What is oogenesis
- The formation of gametes in the ovaries
- Begins in females before they are born
Primordial germ cells
- Migrate from the yolk sac to the ovaries during early fetal development
- Differentiate into the oogonia
What are oogonia
Diploid (2n) stem cells that divide mitotically to produce millions of germ cells
What happens to oogonia before birth
- Most degenerate
- Few develop into larger cells called 1 o oocytes
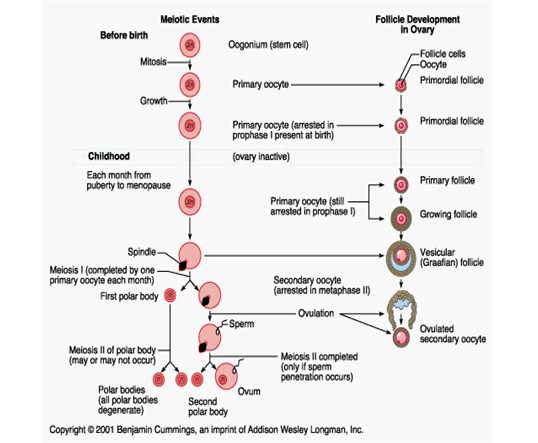
What happens to the 1 o oocytes during fetal development
Enter prophase of meiosis I but do not complete it until a few are called upon to do so during the reproductive years
What occurs to the 1o oocytes during the arrested stage of development
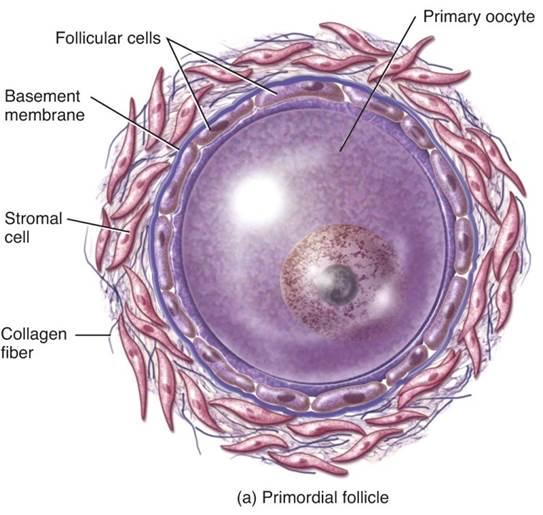
Each 1o oocyte is surrounded by follicular cells in a primordial follicle
What happens to the primordial follicles during puberty
- Under the influence of LH and FSH, several will be stimulated each month
