4. Visual inspection of the appearance of the liver and gallbladder
during surgery is associated with which of the following?
A.
histology
B. physiology
C. gross anatomy
D.
radiology
E. cytology
C
Microscopic examination of a frozen tissue specimen is an application
of which of the following disciplines?
A. histology
B.
physiology
C. gross anatomy
D. radiology
E.
regional anatomy
A
85. The wall of the abdominopelvic cavity is lined by a serous
membrane called the
A. visceral pleural membrane.
B.
parietal peritoneum.
C. visceral mediastinal membrane.
D.
visceral peritoneum.
E. epicardium.
B
The visceral pleura is
A.a double-layered serous membrane that
anchors some of the abdominal organs to the body wall.
B. the
serous membrane that covers the lungs.
C. the serous membrane
that lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
D. space located
between the visceral and parietal pleura.
E. the membrane that
lines the pericardial sac.
B
The parietal peritoneum is
A.a double-layered serous membrane
that anchors some of the abdominal organs to the body wall.
B.
the serous membrane that covers the lungs.
C. the serous
membrane that lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
D. space
located between the visceral and parietal pleura.
E. the
membrane that lines the pericardial sac.
C
The pleural cavity is the
A.a double-layered serous membrane
that anchors some of the abdominal organs to the body wall.
B.
the serous membrane that covers the lungs.
C. the serous
membrane that lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
D. space
located between the visceral and parietal pleura.
E. the
membrane that lines the pericardial sac.
D
16. Organize the following structural levels of the human body from
simplest to most complex.
(1) cell
(2) tissue
(3)
chemical
(4) organ system
(5) organ
A. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B. 2, 3, 1, 4, 5
C. 3, 1, 2, 5, 4
D. 4, 2, 3, 1, 5
E. 3, 1, 2, 4, 5
C
Which level is the basic unit of life?
(1) cell
(2)
tissue
(3) chemical
(4) organ system
(5) organ
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
A
13. Which of the following systems carries necessary compounds like
oxygen and nutrients throughout the body?
A. nervous
B.
cardiovascular
C. urinary
D. lymphatic
E. respiratory
B
Which organ system is the location of blood cell production?
A. cardiovascular
B. skeletal
C. digestive
D.
nervous
E. endocrine
B
Which body system would be affected by degeneration of cartilage in
joints?
A. muscular
B. nervous
C. cardiovascular
D. skeletal
E. lymphatic
D
19. The gallbladder, liver, and stomach are all part of the
A.
endocrine system.
B. cardiovascular system.
C. skeletal
system.
D. respiratory system.
E. digestive system.
E
What system removes nitrogenous waste products from the blood and
regulates blood pH, ion balance, and water balance?
A.
respiratory
B. lymphatic
C. cardiovascular
D.
immune
E. urinary
E
An investigator who conducts an experiment to determine how changes
in pH affect the function of enzymes on digestion is most likely to be
a(n)
A. neurologist.
B. anatomist.
C. engineer.
D. physiologist.
E. histologist.
D
10. The study of tissues is
A. cytology.
B. histology.
C. molecular biology.
D. microbiology.
E. surface anatomy.
B
The study of the structural features and functions of the cell is
A. cytology.
B. histology.
C. molecular biology.
D. microbiology.
E. surface anatomy.
A
Which of the following is consistent with homeostasis?
A. As
body temperature rises, sweating occurs to cool the body.
B.
When a person drinks large quantities of water, urine output decreases
to raise blood volume.
C. Elevated blood glucose levels cause
insulin secretion to decline.
D. Decreases in blood pressure
cause a corresponding decrease in heart rate.
E. As blood
pressure falls, blood flow to the heart decreases.
A
What are examples of homeostatic mechanisms?
A. Blood pH
B. Temperature
C. Blood pressure
D.
Blood sugar
E. All of the above
E
Which of the following is most consistent with homeostasis?
A.
As blood pressure falls, blood flow to cardiac (heart) muscle
decreases.
B. As the mean blood pressure gradually increases in
aging people, the blood vessel walls become thinner.
C. Men
working in a hot environment drink large quantities of water, and
their urine volume increases.
D. As body temperature decreases,
blood vessels in the periphery dilate.
E. Elevated blood
glucose levels cause insulin secretion (insulin causes cells to take
up glucose) to increase.
E
The anatomical term that means "away from the midline of the
body" is
A. medial.
B. proximal.
C. distal.
D. lateral.
E. superficial.
D
46. The thumb is ___ to the fifth digit (little finger).
A.
distal
B. lateral
C. medial
D. proximal
E. superficial
B
Medial means
A. toward the middle or midline of the body.
B. away from the surface.
C. closer to the head.
D. closer than another structure to the point of attachment to the
trunk.
E. toward the back of the body.
A
55. Proximal means
A. toward the middle or midline of the
body.
B. away from the surface.
C. closer to the head.
D. closer than another structure to the point of attachment to
the trunk.
E. toward the back of the body.
D
49. A term that means "toward the attached end of a limb"
is
A. medial.
B. lateral.
C. superficial.
D. distal.
E. proximal.
E
The shoulder is _____ to the elbow.
A. lateral
B.
dorsal
C. distal
D. ventral
E. proximal
E
43. Which of the following sets of directional terms are most
appropriately referred to as opposites?
A. distal and proximal
B. medial and inferior
C. superior and ventral
D.
anterior and deep
E. lateral and superior
A
The study of the microscopic structure of the tissues and organs is
called
A) cytology.
B) astrology.
C) gross
anatomy.
D) histology.
D
A bullet enters the left lung and collapses it. Which cavity has been
entered?
A. mediastinal
B. pericardial
C. pleural
D. vertebral
E. cranial
C
The membrane on the surface of a lung is called the
A) visceral
pleura.
B) parietal pleura.
C) visceral pericardium.
D)
parietal pericardium.
A
Which of the following is NOT an example of a homeostatic
mechanism?
A) Shivering when the body temperature falls below
normal levels
B) Using blankets to cover up when the body feels
cold
C) Secreting insulin to decrease blood sugar concentration
after a meal or whenever the blood sugar level is high
D)
Increasing heart rate and contraction force when blood pressure is low
B
3. Which of the following activities would represent a physiological
study?
A. observing the structure of the interior of the
heart
B. studying a model of the kidney
C. examining the
surface of a bone
D. viewing muscle tissue through a microscope
E.
determining normal blood sugar levels for 20-year-old students
E
83. The suffix "-itis" means inflammation. Which of the
following terms means inflammation of the membrane lining the body
cavity that contains the liver?
A. pericarditis
B.
peritonitis
C. pleurisy
D. colitis
E. hepatitis
B
Tissues are formed by a group of ________ that perform similar
functions.
