The Nephron
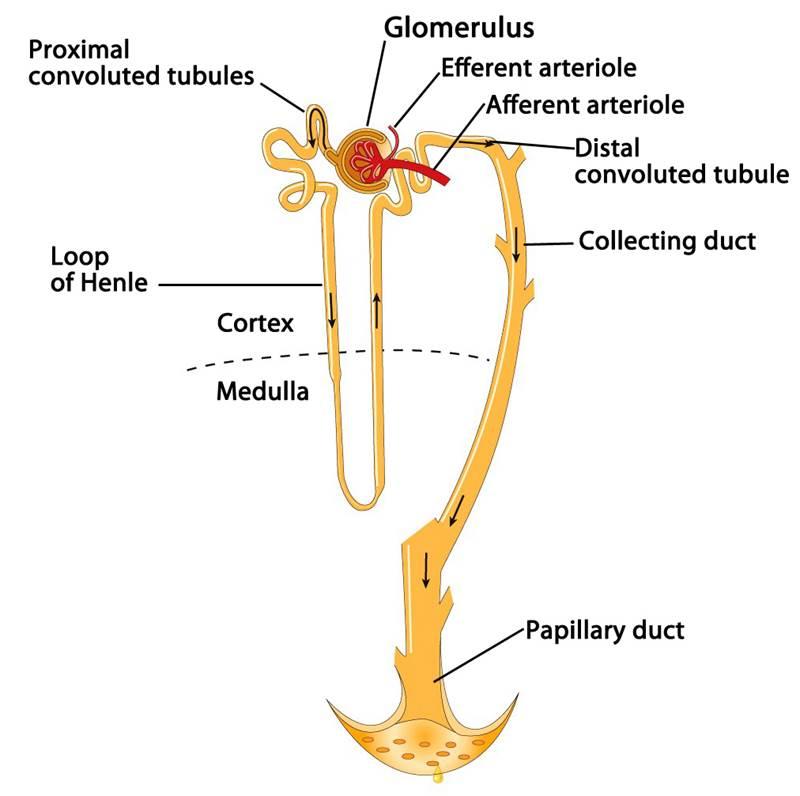
- Functional unit of the kidney
- Microscopic structure composed of blood vessels and tubules that collect the filtrate which will ultimately become urine
Afferent arteriole
- Present in each nephron
- Divides into a tangled, ball shaped capillary network called the glomerulus
Glomerulus
- Capillary network originating from the afferent arteriole that reunite to form an efferent arteriole
Efferent arteriole
- Present in each nephron
- Formed by glomerular capillaries
- Carries blood out of the glomerulus
Why are Glomerular capillaries unique
Positioned between two arteriole instead of an arteriole and a venule
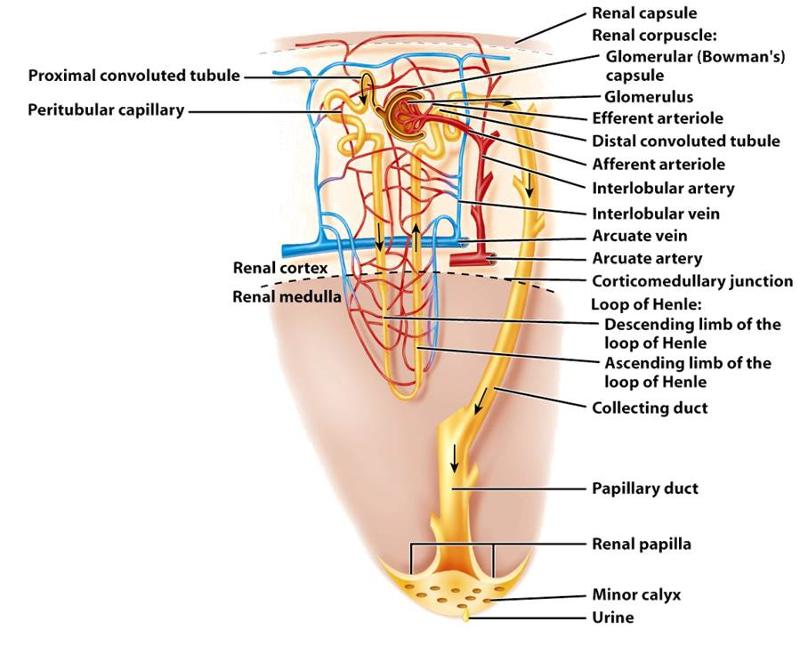
Structure of Renal Corpuscle
- Glomerular capillaries
- Glomerular Capsule
Glomerular Capsule
- A double-walled epithelial cup that surrounds the glomerular capillaries
Festrations
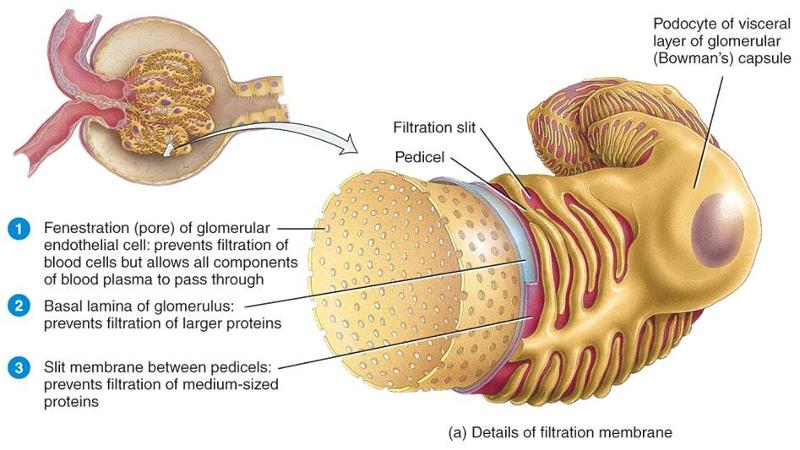
- Pores located in the epithelium of the renal corpuscle
- Act as a filtration membrane
Capsular space
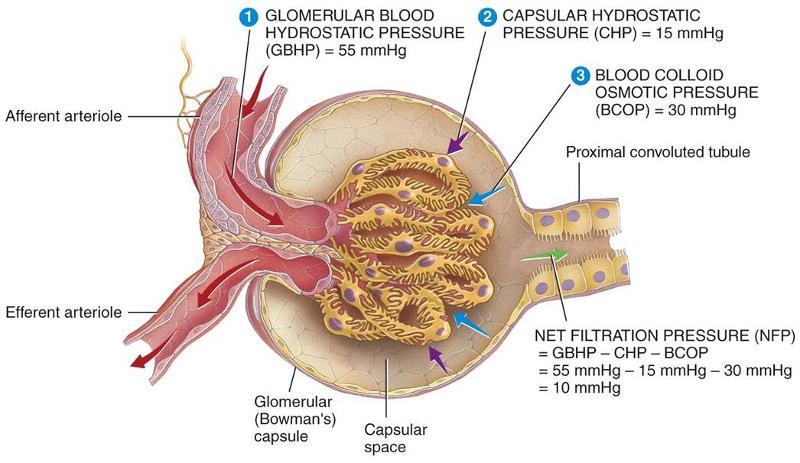