- Only one will typically reach the maturity needed for ovulation
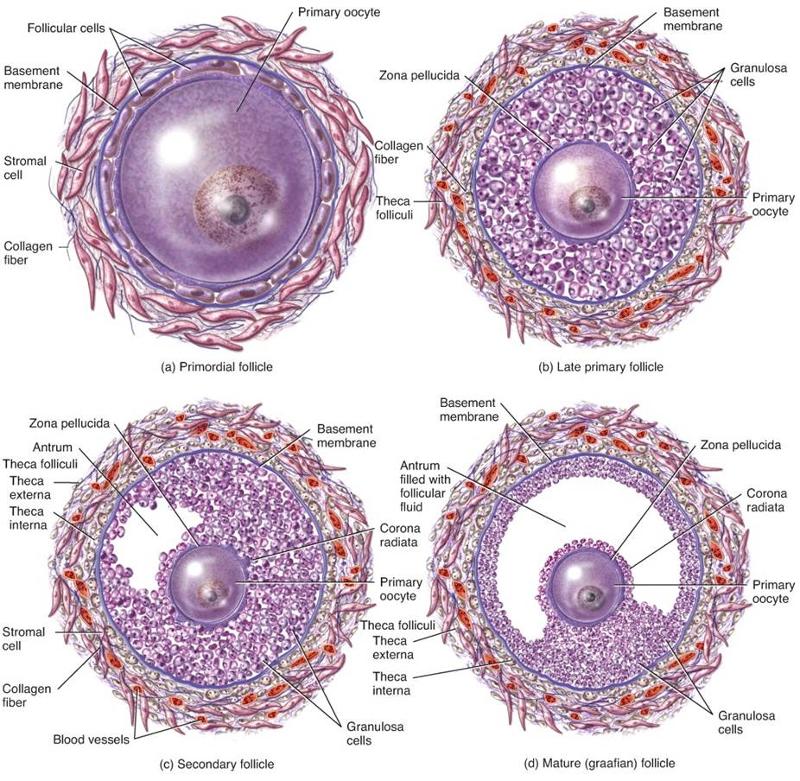
What happens to maturing oocytes within maturing follicles
Undergo a series of developmental stages which ultimately brings a 2 o oocyte within a mature follicle to ovulation
- the ovulated 2 o oocyte will have completed meiosis I, and so have a haploid number of chromosomes (1n)
What is produced when the 1 o oocyte receives the signal to complete meiosis I
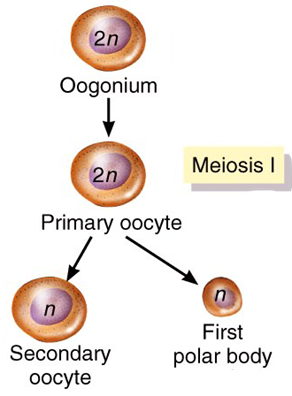
Two haploid (1n) cells of unequal size, each with 23 chromosomes
- Smaller cell is called the first polar body
- Larger 2 o oocyte inherits most of the cytoplasm
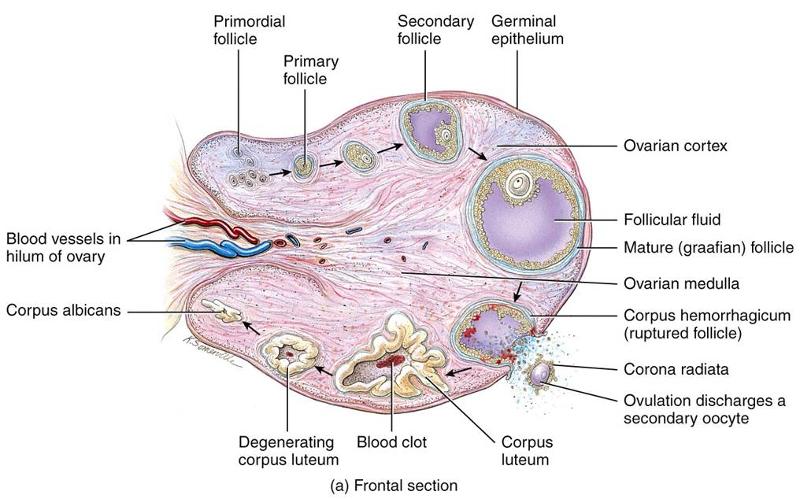
The ovarian cortex contains many follicles in different stages of development (T/F)
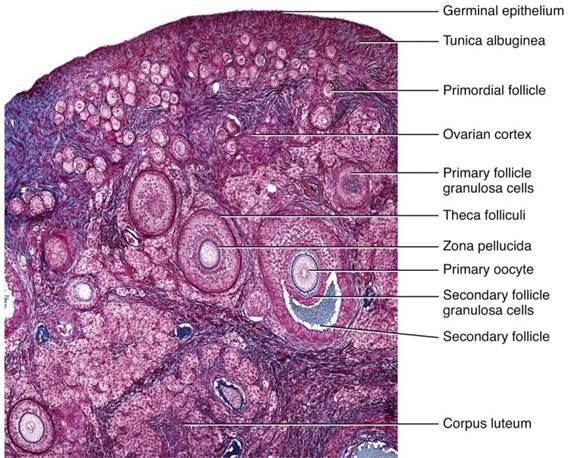
True
The ovarian cycle - picture
`
Oocyte maturation and follicle maturation - picture
The follicle has important functions beyond hosting an oocyte!