A) cells
B) tissues
C) organs
D) atoms
A
Which of the following lists is in the order of increasing levels of
complexity?
A) organelles - tissues - cells - organ systems -
organs
B) cells - macromolecules - tissues - body -
organs
C) organelles - cells - tissues - organs - organ
systems
D) tissues - cells - organs - organelles - organ systems
C
To understand the structure of complex body systems we start from the
structure of the atom and progress to the structure of the organ
systems. This concept is called
A) levels of
deterioration.
B) structural diversity.
C) the hierarchy of
species.
D) levels of organization.
D
The ankle is _______ to the knee.
A) deep
B)
peripheral
C) superior
D) distal
D
The carpus is distal to the
A) manus.
B) tarsus.
C)
digits.
D) acromion.
C
50. Which of the following is most inferior in location?
A. pelvic cavity
B. mediastinum
C. diaphragm
D. pleural cavity
E. pericardial cavity
A
80. The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity by the
A. sternum.
B. diaphragm.
C. mediastinum.
D. mesentery.
E. pericardial cavity.
B
82. The cavity of the body immediately inferior to the diaphragm is
the _____ cavity.
A. pleural
B. thoracic
C.
inguinal
D. pelvic
E. abdominal
E
85. The wall of the abdominopelvic cavity is lined by a serous
membrane called the
A. visceral pleural
membrane.
B. parietal peritoneum.
C. visceral mediastinal
membrane.
D. visceral peritoneum.
E. epicardium.
B
90. The parietal pericardium is
A. a double-layered
serous membrane that anchors some of the abdominal organs to the body
wall.
B. the serous membrane that covers the lungs.
C. the
serous membrane that lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
D.
space located between the visceral and parietal pleura.
E. the
membrane that lines the pericardial sac.
E
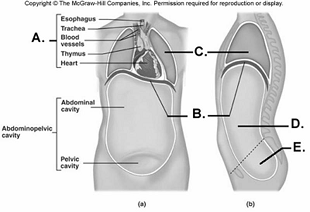
97. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other
structures. What does "A" represent?
A.
diaphragm
B. mediastinum
C. pelvic cavity
D. thoracic
cavity
E. abdominal cavity
B
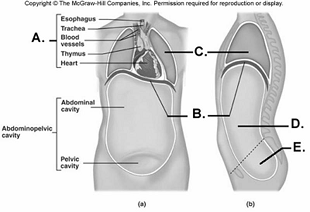
98. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other
structures. What does "B" represent?
A.
diaphragm
B. mediastinum
C. pelvic cavity
D. thoracic
cavity
E. abdominal cavity
A
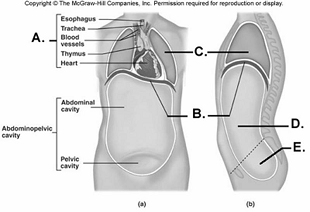
99. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other
structures. What does "C" represent?
A.
diaphragm
B. mediastinum
C. pelvic cavity
D. thoracic
cavity
E. abdominal cavity
D
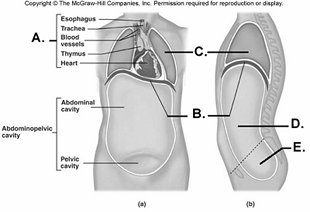
100. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other
structures. What does "D" represent?
A.
diaphragm
B. mediastinum
C. pelvic cavity
D. thoracic
cavity
E. abdominal cavity
E
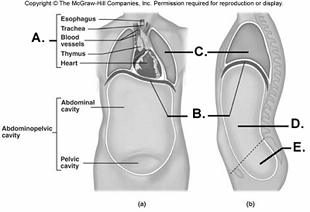
101. Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other
structures. What does "E" represent?
A.
diaphragm
B. mediastinum
C. pelvic cavity
D. thoracic
cavity
E. abdominal cavity
C
The cranial cavity is _______ to the thoracic cavity.
A)
inferior
B) anterior
C) peripheral
D) superior
D
The dorsal cavity includes which of the following smaller
cavities?
A) spinal and cranial
B) abdominal and
pelvic
C) abdominopelvic and thoracic
D) pelvic and mediastinum
A
Given these organ and cavity combinations:
1. heart and
pericardial cavity
2. lungs and pleural cavity
3. stomach
and peritoneal cavity
4. kidney and peritoneal cavity
Which
of the organs is correctly paired with a space that surrounds that
organ?
A) 1,2
B) 1,2,3
C) 1,2,4
D) 2,3,4
E) 1,2,3,4
B
The lungs are
A) part of the mediastinum.
B) surrounded by
the pericardial cavity.
C) found within the thoracic
cavity.
D) separated from each other by the diaphragm.
E)
surrounded by mucous membranes.
C
A term that means nearer the attached end of a limb is
A)
distal.
B) lateral.
C) medial.
D) proximal.
E) superficial.
D
The following events are part of a negative-feedback
mechanism.
1. Blood pressure increases.
2. Control center
compares actual blood pressure to the blood pressure set
point.
3.The heart beats faster.
4. Receptors detect a
decrease in blood pressure.
Choose the arrangement that lists the events in the order they
occur.
A) 1,2,3,4
B) 1,3,2,4
C) 3,1,4,2
D)
4,2,3,1
E) 4,3,2,1
D
The urinary system
A) regulates other organ systems
B)
removes waste products from the blood; maintains water balance
C)
regulates temperature; prevents water loss; provides
protection
D) removes foreign substances from the blood; combats
disease; maintains tissue fluid balance
E) produces movement;
maintains posture; produces body heat
B
The nervous system
A) regulates other organ systems
B)
removes waste products from the blood; maintains water balance
C)
regulates temperature; prevents water loss; provides
protection
D) removes foreign substances from the blood; combats
disease; maintains tissue fluid balance
E) produces movement;
maintains posture; produces body heat
A
The muscular system
A) regulates other organ systems
B)
removes waste products from the blood; maintains water balance
C)
regulates temperature; prevents water loss; provides
protection
D) removes foreign substances from the blood; combats
disease; maintains tissue fluid balance
E) produces movement;
maintains posture; produces body heat
E
The lymphatic system
A) regulates other organ systems
B)
removes waste products from the blood; maintains water balance
C)
regulates temperature; prevents water loss; provides
protection
D) removes foreign substances from the blood; combats
disease; maintains tissue fluid balance
E) produces movement;
maintains posture; produces body heat
D
The integumentary system
A) regulates other organ
systems
B) removes waste products from the blood; maintains water
balance
C) regulates temperature; prevents water loss; provides
protection
D) removes foreign substances from the blood; combats
disease; maintains tissue fluid balance
E) produces movement;
maintains posture; produces body heat
C
The endocrine system
A) regulates other organ systems.
B)
removes waste products from the blood; maintains water
balance.
