stimulates THcell maturation.
Which of the following statements about IL-12 is FALSE?
A) It activates macrophages.
B) It inhibits some tumor cells.
C) It activates the TH1 pathway.
D) It causes autoimmune diseases.
E) It causes THcells to respond to HIV.
D) It causes autoimmune diseases.
Apoptosis results in significant leakage of cellular contents.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
Cytokines are protein-based chemical messengers that allow for communication between cells of the immune system.
TRUE/FALSE
TRUE
Only dendritic cells produce interleukins
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
The production of interferons at an infection site is critical for chemotaxis.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
Cytokine storms negatively impact human health.
TRUE/FALSE
TRUE
The variable region of the antibody is solely responsible the significant diversity of antigen targets
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
Plasma cells will eventually differentiate into memory cells.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
Memory cells do not require B cell receptors.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
The implementation of vaccinations occurred prior to experimental support for the germ theory of disease.
TRUE/FALSE
TRUE
When haptens attach to carrier molecules, an epitope forms on hapten which then can be bound to antibody.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
All of the following are true of hypersensitivity EXCEPT
A) it occurs in the presence of an antigen.
B) it is synonymous with "allergy."
C) it occurs when an individual is exposed to an allergen for the first time.
D) it is due to an altered immune response.
E) it requires previous exposure to an antigen.
C) it occurs when an individual is exposed to an allergen for the first time.
The chemical mediators of anaphylaxis are
A) found in basophils and mast cells.
B) antibodies.
C) antigens.
D) antigen-antibody complexes.
E) the proteins of the complement system.
A) found in basophils and mast cells.
Which of the following may result from systemic anaphylaxis?
A) hay fever
B) asthma
C) shock
D) hives
E) immunodeficiency
C) shock
Which antibodies will be in the serum of a person with blood type B, Rh+?
A) anti-A, anti-B, anti-Rh
B) anti-A, anti-Rh
C) anti-A
D) anti-B, anti-Rh
E) anti-B
C) anti-A
Which of the following types of transplant is least compatible?
A) autograft
B) allograft
C) isograft
D) xenotransplant
E) All of these types of transplant are equally compatible.
D) xenotransplant
When testing donated blood for compatibility you would find a person with O type blood
A) has O type antigens on their red blood cells.
B) will lack plasma antibodies to A and B type antigens.
C) will lack A and B red blood cell antigens.
D) lacks HLA and MHC antigens.
E) will have anti-O antibodies in their plasma.
C) will lack A and B red blood cell antigens.
Graft-versus-host disease will most likely be a complication of a(n)
A) skin graft.
B) bone marrow transplant.
C) blood transfusion.
D) Rh incompatibility between mother and fetus.
E) corneal transplant.
B) bone marrow transplant.
A positive tuberculin skin test is an example of
A) delayed cell-mediated immunity.
B) autoimmunity.
C) acute contact dermatitis.
D) psoriasis.
E) innate immunity.
A) delayed cell-mediated immunity.
A healthy immune system destroys cancer cells with
A) tumor-specific antigens.
B) CTLs.
C) CTLs and activated macrophages.
D) activated macrophages.
E) CD+T cells.
C) CTLs and activated macrophages.
The symptoms of an immune complex reaction are due to
A) destruction of the antigen.
B) complement activation.
C) phagocytosis.
D) antibodies against self.
E) cytokines.
B) complement activation.
Rheumatoid arthritis is due to deposition of
A) IgG and IgA complexes in joints.
B) IgA antibodies in joints.
C) IgD and IgE complexes in joints.
D) complement in joints.
E) complexes of IgM and IgG and also complement in joints.
E) complexes of IgM and IgG and also complement in joints.
Allergic contact dermatitis is due to
A) sensitized T cells.
B) IgG antibodies.
C) IgE antibodies.
D) IgM antibodies.
E) activated macrophages.
A) sensitized T cells.
Attachment of HIV to the target cell depends on
A) gp120 combining with the CD4+
B) gp120 combining with the chemokine receptor CCR5.
