Which group of muscles elevates the first two ribs and flexes and rotates the neck?
the splenius
the iliocostalis
the scalenes
the spinalis
the scalenes
Muscle spasms of the back often are due to the erector spinae contraction.True/False
true
The muscle that divides the ventral body cavity into the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities is the __________.
internal oblique
diaphragm
psoas majo
rtransversus abdominis
diaphragm
Which of the following muscles does the phrenic nerve innervate?
the internal intercostals
the diaphragm
the sternocleidomastoid muscles
the external intercostals
diaphragm
The supraspinatus is named for its location on the posterior aspect of the scapula above the spine. What is its action?
to initiate abduction of the arm, to stabilize the shoulder joint and to help prevent downward dislocation of the humerus
to help hold the head of the humerus in the glenoid cavity and rotate the humerus laterally
to flex and adduct the humerus and to act as a synergist of the pectoralis major
to extend and medially rotate the humerus and to act as a synergist of the latissimus dorsi
to initiate abduction of the arm, to stabilize the shoulder joint and to help prevent downward dislocation of the humerus
Which muscle(s) is (are) contracted to exhale forcibly?
diaphragm alone
external intercostals and diaphragm
internal intercostals and rectus abdominus
rectus abdominis and diaphragm
internal intercostals and rectus abdominus
The diaphragm flattens and moves inferiorly during inspiration.True/False
True
Which of the following is not a muscle primarily involved in the breathing process?
external intercostal
diaphragm
internal intercostal
latissimus dorsi
latissimus dorsi
The ________ runs deep to the internal oblique.
latissimus dorsi
transversus abdominis
external oblique
rectus abdominis
transverse abdominis
The abnormal protrusion of the small intestine through a weak point in the muscle of the abdominal wall is called a ________.
hernia
pulled muscle
hyperextension
sprain
hernia
Which of the following muscles fixes and depresses the ribs and stabilizes the pelvis during walking?
rectus abdominis
transversus abdominis
external oblique
internal oblique
rectus abdominis
Label
label
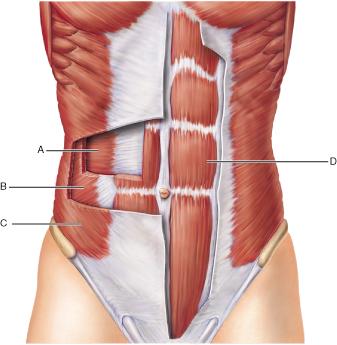
Which of these muscles is visible in the figure but NOT indicated by
a letter?
external oblique
transversus abdominis
serratus anterior
internal oblique
serratus anterior
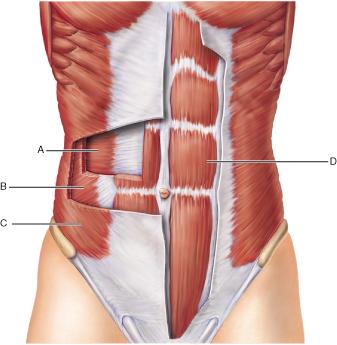
Which muscle originates on the pubic crest and symphysis and inserts on the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of ribs V through VII?
A
B
C
D
D
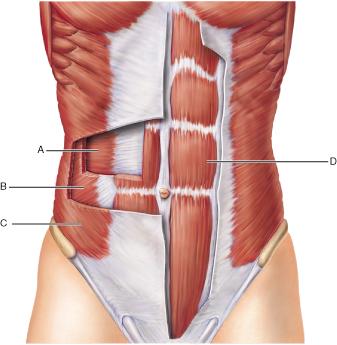
Identify the action of the muscle at A.
flex the spine
compress the abdomen
twist the trunk
extend the spine
compress the abdomen
Donna was rushing to class and slipped on a patch of ice and fell backward. An x-ray revealed a broken coccyx. All the associated muscles were bruised. Which muscles were they?
Perineal muscle, levator ani, and coccygeus
Coccygeus and gluteus maximusIschiocavernosus, coccygeus, and gluteus maximus
Gluteus maximus, coccygeus, and levator ani
Levator ani and coccygeus
Levator ani and coccygeus
A young pregnant woman went to a childbirth class and the instructor informed them about strengthening the muscles of the pelvic floor. What are these muscles, and why should she strengthen them?
