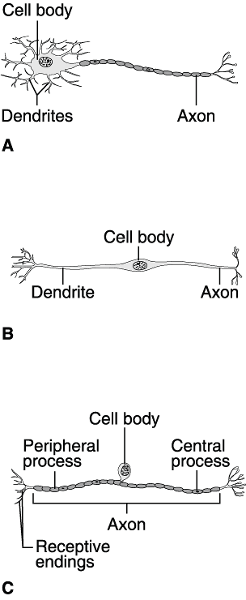
Using Figure 11.1, match the following:
1) Which neuron would
connect to a muscle?
2) Which neuron would be found in
the retina of the eye?
3) Which neuron is a sensory
neuron found in a reflex arc?
4) Which neuron is never
myelinated?
5) Which neuron is rare?
6) In
a reflex arc, which neuron has its cell body inside the spinal cord?
7) Which neuron is common only in dorsal root ganglia of
the spinal cord and sensory ganglia of
cranial nerves?
8) Which is by far the most common neuron type?
1) Answer: A
2) Answer: B
3) Answer: C
4) Answer: B
5) Answer: B
6)
Answer: A
7) Answer: C
8) Answer: A
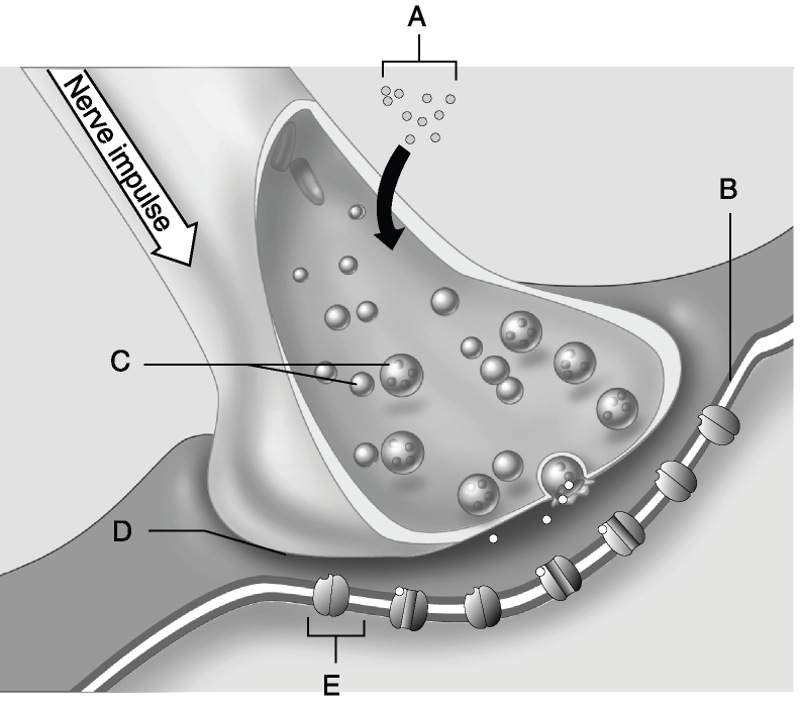
Using Figure 11.2, match the following:
9) Ion channel.
10) Synaptic vesicles.
11) Calcium ions.
12) Postsynaptic membrane.
13) Synaptic cleft.
9) Answer: E
10) Answer: C
11) Answer: A
12) Answer: B
13) Answer: D
Efferent nerve fibers may be described as motor nerve fibers.
True
Cell bodies of sensory neurons may be located in ganglia lying
outside the central nervous
system.
True
Myelination of the nerve fibers in the central nervous system is the job of the oligodendrocyte.
True
The oligodendrocytes can myelinate several axons.
True
Large-diameter nerve fibers conduct impulses much faster than small-diameter fibers.
True
If bacteria invaded the CNS tissue, microglia would migrate to the
area to engulf and destroy
them.