C) regulates temperature; prevents water loss; provides
protection.
D) removes foreign substances from the blood; combats
disease; maintains tissue fluid balance.
E) produces movement;
maintains posture; produces body heat.
A
Physiology
A) deals with the processes or functions of living
things.
B) is the scientific discipline that investigates the
body's structures.
C) is concerned with organisms and does not
deal with different levels of organization, such as cells and
systems.
D) recognizes the static (as opposed to the dynamic)
nature of living things.
E) can be used to study the human body
without considering anatomy.
A
You are doing a handstand. Your head is __________ to your
neck.
A) superior
B) inferior
C) superficial
D)
medial
E) proximal
A
Given these serous membranes: 1. parietal pericardium 2. visceral
pericardium 3. parietal peritoneum 4. visceral peritoneum 5. parietal
pleura 6. visceral pleura
A man had a knife wound that penetrated
the abdomen, passed through the stomach, and hit the diaphragm, but
did not pass all the way through. Arrange the serous membranes in the
correct order as the knife passed through them.
A)
1,2,4,3,5
B) 2,3,4,4,3,2
C) 3,4,4,3
D)
4,3,3,4,5
E) 5,6,6,4
C
Given these directional terms: 1. caudal 2. cephalic 3. distal 4.
inferior 5. proximal Which of these directional terms correctly
describes the relationship of the ankle to the knee?
A)
1,3
B) 1,3,4
C) 2,3,4
D) 3,4
E) 4,5
D
The nose is __________ and __________ to the ears.
A) anterior,
proximal
B) superior, lateral
C) inferior, posterior
D)
anterior, medial
E) superficial, medial
D
The elbow is __________ to the wrist.
A) distal
B)
inferior
C) lateral
D) medial
E) proximal
E
A term that means "away from the midline" is:
A)
distal
B) lateral
C) medial
D) proximal
E) superior
B
Given these terms related to negative(--)feedback: 1. control center
2. effector 3. receptor 4. response 5. stimulus Arrange them in the
correct order as they operate to maintain homeostasis.
A)
1,2,3,4,5
B) 2,3,5,1,4
C) 3,2,1,5,4
D)
4,5,3,2,1
E) 5,3,1,2,4
E
The basic living unit of all plants and animals is the
A)
cell.
B) chemical.
C) organ.
D) organelle.
E) tissue.
A
Ultrasound, X-rays, CT, and MRI are all examples of
A) anatomic
imaging.
B) surface anatomy.
C) regional anatomy.
D)
gross anatomy.
E) cytology.
A
_____________ investigates the body's structure, whereas __________
investigates the processes or functions of living things.
A)
Physiology, cytology
B) Physiology, anatomy
C) Anatomy,
histology
D) Histology, cytology
E) Anatomy, physiology
E
The carpus is distal to the
A) manus.
B) tarsus.
C)
digits.
D) acromion.
D
Examples of serous membranes include
A) pleura,
B)
pericardium.
C) peritoneum.
D) all of the above.
D
The urinary bladder is in the ________ region.
A)
inguinal
B) epigastric
C) umbilical
D) hypogastric
D
The thoracic cavity lies where in relationship to the abdominopelvic
cavity?
A) dorsal (posterior)
B) ventral (anterior)
C)
superior
D) inferior
C
Which of the following organs is located in the abdominopelvic
cavity?
A) heart.
B) trachea.
C) thymus gland.
D)
None of the above.
D
A parietal membrane _______, whereas a visceral membrane
_______.
A) covers organs; lines cavities
B) lines cavities;
covers organs
C) is thick; is thin
D) secretes mucus;
secretes a serous fluid
B
B
The cranial cavity is _______ to the thoracic cavity.
A)
inferior
B) anterior
C) peripheral
D) superior
D
5. Which of the following best describes a proton?
A. one
negative charge, no mass, found in orbitals
B. no charge, mass
of one, found in nucleus
C. one positive charge, mass of one,
found in nucleus
D. subatomic particle with no electric charge
E. None of these choices is correct.
C
6. The mass number of an atom is the number of
A. protons in
the atom.
B. neutrons in the atom.
C. protons plus electrons
in the atom.
D. electrons plus neutrons in the atom.
E.
neutrons plus protons in the atom.
E
7. An atom has an atomic number of 19 and a mass number of 39. This
atom will have
A. 19 neutrons.
B. 20 neutrons.
C. 39
neutrons.
D. 58 neutrons.
E. 20 electrons.
B
8. An atom of chlorine has 17 protons and 18 neutrons. Which of the
following statements is true?
A. Chlorine atoms have 18
electrons.
B. Chlorine has a mass number of 35.
C.
Chlorine has an atomic number of 18.
D. Chlorine has 35
electrons.
E. Chlorine has an atomic number of 35.
B
9. Isotopes of the same element have
A. the same number of
neutrons but different numbers of protons.
B. different numbers
of protons and electrons.
C. the same mass number.
D. the
same atomic number but differ in their mass numbers.
E. no mass number.
D
12. Electrons
A. comprise the majority of the mass of an atom.
B. are located in the nucleus of an atom.
C. have a
positive charge of one.
D. are the subatomic particles most
involved in bonding behavior of atoms.
E. do not participate in
the bonding of atoms.
D
14. In ionic bonding,
A. only non-polar molecules are involved.
B. a "sea of electrons" forms.
C. electrons are
transferred from one atom to another.
D. two hydrogen atoms
share one pair of electrons.
E. the charge of the ion does not
play a role in the bond.
C
15. Covalent bonds form when
A. atomic nuclei fuse.
B.
molecules become ionized.
C. neutrons are transferred from one
atom to another.
D. protons are lost from atoms.
E.
electrons are shared between two atoms.
E
16. Molecules that form when electrons are shared unequally between
atoms are called
A. salt molecules.
B. polar molecules.
C. nonpolar molecules.
D. lopsided molecules.
E.
None of these choices are correct.
B
44. The hydrogen and oxygen atoms in a molecule of water are held
together by
A. ionic bonds.
B. peptide bonds.
C.
savings bonds.
D. polar covalent
bonds.
E. nonpolar bonds.
D
45. A group of water molecules are held together by
A. salt.
B. hydrogen bonds.
C. ionic bonds.
D. double
covalent bonds.
E. polar covalent bonds.
B
12C and 14C are
A) atoms of different elements.
B)
isotopes.
C) atoms with different atomic numbers.
D) atoms
with different numbers of protons.
E) compounds.
B
Electrons in the atom are
A) moving particles in the orbits
surrounding the nucleus.
B) unwanted particles.
C) heavy
particles residing in the nucleus.
D) subatomic particles that
have positive charges.
A
When different forms for the same atom exist due to the difference in
the number of neutrons, they are known as
A) atoms.