- Space between the two layers of the glomerular capsule
- Receives fluid filtered from the glomerular capillaries
- The lumen of the urinary tube
Blood is filtered through the glomerular capillaries into the____
Glomerular capsule
Filtered fluid passes into the renal tubule, which has what 3 sections
- The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT
- The loop of Henle
- The distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Collecting duct
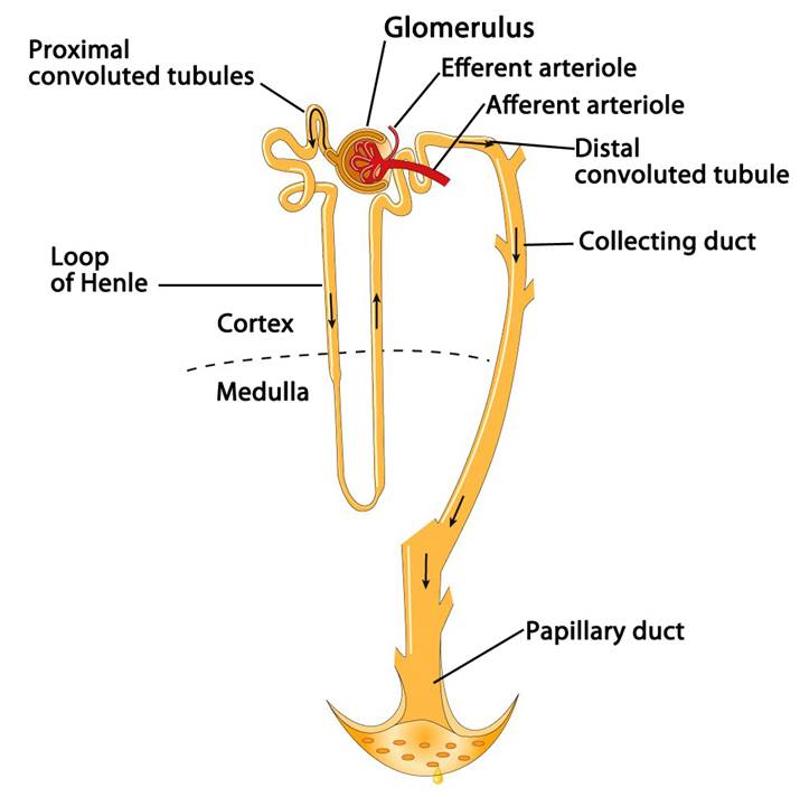
- Collects fluid from the distal convoluted tubules of several nephrons
- Unite and converge into large papillary ducts
Papillary ducts
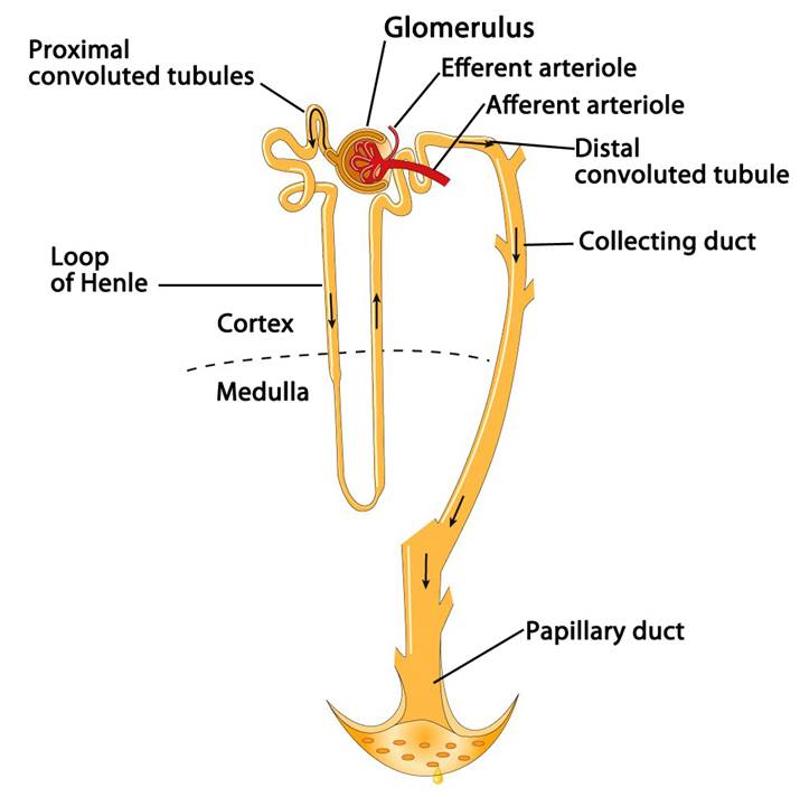
- Collecting ducts unite and converge to form these ducts
- drains into the minor calyces, major calyces, renal pelvis, and ureters
Cortical nephron
- Nephrons with short loops of Henle
- Make up 80-85% of the 1 million microscopic nephrons in each kidney
Where do renal corpuscles lie in cortical nephrons
- Renal corpuscles are located in the outer portion of the cortex
- Short henle loops that penetrate only a small way into the medulla