C) gp41 binding to the CD4+
D) gp120 binding to the CD4+plasma membrane.
E) CXCR4 binding to the CD4+
A) gp120 combining with the CD4+
All of the following pertain to serological tests EXCEPT
A) they can detect antibodies but not antigens.
B) they can be used to diagnose various diseases.
C) reactions can be detected by uptake of trypan blue by damaged cells.
D) they are used to test for specific HLAs on lymphocytes.
E) they are used to detect compatible tissues for transplantation
A) they can detect antibodies but not antigens.
The process of desensitization to prevent allergies involves the injection of increasing amounts of
A) IgE.
B) IgG.
C) antihistamine.
D) antigen.
E) RhoGAM.
D) antigen.
Which of the following statements about type I reactions is FALSE?
A) They involve helper T cells.
B) They involve IgE antibodies.
C) The symptoms are due to histamine.
D) Antibodies bind to mast cells and basophils.
E) The symptoms occur soon after exposure to an antigen.
A) They involve helper T cells.
Which of the following statements about type IV reactions is FALSE?
A) Reactions are primarily due to T cell proliferation.
B) Reactions are not apparent for a day or more.
C) Cytokines initiate tissue damage.
D) Allergic contact dermatitis is an example.
E) Hemolytic disease of the newborn is an example.
E) Hemolytic disease of the newborn is an example.
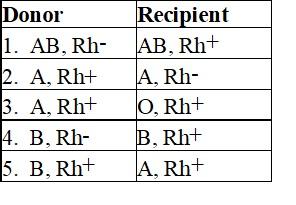
Which blood transfusions in Table 19.1 are incompatible?
A) 2 and 5
B) 1, 2, and 3
C) 2, 3, and 5
D) 3 and 4
E) 1 and 2
C) 2, 3, and 5
Hemolytic disease of the newborn can result from an
A) Rh+mother with an Rh-
B) Rh-mother with an Rh+
C) AB mother with a B fetus.
D) AB mother with an O fetus.
E) Rh-mother and an A fetus.
B) Rh-mother with an Rh+
Which is true regarding Herceptin therapy?
A) It neutralizes the growth factor EGF.
B) It acts as an immunotoxin to target and kill cancer cells.
C) It is used to treat some breast cancer patients.
D) It is a vaccine to prevent the development of cancer.
E) It is an endotoxin that stimulates TNF by macrophages.
C) It is used to treat some breast cancer patients.
Which of the following utilizes a combination of monoclonal antitumor antibody and immunotoxin?
A) immunologic enhancement
B) immunologic surveillance
C) immunotherapy
D) immunosuppression
E) immune complex
C) immunotherapy
All of the following are reasons why an HIV vaccine has not been developed EXCEPT
A) there is no known animal model of natural immunity for HIV infection.
B) use of a weakened virus would potentially transmit the infection.
C) small, inexpensive animals which could be used for HIV vaccine research are not available.
D) vaccines are not effective against viral infections.
E) HIV has a high mutation rate so one vaccination would not be effective to treat the world-wide pandemic.
D) vaccines are not effective against viral infections.
Treatment with certain drugs to reduce transplant rejection can cause
A) immunologic enhancement.
B) immunologic surveillance.
C) immunotherapy.
D) immunosuppression.
E) autoimmunity.
D) immunosuppression.
Which of the following statements about human embryonic stem cells is TRUE?
A) They are obtained in great numbers from umbilical cords of newborns.
B) They express no MHC II antigens.
C) They are pluripotent.
D) They are typically obtained from the zygote stage of embryonic development.
E) They are pluripotent and typically obtained from the blastocyst stage of embryonic development.
E) They are pluripotent and typically obtained from the blastocyst stage of embryonic development.