B)
isotopes.
C) neutrons.
D) molecules.
B
Which statement among the following is true?
A) Electrons are
largely responsible for the weight of the atom.
B) Protons could
easily move from one atom to another for the formation of
molecules.
C) Electrons are most likely to be found in an
electron cloud.
D) Neutrons are another name for protons.
C
The capability of any atom (other than inert elements) to react or to
form any molecule depends on the
A) number of outermost
electrons.
B) number of protons.
C) number of
neutrons.
D) total number of protons and neutrons.
A
An element has 7 electrons, 7 protons, and 7 neutrons, what will be
the atomic weight of that element?
A) 7
B) 14
C)
21
D) 0
B
Atomic number of an element is determined by the
A) number of
neutrons.
B) position of electrons.
C) number of
protons.
D) total number of electrons and protons.
C
A covalent bond is characterized by
A) sharing electrons by the
atoms.
B) sharing electrons by one atom and gaining electrons by
the other.
C) the attractive force between oppositely charged
atoms.
D) involvement of many different forces.
A
When two atoms are held together because their valence electrons
orbit around both of them, they are united by a(n) ________
bond.
A) ionic
B) hydrogen
C) covalent
D) electron
C
When molecules are formed by sharing electrons equally, those
molecules are called
A) salt molecules.
B) polar
covalent.
C) non-polar covalent.
D) macromolecules.
C
An example of macromolecules in our body includes
A) nucleic
acids.
B) proteins.
C) carbohydrates and lipids.
D)
all of the above.
D
Which of the following statements about lipids is true?
A)
Lipids are insoluble in water.
B) Cholesterol and fats are
different varieties of lipids.
C) Fat molecules contain C, H,
and O, but the proportion of oxygen is much smaller than in
carbohydrates.
D) All of the above statements are true about lipids.
D
Which of the following would be classified as a lipid?
A)
cholesterol, a steroid
B) alanine, an amino acid
C) starch,
a polysaccharide
D) catalase, an enzyme
A
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) cholesterol - nucleic
acid
B) enzyme - protein
C) ribose - RNA
D)
triglycerol - fat
A
Energy stored in ATP is a form of _________ energy.
A)
mechanical
B) chemical
C) potential
D) heat
B
__________ is called the energy currency of cells.
A)
Phosphate
B) Sodium chloride
C) ATP
D) DNA
C
Atomic number of an element is determined by the
A) number of
neutrons.
B) position of electrons.
C) number of
protons.
D) total number of electrons and protons.
C
Neutrons are subatomic particles that are located
A) in the
nucleus and have a positive charge.
B) in the nucleus and have
no charge.
C) in the nucleus and have a negative charge.
D) around the nucleus and have a positive charge.
E) around the
nucleus and have a negative charge.
B
The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of
A)
electrons in each atom.
B) neutrons in each atom.
C)
protons in each atom.
D) protons plus electrons in each
atom.
E) neutrons plus electrons in each atom.
C
Which of the pairs below are equal to each other in an atom?
A)
neutrons and protons
B) protons and electrons
C) neutrons
and electrons
D) atomic number and mass number
E) mass
number and electrons
B
14N and 15N are
A) different elements.
B) atoms with
different atomic numbers.
C) isotopes of the same element.
D) identical except for different numbers of electrons.
E)
identical except for different numbers of protons.
C
The chemical behavior of an atom is determined largely by
A)
its number of protons.
B) its outermost electrons.
C) the
size of the electron cloud.
D) its mass.
E) its weight.
B
Chemical bonding occurs when the __________ are transferred or shared
between atoms.
A) outer protons
B) largest neutrons
C) outermost electrons
D) innermost electrons
E) outermost protons
C
Ionic bonding occurs when
A) a cation and an anion are
attracted to each other.
B) two cations are attracted to each
other.
C) two anions are attracted to each other.
D) two
atoms lose protons.
E) two atoms lose neutrons.
A
Most of the volume of an atom is occupied by the
A)
electrons.
B) neutrons.
C) protons.
D) protons and neutrons.
A
Which of the pairs below are equal to each other in an atom?
A)
neutrons and protons
B) protons and electrons
C) neutrons
and electrons
D) atomic number and mass number
E) mass
number and electrons
B
Given that manganese (Mn) has an atomic number of 25 and a mass
number of 55, an atom of manganese has
A) 25 neutrons.
B)
25 electrons.
C) 30 electrons.
D) 55 protons.
E) 80 neutrons.
B
Selenium (Se) has 34 protons and 46 neutrons in each atom, therefore
its atomic number is __________ and its mass number is
__________.
A) 12, 46
B) 34, 46
C) 12, 34
D)
34, 80
E) 46, 80
D
When _____ is broken down, the energy released from the reaction is
frequently used to synthesize other molecules.
A) NaCl.
B)
AMP.
C) ATP.
D) an enzyme.
E) a barrier.
C
In which of these reactions is energy released?
A) hydrolysis
of ATP to ADP
B) production of ATP from ADP
C)
photosynthesis
D) production of glucose from CO2 and H2O
E) all of these
A
Which of these is a monosaccharide?
A) sucrose
B)
starch
C) glycogen
D) glucose
E) cellulose
D
A synthesis reaction
A) may be a dehydration reaction.
B)
results in catabolism.
C) may be a hydrolysis reaction.
D)
breaks down a larger reactant into two or more smaller products.
E) all of these
A
A ____________ fatty acid has one double covalent bond between carbon
atoms.
A) cholesterol
B) monounsaturated
C)
phospholipid
D) polyunsaturated
E) saturated
B
The polysaccharide used for energy storage in the human body is
A) cellulose.
B) glycogen.
C) lactose.
D)
sucrose.
E) starch.
B
A polar covalent bond between two atoms occurs when
A) one atom
attracts shared electrons more strongly than another atom.
B)
atoms attract electrons equally.
C) an electron from one atom is
completely transferred to another atom.
D) the molecule becomes
ionized.
E) a hydrogen atom is shared between two different atoms.
A
3. Subatomic particles located around the nucleus of an atom are
A. protons.
B. electrons.
C. neutrons.
D.
neutrinos.
E. photons.
B
84. Fatty acid A has 10 double covalent bonds scattered throughout
its carbon chain while fatty acid B has only single covalent bonds
between the carbons in its chain.
A. Fatty acid A is saturated.
B. Fatty acid B is unsaturated.
C. Both fatty acids are
saturated.
D. Both fatty acids are unsaturated.
E. Fatty
acid B is saturated.
E
87. Phospholipids
A. contain subunits called amino acids.
B. are water-soluble.
C. are a type of steroid.
D.
are fat-soluble vitamins.
E. are found in cell membranes.
E
89. Eicosanoids
A. are structural proteins.
B. are
fat-soluble vitamins.
