What are the primary reproductive organs of the female reproductive system?
Ovaries
Like the testes, the ovaries produce what 2 products? (Hint: Think a specific cell type and a specific hormone type)
1. Gametes
2. Sex hormones
What are 4 functions of the accessory structures of the female reproductive system in regards to the reproductive cells and/or the fetus?
1. Transport
2. House
3. Nurture
4. Serve the needs of the fetus
The external genitalia of the female reproductive system is also called what?
The vulva
The external genitalia consist of what 8 structures?
1. Mons pubis
2. Labia majora
3. Labia minora
4. Clitoris
5. External urethral orifice
6. Vaginal orifice
7. Hymen
8. Greater vestibular glands
The diamond-shaped region between the anterior end of the labial folds, the ischial tuberosities laterally, and the anus posteriorly is called what?
The perineum
The mons pubis is made up of what type of tissue?
Adipose tissue or fat
What is the function of the mons pubis?
To cushions the pubic symphysis
The mons pubis is covered with what after puberty?
Coarse hair
The labia majora extend from what external genitalia part?
Extends from the mons pubis
The labia majora contain what 3 structures? (Hint: 2 types of glands and 1 type of tissue)
1. Sebaceous glands
2. Apocrine glands
3. Adipose tissue
The labia majora are homolgous to what structure in males?
The scrotum
The labia minora are located medial to what external genitalia part?
The labia majora
Of hair, adipose tissue, and sebaceous glands, the labia minora lack what 2 and contain which one?
Lack hair and adipose tissue but do contain many sebaceous glands
The vestibule is a region that is located between what?
The two labia minora
From anterior to posterior, the vestibule contains what 3 structures of the external genitalia?
1. Clitoris
2. External urethral orifice
3. Vaginal orifice
The clitoris is made up of what tissue type?
Erectile tissue
The clitoris is located where?
Located where the labia minora meet anteriorly
The clitoris is homologous to what male structure?
The penis
The prepuce of the clitoris are skin folds formed by union of what external genitalia structure?
The labia minora
What is the function of the prepuce of the clitoris?
Hood the clitoris
What is the function of the external urethral orifice?
Serves as the outlet for the urinary system
Does the external urethral orifice have any reproductive function?
No reproductive function
The hymen is a thin fold of what type of membrane?
Mucus membrane
The hymen may cover what opening?
The vaginal opening
The greater vestibular glands secrete what substance?
Mucus
What is the function of the greater vestibular glands?
To lubricate the distal end of the vagina with mucus during coitus aka sexual intercourse
The greater vestibular glands are homologous to what glands in males?
The bulbo-urethral glands
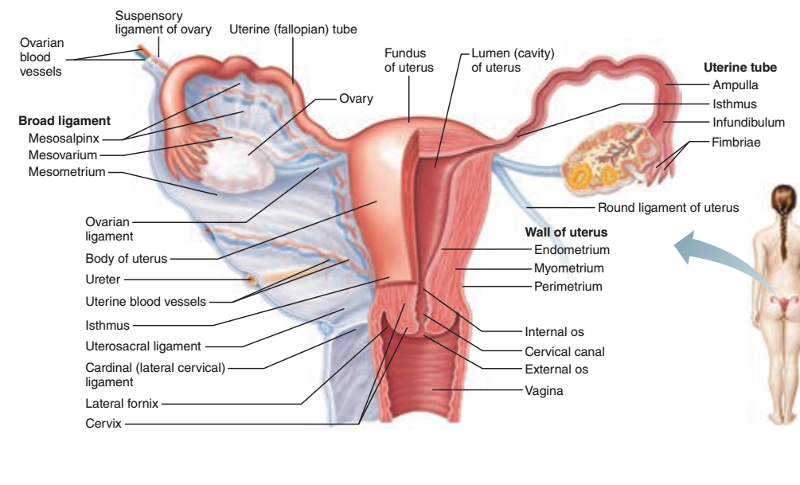
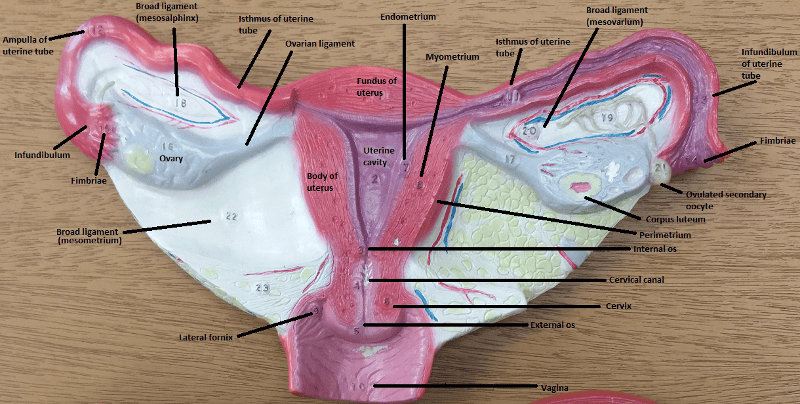
What are 5 internal structures of the female reproductive system?