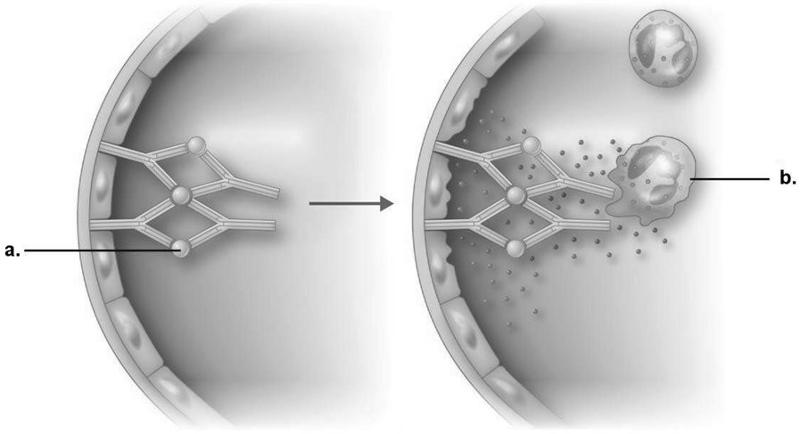
In immune complex reaction shown in Figure 19.1, what is the small, circular/spherical structure labeled "a"?
A) antibody
B) antigen
C) complement
D) neutrophil
E) mast cell
B) antigen
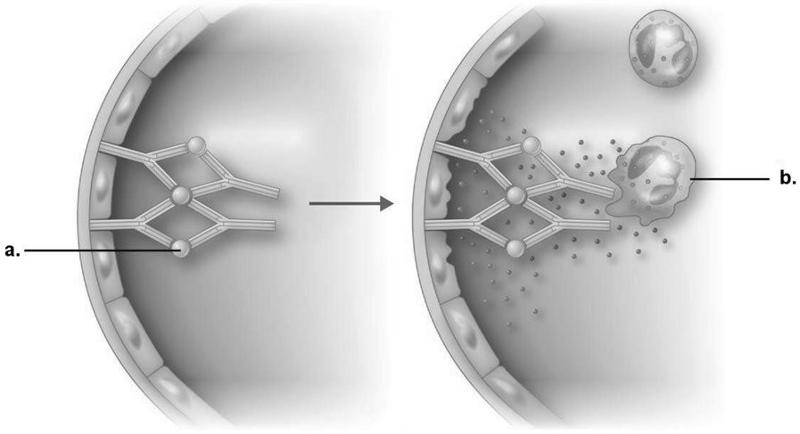
In immune complex reaction shown in Figure 19.1, what is the end result of the reaction?
A) IgG is directed against cell membrane antigens.
B) Complement is activated.
C) Neutrophils are attracted and release enzymes.
D) Endothelial cells are damaged.
E) Antibodies destroy neutrophils.
D) Endothelial cells are damaged.
Worldwide, the primary method of transmission of HIV is
A) heterosexual intercourse.
B) homosexual intercourse.
C) intravenous drug use.
D) blood transfusions.
E) nosocomial.
A) heterosexual intercourse.
HIV spikes attach to CD4+ receptors found on
A) T helper cells.
B) macrophages.
C) dendritic cells.
D) T helper cells and macrophages.
E) T helper cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
E) T helper cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
Which of the following is the least likely vaccine against HIV?
A) attenuated virus
B) glycoprotein
C) protein core
D) subunit
E) All of these vaccines are equally likely.
A) attenuated virus
Which of the following is a possible outcome of an HIV infection?
A) Virions may remain latent.
B) There may be persistent yeast infections.
C) Infection may initially be asymptomatic.
D) The disease does not progress to AIDS.
E) All of the answers are correct.
E) All of the answers are correct.
Which of the following regions has the greatest distribution of HIV infection and AIDS in the world?
A) North America
B) Eastern Europe and Central Asia
C) South and Southeast Asia
D) sub-Saharan Africa
E) Latin America
D) sub-Saharan Africa
Chemotherapy to inhibit the progression of HIV infection utilizes all of the following mechanisms EXCEPT
A) termination of viral DNA.
B) inhibition of viral proteases.
C) blockage of viral attachment.
D) prohibition of viral integration into host cell DNA.
E) destruction of viral ribosomes.
E) destruction of viral ribosomes.