C. are components of the plasma membrane.
D. comprise the genetic material.
E. play a role in the
response of tissues to injuries.
E
90. An example of a fat-soluble vitamin is
A. vitamin C.
B. vitamin D.
C. vitamin B.
D. vitamin F.
E.
vitamin H.
B
91. Which of the following molecules is NOT made from cholesterol?
A. estrogen
B. bile salts
C. testosterone
D.
prostaglandins
E. progesterone
D
83. Triglycerides are composed of
A. monosaccharides.
B.
amino acids.
C. nucleotides.
D. glycerol and fatty
acids.
E. None of these choices are correct.
D
86. All of the following terms relate to lipids. Which does not
belong with the other four?
A. cholesterol
B. estrogen
C. steroid
D. triglyceride
E. bile salts
D
69. Large carbohydrates are formed from smaller units called
A.
phosphate groups.
B. monosaccharides.
C. amino acids.
D. steroids.
E. lipids.
B
71. Polysaccharides
A. are formed when sucrose and glucose
combine.
B. are the smallest carbohydrates.
C. contain
carbon, hydrogen, and phosphate atoms.
D. contain long chains of
monosaccharides.
E. are not found in plants.
D
72. Consider the following five terms. Which term does not belong
with the other four terms?
A. disaccharide
B. sucrose
C. lactose
D. maltose
E. glucose
E
73. Which of the following lists includes only monosaccharides that
are isomers of one another?
A. glycogen, glucose, sucrose
B. starch, glycogen, cellulose
C. glucose, fructose,
galactose
D. ribose, glycogen, glucose
E. deoxyribose,
glycogen, starch
C
76. Glycogen is the
A. storage carbohydrate in animals.
B. storage carbohydrate in plants.
C. nondigestible plant
polysaccharide.
D. major nutrient for most body cells.
E.
sugar found in RNA.
A
78. Starch is the
A. storage carbohydrate in animals.
B.
storage carbohydrate in plants.
C. nondigestible plant
polysaccharide.
D. major nutrient for most body cells.
E.
sugar found in RNA.
B
79. Cellulose is the
A. storage carbohydrate in animals.
B. storage carbohydrate in plants.
C. nondigestible plant
polysaccharide.
D. major nutrient for most body cells.
E.
sugar found in RNA.
C
121. ATP
A. is a nucleotide found in DNA.
B. stores
genetic information.
C. is a sugar found in transfer RNA.
D. serves as the energy currency of the cell.
E. can
store, but cannot release energy in the cell.
D
122. ATP
A. can be synthesized from ADP.
B. stores and
releases energy in the cell.
C. is associated with a reversible
reaction.
D. is associated with anabolism and catabolism.
E. All of these choices are correct.
E
123. Which of the following chemical reactions best represents the
synthesis of ATP?
A. ATP + H2O --> ADP + Pi + energy
B.
ADP + Pi + energy --> ATP + H2O
C. ADP + ADP + ADP --> ATP
+ energy
D. ATP + energy --> ADP + H2O
E. ATP + ADP
--> ATP
B
124. Which of the following chemical reactions best represents the
decomposition of ATP?
A. ATP + ADP --> ATP
B. ADP + ADP
+ ADP --> ATP
C. ATP + energy --> ADP + H2O
D. ADP +
Pi + energy --> ATP + H2O
E. ATP + H2O --> ADP + Pi + energy
E
18. Membrane proteins that extend into the lipid bilayer are called
A. peripheral proteins.
B. extrinsic proteins.
C.
integral proteins.
D. glycoproteins.
E. lipoproteins.
C
20. When a sperm cell comes into contact with an egg cell, there is a
change in the electrical charge across the plasma membrane and various
channel proteins close. These channels would be called
A.
open-gated channels.
B. voltage-gated channels.
C.
chemical-gated channels.
D. ligand-gated channels.
E.
nongated ion channels.
B
22. Molecules that serve as chemical signals to open or close gated
ion channels are
A. isotopes.
B. ligands.
C.
responders.
D. communicators.
E. membrane potentials.
B
29. What type of membrane proteins have an exposed site on the outer
cell surface that can attach to a ligand?
A. marker molecules
B. channel protein
C. receptor proteins
D. enzymes
E. carrier proteins
C
30. What type of membrane proteins are integral proteins that move
ions or molecules across plasma membrane?
A. marker molecules
B. channel protein
C. receptor proteins
D. enzymes
E. carrier proteins
E
31. What type of membrane proteins form a passageway through the
plasma membrane?
A. marker molecules
B. channel protein
C. receptor proteins
D. enzymes
E. carrier proteins
B
27. Membrane-bound receptors
A. are small, lipid soluble
molecules.
B. have their receptor sites on the outer surface of
the plasma membrane.
C. can interact with DNA in the nucleus.
D. do not exhibit specificity.
E. have no effect on the cell.
B
21. Channel proteins
A. are binding sites for other molecules.
B. utilize the G
protein complex to function.
C. are found only on endoplasmic
reticulum.
D. allow cells to recognize one another.
E.
provide a tunnel through which ions or molecules can enter or leave
the cell.
E
23. Cells that respond to ligands
A. possess receptor sites for
specific ligands.
B. generally produce the ligands.
C.
have lysosomes that destroy the ligands.
D. are using electrical
signals in cellular communication.
E. are not functional.
A
26. Communication between cells occurs when chemical messengers from
one cell bind to _____ on another cell.
A. channel proteins
B. receptor proteins
C. marker molecules
D. second
messengers
E. integrins
B
24. A symporter will transport _____ across the cell membrane.
A. two different ions or molecules in opposite directions
B. two different ions or molecules in the same direction
C. two of the same ions or molecules in the same direction
D. one specific ion or molecule
E. two of the same ions or
molecules in opposite directions
B
25. In _______, ions or molecules move in opposite directions.
A. symport
B. uniport
C. antiport
D. comport
E. ionport
C
28. Communication between cells is essential to coordinate the
activity of the trillions of cells that make up the human body. Which
of the following is (are) directly involved in carrying out
communication between cells?
A. lipid bilayer of the plasma
membrane
B. receptor proteins of the plasma membrane
C.
chemical signal molecules released by cells
D. mitochondria
E. both receptor proteins of the plasma membrane and chemical
signal molecules released by cells
E
32. What type of membrane proteins allow cells to identify one
another?
A. marker molecules
B. channel protein
C.
receptor proteins
D. enzymes
E. carrier proteins
A
33. What type of membrane proteins can catalyze chemical reactions on
the inner or outer surfaces of the plasma membrane?
A. marker
molecules
B. channel protein
C. receptor proteins
D.
enzymes
E. carrier proteins
D
34. What type of attachment proteins attach cells to extracellular
molecules?