Coccygeus and gluteus maximus; strengthening these muscles helps in correctly positioning and orienting the child prior to birth.
Perineal muscle, levator ani, and coccygeus; strengthening these muscles helps in the delivery of the child by resisting downward forces when "pushing."
Ischiocavernosus, coccygeus, and gluteus maximus; strengthening these muscles helps in correctly positioning and orienting the child prior to birth.
Gluteus maximus, coccygeus, and levator ani; strengthening these muscles helps in correctly positioning and orienting the child prior to birth.
Levator ani and coccygeus; strengthening these muscles helps in the delivery of the child by resisting downward forces when "pushing."
Levator ani and coccygeus; strengthening these muscles helps in the delivery of the child by resisting downward forces when "pushing."
A nurse can facilitate respiratory functioning by encouraging deep breathing exercises such as diaphragmatic breathing. What is diaphragmatic breathing?
It is the contraction of the external intercostal muscles to lift the ribcage, aiding inspiration.
It is the alternating contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm, causing a decrease in pressure in the abdominopelvic cavity and facilitating blood flow to the heart.
It is the alternating contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm, causing an increase in pressure in the abdominopelvic cavity and facilitating blood flow to the heart.
It is the alternating contraction of the external and internal intercostals muscles to aid inspiration and expiration.
It is the contraction of the internal intercostals muscles to depress the ribcage, aiding expiration.
It is the alternating contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm, causing an increase in pressure in the abdominopelvic cavity and facilitating blood flow to the heart.
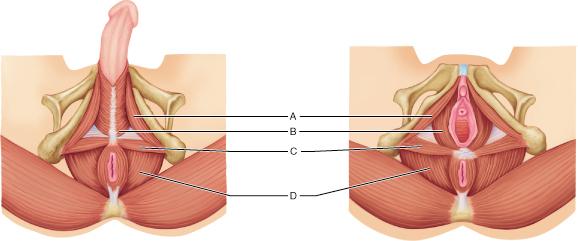
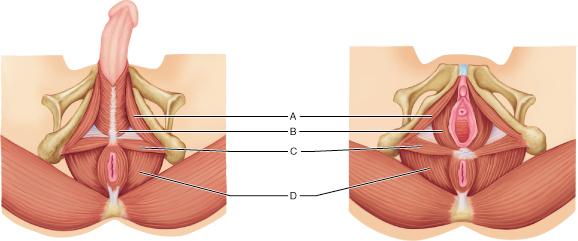
Identify the levator ani muscle.
A
B
C
D
D
What is the name and origin of the muscle at A?
ischiocavernosus; ischial tuberosities
bulbospongiosus; central tendon of perineum
coccygeus; spine of the ischium
superficial transverse perineal; ischial tuberosity
ischiocavernosus; ischial tuberosities
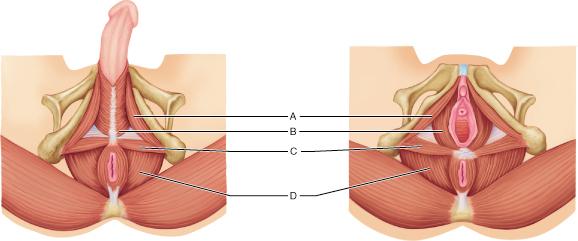
Which muscle is innervated by the S3 nerve, S4 nerve, and the inferior rectal nerve (a branch of the pudendal nerve)?
A
B
C
D
D
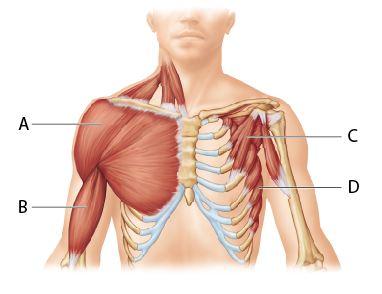
Which muscle is known as the “boxer's muscle” for its ability to move
the arm horizontally, as in throwing a punch?
A B C D
D
The ________ is known as the "boxer's muscle."
rectus abdominis
flexor digitorum longus
serratus anterior
biceps brachii
serratus anterior
Which muscle is a prime mover of arm adduction?