1. Vagina
2. Uterus
3. Uterine tubes
4. Ovaries
5. Suspending and supporting ligaments
The vagina extends for how long?
About 10 cm or 4 inches
The vagina extends from what external structure to what internal structure and in what direction?
The vestibule to the uterus superiorly
The vagina serves as what type of organ and what type of canal?
1. Copulatory organ
2. Birth canal
The vagina also permits what type of flow
The menstrual flow
The uterus is what shape (i.e. like what fruit) and is situated between what 2 body features?
It's pear-shaped and located between the urinary bladder and the rectum
The uterus is what type of organ?
A muscular organ
What is the narrow end of the uterus?
The cervix
How is the cervix directed?
Inferiorly
The major portion of the uterus is referred to as what?
The body
The superior rounded region above the entrance of the uterine tubes is called what?
The fundus
What is implanted in the uterus?
A fertilized egg
What is the function of the uterus during a pregnancy?
To house the embryo or fetus during its development
In some cases, what are 2 other places in which the fertilized egg may implant?
1. Uterine tube
2. Abdominal viscera
When a fertilized egg implants in the uterine tube or the abdominal viscera, what type of pregnancy happens?
An ectopic pregnancy
Are ectopic implantations successful?
No
Why may ectopic implantations in the uterine tubes be dangerous?
The uterine tubes cannot accommodate the increasing size of the fetus
What is the endometrium in regard to the uterus? (Hint: what is it made out of?)
The thick mucosal lining of the uterus
The endometrium has what 2 layers from superficial to deep?
1. Stratum functionalis
2. Stratum basalis
The stratum functionalis sloughs off in approximately how many days?
About 28 days
The stratum functionalis sloughs off in response to what? (Hint: Think cyclic changes and hormones)
In response to cyclic changes in the levels of ovarian hormones in the female's blood
The sloughing-off process is accommodated by what event? (Hint: Think blood)
Bleeding
The sloughing-off process is referred to as what?
Menstruation
What is the function of the stratum basalis?
To form a new stratum functionalis after menstruation ends
The fallopian tubes are also called what?
Uterine tubes
The fallopian tubes are about how long?
10 cm or 4 inches long
The fallopian tubes extend from what internal reproductive structure to what cavity to what region of what internal organ?
Extends from the ovaries in the peritoneal cavity to the superolateral region of the uterus
The distal ends of the tubes have finger-like projections called what?
Fimbriae
Unlike the male system, what is different between the female gonad (ovaries) and the initial part of the female duct system-the uterine tube?
There is no actual contact
Because of the open passageway between the female reproductive organs and the peritoneal cavity, what is the consequence in regard to reproductive system infections?
Reproductive system infections can cause widespread inflammations of the pelvic viscera
Inflammation of the pelvic viscera is called what?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Give an example of a reproductive system infection?
Gonorrhea
1. STIs stand for what?
2. STDs stand for what?
1. Sexually transmitted infections
2. Sexually transmitted diseases
All of the internal female organs are retroperitoneal except for which set?
The ovaries
How are the ovaries supported and suspended? (Hint: Think ligament)
Supported and suspended by ligamentous folds of the peritoneum
What are the 9 supporting structures of the uterus, uterine tubes, and ovaries?
1. Broad ligament
2. Mesometrium
3. Round ligaments
4. Uterosacral ligaments
5. Cardinal (lateral cervical) ligaments
6. Mesosalpinx
7. Mesovarium
8. Suspensory ligaments
9. Ovarian ligaments
What is the function of the broad ligament in regards to the uterus and uterine tubes?
Anchors them to the lateral body walls
The mesometrium supports what internal reproductive structure and in what direction?
Supports the uterus laterally
The round ligaments anchor what internal reproductive structure to which wall?