A. ligands
B. integrins
C. adherins
D. cadherins
B
35. Which type of transport proteins use cell energy to move
molecules across the plasma membrane?
A. cadherins
B.
ligand-gated ion channels
C. ATP-powered pumps
D. leak-ion channels
C
38. Which of the following is CORRECTLY matched with its function?
A. channel proteins - are part of an intercellular communication
system
B. marker molecules - are primarily steroids
C.
receptor proteins - attach to ligand molecules
D. peripheral
proteins - penetrate the lipid bilayer from one surface to the other
E. nongated ion channels - are always closed
C
39. Which of the following is CORRECTLY matched with its function?
A. channel proteins - catalyze chemical reactions inside the
cell
B. cell identity molecules - are primarily steroids
C. receptor proteins – move specific ions or molecules using ATP
D. peripheral proteins - penetrate the lipid bilayer from one
surface to the other
E. carrier proteins – move bound ions or
molecules from one side of the membrane to the other
E
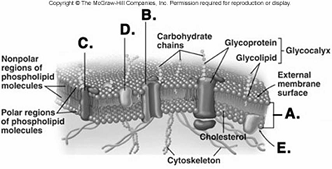
223. What structure does "A" represent on the diagram of
the plasma membrane?
A. membrane channel protein
B.
phospholipid bilayer
C. internal membrane surface
D.
peripheral protein
E. integral protein
B
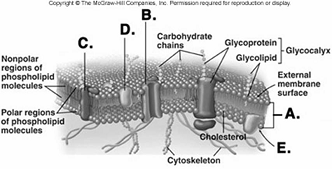
224. What structure does "B" represent on the diagram of
the plasma membrane?
A. membrane channel protein
B.
phospholipid bilayer
C. internal membrane surface
D.
peripheral protein
E. integral protein
A
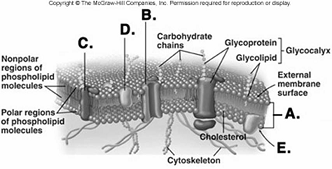
225. What structure does "C" represent on the diagram of
the plasma membrane?
A. membrane channel protein
B.
phospholipid bilayer
C. internal membrane surface
D.
peripheral protein
E. integral protein
C
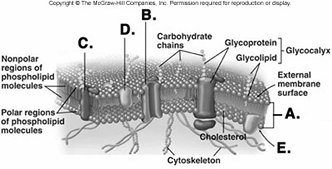
226. What structure does "D" represent on the diagram of
the plasma membrane?
A. membrane channel protein
B.
phospholipid bilayer
C. internal membrane surface
D.
peripheral protein
E. integral protein
D
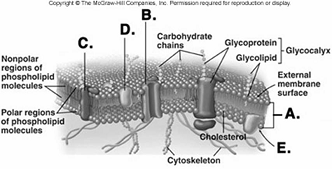
227. What structure does "E" represent on the diagram of
the plasma membrane?
A. membrane channel protein
B.
phospholipid bilayer
C. internal membrane surface
D.
peripheral protein
E. receptor protein
C
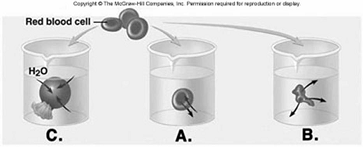
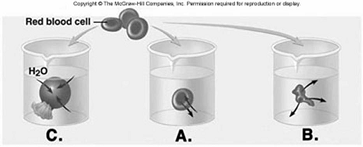
228. Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different
solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is solution
"A" relative to the RBC?
A. hypotonic solution
B. hypertonic solution
C. isotonic solution
D.
hemolyzed
E. crenated
C
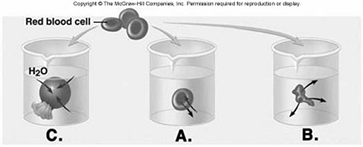
229. Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different
solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is solution
"B" relative to the RBC?
A. hypotonic solution
B. hypertonic solution
C. isotonic solution
D.
hemolyzed
E. crenated
B
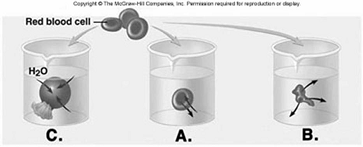
230. Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different
solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is solution
"C" relative to the RBC?
A. hypotonic solution
B. hypertonic solution
C. isotonic solution
D.
hemolyzed
E. crenated
A
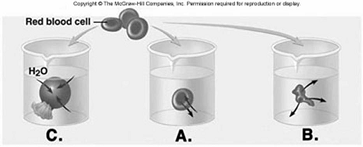
231. Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different
solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is the condition of
the RBC in solution "C"?
A. hypotonic solution
B. hypertonic solution
C. isotonic solution
D. lyzed
E. crenated
D
232. Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different
solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is the condition of
the RBC in solution "B"?
A. hypotonic solution
B. hypertonic solution
C. isotonic solution
D.
hemolyzed
E. crenated
E
60. A particular membrane transport process exhibits saturation, uses
carrier molecules, but does NOT require ATP. The process is probably
A. active transport.
B. facilitated diffusion.
C.
osmosis.
D. pinocytosis.
E. phagocytosis.
B
45. The aroma of cookies baking in the kitchen reaches you in the
living room. The distribution of this odor throughout the house is an
example of
A. active transport.
B. dialysis.
C.
osmosis.
D. filtration.
E. diffusion.
E
46. In the process of diffusion, net movement of substances is always
from a region
A. outside the cell to a region inside the cell.
B. inside the cell to a region outside the cell.
C. of
lower concentration to a region of higher concentration.
D. of
higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
E. None
of these choices are correct.
D
47. Which of the following will increase the rate of diffusion?
A. an increase in the viscosity of the solvent
B. an
increase in the temperature
C. an increase in the molecular
weight of the diffusing particles
D. an increase in the distance
the molecules have to travel
E. All of these choices are correct.
B
48. Salt was added to a beaker of distilled water (the water was not
stirred). A sample taken from the bottom of the beaker was found to be
20% salt. At the same time, a sample taken from the top of the beaker
was found to be 2% salt. After 24 hours
A. the difference in the
percentage of salt between the top and bottom samples would increase.
B. the percentage of salt in top and bottom samples would be
approximately equal.
C. the samples would still be 2% and 20%
respectively.
D. the salt would float to the top.
E. None
of these choices are correct.
B
50. Osmosis is the diffusion of _____ across a selectively permeable
membrane.
A. urea
B. oxygen
C. water
D. sodium
E. sugar
C
51. Solution A contains 5 grams of sugar per liter while solution B
contains 2 grams of sugar per liter. The solutions are separated by a
selectively permeable membrane. If the solvent in both solutions is
water, predict in which direction most of the water molecules will
move.