True
Which of the following is not a function of astrocytes?
A)
support and brace neurons
B) anchor neurons to blood
vessels
C) guide the migration of young neurons, synapse
formation, and helping to determine capillary permeability
D)
control the chemical environment around neurons
E) provide the
defense for the CNS
E) provide the defense for the CNS
Which of the choices below describes the ANS?
A) motor fibers
that conduct nerve impulses from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac
muscle, and glands
B) motor fibers that conduct nerve impulses
from the CNS to skeletal muscles
C) sensory neurons that convey
information from somatic receptors in the head, body wall, and limbs
and from receptors from the special senses of vision, hearing, taste,
and smell to the CNS
D) sensory and motor neurons that supply the
digestive tract
A) motor fibers that conduct nerve impulses from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
What are ciliated CNS neuroglia that play an active role in moving
the cerebrospinal fluid called?
A) ependymal cells
B)
Schwann cells
C) oligodendrocytes
D) astrocytes
A) ependymal cells
The sheath of Schwann is also called the ________.
neurilemma
Which of the following is not characteristic of neurons?
A) They
conduct impulses.
B) They have extreme longevity.
C) They
are mitotic.
D) They have an exceptionally high metabolic rate.
C) They are mitotic.
The part of a neuron that conducts impulses away from its cell body
is called a(n) ________.
A) axon
B) dendrite
C)
neurolemma
D) Schwann cell
A) axon
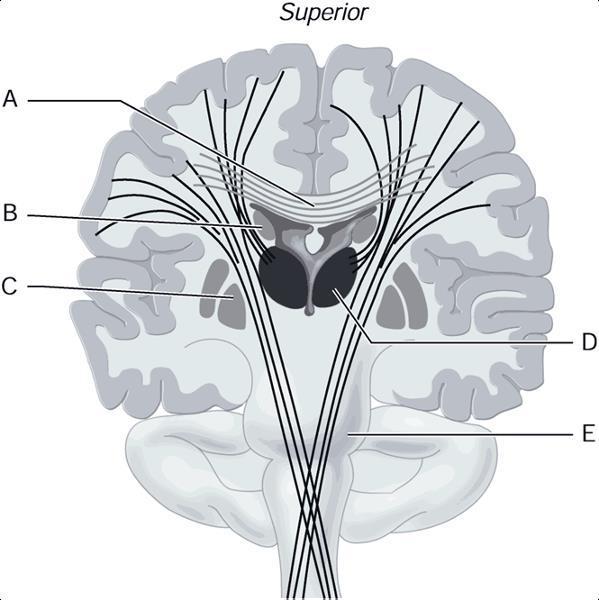
Using Figure, Match the following:
1) Pons
2) Corpus Callosum
3) Caudate Nucleus
4) Globus Pallidus
5) Thalamus
1) E
2) A
3) B
4) C
5) D
Key:
A) Occipital lobe
B) Insula
C) Temporal lobe
D) Parietal lobe
E) Frontal lobe
13) Auditory area
14) Primary sensory cortex
15) Somatic motor cortex
16) Motor speech area
17) Premotor area
18) Visual area
19) Taste (gustatory) area
20) Seat of intelligence, abstract reasoning
13) C
14) D
15) E
16) E
17) E
18) A
19) B
20) E
Specific motor and sensory functions are localized in specific areas called domains whereas memory and language have overlapping domains
True
The corpora quadrigemina superior colliculi are visual reflex centers, whereas the inferior colliculi are auditory reflex centers.
True
Cell bodies of the somatic motor neurons of the spinal nerves are located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord.
True
The adult spinal cord ends between L1 and L2.
True
Cerebrospinal fluid circulates within the ventricles of the brain and in the subarachnoid space outside the brain.
True
The RAS is comprised of specific pathways primarily in the limbic system.
False
The arbor vitae refers to ___________.