A B C D
A
Which of the following is NOT a rotator cuff muscle?
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
teres major
subscapularis
tres major
Which of the following describes the suprahyoid muscles?
They depress the larynx and hyoid bone if the mandible is fixed.
They are often called strap muscles.
They are a group of muscles that lie superior to the hyoid bone and help form the floor of the oral cavity.
They move the pharynx superiorly during swallowing.
They are a group of muscles that lie superior to the hyoid bone and help form the floor of the oral cavity.
LABEL
LABEL
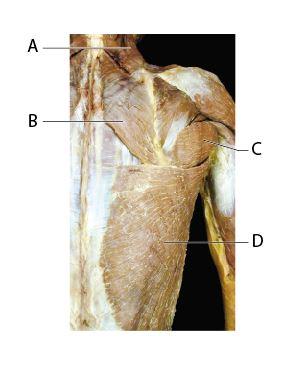
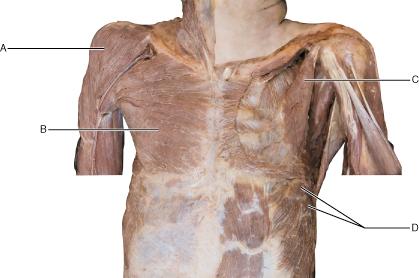
Which of the following muscles is shown on this image but is NOT indicated with a letter?
deltoid
teres major
latissimus dorsi
levator scapulae
deltiod
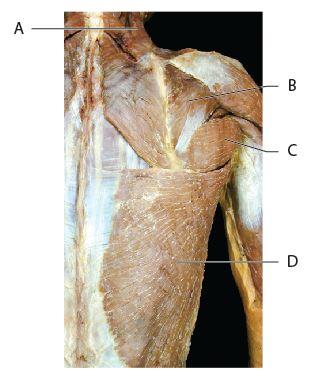
Which of the following letters represents the infraspinatus
muscle?
A B C D
B
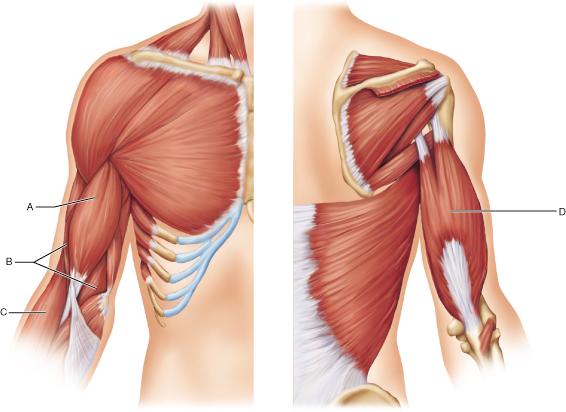
Which letter represents the biceps brachii muscle?
A
B
C
D
A
Which of the muscles indicated by letters has action at only one
joint?
A B D
B: brachiallis
The broadest muscle of the back is the latissimus dorsi.True/False
True
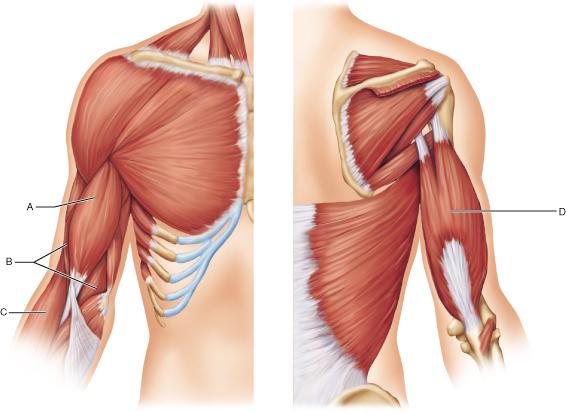
Which muscle is an antagonist to the biceps brachii muscle?