A. move by simple diffusion from solution A to solution B
B. move by osmosis from solution B to solution A
C. move
by active transport from solution B to solution A
D. move by
filtration from solution A to solution B
E. There will be no
movement of water.
B
53. A red blood cell that is placed in a hypertonic solution
A. loses water.
B. gains water.
C. floats.
D.
ruptures.
E. neither gains nor loses water.
A
54. If 0.9% NaCl (saline) solution is isotonic to a cell, then a 0.5%
saline solution
A. is hypertonic to the cell.
B. will
cause crenation of the cell.
C. is hypotonic to the cell.
D. will shrink the cell.
E. will not affect the cell.
C
55. If a 0.9% NaCl (saline) solution is isotonic to a cell, then a
solution of 3.5% NaCl would be
A. hypertonic to the cell.
B. isotonic to the cell.
C. hypotonic to the cell.
D. catatonic to the cell.
E. All of these choices are correct.
A
61. Which of the following are consistent with facilitated diffusion?
(1) movement is against a concentration gradient
(2)
movement is with a concentration gradient
(3) involves a carrier
molecule
(4) involves cotransport
(5) involves counter
transport
(6) exhibits competition and saturation
A. 1, 2,
4, 5, 6
B. 2, 3, 6
C. 2, 3, 5, 6
D. 1, 3, 4, 5, 6
E. 2, 3, 4, 6
B
62. Which of the following would increase the maximum rate of
facilitated diffusion?
A. increase the concentration gradient of
the transported molecule to the saturation point
B. decrease the
concentration gradient of the transported molecule
C. increase
the concentration of the competitive molecules
D. increased ATP
synthesis
E. None of these choices is correct.
E
63. Active transport
A. follows osmotic pressure gradients.
B. can move substances along their concentration gradient.
C. does not require metabolic energy (ATP).
D. involves
vesicle formation.
E. requires ATP.
E
64. Which of the following is NOT consistent with active transport?
A. movement is against a concentration gradient
B.
movement is with a concentration gradient
C. involves a carrier
D. exhibits competition and saturation
E. uses cell energy
B
65. Cyanide stops the production of ATP. Which of the following
processes would be affected?
A. simple diffusion
B.
osmosis
C. active transport
D. facilitated diffusion
E. filtration
C
66. The sodium-potassium pump located in the plasma membrane
A.
actively transports potassium into cells.
B. osmotically moves
sodium into cells.
C. actively transports water out of cells.
D. moves chlorine out of cells.
E. actively transports
sodium into cells.
A
67. Which of the following events occurs in the secondary active
transport of glucose?
A. Na+ ions and glucose are cotransported
by the same carrier molecule.
B. The Na+-K+ pump maintains a Na+
concentration gradient inside the cell.
C. Energy comes from
diffusion of Na+ down their concentration gradient.
D. Glucose
is moved against its concentration gradient into the cell.
E.
All of these choices are correct.
E
68. Certain cells in the liver ingest bacteria and debris from
damaged cells by a process called
A. pinocytosis.
B.
phagocytosis.
C. biocytosis.
D. calmly regulated
diffusion.
E. exocytosis.
B
69. Pinocytosis
A. is a form of exocytosis.
B. involves
ingestion of liquids rather than particles.
C. does not require
ATP.
D. forms vesicles only when large amounts of material are
being transported.
E. does not require the formation of vesicles.
B
70. Endocytosis
A. is movement of water through a selectively
permeable membrane.
B. is a process that requires a carrier
molecule but does not use cellular energy.
C. is the bulk uptake
of material through the plasma membrane by vesicle formation.
D.
moves material out of the cell.
E. ends cell functions.
C
71. White blood cells engulf foreign particles by means of
A.
macrocytosis.
B. pinocytosis.
C. exocytosis.
D.
phagocytosis.
E. prestocytosis.
D
72. All of the following processes can move substances out of a cell
EXCEPT
A. exocytosis.
B. osmosis.
C. active
transport.
D. phagocytosis.
E. diffusion.
D
73. Arrange the following events of exocytosis in the correct
sequence:
(1) vesicle membrane fuses with plasma
membrane
(2) secretory vesicles migrate to plasma
membrane
(3) vesicle contents are expelled from cell
(4)
secretions accumulate within secretory vesicles
A. 2, 1, 4, 3
B. 1, 4, 2, 3
C. 3, 1, 4, 2
D. 4, 2, 1, 3
E.
1, 2, 3, 4
D
74. Receptor-mediated endocytosis
A. does not need ATP; the
receptors supply the energy.
B. exhibits specificity.
C.
occurs if oxygen is available.
D. is a type of passive
transport.
E. moves materials out of the cell.
B
75. Which transport process requires a carrier molecule but does not
use cellular energy?
A. active transport
B. diffusion
C. endocytosis
D. facilitated diffusion
E. osmosis
D
76. The bulk uptake of material by the formation of a vesicle is
called
A. active transport.
B. diffusion.
C.
endocytosis.
D. facilitated diffusion.
E. osmosis.
C
77. The movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to
an area of less concentration is called
A. active transport.
B. diffusion.
C. endocytosis.
D. facilitated
diffusion.
E. osmosis.
B
78. The movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane is
called
A. active transport.
B. diffusion.
C.
endocytosis.
D. facilitated diffusion.
E. osmosis.
E
79. The movement of molecules against their concentration gradient is
called
A. active transport.
B. diffusion.
C.
endocytosis.
D. facilitated diffusion.
E. osmosis.
A
144. What is a large, active phagocytic cell?
A. columnar cells
of upper respiratory tract
B. spermatozoa
C. columnar
cells of small intestines
D. red blood cells
E. macrophage
(large, mobile white blood cell)
E
96. If a toxic drug inhibited mRNA synthesis, which of the following
would be most directly affected?
A. protein synthesis
B.
intracellular digestion
C. microtubule production
D.
secretion of glycoproteins and lipoproteins
E. active transport
A
80. Cytoplasm is found
A. in the nucleus.
B. outside the
nucleus but inside the plasma membrane.
C. in the cisternae of
the endoplasmic reticulum.
D. on the cristae of the
mitochondria.
E. between the phospholipids in the plasma membrane.
B
81. The cytoplasm is made up of
A. cytosol.
B. cytogel.
C. organelles.
D. Both cytosol and organelles.
E.
Both cytogel and organelles.
D
83. The cytoskeleton consists of
A. lipochromes,
microfilaments, and microtubules.
B. actin filaments,
mitochondria, and intermediate filaments.
C. microfilaments,
mitochondria, and lipochromes.
D. microtubules, actin filaments,
and intermediate filaments.
E. ribosomes, the nucleus, and the
Golgi apparatus.
D
85. Microtubules
A. are the smallest components of the
cytoskeleton.