During the asymptomatic phase I of HIV disease, HIV infection is diagnosed by
A) detecting viral RNA.
B) detecting antibodies against HIV.
C) counting CD4+T cells.
D) counting CD8+T cells.
E) the Western blot test.
A) detecting viral RNA.
Anaphylaxis is the term for reactions caused when certain antigens combine with
A) IgE antibodies.
B) macrophages.
C) IgG antibodies.
D) complement.
E) histamine.
A) IgE antibodies.
All of the following regarding "immune privileged sites" are true EXCEPT
A) they include corneal and brain tissue.
B) they do not have lymphatic vessels.
C) they are rarely rejected.
D) they include any tissue transplanted from a pig.
E) they explain how animals tolerate pregnancies without rejecting the fetus.
D) they include any tissue transplanted from a pig.
All of the following are considered examples of type I hypersensitivity EXCEPT
A) asthma.
B) dust allergies.
C) penicillin allergic reactions.
D) pollen allergies.
E) transplant rejections.
E) transplant rejections.
Which of the following describes a cytotoxic autoimmune reaction?
A) Antibodies react to cell-surface antigens.
B) Antibodies are not made.
C) Cells are killed.
D) Immune complexes form.
E) Mediate by T cells.
A) Antibodies react to cell-surface antigens.
Symptoms of delayed cell-mediated reactions are due to
A) IgE antibodies.
B) neutrophils.
C) cytokines.
D) IgG antibodies.
E) antigens.
C) cytokines.
Desensitization involves injection of
A) antigens.
B) IgG antibodies.
C) IgE antibodies.
D) antihistamine.
E) histamine.
A) antigens.
In the serological method for tissue typing, if human cells expressing HLA-I are mixed with anti-HLA-I, complement, and trypan blue, what would indicate the cells are HLA-I?
A) Enzyme is released from neutrophils.
B) Cells are damaged by complement.
C) Trypan blue enters the cells.
D) Anti-HLA antibodies bind to HLAs on lymphocytes.
E) None of the answers are correct; the T cells are missing.
C) Trypan blue enters the cells.
) In rheumatoid arthritis, IgM, IgG, and complement deposit in joints. This is an example of
A) cytotoxic autoimmunity.
B) immune complex autoimmunity.
C) cell-mediated autoimmunity.
D) immunosuppression.
E) acquired immunodeficiency
B) immune complex autoimmunity.
The number of T cells drops to below 200 cells/microliter in which phase of HIV infection?
A) phase 1
B) phase 2
C) phase 3
D) initial phase
E) asymptomatic phase
C) phase 3
HIV can evade host antibodies by
A) remaining an inactive provirus.
B) causing cell-to-cell fusion.
C) remaining an inactive provirus, causing cell to cell fusion, and virions remaining latent in vacuoles.
D) lowering the CD4+ cell count.
E) virions remaining latent in vacuoles.
C) remaining an inactive provirus, causing cell to cell fusion, and virions remaining latent in vacuoles.
Individuals who do not express CCR5 are highly resistant to infection by HIV.
TRUE/FALSE
TRUE
Vaccines against HIV have proven to be very effective in halting the spread of disease.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
All hypersensitivities involve antibody-antigen reactions.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
Skin tests are reliable indicators for the diagnosis of food-related allergies.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
HIV attack of CD4+ T cells causes suppression of both cell-mediated and humoral immune responses.
TRUE/FALSE
TRUE
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system is unable to discriminate "self" from "nonself."
TRUE/FALSE
TRUE
Xenotransplantation is an effective alternative to using isografts.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
All stem cells are derived from embryonic stem cells.
TRUE/FALSE
FALSE
Cancer is similar to an infectious disease in that it is due to a failure of the body's defenses.
TRUE/FALSE
TRUE
HIV is believed to have arisen by mutation of a virus endemic to wild animals in Africa.
TRUE/FALSE
TRUE
A hypersensitivity reaction refers to immune responses to antigens beyond what would be normal.
TRUE/FALSE
TRUE