Anchor the uterus to the anterior pelvic wall
The uterosacral ligaments secure what internal reproductive structure to what bone and in what direction?
Secure the uterus to the sacrum posteriorly
The cardinal ligaments connect what 2 internal reproductive structures to what wall and how directionally?
Connect the cervix and vagina to the pelvic wall laterally
What is the general function of the mesosalpinx? (Hint: Involves a certain tube)
Anchors the fallopian tube
What is the general function of the mesovarium?
Supports the ovaries
The suspensory ligaments attach what set of internal reproductive structures to what wall?
Attach the ovaries to the lateral pelvic wall
The ovarian ligaments anchor what set of internal reproductive structures to what other internal reproductive structure, and how so directionally?
Anchor the ovaries to the uterus medially
Inside the ovaries, the female gametes or eggs, begin their development in what structures?
Follicles
The growing follicles produce what specific group of hormones?
Estrogens
When a developing egg reaches the appropriate stage of maturity, what happens to it?
It is ejected from the ovary
When mature egg is ejected from the ovary, what is this event called?
Ovulation
After ovulation or the ejection of a mature egg from a follicle, what happens to the ruptured follicle? (Hint: what is it converted to? )
The ruptured follicle is converted to a corpus luteum
What is a corpus luteum? (Hint: what type of structure?)
An endocrine structure
The corpus luteum secretes what 2 types of hormones?
1. Progesterones
2. Some estrogens
Are the ovaries connected to the fallopian tubes?
No
An ovulated egg is also called what?
A secondary oocyte
An ovulated egg or secondary oocyte enters what cavity?
The pelvic cavity
An ovulated egg or secondary oocyte enters the pelvic cavity, and how is it drawn into the fallopian tubes?
The waving fimbriae of the fallopian tubes create fluid currents that draw the egg into the lumen of the tubes
Once inside the fallopian tubes, an ovulated egg or secondary oocyte makes its way to what internal reproductive structure?
Makes its way from the fallopian tubes to the uterus
The movement of an ovulated egg or secondary oocyte from the fallopian tubes to the uterus occurs how?
The cilia of the fallopian tubes propel the ovulated egg
What is the usual and most desirable site of fertilization?
The uterine tube
How long is an ovulated egg or secondary oocyte viable for after it is ejected from the ovaries?
24 hours
The journey of an egg from the ovary to the uterus is approximately how long? (Hint: Give range of days)
3-4 days
If the most desirable site of fertilization is the fallopian tubes, then how does the sperm reach the ovulated egg or secondary oocyte? (Hint: The sperm must bypass what 2 internal reproductive structures?)
Must swim through the vagina and uterus and into the fallopian tubes
The journey of a sperm to reach an ovulated egg/secondary oocyte is arduous because of what? (Hint: Think of current)
It must swim against the downward current of ciliary action

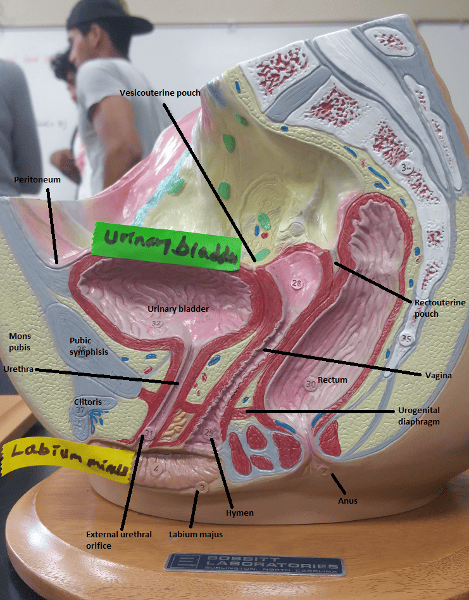
Identify the blanks.

Identify the blanks.
Identify the blanks.