A
B
C
D
D: triceps brachii
Which of the following muscles is not a rotator cuff muscle?
subscapularis
levator scapulae
supraspinatus
teres minor
levator scapulae
A reduction in the lateral angle of the glenohumeral joint in relation to the anatomical position would be called __________.
flexion
abduction
adduction
extension
adduction
Movement of the shoulder laterally away from the body is called __________.
extension
adduction
abduction
flexion
abduction
The transversus abdominus muscle is innervated by the __________.
left scapular nerve
thoracic nerve
intercostals nerve
singuinal nerve
intercostals nerve
Which joint is considered the most flexible joint in the body?
the wrist joint
the elbow joint
the hip joint
the shoulder joint
the shoulder joint
Muscles of the shoulder can be divided into groups based on __________.
size
location (superior and inferior)
location (anterior and posterior)
distribution and functional relationships
distribution and functional relationships
Which of the following groups of muscles are not muscles of the shoulder?
muscles that stabilize and cross the glenohumeral joint
muscles that act on the pectoral girdle
the anterior flexor muscles
the rotator cuff muscles
the anterior flexor muscles
The external intercostals elevate the rib cage during __________
.expiration
neither inspiration nor expiration
both expiration and inspiration
inspiration
inspiration
The gluteus medius muscle is innervated by the __________.
inferior coxial nerve
inferior gluteal nerve
superior gluteal nerve
superior coxial nerve
superior gluteal nerve
The origins of the rectus abdominus muscle are on the __________.
ischial bone
pubic bone
sacral bone
ileum bone
pubic bone
The origins of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle are the __________.
medial condyle and posterior surface of the femur
lateral condyle and posterior surface of the femur
patellar surface and posterior surface of the femur
patellar surface and anterior surface of the femur
lateral condyle and posterior surface of the femur
The gastrocnemius muscle is innervated by the __________.
fibular nerve
tibial nerve
ulnar nerve
plantar nerve
tibial nerve
The two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle converge to insert onto __________.
the posterior surface of the tibia
the calcaneus
digits two through five
the middle phalanx of digit one
calcaneus
The origin of the external obliques includes ribs __________.
five through twelve
eight through twelve
seven through twelve
six through twelve
five through twelve
The majority of the fibers of the gluteus maximus insert onto the __________.
superior border of the os coxae
iliotibial tract
gluteal tuberosity
inferior border of the os coxae
iliotibial tract
The gluteus maximus is the most powerful muscle during __________.
medial rotation
flexion
lateral rotation
extension
extension
The actions of the internal intercostals are most important during __________.
forced inspiration
normal inspiration
normal expiration
forced expiration
forced expiration
The actions of the internal obliques include __________.
compression of the abdomen to assist in forced inspiration
compression of the abdomen to assist in forced expiration
compression of the rib cage to assist in forced expiration
compression of the rib cage to assist in forced inspiration
compression of the abdomen to assist in forced expiration
The insertion of the pectineus muscle is __________ and on the __________.
posterior; femur
posterior; pubis
anterior; pubis
anterior; femur
posterior; femur
The pectineus muscle __________ the thigh and is innervated by the __________ nerve.
abducts and extends; femoral
adducts and flexes; fibular
abducts and extends; fibular
adducts and flexes; femoral
adducts and flexes; femoral
The rhomboid minor muscle sits __________.
inferior to the rhomboid major
superficial to the rhomboid major
superior to the rhomboid major
deep to the rhomboid major
superior to the rhomboid major
The deltoid muscle fibers are separated into __________.
superficial and deep
anterior, middle, and posterior
superior, middle, and inferior
lateral, medial, and proximal
anterior, middle, and posterior
The middle fibers of the deltoid muscle __________.
abduct the arm
adduct the arm
laterally rotate the arm
medially rotate the arm
abduct the arm
The latissimus dorsi inserts __________.
on the lesser tubercle of the humerus
on the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
on the intertubercular groove of the humerus
on the greater tubercle of the humerus
on the intertubercular groove of the humerus
One of the actions of the latissimus dorsi muscle is to __________.
adduct the arm
flex the arm
lateral rotation of the arm
abduct the arm
adduct the arm
All fibers of the triceps brachii are innervated by the __________.
axillary nerve
radial nerve
ulnar nerve
humeral nerve
radial nerve
The infraspinatus inserts on the ____________ of the humerus.
coranoid process of the scapula
acromial process of the scapula
greater tubercle of the humerus
lesser tubercle of the humerus
greater tubercle of the humerus
The infraspinatus muscle is included in the __________ muscles.
rotator cuff
lateral rotator
respiratory muscles of the shoulder
medial rotator
rotator cuff