B. contain the protein myosin.
C. provide
structure and support to the cytoplasm.
D. are solid, supporting
rods of protein.
E. are a component of mitochondria.
C
84. Absence of a cytoskeleton might affect
A. cell shape.
B. the number of channel proteins in the cell membrane.
C.
the ability of the cell to generate energy.
D. vesicle
formation.
E. membrane transport.
A
86. Of the organelles listed, which one does NOT contain
microtubules?
A. cilia
B. flagella
C. centrioles
D. microvilli
E. spindle fibers
D
126. Which of the following cell organelles does not contain
microtubules?
A. cilia
B. flagella
C. spindle fibers
D. centrioles
E. All of these choices contain microtubules.
E
151. Messenger RNA
A. is synthesized when a portion of a DNA
molecule is transcribed.
B. directs the synthesis of DNA.
C. determines the sequence of nucleotides in the anticodons of
tRNA.
D. directs the synthesis of centrioles in the cytoplasm.
E. is not involved in the synthesis of proteins.
A
152. The transfer of information from DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA) is
known as
A. transduction.
B. translocation.
C.
translation.
D. transcription.
E. transmutation.
D
153. Which of the following sequences is correct?
A.
translation protein synthesis transcription
B. transcription
translation protein synthesis
C. transcription protein
synthesis translation
D. translation transcription protein
synthesis
E. protein synthesis translation transcription
B
155. Transcription
A. requires three types of RNA.
B.
synthesizes RNA from DNA.
C. occurs at the ribosomes.
D.
copies information from mRNA to tRNA.
E. synthesizes DNA from RNA.
B
157. Posttranscriptional processing is the modification of
A.
proteins to form pro-proteins.
B. mRNA to form tRNA.
C.
pre-mRNA to form functional mRNA.
D. exons to form introns.
E. DNA.
C
161. If a mRNA molecule is 1800 nucleotides (bases) in length, this
molecule will contain _____ codons.
A. 400
B. 600
C.
800
D. 900
E. 1200
B
163. Translation
A. requires three types of DNA.
B.
requires the pairing of codons on mRNA with anticodons on tRNA.
C. involves synthesis of RNA from DNA molecules.
D. takes
place in the nucleus.
E. requires replication of DNA.
B
167. Which of the following is NOT posttranslational processing?
A. adding polysaccharide side chains to proteins
B.
joining 2 or more amino acid chains
C. conversion of a
pro-protein to a functional protein
D. removal of introns from
pre-mRNA
E. conversion of a pro-enzyme to a functional enzyme
D
169. A mRNA containing introns is a
A. pre-mRNA.
B.
proenzyme.
C. gene.
D. ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
E. codon.
A
43. Which of the following statements concerning membrane transport
across the plasma membrane is true?
A. Polar molecules are
transported more easily than nonpolar molecules.
B.
Lipid-soluble substances pass through the membrane by dissolving in
the lipid bilayer.
C. Water cannot move through the membrane.
D. Generally, cations pass through the membrane more easily than
anions.
E. All molecules are moved across by active transport.
B
Proteins of the plasma membrane serve all of the following functions,
except
A) pumps water out of the cell
B) catalyzes
reactions outside of the cell
C) transports ions from the
outside to the inside of the cell
D) binds neurotransmitters
A
Transport protein specificity means that the protein
A) only
transports certain ions or molecules.
B) requires ATP.
C)
has more that one molecule it can transport.
D) binds hormones.
A
Channel proteins
A) are made of integral membrane
proteins.
B) can be gated.
C) have specificity.
D)
all of the above.
D
Cadherins are
A) extensions of the phospholipids.
B)
modified structures that function as sensory receptors.
C)
proteins that anchor cells together.
D) external projections of microtubules.
C
Which of the following is CORRECTLY matched with its function?
A) channel proteins – place for new protein synthesis
B) marker
molecules – steroids
C) receptor proteins – bind to chemical
signals
D) peripheral proteins – penetrate the lipid bilayer
C
The passive movement of an ion or molecule across a plasma membrane
with the aid of a carrier protein is
A) osmosis.
B)
filtration.
C) facilitated diffusion.
D) active transport.
C
Many gland cells release their secretions by means of _______, a
process somewhat like reverse endocytosis.
A) exocytosis
B) phagocytosis
C) receptor-mediated endocytosis
D)
fluid-phase pinocytosis
A
The greater the concentration of a solute in a solution, the greater
the
A) tendency for water to diffuse from the solution
B)
osmotic pressure of the solution
C) number of carrier molecules
present
D) rate of the active transport
B
What characteristic is shared by simple diffusion and facilitated
diffusion?
A) Both require cellular energy for the transport of
substances.
B) Both involve the movement of water across a
semipermeable membrane.
C) Both require a special carrier
molecule to move substances across the membrane.
D) Both involve
the movement of a substance from regions of a higher concentration to
lower concentration without cellular energy.
D
In simple diffusion, the rate at which a solute passes through a
membrane depends on all of the following EXCEPT the
A) surface
area of the membrane
B) number of carriers in the
membrane
C) temperature of the solution
D) concentration
difference from one side of the membrane to the other
B
When molecules move from the area of lower concentration to the area
of higher concentration and energy is used, it is called
A)
filtration.
B) osmosis.
C) active transport.
D)
passive transport.
C
What change/s occur when red blood cells are placed in a hypertonic
solution?
A) red blood cells gain water
B) red blood cells
lose water and shrink
C) red blood cells neither gain nor lose
water
D) concentration of sodium increases within the cells
B
0.9% NaCl solution (saline) is isotonic to a cell, while seawater
is
A) hypertonic to the cell
B) isotonic to the cell
C) hypotonic to the cell
D) All of the above.
A
What organelle is most active in digesting endocytosed
materials?
A) the lysosomes
B) the rough endoplasmic
reticulum
C) the centriole
D) the nucleus
A
Organelles outside of the nucleus of cell are surrounded by a fluid
called the
A) cisternae.
B) intracellular support.
C) cytosol.
D) cytoplasm.
C
Which of the following organelles have their structure and function
accurately described?
A) Vesicles – membranous sacs; contain
various substances that recently entered or formed in the cell
B) Microfilaments – tiny rods of protein (actin); aid in cellular
movements
C) Microtubules – hollow tubes of globular protein
(tubulin); form internal skeleton of cell
D) all of these
choices are properly matched
D
The microtubule organizing center of a cell is the
A)
nucleus.
B) rER.
C) centrosome.
D) nucleolus.
C
Intermediate filaments are found in the
A) nucleus.
B)
rER.
C) cytosol.
D) extracellular space.
C
An mRNA molecule of 2400 nucleotides (bases) in length, could contain
_______ codons.
A) 800
B) 600
C) 1200
D) 2400
A