Where do cortical nephrons receive their blood supply
Blood supply comes from peritublar capillaries that arise from efferent arterioles
Juxtamedullary nephron
- Nephrons with long loops on Henle
- Make up 15-20% of the nephrons
- Enable the kidneys to create a concentration gradient in the renal medulla and to excrete very dilute or very concentrated urine
Where do renal corpuscles lie in juxtamedullary nephrons
- Renal corpuscles lie deep in the cortex, close to the medulla
- Long loops that extend into the deepest region
Where do juxtamedullary nephrons receive their blood supply
Blood supply comes from the vasa recta that arise from peritubular capillaries before becoming peritubular venules
Peritubular capillaries
- Arise from efferent arterioles
- Provide Cortical nephrons (short loops) with blood supply
Flow of fluid through a cortical nephron
- Glomerular capsule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Descending limb of the nephron loop
- Ascending limb of the nephron loop
- Distal convoluted tubule (drains into collecting duct)
Macula densa
- An area of closely packed columnar tubule cells lining the wall of the distal tubule
- Located where the final part of the loop of Henle makes contact with the afferent arteriole serving that renal corpuscle.
Juxtaglomerular (JG) cells
- Line the wall of the afferent arteriole alongside the macula densa
- Contains modified smooth muscle fibers
Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)
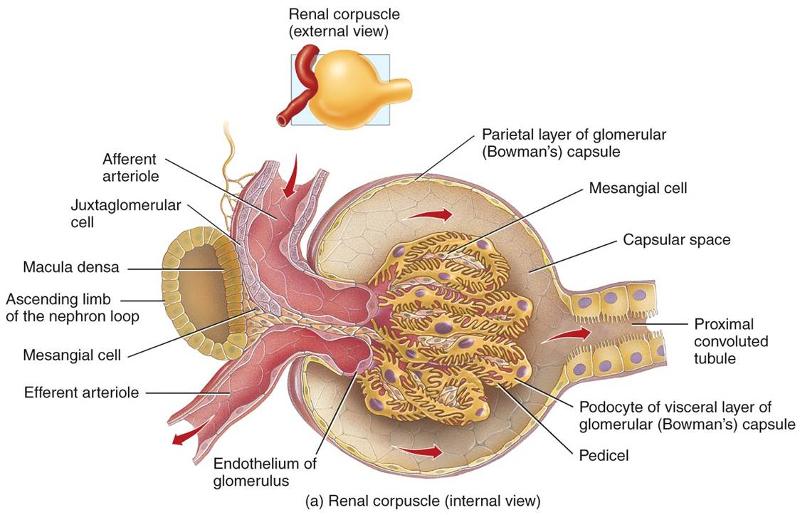
Structure formed by the Macula Densa and the juxtaglomerular cells
What is the function of the Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)
To regulate blood pressure within the kidneys
3 basic functions performed by nephrons and collecting ducts
- Glomerular filtration
- Tubular reabsorption
- Tubular secretion
Glomerular filtration
Water and solutes in blood move across the wall of glomerular capillaries, where they are filtered and move into the capsule then tubule
Tubular reabsorption
The process of returning important substances from the filtrate back to the blood
Tubular secretion
The movement of waste materials from the tubule to the filtrate