A) Flocculonodular nodes
B) Cerebellar gray matter
C) The pleatlike convolutions of the cerebellum
D) Cerebellar white matter
D) Cerebellar white matter
70) The brain stem consists of the ____________.
A) cerebrum, pons, midbrain, and medulla
B) pons, medulla, cerebellum, and midbrain
C) midbrain, medulla, and pons
D) midbrain only
C) midbrain, medulla, and pons
Spinocerebellar tracts _______________.
A) are found in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord.
B) give rise to conscious experience of perception
C) terminate in the spinal cord
D) carry proprioceptive inputs to the cerebellum
D) carry proprioceptive inputs to the cerebellum
What cells line ventricles of the brain?
A) ependymal cell
B) astrocytes
C) neurons
D) epithelial cells
A) ependymal cell
The vital centers for the control of heart rate, respiration, and
blood pressure are located in the ________.
medulla
midbrain
cerebrum
pons
medulla
Cell bodies of the sensory neurons of the spinal nerves are located
in ________.
A. sympathetic ganglia
B. the ventral
root ganglia of the spinal cord
C. the dorsal root ganglia of
the spinal cord
D. the thalamus
C. the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord
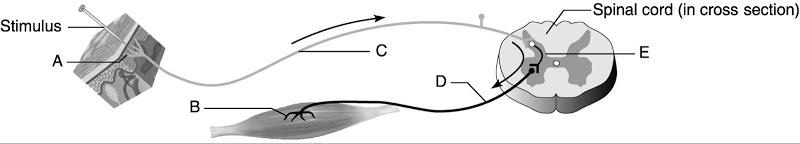
Using Figure 13.2,
identify the following components of the
reflex arc:
7) Integration center.
8)
Sensory neuron.
9) Effector.
10) Motor
neuron.
11) Receptor.
7) Answer: E
8) Answer: C
9) Answer: B
10) Answer: D
11) Answer: A
17) Tests both upper and lower
motor pathways. The sole of
the foot is stimulated with a
dull instrument.
18) Checks the integrity of the
spinal cord and dorsal
rami at
the level of T8 to T12.
19) Produces a
rapid withdrawal
of the body part from a
painful stimulus;
ipsilateral.
20) Prevents muscle
overstretching and
maintains
muscle tone.
21) Produces muscle relaxation and lengthening in response to
tension; the contracting muscle
relaxes as its antagonist is
activated.
A) Stretch
B) Abdominal
C) Flexor
D) Plantar
E) Golgi Tendon
17) D
18) B
19) C
20) A
21) E
Match the following:
26) Controls the outputs of the
cortex and regulates motor
activity.
27)
Central pattern generators.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 519; Fig. 13.13
28) Intermediate relay for
incoming and outgoing
neurons.
29) The cerebellum and basal
nuclei.
30) Includes cortical and brain
stem
motor areas.
31) The neural machinery of the
spinal cord, including spinal
cord circuits.
A) Projection level
B) Segmental level
C) Precommand level
26) C
27) B
28) A
29) C
30) A
31) B
Reciprocal inhibition means that while one sensory nerve is
stimulated, another sensory
neuron for synergistic muscles in
the same area is inhibited and cannot respond.
False
The patellar "knee jerk" reflex is an example of a(n)
________.
crossed-extensor reflex
stretch reflex
extensor thrust reflex
stress reflex
stretch reflex
Which of the following is not an example of an exteroceptor?
baroreceptor
Which of the following is not a main level of neural integration in the somatosensory system?
segmental
Which of the following is an incorrect statement regarding the occurrence of a sensation?
The stimulus energy must be converted into the energy of a graded
potential
called a transduction potential.
A generator potential is the associated sensory neuron must reach threshold
exteroceptors
Potentially damaging stimuli that result in pain are selectively detected by ________
nociceptors
Which receptors adapt most slowly?
nociceptors
Nerves that carry impulses toward the CNS only are ________.
afferent nerves