1st step of ovulation
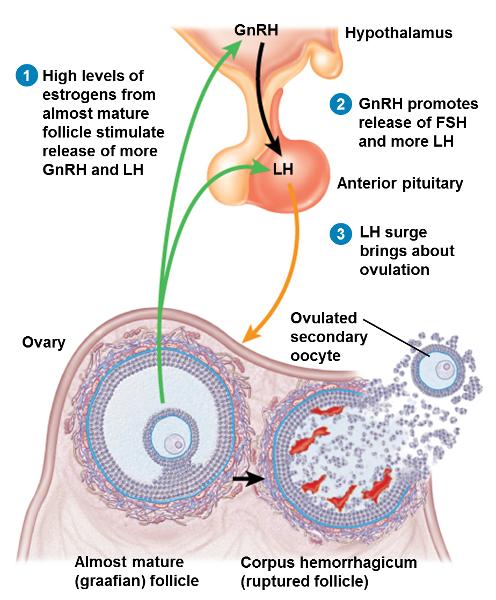
High levels of estrogen from almost mature follicle stimulate release of more GnRH and RH
2nd step of ovulation
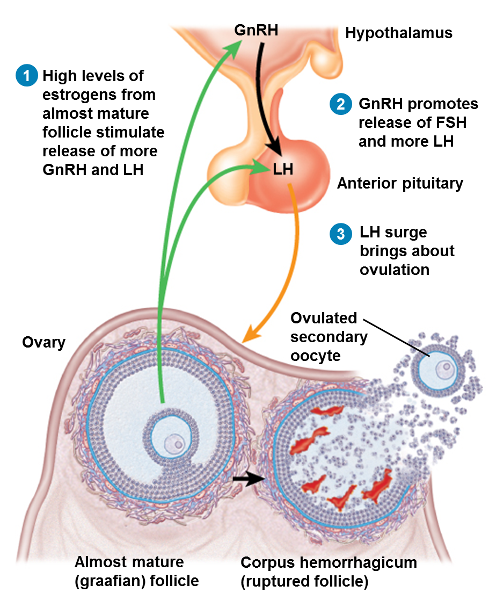
GnRH promotes release of FSH and more LH
3rd step of ovulation
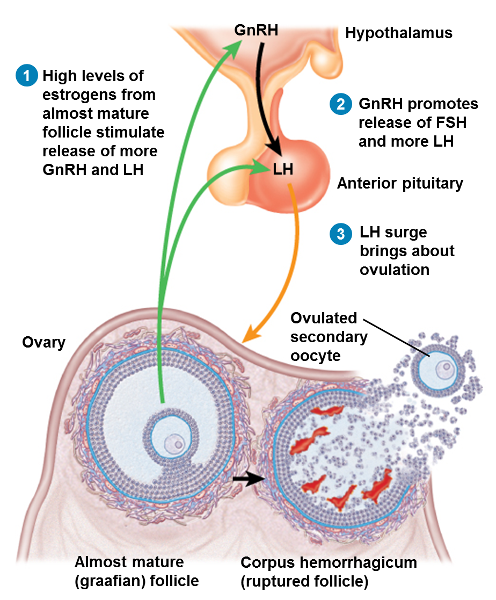
LH surge brings about ovulation
What happens to the mature follicle at ovulation
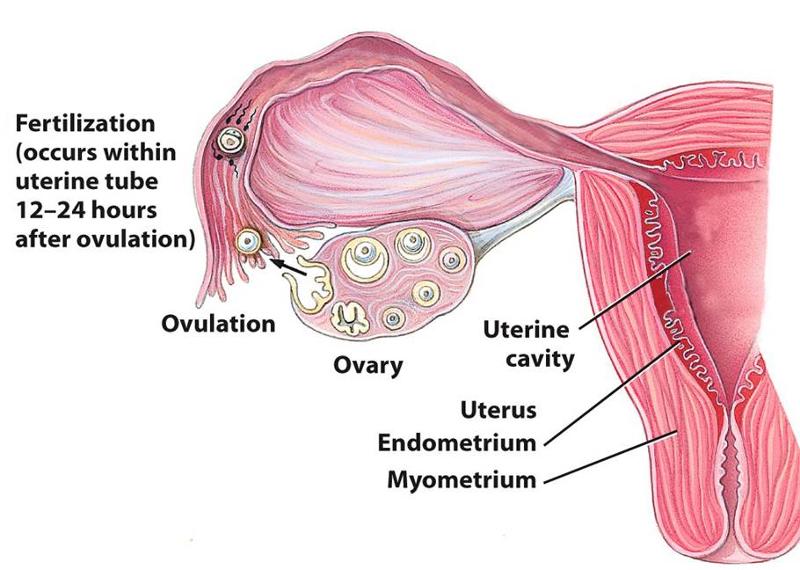
- It ruptures to expel the 2o oocyte into the pelvic cavity, normally to be swept into the uterine tube
What happens to the 2o oocyte after it is swept into the uterine tube
- If not fertilized, it degenerates
- If sperm are present and one penetrates the 2o oocyte , meiosis II resumes
What is the more common name for the 2o oocyte?
The egg
Oogenesis - picture
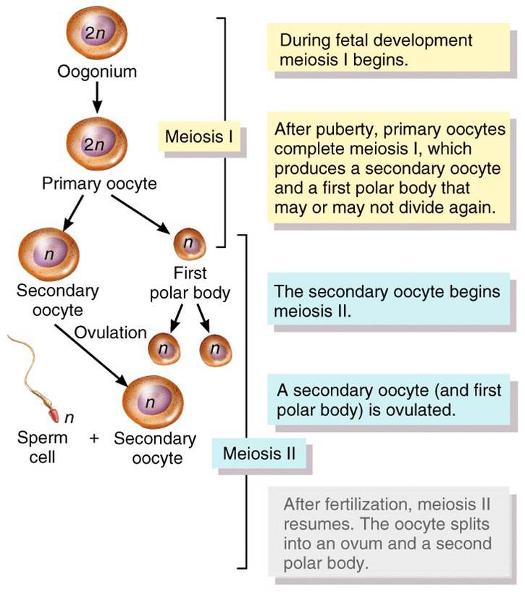
Oogenesis - Meiosis I summary
- Begins during fetal development
- After puberty, primary oocytes complete meiosis I, which produces a secondary oocyte and a first polar body that may or may not divide again
Oogenesis - Meiosis II summary
- The secondary oocyte and first polar body are ovulated
- After fertilization meiosis II resumes and the oocyte splits into an ovum and a second polar body.
Ovarian cycle - picture
What is the corpus luteum
Created from the mature follicle
A temporary structure in the ovary essential for establishing and maintaining pregnancy
What does the corpus luteum secrete
estrogens - responsible for the thickening of the endometrium
progesterone - responsible for the development and maintenance of the endometrium
When happens to the corpus luteum if the 2o oocyte is not fertilized
- After about 14 days it stops secreting progesterone
- Degenerates into a corpus albicans (a mass of fibrous scar tissue)
What occurs in the uterus if the 2o oocyte is not fertilized
Without estrogen, and then with abrupt progesterone withdrawal, the uterine lining cannot be maintained and it sloughs (menses)
What happens to the corpus luteum if pregnancy occurs
- It is “rescued” from degeneration by a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG).
- produces hormones well into the 1st trimester until the placenta can take over
When is the window of opportunity for fertilization to occur
Approximately 2 days before ovulation to 1 day after ovulation.
- Sperm can survive 48-72 hours in the uterine tube
When is meiosis II completed
- At the moment of conception, when the successful sperm penetrates the plasma membrane of the 2 o oocyte
- The nuclear material of the two cells unite to reconstitute the normal number of chromosomes (2n)
What is a zygote
The new diploid cell created at conception / completion of meiosis II
Oogenesis and follicular development - summary - picture