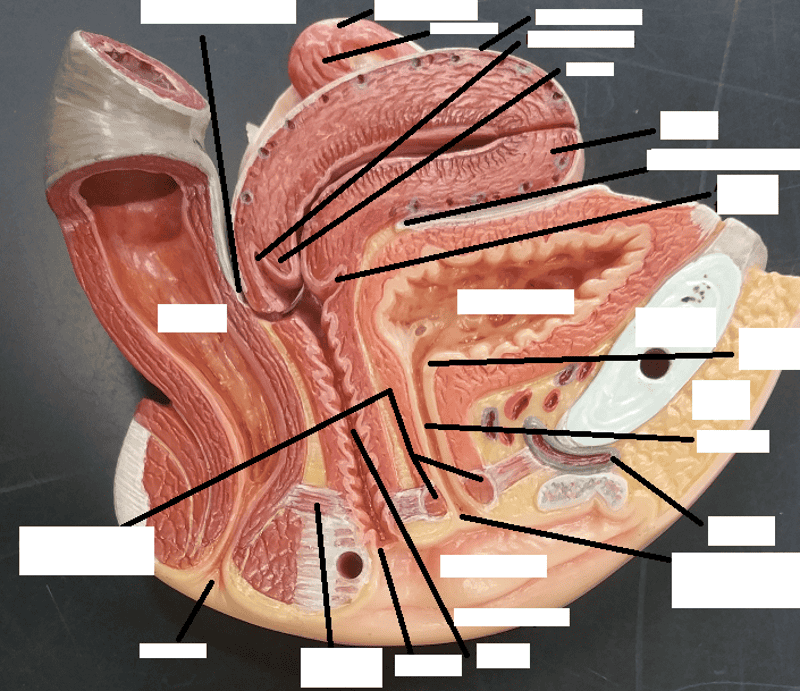
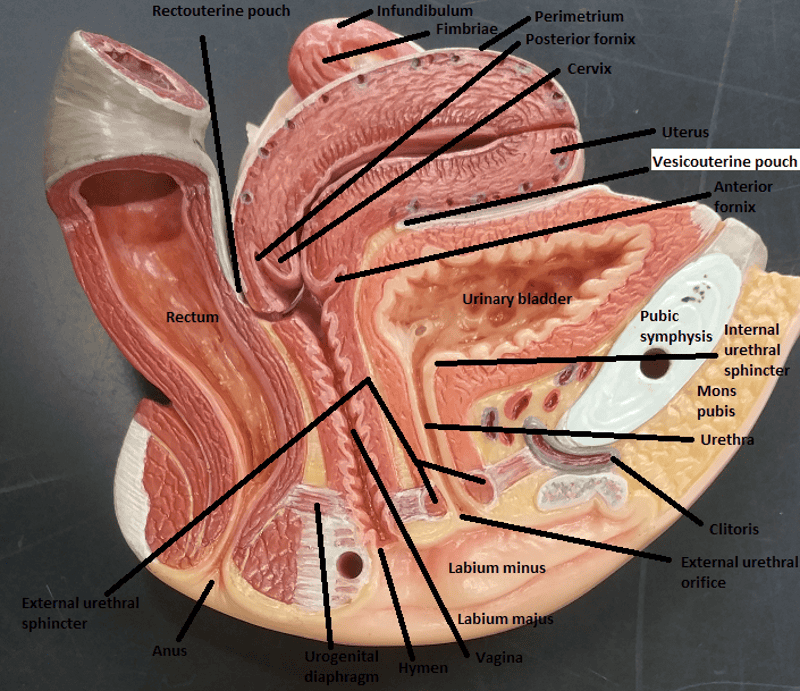
Identify the blanks.
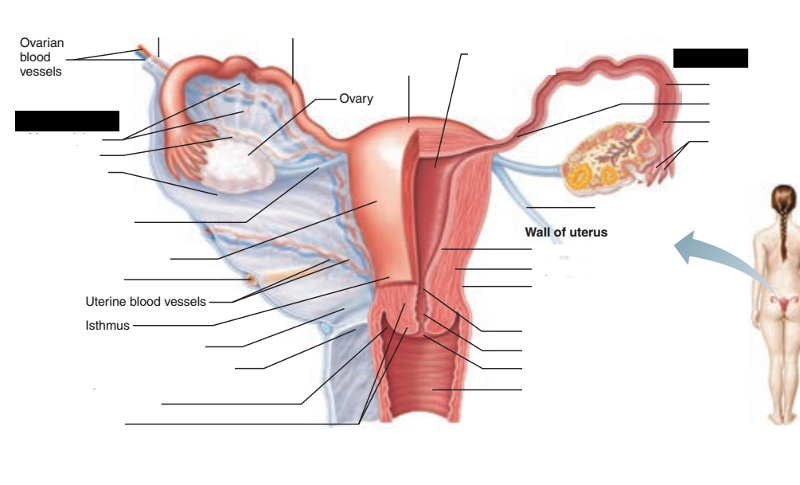
Identify the blanks.